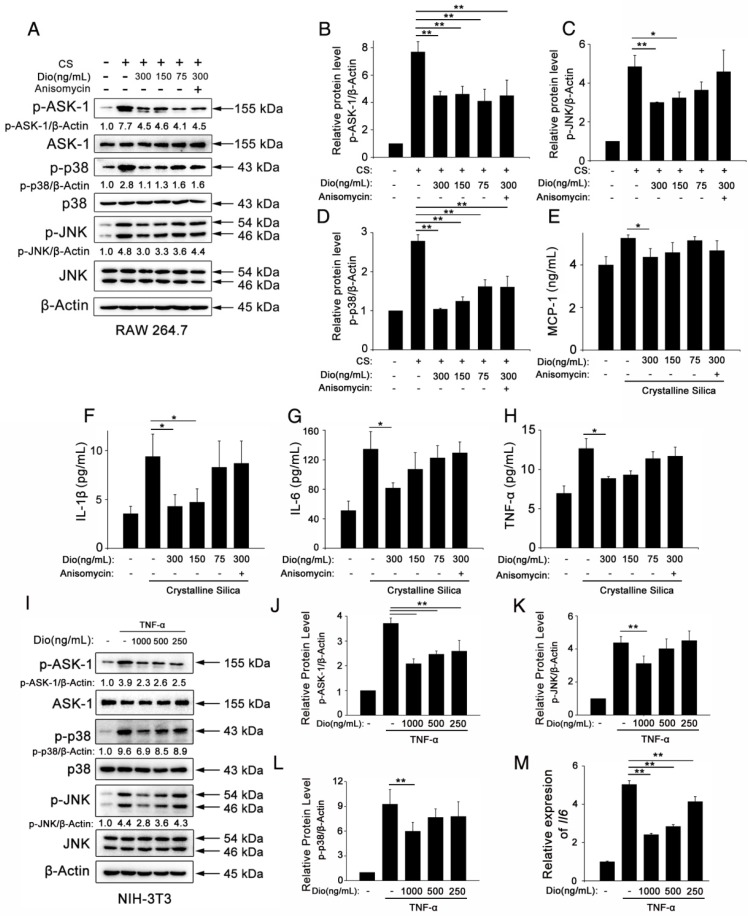
Figure 5.
Dioscin inhibits macrophages and fibroblasts from secreting pro-inflammatory cytokines. (A) Western blot analyses of ASK1 phosphorylation and downstream MAPK proteins (p38 and JNK/SAPK) in LPS-primed RAW 264.7 macrophages treated with CS (50 μg/cm2) together with different does of dioscin for 6 h. Anisomycin was used to reverse dioscin's effect (2 ng/mL). Quantification of each protein level relative to β-Actin is shown below each band. (B-D) The levels of phospho-ASK1, phospho-p38 and phosphor-JNK were normalized to those of β-Actin (n=3). (E-H) ELISA analyses of pro-inflammation cytokines in the culture medium of different treated macrophages at 6 h. (E) MCP-1, (F) IL-1β, (G) IL-6, (H)TNF-α (n=3). Data are the mean of three independent experiments (n=3). (I) Western blot analyses of ASK1 phosphorylation and downstream MAPK proteins (p38 and JNK/SAPK) in TNF-α- (25 ng/mL) treated NIH-3T3 fibroblasts together with different does of dioscin for 30 min. Quantification of each protein level relative to β-Actin is shown below each band. (J-L) The levels of phospho-ASK1, phospho-p38 and phosphor-JNK were normalized to those of β-Actin (n=3). (M) qPCR analysis of Il-6 mRNA levels in TNF-α- (25 ng/mL) treated fibroblasts together with different concentrations of dioscin for 12 h (n=3). *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01. Error bars indicate the mean ± SD. The experiment was performed twice with similar results.