| Summary: |
The invention
in this patent application relates to 6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrazolo[5,1-b][1,3]oxazine derivatives represented
generally by formula I. These compounds are inhibitors of PDE-4 isozymes,
especially with a binding affinity for the PDE-4B isoform, and may
be useful for the treatment of central nervous system (CNS), metabolic,
autoimmune, and inflammatory diseases or disorders. |
| The cyclic nucleotides, 3′,5′-cyclic adenosine
monophosphate (cAMP) and guanosine 3′,5′-cyclic guanosine
monophosphate (cGMP), are examples of second messengers that regulate
many intracellular processes. They are intracellular signaling molecules
released by cells to initiate intracellular signal transduction cascades,
which cause the occurrence of several biological processes such as
proliferation, differentiation, migration, survival, and apoptosis.
An example of their activities is the cAMP activation of the cAMP-dependent
kinases in the neurons of the central nervous system to initiate the
phosphorylation of specific proteins to regulate synaptic transmission
as well as neuronal differentiation and survival. |
| The level of intracellular cAMP is regulated by a balance between
the activities of two types of enzyme: adenylyl cyclases (AC), which
catalyze the formation of cAMP from adenosine triphosphate (ATP),
and phosphdiesterases (PDEs), which degrade cAMP. There are at least
ten known families of adenylyl cyclases and 11 families of phosphodiesterases
to achieve this balance, a testament to the complexity and importance
of the cyclic nucleotide signaling process. |
| Phosphodiesterases (PDEs) are intracellular enzymes that hydrolyze
cAMP and cGMP into the nonsignaling molecules 5′-adenosine
monophosphate (AMP) and 5′-guanosine monophosphate (GMP), respectively.
In addition to the main families of PDEs, different types of neurons
are known to express multiple isozymes of each of these families of
enzymes, and there is good evidence for compartmentalization and specificity
of function for different isozymes within a given neuron. |
| The 11 known families of PDEs are encoded by 21 different
genes; each gene typically yields multiple splice variants that further
contribute to the isozyme diversity. The PDE families are distinguished
functionally based on cyclic nucleotide substrate specificity, mechanism(s)
of regulation, and sensitivity to inhibitors. Furthermore, PDEs are
differentially expressed throughout the organism, including in the
central nervous system. As a result of these distinct enzymatic activities
and localization, different PDE isozymes can serve distinct physiological
functions. Therefore, selective inhibitors of distinct PDE isozymes
may have the advantage of delivering specific therapeutic effects,
fewer side effects, or both. |
| The compounds
described in this patent application display a binding affinity for
the PDE4 family of enzymes (PDE-4A, PDE-4B, PDE-4C, and PDE-4D), particularly
for the PDE-4A, PDE-4B, and PDE-4C isoforms. |
| The function of PDE-4 isozymes can be inhibited by known selective
PDE-4 inhibitors such as Roflumilast (Daliresp), which was approved
for the treatment of severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
(COPD) and Apremilast (Otezla), which was approved for the treatment
of adults with active psoriatic arthritis. |
| It is clear from the above that PDE-4 inhibitors can provide needed
and beneficial pharmacological activities that have been realized
into known therapies. However, their use has been associated with
induction of common gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea,
emesis, and diarrhea. It was hypothesized that these undesirable adverse
effects are associated with the inhibition of the PDE-4D isoform.
Thus, research efforts were directed to develop compounds with selective
affinities for the inhibition of PDE-4B isoform over the PDE-4D isoform.
It is anticipated that compounds with enhanced binding affinity for
the PDE-4B isoform over the PDE-4D isoform can be useful in the treatment
of various diseases and disorders of the central nervous system (CNS)
with fewer side effects. |
| The compounds of
formula I described in this patent application show selective affinity
for the inhibition of PDE-4B isoform, and therefore, they have the
potential to provide useful therapies for the treatment of various
diseases and disorders of the central nervous system (CNS), as well
as metabolic, autoimmune, and inflammatory diseases or disorders.
Their use may also lead to decreased gastrointestinal side effects
(e.g., nausea, emesis, and diarrhea) believed to be associated with
inhibition of the PDE-4D isoform. |
| Important
Compound Classes: |
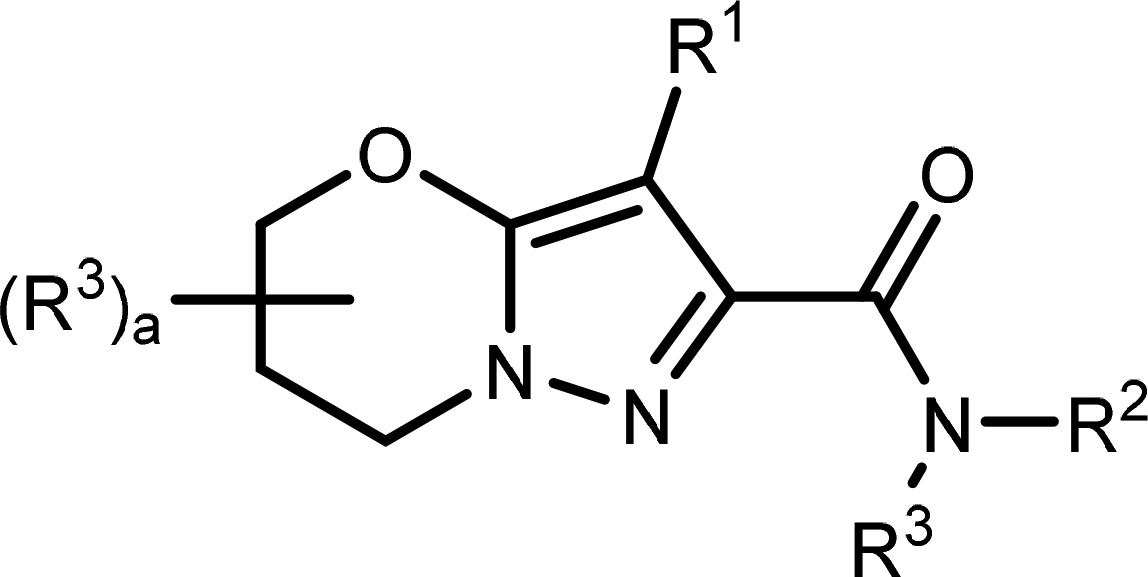 Formula I Formula I |
| Key Structures: |
The inventors reported the structures of 64 compounds of formula
I, including the following representative examples. Few examples were
resolved into enantiomers.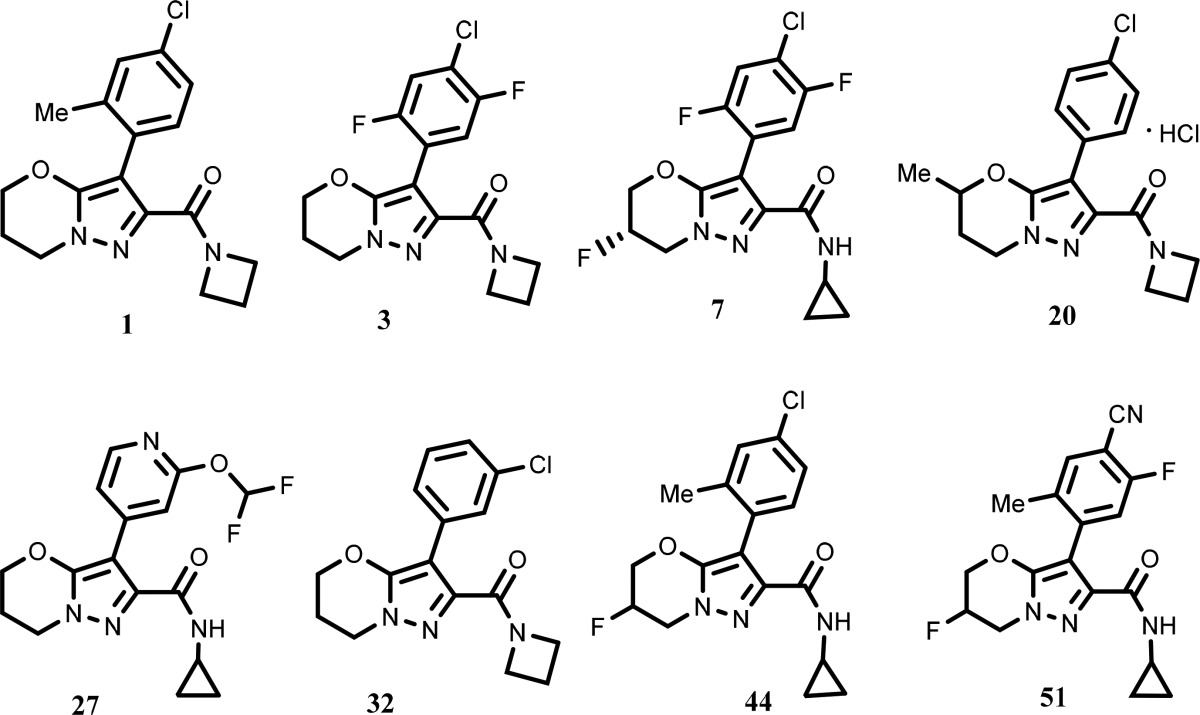
|
| Biological Assay: |
The PDE-4A, PDE-4B, PDE-4C,
and PDE-4D binding affinities for formula
I compounds were determined. |
| Biological
Data: |
The biological data obtained from testing
the above representative examples are shown in the following table: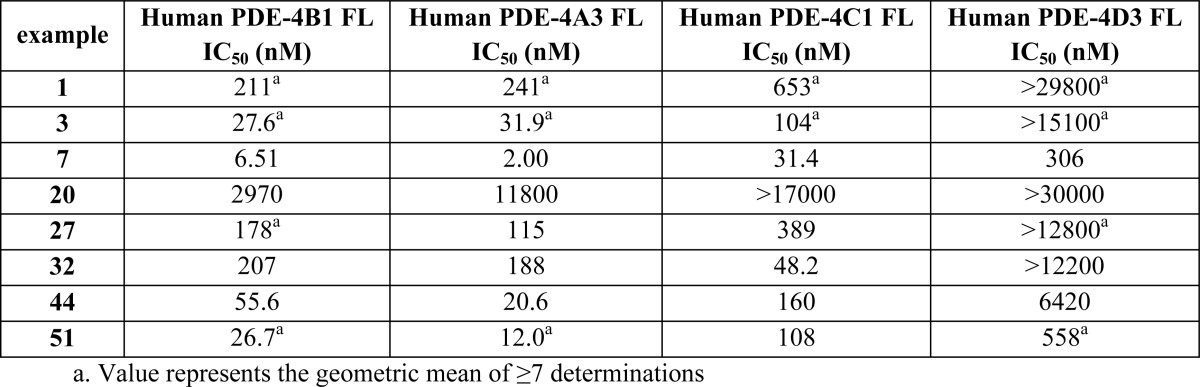
|
| Recent Review Articles: |
Contreras S.; Milara J.; Morcillo E.; Cortijo J.. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23 ( (14), ), 2073–2083. |
| Girdhar A.; Raheja S.; Lather V.; Kharb R.. Innovations Pharm. Pharmacother. 2015, 3 ( (2), ), 565–579. |
| Darout E.; Menhaji-Klotz E.; Chappie T. A.. Methods and Principles
in Medicinal Chemistry 2014, 61, 45–64. |
| Azam M. A.; Tripuraneni N. S.. Sci. Pharm. 2014, 82 ( (3), ), 453–481. |



 Formula I
Formula I
