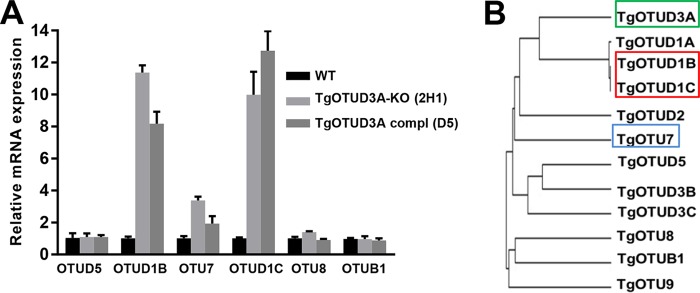
FIG 10 .
Members of the TgOTU family are selectively upregulated in TgOTUD3A-KO parasites, and complementation did not restore wild-type expression. (A) Knockout of TgOTUD3A results in the selective upregulation of specific TgOTUs. Steady-state mRNA expression of unsynchronized wild-type and TgOTUD3A-KO parasites infected for 24 h was quantified using real-time quantitative PCR. Data from quadruplicate samples from 3 independent experiments were analyzed by the ΔΔCT method after being normalized against TgSAG1 expression (template control). The mRNA expression of TgOTU7, one of the other 2 cell cycle-associated TgOTUs (TgOTU5 and TgOTU7), was increased by more than 3-fold. Significantly, the expression of two members of clade D1 TgOTUs (TgOTUD1B and TgOTUD1C) was upregulated 10- to 12-fold. Complemented line D5 (which has a single functional copy of the TgOTUD3A gene) showed an expression profile similar to that of the KO parasites, suggesting a failure of functional complementation even though the complemented gene copy was expressed in a dynamic pattern similar to the expression in the wild type. (B) Phylogenetic analysis revealed that the two significantly upregulated D1 TgOTUs (red box) are phylogenetically among the closest homologs of TgOTUD3A (green box). The position of TgOTU7 in the phylogenetic tree is highlighted by the blue box. Scale bars = 10 µM. Error bars represent standard deviations.