Abstract
Design and objectives
Every organisation has a unique culture. There is a widely held view that a positive organisational culture is related to positive patient outcomes. Following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses statement, we systematically reviewed and synthesised the evidence on the extent to which organisational and workplace cultures are associated with patient outcomes.
Setting
A variety of healthcare facilities, including hospitals, general practices, pharmacies, military hospitals, aged care facilities, mental health and other healthcare contexts.
Participants
The articles included were heterogeneous in terms of participants. This was expected as we allowed scope for wide-ranging health contexts to be included in the review.
Primary and secondary outcome measures
Patient outcomes, inclusive of specific outcomes such as pain level, as well as broader outcomes such as patient experience.
Results
The search strategy identified 2049 relevant articles. A review of abstracts using the inclusion criteria yielded 204 articles eligible for full-text review. Sixty-two articles were included in the final analysis. We assessed studies for risk of bias and quality of evidence. The majority of studies (84%) were from North America or Europe, and conducted in hospital settings (89%). They were largely quantitative (94%) and cross-sectional (81%). The review identified four interventional studies, and no randomised controlled trials, but many good quality social science studies. We found that overall, positive organisational and workplace cultures were consistently associated with a wide range of patient outcomes such as reduced mortality rates, falls, hospital acquired infections and increased patient satisfaction.
Conclusions
Synthesised, although there was no level 1 evidence, our review found a consistently positive association held between culture and outcomes across multiple studies, settings and countries. This supports the argument in favour of activities that promote positive cultures in order to enhance outcomes in healthcare organisations.
Keywords: Health & safety, health policy, public health, quality in healthcare, clinical governance, organisational development
Strengths and limitations of this study.
This review found a consistent association between organisational and workplace culture, and patient outcomes across a variety of health settings; most included studies consisted of observational, cross-sectional studies conducted in hospitals.
The high volume of included studies provides a solid foundation for readers to enhance their knowledge of organisational culture in healthcare.
Most articles included in the final synthesis were rated as high quality, based on the Quality Assessment Tool.
The broad scope of the review, including a wide-ranging search strategy, provided an overarching account of the research topic.
Definitions and measurements of culture, environment and patient outcomes were highly variable across studies, which placed limits on the comparisons that could be drawn.
Introduction
Among policy-makers, managers and clinicians, culture is a much-discussed construct. The discourse is often centred on normative considerations, proposing that an effective, functional or productive culture is preferable to one that is ineffective, dysfunctional or even toxic.1 2 A healthier organisational or workplace culture is believed to be related to positive patient outcomes, such as reduced mortality and length of stay, increased quality of life and decreased pain level.3 4 However, no review has been conducted to weigh the evidence for such beliefs. We examined the extent to which this putative association between culture and patient outcomes holds in healthcare settings.
Across the literature, culture has been defined in numerous ways.4–10 Famously, Kroeber and Kluckhohn found 164 definitions of culture in 1952. Since then, there are most likely many more variations and definitional stances on the culture theme.11 It is not easy to synthesise these different perspectives, but most experts would agree that culture signifies features of institutional life which are shared across a workplace or organisation, between the members, such as their cognitive beliefs, assumptions and attitudes; and their activities, such as their behaviours, practices and interactions. These shared ways of thinking and behaving become normalised, and reflect what comes to be seen as legitimate and acceptable within the workplace or organisation. The cultural expressions also become taken for granted by members of the workplace or organisation. They are the normative, social and cognitive ‘glue’, which bind people within the culture together; culture, then, is ‘the way people think around here’ and ‘the way things are done around here’.
Based on these conceptualisations, we define culture in a summarised way, as the sum of jointly held characteristics, values, thinking and behaviours of people in workplaces or organisations4 (for a list of key terms and definitions, see box 1). For this systematic review, culture is classified in two ways. The first category concerns the overarching culture of an organisation, including consistent practices, beliefs and attitudes, for example, within a whole hospital, general practice group, aged care facility or other institutional setting.12 13 The second category relates to more localised cultural dimensions; workplace cultures, which are specific to group characteristics of the organisation, for example, those identifiable subcultures that manifest in wards, departments or within employee groups such as doctors, allied health professionals or nurses.8 14 15
Box 1. Definitions.
Cohen’s kappa
A statistic commonly used to measure inter-rater reliability, ie, the extent to which individual raters’ scores agree with each other while accounting for chance agreement.31
Climate
Employees’ perception of an organisational or workplace culture.20 Climate and culture are terms often used interchangeably in the literature, without clear-cut boundaries.20 For this purpose of this review, the concept of climate is encompassed in the definition of culture.
Environment
The structural, social and implicit characteristics of the context in which work is done.98 For the purposes of this review, only cultural elements of workplace or organisational environment were considered, for example, cooperation and sense of cohesiveness between the work team. Structural characteristics such as nurse to patient ratios, and employee characteristics such as education, were not included in our definition of work environment.
Organisational culture
The values, behaviours, goals, attitudes, practices and beliefs shared across an entire organisation.99
Patient outcomes
The downstream consequences of patient care. These can be positive (eg, satisfaction with care, reduced length of stay) or negative (eg, disability, hospital acquired infection).20
Quality of care
Within a healthcare environment, there are many facets of quality of care. Types of care that can be assessed include the technical and judgement skill provided by the physician, and the interpersonal care received from healthcare professionals.100
Quality of study
The extent that the study design and the manner in which it is executed are protective from bias and error.101
Risk of bias
The potential for a systematic deviation from facts; an error.101
Workplace culture
A specific type of subculture involving an identifiable grouping within an organisation. In healthcare, such a ‘workplace’ may be a unit, ward or department, or a professional group, eg, medicine or nursing.25
These definitions arise from, and are underpinned by, much conceptual work which has enriched the idea of culture and the way it manifests. Theoretically, there are multiple stances taken in conceptualising culture. One way is to think of culture as a composite, and enduring but relatively static phenomenon; a sort of concrete, tangible, matter-of-fact organisational variable. Here, it is a noun: the culture. Another way is to think of it as dynamic, emergent, longitudinal phenomenon, more a verb than a noun. This distinction is a deep one, springing from a social science perspective which asks whether phenomenon of this kind are a being-realism or a becoming-realism.16
Yet another theoretical distinction lies in whether culture is better understood with reference to shared meanings or shared practices. Scholars including Martin17 and Alvesson18 see that culture can be construed and understood theoretically in many different ways depending on the observers’ interests, ideologies and interpretative or reflexive stance. All in all, theoretically we take the view that culture is a composite, complex construct which changes dynamically over time, but there are enduring behavioural and cognitive patterns to its manifestations in situ.7 19
In this review, we aimed to investigate ways in which organisational and workplace cultures are associated with patient outcomes across a range of healthcare settings. On the basis of the foregoing,4 20 21 we formulated a hypothesis: positive organisational and workplace cultures are related to positive patient outcomes and negative organisational and workplace cultures are related to negative patient outcomes. By positive we mean a cohesive, supportive, collaborative, inclusive culture, and by negative, we mean the converse. We anticipated that this review would provide information for those, such as policy-makers, managers, clinicians, researchers and patient groups who seek to understand, shape or enhance healthcare cultures or subcultures. We expected that such an analysis would provide insights into the evidence for culture and subcultures, and recognise that cultures are deeply embedded in systems and settings in terms of their interacting agents, capacity to evolve and adapt and emergent behaviours.22 23
Methods
The review was carried out in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-analyses statement.24 A literature search of academic databases CINAHL, EMBASE, Ovid MEDLINE, Web of Science and PsycINFO, of studies published since the inception of the databases, was conducted in August 2016. The search strategy consisted of terms pertaining to patient outcomes, inclusive of specific outcomes such as decubitus ulcer and pain level, as well as broader terms such as quality of care and patient experience (see table 1 for the search strategy, using Ovid MEDLINE as an example). The review was undertaken in accordance with a published study protocol, which provides more detailed information regarding information sources, the search strategy, data items and data synthesis (online supplementary file A).25
Table 1.
Database search strategy: Ovid MEDLINE
| Constructs | Search terms |
| Organisational culture/workplace culture | work culture OR work place OR workplace OR work site OR worksite OR organi$ation* culture OR service culture OR corporate culture OR work climate OR organi$ation* climate OR service climate OR corporate climate OR work ethos OR organi$ation* ethos OR service ethos OR corporate ethos OR work environment OR organi$ation* environment OR service environment OR corporate environment |
| AND | |
| Patient outcomes | patient outcome* OR patient satisfaction OR health outcome* OR patient experience* OR mortality OR length of stay OR pain level OR cost of care OR functional abilit* OR patient knowledge OR quality of life OR impairment* OR disabilit* OR readmission rate* OR adverse event* OR medication error* OR patient fall* OR infection* OR decubitus ulcer* |
| AND | |
| Healthcare | health organi$ation* OR hospital* OR health facilit* OR acute care OR primary care OR health OR healthcare OR health care OR health-care |
* and $ symbolise truncation.
bmjopen-2017-017708supp001.pdf (548.7KB, pdf)
Records and abstracts resulting from the database search were downloaded into an EndNote library and duplicates were removed. Pairs of authors (JH:GL; KL:LT) reviewed 5% of records to ensure the article retention process was consistent. Abstracts were assessed against the following inclusion criteria: English language, peer-reviewed journal articles consisting of empirical research conducted in healthcare settings. A broad definition of healthcare was adopted, encompassing settings including hospitals, general practices, pharmacies, military hospitals, aged care facilities, mental health and other healthcare settings. Articles were only included if they assessed the association between organisational or workplace culture, and patient outcomes. Articles that measured safety culture were included if other inclusion criteria were met, as safety culture is an important component of organisational culture.
Discrepancies in article retention were discussed until a consensus was reached, with JB acting as arbitrator in cases of ambiguous study suitability. JH, KL, GL and LT assessed the remaining abstracts against the inclusion criteria followed by a full-text analysis of included articles. Papers evaluating ‘hospital performance’ were eligible for inclusion if the measures concerned patient outcomes. Articles referring to measures of process interventions, for example, ‘adherence to guidelines’ or ‘medication administration error reporting’ were excluded if they did not measure patient outcomes. Articles that only measured healthcare employees’ perceptions of patient outcomes were excluded, as they were classified as a process rather than outcome measure. Only associations relevant to the hypothesis were included in the analysis.
Included articles were summarised using a data extraction sheet (online supplementary file B).26 Key information recorded included country, time frame of data collection, study type, aims, data collection methods, methodology, findings and implications. Bias of studies was assessed by JH and JB using a Risk of Bias Template (online supplementary file C), adapted from the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews, specifically the Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias.27 The quality of articles was assessed by JH, GL, KL and LT using the Quality Assessment Tool by Hawker et al.28 Studies were analysed and synthesised according to direction of association and categorisation of patient outcomes.
bmjopen-2017-017708supp002.pdf (92KB, pdf)
bmjopen-2017-017708supp003.pdf (86.9KB, pdf)
Results
Search strategy
The results of the search strategy are outlined in figure 1. A total of 2049 relevant articles were identified. The Cohen’s kappa for the 5% review of abstracts was 0.2966 (JH:GL) and 0.5032 (KL:LT). It is noted that Kappa Paradox 1 occurred in this instance, due to the prevalence of excluded articles decreasing the kappa value.29 30 This was taken into account through calculating the prevalence-adjusted bias-adjusted kappa, increasing the values to a strong (0.84) and moderate (0.76) level of agreement, respectively.31 Additionally, the prevalence index was calculated as 0.88 and 0.73 for the pairs of reviewers.
Figure 1.
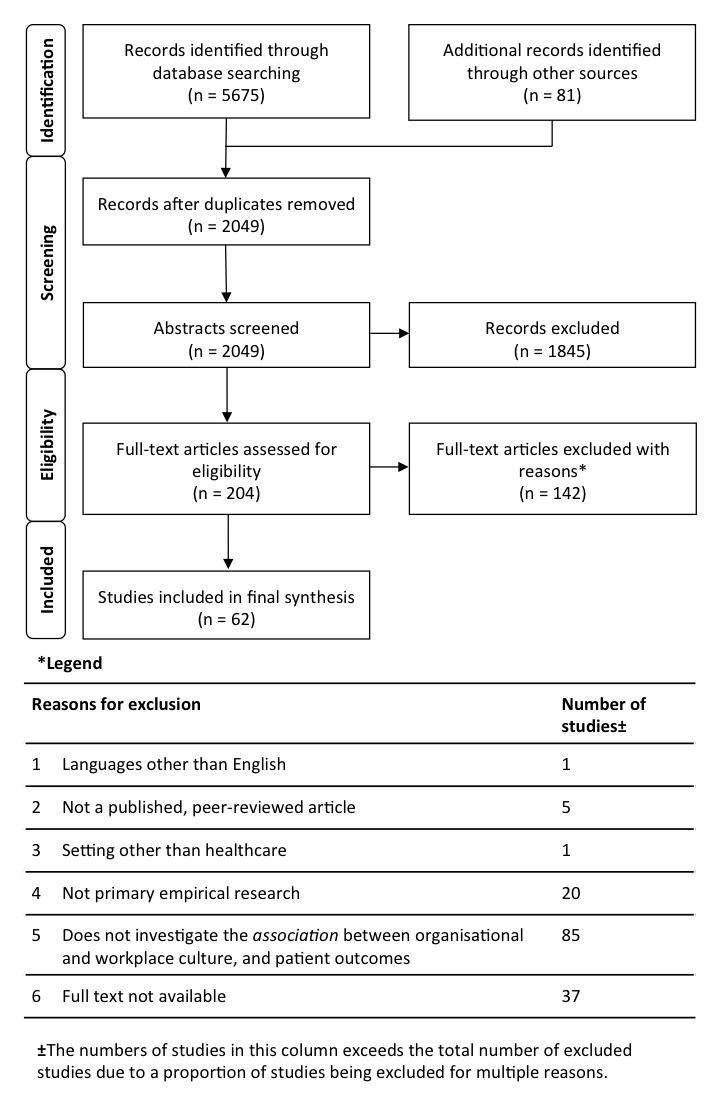
Search strategy.
Two hundred and four abstracts met the inclusion criteria based on the complete review of abstracts. The full-text content review of these included articles resulted in 62 articles included in the final analysis. A comprehensive table of included articles was generated by JH and edited by KL and LT (online supplementary file D).
bmjopen-2017-017708supp004.pdf (310.4KB, pdf)
Study characteristics
A summary of included study characteristics is provided in table 2. The majority of studies employed quantitative methods. Only four studies comprised mixed methods, and no study involved purely qualitative methods. Most studies were observational in nature, with only four intervention studies identified in the final analysis. Of the observational studies, most were classified as cross-sectional. Studies were more commonly conducted in a hospital context, and a US setting. No studies yielding level 1 evidence, that is, randomised controlled trials, were identified. The data obtained from the review was heterogeneous, in terms of participants and outcomes (clinically diverse), and in study design (methodologically diverse).32 Across the studies, organisational and workplace culture and environment were defined and measured in a non-standardised way. For example, some studies focused on broader hospital culture,33–41 while others assessed staff attitudes and values,42–45 or safety climate.46–56 The concept of patient outcomes was also diverse in nature, comprising a variety of specific and broader outcomes and conditions. Due to the heterogeneity of definitions, tools and variables, quantitative meta-analysis of data was of no value.57
Table 2.
Descriptive characteristics of included studies
| Number (%) | |
| Method | |
| Quantitative | 58 (93.6) |
| Qualitative | 0 (0.0) |
| Mixed | 4 (6.5) |
| Study design | |
| Intervention | 4 (6.5) |
| Observational | 58 (93.6) |
| Cross-sectional | 50 (80.7) |
| Longitudinal | 10 (16.1) |
| Level of evidence | |
| 1 | 0 (0.0) |
| Other | 62 (100.0) |
| Setting | |
| Hospital | 55 (88.7) |
| Aged care | 4 (6.5) |
| Other | 3 (4.8) |
| Country | |
| USA | 36 (58.1) |
| Europe | 11 (17.7) |
| Canada | 5 (8.1) |
| Asia | 4 (6.5) |
| Australia | 2 (3.2) |
| Middle East | 2 (3.2) |
| UK | 2 (3.2) |
Risk of bias
The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias is designed for use in clinical trials. Our final collection of articles did not contain data from clinical trials, and therefore, the tool was deemed an inappropriate method by which to assess risk of bias. A new way of assessing risk of bias was established (online supplementary file C) by adapting the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews’ definitions of bias for applicability to quantitative and qualitative non-intervention studies.27 Applying this tool, it was clear that all included articles sustained a risk of bias. It is suggested that classification of articles by quality, rather than exclusively by bias, is more appropriate for this class of review.
Quality assessment
Over 93% of included studies were observational (table 2). The Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews suggests that observational studies rate as low quality in its Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) approach to assessing the quality of articles.58 The Quality Assessment Tool by Hawker et al28 was deemed more suitable for this review as it is designed to evaluate studies covering a variety of research paradigms. The tool developers, Hawker et al28 gave detailed descriptions of what constituted a ‘good’ (four points), ‘fair’ (three points), ‘poor’ (two points) or ‘very poor’ (one point) article in each of the following nine categories: abstract and title; introduction and aims; method and data; sampling; data analysis; ethics and bias; findings/results; transferability/generalisability, and implications and usefulness, allowing for a potential maximum score of 36. Hawker et al28 did not suggest cut-offs for classifying the total quality rating of the article, but this has been proposed by other researchers using the Quality Assessment Tool.28 For example, the rule of thumb developed by Lorenc et al59 suggests the following quality grading system: ‘high quality’ (30–36 points), ‘medium quality’ (24–29 points) and ‘low quality’ (9–24 points).59 This recommendation was modified in the current systematic review where ‘low quality’ was classified as 9–23 points to reduce ambiguity. Quality scores ranged from 17 to 36 across the 62 included studies. Full details on quality scores are provided in table 3. Articles were classified as either high, medium or low quality based on these cut-off values. Quality scores are reported in online supplementary file D.
Table 3.
Methodological rigour and quality of included articles
Overall findings
We found that organisational and workplace cultures were correlated with patient outcomes in over 90% of studies. The majority (74.2%) of associations were classified as ‘positive’, comprising exclusively positive associations (48.4%), or a mixture of positive associations and no associations in articles reporting multiple studies (25.8%) (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
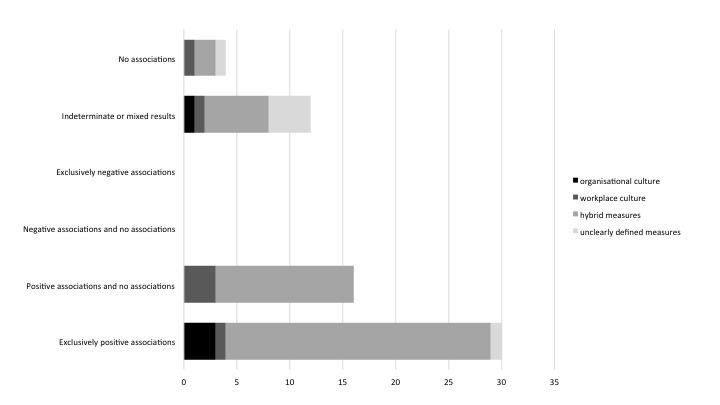
Categorisation of direction of studies (number of studies).
Culture was positively associated with a range of system-related patient outcomes. These comprised four broad, systems-based outcomes: mortality rates,50 51 60–66 failure to rescue,60 62 67 readmission rates47 54 68 69 and adverse events/medication errors.35 52 53 70–73 They also included well-being outcomes, notably, patient satisfaction,34 36 38 40 43 44 74–83 quality of life84 and patient mood.84 More specific clinical outcomes related to culture were pressure ulcers,35 49 85–88 falls,33 35 49 73 86 89 hospital acquired infections,35 42 46 87 90–92 depressive symptoms,93 pulmonary embolism/deep vein thrombosis,49 incontinence,88 symptom burden at the end of life63 and physical and mental health status55 (Figure 3). Table 4 summarises all associations by outcome type. It should be noted that one of the articles that measured hospital-acquired infections as the outcome was low quality according to the Quality Assessment Tool, and only a handful were interventional or had a control group. However, this is not of primary importance in light of the plethora of high-quality studies yielding a positive result.
Figure 3.

Key associations between culture and patient outcomes.
Table 4.
Associations by type of outcome
| System-related patient outcomes | Well-being outcomes | Clinical outcomes | |
| Exclusively positive associations | 15 (24.2) | 13 (21.0) | 5 (8.1) |
| Positive associations and no associations | 8 (12.9) | 6 (9.7) | 8 (12.9) |
| No associations | 2 (3.2) | 3 (4.8) | 1 (1.6) |
| Negative associations and no associations | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Exclusively negative associations | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Indeterminate or mixed results | 8 (12.9) | 4 (6.5) | 5 (8.1) |
Articles showing no significant associations accounted for 8.1% of studies. Indeterminate or results comprising both positive and negative associations, made up 19.4% of the research. There were no studies presenting ‘negative’ associations (exclusively negative associations, or negative associations and no associations).
Positive associations
Almost three in four (74.2%) studies reported exclusively positive associations, or a mixture of positive associations and no associations, between culture and patient outcomes. For example, hospital-based cross-sectional studies found patient mortality rates were nearly 48% lower in hospitals with better work environments,65 and surgical mortality rates were >60% higher in hospitals with poor work environments.94 Some studies moved beyond ‘better’ and ‘poor’ environments by evaluating types of culture positively associated with patient outcomes. For example, a ‘human relations’-type culture was also related to enhanced patient satisfaction.36 Human relations involved focusing on flexibility and supporting internal resources, and embracing values associated with belonging, trust and cohesion.
Organisational and workplace cultures were also positively associated with patient outcomes in contexts other than hospitals. A study of aged care found that residents in facilities with less effective staff cohesion were at significantly greater risk of pressure ulcers and incontinence, compared with residents in facilities with more effective cohesion.88 Depressive symptoms in residents were associated with two dimensions of organisational culture (proficiency and resistance), and three dimensions of climate (stress, engagement and functionality).93 Companionate love culture (ie, feelings of affection, caring and compassion) in aged care facilities was positively correlated with patient mood, quality of life, satisfaction and fewer trips to the emergency room.84 A single study of a community mental health organisation concluded that a positive organisational culture was a strong predictor of physical and mental health status improvements over time, but not changes in quality of life.55 These findings collectively indicate the importance of a positive organisational and workplace culture for a wide variety of patient outcomes, across multiple settings.
A small group of articles reported a combination of positive associations and no associations between culture and patient outcomes. One paper found no correlation between culture or climate and risk-adjusted outcomes, however, teamwork, communication and collaboration was associated with risk-adjusted morbidity.50 Another paper found that nurses’ perceptions of work environment were significantly related to patient hospitalisation rates, but not with patient satisfaction.95 Studies that reported mixed positive and no-association results have also been reported in aged care53 84 and mental health services.55
No associations
Not all studies reported associations between culture and patient outcomes. A primary care-based cross-sectional study found no significant associations between team culture and haemoglobin A1c level, systolic blood pressure and total cholesterol levels in patients with type II diabetes mellitus.45 Other studies, one of which was ranked as low quality, found no association between organisational or workplace culture and patient satisfaction,48 performance indexes,37 prescription errors, rates of adverse events and patient mortality rates.96
Indeterminate studies
Over 17% of included articles reported indeterminate or mixed results. The ‘indeterminate’ category was used in cases where the classification of cultures as positive or negative could not be discerned. For example, higher scores on group culture measures, that is those that emphasised teamwork, cohesiveness and participation, were associated with significantly lower rates of survival without major morbidity, whereas in one study, higher scores on hierarchical culture measures were associated with higher rates of survival without major morbidity.66 ‘Mixed’ refers to both positive and negative associations presented in the one paper. A study reported that intensive care units in which nurses perceived the culture as positive had higher rates of central line-associated bloodstream infections, but were 39% less likely to develop a catheter-associated urinary tract infection.87 In another study with a relatively small sample size, patient falls with injury were positively related to a developmental culture. A developmental culture was one characterised by dynamic and innovative environments that value individual initiatives and growth. Patient falls with injury were negatively related to group culture, characterised by warm, caring environments that value tradition and loyalty.33
Intervention studies
Our review included four intervention studies. A systematic review on culture and performance (rather than outcomes) completed in 2011, included only two interventions.4 A study in rural/small hospitals which implemented 12 nurse-friendly criteria to create a positive work environment observed positive changes in nurses’ perception of their work environment and improvements in quality of care in participating hospitals postintervention.86 A hospital-based intervention study to change organisational culture on frequency of staff handwashing did not improve rates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in two hospitals, but rates of vancomycin-resistant enterococci were significantly reduced in the intervention hospital during implementation.90 A prominent interventional study, the UK Safer Patients Initiative, indicated that while there was a small improvement in staff attitudes to organisational climate in intervention hospitals, the intervention had no significant effect on patient safety outcomes, measured by the proportion of prescription errors, rates of adverse events and mortality rates.96 The fourth intervention study was based on a single hospital in Sweden. The study found that patients’ perceptions of work environment were a significant predictor of patients’ satisfaction with quality of care.74
Discussion
We synthesised a large literature with diverse variables which attempted to measure or study healthcare cultures, or intervene to create enhanced organisational and workplace cultures. Research was conducted across multiple healthcare settings, mostly hospitals, in a range of countries, chiefly North America, Europe and Australasia. The complexity of the synthesising task should not be underestimated in reviews of this kind (see also the work by Greenhalgh et al on synthesising research on diffusion of innovation97). The studies we report on undertook work in complex systems and settings in which care is provided by a layered web of agents interacting dynamically across space and time, producing emergent outcomes.22 23 Cultures in such settings are hard to change, and resist simple, linear improvement strategies. The studies themselves involved nuanced choices in types of measures, multiple mechanisms for studying culture or intervening to improve it and variable ways of reporting their methods and results.
Despite the challenges in combining and assessing disparate research, we found confirmatory evidence for previous work,4 20 21 which suggested that there were positive linkages between cultures in healthcare settings and patient outcomes. In short, healthcare organisational and workplace cultures are related to patient outcomes in the way people have generally assumed they are, and in the positive direction our hypothesis suggested. Thus, we found sufficient evidence to support our hypothesis that there are ubiquitous links between our two culture types across multiple studies. In summary, positive cultures are consistently linked in many studies to better patient outcomes.
Study strengths and weaknesses
The number of included articles in this review compared with systematic reviews on other topics was relatively high, providing comprehensive coverage of the research topic. An overarching account of the association between organisational and workplace culture and patient outcomes was made possible by having a broad scope of review, including multiple types of healthcare settings, and considering patient outcomes as both an all-encompassing concept as well as considering more specific outcomes. However, the broad scope poses a challenge, as there were inherent limitations whereby our core term, culture, was inconsistently defined or measured in the studies we reviewed. The heterogeneity of data complicated attempts to draw precise comparisons across studies, and conclusions. Nevertheless, we rigorously assessed bias and study quality, and the study results point in the same direction. It is important to note, notwithstanding our consistent result, that this review might be limited by the inherent risk of bias across studies, such as publication bias, whereby studies reporting significant results may be viewed more favourably for publication than those that do not.
Both types of culture—organisational, and workplace culture—were considered in this review. As figure 2 shows, the majority of studies used hybrid measures of culture in which both organisational culture and workplace culture were examined, or the type of culture assessed was not clearly defined. Therefore, conclusions could not be drawn on whether organisational or workplace culture, taken individually, were more strongly associated with positive patient outcomes.
Our review aimed to consider and discuss articles across a variety of health settings, but most included studies were conducted in a hospital environment. We propose that more research is needed in other healthcare settings such as aged and community care. Only four studies employed interventional designs in testing out chosen associations, but many studies are high-quality social science articles. More rigorous intervention studies aimed at promoting change in organisational culture could provide valuable information on how improvements in organisational culture can affect outcomes for patients.
Conclusion
Studies examining culture are common. Fewer explore linkages between cultures and patient outcomes. There are no randomised controlled trials, and few intervention studies with strong designs are reported. The consistent trend for most studies is to find that positive cultures are related to better outcomes for patients. Better-quality studies, and those outside of hospitals, would provide confirming or disconfirming evidence for our synthesis.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to record their appreciation to Jeremy Cullis, Clinical Librarian, Macquarie University, for proving his expertise on the use of academic databases and for reviewing the search strategy. The authors would like to thank Ms Hsuen P Ting, Biostatistician, Australian Institute of Health Innovation, Macquarie University, for providing advice, and conducting the statistical analysis of the 5% library analyses. The authors would also like to thank Ms Elise McPherson, Research Assistant, Australian Institute of Health Innovation, Macquarie University, for providing word processing and logistical support.
Footnotes
Contributors: JB led the study and provided a conceptualisation of the topic to the team, and acted as an arbitrator and adviser where necessary. JH, KL, GL and LT did the abstract and full-text reviews of the articles. All authors contributed to the writing of the drafts, and agree with the final version.
Funding: This work is supported by NHMRC Programme Grant 1054146, NHMRC Partnership Centre in Health Systems Sustainability Grant 9100002 and other grants held by JB.
Competing interests: None declared.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data sharing statement: No additional data available.
Author note: Any minor adjustments to the protocol have been documented in this systematic review.
References
- 1.Napier AD, Ancarno C, Butler B, et al. . Culture and health. Lancet 2014;384:1607–39. 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61603-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Smircich L. Concepts of culture and organizational analysis. Adm Sci Q 1983;28:339–58. 10.2307/2392246 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hesselink G, Vernooij-Dassen M, Pijnenborg L, et al. . Organizational culture: an important context for addressing and improving hospital to community patient discharge. Med Care 2013;51:90–8. 10.1097/MLR.0b013e31827632ec [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Parmelli E, Flodgren G, Beyer F, et al. . The effectiveness of strategies to change organisational culture to improve healthcare performance: a systematic review. Implement Sci 2011;6:1–8. 10.1186/1748-5908-6-33 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Scott T, Mannion R, Davies H, et al. . The quantitative measurement of organizational culture in health care: a review of the available instruments. Health Serv Res 2003;38:923–45. 10.1111/1475-6773.00154 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mannion R, Davies H, Marshall M. Cultures for performance in health care. Buckingham, UK: Open University Press, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Braithwaite J, Westbrook MT, Iedema R, et al. . A tale of two hospitals: assessing cultural landscapes and compositions. Soc Sci Med 2005;60:1149–62. 10.1016/j.socscimed.2004.06.046 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Braithwaite J, Hyde P, Pope C. Culture and climate in Health Care Organizations. Basingstoke, London, UK: Palgrave Macmillan, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Braithwaite J. A lasting legacy from Tony Blair? NHS culture change. J R Soc Med 2011;104:87–9. 10.1258/jrsm.2010.100364 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Schein E. Organizational culture and leadership. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kroeber AL, Kluckhohn C. Culture: a critical review of concepts and definitions. Cambridge, MA: Peabody Museum of American Archaeology and Ethnology, Harvard University, 1952. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wagner C, Mannion R, Hammer A, et al. . The associations between organizational culture, organizational structure and quality management in European hospitals. Int J Qual Health Care 2014;26(Suppl 1):74–80. 10.1093/intqhc/mzu027 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ashkanasy NM, Wilderom CPM, Peterson MF. Handbook of organizational culture and climate. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Jacobs R, Mannion R, Davies HT, et al. . The relationship between organizational culture and performance in acute hospitals. Soc Sci Med 2013;76:115–25. 10.1016/j.socscimed.2012.10.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Callen J, Braithwaite J, Westbrook JI. The importance of medical and nursing sub-cultures in the implementation of clinical information systems. Methods Inf Med 2009;48:196–202. 10.3414/ME9212 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chia R. The Problem of reflexivity in organizational research: towards a postmodern science of organization. Organization 1996;3:31–59. 10.1177/135050849631003 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Martin J. Organizational culture: mapping the Terrain. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Alvesson M. Understanding organizational culture. London, UK: Sage Publications, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Braithwaite J, Mannion R. Managing change : Walshe K, Smith J, Healthcare management. 2nd Edn London, UK: Open University Press, 2011:429–51. [Google Scholar]
- 20.MacDavitt K, Chou SS, Stone PW. Organizational climate and health care outcomes. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf 2007;33(11 Suppl):45–56. 10.1016/S1553-7250(07)33112-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Scott T, Mannion R, Marshall M, et al. . Does organisational culture influence health care performance? A review of the evidence. J Health Serv Res Policy 2003;8:105–17. 10.1258/135581903321466085 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Plsek PE, Greenhalgh T. The challenge of complexity in health care. BMJ 2001;323:625–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Braithwaite J, Clay-Williams R, Nugus P, et al. . Health care as a complex adaptive system : Hollbagel E, Braithwaite J, Wears R, Resilient health care. Farnham, Surrey, UK: Ashgate Publishing Ltd, 2013:57–73. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M, et al. . Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: elaboration and explanation. BMJ 2015;349:g7647 10.1136/bmj.g7647 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Braithwaite J, Herkes J, Ludlow K, et al. . Association between organisational and workplace cultures, and patient outcomes: systematic review protocol. BMJ Open 2016;6:e013758 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-013758 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Taylor N, Clay-Williams R, Hogden E, et al. . High performing hospitals: a qualitative systematic review of associated factors and practical strategies for improvement. BMC Health Serv Res 2015;15:244 10.1186/s12913-015-0879-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JAC. Chapter 8. Assessing risk of bias in included studies In: The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. www.handbook.cochrane.org
- 28.Hawker S, Payne S, Kerr C, et al. . Appraising the evidence: reviewing disparate data systematically. Qual Health Res 2002;12:1284–99. 10.1177/1049732302238251 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Byrt T, Bishop J, Carlin JB. Bias, prevalence and kappa. J Clin Epidemiol 1993;46:423–9. 10.1016/0895-4356(93)90018-V [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Feinstein AR, Cicchetti DV. High agreement but low kappa: I. The problems of two paradoxes. J Clin Epidemiol 1990;43:543–9. 10.1016/0895-4356(90)90158-L [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.McHugh ML. Interrater reliability: the kappa statistic. Biochem Med 2012;22:276–82. 10.11613/BM.2012.031 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG. Chapter 9: What is heterogeneity? In: The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. www.handbook.cochrane.org
- 33.Brewer BB. Relationships among teams, culture, safety, and cost outcomes. West J Nurs Res 2006;28:641–53. 10.1177/0193945905282303 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Coustasse A, Mains DA, Lykens K, et al. . Organizational culture in a terminally ill hospital. J Hosp Mark Public Relations 2008;18:39–60. 10.1300/J375v18n01_04 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Dubois CA, D’amour D, Tchouaket E, et al. . Associations of patient safety outcomes with models of nursing care organization at unit level in hospitals. Int J Qual Health Care 2013;25:110–7. 10.1093/intqhc/mzt019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ancarani A, Di Mauro C, Giammanco MD, et al. . Patient satisfaction, managers’ climateorientation and organizational climate. Int J Health Policy Manag 2011;31:224–50. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Nasirpour AA, Gohari MR, Moradi S. The relationship of centralization, organizational culture and performance indexes in teaching hospitals affiliated to Tehran University of Medical Sciences. Acta Med Iran 2010;48:326–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Nowinski CJ, Becker SM, Reynolds KS, et al. . The impact of converting to an electronic health record on organizational culture and quality improvement. Int J Med Inform 2007;76(Suppl 1):S174–83. 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2006.05.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Shortell SM, Jones RH, Rademaker AW, et al. . Assessing the impact of total quality management and organizational culture on multiple outcomes of care for coronary artery bypass graft surgery patients. Med Care 2000;38:207–17. 10.1097/00005650-200002000-00010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Zhou P, Bundorf K, Le Chang J, et al. . Organizational culture and its relationship with hospital performance in public hospitals in China. Health Serv Res 2011;46:2139–60. 10.1111/j.1475-6773.2011.01336.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Maben J, Adams M, Peccei R, et al. . ‘Poppets and parcels’: the links between staff experience of work and acutely ill older peoples’ experience of hospital care. Int J Older People Nurs 2012;7:83–94. 10.1111/j.1748-3743.2012.00326.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Fedorowsky R, Peles-Bortz A, Masarwa S, et al. . Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae carriers in acute care hospitals and postacute-care facilities: the effect of organizational culture on staff attitudes, knowledge, practices, and infection acquisition rates. Am J Infect Control 2015;43:935–9. 10.1016/j.ajic.2015.05.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Saame I, Reino A, Vadi M. Organizational culture based on the example of an Estonian hospital. J Health Organ Manag 2011;25:526–48. 10.1108/14777261111161879 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ancarani A, Di Mauro C, Giammanco MD. How are organisational climate models and patient satisfaction related? A competing value framework approach. Soc Sci Med 2009;69:1813–8. 10.1016/j.socscimed.2009.09.033 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bosch M, Dijkstra R, Wensing M, et al. . Organizational culture, team climate and diabetes care in small office-based practices. BMC Health Serv Res 2008;8:180 10.1186/1472-6963-8-180 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Fan CJ, Pawlik TM, Daniels T, et al. . Association of safety culture with surgical site infection outcomes. J Am Coll Surg 2016;222:122–8. 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2015.11.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Hansen LO, Williams MV, Singer SJ. Perceptions of hospital safety climate and incidence of readmission. Health Serv Res 2011;46:596–616. 10.1111/j.1475-6773.2010.01204.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Ausserhofer D, Schubert M, Desmedt M, et al. . The association of patient safety climate and nurse-related organizational factors with selected patient outcomes: a cross-sectional survey. Int J Nurs Stud 2013;50:240–52. 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2012.04.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Taylor JA, Dominici F, Agnew J, et al. . Do nurse and patient injuries share common antecedents? An analysis of associations with safety climate and working conditions. BMJ Qual Saf 2012;21:101–11. 10.1136/bmjqs-2011-000082 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Davenport DL, Henderson WG, Mosca CL, et al. . Risk-adjusted morbidity in teaching hospitals correlates with reported levels of communication and collaboration on surgical teams but not with scale measures of teamwork climate, safety climate, or working conditions. J Am Coll Surg 2007;205:778–84. 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2007.07.039 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kelly DM, Kutney-Lee A, McHugh MD, et al. . Impact of critical care nursing on 30-day mortality of mechanically ventilated older adults. Crit Care Med 2014;42:1089–95. 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000127 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Mardon RE, Khanna K, Sorra J, et al. . Exploring relationships between hospital patient safety culture and adverse events. J Patient Saf 2010;6:226–32. 10.1097/PTS.0b013e3181fd1a00 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Singer S, Lin S, Falwell A, et al. . Relationship of safety climate and safety performance in hospitals. Health Serv Res 2009;44:399–421. 10.1111/j.1475-6773.2008.00918.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ma C, McHugh MD, Aiken LH. Organization of hospital nursing and 30-day readmissions in medicare patients undergoing surgery. Med Care 2015;53:65–70. 10.1097/MLR.0000000000000258 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Morris A, Bloom JR, Kang S. Organizational and individual factors affecting consumer outcomes of care in mental health services. Adm Policy Ment Health 2007;34:243–53. 10.1007/s10488-006-0104-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Kutney-Lee A, Stimpfel AW, Sloane DM, et al. . Changes in patient and nurse outcomes associated with magnet hospital recognition. Med Care 2015;53:550–7. 10.1097/MLR.0000000000000355 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Haidich AB. Meta-analysis in medical research. Hippokratia 2010;14(Suppl 1):29–37. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Vist GE, et al. . Chapter 12: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions In: The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. www.handbook.cochrane.org
- 59.Lorenc T, Petticrew M, Whitehead M, et al. . Appendix 5. Quality assessment for the systematic review of qualitative evidence Crime, fear of crime and mental health: synthesis of theory and systematic reviews of interventions and qualitative evidence. Southampton, UK: NIHR Journals Library, 2014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Aiken LH, Buchan J, Ball J, et al. . Transformative impact of magnet designation: England case study. J Clin Nurs 2008;17:3330–7. 10.1111/j.1365-2702.2008.02640.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Bradley EH, Curry LA, Spatz ES, et al. . Hospital strategies for reducing risk-standardized mortality rates in acute myocardial infarction. Ann Intern Med 2012;156:618–26. 10.7326/0003-4819-156-9-201205010-00003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Kutney-Lee A, Brennan CW, Meterko M, et al. . Organization of nursing and quality of care for veterans at the end of life. J Pain Symptom Manage 2015;49:570–7. 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2014.07.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Estabrooks CA, Hoben M, Poss JW, et al. . Dying in a nursing home: treatable symptom burden and its link to modifiable features of work context. J Am Med Dir Assoc 2015;16:515–20. 10.1016/j.jamda.2015.02.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Aiken LH, Cimiotti JP, Sloane DM, et al. . Effects of nurse staffing and nurse education on patient deaths in hospitals with different nurse work environments. Med Care 2011;49:1047–53. 10.1097/MLR.0b013e3182330b6e [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Cho E, Sloane DM, Kim EY, et al. . Effects of nurse staffing, work environments, and education on patient mortality: an observational study. Int J Nurs Stud 2015;52:535–42. 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2014.08.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Mahl S, Lee SK, Baker GR, et al. . The Association of organizational culture and quality improvement implementation with neonatal outcomes in the NICU. J Pediatr Health Care 2015;29:435–41. 10.1016/j.pedhc.2015.01.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Aiken LH, Shang J, Xue Y, et al. . Hospital use of agency-employed supplemental nurses and patient mortality and failure to rescue. Health Serv Res 2013;48:931–48. 10.1111/1475-6773.12018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Carthon JM, Lasater KB, Sloane DM, et al. . The quality of hospital work environments and missed nursing care is linked to heart failure readmissions: a cross-sectional study of US hospitals. BMJ Qual Saf 2015;24:255–63. 10.1136/bmjqs-2014-003346 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.McHugh MD, Ma C. Hospital nursing and 30-day readmissions among medicare patients with heart failure, acute myocardial infarction, and pneumonia. Med Care 2013;51:52–9. 10.1097/MLR.0b013e3182763284 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Weinberg DB, Avgar AC, Sugrue NM, et al. . The importance of a high-performance work environment in hospitals. Health Serv Res 2013;48:319–32. 10.1111/j.1475-6773.2012.01438.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Chang Y, Mark B. Effects of learning climate and registered nurse staffing on medication errors. Nurs Res 2011;60:32–9. 10.1097/NNR.0b013e3181ff73cc [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Duffield C, Diers D, O’Brien-Pallas L, et al. . Nursing staffing, nursing workload, the work environment and patient outcomes. Appl Nurs Res 2011;24:244–55. 10.1016/j.apnr.2009.12.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Prezerakos P, Galanis P, Moisoglou I. The work environment of haemodialysis nurses and its impact on patients' outcomes. Int J Nurs Pract 2015;21:132–40. 10.1111/ijn.12223 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Arnetz JE, Arnetz BB. The development and application of a patient satisfaction measurement system for hospital-wide quality improvement. Int J Qual Health Care 1996;8:555–66. 10.1093/intqhc/8.6.555 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Tervo-Heikkinen T, Partanen P, Aalto P, et al. . Nurses' work environment and nursing outcomes: a survey study among Finnish university hospital registered nurses. Int J Nurs Pract 2008;14:357–65. 10.1111/j.1440-172X.2008.00707.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Tzeng HM, Ketefian S, Redman RW. Relationship of nurses' assessment of organizational culture, job satisfaction, and patient satisfaction with nursing care. Int J Nurs Stud 2002;39:79–84. 10.1016/S0020-7489(00)00121-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Tei-Tominaga M, Sato F. Effect of nurses' work environment on patient satisfaction: a cross-sectional study of four hospitals in Japan. Jpn J Nurs Sci 2016;13:105–13. 10.1111/jjns.12091 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Greenslade JH, Jimmieson NL. Organizational factors impacting on patient satisfaction: a cross sectional examination of service climate and linkages to nurses' effort and performance. Int J Nurs Stud 2011;48:1188–98. 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2011.04.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Warren N, Hodgson M, Craig T, et al. . Employee working conditions and healthcare system performance: the Veterans Health Administration experience. J Occup Environ Med 2007;49:417–29. 10.1097/JOM.0b013e31803b94ce [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.You LM, Aiken LH, Sloane DM, et al. . Hospital nursing, care quality, and patient satisfaction: cross-sectional surveys of nurses and patients in hospitals in China and Europe. Int J Nurs Stud 2013;50:154–61. 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2012.05.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Kutney-Lee A, McHugh MD, Sloane DM, et al. . Nursing: a key to patient satisfaction. Health Aff 2009;28:w669–77. 10.1377/hlthaff.28.4.w669 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Scotti DJ, Harmon J, Behson SJ. Links among high-performance work environment, service quality, and customer satisfaction: an extension to the healthcare sector. J Healthc Manag 2007;52:109–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Shortell SM, O’Brien JL, Carman JM, et al. . Assessing the impact of continuous quality improvement/total quality management: concept versus implementation. Health Serv Res 1995;30:377–401. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Barsade SG, O’Neill OA. What’s love got to do with it? a longitudinal study of the culture of companionate love and employee and client outcomes in a long-term care setting. Adm Sci Q 2014;59:551–98. 10.1177/0001839214538636 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Ma C, Park SH. Hospital magnet status, unit work environment, and pressure ulcers. J Nurs Scholarsh 2015;47:565–73. 10.1111/jnu.12173 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Meraviglia M, Grobe SJ, Tabone S, et al. . Nurse-friendly hospital project: enhancing nurse retention and quality of care. J Nurs Care Qual 2008;23:305–13. 10.1097/01.NCQ.0000314728.65721.7c [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Stone PW, Mooney-Kane C, Larson EL, et al. . Nurse working conditions and patient safety outcomes. Med Care 2007;45:571–8. 10.1097/MLR.0b013e3180383667 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Temkin-Greener H, Cai S, Zheng NT, et al. . Nursing home work environment and the risk of pressure ulcers and incontinence. Health Serv Res 2012;47:1179–200. 10.1111/j.1475-6773.2011.01353.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Purdy N, Spence Laschinger HK, Finegan J, et al. . Effects of work environments on nurse and patient outcomes. J Nurs Manag 2010;18:901–13. 10.1111/j.1365-2834.2010.01172.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Larson EL, Early E, Cloonan P, et al. . An organizational climate intervention associated with increased handwashing and decreased nosocomial infections. Behav Med 2000;26:14–22. 10.1080/08964280009595749 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Virtanen M, Kurvinen T, Terho K, et al. . Work hours, work stress, and collaboration among ward staff in relation to risk of hospital-associated infection among patients. Med Care 2009;47:310–8. 10.1097/MLR.0b013e3181893c64 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Borg MA, Waisfisz B, Frank U. Quantitative assessment of organizational culture within hospitals and its relevance to infection prevention and control strategies. J Hosp Infect 2015;90:75–7. 10.1016/j.jhin.2014.12.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Cassie KM, Cassie WE. Organizational and individual conditions associated with depressive symptoms among nursing home residents over time. Gerontologist 2012;52:812–21. 10.1093/geront/gns059 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Aiken LH, Clarke SP, Sloane DM, et al. . Effects of hospital care environment on patient mortality and nurse outcomes. J Nurs Adm 2008;38:223–9. 10.1097/01.NNA.0000312773.42352.d7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Gardner JK, Thomas-Hawkins C, Fogg L, et al. . The relationships between nurses' perceptions of the hemodialysis unit work environment and nurse turnover, patient satisfaction, and hospitalizations. Nephrol Nurs J 2007;34:271–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Benning A, Ghaleb M, Suokas A, et al. . Large scale organisational intervention to improve patient safety in four UK hospitals: mixed method evaluation. BMJ 2011;342:d195 10.1136/bmj.d195 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Greenhalgh T, Robert G, Macfarlane F, et al. . Diffusion of innovations in service organizations: systematic review and recommendations. Milbank Q 2004;82:581–629. 10.1111/j.0887-378X.2004.00325.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Gershon RR, Stone PW, Zeltser M, et al. . Organizational climate and nurse health outcomes in the United States: a systematic review. Ind Health 2007;45:622–36. 10.2486/indhealth.45.622 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Scott T, Mannion R, Davies HT, et al. . Implementing culture change in health care: theory and practice. Int J Qual Health Care 2003;15:111–8. 10.1093/intqhc/mzg021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Donabedian A. The quality of care. How can it be assessed? JAMA 1988;260:1743–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Viswanathan M, Ansari MT, Berkman ND, et al. . Assessing the risk of bias of individual studies in systematic reviews of health care intervention. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality Methods Guide for Comparative Effectiveness Reviews, 2012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
bmjopen-2017-017708supp001.pdf (548.7KB, pdf)
bmjopen-2017-017708supp002.pdf (92KB, pdf)
bmjopen-2017-017708supp003.pdf (86.9KB, pdf)
bmjopen-2017-017708supp004.pdf (310.4KB, pdf)


