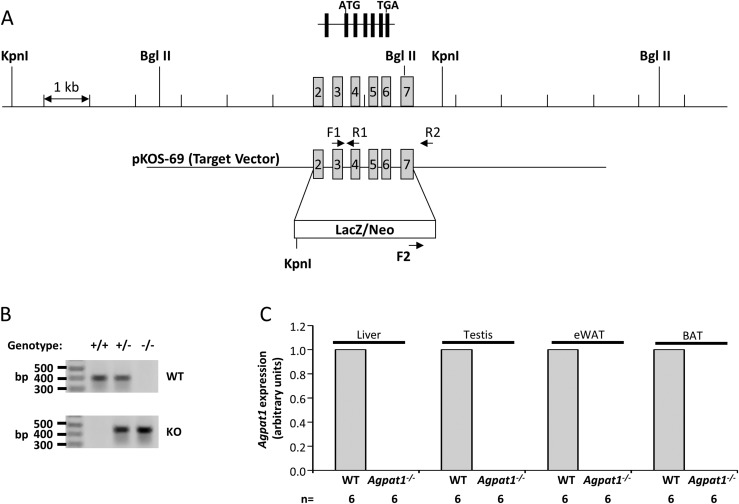
Figure 1.
Strategy for deletion of Agpat1 in the mouse and biochemical confirmation. (A) The WT allele marked with exons 2 to 7 is shown; exon 1 is noncoding in the Agpat1 gene. The homologous gene deletion strategy was such that the β-galactosidase (LacZ) gene was inserted in place of exons 2 to 7. The primers used for amplifying the WT (F1 + R1) and KO (F2 + R2) alleles are marked. (B) The expected genotype for WT, heterozygous, and KO alleles by PCR amplification is shown. The image was cropped from the original image shown as Supplemental Fig. 17 (18.1MB, docx) . The location of the primers used for amplification are noted in (A). (C) Agpat1 mRNA expression in the liver, testis, epididymal white adipose tissue (eWAT), and brown adipose tissue (BAT) of Agpat1−/− mice was undetectable. Six individual samples were analyzed for this assay (n = 6). Agpat1 was normalized to cyclophilin. Primers used for amplification are provided in Supplemental Table 3 (18.1MB, docx) .