Abstract
Background
The re-establishment of malaria has become an important public health issue in and out of China, and receptivity to this disease is key to its re-emergence. Yingjiang is one of the few counties with locally acquired malaria cases in the China–Myanmar border in China. This study aimed to understand receptivity to malaria in Yingjiang County, China, from June to October 2016.
Methods
Light-traps were employed to capture the mosquitoes in 17 villages in eight towns which were categorized into four elevation levels: level 1, 0–599 m; level 2, 600–1199 m; level 3, 1200–1799 m; and level 4, > 1800 m. Species richness, diversity, dominance and evenness were used to picture the community structure. Similarity in species composition was compared between different elevation levels. Data of seasonal abundance of mosquitoes, human biting rate, density of light-trap-captured adult mosquitoes and larvae, parous rate, and height distribution (density) of Anopheles minimus and Anopheles sinensis were collected in two towns (Na Bang and Ping Yuan) each month from June to October, 2016.
Results
Over the study period, 10,053 Anopheles mosquitoes were collected from the eight towns, and 15 Anopheles species were identified, the most-common of which were An. sinensis (75.4%), Anopheles kunmingensis (15.6%), and An. minimus (3.5%). Anopheles minimus was the major malaria vector in low-elevation areas (< 600 m, i.e., Na Bang town), and An. sinensis in medium-elevation areas (600–1200 m, i.e., Ping Yuan town). In Na Bang, the peak human-biting rate of An. minimus at the inner and outer sites of the village occurred in June and August 2016, with 5/bait/night and 15/bait/night, respectively. In Ping Yuan, the peak human-biting rate of An. sinensis was in August, with 9/bait/night at the inner site and 21/bait/night at the outer site. The two towns exhibited seasonal abundance with high density of the two adult vectors: The peak density of An. minimus was in June and that of An. sinensis was in August. Meanwhile, the peak larval density of An. minimus was in July, but that of An. sinensis decreased during the investigation season; the slightly acidic water suited the growth of these vectors. The parous rates of An. sinensis and An. minimus were 90.46 and 93.33%, respectively.
Conclusions
The Anopheles community was spread across different elevation levels. Its structure was complex and stable during the entire epidemic season in low-elevation areas at the border. The high human-biting rates, adult and larval densities, and parous rates of the two Anopheles vectors reveal an exceedingly high receptivity to malaria in the China–Myanmar border in Yingjiang County.
Keywords: Receptivity, Community structure, Anopheles community, Malaria transmission, Re-establishment, China–Myanmar border
Background
Malaria remains a significant public health problem, especially in Africa and Southeast Asia. Owing to the inception of the World Health Organization (WHO)’s Mekong Malaria Programme a decade ago, the annual malaria incidence and mortality have declined continuously in the Greater Mekong Subregion (GMS) [1–3]. However, among the GMS nations, Myanmar has the heaviest disease burden of malaria and is one of the most threatening foci of malaria in Southeast Asia [4, 5]. The border of Kachin State in Myanmar has a high incidence and mortality rate of malaria [6]. It is thus crucial to assess the risk of malaria re-establishment in this border to allow the relevant departments in the region to develop optimal elimination strategies, since China and the GMS counties aim at malaria elimination by 2020 and 2030, respectively [7].
The infectivity-receptivity-vulnerability framework is an important method to assess the risk of malaria re-establishment in many countries [8–12]. The framework defines receptivity as the presence, distribution, seasonal abundance and bionomics of the potential vector [8, 9, 12]. Control of malaria transitions depends on integrated actions [7], and according to “A framework for malaria elimination” announced by the WHO, receptivity is a key point to malaria re-emergence [13]. Considering the high cost of measuring receptivity in an area, it is systematically difficult to obtain first-hand data on receptivity in the China–Myanmar border.
In China, malaria is being rapidly eliminated [7, 14, 15], which has been mainly attributed to malaria control in the China–Myanmar border in Yunnan Province. In 2014 and 2015, Yingjiang County was one of the few counties to report malaria transmission. In 2016, it was the only county to report locally acquired malaria cases in the border. Therefore, it is specifically important to determine receptivity to malaria in this county.
In Southeast Asia, including China and Myanmar, deforestation and cultivation of cash crops (such as banana, rubber, and maize) constitute the most important environmental changes in rural areas [16–18]. For example, field investigation and interview of the local primary public health care provider revealed that the main crop of these regions was rice, which occupied approximately 2 million square kilometres in Na Bang town, Yingjiang County, before 2005. After 2005, banana was grown as the main crop in these regions. Until early 2016, the area of banana production had increased to > 3 million square kilometres, and no rice crops were left. These changes may have led to alterations in the population density, life history [19], and behaviour of vectors such as laying eggs [20]. This change in ecotope in the China–Myanmar border may have resulted to change in receptivity to malaria in the region.
The main malaria vectors in the China–Myanmar border are Anopheles minimus and Anopheles sinensis [5, 19, 21, 22]; the major vectors in China are An. sinensis, Anopheles lesteri, Anopheles dirus, and An. minimus [23, 24]. In recent years, An. minimus in these areas has become the focus of research. Several studies investigated the ecological features of malaria vectors, including species composition and population dynamics, density, human blood index, proportion of sporozoites, and environmental factors (e.g., land use and land cover changes) [6, 18, 19, 21]. These studies provided valuable information for generating targeted intervention strategies for malaria control and elimination along the border areas. However, the community structure of Anopheles mosquitoes at different elevations in the border remains unknown. Moreover, the seasonal receptivity in the county, especially the seasonality of the human-biting rate and larval density, has not been well investigated in recent years.
Therefore, this study aimed to collect mosquitoes from 17 villages in eight towns in Yingjiang County at different elevations; analyse the community structure by species richness, diversity, dominance, and evenness [6, 25–32]; and examine receptivity to major malaria vectors (An. minimus and An. sinensis) in the China–Myanmar border.
Methods
Study area
Yingjiang County (24°24ʹ to 25°20ʹN, 97°31ʹ to 98°16ʹE), located in the west of Yunnan Province, has a population of > 0.3 million, includes 15 towns and 103 villages, and has a boundary line of 214.6 km. Its climate is warm and humid at low altitudes and cold at high altitudes. The main cash crops are rice, banana, coffee, sugarcane, and maize. Buffalo, yellow cattle, pigs, and dogs are also common. This variety in climate, ecology, and environment makes the county favourable for malaria vectors.
Two towns (Na Bang and Ping Yuan) in the county were selected as sentinel sites from June to October 2016. Na Bang, bordering on Myanmar and located west of the county, has a boundary line of 20.5 km and has nine villages, with a total population of 1751. The main cash crop is banana. The town has a tropical-subtropical climate and a low elevation, with the lowest elevation of 210 m. The average annual temperature is 22.7 °C, and the average annual precipitation is 2655 mm. Ping Yuan, the capital town of the county, has a population of 53.5 thousand and has 85 villages. Its main cash crop is rice, and its elevation is 937 m.
In this study, 17 villages in eight towns were included and categorized into four levels according to the elevation of the study sites (Fig. 1): level 1, 0–599 m; level 2, 600–1199 m; level 3, 1200–1799 m; and level 4, > 1800 m (Table 1). In May and October 2016, a cross-sectional study was conducted on the community structure of Anopheles mosquitoes in the 17 villages. To determine the seasonal abundance of mosquitoes, the human-biting rate (ma) [19], density of light-trap-captured adult mosquitoes and larvae, parous rate [20], and height distribution (density) of An. minimus and An. sinensis were investigated in Na Bang and Ping Yuan each month from June to October 2016 (Table 2).
Fig. 1.
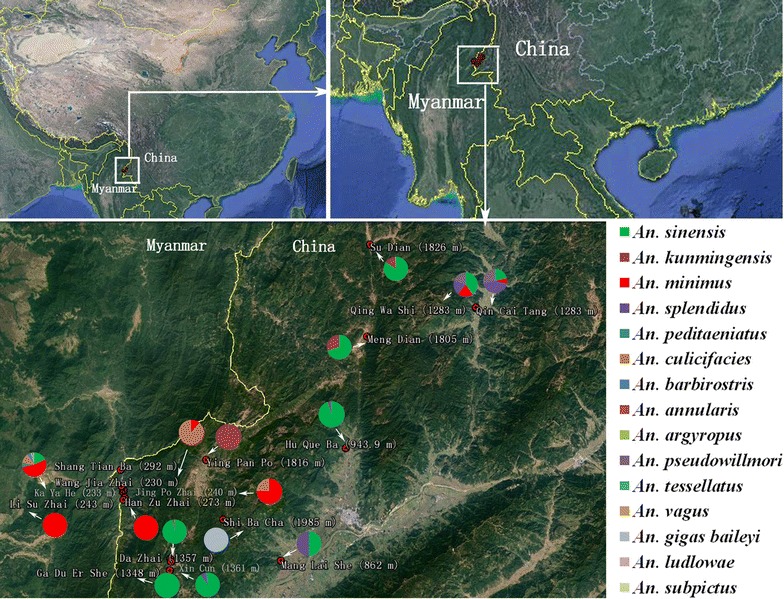
Locations of study sites and a pie-chart showing Anopheles distribution (percentage) in Yingjiang County. (No Anopheles mosquito was captured in Shang Tian Ba.)
Table 1.
Global positioning system information of selected survey sites at different elevations
| Elevation levels | Town | Village | Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (0 m ~) | Na Bang | Ka Ya He | 24.72171 | 97.569687 |
| Jing Po Zhai | 24.724932 | 97.570903 | ||
| Wang Jia Zhai | 24.7302 | 97.567 | ||
| Han Zu Zhai | 24.713553 | 97.573415 | ||
| Li Su Zhai | 24.710657 | 97.571707 | ||
| Shang Tian Ba | 24.753889 | 97.563333 | ||
| 2 (600 m ~) | Ping Yuan | Hu Que Ba | 24.809265 | 97.924073 |
| Tai Ping | Mang Lai She | 24.639444 | 97.832944 | |
| 3 (1200 m ~) | Zhi Na | Qing Wa Shi | 25.02815 | 98.117844 |
| Qin Cai Tang | 25.026906 | 98.118117 | ||
| Tong Bi Guan | Xin Cun | 24.631647 | 97.657962 | |
| Ga Du Er She | 24.614827 | 97.65857 | ||
| Da Zhai | 24.627342 | 97.659831 | ||
| 4 (1800 m ~) | Tai Ping | Shi Ba Cha | 24.694127 | 97.738692 |
| Meng Nong | Meng Dian | 24.97327 | 97.945571 | |
| Su Dian | Su Dian | 25.108227 | 97.939872 | |
| Xi Ma | Ying Pan Po | 24.777837 | 97.703559 |
Table 2.
Height distribution of malaria vectors in selected towns in Yingjiang County
| Elevation levels | Town | Number of villages | Number of light-trap nights |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (0 m ~) | Na Bang | 6 | 92 |
| 2 (600 m ~) | Ping Yuan | 1 | 77 |
| Tai Ping | 1 | 4 | |
| 3 (1200 m ~) | Zhi Na | 2 | 5 |
| Tong Bi Guan | 3 | 4 | |
| 4 (1800 m ~) | Tai Ping | 1 | 3 |
| Meng Nong | 1 | 2 | |
| Su Dian | 1 | 2 | |
| Xi Ma | 1 | 2 | |
| Total | 17 | 191 |
Mosquito collection and species identification
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) light-traps without bait were used to capture mosquitoes. After transport to the laboratory, the mosquitoes were morphologically separated as Anopheles, Culex, Aedes, and other subfamilies or genera [6]. Anopheles mosquitoes were further morphologically sorted according to their species [6, 21]. After identifying the samples, each mosquito was kept in a cryogenic vial (Corning Inc., NY, USA) using 75% alcohol and stored in a − 20 °C freezer immediately to prepare for DNA extraction and identification using multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The DNA of An. minimus groups and the Hyrcanus Group were extracted from legs or wings of each mosquito for further species confirmation [33, 34].
Human-biting rate
In each sentinel town, two survey sites (inner and outer) in each village were used for surveillance of the human-biting rate of An. minimus and An. sinensis. Although the human-landing catch (HLC) is the gold standard for monitoring mosquitoes that bite humans [35–37], it is labour intensive, cumbersome, and hazardous and requires intense supervision [38]. Alternatively, the human-baited double-net (HDN) trap is a simple and cheap method to estimate the human-biting rate outdoors without exposing collectors to vector bites [39]; and so far the best-performing trap, with similar efficiency to HLC. In this study, the human-biting rate of An. minimus and An. sinensis was monitored for 10 nights in four houses using the HDN trap from June to October 2016. One local volunteer was employed to rest inside a small bed net and was consequently fully protected from mosquitoes for the whole night’s duration. A larger bed net was hung over the smaller net and raised 30 cm above the ground. Both nets were protected from the elements by plastic-sheeting roof, but were not treated with any insecticide. One specialized person captured the mosquitoes from inside and outside the larger bed net per hour from 2000 to 0700 h. The species were then identified in the laboratory, and the number of captured mosquitoes was recorded at each survey site to calculate the human-biting rate.
Seasonal abundance of adult mosquitoes
The vectors in human bedrooms and cattle shelters were captured using CDC light-traps from June to October 2016, and the seasonal abundance in terms of density (per light-trap per night) of An. minimus and An. sinensis was calculated accordingly. In each village, four light-traps were hung separately in two human bedrooms and two cattle shelters per night, from 2000 to 0700 h of the next day. In each month, vectors were captured twice on two nights at the same place.
Density of larvae
All kinds of breeding sites (bogs, slow-flowing water bodies, rice paddies, pools, and ditches) of the two vectors were surveyed in the two towns each month during the survey season. Standard dippers with approximately 500 mL volume were used to collect larvae from the water bodies [40]. Ten dips of water were taken to determine the presence of anophelines. If anophelines were present, the larvae in the 10 dips were collected in a small bottle with some water. The bottles were then numbered and transported to the laboratory to count the number of first-, second-, third-, and fourth-instar larvae and pupae of the two vectors [41]. The species of late third- and fourth-instar anopheline larvae were identified under a microscope using commonly accepted guidelines [42]. The identified larvae were preserved in a cryogenic vial (Corning Inc.) containing 75% alcohol for further identification by PCR. The density of larvae (per 10 dips) was calculated accordingly. Additionally, the pH value and location of the breeding sites were surveyed to analyse the relationship between these factors and the density of larvae.
Parous rate
Landing collections were performed by collecting An. minimus and An. sinensis in cattle shelters in Na Bang and Ping Yuan each month, from 2130 to 2200 h per night. Mosquitoes were collected by four collectors using an aspirator. The collected mosquitoes were transported to the laboratory of Yingjiang CDC, where they were killed using chloroform and dissected using minute dissection needles to collect their ovaries. The ovaries were separated from the other internal organs (including the Malpighian tubules and stomach) and teased apart at approximately 40× magnification through a dissection microscope to confirm whether the mosquitoes had laid eggs. The parous rate was calculated accordingly.
Height distribution
The height of each site in the 17 villages of the eight towns, where a light-trap was hung, was recorded using a handset global positioning system (Garmin International Inc., Olathe, KS, USA) to analyse the relationship between the height and the density of the two vectors. The lowest elevation was 210 m in Na Bang town, and the highest was approximately 2000 m in Shi Ba Cha village in Tai Ping town. As mentioned, the towns were divided into four levels. Besides the two sentinel towns, six towns were selected at different elevation levels. The same mosquito-capturing method was adopted as the one used for investigating the seasonal abundance of adult mosquitoes. Thereafter, the captured mosquitoes were transported to the laboratory to confirm whether they were the target vectors.
Data analysis
Species richness of Anopheles mosquitoes was measured using the index N, which represents the number of species [6]. Species dominance was measured by the Berger–Parker dominance index d, which was equal to the fraction of a species with a majority proportion in the study site or area [6]. Species diversity and evenness were evaluated by three indices—Simpson diversity index D, Shannon diversity index H, and evenness index E [25–32]. Similarity among different elevation levels was measured using the Morisita–Horn similarity index C [32–43]. The indices D and H were calculated from the proportion of each species; E, also known as Shannon’s equitability, was calculated by dividing H by richness; and C was calculated by the number of individuals of each species and the total number of mosquitoes [43]. These indices were represented by the following equations:
where N is the richness index, p i is the proportion of a species that belongs to the ith species, n ji is the number of individuals of a species i in an area j, and M j is the number of individuals in an area j.
In the cross-sectional study, the light-trap density (females/trap/night), N, D, H, d, and E were evaluated to determine the community structure of Anopheles mosquitoes in the 17 villages, and C was used to measure the similarity among different elevation areas. The community-structure indicators were used to examine the population dynamics at the two surveillance sites.
Microsoft Excel 2010 (Microsoft Corp., USA) was employed to represent the data. Data analysis was performed using SPSS 13.0 software. Differences between larvae and pH value of water were calculated using the Pearson correlation test and Chi square test. Differences between population density and height were calculated using the Pearson correlation test and curve fitting of the statistical model with observed data.
Results
Community structure and population dynamics of Anopheles mosquitoes
Over the study period, 191 trap nights were conducted, and 56,834 mosquitoes were collected in 17 villages. The majority of captured mosquitoes were Culex (45,180, 79.5%), followed by Anopheles (10,053, 17.7%), Aedes (1430, 2.5%), and other subfamilies or genera (171, 0.3%). Fifteen Anopheles species were identified and observed in the samples: An. sinensis (75.4%), Anopheles kunmingensis (15.6%), and An. minimus (3.5%), followed by 12 other Anopheles species (5.5%) (Table 3). The Anopheles distribution in each village is shown in Fig. 1.
Table 3.
Anopheles species composition by elevation and pooled across study sites and study period
| Species | Composition by elevation | Pooled | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 m ~ | 600 m ~ | 1200 m ~ | 1800 m ~ | n | % | |
| An. sinensis | 16.91 | 95.29 | 91.99 | 17.96 | 7579 | 75.39 |
| An. kunmingensis | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 81.58 | 1572 | 15.64 |
| An. minimus | 51.20 | 0.36 | 0.89 | 0.00 | 351 | 3.49 |
| An. splendidus | 0.64 | 3.07 | 4.09 | 0.00 | 240 | 2.39 |
| An. culicifacies | 16.43 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 104 | 1.03 |
| An. peditaeniatus | 5.74 | 0.91 | 0.71 | 0.05 | 104 | 1.03 |
| An. barbirostris | 4.63 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 30 | 0.30 |
| An. annularis | 0.00 | 0.19 | 0.89 | 0.00 | 18 | 0.18 |
| An. argyropus | 1.44 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 14 | 0.14 |
| An. pseudowillmori | 0.00 | 0.06 | 1.42 | 0.00 | 12 | 0.12 |
| An. tessellatus | 1.59 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 10 | 0.10 |
| An. vagus | 1.44 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 9 | 0.09 |
| An. gigas baileyi | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.42 | 8 | 0.08 |
| An. ludlowae | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1 | 0.01 |
| An. subpictus | 0.00 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1 | 0.01 |
The area with a level 1 elevation had the lowest Anopheles density (6.82 females/trap/night) and dominance index (d = 0.51), but the highest Simpson diversity index (D = 0.68), Shannon diversity index (H = 1.47), and evenness index (E = 0.67) (Table 4). Furthermore, the richness index (N = 9) in such area was lower than that of a level 2 area, but higher than those of level 3 and 4 areas. A level 2 area had the highest species richness index (N = 11) and dominance index (d = 0.95), but the lowest diversity indices D (0.09) and H (0.24) and evenness index E (0.10). Compared with a level 1 area, level 3 and 4 areas had lower N, D, H and E indices but higher d index. Among all Anopheles species, An. minimus, An. sinensis, and An. kunmingensis showed the highest proportion in areas of elevation levels 1, 2/3, and 4, respectively.
Table 4.
Population density and community structure of Anopheles mosquitoes at each elevation level
| Elevation (m) | Density (f/t/n) | N | Diversity index | d | E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | H | |||||
| 0 ~ | 6.82 | 9 | 0.68 | 1.47 | 0.51 | 0.67 |
| 600 ~ | 85.64 | 11 | 0.09 | 0.24 | 0.95 | 0.10 |
| 1200 ~ | 62.44 | 6 | 0.15 | 0.39 | 0.92 | 0.22 |
| 1800 ~ | 214.11 | 4 | 0.30 | 0.50 | 0.82 | 0.36 |
f/t/n, females/trap/night; N, species richness; D, Simpson diversity index; H, Shannon diversity index; d, dominance index; E, evenness index
Similarity analysis showed that the species composition of level 2 and 3 areas had the highest similarity (Morisita–Horn index C = 0.999), but any other two level areas showed low similarities (Morisita–Horn index C range, 0.059–0.274) (Table 5). The results of the two surveillance sites showed that the major Anopheles species in Na Bang was An. minimus, followed by An. sinensis (Table 6). In Na Bang, the pooled density of the entire study season was 6.82 females/trap/night, with a peak of 13.06 females/trap/night in June. Moreover, Na Bang had the highest N (8), D (0.75), H (1.66), and E (0.8) indices in September, but the highest d (0.67) index in June. All indicators of community structure in Na Bang showed a low variation during the season. In contrast, a large variation in these parameters was observed in Ping Yuan. The pooled density of the entire study season was 89.99 females/trap/night, with a peak of 244.60 females/trap/night in August. Additionally, the highest N (9), D (0.69), and H (1.46) indices were observed in October, but the highest d (0.98) index was observed in August, and the highest E (0.70) index in May (Fig. 2).
Table 5.
Similarity in species composition between different elevations
| 0 m ~ | 600 m ~ | 1200 m ~ | 1800 m ~ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 m ~ | 1 | |||
| 600 m ~ | 0.266 | 1 | ||
| 1200 m ~ | 0.274 | 0.999 | 1 | |
| 1800 m ~ | 0.059 | 0.213 | 0.214 | 1 |
Table 6.
Anopheles species composition by month
| Town | Species | May | June | July | August | September | October | Pooled | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | ||||||||
| NB | An. minimus | 33.33 | 66.99 | 63.89 | 65.25 | 8.54 | 17.86 | 321 | 51.20 |
| An. sinensis | 5.56 | 19.62 | 10.19 | 5.93 | 42.68 | 16.07 | 106 | 16.91 | |
| An. culicifacies | 61.11 | 6.70 | 12.04 | 12.71 | 7.32 | 39.29 | 103 | 16.43 | |
| An. peditaeniatus | 0.00 | 1.91 | 0.00 | 7.63 | 13.41 | 21.43 | 36 | 5.74 | |
| An. barbirostris | 0.00 | 2.87 | 6.48 | 1.69 | 15.85 | 1.79 | 29 | 4.63 | |
| An. tessellatus | 0.00 | 1.44 | 1.85 | 3.39 | 1.22 | 0.00 | 10 | 1.59 | |
| An. vagus | 0.00 | 0.00 | 3.70 | 3.39 | 1.22 | 0.00 | 9 | 1.44 | |
| An. argyropus | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 9.76 | 1.79 | 9 | 1.44 | |
| An. splendidus | 0.00 | 0.48 | 1.85 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.79 | 4 | 0.64 | |
| PY | An. sinensis | 54.55 | 94.60 | 97.23 | 97.75 | 94.37 | 45.95 | 6606 | 95.34 |
| An. splendidus | 36.36 | 4.01 | 1.19 | 1.10 | 4.35 | 29.73 | 209 | 3.02 | |
| An. peditaeniatus | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.02 | 1.07 | 10.81 | 63 | 0.91 | |
| An. minimus | 6.82 | 0.77 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 4.05 | 25 | 0.36 | |
| An. annularis | 2.27 | 0.15 | 1.19 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 13 | 0.19 | |
| An. argyropus | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.26 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 2.70 | 5 | 0.07 | |
| An. pseudowillmori | 0.00 | 0.31 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 2.70 | 4 | 0.06 | |
| An. barbirostris | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.35 | 1 | 0.01 | |
| An. ludlowae | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.35 | 1 | 0.01 | |
| An. culicifacies | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.35 | 1 | 0.01 | |
| An. subpictus | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1 | 0.01 | |
NB Na Bang, PY Ping Yuan
Fig. 2.
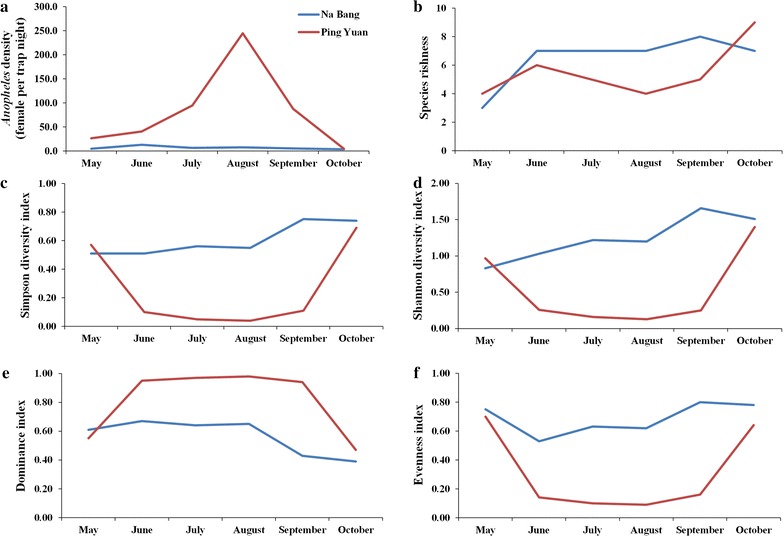
Population dynamics of Anopheles mosquitoes at two study sites in Yingjiang County, May–October 2016. a Pooled population density (females/trap/night) of all Anopheles species. b Species richness. c Simpson diversity index. d Shannon diversity index. e Dominance index. f Evenness index
Human-biting rate
The human-biting rate of An. minimus was 1.4/bait/night at the inner survey site, but 5.2/bait/night at the outer survey site in Na Bang from June to October 2016. Meanwhile, the human-biting rate of An. sinensis was 0/bait/night in Na Bang, irrespective of the location. At the inner site, the peak human-biting rate of An. minimus was in June, with 5/bait/night (Table 7). However, at the outer site, although the human-biting rate of An. minimus was 9/bait/night in June, the peak was 15/bait/night (Fig. 3). Anopheles minimus was more likely to attack at 0100 and 0400 h at the inner site, but only at 0400 h at the outer site (Fig. 3).
Table 7.
Human-biting rate of An. minimus and An. sinensis in Na Bang and Ping Yuan from June to October 2016
| Towns | Location | Number of bait | Number of night | Number of An. minimus | Number of An. sinensis | ma of An. minimus (per bait per night) | ma of An. sinensis (per bait per night) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na Bang | Inner village | 1 | 5 | 7 | 0 | 1.4 | 0 |
| Outer village | 1 | 5 | 26 | 0 | 5.2 | 0 | |
| Ping Yuan | Inner village | 1 | 5 | 0 | 13 | 0 | 2.6 |
| Outer village | 1 | 5 | 0 | 23 | 0 | 4.6 |
Fig. 3.
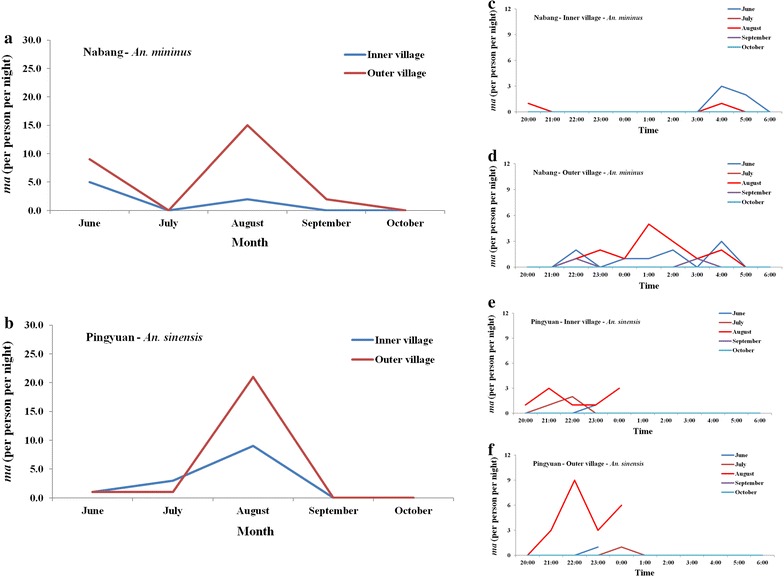
Seasonality of human-biting rate of Anopheles minimus and Anopheles sinensis in two surveillance sites. a Human-biting rate of An. minimus at the inner and outer village sites of Na Bang from June to October 2016. b Human-biting rate of An. sinensis at the inner and outer village sites of Ping Yuan from June to October 2016. c Human-biting rate (per hour) of An. minimus at the inner village site of Na Bang. d Human-biting rate (per hour) of An. minimus at the outer village site of Na Bang. e Human-biting rate (per hour) of An. sinensis at the inner village site of Ping Yuan. f Human-biting rate (per hour) of An. sinensis at the outer village site of Ping Yuan. Data on the human-biting rate in Ping Yuan were only collected at 23:00 h in June and 24:00 h in August because of intense rainfall on those nights
In Ping Yuan, the human-biting rate of An. minimus was 0/bait/night, irrespective of the location. However, the human-biting rate of An. sinensis was 2.6/bait/night at the inner site and 4.6/bait/night at the outer site. The peak human-biting rate of An. sinensis was in August, with 9/bait/night at the inner site and 21/bait/night at the outer site (Fig. 3). Anopheles sinensis was more likely to attack at 2100 and 2400 h at the inner site and 2200 and 2400 h at the outer site (Fig. 3).
Seasonal abundance of adult mosquitoes
In Na Bang, the major vector was An. minimus. Its peak density was observed in human bedrooms in May (5 females/trap/night) and in cattle shelter in June (13.25 females/trap/night). There were two peaks (June and September) of An. sinensis in cattle shelters in the town, with densities of 4.5 females/trap/night and 4.25 females/trap/night, respectively. However, in human bedrooms, the density of An. sinensis decreased from May to October.
In Ping Yuan, the major vector was An. sinensis, the peak density of which was found in cattle shelters in August (422 females/trap/night) and in human bedrooms in September (140.25 females/trap/night). However, the density of An. minimus was low, and the seasonality of this vector was not evident in the town (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4.
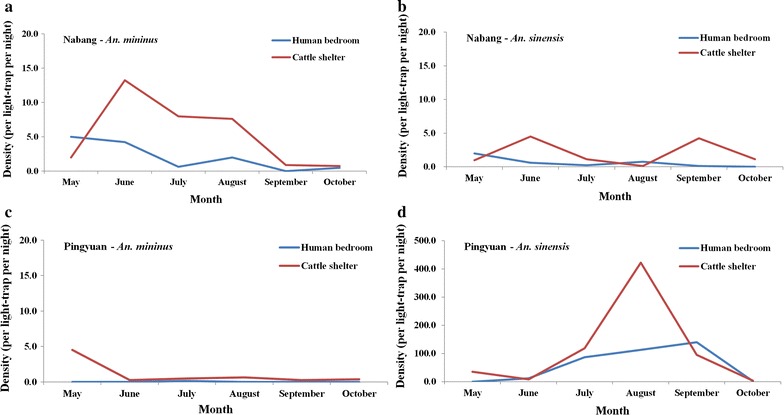
Seasonality of trap-captured Anopheles minimus and Anopheles sinensis at the two surveillance sites. a Density of An. minimus in human bedrooms and cattle shelters in Na Bang. b Density of An. sinensis in human bedrooms and cattle shelters in Na Bang. c Density of An. minimus in human bedrooms and cattle shelters in Ping Yuan. d Density of An. sinensis in human bedrooms and cattle shelters in Ping Yuan
Density of larvae
The seasonality of An. minimus larvae was evident in Na Bang, with a density of 7.5/10 dips. Meanwhile, the peaks of An. sinensis—in Na Bang were in June and September, with densities of 5.5/10 dips and 4.8/10 dips, respectively. Ping Yuan had a lower density of both vectors, and the density of An. sinensis decreased during the investigation season. No larva of An. minimus was detected in Ping Yuan during the investigation (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5.
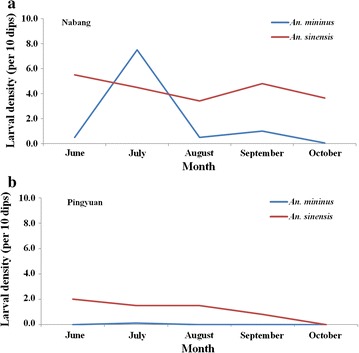
Seasonal abundance of larval density of Anopheles minimus and Anopheles sinensis at two surveillance sites. a Larval density in Na Bang. b Larval density in Ping Yuan
A total of 87 samples were collected from different water bodies. There was a significant difference between the larvae of An. minimus and pH of the water samples surveyed (χ 2 = 4.721, P = 0.030; Table 8). In contrast, no significant difference existed between the larvae of An. sinensis and pH value of the water samples surveyed (χ 2 = 0.001, P = 0.976). However, the density of the larvae was negatively correlated with the pH value; the correlation coefficient (r = − 0.297, P = 0.005) was calculated by the Pearson correlation test. Water samples with low pH showed a high density of An. sinensis larvae (Fig. 6).
Table 8.
Relationship between pH value and larvae of the two vectors
| pH < 7.0 | pH > 7.0 | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| An. minimus | 40 | 47 | 87 |
| Positive | 9 | 3 | 12 |
| Negative | 31 | 44 | 75 |
| An. sinensis | 40 | 47 | 87 |
| Positive | 20 | 26 | 46 |
| Negative | 20 | 21 | 41 |
Fig. 6.
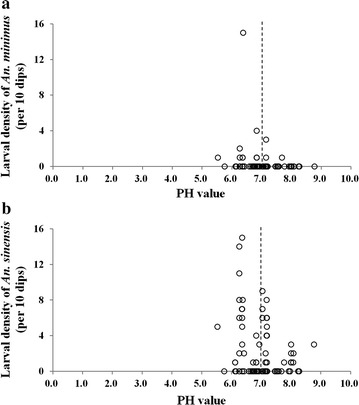
pH value and larval density of Anopheles minimus and Anopheles sinensis in Yingjiang County. a An. minimus. b An. sinensis
Parous rate
In this study, 283 An. sinensis mosquitoes captured in cattle shelters were dissected, among which 256 (90.46; 95% confidence interval, 87.04–93.88%) had laid eggs. Fifteen An. minimus mosquitoes captured in cattle shelters were also dissected, among which 14 (93.33; 95% confidence interval, 80.26–100.00%) had laid eggs.
Height distribution
191 trap nights were performed to capture mosquitoes in eight towns (Table 2). Analysis of data revealed that the density of An. minimus decreased with an increase in area elevation, irrespective of the location of collection (human bedroom: r = − 0.441, P = 0.000; livestock building: r = − 0.297, P = 0.003). A linear model may represent the relationship between the density and height. After analysing the data of 90 densities of captured An. minimus and the related height values, the model in human bedrooms was y = 2.009 − 0.02x (R 2 = 0.194, P = 0.000), where y and x indicate the density of An. minimus and elevation of the area, respectively. After analysing the data of 101 densities of captured An. minimus and the related height values, the model in cattle shelters was y = 6.147 − 0.005x (R 2 = 0.088, P = 0.003).
The density of An. sinensis increased with an elevation < 1200 m but decreased with > 1200 m (Table 9). A quadratic model could be used to represent the relationship between the density and height. Analysis of 90 densities of captured An. sinensis and the related height values showed that the model in human bedrooms was y = − 21.017 + 0.09x + 0.000029x 2 (R 2 = 0.199, P = 0.000), where y and x indicate the density of An. sinensis and height, respectively. Analysing 101 light-trap-captured densities of An. sinensis and the related height values also revealed the following model in cattle shelters: y = − 77.444 + 0.373x + 0.000177x 2 (R 2 = 0.100, P = 0.006).
Table 9.
Density of An. minimus and An. sinensis at different elevations
| Elevation (m) | Number of light-traps | Number of An. minimus | Density of An. minimus (per light-trap per night) | Number of An. sinensis | Density of An. sinensis (per light-trap per night) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human bedroom | 0 ~ | 46 | 76 | 1.65 | 16 | 0.35 |
| 600 ~ | 40 | 1 | 0.03 | 1387 | 34.68 | |
| 1200 ~ | 3 | 0 | 0.00 | 293 | 97.67 | |
| 1800 ~ | 1 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| Total | 90 | 77 | 0.86 | 1696 | 18.84 | |
| Cattle shelter | 0 ~ | 46 | 252 | 5.48 | 89 | 1.93 |
| 600 ~ | 41 | 24 | 0.59 | 5223 | 127.39 | |
| 1200 ~ | 12 | 5 | 0.42 | 570 | 47.50 | |
| 1800 ~ | 2 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | |
| Total | 101 | 281 | 2.78 | 5882 | 58.24 |
Discussion
Although some studies have focused on community structure and receptivity to malaria in the China–Myanmar border (especially in the low-elevation areas) [6, 18, 21, 22], this study focused on other aspects to better understand Anopheles ecological features. Firstly, this study investigated the Anopheles distribution and found different community structure models at different elevation levels. The relationship between An. minimus density and elevation fitted well on a linear equation with one unknown model, but that between An. sinensis density and elevation fitted well on a quadratic equation with one unknown model. Secondly, this study found that high density, human-biting rate, and parous rate may lead to high receptivity to malaria in the border area. Finally, the slightly acidic water suited the growth of the two vectors.
The results of this study showed that the community structure of Anopheles was highly complex in areas below an elevation of 600 m. In these areas, the diversity indices D and H and the evenness index E were the highest, and the species richness index was also high up to 9. Although An. minimus was the major malaria vector in these areas, it was only 51% of the total Anopheles mosquitoes, which made the dominance index to be lowest among the four elevation level. Additionally, the proportion of An. sinensis and Anopheles culicifacies was as high as 16%. These results were slightly different with those of Yu et al. and Wang et al. [6, 21]. They reported that the first three predominant Anopheles species were An. minimus, An. maculatus, and An. culicifacies, with An. sinensis only accounting for < 4% [6]. These differences might be due to the different study years, changes in main cash crops, and different types of mosquito capture sites. Until early 2016, banana totally replaced rice and become the dominant cash crop in Na Bang. Furthermore, while Yu et al. and Wang et al. captured adult mosquitoes in human bedrooms, we captured mosquitoes in both human bedrooms and cattle shelters. Anopheles minimus belongs to four high-transmission-potential vectors in China, the rest being An. sinensis, An. lesteri, and An. dirus [23, 24]. Anopheles sinensis is a major malaria vector in China, especially northern China [23, 24], India [44, 45], Sri Lanka [46], and Iran [47]. The results of the cross-seasonal surveillance showed that the community structure was stable during the study season in the China–Myanmar border. Therefore, choosing the specific vector-control measures was more difficult in this region than in other elevation level because different targeted control measures were based on different ecological features.
The dominant species in the Anopheles community was An. sinensis at an elevation of 600–1800 m, with a dominance index > 0.9, indicating absolute predominance of the vector in the area. The results of the cross-seasonal surveillance in Ping Yuan showed that the density of Anopheles mosquitoes peaked from June to September and > 94% of them were An. sinensis, indicating low diversity and evenness during that period. The highest similarity was observed between areas with elevations of 600–1199 and 1200–1799 m, suggesting that these two areas could be combined into one area, with the target vector to control being An. sinensis. Although An. sinensis prefers biting animals such as cattle or water buffalo over humans [48, 49], its extremely high density in the area could lead to a high probability of malaria transmission. Latest research using membrane feeding assay under laboratory conditions demonstrated that the susceptibility of An. sinensis to Plasmodium vivax is similar to that of Anopheles anthropophagus [24]. In addition, P. vivax is a major parasite of malaria in the China–Myanmar border [50, 51]. Therefore, specific vector-control countermeasures aimed at An. sinensis should be strengthened in the region in case of the re-establishment of malaria.
High elevation of > 1800 m was correlated with low species richness, diversity, and evenness in the area. Anopheles kunmingensis was the major Anopheles mosquito in the high-elevation areas (> 1800 m). One study reported An. kunmingensis as the main malaria vector based on its indoor abundance, relatively high human-biting rate, and the finding of a sporozoite-positive specimen during a peak malaria season in Tengchong County, Yunnan Province, China [52]. However, the role of mosquitoes in transmission of malaria, especially in susceptibility to Plasmodium and receptivity to malaria, remains uncertain. Therefore, further research on Anopheles mosquitos is required to determine the integrated aspects of malaria transmission.
The results of this study further revealed that the human-biting rate of An. minimus was remarkably high in Na Bang, with the highest rate of 15 females/person/night in August. In the same month, the human-biting rate in Ping Yuan was 21 females/person/night. In addition, An. minimus was more likely to attack people after midnight, while An. sinensis before midnight. These findings necessitate the increased use of countermeasures such as bed nets and mosquito repellents for preventing vector bites from May to September, especially in August.
The seasonal abundance of An. minimus was significantly higher than that reported by Wang et al. [6] in Na Bang in 2012–2013. The densities in cattle shelters were higher than those in human bedrooms. Anopheles minimus preferred areas at low elevation and tropical areas and showed a high density in cattle shelters in June, while An. sinensis preferred a medium elevation and showed a high density in August. In areas of low elevation, the conditions in June and September were more suitable to the vector, although the density in these areas was < 5 females/trap/night. Moreover the seasonal peak of An. minimus larvae occurred in July, while that of An. sinensis larva occurred in August. Therefore, more mosquito-control measures such as pesticide sprays should be used in this region before June.
The parous rate of An. sinensis and An. minimus was 90.46% and 93.33%, respectively. If the duration from eclosion to laying eggs is 2.5 days, the daily survival probability of An. sinensis and An. minimus will be 96.07% and 97.28%, respectively, according to the function p = M 1/X, where p, M, and X refer to the daily survival probability, the parous rate, and the duration from eclosion to laying eggs, respectively. According to the MacDonald model [53], vectorial capacity (VCAP) [54–57], which is the indicator of receptivity to malaria, can be presented by the function , where a and n indicate the vector biting rate and the parasite’s extrinsic incubation period that is affected by ambient temperatures, respectively. Therefore, a higher human-biting rate and ratio of vectors having laid eggs lead to a higher VCAP. In this study, these two parameters of An. sinensis and An. minimus in Yingjiang County showed exceedingly high values.
Due to several complicating factors, malaria in the China–Myanmar border might threaten the elimination of malaria in China [5]. Yingjiang County harbours several ethnic minorities, and their subsistence activities associated with forest areas, such as logging, banana or rubber planting, and living in planting areas during the farming season or entire year, are likely to increase the risk of infection [58]. Under conditions of high receptivity and potential exposure of the local people, if imported malaria cases occur in the county without timely and effective control, the probability of re-establishment will be extremely high. Consequently, specified vector-control countermeasures should be strengthened in these areas in case of the re-establishment of malaria, which might affect the progress of malaria elimination in China, and more public health programmes should focus on controlling malaria transmission in the China–Myanmar border region to better achieve malaria elimination in China.
Limitation
The seasonality of species composition, density, ma, and parous rate was only investigated in two towns. Thus, more surveys are necessary across the four elevation levels to investigate the integrated aspects of receptivity to malaria in the China–Myanmar border.
Conclusions
This study showed that the community structure of Anopheles was complex and stable during the entire epidemic season at low elevation areas in the China–Myanmar border in Yingjiang County, China. The highest similarities in vector features were observed in areas with elevations of 600–1199 and 1200–1799 m. These areas of medium elevation showed significant seasonality in the community structure (such as density, diversity, dominance, and richness). Meanwhile, the community structure was relatively simple in areas of elevations > 1800 m compared with other areas. Based on the high human-biting rate, adult and larval density, and parous rate of the two vectors, receptivity to malaria was exceedingly high in the China–Myanmar border in Yingjiang County. These findings can provide insights into the epidemiology of malaria as well as direct and quantified evidence to draw up vector control strategies and promote progress of malaria elimination in China.
Authors’ contributions
SSZ and TC conceived the study. TC, SZ, XW, CL, XZ, XG, ZL, XS, HZ, and HT collected the data. TC, SZ, and XW analysed the data. SSZ and TC wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by Scientific Project of Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning (No. 20164Y0047).
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Abbreviations
- WHO
World Health Organization
- GMS
Greater Mekong Subregion
- CDC
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- PCR
polymerase chain reaction
- HLC
human-landing catch
- HDN
human-baited double-net
- VCAP
vectorial capacity
Contributor Information
Tianmu Chen, Email: 13698665@qq.com.
Shaosen Zhang, Email: shaosen413@163.com.
Shui-Sen Zhou, Email: zss2322170@126.com.
Xuezhong Wang, Email: xzhw@yipd.org.
Chunhai Luo, Email: 765896769@qq.com.
Xucan Zeng, Email: 531044248@qq.com.
Xiangrui Guo, Email: 13988215439@163.com.
Zurui Lin, Email: 964786374@qq.com.
Hong Tu, Email: tuhong372@163.com.
Xiaodong Sun, Email: sxdsxyab@163.com.
Hongning Zhou, Email: zhhn@yipd.org.
References
- 1.Delacollette C, D’Souza C, Christophel E, Thimasarn K, Abdur R, Bell D, et al. Malaria trends and challenges in the Greater Mekong Subregion. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2009;40:674–691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Singhasivanon P. Mekong malaria. Malaria, multi-drug resistance and economic development in the greater Mekong subregion of Southeast Asia. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1999;30(Suppl 4):i–iv. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Socheat D, Denis MB, Fandeur T, Zhang Z, Yang H, Xu J, et al. Mekong malaria. II. Update of malaria, multi-drug resistance and economic development in the Mekong region of Southeast Asia. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2003;34(Suppl 4):1–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.WHO . Global malaria report 2015. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cui L, Yan G, Sattabongkot J, Cao Y, Chen B, Chen X, et al. Malaria in the Greater Mekong Subregion: heterogeneity and complexity. Acta Trop. 2012;121:227–239. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2011.02.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wang Y, Zhong D, Cui L, Lee MC, Yang Z, Yan G, et al. Population dynamics and community structure of Anopheles mosquitoes along the China–Myanmar border. Parasit Vectors. 2015;8:445. doi: 10.1186/s13071-015-1057-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zhou SS, Zhang SS, Zhang L, Rietveld AE, Ramsay AR, Zachariah R, et al. China’s 1-3-7 surveillance and response strategy for malaria elimination: is case reporting, investigation and foci response happening according to plan? Infect Dis Poverty. 2015;4:55. doi: 10.1186/s40249-015-0089-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Romi R, Boccolini D, Vallorani R, Severini F, Toma L, Cocchi M, et al. Assessment of the risk of malaria re-introduction in the Maremma plain (Central Italy) using a multi-factorial approach. Malar J. 2012;11:98. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-11-98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Romi R, Sabatinelli G, Majori G. Could malaria reappear in Italy? Emerg Infect Dis. 2001;7:915–919. doi: 10.3201/eid0706.010601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Danis K, Lenglet A, Tseroni M, Baka A, Tsiodras S, Bonovas S. Malaria in Greece: historical and current reflections on a re-emerging vector borne disease. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2013;11:8–14. doi: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2013.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Poncon N, Tran A, Toty C, Luty AJ, Fontenille D. A quantitative risk assessment approach for mosquito-borne diseases: malaria re-emergence in southern France. Malar J. 2008;7:147. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-7-147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bueno-Mari R, Jimenez-Peydro R. Study of the malariogenic potential of Eastern Spain. Trop Biomed. 2012;29:39–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.WHO . A framework for malaria elimination. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Qian YJ, Zhang L, Xia ZG, Vong S, Yang WZ, Wang DQ, et al. Preparation for malaria resurgence in China: approach in risk assessment and rapid response. Adv Parasitol. 2014;86:267–288. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800869-0.00010-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Zhou XN, Xia ZG, Wang RB, Qian YJ, Zhou SS, Utzinger J, et al. Feasibility and roadmap analysis for malaria elimination in China. Adv Parasitol. 2014;86:21–46. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800869-0.00002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hillman AL, Yu J, Abbott MB, Cooke CA, Bain DJ, Steinman BA. Rapid environmental change during dynastic transitions in Yunnan Province, China. Quat Sci Rev. 2014;98:24–32. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2014.05.019. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Webb EL, Jachowski NRA, Phelps J, Friess DA, Than MM, Ziegler AD. Deforestation in the Ayeyarwady Delta and the conservation implications of an internationally-engaged Myanmar. Global Environ Change. 2014;24:321–333. doi: 10.1016/j.gloenvcha.2013.10.007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wang X, Zhou G, Zhong D, Wang X, Wang Y, Yang Z, et al. Life-table studies revealed significant effects of deforestation on the development and survivorship of Anopheles minimus larvae. Parasit Vectors. 2016;9:323. doi: 10.1186/s13071-016-1611-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zhong D, Wang X, Xu T, Zhou G, Wang Y, Lee MC, et al. Effects of microclimate condition changes due to land use and land cover changes on the survivorship of malaria vectors in China–Myanmar border region. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0155301. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Derek Charlwood J, Nenhep S, Sovannaroth S, Morgan JC, Hemingway J, Chitnis N, et al. ‘Nature or nurture’: survival rate, oviposition interval, and possible gonotrophic discordance among South East Asian anophelines. Malar J. 2016;15:356. doi: 10.1186/s12936-016-1389-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yu G, Yan G, Zhang N, Zhong D, Wang Y, He Z, et al. The Anopheles community and the role of Anopheles minimus on malaria transmission on the China–Myanmar border. Parasit Vectors. 2013;6:264. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-6-264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Meide L, Xuezhong W, Tongyan Z, Du Z, Yande D, Baolin L. Analysis of the relationship between density and dominance of Anopheles minimus (Diptera: Culicidae) with environmental parameters in southern Yunnan Province, Peoples Republic of China. J Med Entomol. 2008;45:1007–1010. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/45.6.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Huang JX, Xia ZG, Zhou SS, Pu XJ, Hu MG, Huang DC, et al. Spatio-temporal analysis of malaria vectors in national malaria surveillance sites in China. Parasit Vectors. 2015;8:146. doi: 10.1186/s13071-015-0741-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Zhu G, Xia H, Zhou H, Li J, Lu F, Liu Y, et al. Susceptibility of Anopheles sinensis to Plasmodium vivax in malarial outbreak areas of central China. Parasit Vectors. 2013;6:176. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-6-176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tubaki RM, Menezes RM, Cardoso RP, Jr, Bergo ES. Studies on entomological monitoring: mosquito species frequency in riverine habitats of the Igarapava Dam, Southern Region, Brazil. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2004;46:223–229. doi: 10.1590/S0036-46652004000400009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Rezende HR, Falqueto A, Urbinatti PR, De Menezes RMT, Natal D, Cerutti C. Comparative study of distribution of Anopheline vectors (Diptera: Culicidae) in areas with and without malaria transmission in the highlands of an Extra-Amazonian region in Brazil. J Med Entomol. 2013;50:598–602. doi: 10.1603/ME12085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Muturi EJ, Shililu J, Jacob B, Gu W, Githure J, Novak R. Mosquito species diversity and abundance in relation to land use in a riceland agroecosystem in Mwea, Kenya. J Vector Ecol. 2006;31:129–137. doi: 10.3376/1081-1710(2006)31[129:MSDAAI]2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Marina CF, Bond JG, Munoz J, Valle J, Novelo-Gutierrez R, Williams T. Efficacy and non-target impact of spinosad, Bti and temephos larvicides for control of Anopheles spp. in an endemic malaria region of southern Mexico. Parasit Vectors. 2014;7:55. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-7-55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kweka EJ, Zhou G, Munga S, Lee MC, Atieli HE, Nyindo M, et al. Anopheline larval habitats seasonality and species distribution: a prerequisite for effective targeted larval habitats control programmes. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e52084. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Dash S, Hazra RK. Mosquito diversity in the Chilika lake area, Orissa, India. Trop Biomed. 2011;28:1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Conde M, Pareja PX, Orjuela LI, Ahumada ML, Duran S, Jara JA, et al. Larval habitat characteristics of the main malaria vectors in the most endemic regions of Colombia: potential implications for larval control. Malar J. 2015;14:476. doi: 10.1186/s12936-015-1002-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bond JG, Casas-Martinez M, Quiroz-Martinez H, Novelo-Gutierrez R, Marina CF, Ulloa A, et al. Diversity of mosquitoes and the aquatic insects associated with their oviposition sites along the Pacific coast of Mexico. Parasit Vectors. 2014;7:41. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-7-41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Garros C, Koekemoer LL, Coetzee M, Coosemans M, Manguin S. A single multiplex assay to identify major malaria vectors within the African Anopheles funestus and the Oriental An. minimus groups. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2004;70:583–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hempolchom C, Otsuka Y, Baimai V, Thongsahuan S, Saeung A, Taai K, et al. Development of a multiplex PCR assay for the identification of eight species members of the Thai Hyrcanus Group (Diptera: Culicidae) Appl Entomol Zool. 2013;48:469–476. doi: 10.1007/s13355-013-0207-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kenea O, Balkew M, Tekie H, Gebre-Michael T, Deressa W, Loha E, et al. Human-biting activities of Anopheles species in south-central Ethiopia. Parasit Vectors. 2016;9:527. doi: 10.1186/s13071-016-1813-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Briet OJ, Huho BJ, Gimnig JE, Bayoh N, Seyoum A, Sikaala CH, et al. Applications and limitations of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention miniature light traps for measuring biting densities of African malaria vector populations: a pooled-analysis of 13 comparisons with human landing catches. Malar J. 2015;14:247. doi: 10.1186/s12936-015-0761-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lima JB, Rosa-Freitas MG, Rodovalho CM, Santos F, Lourenco-de-Oliveira R. Is there an efficient trap or collection method for sampling Anopheles darlingi and other malaria vectors that can describe the essential parameters affecting transmission dynamics as effectively as human landing catches?—a review. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2014;109:685–705. doi: 10.1590/0074-0276140134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Govella NJ, Chaki PP, Geissbuhler Y, Kannady K, Okumu F, Charlwood JD, et al. A new tent trap for sampling exophagic and endophagic members of the Anopheles gambiae complex. Malar J. 2009;8:157. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-8-157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Tangena JA, Thammavong P, Hiscox A, Lindsay SW, Brey PT. The human-baited double net trap: an alternative to human landing catches for collecting outdoor biting mosquitoes in Lao PDR. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0138735. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.McKeon SN, Schlichting CD, Povoa MM, Conn JE. Ecological suitability and spatial distribution of five Anopheles species in Amazonian Brazil. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2013;88:1079–1086. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.12-0203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Liu XB, Liu QY, Guo YH, Jiang JY, Ren DS, Zhou GC, et al. Random repeated cross sectional study on breeding site characterization of Anopheles sinensis larvae in distinct villages of Yongcheng City, People’s Republic of China. Parasit Vectors. 2012;5:58. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-5-58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lee WJ, Klein TA, Kim HC, Choi YM, Yoon SH, Chang KS, et al. Anopheles kleini, Anopheles pullus, and Anopheles sinensis: potential vectors of Plasmodium vivax in the Republic of Korea. J Med Entomol. 2007;44:1086–1090. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/41.5.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Wolda H. Similarity indices, sample size and diversity. Oecologia. 1981;50:296–302. doi: 10.1007/BF00344966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Akhtar N, Nagpal BN, Kapoor N, Srivastava A, Valecha N. Role of An. culicifacies as a vector of malaria in changing ecological scenario of Northeastern states of India. J Vector Borne Dis. 2016;53:264–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Saifi MA, Alyousif MS, Amoudi MA. Anopheline species and their Plasmodium infection status in Aligarh, India. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2016;23:649–653. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.01.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Harischandra IN, Dassanayake RS, De Silva BG. Three sympatric clusters of the malaria vector Anopheles culicifacies E (Diptera: Culicidae) detected in Sri Lanka. Parasit Vectors. 2016;9:3. doi: 10.1186/s13071-015-1286-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Fathian M, Vatandoost H, Moosa-Kazemi SH, Raeisi A, Yaghoobi-Ershadi MR, Oshaghi MA, et al. Susceptibility of Culicidae mosquitoes to some insecticides recommended by WHO in a malaria endemic area of Southeastern Iran. J Arthropod Borne Dis. 2015;9:22–34. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Guo XX, Li CX, Wang G, Zheng Z, Dong YD, Zhang YM, et al. Host feeding patterns of mosquitoes in a rural malaria-endemic region in Hainan Island, China. J Am Mosq Control Assoc. 2014;30:309–311. doi: 10.2987/14-6439R.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Liu XB, Liu QY, Guo YH, Jiang JY, Ren DS, Zhou GC, et al. The abundance and host-seeking behavior of culicine species (Diptera: Culicidae) and Anopheles sinensis in Yongcheng city, People’s Republic of China. Parasit Vectors. 2011;4:221. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-4-221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Feng J, Yan H, Feng XY, Zhang L, Li M, Xia ZG, et al. Imported malaria in China, 2012. Emerg Infect Dis. 2014;20:1778–1780. doi: 10.3201/eid2010.140595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wang D, Li S, Cheng Z, Xiao N, Cotter C, Hwang J, et al. Transmission risk from Imported Plasmodium vivax malaria in the China–Myanmar border region. Emerg Infect Dis. 2015;21:1861–1864. doi: 10.3201/eid2110.150679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Zhang GC, Dong XS, Wang XZ, Lu YR. Quantitative study on transmission of malaria by Anopheles kunmingensis. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi. 1989;7:100–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Macdonald G. Epidemiological basis of malaria control. Bull World Health Organ. 1956;15:613–626. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Mandal S, Sarkar RR, Sinha S. Mathematical models of malaria–a review. Malar J. 2011;10:202. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-10-202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Shi B, Liu J, Zhou XN, Yang GJ. Inferring Plasmodium vivax transmission networks from tempo-spatial surveillance data. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8:e2682. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Ceccato P, Vancutsem C, Klaver R, Rowland J, Connor SJ. A vectorial capacity product to monitor changing malaria transmission potential in epidemic regions of Africa. J Trop Med. 2012;2012:595948. doi: 10.1155/2012/595948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Brady OJ, Godfray HC, Tatem AJ, Gething PW, Cohen JM, McKenzie FE, et al. Vectorial capacity and vector control: reconsidering sensitivity to parameters for malaria elimination. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2016;110:107–117. doi: 10.1093/trstmh/trv113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Erhart A, Ngo DT, Phan VK, Ta TT, Van Overmeir C, Speybroeck N, et al. Epidemiology of forest malaria in central Vietnam: a large scale cross-sectional survey. Malar J. 2005;4:58. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-4-58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.


