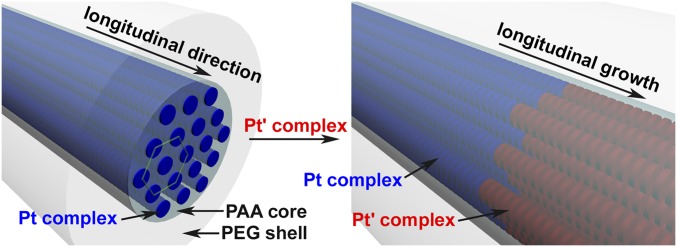
Significance
Living supramolecular polymerization has emerged as an efficient pathway for the fabrication of supramolecular assemblies with precisely controlled dimensions and diverse architectures. This work achieves living supramolecular polymerization by the collaborative assembly of two structurally dissimilar components, namely, the platinum(II) complexes and the block copolymers. This work largely broadens the scope of supramolecular monomers for living supramolecular polymerization and in the construction of supramolecular-based heterojunctions with large lattice mismatch, which represents a distinct advantage over the existing methods based on single-component systems in devising living supramolecular polymerization. This work may open up new, simple one-pot strategies for the fabrication of segmented supramolecular-based heterojunctions with different optical, charge transport, and catalytic properties for directional excitation energy, and electron and hole transport.
Keywords: platinum complexes, living supramolecular polymerization, block copolymers, metal–metal interactions, nanostructures
Abstract
An important feature of biological systems to achieve complexity and precision is the involvement of multiple components where each component plays its own role and collaborates with other components. Mimicking this, we report living supramolecular polymerization achieved by collaborative assembly of two structurally dissimilar components, that is, platinum(II) complexes and poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(acrylic acid) (PEG-b-PAA). The PAA blocks neutralize the charges of the platinum(II) complexes, with the noncovalent metal–metal and π–π interactions directing the longitudinal growth of the platinum(II) complexes into 1D crystalline nanostructures, and the PEG blocks inhibiting the transverse growth of the platinum(II) complexes and providing the whole system with excellent solubility. The ends of the 1D crystalline nanostructures have been found to be active during the assembly and remain active after the assembly. One-dimensional segmented nanostructures with heterojunctions have been produced by sequential growth of two types of platinum(II) complexes. The PAA blocks act as adapters at the heterojunctions for lattice matching between chemically and crystallographically different platinum(II) complexes, achieving heterojunctions with a lattice mismatch as large as 21%.
Platinum(II) complexes containing π-conjugated donor ligands of d8 electronic configuration and square-planar geometry have attracted growing attention because of their intriguing photophysical and spectroscopic properties as well as their rich solid-state polymorphism and solution-state aggregation behaviors (1–9). Their d8 electronic configuration and square-planar geometry have offered them the propensity to form noncovalent metal−metal and π−π stacking interactions. Diverse supramolecular assemblies of platinum(II) complexes with interesting optical and luminescence behavior derived from metal−metal and π−π stacking interactions and other noncovalent interactions have been reported (10–35). Examples include metallogels (14–16), liquid crystals (17, 18), and molecular architectures (19–24) such as molecular hairpins, foldamers, tweezers, and rectangles, as well as nanostructures (25–31) such as nanofibers, nanosheets, vesicles, nanorings, helices, and nanotubes. Despite all these interesting developments, most of the supramolecular assemblies of platinum(II) complexes reported by our group and others are formed in single-component assembly systems (12–35). Furthermore, despite recent interest in living supramolecular polymerization (36–55), living supramolecular assembly based on the platinum(II) system has also been rarely studied (54).
Unlike the well-established living polymerization that involves the formation of polymers linked by covalent bonds, living supramolecular polymerization is a relatively new area of research that has only attracted much attention recently and has emerged as an efficient pathway for the fabrication of supramolecular assemblies with precisely controlled dimensions and diverse architectures (46–55). For example, living crystallization-driven self-assembly based on diblock copolymers containing crystallizable polyferrocenyldimethylsilane blocks has been reported to achieve cylindrical micelles and block comicelles with precise lengths, as well as various complex architectures (46–48). Besides, supramolecular polymerization of a special porphyrin-based monomer has been found to exhibit living characters to form nanofibers with controlled length and narrow polydispersity (51). Recently, a chain-growth supramolecular polymerization has been realized by rationally designed corannulene-based supramolecular monomer and initiator, which allows for the efficient control of chain length, sequence, and stereochemical structure of the linear supramolecular polymer chains formed (52). Moreover, nanotubular heterojunctions prepared from two types of hexabenzocoronene derivatives have been reported to exhibit long-range excitation energy transfer behaviors and enhanced charge transport properties compared with the homotropic nanotubular assemblies of both types of the hexabenzocoronene derivatives (49). One-dimensional heterojunction nanostructures may also show unique properties for their applications in optical, electrical, and optoelectronic devices (56). However, fabrication of segmented architectures with heterojunctions by living supramolecular polymerization remains challenging and less explored (47, 49), due to the relatively strict requirement of lattice matching of different supramolecular monomers for heterojunction formation; a lattice mismatch smaller than 15% has been regarded as a prerequisite for successful heterojunction formation (57, 58). In the reported literature studies (46–55), the heterojunctions can only be prepared either from structurally similar supramolecular monomers (49) or from building blocks with a slight lattice mismatch of 6% (47). This has presented a major drawback as dissimilar components are sometimes preferred for the fabrication of high-performance heterojunctions for energy transport, charge transport, and catalytic functions.
In addition, the reported methods for living supramolecular polymerizations are mainly based on single-component systems, with exceptionally few examples of two-component systems that can be achievable only via the involvement of structurally similar building blocks (46–55). Since the realization of living supramolecular polymerization is largely dependent on the design of the specialized molecules or macromolecules, the types of supramolecular monomers that can be polymerized by living supramolecular polymerization are very limited (46–55). In contrast, biological systems use multicomponent systems where each component plays its own role and collaborates with other components to achieve complexity and precision. Recently, a platinum(II) complex/PEG-b-PAA two-component supramolecular coassembly process developed in our laboratory showed the formation of 1D core–shell crystalline nanostructures (59). Since they are connected by noncovalent metal–metal interactions, π–π interactions, and electrostatic attractions, the 1D crystalline nanostructures can be considered as one type of supramolecular polymers (36–55). In the present study, it is found that the ends of the 1D crystalline nanostructures formed by platinum(II) complexes and PEG-b-PAA diblock copolymers are active during the coassembly and remain active after the coassembly. Addition of more platinum(II) complexes to the 1D nanostructures leads to the growth of the nanostructures while the diameter of the nanostructures remains unchanged. Addition of a different platinum(II) complex to the nanostructures forms segmented nanostructures where segments of different platinum(II) complexes connect to form heterojunctions. At the heterojunctions, PAA blocks act as adapters for lattice matching between chemically and crystallographically different platinum(II) complexes. Heterojunctions with a lattice mismatch as large as 21% can be achieved. The present study represents an example of living supramolecular polymerization achieved by collaborative assembly of two structurally dissimilar components (46–55). The present study also broadens the scope of supramolecular monomers for living supramolecular polymerization and in the construction of supramolecular-based heterojunctions (46–55).
Results and Discussion
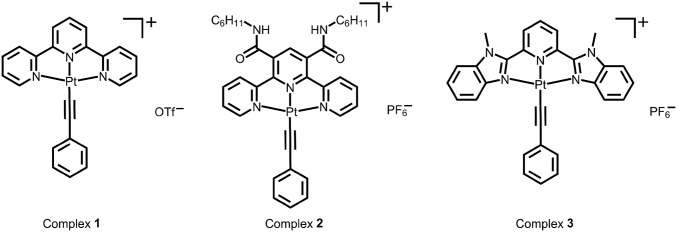
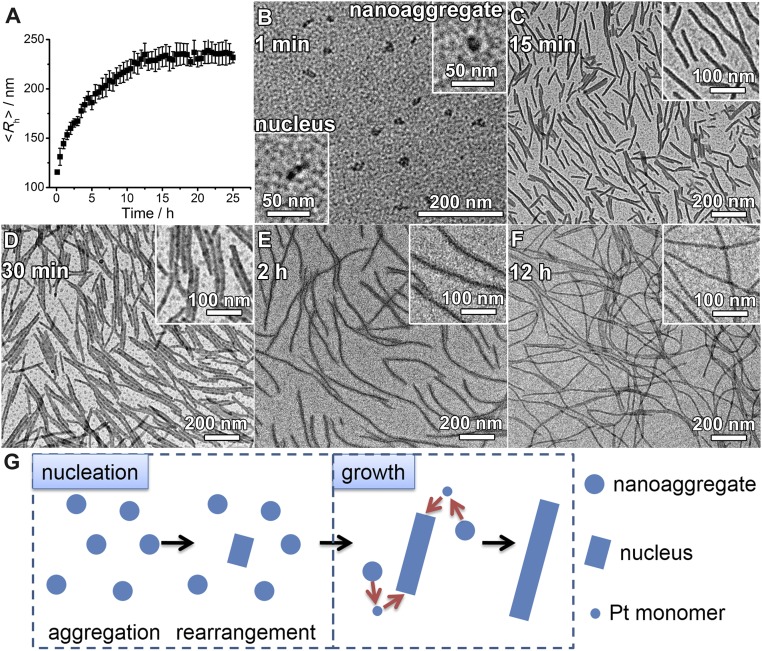
Supramolecular coassembly of complex 1 (Fig. 1) and PEG45-b-PAA69 in a mixed solvent of acetonitrile–methanol–water (1:1:8, vol/vol/v) shows the formation of nanofibers with a diameter of 12.1 ± 1.2 nm and a length of several micrometers after incubation of the coassembly mixture for 1 d (Fig. S1). The nanofibers are found to possess a core–shell crystalline nanostructure with hexagonally packed platinum(II) complexes along the fiber axis (59). The formation mechanism of the nanofibers has been studied by investigating the time course of the supramolecular coassembly process. The nanofibers of complex 1 show low-energy metal–metal-to-ligand charge transfer (MMLCT) absorptions at around 605 nm together with a triplet MMLCT emission at 782 nm (59) (Figs. S2 and S3). UV-vis and steady-state emission measurements of the complex 1/PEG45-b-PAA69 mixture show insignificant changes upon an increase of incubation time (Figs. S2 and S3). Dynamic light-scattering (DLS) studies indicate that the hydrodynamic radius 〈Rh〉 of the nanostructures in the mixture increases with incubation time. The increase in 〈Rh〉 becomes progressively less steep with the elongation of incubation time, and the 〈Rh〉 values level off at around 16 h (Fig. 2A). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) observation of the specimen prepared immediately upon mixing exhibits the formation of nanoobjects with sizes of around 10 nm (Fig. 2B). Some nanoobjects possess a spherical morphology while some others possess small aspect ratios and show signs of anisotropy (Fig. 2B), which are reminiscent of the two-step aggregation-rearrangement nucleation model developed recently (60). After incubation for 15 min, short nanofibers with a diameter of 11.8 ± 1.3 nm and a number-average length (Ln) of 120 nm (Lw/Ln = 1.42, Lw represents weight-average length) are formed (Fig. 2C). By increasing the incubation time to 30 min, nanofibers with Ln of 281 nm (Lw/Ln = 1.14) and 12.4 ± 1.2 nm in diameter have been observed (Fig. 2D). Further increase in the incubation time to 2 h leads to nanofibers with a diameter of 12.5 ± 1.8 nm and a Ln of 700 nm (Lw/Ln = 1.21) (Fig. 2E). At 12 h, nanofibers of 11.5 ± 1.2 nm in diameter, and micrometers in lengths, have been obtained (Fig. 2F). Noticeably, quenching the assembly mixture in an ice bath at the early stage of supramolecular polymerization leads to the formation of short nanofibers (Fig. S4A). Interestingly, the quenched short nanofibers are found to show insignificant change in their lengths and diameters after removal of the ice bath followed by incubation at room temperature for 2 d (Fig. S4B).
Fig. 1.
Chemical structures of platinum(II) complexes.
Fig. 2.
Time course of the supramolecular coassembly process. (A) Changes of hydrodynamic radius 〈Rh〉 during supramolecular coassembly of complex 1 (0.15 mM) and PEG45-b-PAA69 ([carboxylic acid] = 1 mM) in a mixed solvent of acetonitrile–methanol–water (1:1:8, vol/vol/v). (B–F) TEM images of the nanoobjects formed by the supramolecular coassembly at different incubation time. (G) Schematic illustration of the nucleation-growth mechanism of the supramolecular coassembly.
The gradual increase of the lengths of the nanofibers as evidenced by both DLS and TEM can rule out the possibility that the supramolecular polymerization in the present study follows a mechanism like conventional radical polymerization; one distinct feature of conventional radical polymerization is the formation of long polymer chains at the early stage of polymerization. For the formation of long nanofibers from short nanofibers, there are three possible mechanisms, namely (i) the end–end coupling of the short nanofibers, (ii) Ostwald ripening process, and (iii) the growth process of a nucleation-growth mechanism. For the end–end coupling mechanism, the long nanofibers are formed by the fusion of the ends of two short nanofibers. Based on this, one would expect a progressively steep increase of hydrodynamic radius in the DLS time course since DLS is extremely sensitive to objects with large sizes. The end–end coupling mechanism cannot explain the results of gradual increase and the leveling off as observed in the DLS time course (Fig. 2A). For the Ostwald ripening process, platinum(II) complexes dissociate from a short nanofiber and add onto the ends of another short nanofiber. As mentioned above, the short nanofibers obtained by quenching the supramolecular polymerization at the early stage show insignificant change in lengths after incubation at room temperature for 2 d (Fig. S4). This finding suggests that since the short nanofibers have a crystalline nanostructure, the dissociation of platinum(II) complexes from the crystalline nanostructures should be relatively difficult and slow. Therefore, Ostwald ripening process plays an insignificant role for the formation of long nanofibers from short nanofibers.
Based on the above experiments and analysis, and in view of the crystalline nanostructures of the nanofibers, it is proposed that the two-component platinum(II) complex/block copolymer supramolecular polymerization follows a nucleation-growth mechanism (Fig. 2G). Upon the mixing of platinum(II) complexes and block copolymers, nanoaggregates would form as shown in Fig. 2B, and then a part of the nanoaggregates would undergo rearrangement to form the nucleus (60) (Fig. 2 B and G). Addition of free platinum(II) complexes onto the nucleus would then lead to the formation and growth of the short nanofibers. It is noteworthy that the short nanofibers formed in the present study are different from the short patchy nanofibers in our previous study (59); the short patchy nanofibers possess less PEG protection and can couple with each other by attractive end patches, whereas the short nanofibers in the present study only allow the addition of free platinum(II) complexes onto their ends. In the present study, the free platinum(II) complexes are likely to be originated from the dissociation of the nanoaggregates of platinum(II) complexes and block copolymers (Fig. 2G). The dissociation of platinum(II) complexes is relatively easy and fast because the nanoaggregates possess large specific surface areas and the packing of platinum(II) complexes within the nanoaggregates is not quite regular. The binding constant of complex 1 and PEG45-b-PAA69 has been determined by UV-vis titration to be 6.5 × 104 M−1 (Supporting Information). The concentration of free complex 1 is estimated to be 2.7 μM, i.e., 1.8% of the total amount of complex 1 in the assembly mixture. When the nanoaggregates have been exhausted, the growth of nanofibers and the two-component supramolecular polymerization end. In the present system, the ends of the nanofibers are found to be active during supramolecular polymerization, which is one of defining characters for living supramolecular polymerization.
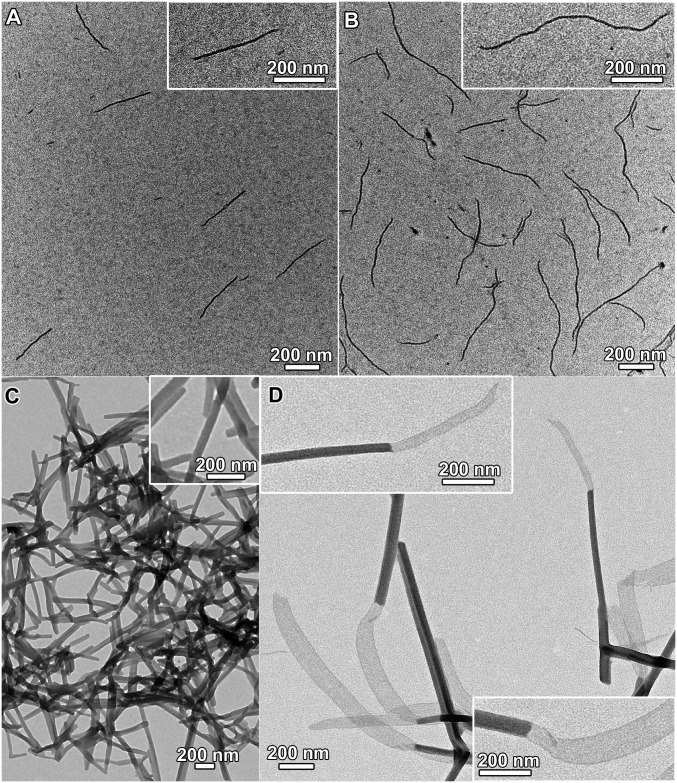
Another defining character of living supramolecular polymerization is that the ends of the supramolecular polymers remain active after supramolecular polymerization. Nanofibers with a diameter of 10.6 ± 1.0 nm and an Ln of 251 nm (Lw/Ln = 1.21), prepared by the mixing of complex 1 and PEG113-b-PAA51 in a mixed solvent of acetonitrile–methanol–water (1:1:8, vol/vol/v) at complex 1/carboxylic acid molar ratio of 0.05/1, followed by incubation at room temperature for 1 d (Fig. 3A), are found to show insignificant change in both the diameter and the length upon further incubation. Interestingly, addition of more complex 1 in acetonitrile to the nanofibers at a final complex 1/carboxylic acid molar ratio of 0.1/1 followed by incubation has been found to produce longer nanofibers with an Ln of 562 nm (Lw/Ln = 1.26) and a diameter of 10.2 ± 1.3 nm (Fig. 3B). DLS analysis shows an increase of an 〈Rh〉 from 94 to 139 nm upon the addition and incubation. The length increase and the unchanged diameter of the nanofibers suggest that the nanofibers possess active ends that serve as sites to seed the growth of the added complex 1 onto their ends.
Fig. 3.
TEM images of (A) nanofibers formed by supramolecular coassembly of complex 1 (0.06 mM) and PEG113-b-PAA51 ([carboxylic acid] = 1.2 mM) in a mixed solvent of acetonitrile–methanol–water (1:1:8, vol/vol/v); (B) longer nanofibers formed after adding more complex 1 to the as-formed nanofibers of A at a final complex 1/carboxylic acid molar ratio of 0.1/1; (C) nanorods formed by supramolecular coassembly of complex 2 (0.11 mM) and PEG45-b-PAA69 ([carboxylic acid] = 1 mM) in a mixed solvent of acetonitrile–methanol–water (1:1:8, vol/vol/v); (D) segmented nanostructures formed after adding complex 1 to the as-formed nanorods of C at a final complex 1/complex 2/carboxylic acid molar ratio of 0.18/0.11/1.
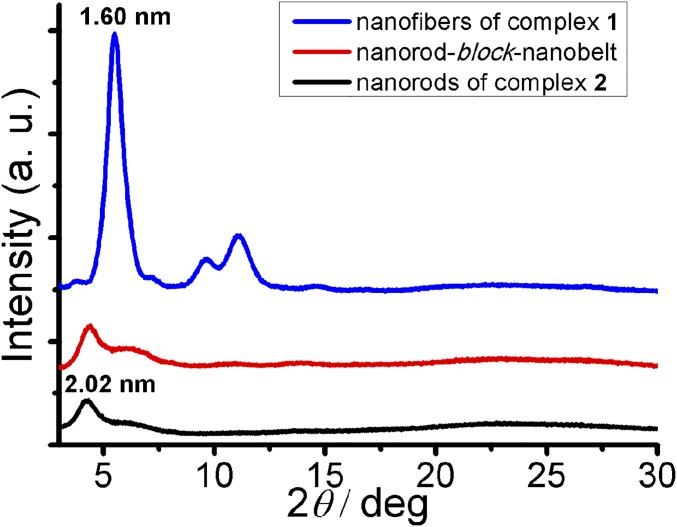
The activity of the ends of the supramolecular polymers has been further explored. Nanorods with a diameter of 45.7 ± 9.3 nm and an average length of ∼1 μm are formed by the supramolecular coassembly of the alkynylplatinum(II) terpyridine complex 2 containing hydrogen-bonding moieties (Fig. 1) and PEG45-b-PAA69 (Fig. 3C), which are used as seeds. TEM-EDX (energy-dispersive X-ray) analysis indicates the presence of platinum in the nanorods (Fig. S5). Selected area electron diffraction (SAED) pattern confirms the existence of metal−metal and π−π stacking interactions within the nanorods (Fig. S6). Addition of complex 1 in acetonitrile to the nanorods followed by incubation has been observed to lead to the formation of 1D segmented nanostructures where the nanorod segments with a high electron contrast are found to connect to nanobelt segments with a low electron contrast in an end-to-end manner (Fig. 3D). At the heterojunction, the width of the nanobelt segment is equal to the diameter of the nanorod segment. In the control experiments, the seed nanorods show insignificant morphological and dimensional changes upon the addition of the same amount of acetonitrile followed by incubation (Fig. S7). Also, it is confirmed that without the presence of nanorod seeds, the supramolecular coassembly of complex 1 and PEG45-b-PAA69 under the same condition can form nanofibers only. Moreover, the diameter of the nanorod segments in the segmented nanostructures (42.3 ± 5.2 nm) shows insignificant change compared with that of the nanorod seeds. These findings indicate that the formation of the 1D segmented nanostructures can be exclusively attributed to the living growth of the nanobelt of complex 1 onto the nanorod seeds. The powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) pattern of the nanorod-block-nanobelt nanostructures is quite similar to that of the seed nanorods, but both of them are very different from the PXRD pattern of the nanofibers formed by supramolecular coassembly of complex 1 and PEG45-b-PAA69 without the presence of the nanorod seeds (Fig. 4). These observations indicate that, for the formation of the nanorod-block-nanobelt nanostructures, supramolecular coassembly of complex 1 and PEG45-b-PAA69 gives up the types of molecular packing in the nanofibers to match the lattice of the seed nanorods to form the nanobelt segments. At the heterojunctions, PAA blocks act as adapters for lattice matching between the nanorods of complex 2 and the nanobelts of complex 1 in the transverse direction, and the noncovalent metal–metal and π–π interactions between complex 1 and complex 2 direct the formation of nanobelt segments in the longitudinal direction (Fig. 5). The nanorod-block-nanobelt nanostructures possess heterojunctions with a lattice mismatch of 21% as calculated from the principal peaks of PXRD patterns (Fig. 4), which is much larger than that in the literature (6%) (47) and breaks the 15% limit for heterojunction formation (57, 58).
Fig. 4.
PXRD patterns of the nanorods formed by complex 2 and PEG45-b-PAA69, the nanorod-block-nanobelt nanostructures formed by addition of complex 1 to nanorods of complex 2, and the nanofibers formed by complex 1 and PEG45-b-PAA69.
Fig. 5.
Longitudinal growth of Pt' complex at the end of the 1D crystalline nanostructure of Pt complex to form 1D segmented nanostructures.
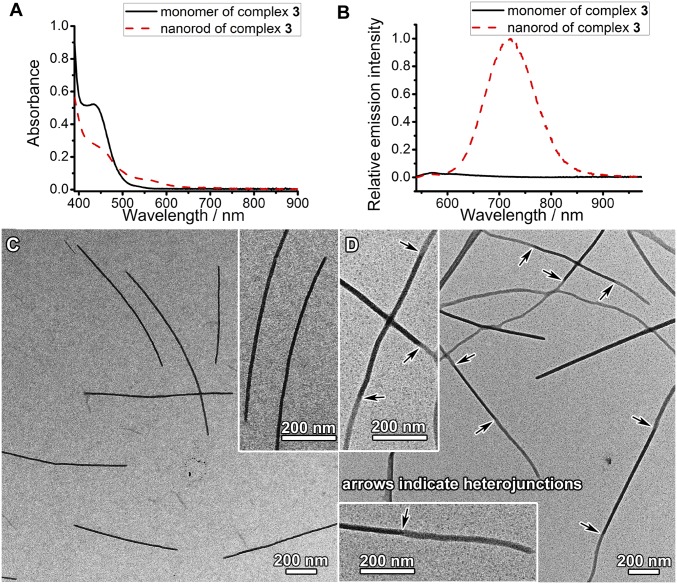
To further demonstrate the capability of the supramolecular coassembly, alkynylplatinum(II) 2,6-bis(N-methylbenzimidazol-2′-yl)pyridine complex 3 (Fig. 1), that possesses larger structural differences from complex 1, has been selected to build heterojunctions between complex 3 and complex 1 (Fig. 6). Complex 3, with a larger π-surface and hydrophobicity, has been found to undergo ready self-assembly in water to form nanorods on its own, which may serve as seeds for subsequent supramolecular growth. Nanorods of complex 3 with a diameter of 13.6 ± 1.4 nm and an average length of ∼900 nm are prepared by addition of complex 3 into water, followed by incubation at room temperature for 1 d (Fig. 6C). Nanorods of complex 3 show the emergence of a low-energy MMLCT absorption band at 570 nm in the UV-vis absorption spectrum and exhibit a drastic intensity enhancement of triplet MMLCT emission at 718 nm with respect to the monomeric form of complex 3 (Fig. 6 A and B). The nanorods show morphological and dimensional stability upon further incubation. By using the as-prepared nanorods as seeds, addition of complex 1 and PEG45-b-PAA69 to the nanorods followed by incubation has been found to form 1D segmented nanostructures where nanofiber segments of complex 1 connect nanorod segments of complex 3 to form heterojunctions (Fig. 6D). At the heterojunction, the diameter of the nanorod segment is equal to that of the nanofiber segment, which indicates that the living growth of the nanofiber segments of complex 1 occurs at the ends of the nanorod seeds. PXRD patterns show that the nanorods, the nanofibers, and the nanorod-block-nanofiber nanostructures possess hexagonally packed molecular columns of platinum(II) complexes within the nanostructures, and the lattice constants of these nanostructures are similar (Fig. S8).
Fig. 6.
(A) UV-Vis absorption spectra and (B) steady-state emission spectra (λex = 482 nm) of complex 3 (0.13 mM) in DMF and the nanorods formed by complex 3 (0.13 mM) in a mixed solvent of DMF–water (1:9, vol/vol). (C) TEM image of nanorods formed by complex 3 in a mixed solvent of DMF–water (1:9, vol/vol). (D) TEM image of segmented nanostructures formed after adding complex 1 and PEG45-b-PAA69 to the as-formed nanorods of complex 3 in C at a final complex 1/complex 3/carboxylic acid molar ratio of 0.15/0.13/1. The arrows in D indicate heterojunctions.
Summary and Prospects
In conclusion, living supramolecular polymerization has been achieved by collaborative assembly of two structurally dissimilar components, that is, platinum(II) complexes and PEG-b-PAA diblock copolymers. In the collaborative assembly, the PAA blocks neutralize the charges of the platinum(II) complexes, while the noncovalent metal–metal and π–π interactions direct the longitudinal growth of the platinum(II) complexes into 1D crystalline nanostructures, and the PEG blocks inhibit the transverse growth of the platinum(II) complexes and provide the entire system with excellent solubility. For the formation of segmented crystalline nanostructures, the PAA blocks act as adapters for lattice matching between different platinum(II) complexes, and living growth of the platinum(II) complexes is achieved by the metal–metal and π–π stacking interactions in the longitudinal direction. Owing to the strategy of the two-component collaborative assembly, the heterojunctions of the segmented nanostructures in the present study possess supramolecular monomers with many more structural and crystallographical differences than those formed by single-component living supramolecular polymerization in the reported literature (47). The unique aggregation behaviors of the platinum(II) complexes, together with the advantages of block copolymers for supramolecular assembly and their collaborations, have been well demonstrated in the present study. It is believed that this strategy of two-component collaborative assembly will further broaden the scope of supramolecular monomers for living supramolecular polymerization that may lead to a new class of supramolecular polymers with diverse compositions, precisely controlled dimensions, and complicated architectures, as well as intriguing spectroscopic and luminescence properties and other functional properties. Since the two-component strategy allows for the fabrication of heterojunctions with large structural differences and large lattice mismatch, it may also open new and simple one-pot strategies for the construction of diverse arrays of segmented supramolecular-based heterojunctions for applications in optical, catalytic, electrical, and optoelectronic devices via directional excitation energy, and electron and hole transport.
Materials and Methods
Nanostructure Growth Experiment for the Preparation of Longer Nanofibers by Using Nanofibers of Complex 1 and PEG113-b-PAA51 as Seeds.
PEG113-b-PAA51 in methanol was first mixed with water, and then platinum(II) complex 1 in acetonitrile was added. The complex 1/carboxylic acid molar ratio in the mixture was 0.05/1. The mixture was homogenized by gentle shaking and incubated at room temperature for 1 d. Nanofibers were formed with a diameter of 10.6 ± 1.0 nm and an Ln of 251 nm (Lw/Ln = 1.21). To perform the nanostructure growth experiment, additional amounts of complex 1 in acetonitrile were added to the as-formed nanofibers, followed by incubation at room temperature for 1 d. The final molar ratio of complex 1/carboxylic acid was 0.1/1.
Nanostructure Growth Experiment for the Fabrication of Nanorod-Block-Nanobelt Nanostructures of Complex 2 and Complex 1 by Using Nanorods of Complex 2 and PEG45-b-PAA69 as Seeds.
PEG45-b-PAA69 in methanol was first mixed with water, and then platinum(II) complex 2 in acetonitrile was added. The complex 2/carboxylic acid molar ratio in the mixture was 0.11/1. The mixture was homogenized by gentle shaking and incubated at room temperature for 1 d. Nanorods were formed with a diameter of 45.7 ± 9.3 nm and a length of ∼1 μm. To perform the nanostructure growth experiment, complex 1 in acetonitrile was added to the as-formed nanorods, followed by incubation at room temperature for 1 d. The final molar ratio of complex 1/complex 2/carboxylic acid was 0.18/0.11/1.
Nanostructure Growth Experiment for the Construction of Nanorod-Block-Nanofiber Nanostructures of Complex 3 and Complex 1 by Using Nanorods of Complex 3 as Seeds.
Platinum(II) complex 3 in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) was mixed with water at DMF/water volume ratio of 1/9, followed by incubation at room temperature for 1 d. Nanorods were formed with a diameter of 13.6 ± 1.4 nm and an average length of ∼900 nm. To perform the nanostructure growth experiment, PEG45-b-PAA69 in methanol was first mixed with platinum(II) complex 1 in acetonitrile, and then the mixture of complex 1 and PEG45-b-PAA69 was added to the as-formed nanorods. The mixture was homogenized by gentle shaking and allowed to stand at room temperature for 1 d. The final molar ratio of complex 1/complex 3/carboxylic acid was 0.15/0.13/1.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
V.W.-W.Y. acknowledges support from The University of Hong Kong under the University Research Committee Strategic Research Theme on New Materials. We also thank the Electron Microscope Unit at The University of Hong Kong for their technical assistance. This work has been supported by the University Grants Committee Areas of Excellence (AoE) Scheme (AoE/P-03/08) and a General Research Fund grant from the Research Grants Council of Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, People's Republic of China (HKU17334216).
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1712827114/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Miskowski VM, Houlding VH. Electronic spectra and photophysics of platinum(II) complexes with α-diimine ligands. Solid-state effects. 1. Monomers and ligand π dimers. Inorg Chem. 1989;28:1529–1533. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Miskowski VM, Houlding VH. Electronic spectra and photophysics of platinum(II) complexes with α-diimine ligands. Solid-state effects. 2. Metal-metal interaction in double salts and linear chains. Inorg Chem. 1991;30:4446–4452. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Houlding VH, Miskowski VM. The effect of linear chain structure on the electronic structure of Pt(II) diimine complexes. Coord Chem Rev. 1991;111:145–152. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bailey JA, et al. Electronic spectroscopy of chloro(terpyridine)platinum(II) Inorg Chem. 1995;34:4591–4599. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Yip H-K, Cheng L-K, Cheung K-K, Che C-M. Luminescent platinum(II) complexes. Electronic spectroscopy of platinum(II) complexes of 2,2′:6,2″-terpyridine (terpy) and p-substituted phenylterpyridines and crystal structure of [Pt(terpy)CI][CF3SO3] J Chem Soc, Dalton Trans. 1993;22:2933–2938. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Herber RH, Croft M, Coyer MJ, Bilash B, Sahiner A. Origin of polychromism of cis square-planar platinum(II) complexes: Comparison of two forms of [Pt(2,2'-bpy)(Cl)2] Inorg Chem. 1994;33:2422–2426. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Connick WB, Marsh RE, Schaefer WP, Gray HB. Linear-chain structures of platinum(II) diimine complexes. Inorg Chem. 1997;36:913–922. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Buchner R, et al. Luminescence properties of salts of the [Pt(4′Ph-terpy)Cl]+ chromophore: Crystal structure of the red form of [Pt(4′Ph-terpy)Cl]BF4 (4′Ph-terpy = 4′-phenyl-2,2′:6′,2″-terpyridine) J Chem Soc, Dalton Trans. 1999;28:711–718. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jennette KW, Lippard SJ, Vassiliades GA, Bauer WR. Metallointercalation reagents. 2-hydroxyethanethiolato(2,2′,2′-terpyridine)-platinum(II) monocation binds strongly to DNA by intercalation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1974;71:3839–3843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yam VW-W, Tang RP-L, Wong KM-C, Cheung K-K. Synthesis, luminescence, electrochemistry, and ion-binding studies of platinum(II) terpyridyl acetylide complexes. Organometallics. 2001;20:4476–4482. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yam VW-W, Wong KM-C, Zhu N. Solvent-induced aggregation through metal...metal/π...π interactions: Large solvatochromism of luminescent organoplatinum(II) terpyridyl complexes. J Am Chem Soc. 2002;124:6506–6507. doi: 10.1021/ja025811c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wong KM-C, Yam VW-W. Self-assembly of luminescent alkynylplatinum(II) terpyridyl complexes: Modulation of photophysical properties through aggregation behavior. Acc Chem Res. 2011;44:424–434. doi: 10.1021/ar100130j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yam VW-W, Au VK-M, Leung SY-L. Light-emitting self-assembled materials based on d8 and d10 transition metal complexes. Chem Rev. 2015;115:7589–7728. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tam AY-Y, Wong KM-C, Wang G, Yam VW-W. Luminescent metallogels of platinum(II) terpyridyl complexes: Interplay of metal...metal, π-π and hydrophobic-hydrophobic interactions on gel formation. Chem Commun (Camb), 2007:2028–2030. doi: 10.1039/b705062c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Tam AY-Y, Wong KM-C, Yam VW-W. Unusual luminescence enhancement of metallogels of alkynylplatinum(II) 2,6-bis(N-alkylbenzimidazol-2′-yl)pyridine complexes upon a gel-to-sol phase transition at elevated temperatures. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:6253–6260. doi: 10.1021/ja900895x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Camerel F, et al. Formation of gels and liquid crystals induced by Pt⋅⋅⋅Pt and π–π* interactions in luminescent σ-alkynyl platinum(II) terpyridine complexes. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2007;46:2659–2662. doi: 10.1002/anie.200604012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lu W, Chen Y, Roy VAL, Chui SS-Y, Che C-M. Supramolecular polymers and chromonic mesophases self-organized from phosphorescent cationic organoplatinum(II) complexes in water. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2009;48:7621–7625. doi: 10.1002/anie.200903109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kozhevnikov VN, Donnio B, Bruce DW. Phosphorescent, terdentate, liquid-crystalline complexes of platinum(II): Stimulus-dependent emission. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2008;47:6286–6289. doi: 10.1002/anie.200802101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yam VW-W, Chan KH-Y, Wong KM-C, Chu BW-K. Luminescent dinuclear platinum(II) terpyridine complexes with a flexible bridge and “sticky ends”. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2006;45:6169–6173. doi: 10.1002/anie.200600962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Leung SY-L, Tam AY-Y, Tao C-H, Chow HS, Yam VW-W. Single-turn helix-coil strands stabilized by metal···metal and π-π interactions of the alkynylplatinum(II) terpyridyl moieties in meta-phenylene ethynylene foldamers. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:1047–1056. doi: 10.1021/ja208444c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gross A, Moriuchi T, Hirao T. A dinuclear alkynylplatinum(II) pyridinedicarboxamide: Conformational change-induced switching of emission properties. Chem Commun (Camb) 2013;49:1163–1165. doi: 10.1039/c2cc37706c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Tanaka Y, Wong KM-C, Yam VW-W. Phosphorescent molecular tweezers based on alkynylplatinum(II) terpyridine system: Turning on of NIR emission via heterologous Pt···M interactions (M = PtII, PdII, AuIII and AuI) Chem Sci (Camb) 2012;3:1185–1191. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Tanaka Y, Wong KM-C, Yam VW-W. Platinum-based phosphorescent double-decker tweezers: A strategy for extended heterologous metal-metal interactions. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2013;52:14117–14120. doi: 10.1002/anie.201306025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Chan AK-W, Lam WH, Tanaka Y, Wong KM-C, Yam VW-W. Multiaddressable molecular rectangles with reversible host-guest interactions: Modulation of pH-controlled guest release and capture. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112:690–695. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1423709112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Po C, Tam AY-Y, Wong KM-C, Yam VW-W. Supramolecular self-assembly of amphiphilic anionic platinum(II) complexes: A correlation between spectroscopic and morphological properties. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:12136–12143. doi: 10.1021/ja203920w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Po C, Tam AY-Y, Yam VW-W. Tuning of spectroscopic properties via variation of the alkyl chain length: A systematic study of molecular structural changes on self-assembly of amphiphilic sulfonate-pendant platinum(II) bzimpy complexes in aqueous medium. Chem Sci (Camb) 2014;5:2688–2695. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Yuen M-Y, et al. Semiconducting and electroluminescent nanowires self-assembled from organoplatinum(II) complexes. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2008;47:9895–9899. doi: 10.1002/anie.200802981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Chen Y, et al. Photoresponsive supramolecular organometallic nanosheets induced by Pt(II)...Pt(II) and C-H...π interactions. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2009;48:9909–9913. doi: 10.1002/anie.200905678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Au-Yeung H-L, Leung SY-L, Tam AY-Y, Yam VW-W. Transformable nanostructures of platinum-containing organosilane hybrids: Non-covalent self-assembly of polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes assisted by Pt···Pt and π-π stacking interactions of alkynylplatinum(II) terpyridine moieties. J Am Chem Soc. 2014;136:17910–17913. doi: 10.1021/ja510048b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lu W, Chui SS-Y, Ng K-M, Che C-M. A submicrometer wire-to-wheel metamorphism of hybrid tridentate cyclometalated platinum(II) complexes. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2008;47:4568–4572. doi: 10.1002/anie.200704450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Leung SY-L, Wong KM-C, Yam VW-W. Self-assembly of alkynylplatinum(II) terpyridine amphiphiles into nanostructures via steric control and metal-metal interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016;113:2845–2850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1601673113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Yu C, Wong KM-C, Chan KH-Y, Yam VW-W. Polymer-induced self-assembly of alkynylplatinum(II) terpyridyl complexes by metal...metal/π...π interactions. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2005;44:791–794. doi: 10.1002/anie.200461261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yu C, Chan KH-Y, Wong KM-C, Yam VW-W. Single-stranded nucleic acid-induced helical self-assembly of alkynylplatinum(II) terpyridyl complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:19652–19657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0604998104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Chung CY-S, Yam VW-W. Induced self-assembly and Förster resonance energy transfer studies of alkynylplatinum(II) terpyridine complex through interaction with water-soluble poly(phenylene ethynylene sulfonate) and the proof-of-principle demonstration of this two-component ensemble for selective label-free detection of human serum albumin. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:18775–18784. doi: 10.1021/ja205996e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Yeung MC-L, Yam VW-W. NIR-emissive alkynylplatinum(II) terpyridyl complex as a turn-on selective probe for heparin quantification by induced helical self-assembly behaviour. Chem Eur J. 2011;17:11987–11990. doi: 10.1002/chem.201101762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lehn J-M. Supramolecular chemistry—scope and perspectives molecules, supermolecules, and molecular devices (Nobel Lecture) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1988;27:89–112. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Fouquey C, Lehn J-M, Levelut A-M. Molecular recognition directed self-assembly of supramolecular liquid crystalline polymers from complementary chiral components. Adv Mater. 1990;2:254–257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Brunsveld L, Folmer BJB, Meijer EW, Sijbesma RP. Supramolecular polymers. Chem Rev. 2001;101:4071–4098. doi: 10.1021/cr990125q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.De Greef TFA, et al. Supramolecular polymerization. Chem Rev. 2009;109:5687–5754. doi: 10.1021/cr900181u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Aida T, Meijer EW, Stupp SI. Functional supramolecular polymers. Science. 2012;335:813–817. doi: 10.1126/science.1205962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Chen Z, Lohr A, Saha-Möller CR, Würthner F. Self-assembled π-stacks of functional dyes in solution: Structural and thermodynamic features. Chem Soc Rev. 2009;38:564–584. doi: 10.1039/b809359h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Fiore GL, Rowan SJ, Weder C. Optically healable polymers. Chem Soc Rev. 2013;42:7278–7288. doi: 10.1039/c3cs35471g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Yang L, Tan X, Wang Z, Zhang X. Supramolecular polymers: Historical development, preparation, characterization, and functions. Chem Rev. 2015;115:7196–7239. doi: 10.1021/cr500633b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Zhang K, Jiang M, Chen D. Self-assembly of particles—The regulatory role of particle flexibility. Prog Polym Sci. 2012;37:445–486. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Zhao Y, et al. Progressive macromolecular self-assembly: From biomimetic chemistry to bio-inspired materials. Adv Mater. 2013;25:5215–5256. doi: 10.1002/adma.201302215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wang X, et al. Cylindrical block copolymer micelles and co-micelles of controlled length and architecture. Science. 2007;317:644–647. doi: 10.1126/science.1141382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Gädt T, Ieong NS, Cambridge G, Winnik MA, Manners I. Complex and hierarchical micelle architectures from diblock copolymers using living, crystallization-driven polymerizations. Nat Mater. 2009;8:144–150. doi: 10.1038/nmat2356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Gilroy JB, et al. Monodisperse cylindrical micelles by crystallization-driven living self-assembly. Nat Chem. 2010;2:566–570. doi: 10.1038/nchem.664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zhang W, et al. Supramolecular linear heterojunction composed of graphite-like semiconducting nanotubular segments. Science. 2011;334:340–343. doi: 10.1126/science.1210369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Anraku Y, Kishimura A, Yamasaki Y, Kataoka K. Living unimodal growth of polyion complex vesicles via two-dimensional supramolecular polymerization. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135:1423–1429. doi: 10.1021/ja3096587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Ogi S, Sugiyasu K, Manna S, Samitsu S, Takeuchi M. Living supramolecular polymerization realized through a biomimetic approach. Nat Chem. 2014;6:188–195. doi: 10.1038/nchem.1849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kang J, et al. A rational strategy for the realization of chain-growth supramolecular polymerization. Science. 2015;347:646–651. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa4249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Ogi S, Stepanenko V, Sugiyasu K, Takeuchi M, Würthner F. Mechanism of self-assembly process and seeded supramolecular polymerization of perylene bisimide organogelator. J Am Chem Soc. 2015;137:3300–3307. doi: 10.1021/ja511952c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Aliprandi A, Mauro M, De Cola L. Controlling and imaging biomimetic self-assembly. Nat Chem. 2016;8:10–15. doi: 10.1038/nchem.2383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Endo M, et al. Photoregulated living supramolecular polymerization established by combining energy landscapes of photoisomerization and nucleation–elongation processes. J Am Chem Soc. 2016;138:14347–14353. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b08145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Guo Y, et al. Self-assembly of functional molecules into 1D crystalline nanostructures. Adv Mater. 2015;27:985–1013. doi: 10.1002/adma.201403846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Wittmann JC, Lotz B. Epitaxial crystallization of polyethylene on organic substrates: A reappraisal of the mode of action of selected nucleating agents. J Polym Sci, Part B: Polym Phys. 1981;19:1837–1851. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Wittmann JC, Hodge AM, Lotz B. Epitaxial crystallization of polymers onto benzoic acid: Polyethylene and paraffins, aliphatic polyesters, and polyamides. J Polym Sci, Part B: Polym Phys. 1983;21:2495–2509. [Google Scholar]
- 59.Zhang K, Yeung MC-L, Leung SY-L, Yam VW-W. Manipulation of nanostructures in the co-assembly of platinum(II) complexes and block copolymers. Chem. 2017;2:825–839. [Google Scholar]
- 60.Erdemir D, Lee AY, Myerson AS. Nucleation of crystals from solution: Classical and two-step models. Acc Chem Res. 2009;42:621–629. doi: 10.1021/ar800217x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Yeung MC-L, Chu BW-K, Yam VW-W. Anion binding properties of alkynylplatinum(II) complexes with amide-functionalized terpyridine: Host–guest interactions and fluoride ion-induced deprotonation. ChemistryOpen. 2014;3:172–176. doi: 10.1002/open.201402019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Tam AY-Y, Lam WH, Wong KM-C, Zhu N, Yam VW-W. Luminescent alkynylplatinum(II) complexes of 2,6-bis(N-alkylbenzimidazol-2′-yl)pyridine-type ligands with ready tunability of the nature of the emissive states by solvent and electronic property modulation. Chem Eur J. 2008;14:4562–4576. doi: 10.1002/chem.200701914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Davis KA, Matyjaszewski K. Atom transfer radical polymerization of tert-butyl acrylate and preparation of block copolymers. Macromolecules. 2000;33:4039–4047. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Jankova K, Chen X, Kops J, Batsberg W. Synthesis of amphiphilic PS-b-PEG-b-PS by atom transfer radical polymerization. Macromolecules. 1998;31:538–541. [Google Scholar]
- 65.Zhang R, et al. Nucleic acid-induced aggregation and pyrene excimer formation. Org Lett. 2009;11:4302–4305. doi: 10.1021/ol901607g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.