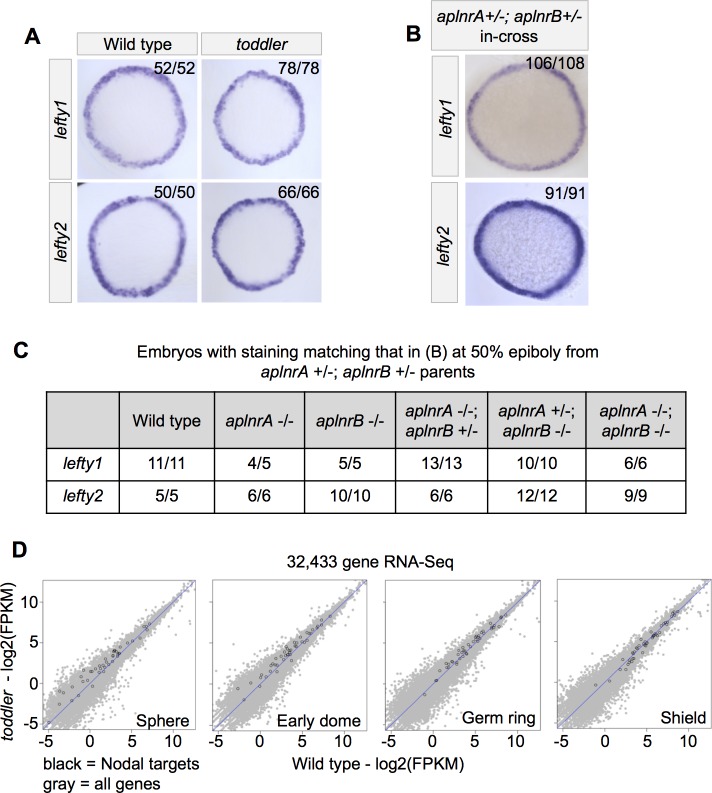
Figure 3. Wild-type and toddler mutant embryos have similar levels of Nodal signaling.
(A) Representative images of Nodal target gene expression in wild-type and toddler mutant embryos based on in situ hybridization at 50% epiboly. Animal pole facing up. Three biological replicates. (B–C) aplnrA;aplnrB double heterozygote parents were incrossed and their progeny examined by in situ hybridization at 50% epiboly. (B) Representative images of Nodal target gene expression in offspring from aplnrA;aplnrB double heterozygote parents. Animal pole facing up. (C) All embryos from B were genotyped. Results for relevant genotypes are shown. Expression of lefty1 and lefty2 in aplnrA;aplnrB double mutant embryos was indistinguishable from wild type. (D) RNA-sequencing before and during early gastrulation reveals no differential transcription of Nodal targets (black dots) between wild-type and toddler mutant embryos. All other genes are shaded in light gray. See also Figure 3—Source data 1.