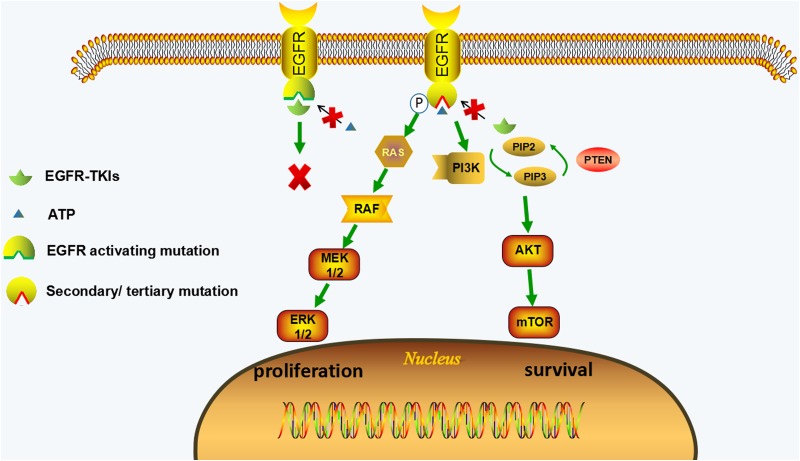
Figure 1. EGFR-dependent resistance mechanisms of irreversible EGFR-TKIs.
EGFR-TKIs compete with ATP for binding to tyrosine kinase domain of EGFR with activating mutations, leading to the inhibition of EGFR and its downstream pathways (MAPK and PI3K/AKT pathways). The secondary or tertiary mutations of EGFR (such as C797S mutation) can change the conformation of tyrosine kinase domain of EGFR, which hinder EGFR-TKIs from binding to EGFR and restore ATP affinity; therefore the downstream pathways are activated leading to the proliferative and anti-apoptotic effect. The activation of downstream signaling is coupled from upstream EGFR activation in EGFR-dependent resistant cells.