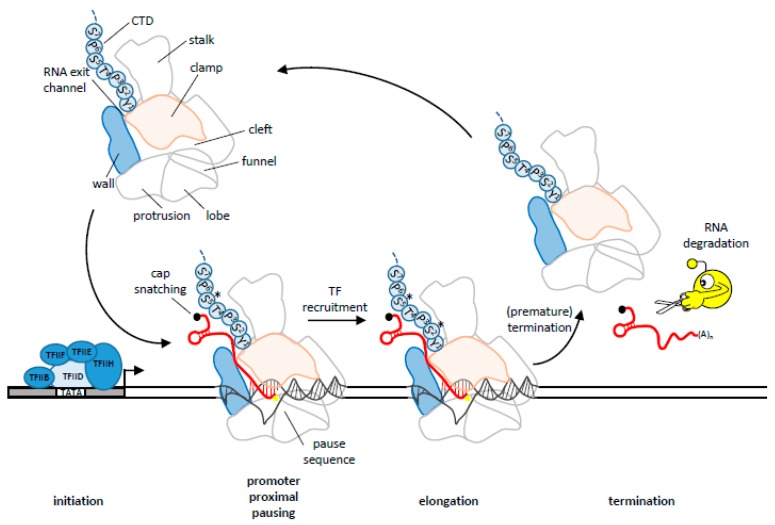
Figure 1.
Transcription cycle. A cartoon depiction of RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) is shown in the upper left, with several domains and modules labelled. The clamp and wall (flap in prokaryotes) modules that make up the RNA-exit channel are depicted in pink and blue, respectively. The first repeat of the RNAPII C-terminal domain (CTD) is shown as a string of amino acids with their respective numbers. Next, the stages of the transcription cycle are shown, with the viral interfering mechanisms. First, general transcription factors assemble at the promoter and direct RNAPII towards the transcription start site. Transcription factor (TF) IIH phosphorylates the RNAPII at Ser5 (black asterisk). TFIIH opens the DNA template, forming the transcription bubble, permitting RNAPII to begin transcribing RNA in its active center (yellow dot). Upon transcribing the first 20–60 nucleotides, most RNAP will pause. Transcription factor recruitment regulates these transcription kinetics and phosphorylate RNAPII at Ser2. When the correct signal is encountered, RNAPII will terminate transcription and release the RNA. Some viruses encode endonucleases (yellow sphere with scissor) that can cleave RNAs, causing RNA degradation.