Abstract
Theranostics is the integration of diagnostic information with pharmaceuticals to increase effectiveness and safety of cancer treatments. Nuclear medicine provides a non-invasive means to visualize drug target expression across primary and metastatic sites, and assess pharmacokinetics and efficacy of companion therapeutic agents. This is significant given the increasing recognition of the importance of clonal heterogeneity in treatment response and resistance. Carbonic anhydrase IX (CA-IX) has been advocated as an attractive diagnostic and therapeutic biomarker for targeting hypoxia in solid malignancies. CA-IX confers cancer cell survival under low oxygen tension, and is associated with increased propensity for metastasis. As such, CA-IX is overexpressed in a broad spectrum of cancers. Different classes of antigen recognition molecules targeting CA-IX including monoclonal antibodies, peptides, small molecule inhibitors, and antibody mimetics have been radiolabeled for imaging and therapeutic applications. cG250, a chimeric monoclonal antibody, has been labeled with an assortment of radionuclides (124I, 111In, 89Zr, 131I, 90Y, and 177Lu) and is the most extensively investigated CA-IX radiopharmaceutical. In recent years, there have been tremendous advancements made by the research community in developing alternatives to cG250. Although still in preclinical settings, several small molecule inhibitors and antibody mimetics hold great promise in improving the management of aggressive and resistant cancers.
Keywords: Nuclear medicine, theranostics, carbonic anhydrase IX, hypoxia, cancer.
Introduction
Tumour hypoxia is a negative prognostic factor as it is associated with increased resistance to radiation therapy and conventional chemotherapy 1. Hypoxia can enhance tumour progression by inducing angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis 1. The salient expression of hypoxia in tumours can potentiate susceptibility to hypoxia-activated prodrugs and novel therapeutics targeting components of the hypoxia signaling cascade 1. Thus, the delineation of hypoxic cells amidst oxygenated cells has a strong bearing on treatment strategies and regimes. Carbonic anhydrase IX (CA-IX) is an endogenous marker for hypoxia that has been touted as a promising therapeutic target for solid malignancies 2, 3. In xenograft models, pharmacological inhibition of CA-IX has been shown to reduce primary tumour growth and its propensity for distant metastasis 4, 5. Previously, Sneddon and Poulsen published a review of the CA-IX targeted imaging agents found in the Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) 6. However, there are only ten entries in MICAD of which six are variants of the monoclonal antibody cG250. Since then, our research group and others have published a large number of vectors designed for theranostic targeting of CA-IX. The goal of this review article is to provide an overview of CA-IX as a target for hypoxia imaging and therapy, characterization of CA-IX radiopharmaceuticals, and future perspectives on the clinical translation of these agents.
CA-IX as a Surrogate Marker of Hypoxia
Hypoxia occurs when the vasculature of the tumour is unable to meet the oxygen demands of rapidly proliferating cells 7. The reduction of oxygen tension stabilizes hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs), which are transcription factors that regulate the cells' response to hypoxia 7. HIF-activated cancer cells alter their metabolism by enhancing glycolytic rates 8. While glycolysis generates energy and biosynthetic precursors for cancer cells, it also produces acidic metabolites that can lower intracellular pH (pHi) 8. When pHi becomes too acidic, membrane stability can be disrupted leading to abrogation of cell survival and proliferation 8. Predictably, cancer cells adapt to this stress by overexpressing proteins to maintain pHi homeostasis 9, 10. CA-IX is the most strongly upregulated protein by hypoxia and HIF-1α, and serves as the key enzyme in modulating pHi. Discovered by Pastorekova et al. as a surface membrane protein in the HeLa human cervical carcinoma cell line 12, CA-IX is 1 of 15 unique but closely related zinc metalloenzymes that belong to the α-family of carbonic anhydrases 13. Notably, CA-IX is the isoform that is most strongly associated with cancer 2, 3. CA-IX promotes cancer cell survival by catalyzing the reversible hydration of carbon dioxide to bicarbonate ion and proton (H2O + CO2 ↔ HCO3- + H+) 14. The HCO3- ions are subsequently imported into the cell via ion transporter systems (ex. Na+/HCO3- cotransporter, Na+ dependent Cl-/HCO3- exchanger, and anion exchanger) to preserve a neutral or slightly alkaline pHi. The other product of the enzymatic reaction, H+ ions, acidifies the tumour microenvironment priming it for invasion and metastasis 15.
CA-IX has been used as an endogenous marker to assess tumour hypoxia and complement pimonidazole staining 16, 17. While this strategy is robust, one needs to be aware of the biological limitations when targeting CA-IX. The approximate biological half-life of CA-IX is 38 h in re-oxygenated cells 18, while the oxygen-dependent degradation of HIF-1α is reportedly between 5-8 min 19. The disparate half-lives led to the observations of discordant expression between CA-IX and HIF-1α. Inherently, there is a risk of overestimating hypoxic fractions within a tumour especially in the context of transient hypoxia.
CA-IX Expression in Normal Tissues and Malignancies
One of the most important considerations for any targeting strategy is the expression of the target of interest in diseased state relative to normal physiology. This has a direct implication on signal to noise ratios for imaging, and on therapeutic index for treatment. The expression of CA-IX is limited in normal tissues, as it is primarily localized to the small intestine 20. CA-IX expression has also been reported in the basolateral membrane of acinar and ductal epithelia of the pancreas and in the male efferent epithelial ducts, at weak diffuse levels 21, 22. Conversely, the overexpression of CA-IX has been observed in many solid malignancies including breast, lung, ovary, head and neck, bladder, colon, cervix, and renal cancers 4, 23-30. Tumour microarray analyses with cohort sizes ranging from 144 to 3630 patient samples, confirmed CA-IX to be a negative prognostic marker for breast cancer, non-small cell lung carcinomas, ovarian cancer and astrocytoma 4, 23-25. CA-IX positivity (16-78%) and staining intensity depend on the tumour subtype being investigated.
CA-IX and Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
In clear cell renal cell carcinomas (ccRCC), CA-IX expression is unique compared to other cancers as it is commonly uncoupled from the hypoxia-induced signaling cascade. ccRCC, the most common RCC histological subtype at 75% 31, is characterized by the impaired functionality of the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) tumour suppressor gene that acts as a negative regulator of HIF-1α 30, 32. For ccRCC, the inactivation of VHL either through mutations, loss of heterozygosity or epigenetic silencing leads to constitutive HIF-1α activation and CA-IX expression, even in the absence of hypoxia 33, 34. The development of CA-IX radiopharmaceuticals, in large part, has been spurred by the pathophysiology of ccRCC.
Limited treatment options are available for ccRCC patients, particularly those with advanced or late stage metastatic disease. Systemic cytokine therapy with interferon-alpha or interleukin-2 was used as first-line treatment of metastatic ccRCC 31. Targeted strategies (inhibitors of rapamycin and vascular epidermal growth factor receptor) have become the standard of care for metastatic ccRCC 31. However, their effectiveness remains poor as the five-year survival rate for patients with distant metastasis is around 12.3% 35. This unmet clinical need has driven the development of radioimmunotherapy (RIT) efforts for ccRCC over the last two decades.
In common with other cancers, early diagnosis of ccRCC can significantly improve patient outcomes. When disease is localized and controllable by surgical intervention, the five-year survival rate is > 90% 35. Approximately 80% of patients are diagnosed with localized tumour at presentation, with a large majority being incidentally detected for nonurological complaints 36. Not surprisingly, anatomical imaging modalities like computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and ultrasonography have difficulty in differentiating between malignant and benign renal lesions, and histologic subtypes 36. Positron emission tomography (PET) imaging with 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose has limited utility for primary lesion detection as it is predominantly excreted by the kidneys 36. As a consequence, it is estimated that up to 20% of patients with benign renal masses received treatment in situations where active surveillance would have been sufficient 36. Independent of hypoxia status, CA-IX imaging allows for the characterization of indeterminate renal masses and facilitates informed decision making by oncologists 36.
Monoclonal Antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have had a significant impact in cancer management as therapeutics. mAbs can induce tumouricidal effects through a variety of mechanisms. mAbs can cause cell death by abrogating cell signaling and inducing apoptosis, or by delivering cytotoxic agents or radiation 37-39. They can recruit immune cells to activate antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity, complement-dependent cytotoxicity, or antibody-dependent cell phagocytosis 37. In recent years, the success of mAbs as immune checkpoint inhibitors has renewed optimism for many treatment strategies 40.
G250/cG250 for Therapy
The most clinically investigated mAb for targeting CA-IX is girentuximab (cG250) (Table 1) 41. This mAb binds to the extracellular proteoglycan (PG)-like domain, which is unique to CA-IX compared to other isoforms and lies adjacent to the catalytic domain. Oosterwijk et al. isolated murine G250 from mice immunized with renal cancer homogenates 42. 131I-labeled G250 (131I-mAbG250) was evaluated in two clinical trials 43, 44. In a phase I study, 16 preoperative patients suspected of having RCC received an intravenous dose of 131I-mAbG250 a week prior to nephrectomy 43. Based on whole-body planar gamma camera imaging conducted 3 d post-injection (p.i.), 12 patients had positive scans. Following surgery and histology, 11 cases were confirmed to be the ccRCC subtype and 1 case being the granular subtype. For the positive lesions, CA-IX expression ranged from < 5% to 100% based on immunohistochemistry. For the 4 negative cases, 3 patients had RCC of the granular or spindle subtype and 1 patient was found to have a non-malignant renal mass.
Table 1.
Overview of therapeutic and imaging studies performed with G250 and cG250. Adapted from Oosterwijk-Wakka et al. 41
| Therapy | |||||||
| Agent | # Patients enrolled* | Indication | Response | Duration of response | Clinical stage | Ref | |
| 131I-mAbG250 | 33 | Metastatic ccRCC | 17 SD | 2-3 mo | Phase I/II dose escalation | 44 | |
| 16 PD | |||||||
| 131I-cG250 | 12(8) | Metastatic ccRCC | 1 PR | 9+ mo | Phase I dose escalation | 45 | |
| 1 SD | 3-6 mo | ||||||
| 6 PD | |||||||
| 131I-cG250 | 15(14) | Metastatic ccRCC | 7 SD | 4-13 mo | Phase I dose fractionation | 46 | |
| 7 PD | |||||||
| 131I-cG250 | 29(15) | Metastatic ccRCC | 5 SD | 3-12 mo | Phase I two doses | 47 | |
| 10 PD | |||||||
| 177Lu-cG250 | 23 | Metastatic ccRCC | 1 PR | 9+ mo | Phase I dose escalation | 49 | |
| 12 SD | 3+ mo | ||||||
| 11 PD | |||||||
| 177Lu-cG250 | 16(14) | Metastatic ccRCC | 1 PR | NR | Phase II | 50 | |
| 8 SD | 3+ mo | ||||||
| 5 PD | |||||||
| Imaging | |||||||
| Agent | # Patients enrolled* | Indication | Detection | Sensitivity and selectivity | Clinical stage | Ref | |
| 131I-mAbG250 | 16 | Primary RCC | 12/12 ccRCC pts | NR | Phase I dose escalation | 43 | |
| 124I-cG250 | 26(25) | Primary RCC | 15/16 ccRCC pts | 94 and 100% | Phase I single dose | 53 | |
| 124I-cG250 | 226(195) | Primary RCC | 124/143 ccRCC pts | 86 and 76% | Phase III | 54 | |
|
111In-cG250 131I-cG250 |
5 | Metastatic ccRCC | 47 lesions 30 lesions |
NR | Intrapatient comparison | 55 | |
| 111In-cG250 | 29(22) | Metastatic ccRCC | 15/16 ccRCC pts | NR | Partly retrospective | 56 | |
*Number in bracket represents the number of patients that satisfied evaluation criteria; G250: murine monoclonal G250 antibody; cG250: chimeric monoclonal G250 antibody; ccRCC: clear cell renal cell carcinoma; RCC: renal cell carcinoma; SD: stable disease; PD: progressive disease; PR: partial response; pts: patients; NR: not reported
A phase I dose fractionation approach based on whole-body radiation absorbed dose was performed by Divgi et al. 46. Fifteen patients were recruited for the study and divided into groups of 3. The first cohort was prescribed an average whole-body absorbed dose of 0.50 Gy. The other cohorts received doses in increasing increments of 0.25 Gy. The first fraction was 1110 MBq/5 mg 131I-cG250, with subsequent fractions given at variable activities at 2-3 d intervals to account for clearance rates. Patients were eligible for retreatment if they did not exhibit disease progression and demonstrated recovery from toxicity as measured by imaging, biochemical and hematological tests. Five patients were eligible for additional cycles with 2 patients having stabilized disease for 7 and 13 mo. Two patients developed HACA reactivity over the course of the study. Overall, fractionated RIT with 131I-cG250 was unable to alleviate myelotoxicity or improve clinical responses for metastatic RCC patients.
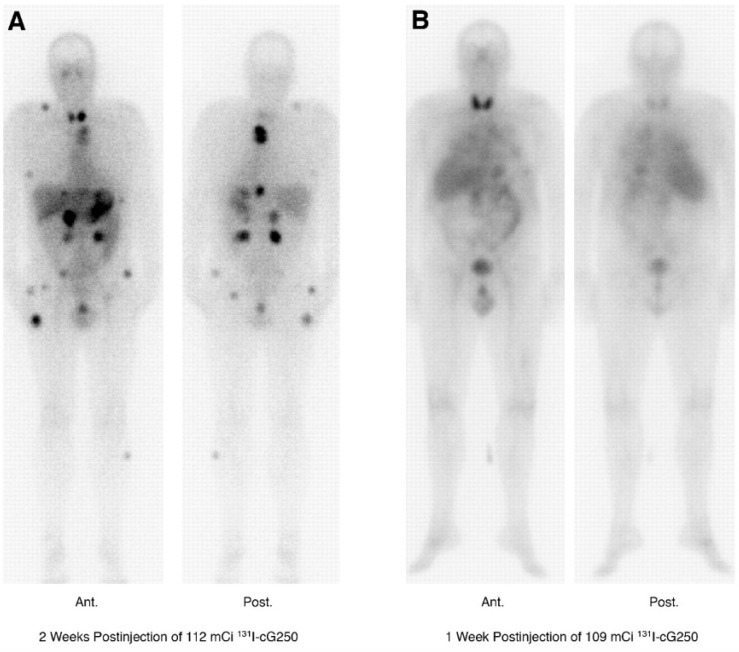
Lastly, a phase I study in which patients received two sequential high doses of 131I-cG250 was reported by Brouwers et al. (Figure 1) 47. Twenty-nine patients with metastatic RCC were recruited for the study. Following an initial imaging dose to assess adequate tumour targeting and antibody accumulation, selected patients (n = 27) were given a therapeutic dose of 2220 MBq/m2. Patients that did not show grade 4 hematological toxicity or develop HACA (n = 19) received a second cycle of low dose diagnostic infusion and high dose therapeutic infusion of 131I-cG250 (1110 MBq/m2 to 1665 MBq/m2). Overall 15 patients were assessable; 5 had stable disease for 3-12 mo while others progressed. The lack of therapeutic efficacy was attributed to insufficient radiation dose delivered to large tumours. Given the limited efficacy of 131I-cG250, the authors concluded that RIT with cG250 should be explored with alternative therapeutic radionuclides.
Figure 1.
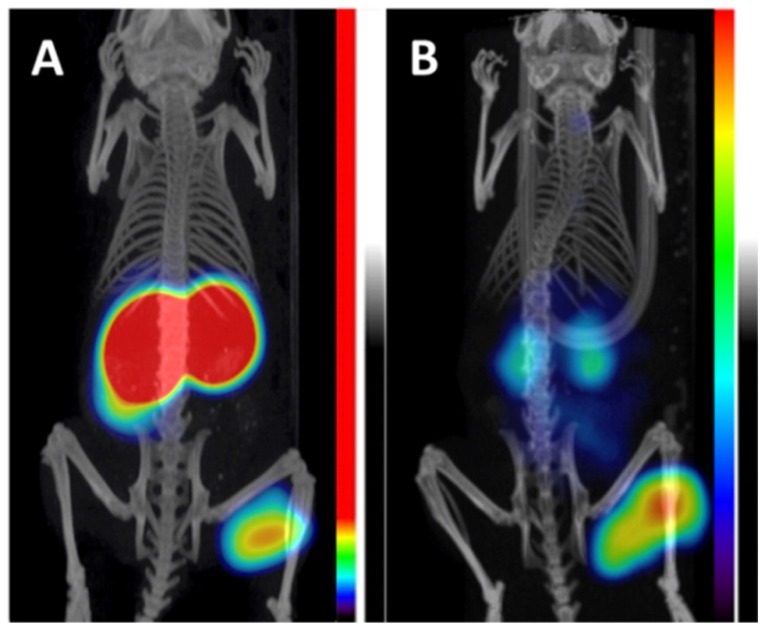
131I-cG250 scintigraphy in two patients with RCC metastases after a RIT infusion. 131I-cG250 enabled good visualization of (sub)cutaneous and muscle metastatic lesions (A) and less clear visualization of lung metastases (B). Uptake in thyroid glands in both patients was observed despite thyroid blocking. Figure reproduced with permissions from Brouwers et al. 47
While 131I-cG250 was being evaluated in the clinic, preclinical data for cG250 radiolabeled with three other beta emitters 90Y, 177Lu, and 186Re were reported by Brouwers et al. 48. Stability, biodistribution and therapeutic efficacy were evaluated in nude mice bearing SK-RC-52 human ccRCC xenografts. 88Y and 125I were used in biodistribution studies, while 90Y and 131I were used in RIT studies. The cG250 conjugates radiolabeled with residualizing radionuclides, 88Y and 177Lu, had significantly higher uptake than the cG250 conjugates labeled with 125I or 186Re. At 7 d p.i., tumour uptake for 177Lu-SCN-Bz-DTPA-cG250 (DTPA: diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid), 88Y-SCN-Bz-DTPA-cG250, 125I-cG250 and 186Re-MAG3-cG250 (MAG3: mercaptoacetyltriglycine) were 87.3 ± 14.0 %ID/g, 70.9 ± 8.4 %ID/g, 9.1 ± 2.0 %ID/g, and 7.9 ± 2.0 %ID/g, respectively. In RIT experiments conducted at MTD, 177Lu-SCN-Bz-DTPA-cG250 was able to deliver a calculated absorbed tumour dose of 807 Gy, while the other radioimmunoconjugates delivered between 76-104 Gy. Compared to 131I-cG250, 177Lu-SCN-Bz-DTPA-cG250 was better at delaying tumour growth (~185 d vs. 25 d) and extending median survival (~300 d vs. 160 d). An added advantage of 177Lu as a therapeutic radionuclide is the sparing of thyroid tissue. While free 177Lu can accumulate in bone, it has low uptake by thyroid. Patients treated with 131I-cG250 were given potassium iodine and potassium perchlorate to reduce uptake of released radioiodine.
Prompted by the promising preclinical results, a phase I study was performed with 177Lu-DOTA-cG250 (177Lu-cG250; DOTA: 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid) 49. Twenty-three patients with progressive metastatic RCC were recruited for the study. Patients were divided into groups, with each group consisting of at least three patients. The first group received a dose level of 1110 MBq/m2, with subsequent groups administered increasing dose increments of 370 MBq/m2. Patients were eligible for retreatment if there was no progression of disease and provided that they recovered from hematological toxicity. Each subsequent dose was given at 75% of the previous dose level. The MTD due to hematological toxicity was found to be 2405 MBq/m2. Of the 23 patients in the study, 13 patients received two cycles of RIT and 4 patients received three cycles of RIT. Disease stabilization 3 mo after first treatment was observed for 17 of the 23 patients (74%) enrolled in the study, but several patients had progression of disease after the second or third cycle. One patient showed partial response that lasted 9 mo after two cycles of RIT.
Recently, Muselaers et al. reported phase II preliminary study data with 177Lu-cG250 50. Fourteen patients were recruited and received an initial infusion of 2405 MBq/m2 177Lu-cG250. As with the phase I study, in the absence of progressive disease and toxicity patients could receive additional cycles of RIT at 75% of the previous dose. Eight patients had stable disease after the first infusion and 1 patient showed partial response. Compared to the phase I study, higher toxicity was observed as many patients had prolonged thrombocytopenia and/or neutropenia. Therefore, only six patients received two cycles of RIT and none received a third cycle. While 177Lu-cG250 RIT can stabilize progressive disease, how it will be integrated into clinical practice remains to be seen. As suggested by the authors, an approach that can be undertaken to improve efficacy and reduce toxicity is to perform personalized dosing based on imaging dosimetric analyses.
G250/cG250 for Imaging
In addition to therapy, G250/cG250 has also been utilized as an imaging agent. 131I-G250 and 131I-cG250, as part of the RIT study protocols, were used for whole body planar scintigraphy to monitor treatment response. However, the high energy gamma emissions of 131I and reliance on collimators for detection can lead to poor resolution images that limit quantification 51. 124I is an alternative iodine radionuclide that has been used for radiolabeling cG250 52. As a positron emitter, 124I facilitates the use of mAbs for PET imaging, which uses coincidence detection to greatly enhance sensitivity and resolution. 124I-cG250 was evaluated in a phase I study for preoperative characterization of ccRCC in patients with renal mass 53. Twenty-six patients received an imaging dose of 185 MBq/10 mg 124I-cG250 1 wk prior to laparotomy. Baseline PET/CT imaging was performed after infusion and prior to surgery. Tumours were designated as positive when tumour-to-kidney (T:K) ratio was >3. Fifteen out of 16 pathologically confirmed cases of ccRCC were identified as positive in PET. The nine patients that did not have ccRCC were negative on PET images. One patient received immunologically inactive 124I-cG250, and was excluded from analyses. For the study, 124I-cG250 had a positive predictive value (PPV) of 100%, a negative predictive value (NPV) of 90%, sensitivity of 94%, and specificity of 100%.
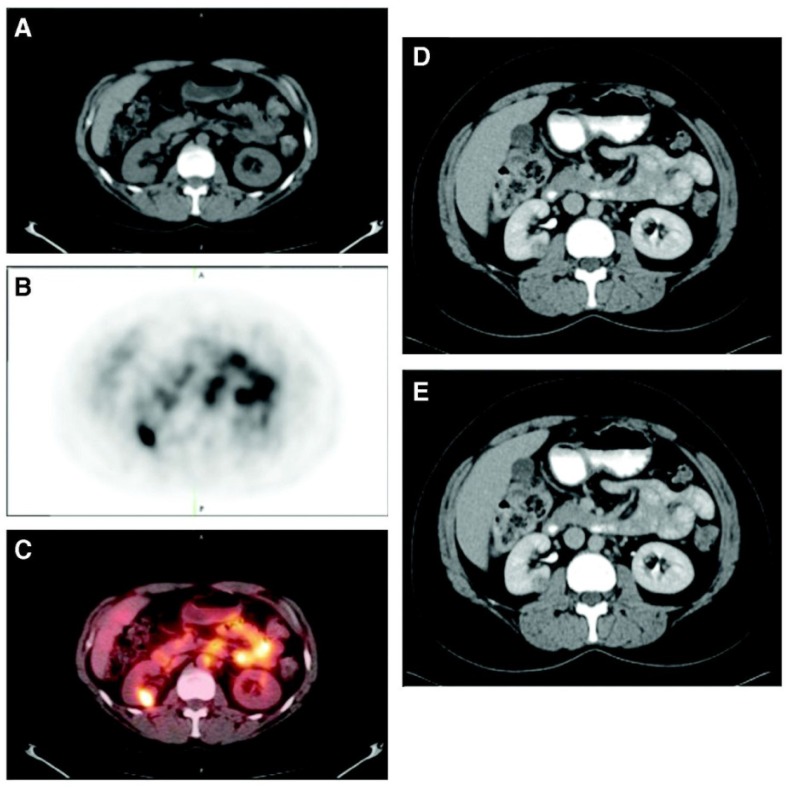
A phase III study was performed comparing the efficacy of 124I-cG250 PET with contrast enhanced CT (CECT) for the detection of ccRCC in pre-treatment setting (Figure 2) 54. Of the 226 patients enrolled in the study, 195 had complete data sets (histopathology, PET/CT and CECT results) for analysis. Patients received 185 MBq/13.7 mg 124I-cG250 and PET/CT acquisition was performed 2-6 d following administration and prior to surgery. CECTs were performed within 48 h of 124I-cG250 PET/CT. 124I-cG250 had better average sensitivity (86% vs. 76%) and selectivity (76% vs. 47%) than CECT for differentiating ccRCC from non-ccRCC. Moreover, 124I-cG250 had PPV and NPV of 94% and 69%, compared to 80% and 41% for CECT. 124I-cG250 should be able to guide cancer management and surgical decisions for patients with indiscriminate renal masses. A second phase III confirmatory study was recommended by the FDA, though this study has yet to be initiated.
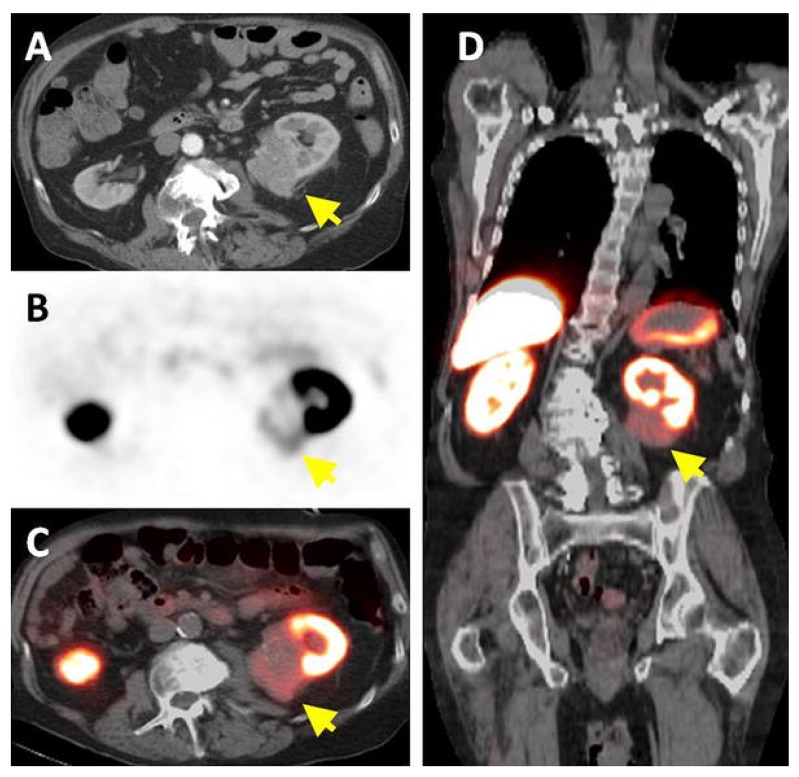
Figure 2.
Patient with a 1.0 cm ccRCC of the right kidney. (A) The mass is visible in the noncontrast CT component of the PET/CT scan, (B) is positive on 124I-cG250 PET, and (C) is clearly evident on the fused image. The mass was deemed to be positive on the CECT scan of the (D) parenchymal component and (E) excretory component by Hounsfield criteria and qualitatively. Figure reproduced with permissions from Divgi et al.54.
Two potential limitations for the clinical adoption of 124I-cG250 are in vivo dehalogenation and the relative cost of 124I production. Subsequently, cG250 was radiolabeled with residualizing radionuclides 111In and 89Zr for immunoSPECT and immunoPET, respectively. cG250 was conjugated with bifunctional chelators DOTA or DTPA for 111In-labeling and DFO (desferoxamine) for 89Zr labeling. 111In-DOTA-cG250 was used as the companion imaging agent for the aforementioned 177Lu RIT studies. Brouwers et al. performed an intrapatient comparison of 111In-DTPA-cG250 and 131I-cG250 scintigraphy for 5 metastatic ccRCC patients55. 111In-DTPA-cG250 was able to visualize more metastatic lesions than 131I-cG250 at 4 d p.i. (n = 47 vs. n = 30). Moreover, higher radioactivity accumulated in lesions and better contrast ratios were obtained. 111In-DTPA-cG250 was evaluated in a small cohort of patients (n = 22)56. Uptake of 111In-DTPA-cG250 was observed in 16 patients. Fifteen of the 16 had histopathology confirmed ccRCC, while the remaining patient had a CA-IX expressing type 2 papillary RCC driven by hypoxia. Shortly thereafter, 89Zr-cG250 was evaluated by Cheal and colleagues in the preclinical setting 57. 89Zr-cG250 performed better than 124I-cG250 in mice bearing human renal cell carcinoma SK-RC-38 xenografts, with tumour uptake of ~20 %ID/g at 11 d p.i. and ~2 %ID/g at 10 d p.i., respectively. In this study, the clearance of 124I from the tumour was approximately 17.5-fold faster than that of 89Zr. The concomitant washout of 124I, was accompanied by thyroid uptake.
cG250 antibody fragments, cG250-Fab and cG250-F(ab')2, have also been investigated as imaging agents58, 59. While it is beneficial for therapeutic mAbs to achieve high concentration at target sites over a prolonged period, the long residence time of mAbs in blood can hinder imaging. For imaging, it is better for the agent to clear rapidly to achieve good contrast earlier. Fab and F(ab')2 fragments, with their reduced molecular weights (55 and 110 kDa) can achieve optimal contrast within the same day of administration 60. This provides logistical advantages in the clinic, and improves turnaround time of test results.
Carlin et al. compared the efficacy of 111In-DOTA-cG250, 111In-DOTA-F(ab')2-cG250 and 111In-DOTA-Fab-cG250 in HT-29 human colorectal cancer xenografts58. At 7 d p.i., 111In-DOTA-cG250 had tumour uptake of 26.4 ± 5.7 %ID/g, which corresponded to tumour-to-blood (T:B) and tumour-to-muscle (T:M) ratios of 6.6 and 69. 111In-DOTA-F(ab')2-cG250 had lower tumour uptake at 9.3 ± 2.1 %ID/g at 24 h p.i., and T:B and T:M ratios of 4.6 and 8.9. 111In-DOTA-Fab-cG250 had the lowest tumour uptake of 3.5 ± 1.7 %ID/g at 24 h p.i., and T:B and T:M ratios of 16.6 and 6.7. It was concluded that imaging with cG250-Fab or cG250-F(ab')2 would be less sensitive and accurate than intact cG250. Hoeben et al. radiolabeled cG250-F(ab')2 with 89Zr and evaluated it in athymic mice inoculated with SCCNij3 human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma59. The uptake of 89Zr-cG250-F(ab')2 at 4 h and 24 h p.i. (3.71 ± 0.97 %ID/g and 1.66 ± 0.48 %ID/g, respectively) correlated with CA-IX expression (r = 0.57-0.74) and pimonidazole staining (r = 0.46-0.68). The T:B and T:M ratios of 89Zr-cG250-F(ab')2 were 8.7 and 7.4 at 24 h p.i., respectively. According to the authors, specific accumulation of 89Zr-cG250-F(ab')2 was achieved by 4 h p.i., compared to 24 h p.i. for 111In-DTPA-cG250.
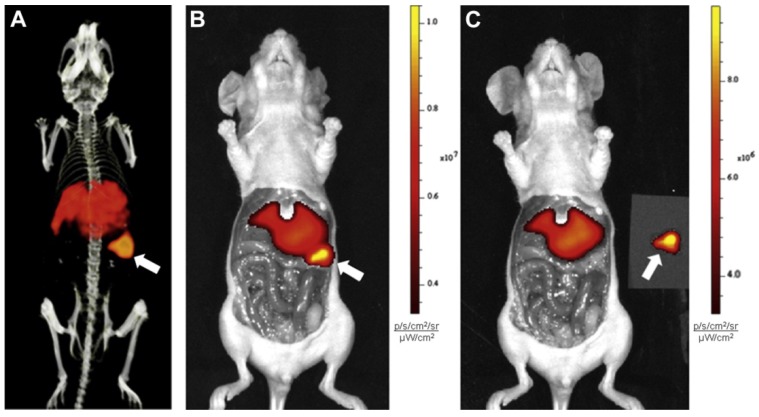
An emergent application of cG250 is dual modality imaging. Muselaers et al. synthesized 111In-DTPA-G250-IRDye800CW, a cG250 derivative that offers SPECT and optical capability (Figure 3) 61. In nude mice bearing SK-RC-52 xenografts, maximum uptake was observed at 1 wk p.i. (58.5 ± 18.7 %ID/g). There was good concordance between SPECT and fluorescence images. While optical agents have limited tissue penetrance due to signal attenuation, they can be useful for complementary intraoperative imaging to ensure that negative surgical resection margins are reached 62. A phase I study of 111In-DTPA-G250-IRDye800CW is planned to assess its safety and efficacy in patients (clinical trials.gov, NCT02497599).
Figure 3.
Preclinical imaging with 111In-DTPA-G250-IRDye800CW in SK-RC-52 bearing nude mice. (A) Preoperative SPECT/CT, and (B) fluorescence images 48 h p.i. showed accumulation in tumour (arrow). Tumour was removed using fluorescence image-guided surgery. (C) After resection, no residual tumour was detected macroscopically or by optical imaging. Figure reproduced with permissions from Muselaers et al.61.
Other mAbs
Besides cG250, other mAbs have been radiolabeled for targeting CA-IX expression, but none have advanced to clinical settings. The M75 mAb binds to the extracellular PG-like domain. 125I-labeled M75 was developed for preclinical imaging of CA-IX in hypoxic niches by Chrastina et al. 125I-M75 showed selective accumulation in both HT-29 human colorectal cancer (15.3 ± 3.6 %ID/g at 48 h p.i.) and HeLa human cervical carcinoma xenografts (~11.5 %ID/g at 48 h p.i.) 63, 64. While initial results were promising, no follow-up work was reported. M75 is commercially available as part of an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit to detect soluble CA-IX in serum/plasma 65.
Ahlskog et al. characterized two humanized mAbs, A3 and CC7, identified through phage-display technology 66. A3 and CC7 bind to the extracellular domain of CA-IX with nanomolar affinity, and were selective for CA-IX over other isoforms. To facilitate faster distribution and clearance, A3 and CC7 were subcloned as single-chain variable fragments (scFv; 25 kDa) and small immunoproteins (SIP; 76 kDa). SIP(A3) was radiolabeled with 177Lu, and biodistribution studies were performed in nude mice bearing LS174T human colorectal adenocarcinoma xenografts. 177Lu-SIP(A3) had low uptake in tumour (2.41 ± 0.19 %ID/g), but generated decent contrast for T:B ratio (16.7). To the best of our knowledge, there have been no subsequent reports of A3 or CC7 as CA-IX imaging agents.
Peptides
Peptides are widely used as theranostic vectors due the aberrant overexpression of peptide receptors in different cancer subtypes (e.g., Somatostatin receptor type 2, CXC chemokine receptor type 4, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor, etc.) 67, 68. Peptides can be readily produced, lack immunogenicity, and offer rapid tumour targeting and quick clearance. The modular design of most peptides provides the flexibility to use different radiolabels, linkers, amino acids (natural or unnatural) to optimize stability, targeting, and pharmacokinetics. A potential limitation of peptide-based tracers is high renal reabsorption leading to nephrotoxicity, though methods to mitigate this risk exist 69.
There are no known endogenous peptides that bind to CA-IX. Therefore, those investigated for targeting applications were identified through phage display technology. Panning against the extracellular domain of recombinant CA-IX, Askoxylakis et al. isolated a dodecapeptide YNTNHVPLSPKY (CaIX-P1) 70. CaIX-P1 was radiolabeled with 125I/131I using the chloramine-T method. Although 125I-CaIX-P1 showed preferential uptake in CA-IX-expressing cell lines in vitro, binding affinity was not determined. Biodistribution studies were performed in SK-RC-52 xenograft mice, with uptake of 131I-CaIX-P1 in tumour being lower than blood at all evaluated time points. Highest contrast was achieved at 1 h p.i., when T:B and T:M ratios were 0.65 ± 0.24 and 4.11 ± 2.44 respectively. Plasma stability study revealed that CaIX-P1 had a half-life of 25 min, and the N-terminal tyrosine residue used for direct iodination was cleaved by serum proteases. Rana et al. attempted to optimize the stability and binding properties of CaIX-P1 by performing alanine scanning and truncation studies 71. This led to the identification of NHVPLSPy (CaIX-P1-4-10) as a candidate. A D-tyrosine residue was added at the C-terminus for binding and radiolabeling with 125I/131I. Compared to CaIX-P1, CaIX-P1-4-10 had approximately 5.8-fold higher binding ratio in vitro and an improved serum stability of 90 min. However, 131I-CaIX-P1-4-10 did not fare any better for planar scintigraphy as it was unable to distinguish SK-RC-52 xenografts (~2.5 %ID/g at 1 h p.i.) from background. The IC50 value for CaIX-P1-4-10 was determined to be in the micromolar range.
Citing concerns of isoform selectivity, the same research group directed a screen against the PG-like domain of CA-IX and isolated the dodecapeptide NMPKDVTTRMSS (PGLR-P1) 72. A C-terminal D-tyrosine was again introduced to facilitate radiolabeling with 125I/131I. 125I-PGLR-P1 showed reduced binding to CA-II and CA-XII in vitro, but affinity remained at micromolar range. Uptake of 131I-PGLR-P1 in SK-RC-52 tumours (0.48 ± 0.20 at 1 h p.i.) was lower than most normal tissues, offering low contrast. With limited success, there has been no further development of short peptides targeting CA-IX.
Small Molecule Inhibitors
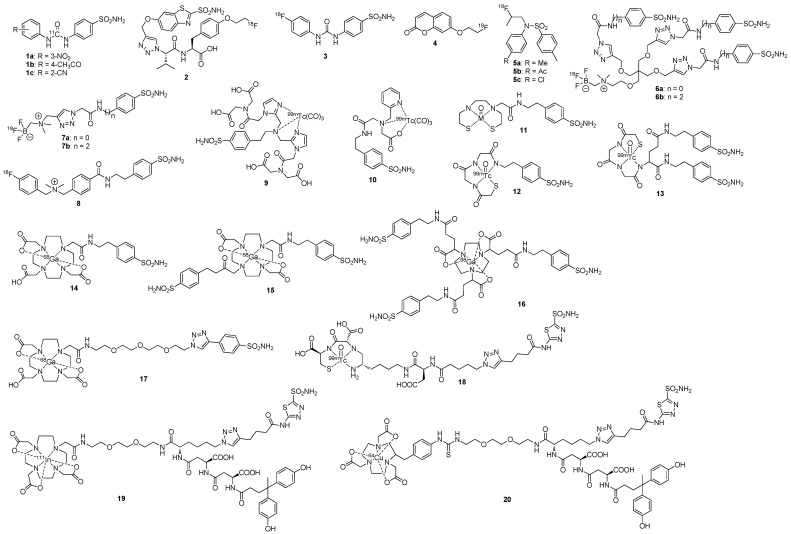
Small molecule inhibitors represent the largest and most diverse class of molecular antigen recognition molecules to be investigated for CA-IX targeting (Figure 4 and Table 2). With low molecular weights, small molecules can more easily transverse the chaotic vasculature in tumours compared to mAbs. Additionally, small molecules are non-immunogenic and generally less expensive to produce. Sulfonamides and coumarins are two classes of small molecules that potently inhibit CAs 73. Sulfonamides attenuate enzyme activity by forming coordination with the Zn2+ ion of the catalytic pocket to displace H2O 2. Coumarins, upon hydrolysis, bind irreversibly at the catalytic pocket entrance to block substrate binding 74. Given the shared homology of the catalytic domain within the CA family, designing inhibitors that target individual isoenzymes is difficult 13, 73. As CA-IX is one of three extracellular transmembrane isoenzymes (others being CA-XII and CA-XIV), many of the CA-IX imaging agents derived from small molecule inhibitors rely on cell impermeability for isoform selectivity.
Figure 4.
Chemical structures of radiolabeled small molecule inhibitors of CA-IX. With the notable exceptions of compounds 1, 3, 4, and 5, these low molecular weight imaging agents attain CA-IX selectivity through cell impermeability.
Table 2.
Summary of preclinical biological evaluation of radiolabeled CA-IX small molecule inhibitors shown in Figure 4.
| Agent | Binding affinity, Ki (nM) | Model | Tumour uptake (%ID/g)* | T:B ratio | T:M ratio | Tumour visualization (Yes/No) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a-c | 0.9 (R = 3-NO2) | - | - | - | - | - | 75 |
| 5.4 (R = 4-Ac) | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 0.3 (R = 2-CN) | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| 2 | 124 | HT-29 | < 0.25 at 2 h | - | - | No | 78 |
| U373 | < 0.25 at 4 h | - | - | No | |||
| 3 | 45 | HT-29 | 0.83 at 1 h | < 1.0 | < 1.0 | No | 79 |
| 4 | 70 | HT-29 | 1.16 at 1 h | < 1.0 | < 2.0 | No | 79 |
| 5a-c | 9.3 (R = Me) | HT-29 | 0.51 at 1 h | ~ 1.0 | ~ 1.0 | No | 81 |
| 9.6 (R = Ac) | 0.59 at 1 h | ~ 2.0 | ~ 1.0 | No | |||
| 9.1 (R = Cl) | 0.98 at 1 h | ~ 1.0 | ~ 1.0 | No | |||
| 6a-b | 8.5 (n = 0) | HT-29 | 0.33 at 1 h | 3.9 | 9.6 | Yes | 82 |
| 35.7 (n = 2) | 0.30 at 1 h | 2.9 | 4.9 | Yes | |||
| 7a-b | 6.6 (n = 0) | HT-29 | 0.64 at 1 h | 1.3 | 2.2 | Yes | 82 |
| 8.0 (n = 2) | 0.56 at 1 h | 1.0 | 3.2 | Yes | |||
| 8 | 220 | HT-29 | 0.41 at 1 h | ~ 1.0 | ~ 2.0 | Yes | 83 |
| 9 | 9† | - | - | - | - | - | 84 |
| 10 | 58 | HT-29 | 0.2 at 0.5 h | < 1.0 | - | - | 85 |
| 11 | 59 | HT-29 | 0.2 at 0.5 h | < 1.0 | - | - | 86 |
| 12 | 66 | HT-29 | 0.5 at 0.5 h | < 1.0 | - | - | 86 |
| 13‡ | - | HT-29 | 0.1 at 0.5 h | < 1.0 | - | - | 86 |
| 0.1 at 0.5 h | < 1.0 | - | - | ||||
| 14 | 10.8 | HT-29 | 0.81 at 1 h | 1.3 | 5.0 | Yes | 87 |
| 15 | 25.4 | HT-29 | 1.93 at 1 h | 1.3 | 4.1 | Yes | 87 |
| 16 | 7.7 | HT-29 | 2.30 at 1 h | 2.7 | 4.2 | Yes | 87 |
| 17 | 63.1 | HCT 116 | - | 2.4 | - | Yes | 89 |
| 18 | - | SK-RC-52 | 22.1 at 3 h | 69.9 | - | Yes | 90 |
| 19 | 108† | SK-RC-52 | 34.0 at 8 h | 77.0 | 34.2 | Yes | 91 |
| 20 | 157† | SK-RC-52 | 19.3 at 4 h | 57.7 | 29.4 | Yes | 92 |
*Maximum uptake
† IC50 value
‡ Diastereoisomers
-not applicable/not reported
T:B: tumour-to-blood ratio at corresponding time point; T:M: tumour-to-muscle ratio at corresponding time point; HT-29: human colorectal cancer cell line; U373: human glioblastoma cell line; HCT 116: human colorectal cancer cell line; SK-RC-52: human clear cell renal cell carcinoma cell line
Carbon-11 (11C) and Fluorine-18 (18F)
Asakawa et al. reported the synthesis of three 11C-labeled ureido-substituted benzenesulfonamides (Figure 4; compounds 1a-c) 75. Compounds 1a-c had excellent affinity for CA-IX (Ki: 0.3-5.4 nM). As compound 1a was previously shown to be efficacious in inhibiting distant metastasis in a preclinical breast cancer model 5, 11C-labeled 1a was evaluated in cell uptake studies. The cellular uptake of 11C-labeled 1a was measured in HT-29 colorectal cancer cells (high CA-IX expression) and in MCF-7 breast cancer cells (low CA-IX expression). The uptake in HT-29 cells was 1.6-fold higher than that of MCF-7 cells at 1 h p.i.; however, no in vivo experiments were performed. Although 11C can be readily incorporated into 1a-c via 11C-labeled phosgene, the short half-life of 11C (t1/2: 20.3 min) limits the number of physiological processes that can be imaged.
The only radiolabeled CA-IX small molecule inhibitor to advance into clinical trials is 18F-VM4-037, an ethoxzolamide derivative (Figure 4, compound 2). At physiological pH, the free carboxylate group of 18F-VM4-037 is deprotonated, introducing a negative charge that renders the compound membrane-impermeable 76. This confers selectivity for CA-IX over intracellular isoenzymes. The biodistribution and dosimetry of 18F-VM4-037 in healthy volunteers was reported by Doss et al. 76 High and sustained uptake was observed in the liver and kidney with minimal clearance for the 2.2 h study duration. The predicted effective dose for a patient injected with a 370 MBq dose was 10 ± 0.5 mSv, with the liver and kidney receiving 89 ± 25 and 101 ± 11 mGy respectively. 18F-VM4-037 was evaluated by Turkbey et al. in a phase II study with 11 patients with renal masses 77. Ten patients had histology-confirmed ccRCC, and 2 patients had metastatic lesions. 18F-VM4-037 showed moderate uptake in primary tumours (SUVmean 3.04), but lesions were difficult to visualize without an accompanying CT due to high uptake in normal renal parenchyma (kidney SUVmean 35.4) (Figure 5). 18F-VM4-037 was able to detect extrarenal lesions in patients that had metastatic disease (SUVmax 5.92). Peeters et al. used 18F-VM4-037 to image expression of CA-IX in U373 human glioma and HT-29 human colorectal cancer xenografts 78. The Ki of 18F-VM4-037 for CA-IX was found to be 124 nM. 18F-VM4-037 showed high accumulation in the gastrointestinal tract and in kidneys, but was unexpectedly unable to detect CA-IX expression in either tumour model. These findings call into question the sensitivity and selectivity of 18F-VM4-037 for targeting CA-IX in vivo.
Figure 5.
A 78 y-old male with left-sided ccRCC, indicated by an arrow, (A) detected on contrast-enhanced CT. (B) Axial 18F-VM4-037 PET and (C) PET/CT show uptake in left kidney lesion with a SUVmean of 1.86. (D) Coronal 18F-VM4-037 PET shows uptake within the lesion as well as the high uptake of the tracer in normal kidney parenchyma and liver. Figure reproduced with permissions from Turkbey et al.77
Our research group reported the synthesis and biological evaluation of two 18F-labeled small molecule inhibitors, 18F-U-104 and 18F-FEC (Figure 4, compounds 3 and 4) 79. Similar to compounds 1a-c, U-104 is an ureido-substituted sulfonamide that had demonstrated anti-metastatic properties in preclinical breast cancer models 4. U-104 was evaluated in a multi-center phase I study to determine safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics in patients with advanced solid tumours (clinical trials.gov, NCT02215850). FEC was selected for radiolabeling to offer a comparison between a sulfonamide and a coumarin derivative. The Ki values against CA-IX were 45 nM and 70 nM for U-104 and FEC, respectively. PET imaging and biodistribution studies were performed in mice bearing HT-29 cancer xenografts at 1 h p.i. The tumour uptake of 18F-U-104 and 18F-FEC were 0.83 ± 0.06 %ID/g and 1.16 ± 0.19 %ID/g. However, neither 18F-U-104 nor 18F-FEC was able to discriminate tumours from background tissues due to low contrast (T:B and T:M ratios were < 2). The high uptake of 18F-U-104 in blood (13.92 ± 3.07 %ID/g) suggested that it may have bound intracellular CA-I and/or CA-II expressed in erythrocytes. Conversely, the inability of 18F-FEC to detect CA-IX in tumours was possibly due to metabolism by cytochrome P450 enzymes.
Métayer and colleagues reported a new series of fluorinated tertiary substituted sulfonamides that showed high selectivity for CA-IX and did not inhibit the CA-II isoenzyme 80. The unique selectivity of these compounds is attributed to a new but unresolved mechanism of binding. From this series, we identified three derivatives (Figure 4, compounds 5a-c) with high binding affinity to CA-IX (Ki: 9.1-9.6 nM) that were amendable to 18F-fluorination 81. Biodistribution and imaging studies were conducted in mice bearing HT-29 cancer xenografts at 1 h p.i. Compounds 5a-c cleared rapidly from blood (< 1 %ID/g), suggesting that they did not bind to CA-II. However, tumour visualization did not improve as T/B and T/M ratios were low (< 2). Notably, compound 5c which had the highest absolute tumour uptake (0.98 ± 0.48 %ID/g) exhibited massive in vivo defluorination (12.61 ± 5.18 %ID/g for bone).
A major breakthrough in the development of 18F-labeled small molecule inhibitors targeting CA-IX came in 2015, when our group successfully leveraged a multivalent approach (Figure 4, compounds 6a-b) to confer in vivo selectivity for CA-IX 82. Azide derivatives of two promiscuous CA inhibitors, 4-(2-aminoethyl)benzenesulfonamide (AEBS) and 4-aminobenzensulfonamide (ABS), were conjugated to a radiosynthon with three alkynes and a pendent ammoniomethyltrifluoroborate (AmBF3) to generate the trivalent enzyme inhibitors 18F-AmBF3-(AEBS)3 and 18F-AmBF3-(ABS)3. We hypothesized that trimerization would increase binding avidity and bulk (>1 kDa) to restrict intracellular accumulation. The Ki values for CA-IX were 35.7 nM and 8.5 nM for 19F-AmBF3-(AEBS)3 and 19F-AmBF3-(ABS)3, respectively. For comparison, we also synthesized two monomeric tracers 18F-AmBF3-AEBS and18F-AmBF3-ABS (Figure 4, compounds 7a-b). Although the trimers had approximately 2-fold lower uptake in HT-29 cancer xenografts compared to the monomers (0.30-0.33 %ID/g vs. 0.54-0.64 %ID/g at 1 h p.i.), they also had 5-fold lower retention in blood (0.07-0.09 %ID/g vs. 0.51-0.56 %ID/g). This enabled clear visualization of tumours in PET images (Figure 6), and some of the highest T:B (3.93 ± 1.26) and T:M (9.55 ± 2.96) ratios ever reported for small molecule based imaging of CA-IX at the time of publication.
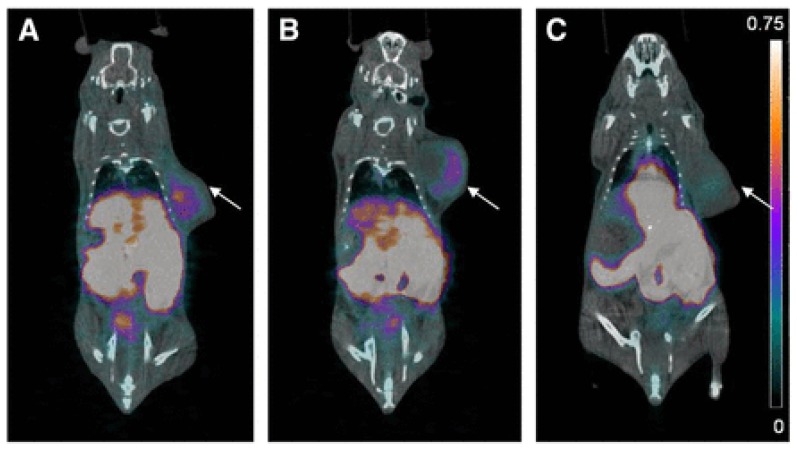
Figure 6.
PET/CT images of trimeric 18F-sulfonamides at 1 h after injection of (A) 18F-AmBF3-(AEBS)3, (B) 18F-AmBF3-(ABS)3, and (C) 18F-AmBF3-(ABS)3 preinjected with 10 mg/kg acetazolamide, a pan CA inhibitor. Tumours are indicated by arrows. Scale bar unit is %ID/g. Preinjection of acetazolamide significantly reduced tumour uptake to near-background levels for 18F-AmBF3-(ABS)3, demonstrating target specificity. Figure reproduced with permissions from Lau et al.82
Most recently, we reported the synthesis and evaluation of an 18F-labeled cationic sulfonamide derivative (Figure 4, compound 8)83. It is axiomatic that charged molecules have limited transport across the cell membrane; the cationic quaternary ammonium group was incorporated in the molecular design to attain CA-IX selectivity. Compound 8 had a Ki value of 0.22 µM for CA-IX. After 18F radiolabeling, compound 8 was evaluated in mice bearing HT-29 cancer xenografts. At 1 h p.i., tumour uptake was 0.41 ± 0.06 %ID/g, which corresponded to T/B and T/M ratios of < 2. Despite the low contrast, tumours can be delineated from background in coronal PET images. While the contrasts achieved were significantly less than that of the multivalent fluorinated sulfonamides, results were encouraging considering the modest affinity of compound 8 to CA-IX.
Radiometals
Lu et al. reported the synthesis of a series of benzenesulfonamide derivatives containing tridentate chelates complexed with Re or 99mTc 84. The IC50 values of the benzenesulfonamide rhenium complexes in hypoxia-induced HeLa cells were determined to be 3-116 nM. 99mTc-3d (Figure 4, compound 9) whose rhenium congener had an IC50 value of 9 nM was used for in vitro studies. 99mTc-3d had 5-fold higher uptake for HeLa cells cultured under hypoxic conditions than cells cultured under normoxic conditions. Furthermore, the uptake in hypoxia-treated cells can be selectively reduced by co-incubation with acetazolamide, a pan CA inhibitor. To date, no imaging experiments have been reported with this series of inhibitors.
Akurathi et al. reported a series of Re/99mTc benzenesulfonamide derivatives (Figure 4, compounds 10-13) of varying physiochemical properties (hydrophilicity, charge, and molecular weight)85, 86. Compound 13 has two diastereoisomers, and both were evaluated in vivo. Binding affinity for CA-IX was determined for compounds 10-12 using Re congeners, with Ki values being 58-66 nM. Biodistribution studies were conducted in mice bearing HT-29 cancer xenografts. The tracers showed limited uptake and retention in tumours (≤ 0.5 %ID/g at 0.5-4 h p.i.) with T:B ratio ≤ 1.0 at all studied time points. The authors attributed the low uptake in tumour to the rapid clearance of the tracers from blood pool.
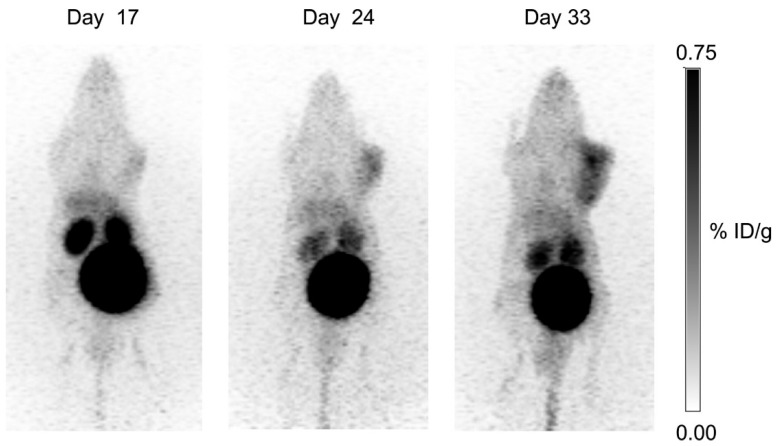
Our group synthesized three 68Ga-labeled sulfonamide derivatives (Figure 4, compounds 14-16) 87. Expanding on the work by Rami et al., who observed that aromatic sulfonamides conjugated to polyaminocarboxylate chelators (DTPA, DOTA, and TETA; TETA: 1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-1,4,8,11-tetraacetic acid) did not bind off-target CA-II88, we synthesized monomeric (Ga-DOTA-AEBSA), dimeric (Ga-DOTA-(AEBSA)2) and trimeric (Ga-NOTGA-(AEBSA)3; NOTGA: 1,4,7-triazacyclononane-1,4,7-tris-(glutaric acid)) sulfonamide inhibitors. The compounds were potent inhibitors of CA-IX, with Ki values ranging from 7.7 nM to 25.4 nM. Imaging studies in HT-29 tumour bearing mice generated good-contrast PET images (Figure 7). The uptake in tumour (0.81-2.30 %ID/g at 1 h p.i.) correlated positively with the number of sulfonamides and the molecular weight of the tracers. The monomeric 68Ga-DOTA-AEBSA had lowest tumour uptake but also the highest contrast (T:M ratio of 5.02 ± 0.22). 68Ga-DOTA-AEBSA exhibited primarily renal clearance, while 68Ga-DOTA-(AEBSA)2 and 68Ga-NOTGA-(AEBSA)3 were cleared by both renal and hepatobiliary pathways. Moreover, we performed a longitudinal study with 68Ga-DOTA-AEBSA to image CA-IX expression changes in one subject over a 16 d period (Figure 8). Over the study period, an increase in radioactivity was observed in the tumour, with a heterogeneous distribution and areas of focal uptake.
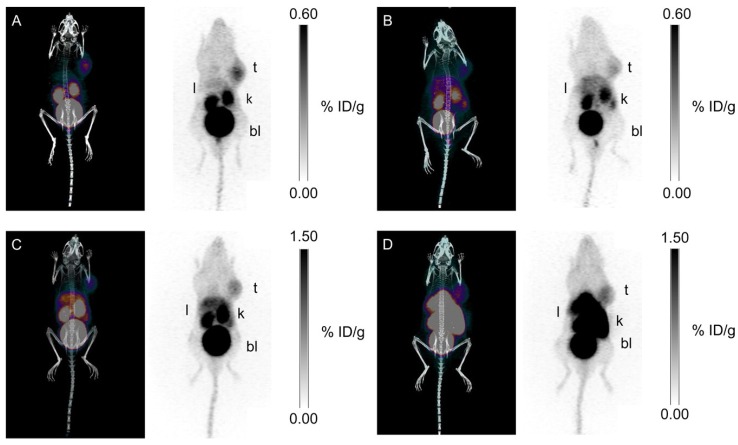
Figure 7.
Maximal intensity projection images of PET/CT and PET with 68Ga tracers at 1 h p.i. (A) 68Ga-DOTA-AEBSA; (B) 68Ga-DOTA-AEBSA preblocked with 10 mg/kg of acetazolamide; (C) 68Ga-DOTA-(AEBSA)2; (D) 68Ga-NOTGA-(AEBSA)3. Tumour uptake was observed for all three compounds with 68Ga-DOTA-AEBSA displaying highest contrast. t = tumour; l = liver; k = kidney; bl = bladder. Adapted with permissions from Lau et al.87 Copyright 2016 American Chemistry Society.
Figure 8.
Longitudinal study: uptake of 68Ga-DOTA-AEBSA in HT-29 cancer xenograft increases as tumour grows. This tumour-bearing mouse was imaged 17 d, 24 d and 33 d post-cell inoculation with 68Ga-DOTA-AEBSA. Adapted with permissions from Lau et al.87 Copyright 2016 American Chemistry Society.
In parallel with our studies, Sneddon and colleagues presented a monomeric 68Ga-DOTA-sulfonamide derivative (Figure 4, compound 17) 89. A polyethylene glycol linker was inserted between the chelator group and sulfonamide as a pharmacokinetic modifier. Compound 17 had a Ki value of 63.1 nM. Imaging studies were performed in mice bearing HCT 116 human colorectal cancer xenografts at 1-4 h p.i. Tumours were only visible in PET images at 1 h p.i., suggesting the tracer was not retained at target site. At 1 h p.i., the T:B ratio for compound 17 was 2.36 ± 0.42 with absolute uptake values not reported.
Krall et al. reported the synthesis and evaluation of a 99mTc-labeled acetazolamide derivative (Figure 4, compound 18) 90. Using surface plasmon resonance, compound 18 was found to have nanomolar binding affinity to CA-IX. Since this radiotracer was developed for ccRCC detection, in vivo studies were performed with the CA-IX constitutively expressing SK-RC-52 model. Excellent tumour targeting and high contrast SPECT images were obtained. The highest uptake was observed at 3 h p.i. (22.1 ± 0.16 %ID/g), which corresponded to a T:B ratio of 69.9 ± 0.21. Unlike other small molecule inhibitors utilized for CA-IX targeted imaging, this compound exhibited good retention in tumour (19.8 ± 0.13 %ID/g at 6 h p.i.).
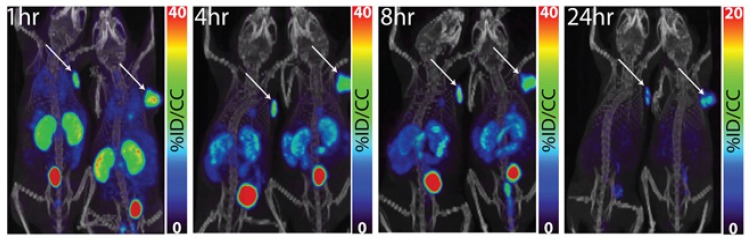
Lastly, Pomper and colleagues radiolabeled a dual motif inhibitor with 111In via DOTA and 64Cu via NOTA (1,4,7-triazacyclononane-1,4,7-triacetic acid) for imaging ccRCC (Figure 4, compounds 19 and 20)91, 92. The targeting vector was first identified by Wichert et al. using a dual pharmacophore DNA encoded chemical library 93. Both compounds showed exceptional tumour targeting and retention in SK-RC-52 xenografts (Figure 9). Maximal tumour uptake of 111In-XYIMSR-01 was observed at 8 h p.i. (34.0 ± 15.2 %ID/g), which corresponded to T:B, T:M and T:K ratios of 77.0 ± 32.5, 34.2 ± 16.0, and 3.1 ± 3.1, respectively. At 24 h p.i., tumour uptake decreased to 25.6 ± 17.7 %ID/g, but most contrast ratios improved (T:B, T:M and T:K ratios of 178.1 ± 145.4, 68.4 ± 29.0, and 1.7 ± 1.2). With 64Cu-XYIMSR-06, maximal tumour uptake was observed at 4 h p.i. (19.3 ± 4.51 %ID/g) with T:B, T:M and T:K ratios at 57.7 ± 9.3, 29.4 ± 9.9, and 1.0 ± 0.1. At 24 h p.i., uptake in tumour was 6.23 ± 1.41 %ID/g and T:B, T:M and T:K ratios were 142.6 ± 115.8, 261.3 ± 47.3, and 7.1 ± 2.5. Based on pharmacokinetic profile and imaging modality, 64Cu-XYIMSR-06 performed better than 111In-XYIMSR-01. Although these two tracers have not been evaluated in hypoxia models, they are currently the most promising CA-IX imaging agents derived from small molecule inhibitors.
Figure 9.
PET/CT images of 64Cu-XYIMSR-06 enabled the detection of CA-IX-expressing SK-RC-52 tumour in vivo. Images were obtained at 1 h, 4 h, 8 h, and 24 h p.i. Arrows indicate location of tumours. Scales were adjusted to percent injected dose per volume (%ID/cc). Figure reproduced with permissions from Minn et al.92, in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/legalcode).
Affibodies
Affibodies are a class of antibody mimetics derived from the immunoglobulin G binding domain of staphylococcal protein A 94. They are cysteine-free scaffolds composed of 58 amino acid residues (~7 kDa) that fold into three alpha-helices 94. Affibodies generally bind to their targets of interest with nano or picomolar affinities, and selectivity is mediated by the permutation of 13 amino acid residues 94. In addition to being tolerant to high temperatures and extreme pHs, affibodies have much faster pharmacokinetics than antibodies. These features make them ideal for radiolabeling and in vivo applications. Tolmachev and colleagues have successfully leveraged this technology to develop affibodies for imaging different oncotargets including human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, epidermal growth factor receptor, insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor, platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta, human epidermal growth factor receptor 3, and CA-IX 95.
The first affibody used for CA-IX imaging was ZCAIX:1 reported by Honarvar et al. 96 ZCAIX:1 was radiolabeled with 99mTc by introducing a histidine-glutamate-histidine-glutamate-histidine-glutamate (HE)3-motif at the N-terminus of the affibody, and with 125I by indirect iodination using the prosthetic group, N-succinimidyl-para-(trimethylstannyl)-benzoate. 99mTc-(HE)3-ZCAIX:1 was found to have a KD value of 1.3 nM for CA-IX, while binding affinity was not reported for 125I-ZCAIX:1. In vivo SPECT imaging and biodistribution were performed in SK-RC-52 cancer xenograft bearing mice. 99mTc-(HE)3-ZCAIX:1 cleared rapidly from blood and normal tissues. At 4 h p.i., tumour uptake was 9.7 ± 0.7 %ID/g, which corresponded to T:B and T:M ratios of 53 ± 10 and 104 ± 52, respectively. 99mTc-(HE)3-ZCAIX:1 generated high contrast images, despite high retention in kidneys (141 ± 45 %ID/g). Biodistribution studies were also performed for 125I-ZCAIX:1. While renal uptake (2.7 ± 1.4 %ID/g at 6 h p.i.) was significantly reduced by the use of the non-residualizing radionuclide, this was accompanied by the concomitant decrease in tumour uptake (2.2 ± 1.4 %ID/g at 6 h p.i.). The authors concluded that neither derivative would be suitable for imaging primary ccRCC lesions. However, 99mTc-(HE)3-ZCAIX:1 could be valuable for detecting extrarenal CA-IX expression. At the time of publication, 99mTc-(HE)3-ZCAIX:1 exhibited higher T:B ratios than any other non-mAb CA-IX radiopharmaceutical agent.
Following this work, Garousi et al. evaluated three additional affibody constructs (ZCAIX:2, ZCAIX:3, and ZCAIX:4) for systematic comparison with ZCAIX:1(Figure 10) 97. These variants were also radiolabeled with 99mTc or 125I, following procedures performed with ZCAIX:1. The affibodies had nanomolar binding affinity (KD: 1.2-7.3 nM) against SK-RC-52 cells. For the 99mTc-labeled derivatives, tumour uptake ranged from 4.3 ± 0.7 %ID/g to 16.3 ± 0.9 %ID/g at 4 h p.i., with 99mTc-(HE)3-ZCAIX:2 having the highest absolute uptake and contrasts (T:B and T:M ratios of 44 ± 7 and 109 ± 11, respectively). High activity was observed in kidneys (>100 %ID/g) at the evaluated time points. The 125I-labeled conjugates had approximately 5 to 50-fold lower retention in kidneys (4-22 %ID/g at 4 h p.i.), but clearance was slower in blood pools. While 125I-ZCAIX:2 demonstrated the highest tumour uptake (19 ± 2 %ID/g) and contrast (T:B and T:M ratios of 21 ± 5 and 129 ± 42, respectively), tumour uptake was lower than kidney retention. 125I-ZCAIX:4 was the only derivative to provide a T:K ratio >1 (2.1 ± 0.5 at 4 h p.i.), suggesting the selection of a non-residualizing radionuclide can enable imaging of primary ccRCC.
Figure 10.
Maximum intensity projections of microSPECT/CT using CA-IX targeting affibodies at 4 h p.i. (A) Imaging using 99mTc-(HE)3-ZCAIX:2. The linear color scale was adjusted to provide clear visualization of a tumour. (B) Imaging using 125I-(HE)3-ZCAIX:4. Full linear colour scale was applied. Adapted with permissions from Garousi et al.97 Copyright 2016 American Chemistry Society.
Clinical Implications and Future Directions
CA-IX is considered a surrogate marker for tumour hypoxia, and its expression is negatively correlated with patient survival. CA-IX has emerged as a theranostic target due to its role in mediating cell survival and distant metastasis under hypoxic conditions. The ectopic expression of CA-IX complemented with a restricted profile in normal tissues provides an opportunity for personalized medicine. Central to this discussion, the increasing repertoire of CA-IX radiopharmaceuticals (mAbs, peptides, small molecules and antibody mimetics) has largely revolved around the unique pathophysiology driving ccRCC. For future studies, it will be beneficial to evaluate these agents, especially the potent small molecule inhibitors and antibody mimetics, in hypoxia cancer models. In practice, CA-IX based imaging can overcome inherent drawbacks in the invasive methods currently available for measuring hypoxia, and offer faster pharmacokinetics and higher contrast than existing nitroimidazole derivatives used for PET imaging98.
In a retrospective subset study analysis, Chamie et al. revealed that ccRCC patients with high CA-IX expression (>2.0) treated with unmodified cG250 experienced significant improvements in disease-free survival 99. CA-IX expression scoring was derived by multiplying staining intensity (1-3) by the fraction of positive cells (0-1). This underscores the potential efficacy of CA-IX therapeutics given proper patient stratification. For hypoxic tumours that are resistant to radiation and chemotherapies, the treatment for these aggressive cancers often entails combinatorial treatments especially at a disseminated stage. In this setting, CA-IX can serve as a co-target in synergy with other targeted treatments. Indeed 177Lu-cG250 RIT has been proposed for use in adjuvant setting with vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors 100, assuming that myelotoxicity associated with RIT can be safely mitigated or controlled. Several of the small molecules presented in this review also warrant further investigation as radiotherapeutic agents. Considering their shorter residence time and faster pharmacokinetics, they are likely to be less toxic, thus providing better therapeutic indexes. Given the broad expression of CA-IX in solid malignancies, we anticipate that these CA-IX theranostic agents will be able to improve cancer management and patient outcomes.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Drs. Etienne Rousseau and Hsiou-Ting Kuo for providing insightful discussions and constructive feedback. This work was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (FDN-148465) and the BC Leading Edge Endowment Fund.
Abbreviations
- ABS
4-aminobenzensulfonamide;
- AEBS
4-(2-aminoethyl)benzenesulfonamide;
- AmBF3
ammoniomethyltrifluoroborate;
- CA
carbonic anhydrase;
- CA-IX
carbonic anhydrase IX;
- ccRCC
clear cell renal cell carcinoma;
- cG250
chimeric monoclonal G250 antibody;
- CECT
contrast enhanced computed tomography;
- CT
computed tomography;
- DFO
desferoxamine;
- DOTA
1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid;
- DTPA
diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid;
- FDA
Food and Drug Administration;
- G250
a murine monoclonal antibody against CA-IX;
- HACA
human anti-chimeric antibodies;
- HAMA
human anti-mouse antibodies;
- (HE)3
histidine-glutamate-histidine-glutamate-histidine-glutamate motif;
- HIF
hypoxia-inducible factor;
- HIF-1α
hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha;
- IC50
half maximal inhibitory concentration;
- KD
disassociation constant;
- Ki
inhibition constant;
- mAb
monoclonal antibody;
- MAG3
mercaptoacetyltriglycine;
- MICAD
Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database;
- MTD
maximum tolerated dose;
- NOTA
1,4,7-triazacyclononane-1,4,7-triacetic acid;
- NOTGA
1,4,7-triazacyclononane-1,4,7-tris-(glutaric acid);
- NPV
negative predictive value;
- PET
positron emission tomography;
- PG
proteoglycan;
- pHi
intracellular pH;
- PPV
positive predictive value;
- RCC
renal cell carcinoma;
- RIT
radioimmunotherapy;
- scFv
single-chain variable fragment;
- SIP
small immunoprotein;
- SPECT
single photon emission computed tomography;
- SUV
standardized uptake value;
- TETA
1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-1,4,8,11-tetraacetic acid;
- T:B
tumour-to-blood ratio;
- T:K
tumour-to-kidney ratio;
- T:M
tumour-to-muscle ratio;
- VHL
von Hippel-Lindau.
References
- 1.Harris AL. Hypoxia-a key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nature reviews Cancer. 2002;2:38–47. doi: 10.1038/nrc704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Supuran CT. Carbonic anhydrases: novel therapeutic applications for inhibitors and activators. Nature reviews Drug discovery. 2008;7:168–81. doi: 10.1038/nrd2467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.McDonald PC, Winum JY, Supuran CT, Dedhar S. Recent developments in targeting carbonic anhydrase IX for cancer therapeutics. Oncotarget. 2012;3:84–97. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lou Y, McDonald PC, Oloumi A, Chia S, Ostlund C, Ahmadi A. et al. Targeting tumor hypoxia: suppression of breast tumor growth and metastasis by novel carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitors. Cancer research. 2011;71:3364–76. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-4261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Pacchiano F, Carta F, McDonald PC, Lou Y, Vullo D, Scozzafava A. et al. Ureido-substituted benzenesulfonamides potently inhibit carbonic anhydrase IX and show antimetastatic activity in a model of breast cancer metastasis. Journal of medicinal chemistry. 2011;54:1896–902. doi: 10.1021/jm101541x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sneddon D, Poulsen SA. Agents described in the Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database for imaging carbonic anhydrase IX expression. Journal of enzyme inhibition and medicinal chemistry. 2014;29:753–63. doi: 10.3109/14756366.2013.848205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wilson WR, Hay MP. Targeting hypoxia in cancer therapy. Nature reviews Cancer. 2011;11:393–410. doi: 10.1038/nrc3064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Parks SK, Chiche J, Pouyssegur J. pH Control Mechanisms of Tumor Survival and Growth. J Cell Physiol. 2011;226:299–308. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Brahimi-Horn MC, Pouyssegur J. Hypoxia in cancer cell metabolism and pH regulation. Essays Biochem. 2007;43:165–78. doi: 10.1042/BSE0430165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Boyer MJ, Tannock IF. Regulation of Intracellular Ph in Tumor-Cell Lines - Influence of Microenvironmental Conditions. Cancer research. 1992;52:4441–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Potter C, Harris AL. Hypoxia inducible carbonic anhydrase IX, marker of tumour hypoxia, survival pathway and therapy target. Cell Cycle. 2004;3:164–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Pastorekova S, Zavadova Z, Kostal M, Babusikova O, Zavada J. A novel quasi-viral agent, MaTu, is a two-component system. Virology. 1992;187:620–6. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90464-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Alterio V, Di Fiore A, D'Ambrosio K, Supuran CT, De Simone G. Multiple binding modes of inhibitors to carbonic anhydrases: how to design specific drugs targeting 15 different isoforms? Chemical reviews. 2012;112:4421–68. doi: 10.1021/cr200176r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hilvo M, Baranauskiene L, Salzano AM, Scaloni A, Matulis D, Innocenti A. et al. Biochemical characterization of CA IX, one of the most active carbonic anhydrase isozymes. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2008;283:27799–809. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800938200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kessenbrock K, Plaks V, Werb Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell. 2010;141:52–67. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.He F, Deng X, Wen B, Liu Y, Sun X, Xing L. et al. Noninvasive molecular imaging of hypoxia in human xenografts: comparing hypoxia-induced gene expression with endogenous and exogenous hypoxia markers. Cancer research. 2008;68:8597–606. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-0677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Olive PL, Aquino-Parsons C, MacPhail SH, Liao SY, Raleigh JA, Lerman MI. et al. Carbonic anhydrase 9 as an endogenous marker for hypoxic cells in cervical cancer. Cancer research. 2001;61:8924–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rafajova M, Zatovicova M, Kettmann R, Pastorek J, Pastorekova S. Induction by hypoxia combined with low glucose or low bicarbonate and high posttranslational stability upon reoxygenation contribute to carbonic anhydrase IX expression in cancer cells. International journal of oncology. 2004;24:995–1004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Moroz E, Carlin S, Dyomina K, Burke S, Thaler HT, Blasberg R. et al. Real-time imaging of HIF-1alpha stabilization and degradation. PloS one. 2009;4:e5077. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Saarnio J, Parkkila S, Parkkila AK, Waheed A, Casey MC, Zhou XY. et al. Immunohistochemistry of carbonic anhydrase isozyme IX (MN/CA IX) in human gut reveals polarized expression in the epithelial cells with the highest proliferative capacity. The journal of histochemistry and cytochemistry: official journal of the Histochemistry Society. 1998;46:497–504. doi: 10.1177/002215549804600409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kivela AJ, Parkkila S, Saarnio J, Karttunen TJ, Kivela J, Parkkila AK. et al. Expression of transmembrane carbonic anhydrase isoenzymes IX and XII in normal human pancreas and pancreatic tumours. Histochemistry and cell biology. 2000;114:197–204. doi: 10.1007/s004180000181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Karhumaa P, Kaunisto K, Parkkila S, Waheed A, Pastorekova S, Pastorek J. et al. Expression of the transmembrane carbonic anhydrases, CA IX and CA XII, in the human male excurrent ducts. Molecular human reproduction. 2001;7:611–6. doi: 10.1093/molehr/7.7.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ilie M, Mazure NM, Hofman V, Ammadi RE, Ortholan C, Bonnetaud C. et al. High levels of carbonic anhydrase IX in tumour tissue and plasma are biomarkers of poor prognostic in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. British journal of cancer. 2010;102:1627–35. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Choschzick M, Oosterwijk E, Muller V, Woelber L, Simon R, Moch H. et al. Overexpression of carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX) is an independent unfavorable prognostic marker in endometrioid ovarian cancer. Virchows Archiv: an international journal of pathology. 2011;459:193–200. doi: 10.1007/s00428-011-1105-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Haapasalo JA, Nordfors KM, Hilvo M, Rantala IJ, Soini Y, Parkkila AK. et al. Expression of carbonic anhydrase IX in astrocytic tumors predicts poor prognosis. Clinical cancer research: an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2006;12:473–7. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hoogsteen IJ, Marres HA, Wijffels KI, Rijken PF, Peters JP, van den Hoogen FJ. et al. Colocalization of carbonic anhydrase 9 expression and cell proliferation in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Clinical cancer research: an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2005;11:97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Klatte T, Seligson DB, Rao JY, Yu H, de Martino M, Kawaoka K. et al. Carbonic anhydrase IX in bladder cancer: a diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic molecular marker. Cancer. 2009;115:1448–58. doi: 10.1002/cncr.24163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Korkeila E, Talvinen K, Jaakkola PM, Minn H, Syrjanen K, Sundstrom J. et al. Expression of carbonic anhydrase IX suggests poor outcome in rectal cancer. British journal of cancer. 2009;100:874–80. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hutchison GJ, Valentine HR, Loncaster JA, Davidson SE, Hunter RD, Roberts SA. et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression as an intrinsic marker of hypoxia: correlation with tumor oxygen, pimonidazole measurements, and outcome in locally advanced carcinoma of the cervix. Clinical cancer research: an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2004;10:8405–12. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-03-0135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Stillebroer AB, Mulders PF, Boerman OC, Oyen WJ, Oosterwijk E. Carbonic anhydrase IX in renal cell carcinoma: implications for prognosis, diagnosis, and therapy. European urology. 2010;58:75–83. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2010.03.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hsieh JJ, Purdue MP, Signoretti S, Swanton C, Albiges L, Schmidinger M. et al. Renal cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17009. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2017.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Muglia VF, Prando A. Renal cell carcinoma: histological classification and correlation with imaging findings. Radiologia brasileira. 2015;48:166–74. doi: 10.1590/0100-3984.2013.1927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Shuin T, Kondo K, Torigoe S, Kishida T, Kubota Y, Hosaka M. et al. Frequent somatic mutations and loss of heterozygosity of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor gene in primary human renal cell carcinomas. Cancer research. 1994;54:2852–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Herman JG, Latif F, Weng Y, Lerman MI, Zbar B, Liu S. et al. Silencing of the VHL tumor-suppressor gene by DNA methylation in renal carcinoma. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1994;91:9700–4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.9700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ridge CA, Pua BB, Madoff DC. Epidemiology and staging of renal cell carcinoma. Seminars in interventional radiology. 2014;31:3–8. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1363837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Gorin MA, Rowe SP, Allaf ME. Nuclear imaging of renal tumours: a step towards improved risk stratification. Nature reviews Urology. 2015;12:445–50. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2015.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Scott AM, Wolchok JD, Old LJ. Antibody therapy of cancer. Nature reviews Cancer. 2012;12:278–87. doi: 10.1038/nrc3236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Peters C, Brown S. Antibody-drug conjugates as novel anti-cancer chemotherapeutics. Bioscience reports; 2015. p. 35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Larson SM, Carrasquillo JA, Cheung NK, Press OW. Radioimmunotherapy of human tumours. Nature reviews Cancer. 2015;15:347–60. doi: 10.1038/nrc3925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Pardoll DM. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nature reviews Cancer. 2012;12:252–64. doi: 10.1038/nrc3239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Oosterwijk-Wakka JC, Boerman OC, Mulders PF, Oosterwijk E. Application of monoclonal antibody G250 recognizing carbonic anhydrase IX in renal cell carcinoma. International journal of molecular sciences. 2013;14:11402–23. doi: 10.3390/ijms140611402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Oosterwijk E, Ruiter DJ, Hoedemaeker PJ, Pauwels EK, Jonas U, Zwartendijk J. et al. Monoclonal antibody G 250 recognizes a determinant present in renal-cell carcinoma and absent from normal kidney. International journal of cancer. 1986;38:489–94. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910380406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Oosterwijk E, Bander NH, Divgi CR, Welt S, Wakka JC, Finn RD. et al. Antibody localization in human renal cell carcinoma: a phase I study of monoclonal antibody G250. Journal of clinical oncology: official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 1993;11:738–50. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1993.11.4.738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Divgi CR, Bander NH, Scott AM, O'Donoghue JA, Sgouros G, Welt S. et al. Phase I/II radioimmunotherapy trial with iodine-131-labeled monoclonal antibody G250 in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clinical cancer research: an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 1998;4:2729–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Steffens MG, Boerman OC, de Mulder PH, Oyen WJ, Buijs WC, Witjes JA. et al. Phase I radioimmunotherapy of metastatic renal cell carcinoma with 131I-labeled chimeric monoclonal antibody G250. Clinical cancer research: an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 1999;5:3268s–74s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Divgi CR, O'Donoghue JA, Welt S, O'Neel J, Finn R, Motzer RJ. et al. Phase I clinical trial with fractionated radioimmunotherapy using 131I-labeled chimeric G250 in metastatic renal cancer. J Nucl Med. 2004;45:1412–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Brouwers AH, Mulders PF, de Mulder PH, van den Broek WJ, Buijs WC, Mala C. et al. Lack of efficacy of two consecutive treatments of radioimmunotherapy with 131I-cG250 in patients with metastasized clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Journal of clinical oncology: official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2005;23:6540–8. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.07.732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Brouwers AH, van Eerd JE, Frielink C, Oosterwijk E, Oyen WJ, Corstens FH. et al. Optimization of radioimmunotherapy of renal cell carcinoma: labeling of monoclonal antibody cG250 with 131I, 90Y, 177Lu, or 186Re. J Nucl Med. 2004;45:327–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Stillebroer AB, Boerman OC, Desar IM, Boers-Sonderen MJ, van Herpen CM, Langenhuijsen JF. et al. Phase 1 radioimmunotherapy study with lutetium 177-labeled anti-carbonic anhydrase IX monoclonal antibody girentuximab in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. European urology. 2013;64:478–85. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2012.08.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Muselaers CH, Boers-Sonderen MJ, van Oostenbrugge TJ, Boerman OC, Desar IM, Stillebroer AB. et al. Phase 2 Study of Lutetium 177-Labeled Anti-Carbonic Anhydrase IX Monoclonal Antibody Girentuximab in Patients with Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. European urology. 2016;69:767–70. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.11.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Rault E, Vandenberghe S, Van Holen R, De Beenhouwer J, Staelens S, Lemahieu I. Comparison of image quality of different iodine isotopes (I-123, I-124, and I-131) Cancer biotherapy & radiopharmaceuticals. 2007;22:423–30. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2006.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Cascini GL, Niccoli Asabella A, Notaristefano A, Restuccia A, Ferrari C, Rubini D. et al. 124 Iodine: a longer-life positron emitter isotope-new opportunities in molecular imaging. BioMed research international. 2014;2014:672094. doi: 10.1155/2014/672094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Divgi CR, Pandit-Taskar N, Jungbluth AA, Reuter VE, Gonen M, Ruan S. et al. Preoperative characterisation of clear-cell renal carcinoma using iodine-124-labelled antibody chimeric G250 (124I-cG250) and PET in patients with renal masses: a phase I trial. The Lancet Oncology. 2007;8:304–10. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(07)70044-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Divgi CR, Uzzo RG, Gatsonis C, Bartz R, Treutner S, Yu JQ. et al. Positron emission tomography/computed tomography identification of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: results from the REDECT trial. Journal of clinical oncology: official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2013;31:187–94. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.41.2445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Brouwers AH, Buijs WC, Oosterwijk E, Boerman OC, Mala C, De Mulder PH. et al. Targeting of metastatic renal cell carcinoma with the chimeric monoclonal antibody G250 labeled with (131)I or (111)In: an intrapatient comparison. Clinical cancer research: an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research. 2003;9:3953S–60S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Muselaers CH, Boerman OC, Oosterwijk E, Langenhuijsen JF, Oyen WJ, Mulders PF. Indium-111-labeled girentuximab immunoSPECT as a diagnostic tool in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. European urology. 2013;63:1101–6. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2013.02.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Cheal SM, Punzalan B, Doran MG, Evans MJ, Osborne JR, Lewis JS. et al. Pairwise comparison of 89Zr- and 124I-labeled cG250 based on positron emission tomography imaging and nonlinear immunokinetic modeling: in vivo carbonic anhydrase IX receptor binding and internalization in mouse xenografts of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014;41:985–94. doi: 10.1007/s00259-013-2679-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Carlin S, Khan N, Ku T, Longo VA, Larson SM, Smith-Jones PM. Molecular targeting of carbonic anhydrase IX in mice with hypoxic HT29 colorectal tumor xenografts. PloS one. 2010;5:e10857. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Hoeben BA, Kaanders JH, Franssen GM, Troost EG, Rijken PF, Oosterwijk E. et al. PET of hypoxia with 89Zr-labeled cG250-F(ab')2 in head and neck tumors. J Nucl Med. 2010;51:1076–83. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.109.073189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Freise AC, Wu AM. In vivo imaging with antibodies and engineered fragments. Molecular immunology. 2015;67:142–52. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Muselaers CH, Rijpkema M, Bos DL, Langenhuijsen JF, Oyen WJ, Mulders PF. et al. Radionuclide and Fluorescence Imaging of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Using Dual Labeled Anti-Carbonic Anhydrase IX Antibody G250. The Journal of urology. 2015;194:532–8. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2015.02.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.van Leeuwen FW, de Jong M, Committee ETMI. Molecular imaging: the emerging role of optical imaging in nuclear medicine. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2014;41:2150–3. doi: 10.1007/s00259-014-2845-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Chrastina A, Zavada J, Parkkila S, Kaluz S, Kaluzova M, Rajcani J. et al. Biodistribution and pharmacokinetics of 125I-labeled monoclonal antibody M75 specific for carbonic anhydrase IX, an intrinsic marker of hypoxia, in nude mice xenografted with human colorectal carcinoma. International journal of cancer. 2003;105:873–81. doi: 10.1002/ijc.11142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Chrastina A, Pastorekova S, Pastorek J. Immunotargeting of human cervical carcinoma xenograft expressing CA IX tumor-associated antigen by 125I-labeled M75 monoclonal antibody. Neoplasma. 2003;50:13–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Wind TC, Messenger MP, Thompson D, Selby PJ, Banks RE. Measuring carbonic anhydrase IX as a hypoxia biomarker: differences in concentrations in serum and plasma using a commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay due to influences of metal ions. Annals of clinical biochemistry. 2011;48:112–20. doi: 10.1258/acb.2010.010240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Ahlskog JK, Schliemann C, Marlind J, Qureshi U, Ammar A, Pedley RB. et al. Human monoclonal antibodies targeting carbonic anhydrase IX for the molecular imaging of hypoxic regions in solid tumours. British journal of cancer. 2009;101:645–57. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Fani M, Maecke HR. Radiopharmaceutical development of radiolabelled peptides. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012;39(Suppl 1):S11–30. doi: 10.1007/s00259-011-2001-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Reubi JC. Peptide receptors as molecular targets for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Endocrine reviews. 2003;24:389–427. doi: 10.1210/er.2002-0007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Vegt E, de Jong M, Wetzels JF, Masereeuw R, Melis M, Oyen WJ. et al. Renal toxicity of radiolabeled peptides and antibody fragments: mechanisms, impact on radionuclide therapy, and strategies for prevention. J Nucl Med. 2010;51:1049–58. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.110.075101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Askoxylakis V, Garcia-Boy R, Rana S, Kramer S, Hebling U, Mier W. et al. A new peptide ligand for targeting human carbonic anhydrase IX, identified through the phage display technology. PloS one. 2010;5:e15962. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Rana S, Nissen F, Marr A, Markert A, Altmann A, Mier W. et al. Optimization of a novel peptide ligand targeting human carbonic anhydrase IX. PloS one. 2012;7:e38279. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Rana S, Nissen F, Lindner T, Altmann A, Mier W, Debus J, Screening of a novel peptide targeting the proteoglycan-like region of human carbonic anhydrase IX. Molecular imaging; 2013. p. 12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Mahon BP, Pinard MA, McKenna R. Targeting carbonic anhydrase IX activity and expression. Molecules. 2015;20:2323–48. doi: 10.3390/molecules20022323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Carta F, Maresca A, Scozzafava A, Supuran CT. Novel coumarins and 2-thioxo-coumarins as inhibitors of the tumor-associated carbonic anhydrases IX and XII. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry. 2012;20:2266–73. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2012.02.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Asakawa C, Ogawa M, Kumata K, Fujinaga M, Yamasaki T, Xie L. et al. Radiosynthesis of three [11C]ureido-substituted benzenesulfonamides as PET probes for carbonic anhydrase IX in tumors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011;21:7017–20. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.09.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Doss M, Kolb HC, Walsh JC, Mocharla VP, Zhu Z, Haka M. et al. Biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of the carbonic anhydrase IX imaging agent [(18) F]VM4-037 determined from PET/CT scans in healthy volunteers. Molecular imaging and biology: MIB: the official publication of the Academy of Molecular Imaging. 2014;16:739–46. doi: 10.1007/s11307-014-0730-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Turkbey B, Lindenberg ML, Adler S, Kurdziel KA, McKinney YL, Weaver J. et al. PET/CT imaging of renal cell carcinoma with (18)F-VM4-037: a phase II pilot study. Abdominal radiology. 2016;41:109–18. doi: 10.1007/s00261-015-0599-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Peeters SG, Dubois L, Lieuwes NG, Laan D, Mooijer M, Schuit RC. et al. [(18)F]VM4-037 MicroPET Imaging and Biodistribution of Two In Vivo CAIX-Expressing Tumor Models. Molecular imaging and biology: MIB: the official publication of the Academy of Molecular Imaging. 2015;17:615–9. doi: 10.1007/s11307-015-0831-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Pan JH, Lau J, Mesak F, Hundal N, Pourghiasian M, Liu ZB. et al. Synthesis and evaluation of F-18-labeled carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitors for imaging with positron emission tomography. Journal of enzyme inhibition and medicinal chemistry. 2014;29:249–55. doi: 10.3109/14756366.2013.773994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Metayer B, Mingot A, Vullo D, Supuran CT, Thibaudeau S. New superacid synthesized (fluorinated) tertiary benzenesulfonamides acting as selective hCA IX inhibitors: toward a new mode of carbonic anhydrase inhibition by sulfonamides. Chemical communications. 2013;49:6015–7. doi: 10.1039/c3cc40858b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Lau J, Pan JH, Zhang ZX, Hundal-Jabal N, Liu ZB, Benard F. et al. Synthesis and evaluation of F-18-labeled tertiary benzenesulfonamides for imaging carbonic anhydrase IX expression in tumours with positron emission tomography. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014;24:3064–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.05.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Lau J, Liu ZB, Lin KS, Pan JH, Zhang ZX, Vullo D. et al. Trimeric Radiofluorinated Sulfonamide Derivatives to Achieve In Vivo Selectivity for Carbonic Anhydrase IX-Targeted PET Imaging. J Nucl Med. 2015;56:1434–40. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.114.153288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Zhang ZX, Lau J, Zhang CC, Colpo N, Nocentini A, Supuran CT. et al. Design, synthesis and evaluation of F-18-labeled cationic carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitors for PET imaging. Journal of enzyme inhibition and medicinal chemistry. 2017;32:722–30. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2017.1308928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Lu G, Hillier SM, Maresca KP, Zimmerman CN, Eckelman WC, Joyal JL. et al. Synthesis and SAR of novel Re/99mTc-labeled benzenesulfonamide carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitors for molecular imaging of tumor hypoxia. Journal of medicinal chemistry. 2013;56:510–20. doi: 10.1021/jm3015348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Akurathi V, Dubois L, Lieuwes NG, Chitneni SK, Cleynhens BJ, Vullo D. et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of a 99mTc-labelled sulfonamide conjugate for in vivo visualization of carbonic anhydrase IX expression in tumor hypoxia. Nuclear medicine and biology. 2010;37:557–64. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2010.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Akurathi V, Dubois L, Celen S, Lieuwes NG, Chitneni SK, Cleynhens BJ. et al. Development and biological evaluation of (99m)Tc-sulfonamide derivatives for in vivo visualization of CA IX as surrogate tumor hypoxia markers. European journal of medicinal chemistry. 2014;71:374–84. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2013.10.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Lau J, Zhang ZX, Jenni S, Kuo HT, Liu ZB, Vullo D. et al. PET Imaging of Carbonic Anhydrase IX Expression of HT-29 Tumor Xenograft Mice with Ga-68-Labeled Benzenesulfonamides. Mol Pharmaceut. 2016;13:1137–46. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Rami M, Cecchi A, Montero JL, Innocenti A, Vullo D, Scozzafava A. et al. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: design of membrane-impermeant copper(II) complexes of DTPA-, DOTA-, and TETA-tailed sulfonamides targeting the tumor-associated transmembrane isoform IX. ChemMedChem. 2008;3:1780–8. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.200800267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Sneddon D, Niemans R, Bauwens M, Yaromina A, van Kuijk SJ, Lieuwes NG. et al. Synthesis and in Vivo Biological Evaluation of (68)Ga-Labeled Carbonic Anhydrase IX Targeting Small Molecules for Positron Emission Tomography. Journal of medicinal chemistry. 2016;59:6431–43. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Krall N, Pretto F, Mattarella M, Muller C, Neri D. A 99mTc-Labeled Ligand of Carbonic Anhydrase IX Selectively Targets Renal Cell Carcinoma In Vivo. J Nucl Med. 2016;57:943–9. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.115.170514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Yang X, Minn I, Rowe SP, Banerjee SR, Gorin MA, Brummet M. et al. Imaging of carbonic anhydrase IX with an 111In-labeled dual-motif inhibitor. Oncotarget. 2015;6:33733–42. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Minn I, Koo SM, Lee HS, Brummet M, Rowe SP, Gorin MA. et al. [64Cu]XYIMSR-06: A dual-motif CAIX ligand for PET imaging of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2016;7:56471–9. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Wichert M, Krall N, Decurtins W, Franzini RM, Pretto F, Schneider P. et al. Dual-display of small molecules enables the discovery of ligand pairs and facilitates affinity maturation. Nature chemistry. 2015;7:241–9. doi: 10.1038/nchem.2158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Feldwisch J, Tolmachev V. Engineering of affibody molecules for therapy and diagnostics. Methods in molecular biology. 2012;899:103–26. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-921-1_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Stahl S, Graslund T, Eriksson Karlstrom A, Frejd FY, Nygren PA, Lofblom J. Affibody Molecules in Biotechnological and Medical Applications. Trends in biotechnology; 2017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Honarvar H, Garousi J, Gunneriusson E, Hoiden-Guthenberg I, Altai M, Widstrom C. et al. Imaging of CAIX-expressing xenografts in vivo using 99mTc-HEHEHE-ZCAIX:1 affibody molecule. International journal of oncology. 2015;46:513–20. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Garousi J, Honarvar H, Andersson KG, Mitran B, Orlova A, Buijs J. et al. Comparative Evaluation of Affibody Molecules for Radionuclide Imaging of in Vivo Expression of Carbonic Anhydrase IX. Mol Pharm. 2016;13:3676–87. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.6b00502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Fleming IN, Manavaki R, Blower PJ, West C, Williams KJ, Harris AL. et al. Imaging tumour hypoxia with positron emission tomography. British journal of cancer. 2015;112:238–50. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Chamie K, Klopfer P, Bevan P, Storkel S, Said J, Fall B. et al. Carbonic anhydrase-IX score is a novel biomarker that predicts recurrence and survival for high-risk, nonmetastatic renal cell carcinoma: Data from the phase III ARISER clinical trial. Urologic oncology. 2015;33:204. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2015.02.013. e25-33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Oosterwijk-Wakka JC, de Weijert MC, Franssen GM, Leenders WP, van der Laak JA, Boerman OC. et al. Successful combination of sunitinib and girentuximab in two renal cell carcinoma animal models: a rationale for combination treatment of patients with advanced RCC. Neoplasia. 2015;17:215–24. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2014.12.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]