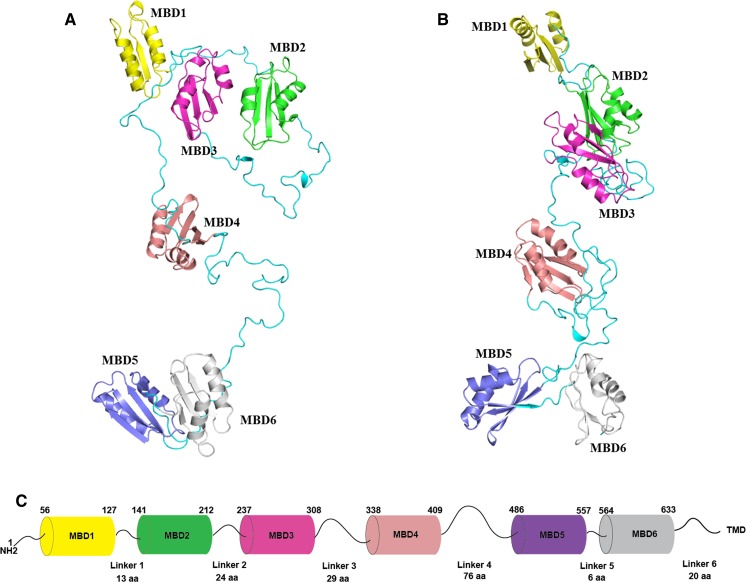
Fig. 3.
An all-atom full-length model of MBD1-6. A The initial model. B The optimized model. Six subdomains are colored differently, and their unstructured linkers are colored in cyan. NMR structures in Table 2 were used. The initial domain arrangement was determined based on the sequence length of linkers and electrostatic complementarity of the protein surfaces between different domains. 3D coordinates of the missing linkers were generated by SWISS-MODEL (Biasini et al. 2014) server using the arranged model as a template, leading to a full-length model of MBD1-6 without the inclusion of the first 56 residues. The initial model was then optimized by MD simulations using NAMD (version 2.12) (Phillips et al. 2005) for 5 nanoseconds (ns). The solvent was presented in the generalized Born/solvent-accessible surface area implicit solvent model (Tanner et al. 2011), and the protein system was described in CHARMM36 force field (Huang and MacKerell 2013). C The schematic representation of N-terminal MBDs of ATP7B in tandem. The length of each MBD and linkers (as the position of amino acids) in between is indicated according to the PDB structures of the respective MBDs (Table 2). A linker is defined as the segment between folded 70-aa MBDs except only for MBD6 which is 68-aa long. TMD represents the transmembrane part of ATP7B and the linker between MBD6 and transmembrane helix 1 (TMD1) is 20-aa long (Lorinczi et al. 2008)