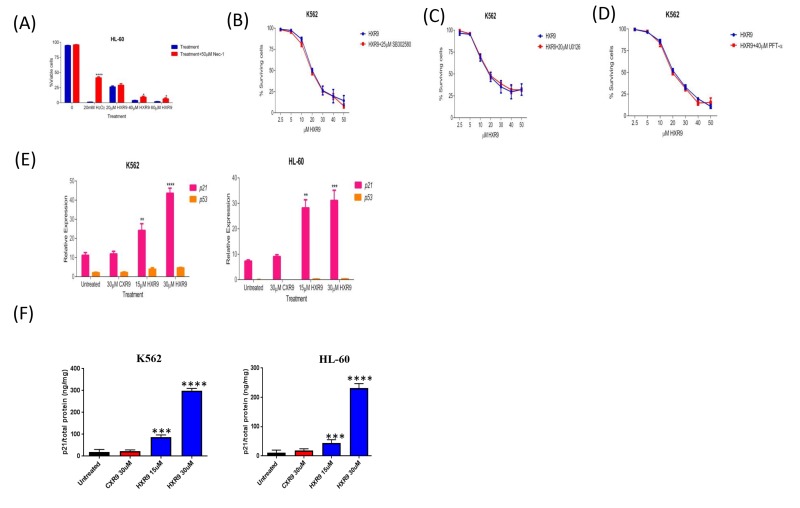
Figure 5. Evaluation of potential cell death pathways.
A. Inhibition of RIP1 rescues HL-60 cells from HXR9-mediated cell killing. RIP1 was inhibited using 50 μM Nec1. Hydrogen peroxide was used as a positive control as it has previously been shown to induce RIP1-dependent cell killing. B. Cells were pre-treated with or without 25 μM of the p38 inhibitor SB302580 for 1 hour, and then with a titration of HXR9 prepared in media with or without 25 μM SB302580, red and blue curves, respectively. The cytotoxicity of HXR9 was analysed by measuring LDH enzyme activity in cell-free supernatants. Pre- and co-treatment of cells with 25 μM SB302580 did not affect the cytotoxicity of HXR9. Statistical significance was tested using the student's t-test. Graphs show the mean of 3 independent experiments and error bars show the SEM. C. Cells were pre-treated with or without 20 μM of the MEK/ERK inhibitor U0126 for 1 hour, and then with increasing concentrations of HXR9 prepared in media with or without 20 μM U0126, red and blue curves, respectively. The proportion of surviving cells was then measured using the LDH assay. Pre- and co-treatment of cells with 20μM U0126 did not prevent HXR9 cytotoxicity. Graphs show the mean of three independent experiments and error bars show the SEM. D. The effect of blocking p53 protein on HXR9 cytotoxicity. Cells were pre-treated with or without 40 μM PFT-α for 1 hour, and then for 2 hours with a titration of HXR9 prepared in media supplemented with or without 40 μM PFT-α, red and blue curves, respectively. Graphs show the mean of 3 independent experiments and error bars show the SEM. E. HXR9 treatment of K562 and HL-60 cells leads to a significant increase in expression of the p21 tumor suppressor gene. p21 expression was measured using quantitative PCR after 2 hours of incubation with the IC50 concentration of HXR9 for each cell type. F. p21 protein expression was measured using an ELISA with the same concentrations of HXR9.