Abstract
Precision in redox signaling is attained through posttranslational protein modifications such as oxidation of protein thiols. The peroxidase peroxiredoxin 1 (PRDX1) regulates signal transduction through changes in thiol oxidation of its cysteines. We demonstrate here that PRDX1 is a binding partner for the tumor suppressive transcription factor FOXO3 that directly regulates the FOXO3 stress response. Heightened oxidative stress evokes formation of disulfide-bound heterotrimers linking dimeric PRDX1 to monomeric FOXO3. Absence of PRDX1 enhances FOXO3 nuclear localization and transcription that are dependent on the presence of Cys31 or Cys150 within FOXO3. Notably, FOXO3-T32 phosphorylation is constitutively enhanced in these mutants, but nuclear translocation of mutant FOXO3 is restored with PI3K inhibition. Here we show that on H2O2 exposure, transcription of tumor suppressive miRNAs let-7b and let-7c is regulated by FOXO3 or PRDX1 expression levels and that let-7c is a novel target for FOXO3. Conjointly, inhibition of let-7 microRNAs increases let-7-phenotypes in PRDX1-deficient breast cancer cells. Altogether, these data ascertain the existence of an H2O2-sensitive PRDX1-FOXO3 signaling axis that fine tunes FOXO3 activity toward the transcription of gene targets in response to oxidative stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 28, 62–77.
Keywords: : FOXO3, PRDX1, let-7, oxidative stress, breast cancer, tumor suppressor
Introduction
Appropriate cell responses to stress are necessary to decide cell fate. Recent evidence establishes protein sulfhydryl groups as modulators of signaling events through oxidation state changes, which impact protein interactions and activity (15). This posttranslational calibration requires a dynamic reversibility of the protein modification. Interestingly, in contrast to (de)/phosphorylation events induced by the interplay of protein kinases and phosphatases, protein sulfhydryl group oxidation to highly oxidized forms such as sulfonic acid can be irreversible, resulting in protein degradation or in the case of peroxiredoxins, a change of function. Peroxiredoxin (PRDX) family members (typical 2-Cys: PRDX1-4, atypical 2-Cys: PRDX5, and 1-Cys: PRDX6) are antioxidant enzymes that reduce peroxides via catalytic cysteine oxidation to sulfenic acid. Evidence is accumulating that demonstrates 2-Cys PRDXs as important redox sensors in signaling (36) through two unique features: (a) a highly reactive catalytic cysteine that converts to a protein sulfenic acid moiety that produces a disulfide bond with a resolving cysteine, which can be reduced via thioredoxin to reset catalytic function (22); and (b) during recycling the catalytic cysteine of PRDX can be further oxidized, which promotes formation of PRDX decamers that display chaperone functionality, but lack peroxidase activity (36). These features equip PRDX1 to sense and react to changes in redox signaling accordingly by controlling protein-binding partners. For example, we have recently shown heightened oxidative stress can over-oxidize PRDX1, which causes PRDX1 to dissociate from MKP1 as well as increase association and activity of MKP5, thereby regulating senescence (61). A similar mechanism has been described for PRDX1 and PTEN (9) or MST1 (35) and for PRDX2 and ERp46 (41). Recently, PRDXs have gained attention to act as redox relays involving the catalytic and resolving cysteine to form disulfides with the partnering protein to transfer oxidative equivalents. This has been suggested for PRDX1 and ASK1 (28, 30) and most recently, a transient PRDX2-STAT3 redox relay has been described that resulted in STAT3 oligomerization and inactivation (57).
Innovation.
It is widely established that free radicals such as H2O2 cause oxidative stress and promote disease. Members of the mammalian forkhead (FOXO) family of transcription factors are tumor suppressors that oppose oxidative stress, but the mechanisms by which FOXOs sense and respond to oxidative stress are not well understood. Peroxiredoxins are H2O2 scavenger proteins that destroy peroxides. Herein, we show that peroxiredoxin 1 (PRDX1) directly binds to FOXO3 in a peroxide dependent fashion, which in turn regulates FOXO activity differently toward pro-apoptotic and antioxidant response genes. These findings are highly significant as they reveal an oxidative stress-sensitive FOXO-PRDX1 signaling pathway that calibrates FOXO responses in tumor suppression and aging toward the regulated expression of genetic and epigenetic factors when PRDX1 detects increased cellular peroxide levels.
Our studies shown here demonstrate that PRDX1 interacts with the transcription factor FOXO3 through disulfide bonds. The mammalian forkhead box transcription factors of the O class (FOXOs) comprise four family members (FOXO1, 3, 4, and 6), which are highly related tumor suppressors that provide resistance to oxidative stress, halt cell cycle progression, and control the induction of cellular apoptosis. Although FOXOs serve as major cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) arbitrators (45), the mechanisms by which FOXOs sense and integrate ROS signals to define transcriptional outcomes are still poorly understood (17). A recent mass spectrometry analysis indicated FOXO cysteines to be involved in protein binding, underscoring their role for redox sensing (46). In response to oxidative stress, FOXO proteins translocate to the nucleus due to phosphorylation by mammalian sterile 20-like kinase 1 (MST1) and Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), as well as monoubiquitination (7). FOXO is negatively regulated through the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT signaling pathway, which promotes cytoplasmic sequestration of FOXO via AKT-induced phosphorylation and therefore causing FOXO inactivation in many cancers (7, 62).
As cancer cells carry a higher pro-oxidant burden compared to normal cells (32), we examined the role of PRDX1 in FOXO3 function and binding under pro-oxidant conditions. We establish that PRDX1 binds FOXO3 under H2O2 stress and regulates FOXO3 nuclear localization and activity through disulfide bridges involving the PRDX1 peroxidatic C52 and resolving C173 and surprisingly C71, which has not been previously seen. Within FOXO3, PRDX1 binding engages C31 and 150, the latter of which is not conserved among FOXO family members. Mutation of these FOXO3 cysteines causes changes to the phosphorylation levels of AKT substrate sites and heightened cytoplasmic localization that is responsive to PI3K inhibition in comparison to FOXO3WT. We also demonstrate for the first time that let-7c, a member of the let-7 family widely regarded as a tumor suppressor microRNA (miRNA), is a novel FOXO3 target. let-7c and let-7b miRNAs are significantly increased by H2O2 exposure in a FOXO3- and PRDX1-dependent manner, and inhibit breast cancer cell migration. Notably, several functional and mechanistic parallels exist for FOXO proteins and let-7. Both mediate tumor suppression and glucose homeostasis (60), and expression of the let-7 miRNA family has similarly been shown to be governed by various ROS-inducing stressors (52, 53). Importantly, loss of let-7c expression in cancer cells promotes migration and invasion (33, 66). Taken together, these data provide compelling evidence for an existence of a redox-specific signaling axis comprising PRDX1, FOXO3, and let-7c miRNAs in regulating oxidative stress signaling in breast cancer.
Results
PRDX1 interacts with FOXO3 and regulates its nuclear function
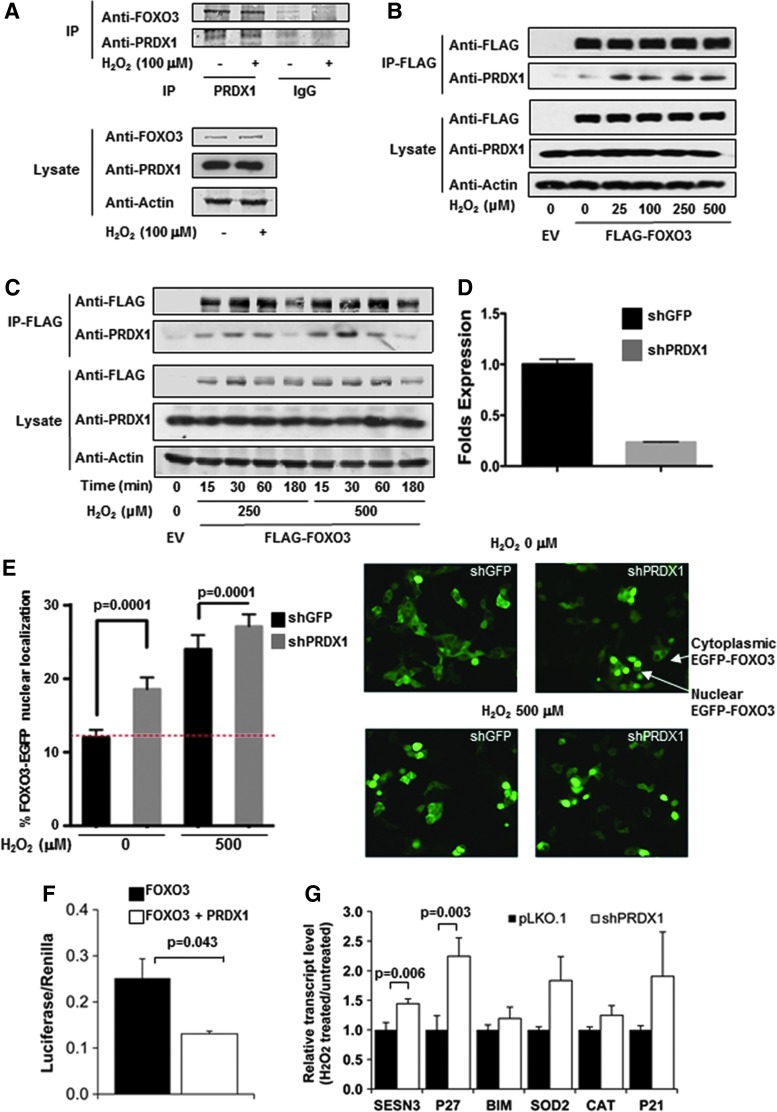
We confirmed a PRDX1 FOXO3 interaction by precipitating endogenous FOXO3 bound to PRDX1 by immunoblot (Fig. 1A and Supplementary Slide S1A; Supplementary Data are available online at www.liebertpub.com/ars). Precipitation of FLAG-FOXO3 from transfected 293T cells indicated that PRDX1 binding was elevated following treatment with 25–500 μM H2O2 in the presence of lysis buffer containing N-ethylmaleimide (NEM), a chemical agent that alkylates the thiol group on cysteines, therefore reducing postlysis oxidation events that might otherwise occur (Fig. 1B and Supplementary Slide S1B). Interestingly, the PRDX1-FOXO3 complex displayed time-dependent binding dynamics when transfected 293T cells were treated with 250 and 500 μM H2O2 (Fig. 1C and Supplementary Slide S1C). Maximal PRDX1-FOXO3 oligomerization was seen at 30 min, which returned to baseline after 3 h. An assay to measure apoptosis, cell viability, and cytotoxicity found no significant changes in any of the three measurements, between treatment and no treatment over a period of 3 h, suggesting that the decrease in PRDX1-FOXO3 binding was not a result of cell death (Supplementary Fig. S1B). Further experiments in the absence of NEM found that binding dynamics of FLAG-FOXO3 and PRDX1 followed a U-shaped H2O2 dose curve with maximal binding at 100 μM H2O2 and complex dissociation at higher concentrations (Supplementary Fig. S1A and Supplementary Slide S1A). In addition, we could not detect any over-oxidized PRDX1 binding to FOXO3, suggesting that PRDX1 over-oxidation on its catalytic cysteine may induce FOXO3 release (Supplementary Fig. S1A and Supplementary Slide S1A).
FIG. 1.
PRDX1 binds to FOXO3 in an H2O2 dose-dependent manner and regulates FOXO3 nuclear localization. (A) Immunoprecipitation of precleared lysate with PRDX1 or IgG antibodies found PRDX1 bound FOXO3. 293T cells underwent serum starvation for 30 min and were then treated with the 0 or 100 μM H2O2 for an additional 30 min. (B and C) 293T cells were transfected with pcDNA3-FLAG-FOXO3A or EV and treated with increasing concentrations of H2O2 for the indicated times. Before lysis, cells were washed with 20 mM NEM in phosphate-buffered saline to block lysis-induced disulfide bond formation. FLAG-labeled proteins were immunoprecipitated and detected by immunoblot with FLAG and PRDX1 antibodies. (D and E) The percentage of 293T cells displaying nuclear FOXO3-EGFP localization was enhanced with reduction of PRDX1; 150 or more cells analyzed per sample, p < 0.0001 (t-test). Cells infected with shPRDX1A or control lentivirus for 48 h, followed by transfection with FOXO3-EGFP for 24 h. H2O2 was added during the last 30 min. (F) HA-PRDX reduced FLAG-FOXO3 activity when transiently cotransfected into MEF and analyzed utilizing a dual-luciferase reporter assay. Values (mean + SE) were normalized to vehicle treatment. *p < 0.05, t-test (N = 3). (G) qPCR gene transcription of SESN3 and P27 was increased in PRDX1-deficient 293T cells (white bars) treated with 250 μM H2O2 compared to pLKO.1 control cells (black bars) after 16 h. Values (mean + SE) were normalized to vehicle treatment. *p < 0.05, t-test (N = 3). MEF, murine embryonic fibroblast; NEM, N-ethylmaleimide; SE, standard error.
To investigate if PRDX1 binding to FOXO3 has a functional impact, we assessed FOXO3 nuclear translocation in Prdx1−/− and Prdx1+/+ murine embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs). Interestingly, MEFs lacking PRDX1 displayed primarily nuclear FOXO3 localization in contrast to wild-type MEFs expressing PRDX1 (Supplementary Fig. S1C). Given the low transfection efficiency of MEFs, we next utilized 293T cells with reduced PRDX1 expression transfected with a FOXO3-EGFP reporter construct (Fig. 1D, Supplementary Fig. S1D and Supplementary Slide S1D). As Figure 1E shows, FOXO3 nuclear localization was significantly increased in 293T cells harboring 90% less PRDX1, suggesting PRDX1 deterred FOXO3 nuclear translocation. Investigating the role of PRDX1 on FOXO3 function further, we next evaluated FOXO3 activity specifically using a dual-luciferase reporter assay in Prdx1−/− MEFs transiently transfected with FOXO3 and/or PRDX1. As expected, PRDX1 decreased luciferase signals by 50% (Fig. 1F). Investigating FOXO3 target gene expression by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) showed that PRDX1 knockdown increased expression of several FOXO3 targets in H2O2-treated 293T cells compared to control, where SESN3 and P27 differences were significantly enhanced (Fig. 1G).
PRDX1 and FOXO3 associate through disulfide bonds
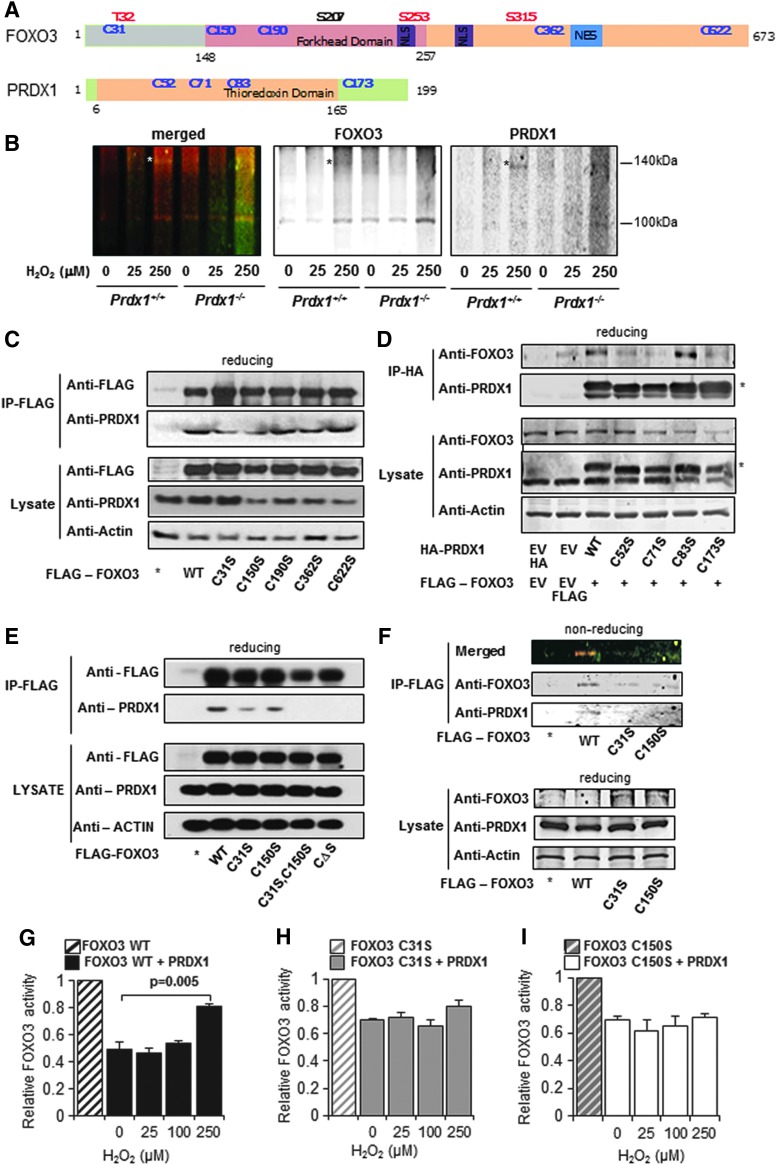
2-Cys peroxiredoxins and FOXO proteins have been suggested to form disulfide bonds with target proteins (46). We explored whether covalent cysteine disulfide bridges exist between PRDX1 and FOXO3. Five cysteines are present in FOXO3 at positions 31, 150, 190, 362, and 622, while PRDX1 has four cysteines at positions 52, 71, 83, and 173 (Fig. 2A). To investigate possible disulfide bridge interactions between PRDX1 and FOXO3, we analyzed Prdx1+/+ and Prdx1−/− MEFs using two-color infrared (IR) antibody detection and identified one band staining positive for both PRDX1 and FOXO3 around 140 kDa after H2O2 treatment (Fig. 2B), which was reduced when lysates were treated with β-ME (Supplementary Fig. S2A). This suggests an oligomeric PRDX1-FOXO3 protein complex composed of monomeric FOXO3 (90 kDa) disulfide bound to dimeric PRDX1 (2 × 23 kDa). To gain further insight into the specific cysteines responsible for the PRDX1-FOXO3 interaction, coimmunoprecipitations (co-IPs) of endogenous PRDX1 with FLAG-FOXO3 single cysteine mutants revealed that loss of FOXO3 C31 or C150 decreased binding to PRDX1 (Fig. 2C and Supplementary Slide S2C). Conversely, coprecipitating endogenous FOXO3 with HA-PRDX1 single cysteine mutants showed that PRDX1 C52, C71, or C173 mutants decreased binding of endogenous FOXO3 as well (Fig. 2D and Supplementary Slide S2D). PRDX1 C71 is yet to be described to play a role in PRDX1 protein associations. In addition, disulfide-dependent complex formation was further analyzed and demonstrated that, as shown in Figure 2C, while H2O2 treatment induced endogenous PRDX1 binding to wild-type FLAG-FOXO3, and decreased PRDX1 binding to C31 and C150 single mutants, the FLAG-FOXO3 double mutant (C31,150S), and the quintuple cysteine to serine mutant FLAG-FOXO3 (CΔS) showed no PRDX1 binding (Fig. 2E and Supplementary Slide S2E). To further examine the importance of FOXO3 C31 and C150 in oligomeric formation, we expressed FLAG-FOXO3WT, C31S, and C150S in 293T cells. Figure 2F (Supplementary Slide S2F) shows that the FOXO3-PRDX1 oligomer can be detected with wild-type FLAG-FOXO3, but not with single cysteine FOXO3 mutants. As FOXO3C31 and FOXOC150 are important for PRDX1 binding, we next examined how cysteine mutant FOXO3 activities were responding to PRDX1-mediated decrease under H2O2-induced stress. Using a dual-luciferase reporter assay, we observed that under lower H2O2 treatments PRDX1 is able to decrease FOXO3 activity significantly, and under higher H2O2 doses (250 μM), PRDX1-induced decrease of FOXO3 was abrogated (Fig. 2G). In addition, PRDX1 did not further decrease FOXO3 C31 or C150 activity, nor did higher H2O2 doses increase mutant activity (Fig. 2H, I). In contrast to wild-type FOXO3, PRDX1 was unable to lower FOXO3 (ΔC) luciferase activity (Supplementary Fig. S2B).
FIG. 2.
PRDX1 and FOXO3 form disulfide bonds. (A) Domain structures of FOXO3 and PRDX1 proteins. (B) A PRDX1-FOXO3 complex was detected under nonreducing conditions in Prdx1+/+, but not Prdx1−/− MEFs, when treated with the indicated concentrations of H2O2 for 30 min by immunoblot with two-color IR antibody detection. (C) Anti-FLAG IP of 293T cells transfected with EV or FLAG-FOXO3 (WT or single C-to-S mutants) displayed reduced PRDX1 binding to FOXO3 C31S or C150S when treated with H2O2 for 30 min by immunoblot. (D) Anti-HA IP of 293T cells transfected with EV or HA-PRDX1 (WT or C-to-S mutants) showed reduced FOXO3 binding with PRDX1 C52S, C71S, or C173S mutants when treated with H2O2 for 30 min (*HA-PRDX1). (E) Mutation of FOXO3 cysteines reduced PRDX1 binding when treated with 25 μM H2O2 for 30 min. Anti-FLAG IP of 293T cells transfected with EV or FLAG-FOXO3 (WT, C31S, C150S, C31, 150S double mutant, or ΔCys mutants) was detected by immunoblot. (F) A PRDX1-FOXO3 complex was detected in FLAG-FOXO3 WT, but not C31S or C150S mutant Anti-FLAG samples under nonreducing conditions in 293T cells cotransfected with FLAG-FOXO3 constructs and HA-PRDX1 treated with 25 μM H2O2 for 30 min. (G–I) The ability of PRDX1 to reduce FOXO3 activity was inhibited with H2O2 treatment in 293T cells in FOXO3 WT, but not C31S or C150S mutants. Cells were transiently transfected with FOXO3 and PRDX1 constructs in a dual-luciferase assay treated with 0–250 μM H2O2. Values (mean + SE) were normalized to FOXO3 vehicle treatment. *p < 0.05, t-test (N = 3). NES, nuclear export sequence; NLS, nuclear localization signal.
FOXO3 disulfide bonding with PRDX1 determines subcellular localization under H2O2 stress
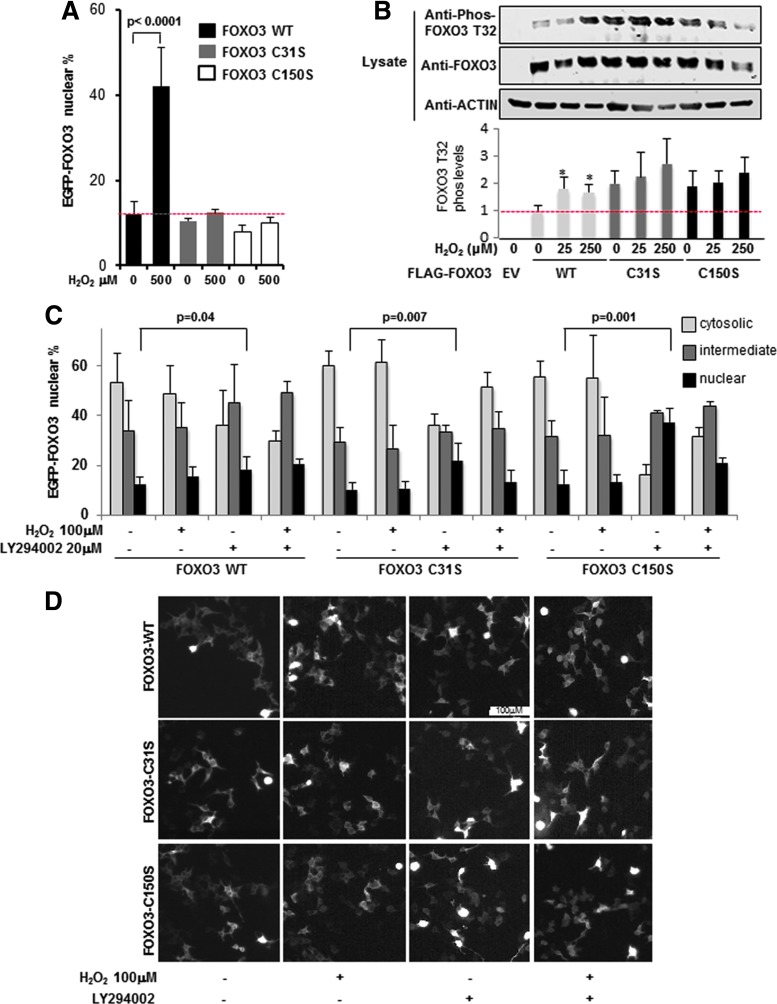
Several lines of evidence demonstrate that FOXO proteins translocate to the nucleus under increased levels of ROS, reviewed in Ref. (16). Importantly, nuclear localization of FOXO proteins is a prerequisite for their transcriptional activity, as such FOXOs are highly regulated through mechanisms that alter nucleocytoplasmic shuttling (17). To address if the PRDX1-FOXO3 disulfide bound complex influences FOXO3 protein nuclear localization, we expressed WT-, C31S-, or C150S-FOXO3-EGFP reporter constructs in 293T cells and quantified nuclear localization following H2O2 exposure for 1 h. Figure 3A and Supplementary Figure S3A show that unlike WT FOXO3, C31S- and C150S-mutant FOXO3s fail to translocate to the nucleus, even during a high-dose H2O2 treatment. These data indicate that FOXO3 C31 and C150 regulate FOXO3 nuclear translocation. A well-known mechanism regulating FOXO3 nuclear localization is phosphorylation on T32 by AKT, which sequesters FOXO3 in the cytosol (6). We therefore examined the AKT phosphorylation status of C31S and C150S FOXO3 mutants. Figure 3B (Supplementary Slide S3B) shows that FOXO3 WT T32 phosphorylation levels were increasing following treatment with H2O2, which corresponded with binding of 14-3-3 to the PRDX1-FOXO3 complex (Supplementary Fig. S3B and Supplementary Slide S3B). Interestingly, both mutants showed increased basal levels of T32 phosphorylation compared to FOXO3 WT, with phosphorylation further increasing with additional H2O2 treatment. We also examined phosphorylation at S318, another AKT phosphorylation site known to enhance FOXO3 nuclear export (48), and found no change in phosphorylation levels between FOXO3 WT and the C31S and C150S single FOXO3 mutants (Supplementary Fig. S3C and Supplementary Slide S3C), suggesting the binding of PRDX1 to FOXO3 has a site-specific effect on FOXO3 phosphorylation. Given that FOXO3 C31S and C150S mutants have increased T32 phosphorylation and dysfunctional translocation in response to high doses of H2O2 (Fig. 3A, B), we questioned if PI3K inhibition is capable of promoting FOXO3 C31S and C150S mutant nuclear translocation. To do so, we applied experimental conditions that would decrease the activation of kinases such as STK4/MST1, JNK, and p38 (23, 31), known to induce FOXO3 nuclear localization by phosphorylating FOXO3. For example, MST1 phosphorylation on FOXO3 is known to overcome its AKT-induced cytoplasmic retention by decreasing 14-3-3 binding to FOXO3 (31). EGFP-FOXO3 localization was compared in 293T cells treated with 100 μM H2O2 for 30 min. Under this treatment, 14-3-3 binding to FOXO3 was not decreased (Supplementary Fig. S3B). In addition, as FOXO3 nuclear localization is dependent on DNA concentration (Supplementary Fig. S3D), we assessed EGFP-FOXO3 localization of 50 ng of EGFP-FOXO3 in a subconfluent population of cells to ensure AKT activity toward FOXO3 (26). We found that LY294002 (PI3K inhibitor) treatment significantly increased nuclear localization by 5.7%, 11.7%, and 25% in FOXO3WT, FOXOC31S, and FOXOC150C, respectively, compared to untreated cells (Fig. 3C, D). These results suggest again that AKT-induced phosphorylation of FOXO3 sequesters FOXO3 cysteine mutants in the cytosol.
FIG. 3.
Interdisulfides between PRDX1 and FOXO3 modulate FOXO3 subcellular localization and FOXO3 phosphorylation. (A) Thirty minutes of H2O2 treatment enhanced nuclear EGFP-FOXO3 content in WT, but not C31 or C150 mutant constructs, 48 h following transfection in 293T cells. Percentage of cells displaying nuclear FOXO3-EGFP localization is indicated. (B) T32 phosphorylation of FOXO3 C31S or C150S was heightened under basal conditions compared to FOXO3 WT. 293T cells transfected with FLAG-FOXO3 (WT, C31, or C150 mutants) were treated with H2O2 and detected by immunoblot for FOXO3 Phospho-T32, FOXO3, and Actin. Phospho-T32 signals were normalized to total FOXO3. Values represent mean + SD normalized to WT 0 μM H2O2. *p < 0.05 (N = 3). (C) PI3K inhibition with 20 μM LY294002 enhanced nuclear FOXO3-EGFP WT, C1S, or C2S mutants in transiently transfected 293T cells after 24 h. Values represent mean + SE (N = 3) with 150–400 cells counted per sample by fluorescence microscopy. Experiment was repeated twice. (D) Representative pictures of (C).
Loss of PRDX1 enhances FOXO3-dependent H2O2-induced let-7 miRNA upregulation
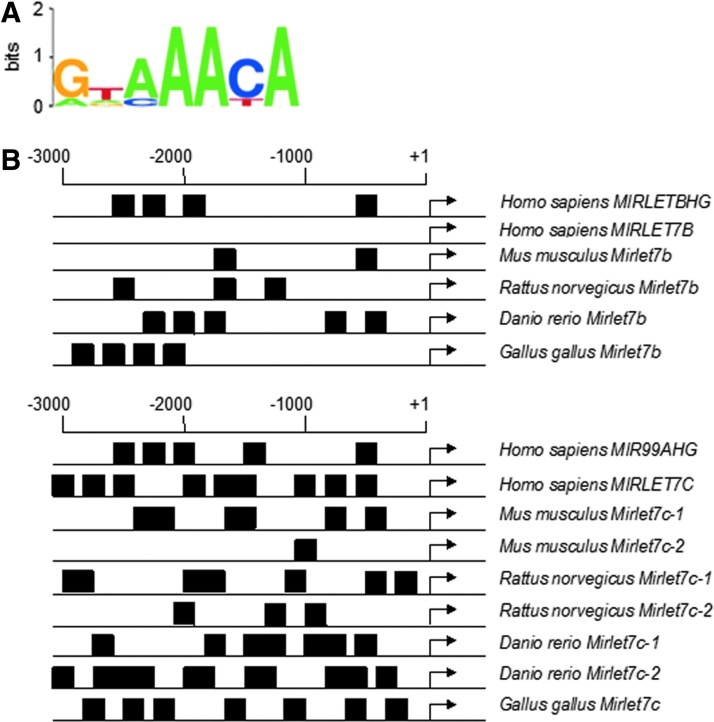
As prior studies have reported, increased let-7 family member expression is induced by ionizing radiation, genotoxic stress, and peroxide (52, 53). In Caeorhabditis elegans, let-7 family members have overlapping functions with FOXO proteins to regulate development, aging, glucose metabolism, stress responses, and act as tumor suppressors (5). We were interested to examine if let-7 miRNAs are regulated by FOXO3 under oxidative stress. Using the University of California Santa Cruz Genome Browser, we analyzed the 5′ untranslated region (UTR) of let-7b and let-7c in several species for putative FOXO3 binding sequences (YTXXACA) (10). As shown in Figure 4A and B, FOXO3 binding sites are preserved in the 5′ UTR of MIRLET7B and MIRLET7C.
FIG. 4.
FOXO3 consensus binding sequence found in let-7b and let-7c promoter region. (A) Putative FOXO3 binding sequence (10). (B) Putative FOXO binding motifs in forward and reverse are located in the 5′ UTR of let-7b and -7c in several species. The consensus FOXO binding sequences in the WebLogo (black boxes) are indicated. Numbering is relative to the transcription start site obtained through the University of California Santa Cruz Genome Browser. UTR, untranslated region.
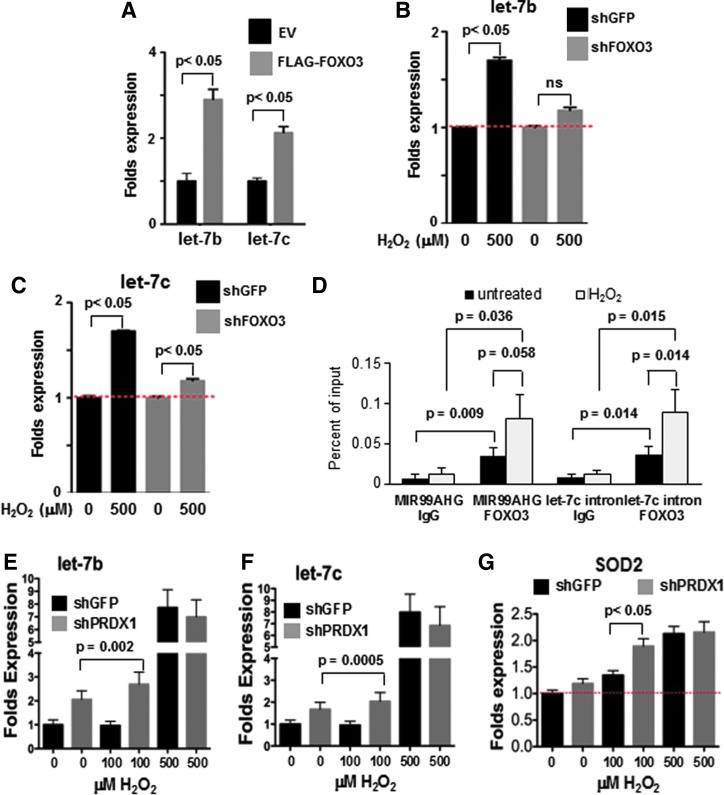
To confirm let-7 miRNAs as a potential novel FOXO3 target, we established that H2O2 treatment of HeLa cells enhanced the expression of both let-7b and let-7c miRNAs (Supplementary Fig. S4A). To determine if FOXO3 is involved in H2O2-mediated enhanced expression of let-7b and let-7c in HeLa cells, we performed either an overexpression or a shRNA-mediated knockdown of FOXO3 before treatment with H2O2. When FOXO3 expression increased, levels of let-7b and let-7c were threefold and twofold higher, respectively (Fig. 5A and Supplementary Fig. S4B). As FOXO3 expression was significantly diminished, the ability of H2O2 to induce either let-7b or let-7c miRNA expression was lost (Fig. 5B, C, and Supplementary Fig. S4C). As a final confirmation of FOXO3s role in the H2O2-mediated enhancement of let-7 expression, a chromatin IP (ChIP) assay was performed showing that FOXO3 binds directly to both of the let-7c promoter regions, the distal host gene and the proximal intronic promoter, both considered functional in let-7c transcription (44) (Fig. 5D and Supplementary Fig. S4D). FOXO3 promoter binding was further enhanced following 100 μM H2O2 treatment compared to no treatment. These data suggested that FOXO3 very likely regulates the expression of MIRLET7B and MIRLET7C. Next, we examined if loss of PRDX1 magnifies let-7 miRNA transcription in the context of H2O2 addition. Figure 5E and F show when PRDX1 expression was more than 90% reduced (Supplementary Fig. S4E), let-7b and let-7c expression levels were augmented. This effect was further enhanced with 100 μM H2O2 treatment. Moreover, SOD2, an established target of FOXO3, was also increased on H2O2 treatment in the context of PRDX1 knockdown (Fig. 5G). In conclusion, these data suggest that a PRDX1/FOXO3 signaling axis exists that directly regulates let-7c expression under H2O2-induced stress.
FIG. 5.
FOXO3 regulates expression of let-7 miRNAs under H2O2. (A) Overexpression of FLAG-FOXO3 enhanced let-7b and c transcription in Hela cells 48 h after transfection. Cells were harvested, lysed, and analyzed for miRNA expression by TaqMan assays, using the delta CT method with mir-30c as the internal standard. (B, C) FOXO3-deficient HeLa cells were nonresponsive to H2O2 treatment. Thirty hours following transfection of shGFP or shFOXO3, cells were treated with or without H2O2 for 18 h. Expression profiles of let-7b and let-7c were assessed by individual TaqMan assays with U18 as the internal standard (N = 3). (D) ChIP assays indicate transfected FLAG-FOXO3 binds to the MIR99AHG and intronic let-7c promoter regions and is enhanced following 100 μM H2O2 treatment for 30 min in 293T cells. Quantification of immunoprecipitated DNA was performed in triplicate by quantitative PCR and evaluated by the delta CT method. Values of each immunoprecipitated sample are expressed as a percentage relative to their respective input (no antibody). (E–G) let-7b and c transcription was increased in PRDX1-deficient cells. HeLa cells were transfected with either a shGFP or shPRDX1 construct for 56 h, followed by treatment with or without H2O2 for 18 h. HeLa cells were analyzed for gene expression by TaqMan expression assays using the delta CT method with U18 as the internal standard (F, G) or β-actin as the internal standard (H).
The PRDX1-FOXO3-let-7 axis regulates breast cancer cell migration
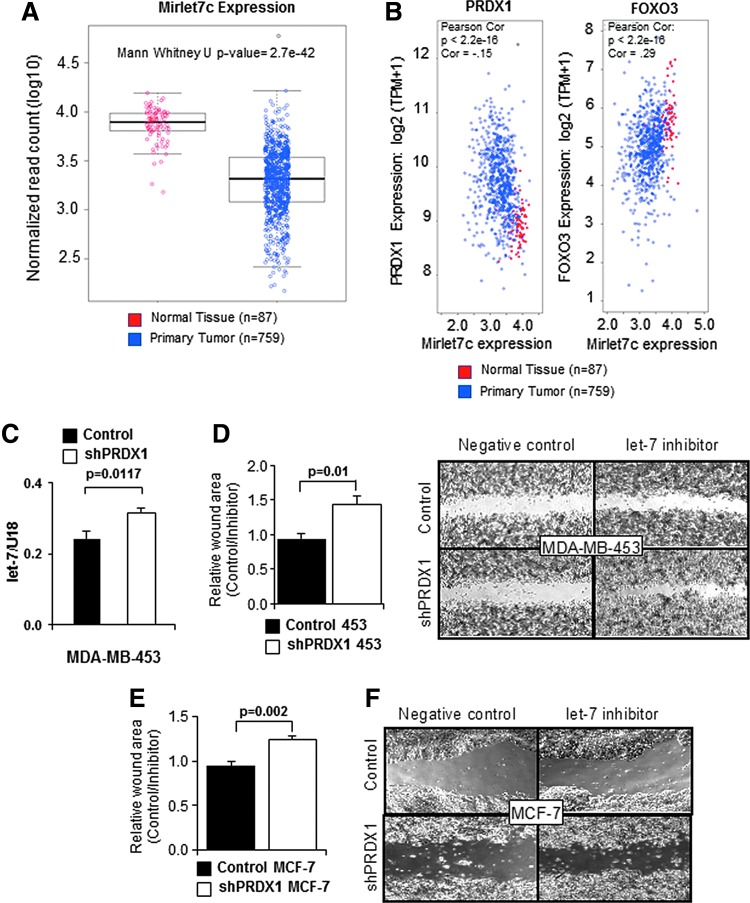
Finally, we sought functional confirmation of the PRDX1-FOXO3-let-7 axis. As genetic alterations in cancer cells elevate the production of ROS, reviewed in Ref. (43) and let-7b and let-7c suppress cancer development (5), including breast cancer (13, 59, 65), we compared let-7c expression levels in normal and breast cancer cases (8). We found let-7c expression to be significantly lower in breast cancer tissues compared to normal breast tissue (Fig. 6A). FOXO3 showed a similar expression pattern to let-7c, while PRDX1 expression was increased in breast cancer compared to normal tissue (Supplementary Fig. S5A, B). Comparing changes to PRDX1 and FOXO3 expression in normal and breast cancerous tissues using Pearson correlation demonstrated a significant negative correlation for PRDX1 and FOXO3 in this data set downloaded from GEO Accession: GSE62944 (47) (Fig. 6B), suggesting functional significance of our findings. This was further substantiated analyzing breast cancer patient survival in data sets from the Kaplan–Meier Plotter (21) and the Gene Expression-based Outcome for Breast Cancer Online (GOBO) (18), which showed that a lower expression of FOXO3 and a higher expression of PRDX1 correlate with shortened patient survival (Supplementary Fig. S5C–F).
FIG. 6.
Lack of PRDX1 enhances levels and function of let-7 miRNAs under H2O2. (A) Mirlet7 expression in normal and breast cancer tissue from TCGA. (B) Expression of FOXO3 and PRDX1 from TCGA breast cancer cases and normal tissue was compared to Mirlet7c expression. (C) EV or shPRDX1 MDA-MB-453 cells were harvested, lysed, and analyzed for miRNA expression by TaqMan assays using the delta CT method with U18 as the internal standard (N = 3). (D–E) Wound healing was increased following let-7 inhibition in PRDX1-deficient breast cancer cells. 1 × 106 shPRDX1 MDA-MB-453 or MCF-7 (white bar) cells or control (black bar) cells were transfected with a let-7 miRNA inhibitor in a 12-well plate and wound healing was assessed after 48 h (MDA-MB-453) or 24 h (MCF-7) in the presence of mitomycin C (0.5 μg/ml). Wound area of let-7 inhibitor-treated cells was normalized to control miRNA inhibitor-treated cells (mean + SE) N = 4. Right side, representative photographs of wound healing assays in MDA-MB-453 or MCF-7 cells. TCGA, The Cancer Genome Atlas.
FOXO3 suppresses cancer development in different ways, including the inhibition of cell motility (2, 4, 34, 40, 55, 56). In contrast, while PRDX1 prevents cancer initiation (37, 38), its role in cancer is less understood. Interestingly, we have previously shown that PRDX1 deficiency in MCF-10A, MCF-7, and MDA-MB-231 cells increased p38 activation (61), which induces FOXO3 nuclear localization in MCF-7 cells (12, 23). We therefore hypothesized that inhibition of let-7b and let-7c would affect migration differently in breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-453 or MCF-7) with knockdown of PRDX1 (shPRDX1) (Supplementary Fig. S5G and Supplementary Slide S5G) compared to control vector treatment. Intriguingly, cells with reduced PRDX1 showed a 30% increase in let-7 expression (Fig. 6C) and a 50% (MDA-MB-453) and a 30% (MCF-7) increased wound closure, respectively, when transfected with single-stranded RNA oligonucleotide inhibitors that compete with let-7b and let-7c seed sequences (Fig. 6D, E). However, when compared with a negative control single-strand RNA oligonucleotide, we saw little to no wound closure between the control and shPRDX1 cells. Altogether, these data demonstrate that a PRDX1 regulated signaling axis exists in breast cancer and is required for FOXO3 and let-7 miRNA upregulation to suppress breast cancer cell migration.
Discussion
H2O2 is an important second messenger in cell signaling, where it can directly induce oxidation of cysteine sulfhydryl groups in proteins, thereby impacting protein activity and facilitating rapid signal transfer comparable to other posttranslational modifications (49). Thus, oxidative equivalents can be passed on by H2O2-scavenging enzymes such as peroxidases (50). This reaction entails a transient disulfide exchange reaction between cysteine thiols, which requires close proximity of the peroxidase with a partnering protein (20). Peroxiredoxins have been suggested to form disulfide bridges with partnering proteins to pass oxidizing equivalents this way, thereby modulating protein activity of their binding partners (28, 57). Our data suggest a similar mechanism between PRDX1 and the transcription factor FOXO3. As the disulfide exchange reaction is transient, capture of stable complexes by co-IP is low as demonstrated by weak PRDX1 staining FLAG-FOXO3 pull down experiments despite the high abundance of PRDX1 in cell lysate (Fig. 1B, C).
FOXO family members have been implicated in ROS signaling involving cysteine thiols. For example, a recent study showed p300 to form disulfide reactions with FOXO4 that result in its acetylation and nuclear localization (14). However, more examples are needed to fully understand specific roles of FOXO proteins in redox response. We present for the first time, evidence of an H2O2-dependent regulation of FOXO3 activity directly through the oxidative stress-signaling sensor PRDX1. Our data suggest the formation of a disulfide bond between a PRDX1 dimer and FOXO3 monomer involving the PRDX1 peroxidatic and resolving cysteines C52 and C173, respectively, as well as C71. In FOXO3, the FOXO3 C31 is a shared cysteine among FOXO family members, while C150 is unique to FOXO3, suggesting a redox regulation that is specific for FOXO3 (Fig. 2). We further show the importance of PRDX1-FOXO3 binding by demonstrating increased FOXO3 cytoplasmic sequestration (Fig. 3A) due to increased AKT phosphorylation of FOXO3 mutants impaired in PRDX1 binding after H2O2 treatment (Fig. 3B–D). However, a further delineation of the FOXO-PRDX1 signaling pathway is warranted to determine the role that other family members may play, as a recent proteomic profiling report found that PRDX1, 2, and 5 are cysteine-dependent binding partners of FOXO3 and suggested that competition among PRDX family members may be present for FOXO3 binding (45).
We show that the PRDX1-FOXO3 complex formed in the presence of elevated H2O2 is a cysteine-dependent oligomer. A unique property to the PRDX1-FOXO3 axis is the utilization of C150 of FOXO3, which is exclusive to FOXO3, suggesting specificity of the PRDX1-FOXO3 interaction. Mutation of C31 or C150 inhibits FOXO3 complex formation with PRDX1 and renders these FOXO3 mutants unresponsive to oxidative insult, exhibiting cytoplasmic accumulation, which suggests PRDX1 binding of FOXO3 via disulfide bonds is critical for regulating FOXO3 in response to oxidative stress (Figs. 2 and 3). Luciferase reporter assays indicated FOXO3 becomes unresponsive to PRDX1-induced control following treatment with high doses of H2O2 (Fig. 2G–I), suggesting over-oxidation of PRDX1 impairs FOXO3 binding and may also allow FOXO3 posttranslational modifications to induce nuclear translocation (Fig. 1E). FOXO3 C31 or C150 mutants (Fig. 3C, D) were unresponsive to PRDX1 regulation, but surprisingly correlated with cytosolic sequestration under H2O2-induced stress (Fig. 3A) compared to FOXO3WT. To determine why FOXO3 C31S and C150S mutants could not bind PRDX1, but were sequestered from the nucleus (Fig. 3A), the phosphorylation status of FOXO3 T32 and S318, which represses FOXO3 through AKT and SGK signaling (7), was probed. Interestingly, wild-type FOXO3 showed an H2O2-dependent increase in T32 phosphorylation, however, FOXO3 cysteine mutants displayed much higher phosphorylation. FOXO3C31S showed an overall higher phosphorylation of T32, while FOXO3C150 T32 phosphorylation was higher than FOXO3WT but not as responsive to H2O2 stimulation (Fig. 3B). Analysis of S318 phosphorylation, however, showed no difference between wild-type FOXO3 and the FOXO3 cysteine mutants (Supplementary Fig. S3C), suggesting that PRDX1 binding to FOXO3 is site specific and calibrates T32 phosphorylation, but not S318.
FOXO3 nuclear localization is regulated by AKT and SGK phosphorylation inducing 14-3-3 binding and cytoplasmic sequestration or kinases that induce nuclear localization. Candidate kinases include MST1, JNK, or p38 (19, 23) (Fig. 7), where MST1 can induce nuclear localization of an AKT phosphorylated FOXO3 protein (31). Interestingly, all three kinases are subject to PRDX1 binding and subsequent regulation, indicating another layer of control in the PRDX1/FOXO3/let-7c axis that requires future analysis. We suspect that under high oxidative stress, MST1, an essential activator of FOXO and repressor of AKT (11, 31), is activated by PRDX1 decamers (formed by 10 over-oxidized PRDX1 proteins) (35) under higher oxidative stress causing phosphorylation of FOXO3 on S207. This suggests that FOXO3 nuclear localization under H2O2-induced stress may increase in the presence of decameric (over-oxidized) PRDX1. This is in alignment with our findings that PRDX1 binding to FOXO3 does not include over-oxidized PRDX1 protein (Supplementary Fig. S1A) and is dynamic as it decreases after 30 min in H2O2-treated cells (Fig. 1C). On the contrary, kinase activity of JNK and p38 is inhibited by PRDX1, perhaps accounting for the increased localization of FOXO3 in the nucleus in PRDX1-deficient cells compared to PRDX1-proficient cells (Fig. 1E and Supplementary Fig. S1C). This suggests different roles for PRDX1 on FOXO3 signaling and needs further exploration in future studies. Further exploring our findings that PRDX1 binding to FOXO3 calibrates FOXO3 nuclear translocation through modulating AKT phosphorylation, we demonstrate that PI3K inhibition rescued translocation of C31S and C150S mutant FOXO3 to FOXOWT levels following H2O2 exposure (Fig. 3C, D).
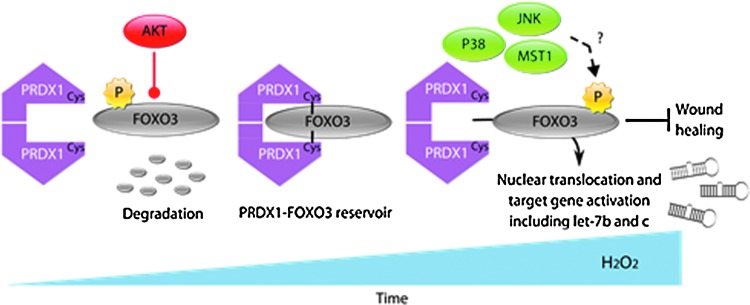
FIG. 7.
Model: stepwise oxidation of PRDX1 regulates FOXO3 under oxidative stress. PRDX1 and FOXO3 interact in an oxidative stress-dependent way. This involves the catalytic/peroxidatic cysteine and C71 of PRDX1 and C31 and C150 of FOXO3. Our data strongly suggest disulfide bonding between PRDX1 and FOXO3 involving PRDX1 C52, C71, and C173 and FOXO3 C31 and C150 regulating the AKT-induced phosphorylation of T32 on FOXO3 and 14-3-3 binding and dissociation. Nuclear localization and 14-3-3 dissociation of FOXO3 may be promoted by monoubiquitination or phosphorylation by over-oxidized PRDX1 activating MST1 or oxidative stress activation of JNK or p38. This results in expression in let-7b and let-7c and inhibition of migration.
Collectively, these data suggest an oxidative stress-dependent mechanism of FOXO3 cytoplasmic loading, a protection and release that are directed through PRDX1 by binding to FOXO3 and coordinating its posttranslational modifications (Fig. 7). Accordingly, PRDX1-dependent protection of FOXO3 from repressive phosphorylation and degradation pathways would enable a FOXO3 reservoir not reliant on de novo synthesis of FOXO3 or T32 dephosphorylation. The PRDX1-FOXO3 axis therefore is more than simply an inhibitory pathway, but rather, a redox-dependent signaling modulator enabling controlled bursts of FOXO3 nuclear translocation and gene expression. Based on our data shown here, we propose that PRDX1 builds a stepwise and redox-dependent FOXO3 cytoplasmic reservoir that is readily available once high H2O2 levels stimulate FOXO3 nuclear function (Supplementary Fig. S6).
miRNAs are direct targets of transcription factors that are known as important tumor suppressors or oncogenic proteins. Yet, remarkably little is understood of miRNAs that are responsive to FOXOs. Consensus FOXO DNA binding motifs are present in the 5′ UTR of let-7b and let-7c in several species (Fig. 4). Interestingly, let-7b and let-7c-2 in Mus musculus and Rattus norvegicus are located in tandem and separated by 621 and 319 nucleotides, respectively. Our results establish for the first time that let-7b and let-7c are upregulated by FOXO3 (Fig. 5) directly to both of let-7c promoter regions (the distal host gene and the proximal intronic promoter) considered functional in let-7c transcription (44) (Fig. 5D and Supplementary Fig. S4D). In addition, FOXO3 promoter binding is enhanced following 100 μM H2O2 treatment compared to no treatment (Fig. 5D). These data define a new facet of FOXO3-mediated responses to oxidative stress, as our findings are consistent with prior reports that show let-7 members are upregulated by ionizing radiation, genotoxic stress, and peroxide (52, 53). Intriguingly, we identified a novel FOXO3 target with direct tumor suppressive activity, as let-7 miRNAs bind to 3′ UTRs of target oncogenes and cell cycle regulators and that reduced let-7 expression has been shown to correlate with the development of cancers (64).
Systemic deletion of FOXOs results in cancer in murine models in vivo, underscoring their role as bona fide tumor suppressors (42). In addition, inactivating genetic mutations and reduced expression of FOXOs occur in human cancers (3, 24), and suppression of FOXO function is critical in promoting evasion of apoptosis and is a significant occurrence in several hematological malignancies, including Bcr-Abl+ leukemia (17, 27). Notably, a more specific role has been identified for FOXO3 as an inhibitor of cancer cell motility (40, 56) and wound healing (51), suggesting that FOXO3 may regulate cell motility.
Similar to FOXOs, PRDX1 protects from tumor initiation (38), however, in contrast to FOXO3, several reports indicate poor prognosis for cancers with high expression of PRDX1 (29, 58, 67). This is in line with The Cancer Genome Atlas and survival analyses showing PRDX1 expression elevated in breast cancer patients with decreased survival (Fig. 6B and Supplementary Fig. S5C–F). Importantly, these data support our findings that a PRDX1-FOXO3-let-7 axis exists in tumorigenesis. Furthermore, PRDX1-deficient MDA-MB-453 cells showed increased levels of let-7c (Fig. 6C) and let-7 inhibition increased cell motility of MDA-MB-453 and MCF-7 breast cancer cells, both of which show low motility (1), with decreased PRDX1 expression (Fig. 6D, E). This finding is consistent with earlier studies showing that let-7 miRNAs inhibit motility of breast cancer cells by regulating genes in the actin cytoskeleton pathway (25). Given the findings of these studies and those presented here, it would be interesting in future studies to determine let-7 miRNA targets that are controlled by PRDX1 and FOXO3 in cancer development.
The free radical theory of aging posits that accumulated damage from oxidative events shortens life span. The fundamental importance of PRDX1 in protecting from the deleterious effects of oxidative stress is best illustrated by the multiple cancers and shortened life span in Prdx1-deficient mice (38). Moreover, hyperactivation of FOXO proteins has been implicated in extending life span (63). Our data suggest that FOXO3 fine tunes cellular homeostasis in response to cellular redox through integration with PRDX1. Because ROS are fundamental in driving the aging process and in the development of cancers, this new mechanism we describe here adds to our understanding of how the evolutionarily conserved FOXO C31 in conjunction with C150 may be instrumental in the regulation of aging and tumor suppression.
Materials and Methods
Cell culture
293T (HEK 293T) and HeLa cells were obtained from ATCC. These cells were grown in DMEM (Mediatech) supplied with 10% heat-inactivated FBS (HyClone), 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 mg/ml streptomycin (Mediatech), and 2 mM l-glutamine (Mediatech) (complete DMEM) in a 37°C incubator supplied with 5% CO2. Prdx1+/+ and Prdx1−/− MEFs were generated as described in Ref. (9) from Prdx1 knockout and parental mice (38) and grown in the same conditions as the 293T. Except when otherwise stated, chemicals used were obtained from Sigma.
Plasmids
pcDNA3-FLAG, pcDNA3-FLAG-HA, pcDNA3-FLAG-FOXO3, and pcDNA3-FLAG-HA-FOXO3 have previously been described (54). Site-directed mutagenesis of FOXO3 plasmids was performed using the Stratagene QuikChange II XL kit (Agilent Technologies) following the manufacturer's guidelines. The oligonucleotides used were designed using the online QuikChange Primer design application (Agilent Technologies) and were synthesized from Integrated DNA Technologies. The pcDNA3-FLAG-HA-FOXO3 plasmid was used as a template to generate all five single C-to-S mutants. Each clone obtained was sequenced with four different sequencing primers to span, with overlaps, the entire coding sequence. To generate the double, quadruple, and quintuple C-to-S mutants, newly synthesized single Cys-to-Ser mutants were used as templates for successive mutagenesis rounds with full-length sequencing after each round. To generate the Cys-to-Ser mutants of pcDNA3-FLAG-FOXO3, the inserts of the several C-to-S mutants of pcDNA3-FLAG-HA-FOXO3 were excised with a BamH1-Xho1 (New England Biolabs) restriction enzyme digestion and cloned into the pcDNA3-FLAG-FOXO3 plasmid, also digested with BamH1 and Xho1 to remove the unmutated FOXO3 insert. shRNA for FOXO3 (NM_001455.x-2766s1c1 clone) was purchased from Sigma. shPRDX1 expression constructs were used as previously described (61).
FOXO3–H2O2 dosage
HEK 293T cells (5 × 105) were transiently transfected with 2 μg pcDNA3-FLAG-HA (EV) or pcDNA3-FLAG-FOXO3 plasmids, using the FuGENE 6 system for 48 h. Cells were serum starved for 30 min and then treated with 0, 25, 100, 250, or 500 μM H2O2 for 30 min. Samples were lysed using a tris lysis buffer (50 mM Tris; 2% Triton X-100; 0.5 mM EDTA; 0.5 mM EGTA; 150 mM NaCl; 10% glycerol; 50 mM NaF; 1 mM NaVO4; 40 mM β-glycerophosphate), supplemented with 30 μg/ml catalase from bovine liver (Sigma), and proteinase inhibitors. Protein concentrations were quantified using the Pierce BCA Protein Assay kit, according to the manufacturer's instructions (Thermo). One milligram of cell lysate was incubated with 20 μl of acid-treated Anti-FLAG M2 Affinity Gel (Sigma) and 400 μl lysis buffer, at 25°C for 3 h, with rotation. Precipitated samples were collected and washed four times with lysis buffer and once with 1 × TBS. Beads were boiled in Laemmli sample buffer (BioRad) in the presence or absence of β-mercaptoethanol (Sigma) for 10 min. Twenty micrograms of whole cell lysate input was prepared in Laemmli sample buffer as above for 5 min.
FOXO3 C-to-S mutant transfection
HEK 293T cells (5 × 105) were transiently transfected with 2 μg EV, pcDNA3-FLAG-FOXO3, or pcDNA-FLAG-HA-FOXO3 constructs containing various C-to-S mutations, using the FuGENE 6 system for 48 h. Cells were serum starved for 30 min and then treated with 0 or 25 μM H2O2. Samples were lysed using the tris lysis buffer detailed above, supplemented with 30 μg/ml catalase from bovine liver (Sigma), and proteinase inhibitors. Protein concentrations were quantified using the BCA protein assay (Thermo). IP of 1000 μg (or 1500 μg for nuclear localization) of cell lysate was processed as detailed above.
PRDX1 C-to-S mutant transfection
HEK 293T cells (5 × 105) were cotransfected with pcDNA-FLAG-FOXO3 and pcDNA3-HA-PRDX1 or pcDNA3-HA-PRDX1 constructs containing various C-to-S mutations using the FuGENE 6 system for 48 h. Cells were serum starved for 30 min and then treated with 0 or 25 μM H2O2. IP samples were prepared as above with 1.5 mg of cell lysate for relative protein quantification.
FOXO3-PRDX1 interaction in MEFs
Confluent Prdx1+/+ and Prdx1−/− MEFs were serum starved for 30 min and then treated with 0, 25, or 250 μM H2O2 for 30 min. Cells were lysed in the aforementioned tris lysis buffer and 80 μg of cell lysate was used for relative protein quantification.
Western blotting
Prepared IP samples and corresponding whole cell lysates were fractionated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane according to the manufacturer (BioRad). Membranes were blocked with 5% BSA in TBS for 30 min and incubated with antibodies against FOXO3 (1:1000; Abcam), P-FOXO3 T32 (1:1000; Cell Signaling), PRDX1 (1:4000; Abcam), PRDX-SO3 (1:500; Abcam), 14-3-3 (1:1000; Cell Signaling), or actin (1:1000; Oncogene) overnight at 4°C. Membranes were washed four times for 5 min in TBST (0.05% Tween-20) and visualized by IR or chemiluminescent detection. For IR processing, membranes were incubated with a 1:15,000 dilution of anti-goat, anti-rabbit, or anti-mouse IRDye (LI-COR) for 30 min at 25°C. Blots were washed with TBST three times and with TBS once, and imaged on an Odyssey (LI-COR) imager. Membranes processed by chemiluminescence were incubated in a 1:10,000 dilution of HRP-conjugated anti-mouse or anti-rabbit antibodies for 1 h at 25°C. Blots were washed four times with TBST for 5 min and exposed to ECL for 1 min.
FOXO3 nuclear localization in 293T cells
Nuclear localization of 5.0 × 104 293T cells transiently transfected with FuGENE 6 for 24 h with 50 ng EGFP-FOXO3 or FOXO3-EGFP C31S or C150S mutants, transferred to complete media for 24 h, serum starved for 1 h, then treated with 100 μM H2O2 or vehicle and 20 μM LY294002 or vehicle for 30 min, fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde for 15 min, and quantified by blinded scoring of triplicate images from three separate experiments using a IX83 microscope (Olympus).
FOXO luciferase assay
FOXO signaling activity was quantified in mouse embryonic fibroblasts or HEK 293T cells utilizing the dual-luciferase Cignal FOXO Luciferase Reporter assay (Qiagen). 2.5 × 105 MEFs were transiently cotransfected with 350 ng Cignal reporter plasmids, 0.5 μg of PRDX1 and FOXO3 or FOXO3 cysteine mutant plasmids, and compared to FOXO3 plus vector control samples. Transfections were performed with FuGENE 6 for 24 h. Luciferase activity was normalized to the internal Renilla control. The effect of oxidative stress on FOXO3 activity was quantified in 293T cells by transfection with 350 ng Cignal reporter plasmid, 50 ng FOXO3, or the FOXO cysteine mutants. Five hundred nanograms of PRDX1 was transfected into the cells 8 h later and incubated for an additional 14 h. Luciferase activity was measured 1.5 h following 30 min of 0–250 μM H2O2 treatment. Dual-luciferase activity was measured in 1 × passive lysis buffer using the manufacturer's protocol (Promega).
Endogenous transcript quantification in 293T cells
293T cells (2.5 × 105) infected with pLKO.1 control or shPRDX1 plasmids were serum starved for 1 h and then treated with 0 or 250 μM H2O2 for 16 h. RNA was isolated utilizing the GeneJET RNA Purification Kit (Thermo Scientific) and converted to cDNA with the qScript cDNA synthesis kit (Quanta Biosciences). SESN3, P27, BIM, SOD2, CAT, and P21 transcripts were quantified by SYBR green real-time PCR (BioRad) relative to YWHAZ control using custom primers (Supplementary Table S1) and accounting for PCR efficiency.
Quantitative real-time-qPCR
Cell lysates were generated with the Cells-to-CT kit (Life Technologies). RT enzymes, individual TaqMan assays, and all PCR enzymes, dyes, and buffers were purchased from Life Technologies and used according to the manufacturer's suggestions. All qPCRs were run on an ABI 7900HT instrument.
Cell viability assay
HEK 293T cells (5 × 105) were transiently transfected with 2 μg pcDNA3-FLAG-FOXO3 plasmids, using the FuGENE 6 system for 24 h. Cells were then trypsinized and then 2 × 104 cells were plated into the wells of a 96-well assay plate. The next day, the cells were treated with 0, 250, or 500 μM H2O2 for 3 h. Viability, cytotoxicity, and apoptosis were then measured using the ApoTox-Glo Triplex Assay (Promega), following the manufacturer's protocol.
Wound healing assay
One million MDA-MB-453 cells were infected with a pLKO.1 shPRDX1 or control construct and then transfected in a 12-well plate with 25 nM let-7 miRIDIAN microRNA hairpin inhibitor (GE Dharmacon) or miRIDIAN microRNA hairpin inhibitor negative control #1 (GE Dharmacon) and 25 nM siGLO Green Transfection Indicator (GE Dharmacon) utilizing 5 μl DharmaFECT 2 transfection reagent (GE Dharmacon) per well. Confluent cultures were scratched with a 10 μl pipette tip in the presence of mitomycin C and photographed after 48 h to measure wound healing. Wound area was quantified with the ImageJ plugin MRI Wound Healing Tool (Volker Bäcker). let-7b expression was used as an indicator of let-7 inhibition. The relative wound area was compared in PRDX1-deficient cells and control cells treated with the let-7 miRIDIAN inhibitor normalized to control microRNA hairpin inhibitor. Average values were compared from four separate experiments + standard error of the mean.
ChIP Assay
293T cells were seeded (4 × 106 cells/dish 150 mm) and 24 h later transfected with EGFP-FOXO3 plasmid (14 μg/dish) by the calcium phosphate method. Forty-eight hours after transfection, complete medium was replaced with serum-free medium for 30 min, followed by H2O2 (100 μM) treatment for 30 min. Cells were crosslinked with 1% formaldehyde for 10 min at 25°C and then the reaction was stopped by addition of glycine to a final concentration of 0.125 M. Crosslinked chromatin was immunoprecipitated with 1 μg of FOXO3 antibody (ab12162; Abcam) as previously described (44). The genomic regions in the host gene and intronic promoter, close to FOXO3 binding sites, were amplified with primers designed by the Primer-Blast NCBI software (www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/tools/primer-blast). The following primer sequences were used: MIR99HG oligo#1 FW: 5′-CTATGCGCCACTCTGTGCAA-3′; MIR99HG oligo#1 RV: 5′-CTAATTACCGCGCACAAGCTG-3′; let-7c intronic prom oligo #2 FW: 5′-GGCATAAACCCGTAGA TCCG-3′; let-7c intronic prom oligo #2 RV: 5′-GAG CTTGTGCGGTCCACTT-3. Quantification of cDNA was performed in triplicate on an Applied Biosystems 7500 Real-Time PCR System SDS v1,2, using the SYBR green dye detection method. ChIP assay results were evaluated by the double delta CT method.
Supplementary Material
Abbreviations Used
- β-ME
beta-mercaptoethanol
- ASK1
apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1
- CAT
catalase
- ChIP
chromatin immunoprecipitation
- co-IP
coimmunoprecipitation
- Cys
cysteine
- EGFP
enhanced green fluorescent protein
- ERp46
endoplasmic reticulum protein 46
- FLAG
FLAG-epitope tag
- FOXO
forkhead box transcription factors of the O class
- HA
human influenza hemagglutinin
- JNK
Jun N-terminal kinase
- MEF
murine embryonic fibroblast
- miRNA
microRNA
- MKP
map kinase phosphatase
- MST
mammalian sterile 20-like kinase 1
- NEM
N-ethylmaleimide
- p21
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor1
- p27
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor1B
- PI3K
phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase
- PRDX
peroxiredoxin
- qPCR
quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- ROS
reactive oxygen species
- SGK
serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1
- sh
small hairpin
- SOD2
superoxide dismutase 2
- STAT3
signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
- UTR
untranslated region
- WT
wild type
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NIH CA131350 and BBA UPITT (CAN), P30CA047904 (UPCI), the Cotswold Foundation postdoctoral fellowship (J.J.S.), and NIH CA131664 (R.K.-F.).
Author Disclosure Statement
No competing financial interests exist.
References
- 1.Bailey CK, Mittal MK, Misra S, and Chaudhuri G. High motility of triple-negative breast cancer cells is due to repression of plakoglobin gene by metastasis modulator protein SLUG. J Biol Chem 287: 19472–19486, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Belguise K, Guo S, and Sonenshein GE. Activation of FOXO3a by the green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces estrogen receptor alpha expression reversing invasive phenotype of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 67: 5763–5770, 2007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Blake DC, Jr, Mikse OR, Freeman WM, and Herzog CR. FOXO3a elicits a pro-apoptotic transcription program and cellular response to human lung carcinogen nicotine-derived nitrosaminoketone (NNK). Lung Cancer 67: 37–47 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Borniquel S, Garcia-Quintans N, Valle I, Olmos Y, Wild B, Martinez-Granero F, Soria E, Lamas S, and Monsalve M. Inactivation of Foxo3a and subsequent downregulation of PGC-1 alpha mediate nitric oxide-induced endothelial cell migration. Mol Cell Biol 30: 4035–4044, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Boyerinas B, Park SM, Hau A, Murmann AE, and Peter ME. The role of let-7 in cell differentiation and cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 17: F19–F36, 2010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J, and Greenberg ME. Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96: 857–868, 1999 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Calnan DR. and Brunet A. The FoxO code. Oncogene 27: 2276–2288, 2008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cancer Genome Atlas N. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 490: 61–70, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cao J, Schulte J, Knight A, Leslie NR, Zagozdzon A, Bronson R, Manevich Y, Beeson C, and Neumann CA. Prdx1 inhibits tumorigenesis via regulating PTEN/AKT activity. EMBO J 28: 1505–1517, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chen X, Ji Z, Webber A, and Sharrocks AD. Genome-wide binding studies reveal DNA binding specificity mechanisms and functional interplay amongst Forkhead transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res 44: 1566–1578, 2016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cinar B, Fang PK, Lutchman M, Di Vizio D, Adam RM, Pavlova N, Rubin MA, Yelick PC, and Freeman MR. The pro-apoptotic kinase Mst1 and its caspase cleavage products are direct inhibitors of Akt1. EMBO J 26: 4523–4534, 2007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Clavel S, Siffroi-Fernandez S, Coldefy AS, Boulukos K, Pisani DF, and Derijard B. Regulation of the intracellular localization of Foxo3a by stress-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in skeletal muscle cells. Mol Cell Biol 30: 470–480, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.D'Ippolito E. and Iorio MV. MicroRNAs and triple negative breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci 14: 22202–22220, 2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dansen TB, Smits LM, van Triest MH, de Keizer PL, van Leenen D, Koerkamp MG, Szypowska A, Meppelink A, Brenkman AB, Yodoi J, Holstege FC, and Burgering BM. Redox-sensitive cysteines bridge p300/CBP-mediated acetylation and FoxO4 activity. Nat Chem Biol 5: 664–672, 2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Davies MJ. Protein oxidation and peroxidation. Biochem J 473: 805–825, 2016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.de Keizer PL, Burgering BM, and Dansen TB. Forkhead box o as a sensor, mediator, and regulator of redox signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal 14: 1093–1106, 2011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Eijkelenboom A. and Burgering BM. FOXOs: signalling integrators for homeostasis maintenance. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 14: 83–97, 2013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Fredlund E, Staaf J, Rantala JK, Kallioniemi O, Borg A, and Ringner M. The gene expression landscape of breast cancer is shaped by tumor protein p53 status and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Breast Cancer Res 14: R113, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fu Z. and Tindall DJ. FOXOs, cancer and regulation of apoptosis. Oncogene 27: 2312–2319, 2008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gutscher M, Sobotta MC, Wabnitz GH, Ballikaya S, Meyer AJ, Samstag Y, and Dick TP. Proximity-based protein thiol oxidation by H2O2-scavenging peroxidases. J Biol Chem 284: 31532–31540, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gyorffy B, Lanczky A, Eklund AC, Denkert C, Budczies J, Li Q, and Szallasi Z. An online survival analysis tool to rapidly assess the effect of 22,277 genes on breast cancer prognosis using microarray data of 1,809 patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 123: 725–731, 2010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hall A, Karplus PA, and Poole LB. Typical 2-Cys peroxiredoxins—structures, mechanisms and functions. Febs J 276: 2469–2477, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ho KK, McGuire VA, Koo CY, Muir KW, de Olano N, Maifoshie E, Kelly DJ, McGovern UB, Monteiro LJ, Gomes AR, Nebreda AR, Campbell DG, Arthur JS, and Lam EW. Phosphorylation of FOXO3a on Ser-7 by p38 promotes its nuclear localization in response to doxorubicin. J Biol Chem 287: 1545–1555, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hu MC, Lee DF, Xia W, Golfman LS, Ou-Yang F, Yang JY, Zou Y, Bao S, Hanada N, Saso H, Kobayashi R, and Hung MC. IkappaB kinase promotes tumorigenesis through inhibition of forkhead FOXO3a. Cell 117: 225–237, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hu X, Guo J, Zheng L, Li C, Zheng TM, Tanyi JL, Liang S, Benedetto C, Mitidieri M, Katsaros D, Zhao X, Zhang Y, Huang Q, and Zhang L. The heterochronic microRNA let-7 inhibits cell motility by regulating the genes in the actin cytoskeleton pathway in breast cancer. Mol Cancer Res 11: 240–250, 2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Imai Y, Takahashi A, Hanyu A, Hori S, Sato S, Naka K, Hirao A, Ohtani N, and Hara E. Crosstalk between the Rb pathway and AKT signaling forms a quiescence-senescence switch. Cell Rep 7: 194–207, 2014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Jagani Z, Singh A, and Khosravi-Far R. FoxO tumor suppressors and BCR-ABL-induced leukemia: a matter of evasion of apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1785: 63–84, 2008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Jarvis RM, Hughes SM, and Ledgerwood EC. Peroxiredoxin 1 functions as a signal peroxidase to receive, transduce, and transmit peroxide signals in mammalian cells. Free Radic Biol Med 53: 1522–1530, 2012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jiang H, Wu L, Mishra M, Chawsheen HA, and Wei Q. Expression of peroxiredoxin 1 and 4 promotes human lung cancer malignancy. Am J Cancer Res 4: 445–460, 2014 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kim SY, Kim TJ, and Lee KY. A novel function of peroxiredoxin 1 (Prx-1) in apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1)-mediated signaling pathway. FEBS Lett 582: 1913–1918, 2008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lehtinen MK, Yuan Z, Boag PR, Yang Y, Villen J, Becker EB, DiBacco S, de la Iglesia N, Gygi S, Blackwell TK, and Bonni A. A conserved MST-FOXO signaling pathway mediates oxidative-stress responses and extends life span. Cell 125: 987–1001, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Liou GY. and Storz P. Reactive oxygen species in cancer. Free Radic Res 44: 479–496, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Madison BB, Jeganathan AN, Mizuno R, Winslow MM, Castells A, Cuatrecasas M, and Rustgi AK. Let-7 represses carcinogenesis and a stem cell phenotype in the intestine via regulation of Hmga2. PLoS Genet 11: e1005408, 2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Mishra R, Thorat D, Soundararajan G, Pradhan SJ, Chakraborty G, Lohite K, Karnik S, and Kundu GC. Semaphorin 3A upregulates FOXO 3a-dependent MelCAM expression leading to attenuation of breast tumor growth and angiogenesis. Oncogene 34: 1584–1595, 2015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Morinaka A, Funato Y, Uesugi K, and Miki H. Oligomeric peroxiredoxin-I is an essential intermediate for p53 to activate MST1 kinase and apoptosis. Oncogene 30: 4208–4218, 2011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Neumann CA, Cao J, and Manevich Y. Peroxiredoxin 1 and its role in cell signaling. Cell Cycle 8: 4072–4078, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Neumann CA. and Fang Q. Are peroxiredoxins tumor suppressors? Curr Opin Pharmacol 7: 375–380, 2007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Neumann CA, Krause DS, Carman CV, Das S, Devendra D, Abraham JL, Bronson RT, Fujiwara Y, Orkin SH, and Van Etten RA. Essential role for the peroxiredoxin Prdx1 in erythrocyte antioxidant defense and tumor suppression. Nature 424: 561–565, 2003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. This reference has been deleted.
- 40.Ni D, Ma X, Li HZ, Gao Y, Li XT, Zhang Y, Ai Q, Zhang P, Song EL, Huang QB, Fan Y, and Zhang X. Downregulation of FOXO3a promotes tumor metastasis and is associated with metastasis-free survival of patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 20: 1779–1790, 2014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pace PE, Peskin AV, Han MH, Hampton MB, and Winterbourn CC. Hyperoxidized peroxiredoxin 2 interacts with the protein disulfide-isomerase ERp46. Biochem J 453: 475–485, 2013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Paik JH, Kollipara R, Chu G, Ji H, Xiao Y, Ding Z, Miao L, Tothova Z, Horner JW, Carrasco DR, Jiang S, Gilliland DG, Chin L, Wong WH, Castrillon DH, and DePinho RA. FoxOs are lineage-restricted redundant tumor suppressors and regulate endothelial cell homeostasis. Cell 128: 309–323, 2007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Panieri E. and Santoro MM. ROS homeostasis and metabolism: a dangerous liason in cancer cells. Cell Death Dis 7: e2253, 2016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Pelosi A, Careccia S, Sagrestani G, Nanni S, Manni I, Schinzari V, Martens JH, Farsetti A, Stunnenberg HG, Gentileschi MP, Del Bufalo D, De Maria R, Piaggio G, and Rizzo MG. Dual promoter usage as regulatory mechanism of let-7c expression in leukemic and solid tumors. Mol Cancer Res 12: 878–889, 2014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Putker M, Vos HR, and Dansen TB. Intermolecular disulfide-dependent redox signalling. Biochem Soc Trans 42: 971–978, 2014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Putker M, Vos HR, van Dorenmalen K, de Ruiter H, Duran AG, Snel B, Burgering BM, Vermeulen M, and Dansen TB. Evolutionary acquisition of cysteines determines FOXO paralog-specific redox signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal 22: 15–28, 2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Rahman M, Jackson LK, Johnson WE, Li DY, Bild AH, and Piccolo SR. Alternative preprocessing of RNA-sequencing data in The Cancer Genome Atlas leads to improved analysis results. Bioinformatics 31: 3666–3672, 2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Rena G, Woods YL, Prescott AR, Peggie M, Unterman TG, Williams MR, and Cohen P. Two novel phosphorylation sites on FKHR that are critical for its nuclear exclusion. EMBO J 21: 2263–2271, 2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Rhee SG. Cell signaling. H2O2, a necessary evil for cell signaling. Science 312: 1882–1883, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Rhee SG, Woo HA, Kil IS, and Bae SH. Peroxiredoxin functions as a peroxidase and a regulator and sensor of local peroxides. J Biol Chem 287: 4403–4410, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Roupe KM, Veerla S, Olson J, Stone EL, Sorensen OE, Hedrick SM, and Nizet V. Transcription factor binding site analysis identifies FOXO transcription factors as regulators of the cutaneous wound healing process. PLoS One 9: e89274, 2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Saleh AD, Savage JE, Cao L, Soule BP, Ly D, DeGraff W, Harris CC, Mitchell JB, and Simone NL. Cellular stress induced alterations in microRNA let-7a and let-7b expression are dependent on p53. PLoS One 6: e24429, 2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Simone NL, Soule BP, Ly D, Saleh AD, Savage JE, Degraff W, Cook J, Harris CC, Gius D, and Mitchell JB. Ionizing radiation-induced oxidative stress alters miRNA expression. PLoS One 4: e6377, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Singh A, Ye M, Bucur O, Zhu S, Tanya Santos M, Rabinovitz I, Wei W, Gao D, Hahn WC, and Khosravi-Far R. Protein phosphatase 2A reactivates FOXO3a through a dynamic interplay with 14–3-3 and AKT. Mol Biol Cell 21: 1140–1152, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Sisci D, Maris P, Cesario MG, Anselmo W, Coroniti R, Trombino GE, Romeo F, Ferraro A, Lanzino M, Aquila S, Maggiolini M, Mauro L, Morelli C, and Ando S. The estrogen receptor alpha is the key regulator of the bifunctional role of FoxO3a transcription factor in breast cancer motility and invasiveness. Cell Cycle 12: 3405–3420, 2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Sobolesky PM, Halushka PV, Garrett-Mayer E, Smith MT, and Moussa O. Regulation of the tumor suppressor FOXO3 by the thromboxane-A2 receptors in urothelial cancer. PLoS One 9: e107530, 2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Sobotta MC, Liou W, Stocker S, Talwar D, Oehler M, Ruppert T, Scharf AN, and Dick TP. Peroxiredoxin-2 and STAT3 form a redox relay for H2O2 signaling. Nat Chem Biol 11: 64–70, 2015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Sun QK, Zhu JY, Wang W, Lv Y, Zhou HC, Yu JH, Xu GL, Ma JL, Zhong W, and Jia WD. Diagnostic and prognostic significance of peroxiredoxin 1 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Oncol 31: 786, 2014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Tang J, Ahmad A, and Sarkar FH. The role of microRNAs in breast cancer migration, invasion and metastasis. Int J Mol Sci 13: 13414–13437, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Thornton JE. and Gregory RI. How does Lin28 let-7 control development and disease? Trends Cell Biol 22: 474–482, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Turner-Ivey B, Manevich Y, Schulte J, Kistner-Griffin E, Jezierska-Drutel A, Liu Y, and Neumann CA. Role for Prdx1 as a specific sensor in redox-regulated senescence in breast cancer. Oncogene 32: 5302–5314, 2013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Tzivion G. and Hay N. PI3K-AKT-FoxO axis in cancer and aging. Biochim Biophys Acta 1813: 1925, 2011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.van der Horst A. and Burgering BM. Stressing the role of FoxO proteins in lifespan and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8: 440–450, 2007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Wang X, Cao L, Wang Y, Wang X, Liu N, and You Y. Regulation of let-7 and its target oncogenes (Review). Oncol Lett 3: 955–960, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Yan L, Zhou J, Gao Y, Ghazal S, Lu L, Bellone S, Yang Y, Liu N, Zhao X, Santin AD, Taylor H, and Huang Y. Regulation of tumor cell migration and invasion by the H19/let-7 axis is antagonized by metformin-induced DNA methylation. Oncogene 34: 3076–3084, 2015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Zhao B, Han H, Chen J, Zhang Z, Li S, Fang F, Zheng Q, Ma Y, Zhang J, Wu N, and Yang Y. MicroRNA let-7c inhibits migration and invasion of human non-small cell lung cancer by targeting ITGB3 and MAP4K3. Cancer Lett 342: 43–51, 2014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Zhou J, Shen W, He X, Qian J, Liu S, and Yu G. Overexpression of Prdx1 in hilar cholangiocarcinoma: a predictor for recurrence and prognosis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8: 9863–9874, 2015 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.