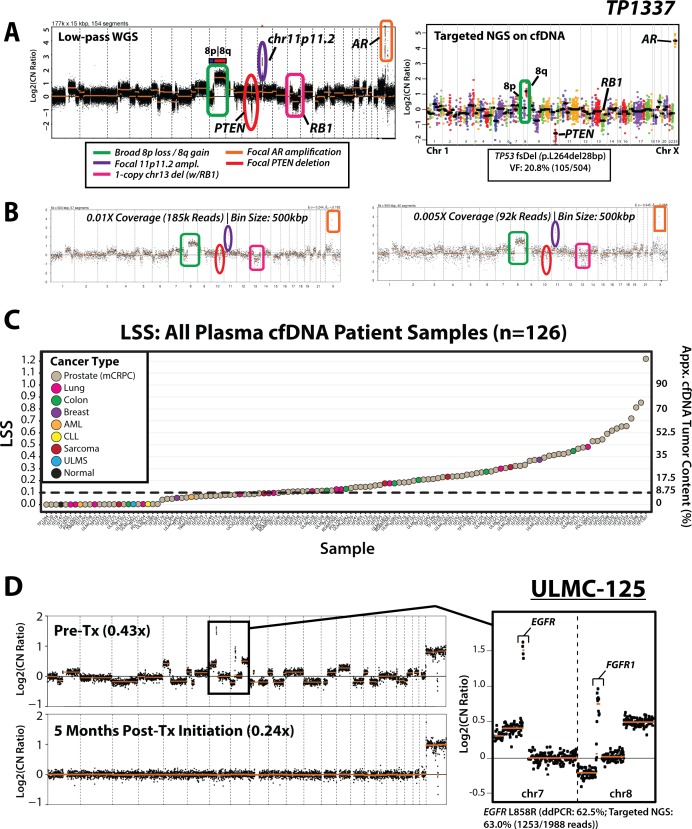
Figure 2. cfDNA tumor content approximation and disease monitoring applications for targeted and ultra-low-pass whole-genome sequencing (WGS) of cell-free DNA from patients with advanced cancer.
(A) Genome-wide log2(CopyNumberRatio) (Log2CN) calls for TP1337, a high tumor content cfDNA sample from a patient with mCRPC, are displayed for low-pass WGS data (0.82x whole-genome coverage) and targeted NGS data. Key copy-number alterations (CNA) detected are circled, including broad gain of 8q (green), focal amplification of chr11p11.2 (purple) and AR (orange), and focal RB1 (1-copy; pink) and PTEN (2-copy; red) deletions. Copy number and mutation data from deep coverage targeted NGS data is provided at right from unamplified TP1337 cfDNA (1,102× targeted NGS coverage) using the DNA component of the Oncomine Comprehensive Assay (OCP), a pan cancer NGS panel developed for FFPE tissue samples. For genes with sufficient amplicons for CNA calling, amplicon (dots) and gene (black bars)-level log base 2 copy number ratio (Log2 [CN Ratio]) estimates (compared to a composite reference sample) are plotted. All CNAs seen by low-pass WGS are detected via targeted NGS CNA analysis (chr11p11.2 is not targeted by OCP). A prioritized high confidence somatic 28 bp frameshift deletion in TP53 (p.L264del28bp; variant fraction (VF) = 20.8% (105/504 total sequencing reads)) detected by OCP is shown in the inset box. (B) In silico downsampling experiments highlight the ability to detect both focal and broad copy-number alterations from TP1337 cfDNA WGS data at whole-genome coverages down to 0.005×. Bin size and number of high-quality (MAPQ ≥ 37) mapped reads used for copy-number analysis are indicated at each coverage, and regions affected by copy-number alterations detected in original low-pass WGS are circled. (C) Distribution of cfDNA tumor content estimates (right axis) from least-squares distance metric (LSS) values (left axis) for 124 patient cfDNA samples (123 from patients with advanced cancer, including TP1178 (from a patient with untreated advanced prostate cancer), along with 1 normal control sample (TP1147). All patient samples are colored by cancer type (indicated in the legend). (D) Low-pass WGS copy-number for pre- and post- EGFR inhibitor (erlotonib) treatment plasma cfDNA samples from ULMC-125, a patient with metastatic lung cancer. Multiple whole-chromosome and arm-level gains/losses as well as focal amplifications are present in the pre-treatment cfDNA sample with high tumor content. A zoomed view of chromosomes 7 and 8 show focal EGFR and FGFR1 amplifications in the pre-treatment sample (an activating EGFR L858R mutation was previously detected at 62.5% variant fraction by digital droplet PCR [ddPCR]). Low-pass WGS sequencing of a cfDNA sample taken 5 months post-treatment initiation (bottom) showed no detectable copy-number alterations genome-wide, and no detectable L858R mutation by ddPCR analysis (L858R variant fraction: 0.0%). Low-pass WGS copy-number bin size: 500 kbp; segmentation p-value threshold: 0.01.