Abstract
Pulmonary thrombosis is a significant cause of patient mortality, however, there are no effective in vitro models of thrombi formation in human lung microvessels, that could also assess therapeutics and toxicology of antithrombotic drugs. Here we show that a microfluidic lung alveolus-on-a-chip lined by human primary alveolar epithelium interfaced with endothelium, and cultured under flowing whole blood can be used to perform quantitative analysis of organ-level contributions to inflammation-induced thrombosis. This microfluidic chip recapitulates in vivo responses, including platelet-endothelial dynamics and revealed that lipopolysaccharide (LPS) endotoxin indirectly stimulates intravascular thrombosis by activating the alveolar epithelium, rather than acting directly on endothelium. This model is also used to analyze inhibition of endothelial activation and thrombosis due to a protease activated receptor-1 (PAR-1) antagonist, demonstrating its ability to dissect complex responses and identify antithrombotic therapeutics. Thus, this methodology offers a new approach to study human pathophysiology of pulmonary thrombosis and advance drug development.
INTRODUCTION
Thrombi that form within lung vessels due to activation of platelets and inflammatory stimulation of the pulmonary vascular endothelium are a major cause of patient mortality and morbidity in many lung diseases, including acute lung injury 1–5. Intense basic research efforts have provided new biological insights into the pathology of pulmonary thrombosis 2,4,6; however, development of new therapies that target thromboinflammatory mechanisms has been hampered by the lack of models and methods that permit analysis of the organ-level responses that underlie this lung condition in humans. Animal models of pulmonary microvascular thrombosis exist, but they do not mimic the altered hemostasis and hemodynamic complexity of human lung 7,8. With animal models, it is also not possible to separate contributions of platelet-endothelial interactions versus tissue-tissue (e.g., epithelial-endothelial) interactions that can contribute to development of thrombotic lesions in response to epithelial injury or inflammation induced by chemicals or mechanical injury 9,10. In addition, there is a critical need to develop in vitro disease models that can more effectively predict responses in humans because of ethical issues associated with animal testing 11,12. Although there are existing in vitro coagulation and platelet function assays, they do not incorporate physiological organ-level signaling between endothelial and parenchymal tissues, inflammatory activities, or relevant fluid hemodynamics which are all key determinants of thrombosis 13–18. Due to these existing deficiencies, we explored whether microfluidic organ-on-a-chip (organ chip) technology 12,19 can be used to address this challenge.
Human organs chips are microfluidic culture systems created with microchip manufacturing methods that contain hollow microchannels lined by living human cells that recapitulate organ-specific tissue-tissue interfaces and physical microenvironments (including fluid flow, air-liquid interfaces, and cyclic deformation in the case of the lung) that are necessary to mimic human organ level pathophysiology 12. Here, we significantly modified a previously described human lung chip 20,21 by replacing the established lung alveolar epithelial cell line (A549) originally isolated from a lung tumor 22 with primary human lung alveolar epithelial cells. We also lined all four walls of the second microchannel with human vascular endothelial cells to form a continuous endothelium-lined tube that enables human whole blood to be perfused through the chip instead of culture medium. This new primary human lung alveolus chip design enables whole human blood to be perfused through the vascular channel without producing thrombus formation under control conditions, while allowing high resolution, real-time analysis of interactions between human blood cells and endothelial cells in an organ-relevant context. Using this technology in combination with novel analytical tools for quantitation of dynamic platelet-endothelial interactions and clot formation, we demonstrate a key role of the epithelium in inflammation-driven vascular thrombosis during lipopolysaccharide endotoxin (LPS)-induced acute lung injury, and show that the model can be used to evaluate cytoprotective effects of a potential therapeutic with anti-thrombotic and anti-inflammatory activities in vitro.
RESULTS
Primary human lung alveolus chip
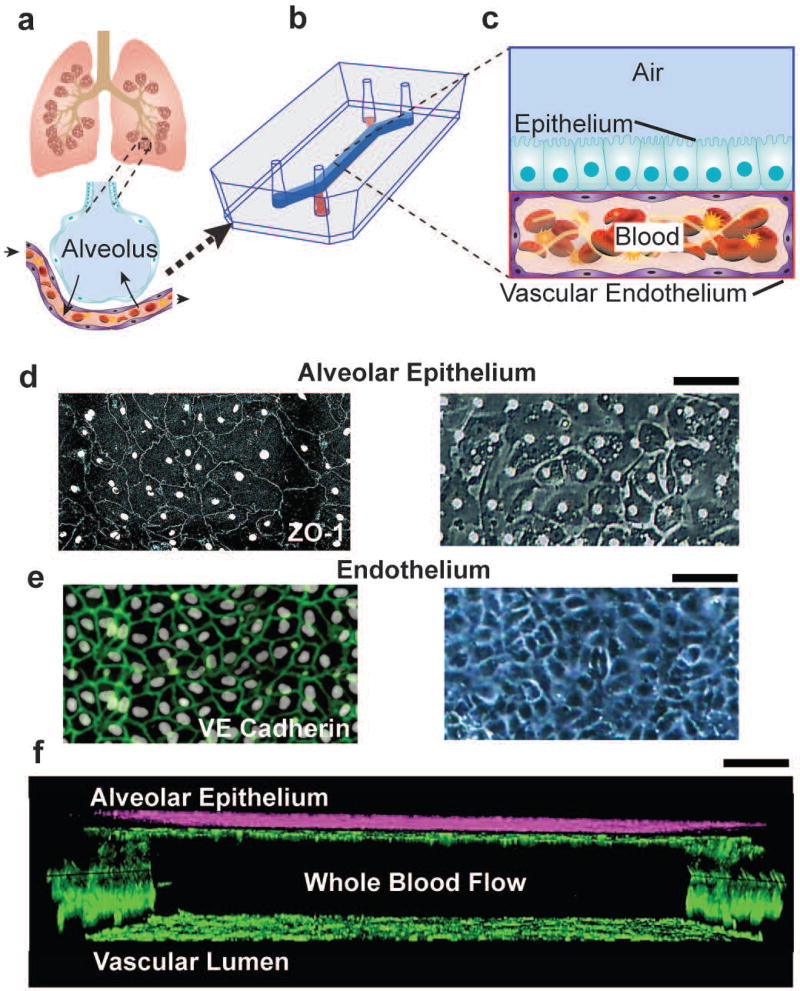
To develop an organ-level model of vascular inflammation-induced human pulmonary thrombosis in vitro that is also capable of dissection of intercellular communication, we modified a previously described lung chip microfluidic device that consists of two parallel rectangular microchannels separated by a thin, porous, flexible membrane coated with extracellular matrix (ECM) 20,21,23. First, we increased the microchannel dimensions of both the chambers in order to maximize the surface area exposed to blood and soluble factors. Then we covered all surfaces of the bottom microchannel with human umbilical vascular endothelial cells (HUVECs) in order to engineer a three dimensional (3D) microvessel that prevents contact of blood with the surrounding pro-thrombotic ECM-lined channel walls as occurs in living vessels (Fig. 1a–c; see METHODS for details). Finally, primary human alveolar (mixture of type I and II) epithelial cells were cultured on the upper surface of the ECM-coated porous membrane instead of cells of an established, tumor-derived lung epithelial cell line as used in past lung chip studies. Using this new method, we were able to recreate a 3D cross-section of a human lung alveolus composed of an alveolar-capillary interface and a vascular lumen through which human whole blood can be perfused (Fig. 1c and Fig. S1). This improved lung alveolus chip maintained a viable epithelial-endothelial interface for more than 12 days under laminar flow (Fig. 1d–f), with both layers lined by cells joined via continuous intact cell-cell junctions lined by ZO-1 in the epithelium (Fig. 1d) and VE-cadherin in the endothelium (Fig. 1e, Movie 1).
Figure 1. Microengineered model of human pulmonary thrombosis-on-chip.
a) A conceptual schematic of the human lung showing that the alveoli interact with the neighboring blood vessels during hemostasis or pulmonary dysfunction. b) Engineering drawing of the microdevice containing two PDMS compartments separated by a thin porous membrane that reproduces the microarchitecture of the alveolar-capillary interface. c) Graphic illustration showing the top compartment (1 mm wide and 1 mm tall) is cultured with human primary alveolar epithelial cells and the entire bottom chamber (1 mm wide and 250 µm tall) lined with human endothelial cells forming a lumen. Whole blood is perfused through the bottom chamber and thrombus formation is visualized using fluorescence microscopy from the bottom. d) Micrograph of human lung alveolar epithelial cells (ZO1, left; brightfield, right; Scale bar, 50 µm) and e) vascular endothelial cells (VE-cadherin, left; brightfield, right, Scale bar, 50 µm) f) Sideview of confocal micrographs showing junctional structures, after twelve days of co-culture, of a single layer of the primary alveolar epithelium at the top chamber (purple, stained with E-cadherin) and endothelial monolayers covering the entire surface of the lower chamber (green, stained with VE-cadherin), through which blood perfusion takes place. Scale bar: 100 µm.
Dynamic quantitative analysis of pulmonary thrombus formation in vitro
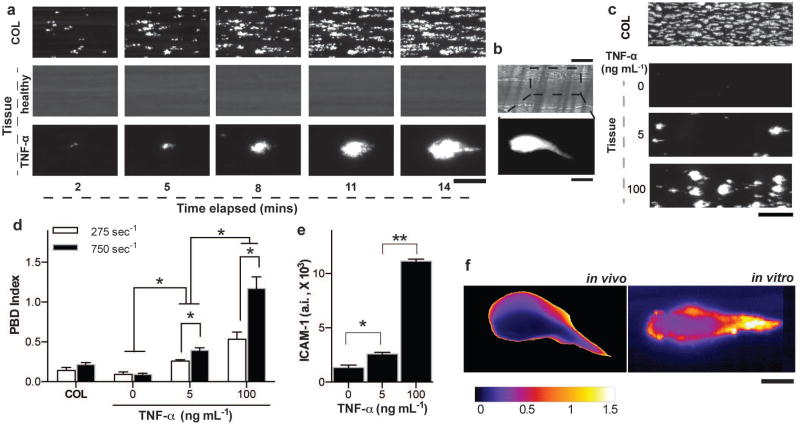
Before we initiated studies at the organ-level with the lung alveolus chip, we performed experiments to confirm that the engineered endothelium-lined tube within the lower vascular channel can be used to quantify thrombus formation under fluid shear conditions in vitro. As a positive control, we first perfused re-calcified (coagulation-activated) citrated human whole blood (shear stress: 3 N m−2) containing fluorescently-labeled platelets through a collagen-coated lower microchannel that did not have an endothelial cell lining. As expected 24,25, collagen exposure led to rapid platelet adhesion to the walls of the microchannel within minutes (Fig. 2a, top; Movie 2), similarly to what is observed during hemostatic plug formation induced by vascular injury in vivo 26. In contrast, when endothelial cells were cultured on all the surfaces of all four walls of the ECM-coated microchannel to form a hollow microvessel lined by a continuous vascular endothelium (Fig. 1f and Fig. S1) and human whole blood was perfused through its lumen for 20 minutes, both platelet adhesion and thrombi formation were completely prevented in this healthy engineered microvessel (Fig. 2a, middle; Movie 3). However, when the endothelium was stimulated with the inflammatory cytokine, tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α; 100 ng mL−1) prior to initiating blood flow, the inflamed vascular endothelium promoted rapid platelet recruitment and thrombus formation (Fig. 2a, bottom; Movie 4), as occurs within inflamed microvessels in vivo 27,28.
Figure 2. Analysis of dynamical progression of thrombus formation in the alveolus chip.
a) Fluorescence micrographs depicting a section of the imaged microchannel (Scale bar, 25 µm) showing platelet accumulation over time (left to right) on collagen (top), a healthy blood vessel (middle), TNF-α stimulated vessel (bottom) and b) platelet accumulation after 4 minutes of laser-induced injury on a mouse cremaster arteriole (top, bright field and bottom, fluorescence; Scale bar, 25 µm, top and bottom). c) Fluorescent micrographs of a large section of the vascular chamber showing luminal thrombus formation on bare collagen (topmost) and TNF-α stimulated endothelium in a dose dependent manner (bottom three; Scale bar, 100 µm). d) Sensitivity analysis of the platelet-endothelial dynamics algorithm (PBD index), showing that in conditions of vascular injury/collagen or healthy endothelium, the dynamical events characterizing clot formation are nearly absent but they increase in a TNF-α dose dependent manner. The PBD index is also sensitive to applied shear rate (n = 3, *P<0.05, 2-way ANOVA). e) ICAM-1 expression on the endothelial cells after stimulation of the vessel with TNF-α (n = 4, *P<0.05, unpaired t-test). f) Image colormap showing the coefficient of variability (calculated from the fluorescence image timeseries) within a laser-induced thrombus in vivo (left) and TNF-α induced thrombus on a vsacular lumen in vitro (right). Scale bar, 20 µm.
Interestingly, in contrast to the distributed fibrillar pattern of platelet-rich thrombi formed on the exposed collagen surface (Fig. 2a, top), the thrombi formed on the inflamed endothelium exhibited a distinct tear drop-like morphology (Fig. 2a, bottom right). While this unique thrombus morphology has not been observed in previous in vitro platelet adhesion studies that used collagen-coated microfluidic chambers 24,25, platelet aggregates have been reported to progressively grow and move downstream along the endothelial surface under flow in vivo 29–31. Indeed, we could detect that this type of dynamic platelet-endothelium binding behaviour is responsible for this tear drop morphology when we performed video microscopic analysis of thrombi formation in the endothelium-lined vascular channel (Movie 2–4). Moreover, we observed formation of thrombi with a nearly identical tear drop shape and similar rapid platelet binding dynamics when we analyzed thrombi formation in vivo (Fig. 2b and Movie 5) in a previously described living mouse model of laser-induced thrombosis 30,32. Thus, these initial studies suggest that the engineered microvessel within this microfluidic chip appears to recapitulate the unique shape and platelet dynamics associated with thrombus formation in vivo, whereas this is not observed in ECM-coated microfluidic devices that are commonly used for in vitro analysis of thrombus formation under flow 33.
To quantify these dynamic binding interactions between platelets and endothelium, we applied a recently developed automated imaging program 28 in order to measure the kinetics of platelet binding along the length of the microfluidic channel, and we derived a non-dimensional statistical method to arrive at a novel quantitative index of platelet binding dynamics (PBD index; Fig S2; see METHODS for details). When we calculated the PBD index for platelet interactions measured on collagen under flow, we found it to be extremely low because once the platelets adhere, they do not change their position (Fig. 2c, top and Fig. 2d). In contrast, when we stimulated the endothelium in the microchannel with increasing doses of TNF-α that induce a dose-dependent increase in expression of the surface adhesion molecule ICAM-1 (Fig. 2e), we observed a corresponding dose-dependent rise in both platelet binding to the endothelium (Fig. 2c) and in the PBD index (Fig. 2d), confirming the sensitivity of this method to detect dynamic thromboinflammatory interactions between platelets and endothelium associated with vascular inflammation. Moreover, this dynamic analytical method can distinguish platelet accumulation due to vascular injury (ECM exposure) in a healthy endothelium compared to thrombosis caused by endothelial activation by inflammatory stimuli, whereas quantitation of the average area of platelet adhesion (percentage platelet coverage relative to total area of channel) frequently used to analyse thrombosis on exposed ECM-coated substrates in vitro 25 cannot (Fig. S3). Additionally, we found that this PBD index increased when we raised the hemodynamic shear rate from 275 s−1 to 750 s−1 in the microfluidic channel (by altering pumping rates), indicating a higher tendency to form platelet-rich thrombi and promote platelet-endothelial binding interactions in vitro (Fig. 2d), as reported in past studies 34,35. In contrast, quantification of the average area of platelet adhesion 24,25 was not sensitive to this change in shear (Fig. S3). Finally, we used the same method to analyse a single thrombus formed in a laser-injured mouse vessel to confirm the relevance of the PBD index in a physiologically-relevant in vivo model of thrombosis. Again, using the same analytical method in combination with pseudo-colouring of images to indicate the local PBD index, we confirmed that the dynamics of platelet-endothelial binding were more rapid along the boundary of the thrombus compared to its central core (Fig. 2f, left), and we observed a pattern of platelet-endothelial binding dynamics within individual thrombi that was nearly identical to that seen within thrombi that formed in our endothelium-lined microfluidic channel in vitro (Fig. 2f, right). These regional heterogeneities in thrombus dynamics have been shown to be due to the thrombus consisting of a stable core region surrounded by reactive unstable shell 31,36, but to our knowledge, they have not been previously shown in cultured living endothelium or characterized in vitro.
Inflammatory cytokine-induced pulmonary thrombosis in the human lung alveolus chip
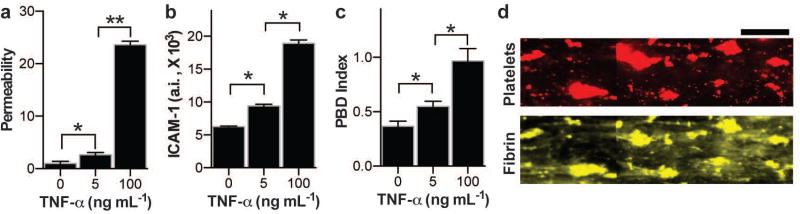
We then explored whether we could study organ-level contributions (as opposed to endothelial tissue-level contributions alone as done above) to vascular inflammation-driven thrombus formation using the human lung alveolus chip that contains human primary alveolar epithelium on the top of the ECM-coated membrane, closely interfaced with the human endothelium-lined vascular channel below (Fig. 1). When we perfused fluorescent tracer dye (4 kDa dextran) through the vascular channel of alveolus chip cultured for 12 days, we found that the alveolar-capillary interface formed on-chip retained a high level of pulmonary barrier function with low permeability to the dye (Fig. 3a), confirming past results using lung chips lined by an established human A549 alveolar cell line 20,21. Importantly, we also were able to perfuse recalcified, citrated human whole blood for up to 20 minutes (shear rate: 275 sec−1) through the vascular lumen of the lung alveolus chip without producing any significant platelet adhesion or blood clotting (Movie 6), as observed using a microfluidic system lined only by endothelium (Fig. 2a, middle; Movie 2). Direct addition of increasing doses of TNF-α to the alveolar epithelium compartment resulted in a dose-dependent increase in pulmonary vascular permeability (Fig. 3a) as well as a concomitant increase in ICAM-1 expression on the endothelium below (Fig. 3b). As expected, induction of ICAM-1 expression on the endothelium by delivery of TNF-α into the epithelial compartment of this organ-level model of an inflamed endothelium was accompanied by a dose-dependent increase in platelet-endothelial binding dynamics (Fig. 3c), as previously observed when TNF-α was infused directly through the endothelium-lined vascular channel (Fig. 2d). Thrombi formed over the entire endothelial surface within the vascular compartment of the lung alveolus chip, and they contained both platelets and fibrin by the end of the assay (Fig. 3d). Thus, this microfluidic system can effectively model the pro-inflammatory effects of TNF-α released into the epithelial compartment that lead to activation of the underlying endothelium and subsequent induction of intravascular blood thrombus formation.
Figure 3. TNF-α induced endothelial disruption and thrombus formation in alveolus chip.
Inside the lung alveolus-on-a-chip that was either left untreated (0 ng mL−1) or treated with 5 or 100 ng mL−1 of TNF-α, a) measurement of vascular permeability (fluorescence normalized by untreated vascular tissue; n=4), b) vascular ICAM-1 measured on the vascular surface (n=4), and c) measurement of PBD index after whole blood perfusion (n=3). a–c, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, 1-way ANOVA. d) Representative fluorescence micrographs showing platelet aggregates (red) and fibrin (yellow) at the end of blood perfusion through the alveolus-chip after TNF-α stimulation (Scale bar, 100 µm).
LPS-induced pulmonary thrombosis is mediated by activation of the epithelium
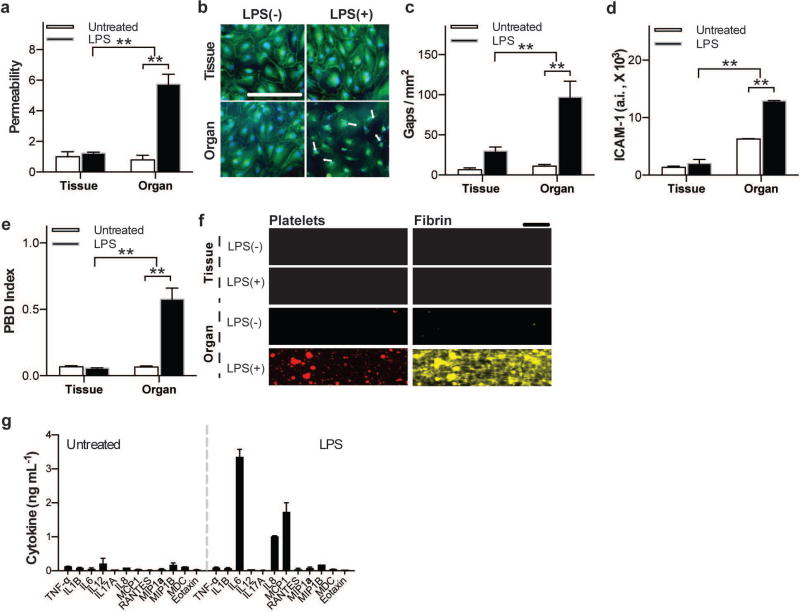
Then we tested the effects of LPS on vascular thrombus formation using the pulmonary alveolus chip because this Gram negative bacterial endotoxin has been shown to cause acute lung injury and induce pulmonary thrombosis in vivo 37,38. When we first added LPS (100 ng mL−1) directly to medium flowing through the vascular channel lined by the endothelial tissue (in the absence of the alveolar epithelium) for 2 hours, we could not detect any significant change in barrier permeability (Fig. 4a), endothelial junctional integrity (Fig. 4b,c) or ICAM-1 staining (Fig. 4d) compared to untreated organ chips. Thus, LPS does not exhibit its reported ability to induce pulmonary thrombosis when analyzed at the tissue level alone (i.e., using only vascular endothelium under flow) at the dosage and time that we applied. In contrast, we observed a large increase in permeability of the tissue-tissue interface within 2 hours when we added LPS to the lumen of the upper channel lined by alveolar epithelium in the lung alveolus chip (Fig. 4a). This correlated with disruption of endothelial cell-cell junctions, as demonstrated by immunofluorescence microscopic analysis of VE-cadherin (Fig. 4b,c) and quantitation of the size of the gaps exposed between junctions in the endothelium (Fig. 4c), as well as endothelial activation measured by increased expression of ICAM-1 (Fig. 4d). Importantly, this also correlated with a significant increase in the PBD index in the intact lung chip treated in this manner with LPS and perfused with whole blood, whereas there was no detectable change in platelet-endothelial binding interactions in the absence of the alveolar epithelium (Fig. 4e). Additionally, we observed that large fibrin-containing platelet aggregates appeared in the vascular channel only in intact organ chips containing both the alveolar epithelium and endothelium (Fig. 4f). Furthermore, to confirm that this unique organ-level response to LPS is relevant for pulmonary thrombosis per se, we fabricated similar chips using primary human lung microvascular endothelial cells instead of HUVECs in the vascular channel (Fig. S4a). In these studies, addition of LPS to the alveolar epithelium channel produced similar activation of ICAM-1 in the human pulmonary microvascular endothelium within the vascular channel (Fig. S4b,c).
Figure 4. LPS-induced endothelial disruption and thrombus formation when LPS was added to the vascular channel of a chip lined only by vascular endothelium or to the epithelial channel of an intact lung alveolus chip.
a) Vascular permeability measurements (fluorescence normalized by untreated vascular tissue; n=4) demonstrate that LPS only compromised barrier function when presented to the epithelium in an organ-level context. b) Representative confocal micrographs showing that VE cadherin-labeled endothelial cell-cell adhesions (green) open and retract when LPS was added to the chip containing both the epithelium and endothelium in an organ context (Organ), but not when added directly to the endothelium alone (tissue) (bar, 100 µm; arrows indicate gaps; blue, DAPI-stained nuclei). c) Quantification of averaged gap areas resulting from discontinuous VE-cadherin staining, as shown in b (n=4).d) Quantification of vascular ICAM-1 on the endothelial cell surface under the conditions shown in b (n=4). e) Measurement of PBD indices after whole blood perfusion through the control and LPS-treated lung alveolus chips (n=3). f) Representative fluorescence micrographs showing platelet aggregates and fibrin within the vascular channel at the end of blood perfusion through the alveolus chip (bar, 100 µm;a,c,d,e *P<0.05, **P<0.01, 2-way ANOVA). g) Quantification of cytokines released, as measured within the effluent of the vascular channel, showing significant differences in a subset of cytokines following 2h of LPS stimulation compared to untreated conditions (n=2).
To better characterize this organ-level response to LPS, we took advantage of our ability to collect effluent from the vascular channel of the chips and analyzed cytokine release profiles produced in the lung alveolus-on-a-chip when stimulated with LPS. Of twelve cytokines tested, only three exhibited significant elevation in response to LPS stimulation specifically when the alveolar epithelium was present: interleukin-6 (IL-6), interleukin-8 (IL-8) and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) (Fig. 4f). Thus, this tissue-tissue interaction that leads to microvascular thrombosis in this model may be mediated at least in part by IL-6 as it has been previously shown to induce ICAM-1 expression in endothelium 39.
Finally, to determine the physiological relevance of these findings, we used our automated imaging technique to analyse the effects of LPS delivered intraperitoneally on platelet-endothelial binding interactions in the mouse cremaster arteriole and vein in vivo. Quantitative imaging confirmed that intravenous injection of LPS alone was not sufficient to directly stimulate increased platelet-endothelial binding interactions in vivo in both the arteriole and the vein (Fig. S5a,b). In contrast, when these vessels were injured with a laser, thereby releasing inflammatory factors locally, we observed an increase in both platelet-endothelial binding and intravascular thrombus formation (Fig. S5a,b). Taken together, these findings confirm that induction of intravascular pulmonary thrombosis by LPS involves tissue-tissue interactions between the lung alveolar epithelium and vascular endothelium that lead to activation of a cytokine cascade generated by the epithelium which induces the endothelium to become prothrombotic, as suggested by our alveolus chip studies. This insight into the role of epithelium in vascular inflammation-led alveolar thrombus formation could not have easily been made using in vivo animal models or human clinical studies.
Testing of potential antithrombotic therapeutic in the human lung alveolus chip
To further explore the potential value of this model as a preclinical drug development tool, we used the primary lung alveolus chip to analyze the anti-thrombotic and anti-inflammatory activities of a potential drug candidate. Protease activated receptor-1 (PAR-1) has been shown to mediate tissue inflammation and hemostasis, and therefore, it represents a potential target for the treatment of various pathologies leading to coagulation abnormalities, such as, sepsis 40. Here, we analyzed the effects of parmodulin-2 (PM2), which is a potent PAR-1 inhibitor that has been recently shown to have antithrombotic and vascular protective effects comparable to those of activated protein C (APC) when tested in both a bioengineered endothelium-lined vessel in vitro and a recently developed mouse model 41.
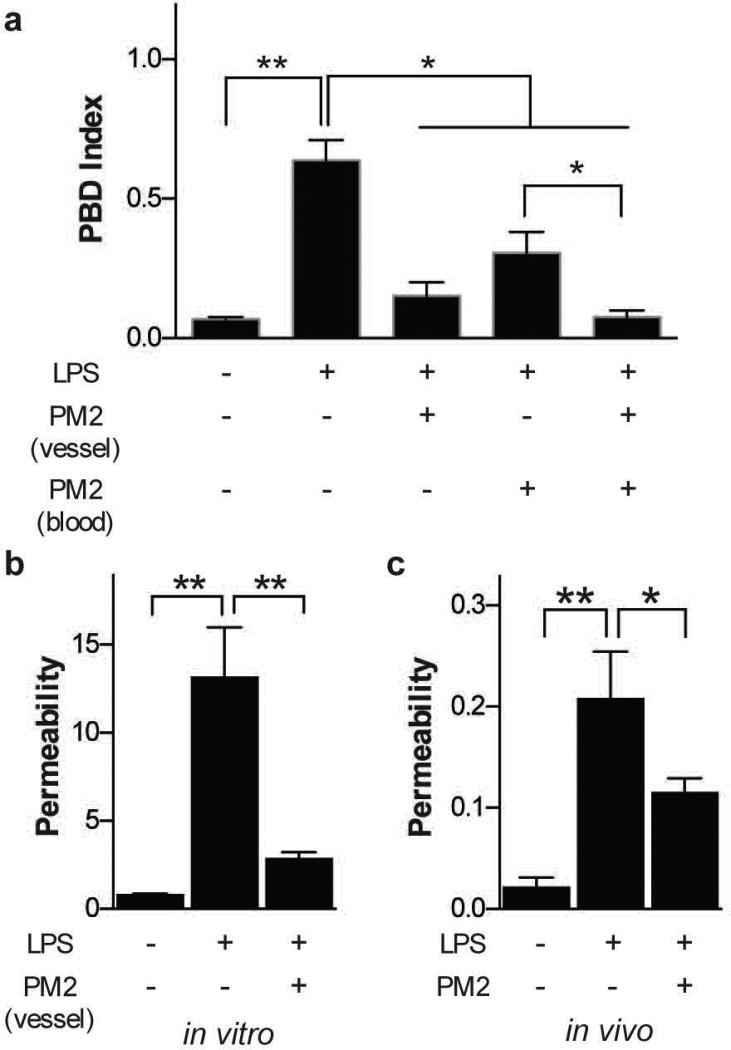
In platelets, PAR-1 mediated signaling is critical for platelet activation 42. Not surprisingly, when we pre-incubated human whole blood with PM2 (30 µM) for 30 minutes before perfusing it through the vascular channel of a LPS-treated alveolus chip, we observed a significant reduction in platelet-endothelial binding in comparison to untreated blood (Fig. 5a). Interestingly, when we first incubated the endothelium-lined vascular channel of the lung chip with PM2 for 4 hours before adding LPS to the alveolar lumen and then perfused human whole blood through the endothelial channel, we found that PM2 treatment of the endothelium significantly decreased thrombi formation (Fig. 5a) as well as pulmonary vascular leakage (Fig. 5b) induced by LPS. Furthermore, preincubation of both the endothelium (4 hours) and blood (30 minutes) with PM2 completely inhibited platelet binding to the endothelium and thrombus formation in the LPS-stimulated alveolus chip (Fig. 5a). Together, these studies with our model indicate that PM2 exhibits potent cytoprotective, as well as anti-thrombotic, activities in human acute lung dysfunction.
Figure 5. Therapeutic effect of a PAR-1 inhibitor (parmodulin) in lung injury.
a) PBD index measured in the chip after blood perfusion through the vascular channel of an alveolus chip previously exposed to LPS (100 ng mL−1 for 2 hours) on the epithelial side, while the blood, the endothelium or both were treated with parmodulin (PM2) before perfusion. b) Vascular permeability (fluorescence normalized by untreated vascular tissue) measured inside the LPS-treated microdevice with or without treatment of parmodulin 2. c) Vascular permeability measurements in vivo after intratracheal delivery of LPS (1 µg per mouse) for 2 hours and systemic delivery of parmodulin (PM2, 30 µM) for 4 hours (a-c, n=3. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, 1-way ANOVA).
To validate the physiological relevance of these results, we carried out similar studies in an in vivo model of LPS-induced lung injury 43. Intratracheal delivery of LPS (1 µg/mouse) to the airway and alveolar epithelium of a mouse (Fig. S6a) resulted in a dose-dependent increase vascular barrier disruption in vivo (Fig. S6b). Notably, intravenous administration of the same dose of PM2 as used in our in vitro studies (30 µM) significantly reduced the LPS-induced injury of the alveolar tissue in vivo, as indicated by a significant improvement of vascular permeability (Fig. S6c), thus confirming the findings we obtained using the lung alveolus chip (Fig. S6b).
DISCUSSION
These studies demonstrate that the primary human lung alveolus chip permits visualization and quantitative real-time analysis of organ-level interactions relevant to in situ thrombus formation in human lung. This organ chip technology allowed us to dissect contributions of various human cell types and tissues (epithelium, endothelium and platelets), pro-inflammatory signals (TNF-α and LPS), and fluid flow, as well as a potential antithrombotic and anti-inflammatory therapeutic (PM2), which would be nearly impossible to perform in vivo. Thus, this new in vitro model of human pulmonary thrombosis offers unique capabilities that may prove useful for drug development as well as analysis of the pathophysiology of thrombotic diseases.
While it has been recognized that whole blood rheology, mechanics and cellular composition impact vascular biology, immune function, platelet function and signaling pathways involved in hemostasis 44–46, most contemporary in vitro analytical devices have not incorporated native whole blood flow in their assessment due to technical difficulties 24,47–50. A salient feature of the pulmonary organ chip microfluidic system presented here is that it is able to perfuse human whole blood in its native state (recalcified after anticoagulation in sodium citrate) at any desirable shear rate, thereby providing a more physiologically relevant in vitro platform to study and analyze intravascular thromboinflammation in the lung. Secondly, by harnessing the potential of modern automated fluorescence microscopy and mathematical modeling, we developed a new way to assess platelet-surface interactions over large spatiotemporal scales. Our analysis shows that the integrated interplay between platelets, thrombi, the vessel wall, and blood flow dynamics can be analyzed in this integrated system-level assay. Significantly, we showed that the pulmonary thrombus formation caused due to endothelial activation in this in vitro model correlates well with thrombosis that occurs in vivo in response to laser injury in mice, both in terms of morphology and regional heterogeneity, and well as platelet binding dynamics 31,36.
By incorporating primary human alveolar epithelial cells in this modified system, we overcame a limitation of the previously described lung chip that used a human lung tumor-derived alveolar epithelial cell line 20,21, which could exhibit pro-thrombotic activities and thereby complicate studies involving inflammatory activation. The co-culture of this primary alveolar epithelium with human vascular endothelium inside the alveolus-chip for up to 2 weeks allowed us to highlight the critical role that alveolar epithelium plays in pulmonary thrombosis induced by LPS endotoxin. The finding that the presence of LPS in lung does not promote thrombosis by acting directly on the endothelium would be very difficult to show in vivo in real-time, as individual tissue and cellular compartments inside the organ cannot be regulated separately, and blood flow inside the lung vessels cannot be controlled or observed over large areas as we can do using the organ chip technology.
However, the full potential of the current model has not yet been explored. For example, in the present study, we did not mimic lung breathing motions which were previously shown to have important effects on lung physiology (e.g., surfactant production, absorption of nanoparticulates, induction of pulmonary edema by interleukin-2) 20,21, and which also could potentially influence pulmonary thrombosis. Another potential caveat is that we used HUVECs, and not lung-specific endothelial cells, in most of our studies; however, when we replaced them with primary human microvascular endothelial cells in our LPS stimulation experiments, we obtained nearly identical results and similar findings were reported using HUVECs and lung microvascular endothelium in prior lung chip studies20. We did not analyze the role of immune cells (e.g, neutrophils) in this study for simplicity and to accommodate high-speed imaging with fewer fluorescent channels, but this could be done in future studies as shown in past work with the human organ chips19,20.
Nevertheless, this primary human lung alveolus chip methodology allowed us to recapitulate many features of vascular thrombosis in vitro that have only previously been observed in vivo. Notably, we were able to dissect the significance of alveolar epithelium in the onset and propagation of platelet function and thrombosis in acute lung injury. It also allowed us to unravel the cytoprotective and anti-thrombotic effects of a novel PAR-1 antagonist in the setting of acute lung injury and whole blood perfusion. Thus, this human pulmonary alveolar chip model may offer a new tool for pre-clinical testing of antithrombotic drugs that can potentially detect their unwanted thrombotic side effects before they enter human clinical trials. This system also can be used to study fundamental mechanisms of hemostasis regulation in a more physiologically relevant organ-level context. Finally, this tool could offer a new method for a personalized assessment of drug responses to therapy, as well as potential toxicities, by obtaining lung cells (e.g, from biopsies or using lung cells differentiated from induced pluripotent stem cells) and blood from the same patient, and thereby help to individualize therapeutic regimens in the future.
METHODS
Materials and Methods are available in Supplementary Information
Supplementary Material
Confocal immunofluorescence microscopic images showing a section of the microchannel with HUVECs when viewed from front (‘xy’) and reconstruction of cross-sectional views from the bottom and the side (‘yz’ and ‘xz’, respectively) demonstrating full coverage of all microfluidic channel walls. (green, VE-Cadherin; bar, 100 µm).
Platelet coverage (red) upon whole blood perfusion on lower microchannel of the lung alveolus-chip containing healthy endothelium lined over collagen. Magnification 10X, Frame Rate: Six frames per minute, Total runtime: 12 minutes
Platelet coverage (red) upon whole blood perfusion on lower microchannel of the lung alveolus-on-chip containing endothelium treated with TNFα. Magnification 10X, Frame Rate: Six frames per minute, Total runtime: 12 minutes
Platelet coverage on a laser-injured mouse blood vessel in vivo. Magnification 20X, Frame Rate: Five frames per second, Total runtime: 4 minutes
Whole blood flow (recalcified citrated blood)) in the lung alveolus- chip containing an intact primary human alveolar epithelium overlying an untreated endothelium (not shown). Magnification 10X, Frame Rate: Two frames per minute, Total runtime: 20 minutes
a–c) (Top) Representative kymographs of a small section of a channel showing attachment and detachment pattern of platelets on a collagen surface (a) versus an endothelium-lined microchannel without (b) or with TNF-α treatment (c). (Bottom) Graphs showing fluorescence (linear trend removed) across time at a representative pixel location of the image timeseries for collagen (a), untreated vessel (b) and vessel, treated with TNF-α (c). d) The coefficient of variance (CV) of fluorescence signal observed over time at a representative single pixel location of an image timeseries of platelet accumulation, as plotted in graphs (a–c). e–g) Visualization and analysis of platelet-endothelial spatial dynamics. (Top) Representative CV-color maps of a large section of the vessel where each pixel in the map represents the temporal CV of platelet dynamics on a collagen surface or an endothelium-lined microchannel with or without TNF-α treatment. (bar, 100 µm). (Bottom) Graphs showing CV across the length of the channel at representative width locations for collagen (e), untreated endothelium (f) and endothelium treated with TNF-α (g). The blue dotted lines are drawn at the 95th percentile and 5th percentile value of the CV respectively. h) The interpercentile range (95th – 5th percentile value) of the CVs plotted in the graphs (e–g), as a measure of spatial heterogeneity in platelet accumulation.
Area-averaged platelet coverage measured on microchips covered with collagen or endothelium without or with TNF-α treatment at the doses indicated (n=3, *P<0.05, 2-way ANOVA).
a) Confocal immunofluorescence microscopic images showing a section of the vascular microchannel with HPMECs when viewed from front (‘xy’) and 3D reconstruction of cross-sectional views from the bottom (‘xyz’) demonstrating full coverage of all four channel walls (green, VE-Cadherin; bar, 200 µm). b) Representative images of the alveolar lung chip lined with HPMECs and stained for VE-Cadherin (green), ICAM1 (purple) and DAPI (nuclei, grey) under control (untreated) or LPS-treated conditions (bar, 50 µm). c) Vascular ICAM-1 levels measured on the endothelial cell surface (n=3) of untreated and LPS-treated endothelium on-chip (*P<0.05, 1-way ANOVA).
a) Fluorescent micrographs showing evolution of blood clots (left to right) in a cremaster artery of a mouse that was either untreated or treated with systemic injection of LPS in the presence or absence of laser injury (bar, 25 µm). b) Platelet binding dynamics (PBD) index computed from fluorescent time series images of platelets adhering to a cremaster artery or a vein of a mouse when exposed to the same experimental conditions as described in a (n=3, *P<0.05, 1-way ANOVA).
a) Photograph showing intratracheal delivery of LPS to an anesthetized mouse. b) Vascular permeability measurements in vivo after intratracheal delivery of LPS for 2 hours at the indicated doses (n=3, *P<0.05, 1-way ANOVA).
Supplementary Text: MATERIALS AND METHODS
3D confocal reconstruction of the lung alveolus-on-chip showing epithelial junctions (yellow) and endothelial junctions (green)
Platelet coverage (red) upon whole blood perfusion on collagen coated lower microchannel of the lung alveoli-on-a-chip containing no endothelium. Magnification 10X, Frame Rate: Six frames per minute, Total runtime: 12 minutes
STUDY HIGHLIGHTS.
What is the current knowledge on the topic?
Animal models have been used to model the effects of drugs on pulmonary thrombosis, however, they do not mimic the physiology, altered hemostasis or vasculopathies observed in human lung.
What question did this study address?
This study explored whether microfluidic organ-on-a-chip cell culture device can be used to model pulmonary thrombosis at organ level, and measure the effects of drugs on this process.
What this study adds to our knowledge?
This study demonstrates that key elements of human pulmonary thrombosis can be modelled in vitro using organs-on-chips. This model showed that LPS endotoxin indirectly stimulates intravascular thrombosis, and inhibitory effects on endothelial activation and thrombosis of a prospective antithrombotic therapeutic can be recapitulated.
How this might change clinical pharmacology or translational science?
This new methodology will enable in vitro analysis of human thrombotic responses to potential new therapeutics within the lung microvasculature at the cell, tissue and organ levels, not currently possible with animal models.
Acknowledgments
We thank R. Novak, B. Boettner, J. Fraser, D. Conegliano, S. Denagamage, T. Ferrante, M. Ingram, A. Vernet and G. Merrill-Skoloff for their helpful input and technical support. This work was funded by DARPA contract N66001-11-1-4180, HR0011-13-C-0025, Janssen Pharmaceuticals and the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University.
NIH Grant R01 EB02004-01
Footnotes
CONFLICT OF INTEREST DISCLOSURE: D.E.I and G.A.H. are founders, and hold equity in Emulate, Inc. and D.E.I. chairs it scientific advisory board; A.D.v.d.M serves as a scientific consultant to the company.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS:
D.E.I., A.J., and R.B. wrote the manuscript; D.E.I., A.J., R.B., A.D.v.d.M., K.D.C., and R.F. designed the research; A.J., R.B., A.D.v.d.M., A.M., T.M., and K.D.C. performed the research; D.E.I., A.J., R.B., K.D.C., M.A.O., C.S.L., and G.A.H. analyzed the data; A.M., T.M., K.D.C., and O.A. contributed new reagents/analytical tools.
References
- 1.Glas GJ, et al. Bronchoalveolar hemostasis in lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013;11:17–25. doi: 10.1111/jth.12047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wygrecka M, Jablonska E, Guenther A, Preissner KT, Markart P. Current view on alveolar coagulation and fibrinolysis in acute inflammatory and chronic interstitial lung diseases. Thromb. Haemost. 2008;99:494–501. doi: 10.1160/TH07-11-0666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bozza FA, Shah AM, Weyrich AS, Zimmerman GA. Amicus or Adversary: Platelets in Lung Biology, Acute Injury, and Inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2009;40:123–134. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2008-0241TR. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Finigan JH. The coagulation system and pulmonary endothelial function in acute lung injury. Microvasc. Res. 2009;77:35–38. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2008.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cuttica MJ, Machado R. Pulmonary artery thrombosis: another piece to the acute chest syndrome puzzle. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011;184:990–991. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201107-1312ED. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Herve P, et al. Pathobiology of pulmonary hypertension. The role of platelets and thrombosis. Clin. Chest Med. 2001;22:451–458. doi: 10.1016/s0272-5231(05)70283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Toshner* M, Pepke-Zaba* J. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: time for research in pathophysiology to catch up with developments in treatment. F1000Prime Rep. 2014;6 doi: 10.12703/P6-38. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Matute-Bello G, Frevert CW, Martin TR. Animal models of acute lung injury. Am. J. Physiol. - Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2008;295:L379–L399. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00010.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Vivero M, Padera RF. Histopathology of Lung Disease in the Connective Tissue Diseases. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2015;41:197–211. doi: 10.1016/j.rdc.2014.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Johnson SR, Granton JT, Mehta S. Thrombotic arteriopathy and anticoagulation in pulmonary hypertension. Chest. 2006;130:545–552. doi: 10.1378/chest.130.2.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Benam KH, et al. Engineered in vitro disease models. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2015;10:195–262. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-012414-040418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bhatia SN, Ingber DE. Microfluidic organs-on-chips. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014;32:760–772. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Jackson SP. The growing complexity of platelet aggregation. Blood. 2007;109:5087–5095. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-12-027698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sagripanti A, Carpi A. Antithrombotic and prothrombotic activities of the vascular endothelium. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2000;54:107–111. doi: 10.1016/S0753-3322(00)88861-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wolberg AS, Aleman MM, Leiderman K, Machlus KR. Procoagulant activity in hemostasis and thrombosis: Virchow’s triad revisited. Anesth. Analg. 2012;114:275–285. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e31823a088c. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Andrews DA, Low PS. Role of red blood cells in thrombosis. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 1999;6:76. doi: 10.1097/00062752-199903000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Weyrich AS, Zimmerman GA. Platelets in lung biology. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013;75:569–591. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-030212-183752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Casa LD, Deaton DH, Ku DN. Role of high shear rate in thrombosis. J. Vasc. Surg. 2015;61:1068–1080. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2014.12.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ingber DE. Reverse Engineering Human Pathophysiology with Organs-on-Chips. Cell. 2016;164:1105–1109. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.02.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Huh D, et al. Reconstituting Organ-Level Lung Functions on a Chip. Science. 2010;328:1662–1668. doi: 10.1126/science.1188302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Huh D, et al. A Human Disease Model of Drug Toxicity-Induced Pulmonary Edema in a Lung-on-a-Chip Microdevice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012;4:159ra147. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3004249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lieber M, Smith B, Szakal A, Nelson-Rees W, Todaro G. A continuous tumor-cell line from a human lung carcinoma with properties of type II alveolar epithelial cells. Int. J. Cancer. 1976;17:62–70. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Benam KH, et al. Small airway-on-a-chip enables analysis of human lung inflammation and drug responses in vitro. Nat. Methods. 2015 doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Colace T, Falls E, Zheng XL, Diamond SL. Analysis of morphology of platelet aggregates formed on collagen under laminar blood flow. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2011;39:922–929. doi: 10.1007/s10439-010-0182-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Neeves KB, et al. Sources of variability in platelet accumulation on type 1 fibrillar collagen in microfluidic flow assays. PloS One. 2013;8:e54680. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Cosemans JM, Angelillo-Scherrer A, Mattheij NJ, Heemskerk JW. The effects of arterial flow on platelet activation, thrombus growth, and stabilization. Cardiovasc. Res. 2013;99:342–352. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvt110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Pircher J, et al. Prothrombotic effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha in vivo are amplified by the absence of TNF-alpha receptor subtype 1 and require TNF-alpha receptor subtype 2. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012;14:R225. doi: 10.1186/ar4064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Jain A, et al. Assessment of whole blood thrombosis in a microfluidic device lined by fixed human endothelium. Biomed. Microdevices. 2016;18:73. doi: 10.1007/s10544-016-0095-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Furie B, Furie BC. Mechanisms of thrombus formation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008;359:938–949. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra0801082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cooley BC. In vivo fluorescence imaging of large-vessel thrombosis in mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011;31:1351–1356. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.225334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Stalker TJ, et al. A systems approach to hemostasis: 3. Thrombus consolidation regulates intrathrombus solute transport and local thrombin activity. Blood. 2014;124:1824–1831. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-01-550319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Falati S, Gross P, Merrill-Skoloff G, Furie BC, Furie B. Real-time in vivo imaging of platelets, tissue factor and fibrin during arterial thrombus formation in the mouse. Nat. Med. 2002;8:1175–1181. doi: 10.1038/nm782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Westein E, Witt S, de Lamers M, Cosemans JM, Heemskerk JW. Monitoring in vitro thrombus formation with novel microfluidic devices. Platelets. 2012;23:501–509. doi: 10.3109/09537104.2012.709653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hansen RR, et al. High content evaluation of shear dependent platelet function in a microfluidic flow assay. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2013;41:250–262. doi: 10.1007/s10439-012-0658-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jain A, et al. A shear gradient-activated microfluidic device for automated monitoring of whole blood haemostasis and platelet function. Nat. Commun. 2016;7:10176. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Welsh JD, et al. A systems approach to hemostasis: 1. The interdependence of thrombus architecture and agonist movements in the gaps between platelets. Blood. 2014;124:1808–1815. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-01-550335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Proudfoot AG, McAuley DF, Griffiths MJD, Hind M. Human models of acute lung injury. Dis. Model. Mech. 2011;4:145–153. doi: 10.1242/dmm.006213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Liu F, Li W, Pauluhn J, Trübel H, Wang C. Lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats: comparative assessment of intratracheal instillation and aerosol inhalation. Toxicology. 2013;304:158–166. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2012.12.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wung BS, Ni CW, Wang DL. ICAM-1 induction by TNFalpha and IL-6 is mediated by distinct pathways via Rac in endothelial cells. J. Biomed. Sci. 2005;12:91–101. doi: 10.1007/s11373-004-8170-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hawiger J, Veach RA, Zienkiewicz J. New paradigms in sepsis: from prevention to protection of failing microcirculation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015:1743–56. doi: 10.1111/jth.13061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.De Ceunynck K, et al. A chemical APC mimetic protects endothelium from thromboinflammatory injury. Rev [Google Scholar]
- 42.Aisiku O, et al. Parmodulins inhibit thrombus formation without inducing endothelial injury caused by vorapaxar. Blood. 2015;125:1976–1985. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-09-599910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Conti G, et al. Evaluation of lung inflammation induced by intratracheal administration of LPS in mice: comparison between MRI and histology. Magn. Reson. Mater. Phys. Biol. Med. 2010;23:93–101. doi: 10.1007/s10334-010-0203-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Wootton DM, Ku DN. Fluid mechanics of vascular systems, diseases, and thrombosis. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 1999;1:299–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bioeng.1.1.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Fogelson AL, Neeves KB. Fluid Mechanics of Blood Clot Formation. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2015;47:377–403. doi: 10.1146/annurev-fluid-010814-014513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Flamm MH, Diamond SL. Multiscale systems biology and physics of thrombosis under flow. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2012;40:2355–2364. doi: 10.1007/s10439-012-0557-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Zheng Y, et al. In vitro microvessels for the study of angiogenesis and thrombosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2012;109:9342–9347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1201240109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Zhang B, Peticone C, Murthy SK, Radisic M. A standalone perfusion platform for drug testing and target validation in micro-vessel networks. Biomicrofluidics. 2013;7:44125. doi: 10.1063/1.4818837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Tsai M, et al. In vitro modeling of the microvascular occlusion and thrombosis that occur in hematologic diseases using microfluidic technology. J. Clin. Invest. 2012;122:408–418. doi: 10.1172/JCI58753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Li X, Xu S, He P, Liu Y. In Vitro Recapitulation of Functional Microvessels for the Study of Endothelial Shear Response, Nitric Oxide and [Ca2+]i. PLOS One. 2015;10:e0126797. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Confocal immunofluorescence microscopic images showing a section of the microchannel with HUVECs when viewed from front (‘xy’) and reconstruction of cross-sectional views from the bottom and the side (‘yz’ and ‘xz’, respectively) demonstrating full coverage of all microfluidic channel walls. (green, VE-Cadherin; bar, 100 µm).
Platelet coverage (red) upon whole blood perfusion on lower microchannel of the lung alveolus-chip containing healthy endothelium lined over collagen. Magnification 10X, Frame Rate: Six frames per minute, Total runtime: 12 minutes
Platelet coverage (red) upon whole blood perfusion on lower microchannel of the lung alveolus-on-chip containing endothelium treated with TNFα. Magnification 10X, Frame Rate: Six frames per minute, Total runtime: 12 minutes
Platelet coverage on a laser-injured mouse blood vessel in vivo. Magnification 20X, Frame Rate: Five frames per second, Total runtime: 4 minutes
Whole blood flow (recalcified citrated blood)) in the lung alveolus- chip containing an intact primary human alveolar epithelium overlying an untreated endothelium (not shown). Magnification 10X, Frame Rate: Two frames per minute, Total runtime: 20 minutes
a–c) (Top) Representative kymographs of a small section of a channel showing attachment and detachment pattern of platelets on a collagen surface (a) versus an endothelium-lined microchannel without (b) or with TNF-α treatment (c). (Bottom) Graphs showing fluorescence (linear trend removed) across time at a representative pixel location of the image timeseries for collagen (a), untreated vessel (b) and vessel, treated with TNF-α (c). d) The coefficient of variance (CV) of fluorescence signal observed over time at a representative single pixel location of an image timeseries of platelet accumulation, as plotted in graphs (a–c). e–g) Visualization and analysis of platelet-endothelial spatial dynamics. (Top) Representative CV-color maps of a large section of the vessel where each pixel in the map represents the temporal CV of platelet dynamics on a collagen surface or an endothelium-lined microchannel with or without TNF-α treatment. (bar, 100 µm). (Bottom) Graphs showing CV across the length of the channel at representative width locations for collagen (e), untreated endothelium (f) and endothelium treated with TNF-α (g). The blue dotted lines are drawn at the 95th percentile and 5th percentile value of the CV respectively. h) The interpercentile range (95th – 5th percentile value) of the CVs plotted in the graphs (e–g), as a measure of spatial heterogeneity in platelet accumulation.
Area-averaged platelet coverage measured on microchips covered with collagen or endothelium without or with TNF-α treatment at the doses indicated (n=3, *P<0.05, 2-way ANOVA).
a) Confocal immunofluorescence microscopic images showing a section of the vascular microchannel with HPMECs when viewed from front (‘xy’) and 3D reconstruction of cross-sectional views from the bottom (‘xyz’) demonstrating full coverage of all four channel walls (green, VE-Cadherin; bar, 200 µm). b) Representative images of the alveolar lung chip lined with HPMECs and stained for VE-Cadherin (green), ICAM1 (purple) and DAPI (nuclei, grey) under control (untreated) or LPS-treated conditions (bar, 50 µm). c) Vascular ICAM-1 levels measured on the endothelial cell surface (n=3) of untreated and LPS-treated endothelium on-chip (*P<0.05, 1-way ANOVA).
a) Fluorescent micrographs showing evolution of blood clots (left to right) in a cremaster artery of a mouse that was either untreated or treated with systemic injection of LPS in the presence or absence of laser injury (bar, 25 µm). b) Platelet binding dynamics (PBD) index computed from fluorescent time series images of platelets adhering to a cremaster artery or a vein of a mouse when exposed to the same experimental conditions as described in a (n=3, *P<0.05, 1-way ANOVA).
a) Photograph showing intratracheal delivery of LPS to an anesthetized mouse. b) Vascular permeability measurements in vivo after intratracheal delivery of LPS for 2 hours at the indicated doses (n=3, *P<0.05, 1-way ANOVA).
Supplementary Text: MATERIALS AND METHODS
3D confocal reconstruction of the lung alveolus-on-chip showing epithelial junctions (yellow) and endothelial junctions (green)
Platelet coverage (red) upon whole blood perfusion on collagen coated lower microchannel of the lung alveoli-on-a-chip containing no endothelium. Magnification 10X, Frame Rate: Six frames per minute, Total runtime: 12 minutes