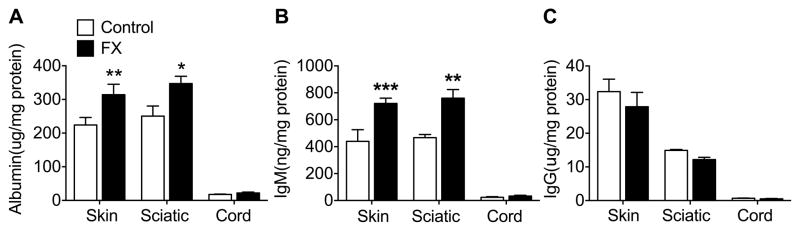
Fig. 6. IgM protein levels were elevated in hindpaw skin and sciatic nerve at 3 weeks post-fracture (FX) in the wildtype (WT) mice.
Enzyme immunoassays were used to measure albumin, IgM, and IgG protein levels in the FX limb hindpaw skin, sciatic nerve, and corresponding lumbar spinal cord. Compared with tissues collected from control nonfractured WT mice, both albumin (A) and IgM (B) protein levels were increased in the hindpaw skin and sciatic nerve after FX, but not in the spinal cord. Control mouse IgG protein levels were almost 80 and 40 fold greater in skin and sciatic nerve than IgM levels, but were unchanged after FX. Spinal cord levels of albumin, IgM and IgG were extremely low. A one-way analysis of variance was performed followed by a Holm-Sidak test for post hoc contrasts. Data are expressed as mean values ± SEM. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 FX (n = 7–8) vs Control (n = 7–8). Control: nonfractured wildtype mice, FX: 3 week post-fracture wildtype mice, Skin: hindpaw skin in FX limb, Sciatic: sciatic nerve in FX limb, Cord: lumbar spinal cord corresponding to FX limb