Abstract
A 39-year-old female with dengue fever presented with decreased vision in both eyes. Visual acuity was 20/200 and 20/80 in the right eye (OD) and left eye (OS), respectively. Fundus showed granular, grayish-white lesions in the parafoveal region in OD. Multimodal imaging including optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA), optical coherence tomography (OCT), and fluorescein angiography (FA) was performed. FA showed late hyperfluorescence with few microaneurysms in OS. OCT showed hyperreflectivity in various layers, suggestive of acute macular neuroretinopathy (AMN). OCTA showed disruption of retinal capillary plexuses. This case shows how OCTA provides newer insights into the pathogenesis of AMN lesions in dengue fever.
Keywords: Acute macular neuroretinopathy, dengue fever, foveolitis, maculopathy, optical coherence tomography angiography
Ocular involvement in dengue fever is a relatively rare occurrence, with reported incidence varying from 7.9% to 40.3%.[1,2] The posterior segment is most commonly affected, and sight-threatening complications can occur in 5%–8% of cases.[3] The reported manifestations of dengue maculopathy include macular hemorrhage, retinal edema, foveolitis, along with other associated findings such as arteriolar sheathing, cotton-wool spots, perifoveal telangiectasia, and microaneurysms. Recently, acute macular neuroretinopathy (AMN) has been associated with dengue maculopathy.[4] AMN lesions are characterized by hyporeflective parafoveal wedge-shaped areas on near-infrared imaging due to underlying deep capillary plexus (DCP) ischemia which shows as hyperreflectivity of the outer retinal layers on optical coherence tomography (OCT).[5] Such DCP ischemic changes are usually not discernible by fluorescein angiography (FA). Optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) is a newer modality that allows noninvasive and high-resolution three-dimensional mapping of the retinal and choroidal circulations using endoluminal flow as contrast.[6] This case report highlights the role of OCTA in delineating the level of pathological microvascular alterations in AMN associated with dengue maculopathy.
Case Report
A 39-year-old female of Indian origin presented with complaints of diminution of vision in both eyes for the past 7 days. The decreased vision was associated with pain and redness in the right eye (OD) and was painless in the left eye (OS). She provided a history of febrile illness 15 days before the onset of ocular complaints, for which she had received treatment from outside. Laboratory workup revealed serology (immunoglobulin M) positive for dengue. On examination, her best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) was 20/200 in the OD and 20/80 in the OS with intraocular pressure of 14 and 15 mmHg, respectively. Anterior segment examination revealed occasional cells in the anterior chamber and anterior vitreous in both eyes. Posterior segment examination showed the presence of grayish-white lesions with a granular appearance in the parafoveal region in OD and a few hard exudates and microaneurysms in OS [Fig. 1]. FA was essentially normal in the early phase, with late phase showing mild parafoveal leakage in both eyes with microaneurysms in the OS. OCT scan passing through the macula of OD showed the presence of hyperreflectivity in the inner nuclear layer, outer plexiform layer (OPL), and outer nuclear layer (ONL) with disruption of the external limiting membrane (ELM), ellipsoid zone (EZ), and interdigitation zone (IZ) in the subfoveal region [Fig. 2]. The OCT scan of OS revealed the presence of retinal thickening with a few intraretinal cystoid spaces [Fig. 3]. OCTA en face images showed disruption of both the superficial capillary plexus (SCP) and DCP with flow deficit in the foveal region. There was an increase in the size of the foveal avascular zone. There was the presence of hairpin loop configuration of the adjacent retinal capillaries, suggestive of retinal capillary ischemia in OD. These changes persisted till the last follow-up visit at 6 months [Fig. 4]. OCTA image of OS showed the presence of a hyperreflective round lesion corresponding to the microaneurysm seen on FA without any loss of SCP or DCP flow. The patient was treated with oral corticosteroids (1 mg/day oral prednisone) tapered over a 2-month period. The final BCVA at 6-month follow-up improved to 20/40 in OD and 20/50 in OS [Fig. 1].
Figure 1.
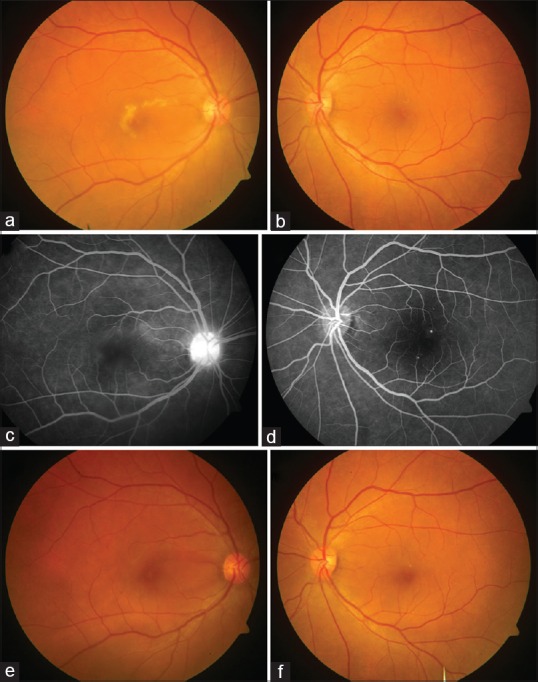
Serial fundus photography of the patient with dengue acute macular neuroretinopathy. (a) Colored fundus photograph of the right eye at baseline shows a grayish-yellow lesion with granular appearance and irregular borders surrounding fovea. (b) The left eye had the presence of a few hard exudates and one visible microaneurysm. (c) The late-phase angiogram of the right eye shows ill-defined faint hyperfluorescence in the perifoveal region along with disc staining. (d) The late arteriovenous phase angiogram of the left eye shows the presence of a few microaneurysms. (e) Colored fundus photograph of the right eye at 6-month follow-up shows near complete resolution of the grayish-white macular lesion, while the left eye shows some residual hard exudates with improvement in foveal transparency (f)
Figure 2.
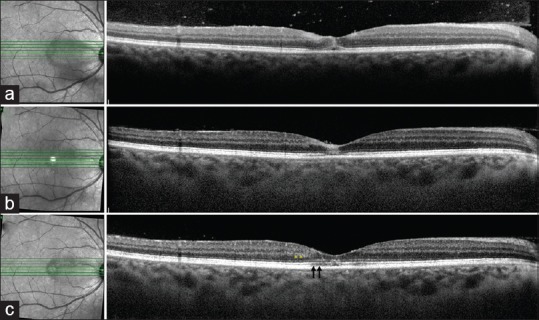
(a) Optical coherence tomography line scan passing through the lesion in the right eye shows hyperreflectivity of the inner retinal layers (i.e. the ganglion cell layer, the outer plexiform layer, and the inner nuclear layer) in the parafoveal region along with hyperreflectivity of the outer retinal layers (outer plexiform layer, Henle's layer, and outer nuclear layer) at the fovea. In addition, there is disruption of the external limiting membrane, the ellipsoid zone, and the interdigitation zone in the foveal region. There is presence of hyperreflective dots in the preretinal space suggestive of vitreous cells. (b) The corresponding optical coherence tomography line scan at 4-week follow-up shows partial resolution of the hyperreflectivity of the inner retinal layers with restoration of the foveal contour. There is only partial restoration of the external limiting membrane, ellipsoid zone, and interdigitation zone layers. (c) The optical coherence tomography line scan at 6-month follow-up shows further resolution of the inner and outer layer hyperreflectivity with better delineation of the individual layers. However, there is mild residual disruption of the external limiting membrane, ellipsoid zone, and interdigitation zone layers (black arrows) with thinning of the outer nuclear layer (yellow asterisk). There is complete resolution of the overlying vitritis
Figure 3.
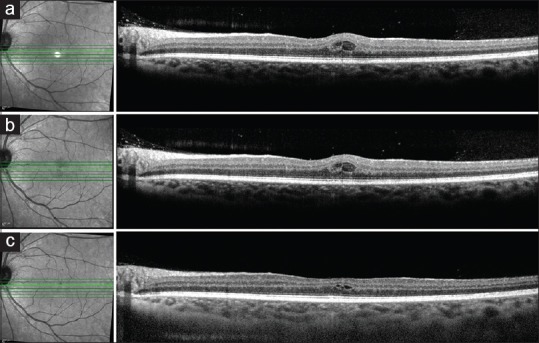
(a) Optical coherence tomography line scan of the left eye shows the presence of intraretinal cystoid spaces which did not show any change at 4-week follow-up (b). Optical coherence tomography line scan at the 6-month follow-up shows partial resolution of the intraretinal cystoid spaces (c)
Figure 4.
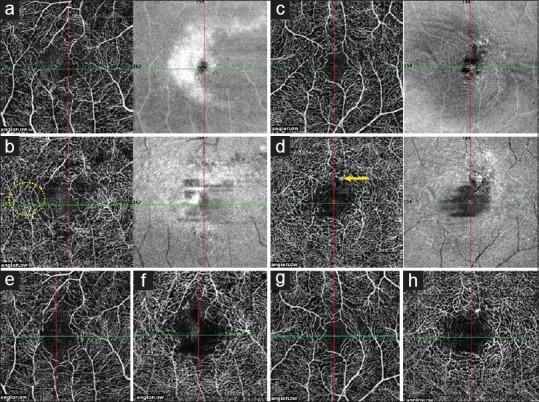
Optical coherence tomography angiography findings in dengue-associated acute macular neuroretinopathy. (a) Baseline optical coherence tomography angiography en face image of the superficial capillary plexus in the right eye shows disruption of the normal flow pattern of the superficial capillary plexus in the parafoveal region, leading to enlargement of the foveal avascular zone. (b) Baseline optical coherence tomography angiography en face image of the deep capillary plexus of the right eye showing similar disruption of capillary flow with hairpin loop configuration (yellow circle) of the surrounding capillaries. (c) Baseline optical coherence tomography angiography en face image of the superficial capillary plexus of the left eye shows a normal capillary flow pattern. (d) Baseline optical coherence tomography angiography en face image of the deep capillary plexus of the left eye shows the presence of a hyperreflective round structure corresponding to the microaneurysm seen on fluorescein angiography (yellow arrow). (e and f) Optical coherence tomography angiography en face images of the superficial capillary plexus and deep capillary plexus respectively at 6-month follow-up visit shows no reduction in the capillary flow void in the right eye. (g and h) Optical coherence tomography angiography en face images of the left eye at 6-month follow-up shows a normal flow pattern in the superficial capillary plexus (g), while the deep capillary plexus shows the persistence of the microaneurysm (h)
Discussion
Classically, dengue maculopathy has been associated with retinal edema, hemorrhages, and foveolitis, which is characterized by the foveal outer neurosensory retinal disruption.[7] AMN is a recently reported unusual manifestation of dengue maculopathy.[4] As such, AMN has been associated with conditions such as oral contraceptives, flu-like illness, and certain hypotensive states such as nocturnal hypotension.[5,8] The lesions of AMN are characteristic and typically localized to the outer retina due to ischemia of the DCP. Features of AMN include hyperreflectivity of the OPL and ONL and disruption of EZ, ELM, and IZ. In our index case, such features were observed on OCT scans along with deep capillary ischemia on OCTA. In addition, there was superficial retinal plexus ischemia as well. Capillary endothelial dysfunction or occlusion of precapillary arterioles due to immune complex deposition is the likely underlying mechanism of SCP and DCP ischemia in dengue maculopathy. Such arteriolar hypoperfusion has been postulated to be the pathophysiologic mechanism of retinal plexus ischemic entities such as AMN, cotton-wool spots, and paracentral acute middle maculopathy.[9] In conditions with arteriolar ischemia, such as dengue, variable involvement of superficial/deep retinal vascular plexus can occur as in our case, who had AMN with superficial plexus involvement [Fig. 4]. In addition, our patient showed the presence of microaneurysms with mild leakage resulting in retinal edema in OS [Figs. 1 and 3]. While there was an improvement in macular edema in OS over the follow-up, OD showed the persistence of ischemia and thinning of ONL over time [Fig. 2].
Using OCTA, changes of AMN in our patient with dengue maculopathy are well appreciated at baseline and follow-up. In a recent case, retinal microvascular changes were demonstrated using OCTA in a patient with dengue fever with no clinically appreciable fundus lesions.[10] However, our patient shows features of AMN clinically, on imaging and OCTA without much change in ischemia at 6-month follow-up.
Conclusion
This case highlights the involvement of retinal capillaries at various levels (superficial/intermediate and deep) among patients with dengue maculopathy. OCTA appears to hold great value in demonstrating the spectrum of retinal ischemic changes from ophthalmoscopically undetectable lesion to AMN-like features in patients of dengue maculopathy. This technology provides insights into the level of pathophysiological alterations in these eyes and helps in determining the visual prognosis.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Gupta A, Srinivasan R, Setia S, Soundravally R, Pandian DG. Uveitis following dengue fever. Eye (Lond) 2009;23:873–6. doi: 10.1038/eye.2008.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Beral L, Merle H, David T. Ocular complications of dengue fever. Ophthalmology. 2008;115:1100–1. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2008.02.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Su DH, Bacsal K, Chee SP, Flores JV, Lim WK, Cheng BC, et al. Prevalence of dengue maculopathy in patients hospitalized for dengue fever. Ophthalmology. 2007;114:1743–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2007.03.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Munk MR, Jampol LM, Cunha Souza E, de Andrade GC, Esmaili DD, Sarraf D, et al. New associations of classic acute macular neuroretinopathy. Br J Ophthalmol. 2016;100:389–94. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2015-306845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bhavsar KV, Lin S, Rahimy E, Joseph A, Freund KB, Sarraf D, et al. Acute macular neuroretinopathy: A comprehensive review of the literature. Surv Ophthalmol. 2016;61:538–65. doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2016.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Agrawal R, Xin W, Keane PA, Chhablani J, Agarwal A. Optical coherence tomography angiography: A non-invasive tool to image end-arterial system. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2016;13:519–21. doi: 10.1080/17434440.2016.1186540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Juanarita J, Azmi MN, Azhany Y, Liza-Sharmini AT. Dengue related maculopathy and foveolitis. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2012;2:755–6. doi: 10.1016/S2221-1691(12)60223-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Thanos A, Faia LJ, Yonekawa Y, Randhawa S. Optical coherence tomographic angiography in acute macular neuroretinopathy. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016;134:1310–4. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2016.3513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Yu S, Pang CE, Gong Y, Freund KB, Yannuzzi LA, Rahimy E, et al. The spectrum of superficial and deep capillary ischemia in retinal artery occlusion. Am J Ophthalmol. 2015;159:53–630. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2014.09.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tavassoli S, Carreño E, Teoh SC, Theodoropoulou S, Bailey C, Lee RW, et al. Optical coherence tomography angiography findings in dengue-related maculopathy: A Case report. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging Retina. 2016;47:1057–60. doi: 10.3928/23258160-20161031-12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


