Abstract
Smith–Magenis syndrome (SMS; OMIM #182290) is a complex genetic disorder characterized by distinctive physical features, developmental delay, cognitive impairment, and a typical behavioral phenotype. SMS is caused by interstitial 17p11.2 deletions, encompassing multiple genes and including the retinoic acid-induced 1 gene (RAI1), or by mutations in RAI1 itself. About 10% of all the SMS patients, in fact, carry an RAI1 mutation responsible for the phenotype. RAI1 (OMIM *607642) is a dosage-sensitive gene expressed in many tissues and highly conserved among species. Over the years, several studies have demonstrated that RAI1 (or its homologs in animal models) acts as a transcriptional factor implicated in embryonic neurodevelopment, neuronal differentiation, cell growth and cell cycle regulation, bone and skeletal development, lipid and glucose metabolisms, behavioral functions, and circadian activity. Patients with RAI1 pathogenic variants show some phenotypic differences when compared to those carrying the typical deletion. They usually have lower incidence of hypotonia and less cognitive impairment than those with 17p11.2 deletions but more frequently show the behavioral characteristics of the syndrome and overeating issues. These differences reflect the primary pathogenetic role of RAI1 without the pathogenetic contribution of the other genes included in the typical 17p11.2 deletion. The better comprehension of physiological roles of RAI1, its molecular co-workers and interactors, and its contribution in determining the typical SMS phenotype will certainly open a new path for therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: 17p11.2, neurogenesis, sleep disorders, syndromic obesity, craniofacial abnormalities
Introduction
The Smith–Magenis syndrome
Smith–Magenis syndrome (SMS; OMIM #182290) is a complex genetic disorder firstly described by Smith in 1982.1 Actual prevalence of SMS is one in 15,000, while birth incidence is estimated at one in 25,000, although this value may be consistently underreported, with no gender differences observed.2–4
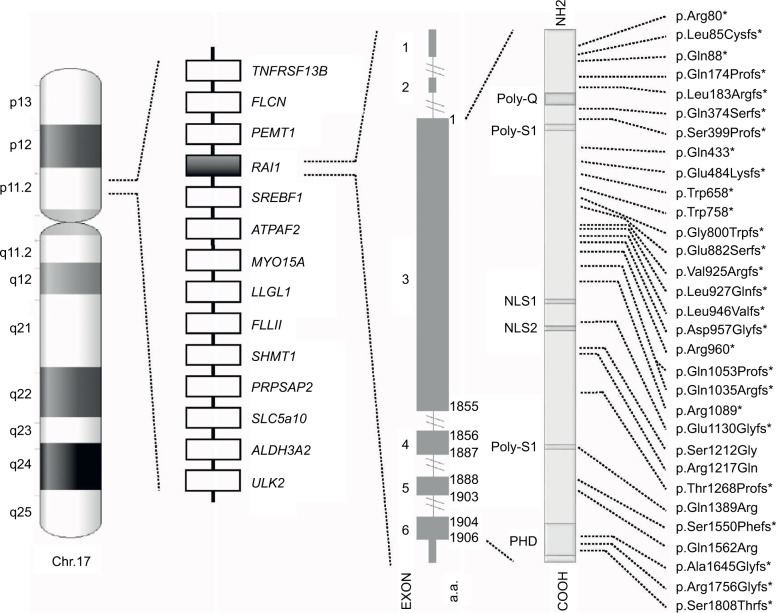
The syndrome is due to interstitial 17p11.2 deletions, encompassing multiple genes and including the retinoic acid-induced 1 gene (RAI1), or to mutations in RAI1 itself.5,6 SMS is considered a sporadic condition. The vast majority of cases are due to de novo mutations, although familial cases have been described and others are anecdotally known.7–9 A recurrent deletion of approximately 3.7 Mb due to nonallelic homologous recombination using flanking low copy repeats as substrates is observed in about 70–80% of all the deleted patients.3,10,11 This deletion encompasses RAI1, whose haploinsufficiency is considered the primary cause for most of the SMS features.6,12,13 About 10% of all the SMS patients, in fact, carry an RAI1 mutation responsible for the phenotype (Figure 1).9 Despite great overlap, some phenotypic differences have been reported between patients with 17p11.2 deletion and those with mutations in RAI1. Genotype–phenotype correlation studies have proposed that the other genes included in the commonly deleted region are responsible for the variability in phenotypic expression and severity seen between those two categories of SMS patients.14–17
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of chromosome 17, common 17p11.2 deletion, and RAI1. From left to right, the following are shown: the ideogram of G-band pattern of human chromosome 17; a schematic representation of the Smith–Magenis syndrome region with some representative genes; the RAI1 genomic and protein structure – glutamine-rich domain (Poly-Q), bipartite nuclear localization signals (NLS1 and NLS2), two serine-rich domains (Poly-S1 and Poly-S2), and C-terminal plant homeodomain (PHD); and the RAI1 mutations indexed in the HGMD™ Professional (version December 2015.4) known to date. *Indicates either frameshift or nonsense mutations.
SMS is, in fact, a multiple congenital anomalies and intellectual disability syndrome with a clinically recognizable phenotype mainly characterized by physical and neurobe-havioral features that become more evident with age.3,9,14,18–24
Physical and craniofacial features
Infants are usually born at term after a pregnancy remarkable for decreased fetal movement. Auxology at birth is normal; however, soon after birth, a deceleration of the growth curves is often observed, and several patients have head circumference below the third percentile for age. Feeding difficulties leading to failure to thrive are common, and hypotonia, accompanied by hyporeflexia, is reported in most infants.25
The facial appearance is characteristic and typically changes with age with features that become coarser. In the infancy/childhood age, a broad square-shaped face is common, with brachycephaly and prominent forehead, deep-set eyes with synophrys, and up-slanting palpebral fissures. The nasal bridge is broad. Midfacial hypoplasia with micrognathia and a fleshy everted vermilion of the upper lip is common. Over time, micrognathia changes into relative prognathism because of an excessive growth of the mandible with persisting midfacial retrusion, and eyebrows become thicker.
Additional findings might include skeletal abnormalities (brachydactyly, short stature, mild-to-moderate scoliosis, small arched feet conferring unusual gait), teeth anomalies (in particular malocclusion, taurodontism, and dental agenesis), and ocular and otolaryngological issues (strabismus, myopia, iris anomalies, and/or microcornea which may progress with age; recurrent otitis media, laryngeal anomalies, velopharyngeal insufficiency, oral sensorimotor dysfunction). Cardiac, urogenital, and thyroid abnormalities can occur; renal anomalies and cleft lip and/or palate occur in fewer than 25% of individuals.18,25–27
Neurobehavioral features
SMS patients might show a wide range of variability in cognitive and adaptive functioning with the majority of them having mild-to-moderate intellectual disability. The behavioral phenotype is typical and includes sleep disturbance, stereotypies, and maladaptive and self-injurious behaviors. Phenotypic food-related behaviors are also common. The neurobehavioral phenotype becomes recognizable, usually, from the second year of life and changes throughout the individual growth.19,20,28,29
In infancy, SMS patients present lethargy, hypotonia, and daytime sleepiness. Although some authors have documented fragmented sleep with shortened sleep cycles as early as 6 months of age, the typical sleep disturbance due to the inverted circadian rhythm of melatonin is not yet recognizable at this age.29 Neurodevelopmental delay, for both gross and fine motor skills and speech delay, is common together with minimal maladaptive behaviors and normally developed social skills.30,31 Global developmental delay, significant expressive language deficit, and emerging maladaptive behaviors are, usually, recognized by three years of age.29,30 The final cognitive impairment, generally, falls into the mild-to-moderate range with relative weaknesses in sequential processing and short-term memory, and relative strengths in long-term memory.
Slowly, the typical behavior emerges and escalates with age. Head banging may begin as early as 18 months of age. Most patients exhibit inattention with or without hyperactivity and meet the clinical criteria for the pervasive developmental disorder. Maladaptive behaviors, which often escalate with onset of puberty, embrace outbursts and temper tantrums, attention seeking, impulsivity, aggression, and the typical self-injury behaviors including self-hitting, self-biting, skin picking, the distinctive spasmodic upper-body squeeze or “self-hug” behavior, the onychotillomania (nail yanking), and the polyembolokoilamania (insertion of foreign objects into body orifices).3,19,32–35 A recent study pointed out that aggressive or destructive behaviors are not only self-inflicted but often directed toward others.36
Food-related behaviors, hyperphagia with deriving obesity, usually appear in adolescence and continue through the adult age and are the consequence of an impaired satiety signaling.37 These disorders are similar, although less serious, to those observed in patients with Prader–Willi, the most frequent neurodevelopmental disorder with syndromic obesity due to hyperphagia caused by a severe impairment of satiety signals.36
While age and degree of developmental delay correlate with maladaptive behaviors, the degree of sleep disturbance remains a strong predictor of maladaptive behavior.33,34 Individuals with SMS have difficulties in falling asleep, frequent awakenings during the nighttime sleep, and excessive daytime sleepiness. This issue is chronic and ends affecting the caregivers’ sleep attitude as well.38 The sleep disturbances are in strict correlation with the inverted circadian rhythm of endogenous melatonin pattern, although some patients are described to have the typical sleep disturbances but a normal pattern of melatonin secretion suggesting the involvement of other factor.39–42
The 17p11.2 deletion
The vast majority of SMS patients carry interstitial 17p11.2 deletions, encompassing multiple genes and including RAI1 (Figure 1).5 A recurrent deletion of approximately 3.7 Mb is observed in about 70%–80% of all the deleted patients, with the smallest deletion associated with the SMS phenotype spanning at least 650 kb.43 The common deletion includes the region from TNFRSF13B to ULK2, while the minimal critical region spans from PEMT to MYO15A.3,4,10,11,43–45
RAI1 haploinsufficiency is considered responsible for most of the SMS features, although some phenotypic differences between deleted patients and those with RAI1 mutations exist and probably reflect the role of the other genes included in the region.6,12–17
A genotype–phenotype correlation study, performed comparing patients with deletions of different sizes, suggested that the region between SREBF1 and SHMT1 could be implicated in the short stature, while the hearing loss could be influenced by haploinsufficiency of LLGL1, FLCN, and MYO15A.15 In particular, mutations in MYO15A, which are responsible for the non-syndromic deafness (DFNB3; OMIM #600316), have been described in SMS patients with sensorineural hearing loss.46,47
Several other genes within the deletion interval have been implicated in other disorders, and the hemizygosity caused by the deletion may unmask the existence of autosomal recessive alleles leading to the possibility of two distinct genetic disorders coexisting in the same individual.
Mutations in TNFRSF13B are responsible for the immunoglobulin A (IgA) deficiency-2 (OMIM #609529) and for the common variable immunodeficiency 2 (OMIM #240500) and could be involved in the IgA deficiency described in some SMS patients.3,5,15,18,48
FLCN is a tumor suppressor gene located in the commonly deleted region and associated with the Birt–Hogg–Dubè syndrome (OMIM #135150), a genodermatosis which predisposes to pulmonary cysts, spontaneous pneumothorax, and renal and skin tumors.49 Intriguingly, recently a 58-year-old woman with SMS has been reported for having developed a bilateral renal tumor.50
Mutations in ALDH3A2 gene cause the Sjogren–Larsson syndrome (OMIM #270200), an autosomal recessive neurocutaneous disease with ichthyosis, intellectual disabilities, spastic paraparesis, macular dystrophy, and leukoencephalopathy.51 It has been observed that SMS patients with deletions present more frequently dry skin than those with mutations, suggesting a possible role of this gene in this feature.15
Many other genes are included in the region, but further studies are needed to determine whether these genes could contribute to specific features of the syndrome.
RAI1
RAI1 was firstly identified in 1995 as a main regulator of neuronal and glial differentiation in a mouse model of embryonal carcinoma cell line after treatment with high doses of retinoic acid.52 Mutations causing haploinsufficiency of RAI1, identified for the first time by Slager et al in 2003, are responsible for a phenotype similar, but not completely overlapping, to that described for the 17p11.2 deletion syndrome.6,12,13
RAI1 is a dosage-sensitive gene. The chromosomal segment that includes RAI1 is within the critical interval involved in both SMS and Potocki–Lupski syndrome (PTLS; OMIM #610883), with deletions and duplications, respectively. Murine models of SMS, deletions of the region containing Rai1 or targeted gene inactivation, cause most of the clinical features observed in the SMS patients (obesity, craniofacial abnormalities, abnormal circadian rhythm, and seizures). On the other hand, murine models with duplication encompassing Rai1 or with extra copies of Rai1 showed diametrically opposing phenotypes in head circumference, body weight, percent of body fat, anxiety, preference for social novelty, dominant behavior, and activity levels.16,17,37,53,54
Expression
RAI1 is widely expressed in many tissues with particularly high levels in brain, suggesting its crucial role in this tissue.55 The subcellular distribution of human neuronal RAI1 indicated its presence in both cytoplasm and nucleus.56 Expression studies performed in mice showed that Rai1, the mouse homolog of the human RAI1, is primarily expressed in neurons, including pyramidal cells of the hippocampus, granule cells of the dentate gyrus, neurons in the neocortex, and Purkinje cells of the cerebellum.54 Similarly, human RAI1 is highly expressed in hippocampal neurons, but not in glia, and in neurons of the occipital cortex. In the cerebellum, the second region of high expression, RAI1 is detected in Purkinje cells, but not granule cells. Northern blot analysis detected RAI1 mRNA in human frontal and temporal lobes.56,57
Aiming to investigate the possible role of RAI1 as a contributor to the pathogenesis of neuropsychiatric disorders, a recent study identified two SNPs (rs9907986 and rs4925102) in the 5′-upstream region (5′-UTR) as putative regulatory elements. These two SNPs, that fall within the binding sites for the transcription factors DEAF1 and for the retinoic acid RXRα-RARα, account together for approximately 30–40% of the variance in RAI1 mRNA expression in prefrontal cortex and temporal cortex.58–61 Further supporting the role of DEAF1 in regulating the RAI1 expression is a recent study that identified, by exome sequencing, a mutation in DEAF1 in a patient with clinical features resembling the typical SMS but negative for both the 17p11.2 deletion and RAI1 mutations.62
Structure
RAI1 is highly conserved among species. Human RAI1, which shows high levels of homology to the mouse Rai1, contains six exons and encodes for a 1906-amino-acid protein localized in the cellular nucleus (Figure 1).55,57,63
RAI1 is a nuclear chromatin-binding protein with several functional domains (Figure. 1). Moving forward from N-terminus, the following have been identified: a polyglutamine-rich domain (Poly-Q), a first polyserine-rich domain (Poly-S1), bipartite nuclear localization signals (NLS1 and NLS2), a second polyserine-rich domain (Poly-S2), and a plant homeodomain (PHD).63,64
Function
Despite great advancement in our knowledge about RAI1 functions, much is yet to be clarified. In brief, RAI1 is a transcriptional factor implicated in cell growth and cell cycle regulation, bone and skeletal development, lipid and glucose metabolisms, embryonic neurodevelopment and neuronal differentiation, behavioral functions, and circadian activity.64–66
A recent study in genetically engineered mice shows that Rai1 interacts with chromatin, occupies DNA regions near active promoters (CpG islands, 5′-UTRs, and promoters, but not intergenic or repetitive regions), and enhances the expression of genes involved in circuit assembly and neuronal communication. In this study, the authors also show that pan-neuronal loss of Rai1 causes a severe SMS-like phenotype. They also point out that the haploinsufficiency of RAI1 in specific cellular types causes deficits in motor function, learning, and food intake. These data underlie the relevant role of the subcortical excitatory neurons in the pathogenesis of the SMS.64
Bioinformatic analyses and gene expression assays strongly suggest that human RAI1 directly or indirectly influences transcription. First, the presence of a nuclear localization signal is consistent with the role in the regulation of gene expression. Second, the Poly-Q tracts are common in regulatory proteins, such as transcription factors, and contribute to transcriptional activation in mammalian cells. Furthermore, the PHD motif at the C-terminal is homologous to the PHD motif of the transcriptional co-activator TCF20 and is presumably important, in both proteins, to carry out their role as “histone readers.” RAI1, thus, is able to “read” the specific posttranslational modifications of histones and to recruit proteins that regulate, among other metabolic functions, the transcription of specific DNA regions.12,37,63,67–69
RAI1 mutations
To date, more than 30 variations in RAI1 have been associated with SMS (HGMD Professional, version December 2015.4), all clustered in exon 3, which encodes more than 95% of the protein (Figure 1). Most are frameshift, predicted to inactivate the gene product, whereas few are missense mutations occurring within highly conserved sequences. All of them, hampering with the gene expression and/or the normal protein structure/function, and thus, result in haploinsufficiency and lead to the SMS phenotype.6,13,70
Animal models
To investigate in vivo the SMS disease mechanisms and the RAI1 functions, several animal models, in particular mouse and Xenopus models, have been created and extensively used.
In 2003, Walz et al generated the first SMS mouse model bearing the 17p11.2 deletion in the mouse chromosome region syntenic to the SMS critical interval. The deleted mice showed craniofacial abnormalities, seizures, and weight abnormality as many SMS patients do.53
Following the publication of reports on SMS patients carrying mutations in RAI1 in place of the 17p11.2 deletion, engineered mouse models were generated to investigate RAI1 expression patterns and to explore its functions. In 2005, Bi et al generated mice with an Rai1 null allele (Rai1+/−) through the insertion of a lacZ reporter gene encoding β-galactosidase. These mice allowed to define the endogenous expression pattern of Rai1 and to prove that some SMS phenotypes, already reported in mice carrying the 17p11.2 deletion, were also observed in a mouse model of Rai1 haploinsufficiency.71 In addition, it was observed that homozygous null mice (Rai1−/−) displayed embryonic lethality and almost all died in utero; the few mice that survived exhibited severe postnatal growth retardation, craniofacial and skeletal abnormalities, motor dysfunction, and fear-learning deficits.54
To determine whether specific symptoms/phenotypes observed in the affected patients were the results of Rai1 requirement in specific cell types, in 2016 Huang et al generated Rai1 knock-in and Rai1 conditional knock-out mouse models.64 They engineered Rai1 alleles in order to characterize Rai1 expression patterns (knock-in mice with tandem FLAG and myc peptides fused to the carboxyl terminus of endogenous Rai1). Also, they explored the neural functions of Rai1, and how the loss of Rai1 affects the transcriptome, by conditionally deleting Rai1 in the nervous system using a pan-neural NestinCre line and producing NestinCre;Rai1CKO mice.64 Furthermore, they explored if the phenotypic consequences of RAI1 haploinsufficiency were the result of RAI1 loss in specific neuronal subtypes. To do that, they knocked out Rai1 in different neuronal cell types using Gad2Cre that targets most GABAergic inhibitory neurons, Emx1Cre that targets cortical and hippocampal excitatory neurons and glia, mGfapCre that targets astrocytes and subsets of adult neural progenitors, and Vglut2Cre that targets subcortical excitatory neurons.64
On the other hand, these studies also pointed out that Rai1+/− mice have a significantly reduced fecundity and an altered transmission pattern of the mutant Rai1 allele. These observations limited the use of these models for large, extended studies. In 2014, Alaimo et al created an Rai1+/− mouse model by breeding C57Bl/6J Rai1+/− mice with FVB/NJ mice to create offspring in a mixed genetic background, which ameliorated both fecundity and Rai1 allele transmission throughout generations and provided a more robust platform for larger phenotypic studies.72
Finally, in 2014, Tahir et al used the Xenopus as a tool to uncover the developmental mechanisms regulated by Rai1. They took advantages by the fact that, unlike the mouse, Xenopus embryo develops externally. Both Xenopus tropicalis and Xenopus laevis share 44% and 42% overall identity, respectively, with the human RAI1 protein with even higher shared identity in specific functional domains, such as the PHD domain. A targeted knock-down approach using anti-sense oligos stabilized with morpholino was used to generate this animal model.73
RAI1 functions and mechanisms for the SMS phenotype
RAI1 and neurogenesis
RAI1 influences memory, behavior, and motor function through the retinoic acid metabolism. Expression studies demonstrate, overall, that human RAI1 is a highly expressed neuronal protein whose distribution matches with its role in cognitive and motor skills.56
Recent studies in mouse models show that Rai1 is highly expressed during the early stage of neurodevelopment. Specifically, Rai1 is expressed in the post-mitotic neurons of the cortical plate but not in progenitor neurons actively proliferating. This suggests its role in maintaining the functions or differentiation of correct mature neurons.64
Transgenic Rai1+/− mice show abnormal electroencephalogram (EEG) with overt seizure and neurobehavioral abnormities, learning impairment, and motor dysfunction. Moreover, Rai1 null mice die during embryogenesis in almost all cases. Surviving Rai1−/− mice exhibit craniofacial and skeletal abnormalities, more severe neurobehavioral issues with less learning ability, overt seizures at younger age, motor dysfunction, and fear-learning deficits delineating a more severe clinical phenotype. These observations confirm a dosage-sensitive effect of Rai1 in neurodevelopment.54
Mutations in RAI1 are, thus, considered to have a causal, leading, role in the pathogenesis of most of the neurobehavioral features typically observed in the SMS patients, including autistic trait, intellectual disability, self-injurious behavior, EEG abnormalities, and sleep disturbances.
Moreover, further supporting its role in the neurodevelopment, RAI1 is associated with non-syndromic autism disorder, spinocerebellar ataxia 2 (SCA2; OMIM #183090), and neuroleptic response in patients with schizophrenia.54
RAI1 and sleep disorders
Several studies, both in vitro and in vivo, demonstrated the crucial rule of RAI1 as a circadian regulator. RAI1 positively regulates the transcription of Circadian Locomotor Output Cycles Kaput (CLOCK), a key component of the mammalian circadian oscillator that, in turn, transcriptionally regulates many critical circadian genes such as PER2, PER3, CRY1, and BMAL1. Haploinsufficiency of RAI1, thus, results in the disruption of the circadian rhythm with consequence on the sleep–wake cycle.66 Sleep disturbances, including difficulty in falling asleep, abnormality in rapid eye movement phase of sleep, and daily sleepiness represent the typical features in SMS, present in almost all cases.74
RAI1 and obesity
Obesity and overeating issues are more frequently observed in individuals with RAI1 mutations compared to those carrying the 17p11.2 deletions.14 Food intake, moreover, can alter the function of brain regions responsible for the regulation of the circadian rhythm, reinforcing humoral signals and connecting metabolism, circadian rhythm, behaviors, and development.75
Several evidences show how RAI1 contributes to the hyperphagia and obesity seen in SMS. The brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is a growth factor involved in development, differentiation, and survival of neurons and in the energy homeostasis. It is expressed both in the central nervous system and in peripheral tissues, such as liver, muscle, and adipose tissue.76 Low serum levels of BDNF have been associated with obesity, hyperphagia, and behavioral abnormalities even in humans.77 Studies in mice demonstrate that Rai1 haploinsufficiency downregulates Bdnf and contributes to the obesity with hyperphagia and abnormal fat distribution. Rai1 regulates, through its PHD domain, the transcription of Bdnf via intronic enhancer element. Rai1 haploinsufficiency is also responsible for altered hypothalamic expression of other genes. It downregulates proopiomelanocortin (Pomc), a precursor of melanocortins involved in energy homeostasis, whose mutations have been associated with obesity in mice and human.37
RAI1 and coarse face
Craniofacial abnormalities have been observed in both 17p11.2-deleted and RAI1-mutated patients suggesting that RAI1 might also play a crucial rule in the onset of facial dysmorphism in SMS. Similar midface abnormalities have also been reported in mouse models and in rai1 Xenopus morphants.17,73
Yan et al observed, in fact, that, in mouse models, deletion size and genetic background influenced the penetrance of the craniofacial phenotype suggesting that Rai1 was playing a major role in determining this phenotype but also that Rai1-surrounding regions might contain regulatory elements which could modify the phenotype penetrance.17
More recently, Tahir et al showed, in vertebrate models X. laevis and X. tropicalis, that rai1, the frog homologous of RAI1, is expressed in the developing craniofacial tissues and that its haploinsufficiency results in defects in the developing brain and face which exhibits midface hypoplasia and malformed mouth shape. They also offer insight about the mechanism. The formation of the face depends largely on neural crest development. During the embryogenesis, the neural crest was not migrating properly. The authors, in fact, observed fewer neural crest cells, and the migration itself seemed delayed and with migratory streams less defined. This defective neural crest development affected the formation of its derivative cartilage (ethmoid plate, infrarostral, Meckel’s, ceratohyal and gill cartilages) which appeared reduced in size. The whole process was considered responsible for the observed malformation.73
RAI1 role in other disorders
RAI1 is not only associated with SMS. Duplications of the chromosomal segment that includes RAI1 are responsible for the PTLS. Furthermore, RAI1 mutations have, also, been linked to other neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric disorders. The length of the polyglutamine rich domain (Poly-Q) at the N-terminus of the protein is associated with the response to neuroleptics in schizophrenia and with the age of onset of SCA2. Additionally, RAI1 has been identified as a candidate gene for the susceptibility to non-syndromic autism spectrum disorder.78–83
A recent study by Thaker et al identified a de novo RAI1 mutation in a child with morbid obesity and a clinical diagnosis of the Rapid-onset Obesity with Hypothalamic dysfunction, Hypoventilation and Autonomic Dysregulation (ROHHAD) syndrome. The authors suggest to consider RAI1 as a candidate gene in children with morbid obesity, especially if presenting a phenotype consistent with the SMS or the ROHHAD syndrome.84
Finally, whole-exome sequencing analyses performed on 123 patients affected by non-syndromic hearing loss and negative for mutations in GJB2 revealed in several affected members of two unrelated families a homozygous missense mutation of RAI1. Despite the genotype–phenotype correlation studies indicating that the hearing issues in the SMS patients appear to be more frequently associated with the deletions, and thus, with the influence of genes other than RAI1, the authors of this study speculate about the possible role of RAI1, and of the retinoic acid signaling, in the mammalian organ of Corti development and, thus, in the pathogenesis of the hearing loss.14,15,85
Discussion
Accurate phenotype description and molecular mechanism underlying a phenotype are two aspects strictly entwined in medical genetics. The better a phenotype is described, the more successful the diagnostic path will be. Besides, a well-described phenotype can be further analyzed in its different traits and, as a consequence, each trait can be investigated under a pathogenetic point of view. On the other hand, experimental models of diseases allow to investigate, and understand, the biological pathways underlying the onset of a specific phenotype, or a trait of a phenotype, giving eventually insight for specific medical interventions.
To date, there is no specific treatment for the SMS, and all the available therapeutic approaches are symptomatic treatments.40,92–94 As for most genetic conditions, the only way to find a cure is to better understand the biological role of the gene causing disease. This is true for the monogenic conditions but also for the contiguous gene deletion/duplication syndromes in which the definite contribution of one (or more) gene has been established. That is why, in our opinion, studies aiming to further elucidate the biological role of RAI1 are essential to identify putative biological targets for better medical strategies. Interest toward the clinical research and the translational medicine in order to improve the living conditions of the patients is noteworthy, and necessary. Nevertheless, we should give proper credit to the amount of knowledge acquired after years of basic-research studies in cellular and animal models. The studies, reviewed herein, have contributed in elucidating structure, expression pattern, and biological function of RAI1 among different tissues. All these studies offer hypothesis on how RAI1 can be responsible, when disrupted, for the onset of the SMS, a complex syndrome with different clinical manifestations.
Moreover, other recent publications identified a cohort of genes which might interact, directly or indirectly, with RAI1 and its network.62,95 These works provide a good example of how entwined “good characterization of a phenotype”, on one side, and “molecular basis of a disease”, on the other, are. In fact, in those two studies starting from a phenotype strongly resembling the SMS (which was excluded by the molecular testing) and applying new testing technologies (the whole-exome sequencing), the authors identified a cohort of putative candidate genes causing disease and proposed a common disease network. All these studies and hypotheses are essential to further elucidate the mechanism of the SMS pathogenesis and to develop new targeted therapies.
Conclusion
About 10% of all the SMS patients carry an RAI1 mutation which is responsible for the phenotype.9 Despite great overlap, these patients show several phenotypic differences when compared to those carrying the typical deletion. They usually have less cognitive impairment and lower incidence of hypotonia, short stature, hearing loss, and cardiac and renal defects than those with 17p11.2 deletions suggesting a minor role for RAI1 in these clinical features and, most likely, reflecting the haploinsufficiency of other genes as for typical contiguous gene deletion syndromes.14,15 On the other hand, they are more likely to exhibit overgrowth phenotypes, and the behavioral characteristics of the syndrome – including polyembolokoilamania, skin picking, and self-hugging – and overeating issues with obesity tendency.4
RAI1 is a dosage-sensitive gene, highly expressed in neurons during the early stage of neurodevelopment, and its protein distribution matches with its role in cognitive and motor skills neurodevelopment.54,56 RAI1 carries out its role as a circadian regulator influencing the transcription of CLOCK. Therefore, RAI1 haploinsufficiency results in the disruption of the circadian rhythm with a consequence on the sleep–wake cycle.66 Likewise, RAI1 haploinsufficiency downregulates Bdnf and Pomc contributing to obesity with hyperphagia and abnormal fat distribution.37 Rai1 also affects the neural crest migration and the development of the derivative cartilage elements. This partially explains its role in the pathogenesis of the craniofacial abnormalities observed in the SMS patients.73 As observed by Tahir et al, in fact, craniofacial abnormalities have already been linked to anomalies in the neural crest development also in different conditions, such as the Williams–Beuren syndrome (OMIM #194050), the DiGeorge syndrome (OMIM #188400), the fragile-X syndrome (OMIM #300624), the Prader–Willi syndrome (OMIM #176270), and the Down syndrome (OMIM #190685), sharing common features with the SMS.86–91
Finally, it is worth mentioning that, besides the SMS, RAI1 is associated with non-syndromic autism disorder, SCA2, and neuroleptic response in patients with schizophrenia.54
Footnotes
Disclosure
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
References
- 1.Smith ACM. Deletion of the 17 short arm in 2 patients with facial clefts and congenital heart-disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1982;32(6):A146. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Smith AC, Magenis RE, Elsea SH. Overview of Smith-Magenis syndrome. J Assoc Genet Technol. 2005;31(4):163–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Greenberg F, Guzzetta V, Montes de Oca-Luna R, et al. Molecular analysis of the Smith-Magenis syndrome: a possible contiguous-gene syndrome associated with del(17)(p11.2) Am J Hum Genet. 1991;49(6):1207–1218. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Elsea SH, Girirajan S. Smith–Magenis syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet. 2008;16(4):412–421. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejhg.5202009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Smith AC, McGavran L, Robinson J, et al. Interstitial deletion of (17) (p11.2p11.2) in nine patients. Am J Med Genet. 1986;24(3):393–414. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320240303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Slager RE, Newton TL, Vlangos CN, Finucane B, Elsea SH. Mutations in RAI1 associated with Smith–Magenis syndrome. Nat Genet. 2003;33(4):466–468. doi: 10.1038/ng1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zori RT, Lupski JR, Heju Z, et al. Clinical, cytogenetic, and molecular evidence for an infant with Smith-Magenis syndrome born from a mother having a mosaic 17p11.2p12 deletion. Am J Med Genet. 1993;47(4):504–511. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320470414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Campbell IM, Yuan B, Robberecht C, et al. Parental somatic mosaicism is underrecognized and influences recurrence risk of genomic disorders. Am J Hum Genet. 2014;95(2):173–182. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.07.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Acquaviva F, Sana ME, Della Monica M, et al. First evidence of Smith-Magenis syndrome in mother and daughter due to a novel RAI mutation. Am J Med Genet A. 2017;173(1):231–238. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.37989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Juyal RC, Figuera LE, Hauge X, et al. Molecular analyses of 17p11.2 deletions in 62 Smith-Magenis syndrome patients. Am J Hum Genet. 1996;58(5):998–1007. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chen KS, Manian P, Koeuth T, et al. Homologous recombination of a flanking repeat gene cluster is a mechanism for a common contiguous gene deletion syndrome. Nat Genet. 1997;17(2):154–163. doi: 10.1038/ng1097-154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bi W, Saifi GM, Shaw CJ, et al. Mutations of RAI1, a PHD-containing protein, in nondeletion patients with Smith-Magenis syndrome. Hum Genet. 2004;115(6):515–524. doi: 10.1007/s00439-004-1187-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Girirajan S, Elsas LJ, Devriendt K, Elsea SH. RAI1 variations in Smith-Magenis syndrome patients without 17p11.2 deletions. J Med Genet. 2005;42(11):820–828. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2005.031211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Edelman EA, Girirajan S, Finucane B, et al. Gender, genotype, and phenotype differences in Smith-Magenis syndrome: a meta-analysis of 105 cases. Clin Genet. 2007;71(6):540–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2007.00815.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Girirajan S, Vlangos CN, Szomju BB, et al. Genotype-phenotype correlation in Smith-Magenis syndrome: evidence that multiple genes in 17p11.2 contribute to the clinical spectrum. Genet Med. 2006;8(7):417–427. doi: 10.1097/01.gim.0000228215.32110.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ricard G, Molina J, Chrast J, et al. Phenotypic consequences of copy number variation: insights from Smith-Magenis and Potocki-Lupski syndrome mouse models. PLoS Biol. 2010;8(11):e1000543. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Yan J, Bi W, Lupski JR. Penetrance of craniofacial anomalies in mouse models of Smith-Magenis syndrome is modified by genomic sequence surrounding Rai1: not all null alleles are alike. Am J Hum Genet. 2007;80(3):518–525. doi: 10.1086/512043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Greenberg F, Lewis RA, Potocki L, et al. Multi-disciplinary clinical study of Smith-Magenis syndrome (deletion 17p11.2) Am J Med Genet. 1996;62(3):247–254. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19960329)62:3<247::AID-AJMG9>3.0.CO;2-Q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Dykens EMM, Smith ACC. Distinctiveness and correlates of maladaptive behaviour in children and adolescents with Smith-Magenis syndrome. J Intellect Disabil Res. 1998;42(Pt 6):481–489. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2788.1998.4260481.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Smith AC, Dykens E, Greenberg F. Behavioral phenotype of Smith-Magenis syndrome (del 17p11.2) Am J Med Genet. 1998;81(2):179–185. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-8628(19980328)81:2<179::aid-ajmg10>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Smith AC, Gropman AL, Bailey-Wilson JE, et al. Hypercholesterolemia in children with Smith-Magenis syndrome: del (17) (p11.2p11.2) Genet Med. 2002;4(3):118–125. doi: 10.1097/00125817-200205000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Dubourg C, Bonnet-Brilhault F, Toutain A, et al. Identification of nine new RAI1-truncating mutations in Smith-Magenis syndrome patients without 17p11.2 deletions. Mol Syndromol. 2014;5(2):57–64. doi: 10.1159/000357359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Finucane BM, Konar D, Haas-Givler B, Kurtz MB, Scott CI., Jr The spasmodic upper-body squeeze: a characteristic behavior in Smith-Magenis syndrome. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1994;36(1):78–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1994.tb11770.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Truong HT, Dudding T, Blanchard CL, Elsea SH. Frameshift mutation hotspot identified in Smith-Magenis syndrome: case report and review of literature. BMC Med Genet. 2010;11(1):142. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-11-142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Smith ACM, Gropman A. Smith-Magenis syndrome. In: Cassidy SB, Allanson JE, editors. Management of Genetic Syndromes. 3rd ed. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc; 2010. pp. 739–768. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Allanson JE, Greenberg F, Smith AC. The face of Smith-Magenis syndrome: a subjective and objective study. J Med Genet. 1999;36(5):394–397. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Tomona N, Smith AC, Guadagnini JP, Hart TC. Craniofacial and dental phenotype of Smith–Magenis syndrome. Am J Med Genet A. 2006;140A(23):2556–2561. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.31371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sarimski K. Communicative competence and behavioural phenotype in children with Smith-Magenis syndrome. Genet Couns. 2004;15(3):347–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gropman AL, Duncan WC, Smith AC. Neurologic and developmental features of the Smith-Magenis syndrome (del 17p11.2) Pediatr Neurol. 2006;34(5):337–350. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2005.08.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wolters PL, Gropman AL, Martin SC, et al. Neurodevelopment of children under 3 years of age with Smith-Magenis syndrome. Pediatr Neurol. 2009;41(4):250–258. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2009.04.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hildenbrand HL, Smith AC. Analysis of the sensory profile in children with Smith-Magenis syndrome. Phys Occup Ther Pediatr. 2012;32(1):48–65. doi: 10.3109/01942638.2011.572152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Laje G, Morse R, Richter W, Ball J, Pao M, Smith AC. Autism spectrum features in Smith-Magenis syndrome. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2010;154(4):456–462. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.30275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Arron K, Oliver C, Moss J, Berg K, Burbidge C. The prevalence and phenomenology of self-injurious and aggressive behaviour in genetic syndromes. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2011;55(2):109–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.2010.01337.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sloneem J, Oliver C, Udwin O, Woodcock KA. Prevalence, phenomenology, aetiology and predictors of challenging behaviour in Smith-Magenis syndrome. J Intellect Disabil Res. 2011;55(2):138–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.2010.01371.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Finucane B, Dirrigl KH, Simon EW. Characterization of self-injurious behaviors in children and adults with Smith-Magenis syndrome. Am J Ment Retard. 2001;106(1):52–58. doi: 10.1352/0895-8017(2001)106<0052:COSIBI>2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Alaimo JT, Barton LV, Mullegama SV, Wills RD, Foster RH, Elsea SH. Individuals with Smith-Magenis syndrome display profound neurodevelopmental behavioral deficiencies and exhibit food-related behaviors equivalent to Prader-Willi syndrome. Res Dev Disabil. 2015;47:27–38. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2015.08.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Burns B, Schmidt K, Williams SR, Kim S, Girirajan S, Elsea SH. Rai1 haploinsufficiency causes reduced Bdnf expression resulting in hyperphagia, obesity and altered fat distribution in mice and humans with no evidence of metabolic syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 2010;19(20):4026–4042. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Foster RH, Kozachek S, Stern M, Elsea SH. Caring for the caregivers: an investigation of factors related to well-being among parents caring for a child with Smith-Magenis syndrome. J Genet Couns. 2010;19(2):187–198. doi: 10.1007/s10897-009-9273-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Potocki L, Glaze D, Tan DX, et al. Circadian rhythm abnormalities of melatonin in Smith-Magenis syndrome. J Med Genet. 2000;37(6):428–433. doi: 10.1136/jmg.37.6.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.De Leersnyder H, De Blois MC, Claustrat B, et al. Inversion of the circadian rhythm of melatonin in the Smith-Magenis syndrome. J Pediatr. 2001;139(1):111–116. doi: 10.1067/mpd.2001.115018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Boone PM, Reiter RJ, Glaze DG, Tan DX, Lupski JR, Potocki L. Abnormal circadian rhythm of melatonin in Smith-Magenis syndrome patients with RAI1 point mutations. Am J Med Genet A. 2011;155(8):2024–2027. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.34098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Boudreau EA, Johnson KP, Jackman AR, et al. Review of disrupted sleep patterns in Smith-Magenis syndrome and normal melatonin secretion in a patient with an atypical interstitial 17p11.2 deletion. Am J Med Genet A. 2009;149(7):1382–1391. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.32846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Schoumans J, Staaf J, Jönsson G, et al. Detection and delineation of an unusual 17p11.2 deletion by array-CGH and refinement of the Smith-Magenis syndrome minimum deletion to approximately 650 kb. Eur J Med Genet. 2005;48(3):290–300. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2005.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Vlangos CN, Yim DK, Elsea SH. Refinement of the Smith-Magenis syndrome critical region to approximately 950kb and assessment of 17p11.2 deletions. Are all deletions created equally? Mol Genet Metab. 2003;79(2):134–141. doi: 10.1016/s1096-7192(03)00048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Vlangos CN, Wilson M, Blancato J, Smith AC, Elsea SH. Diagnostic FISH probes for del(17)(p11.2p11.2) associated with Smith-Magenis syndrome should contain the RAI1 gene. Am J Med Genet A. 2005;132A(3):278–282. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.30461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Liburd N, Ghosh M, Riazuddin S, et al. Novel mutations of MYO15A associated with profound deafness in consanguineous families and moderately severe hearing loss in a patient with Smith-Magenis syndrome. Hum Genet. 2001;109(5):535–541. doi: 10.1007/s004390100604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wang A, Liang Y, Fridell RA, et al. Association of unconventional myosin MYO15 mutations with human nonsyndromic deafness DFNB3. Science. 1998;280(5368):1447–1451. doi: 10.1126/science.280.5368.1447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Castigli E, Wilson SA, Garibyan L, et al. TACI is mutant in common variable immunodeficiency and IgA deficiency. Nat Genet. 2005;37(8):829–834. doi: 10.1038/ng1601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Nickerson ML, Warren MB, Toro JR, et al. Mutations in a novel gene lead to kidney tumors, lung wall defects, and benign tumors of the hair follicle in patients with the Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome. Cancer Cell. 2002;2(2):157–164. doi: 10.1016/s1535-6108(02)00104-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Dardour L, Verleyen P, Lesage K, Holvoet M, Devriendt K. Bilateral renal tumors in an adult man with Smith-Magenis syndrome: the role of the FLCN gene. Eur J Med Genet. 2016;59(10):499–501. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2016.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Carney G, Wei S, Rizzo WB. Sjögren-Larsson syndrome: seven novel mutations in the fatty aldehyde dehydrogenase gene ALDH3A2. Hum Mutat. 2004;24(2):186. doi: 10.1002/humu.9262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Imai Y, Suzuki Y, Matsui T, Tohyama M, Wanaka A, Takagi T. Cloning of a retinoic acid-induced gene, GT1, in the embryonal carcinoma cell line P19: neuron-specific expression in the mouse brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1995;31(1–2):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(95)00020-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Walz K, Caratini-Rivera S, Bi W, et al. Modeling del(17)(p11.2p11.2) and dup(17)(p11.2p11.2) contiguous gene syndromes by chromosome engineering in mice: phenotypic consequences of gene dosage imbalance. Mol Cell Biol. 2003;23(10):3646–3655. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.10.3646-3655.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Bi W, Yan J, Shi X, et al. Rai1 deficiency in mice causes learning impairment and motor dysfunction, whereas Rai1 heterozygous mice display minimal behavioral phenotypes. Hum Mol Genet. 2007;16(15):1802–1813. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Toulouse A, Rochefort D, Roussel J, Joober R, Rouleau GA. Molecular cloning and characterization of human RAI1, a gene associated with schizophrenia. Genomics. 2003;82(2):162–171. doi: 10.1016/s0888-7543(03)00101-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Fragoso YD, Stoney PN, Shearer KD, et al. Expression in the human brain of retinoic acid induced 1, a protein associated with neurobehav-ioural disorders. Brain Struct Funct. 2015;220(2):1195–1203. doi: 10.1007/s00429-014-0712-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Seranski P, Hoff C, Radelof U, et al. RAI1 is a novel polyglutamine encoding gene that is deleted in Smith-Magenis syndrome patients. Gene. 2001;270(1–2):69–76. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(01)00415-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Vulto-van Silfhout AT, Rajamanickam S, Jensik PJ, et al. Mutations affecting the SAND domain of DEAF1 cause intellectual disability with severe speech impairment and behavioral problems. Am J Hum Genet. 2014;94(5):649–661. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.03.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Faqeih EA, Al-Owain M, Colak D, et al. Novel homozygous DEAF1 variant suspected in causing white matter disease, intellectual disability, and microcephaly. Am J Med Genet A. 2014;164A(6):1565–1570. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.36482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Luo T, Wagner E, Crandall JE, Dräger UC. A retinoic-acid critical period in the early postnatal mouse brain. Biol Psychiatry. 2004;56(12):971–980. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.09.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Chen L, Tao Y, Song F, Yuan X, Wang J, Saffen D. Evidence for genetic regulation of mRNA expression of the dosage-sensitive gene retinoic acid induced-1 (RAI1) in human brain. Sci Rep. 2016;6:19010. doi: 10.1038/srep19010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Berger SI, Ciccone C, Simon KL, et al. Exome analysis of Smith-Magenis-like syndrome cohort identifies de novo likely pathogenic variants. Hum Genet. 2017;136(4):409–420. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Carmona-Mora P, Encina CA, Canales CP, et al. Functional and cellular characterization of human Retinoic Acid Induced 1 (RAI1) mutations associated with Smith-Magenis Syndrome. BMC Mol Biol. 2010;11(1):63. doi: 10.1186/1471-2199-11-63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Huang WH, Guenthner CJ, Xu J, et al. Molecular and neural functions of RAI1, the causal gene for Smith-Magenis syndrome. Neuron. 2016;92(2):392–406. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.09.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Girirajan S, Truong HT, Blanchard CL, Elsea SH. A functional network module for Smith-Magenis syndrome. Clin Genet. 2009;75(4):364–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2008.01135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Williams SR, Zies D, Mullegama SV, Grotewiel MS, Elsea SH. Smithmagenis syndrome results in disruption of CLOCK gene transcription and reveals an integral role for RAI1 in the maintenance of circadian rhythmicity. Am J Hum Genet. 2012;90(6):941–949. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.04.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Darvekar S, Johnsen SS, Eriksen AB, Johansen T, Sjøttem E. Identification of two independent nucleosome-binding domains in the transcriptional co-activator SPBP. Biochem J. 2012;442(1):65–75. doi: 10.1042/BJ20111230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Yun M, Wu J, Workman JL, Li B. Readers of histone modifications. Cell Res. 2011;21(4):564–578. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Atanesyan L, Günther V, Dichtl B, Georgiev O, Schaffner W. Polyglutamine tracts as modulators of transcriptional activation from yeast to mammals. Biol Chem. 2012;393(1–2):63–70. doi: 10.1515/BC-2011-252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Vilboux T, Ciccone C, Blancato JK, et al. Molecular analysis of the Retinoic Acid Induced 1 gene (RAI1) in patients with suspected smith-magenis syndrome without the 17p11.2 deletion. PLoS One. 2011;6(8) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Bi W, Ohyama T, Nakamura H, et al. Inactivation of Rai1 in mice recapitulates phenotypes observed in chromosome engineered mouse models for Smith-Magenis syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 2005;14(8):983–995. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Alaimo JT, Hahn NC, Mullegama SV, Elsea SH. Dietary regimens modify early onset of obesity in mice haploinsufficient for Rai1. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e105077. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Tahir R, Kennedy A, Elsea SH, Dickinson AJ. Retinoic acid induced-1 (Rai1) regulates craniofacial and brain development in Xenopus. Mech Dev. 2014;133:91–104. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2014.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Chen L, Mullegama SV, Alaimo JT, Elsea SH. Smith-Magenis syndrome and its circadian influence on development, behavior, and obesity – own experience. Dev Period Med. 2015;19(2):149–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Carneiro BT, Araujo JF. The food-entrainable oscillator: a network of interconnected brain structures entrained by humoral signals? Chronobiol Int. 2009;26(7):1273–1289. doi: 10.3109/07420520903404480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Noble EE, Billington CJ, Kotz CM, Wang C. The lighter side of BDNF. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011;300(5):R1053–R1069. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00776.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Gray J, Yeo GS, Cox JJ, et al. Hyperphagia, severe obesity, impaired cognitive function, and hyperactivity associated with functional loss of one copy of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene. Diabetes. 2006;55(12):3366–3371. doi: 10.2337/db06-0550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Joober R, Benkelfat C, Toulouse A, et al. Analysis of 14 CAG repeat-containing genes in schizophrenia. Am J Med Genet. 1999;88(6):694–699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Hayes S, Turecki G, Brisebois K, et al. CAG repeat length in RAI1 is associated with age at onset variability in spinocerebellar ataxia type 2 (SCA2) Hum Mol Genet. 2000;9(12):1753–1758. doi: 10.1093/hmg/9.12.1753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Potocki L, Bi W, Treadwell-Deering D, et al. Characterization of Potocki-Lupski syndrome (dup(17)(p11.2p11.2)) and delineation of a dosage-sensitive critical interval that can convey an autism phenotype. Am J Hum Genet. 2007;80(4):633–649. doi: 10.1086/512864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.van der Zwaag B, Franke L, Poot M, et al. Gene-network analysis identifies susceptibility genes related to glycobiology in autism. PLoS One. 2009;4(5):e5324. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Carmona-Mora P, Walz K. Retinoic acid induced 1, RAI1: a dosage sensitive gene related to neurobehavioral alterations including autistic behavior. Curr Genomics. 2010;11(8):607–617. doi: 10.2174/138920210793360952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Redin C, Gérard B, Lauer J, et al. Efficient strategy for the molecular diagnosis of intellectual disability using targeted high-throughput sequencing. J Med Genet. 2014;51(11):724–736. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2014-102554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Thaker VV, Esteves KM, Towne MC, et al. Whole exome sequencing identifies RAI1 mutation in a morbidly obese child diagnosed with ROHHAD syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(5):1723–1730. doi: 10.1210/jc.2014-4215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Churbanov AY, Karafet TM, Morozov IV, et al. Whole exome sequencing reveals homozygous mutations in RAI1, OTOF, and SLC26A4 genes associated with nonsyndromic hearing loss in Altaian families (South Siberia) PLoS One. 2016;11(4):e0153841. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Barnett C, Yazgan O, Kuo HC, et al. Williams syndrome transcription factor is critical for neural crest cell function in Xenopus laevis. Mech Dev. 2012;129(9–12):324–338. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2012.06.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Hittner HM, King RA, Riccardi VM, et al. Oculocutaneous albinoidism as a manifestation of reduced neural crest derivatives in the Prader-Willi syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 1982;94(3):328–337. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(82)90358-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Kochilas L, Merscher-Gomez S, Lu MM, et al. The role of neural crest during cardiac development in a mouse model of DiGeorge syndrome. Dev Biol. 2002;251(1):157–166. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2002.0819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Lim JH, Luo T, Sargent TD, Fallon JR. Developmental expression of Xenopus fragile X mental retardation-1 gene. Int J Dev Biol. 2005;49(8):981–984. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.052070jl. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Roper RJ, VanHorn JF, Cain CC, Reeves RH. A neural crest deficit in Down syndrome mice is associated with deficient mitotic response to Sonic hedgehog. Mech Dev. 2009;126(3–4):212–219. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2008.11.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Wurdak H, Ittner LM, Lang KS, et al. Inactivation of TGFbeta signaling in neural crest stem cells leads to multiple defects reminiscent of DiGeorge syndrome. Genes Dev. 2005;19(5):530–535. doi: 10.1101/gad.317405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Laje G, Bernert R, Morse R, Pao M, Smith AC. Pharmacological treatment of disruptive behavior in Smith-Magenis syndrome. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2010;154C(4):463–468. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.30282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Poisson A, Nicolas A, Cochat P, et al. Behavioral disturbance and treatment strategies in Smith-Magenis syndrome. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2015;10(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s13023-015-0330-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.De Leersnyder H, Bresson JL, de Blois MC, et al. Beta 1-adrenergic antagonists and melatonin reset the clock and restore sleep in a circadian disorder, Smith-Magenis syndrome. J Med Genet. 2003;40(1):74–78. doi: 10.1136/jmg.40.1.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Loviglio MN, Beck CR, White JJ, et al. Identification of a RAI1-associated disease network through integration of exome sequencing, transcriptomics, and 3D genomics. Genome Med. 2016;8(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s13073-016-0359-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]