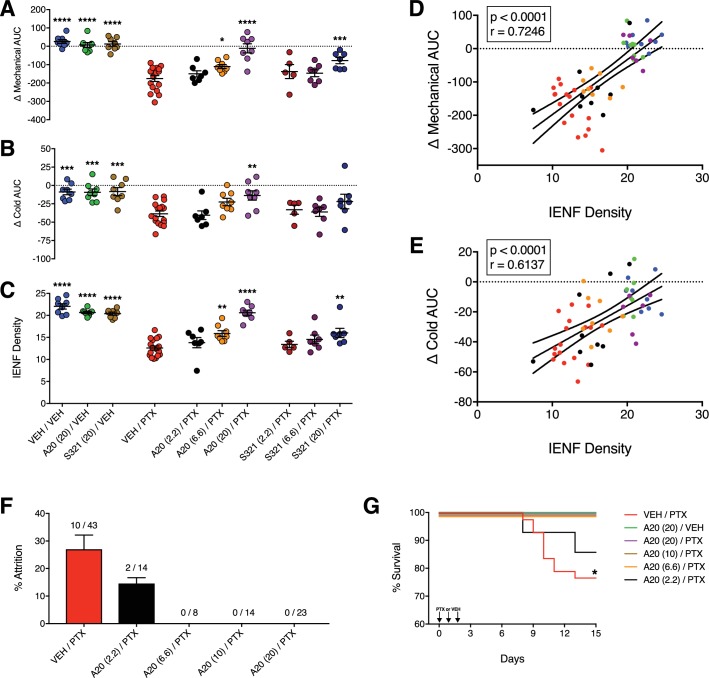
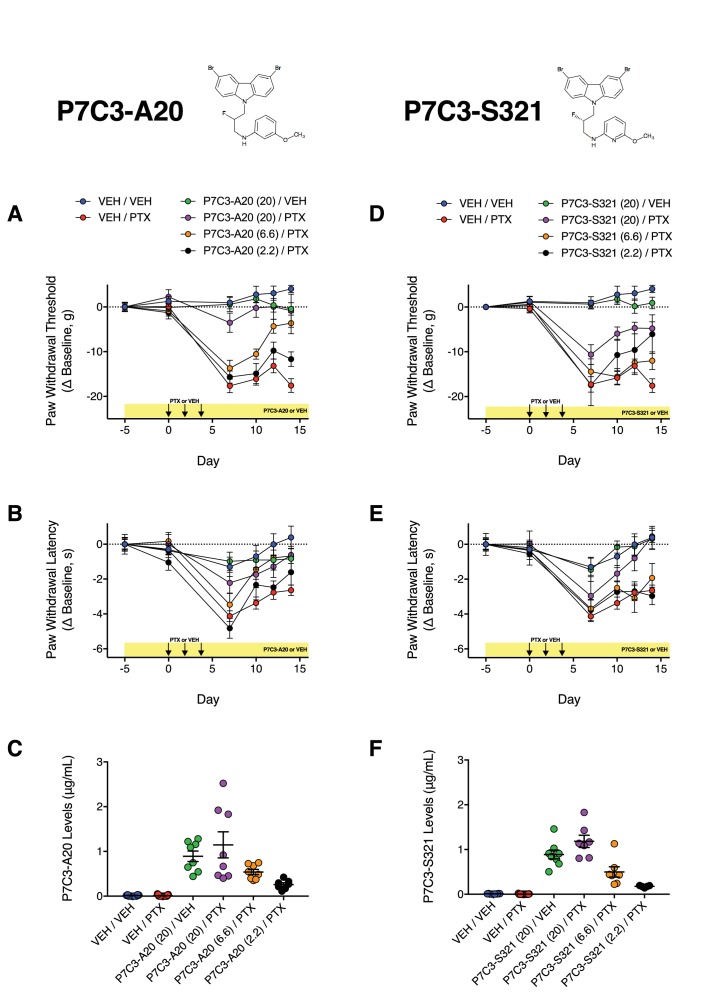
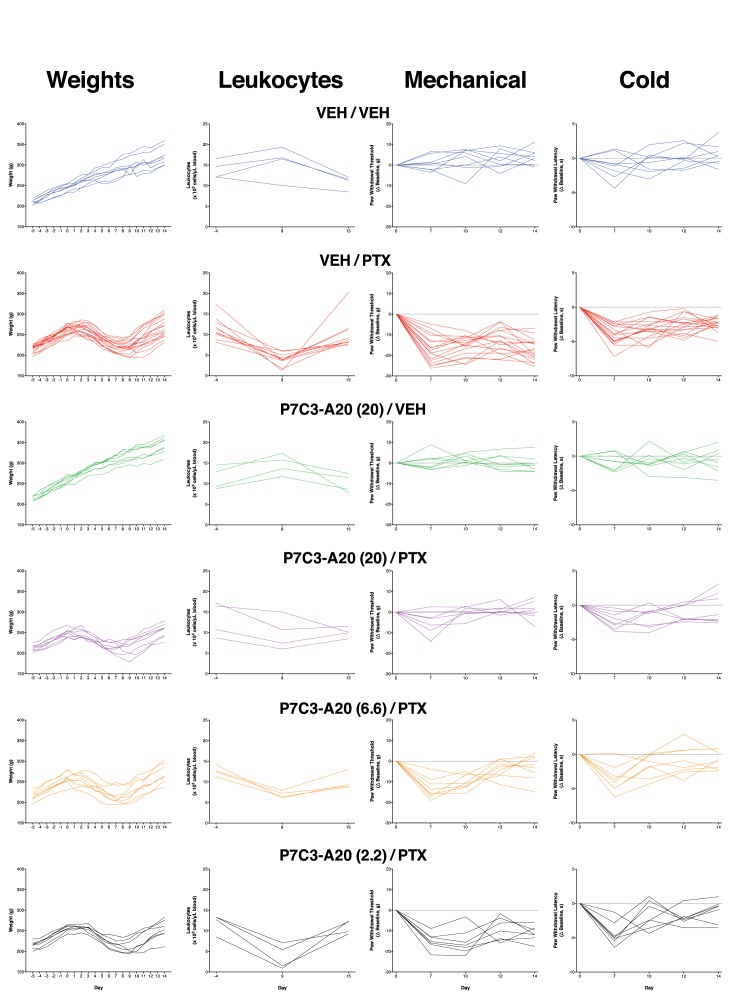
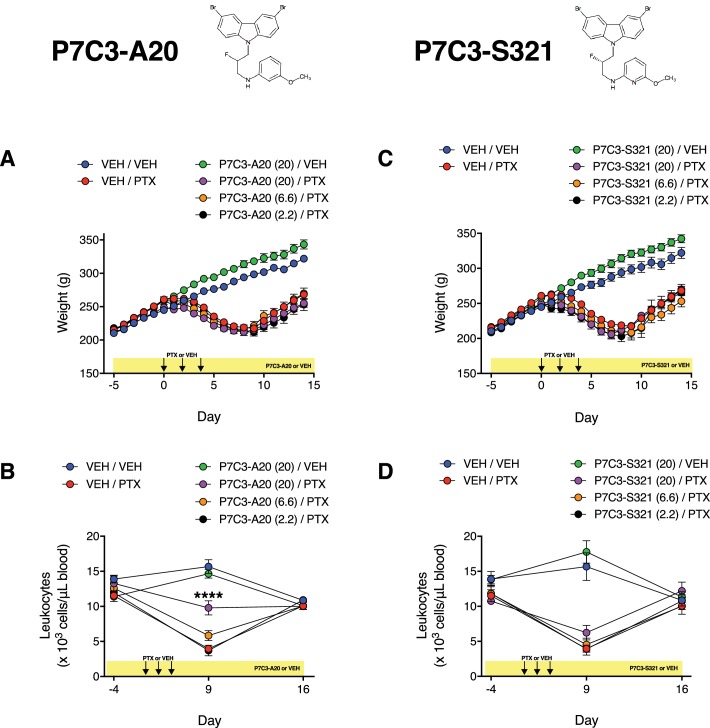
Figure 3. P7C3-A20 and P7C3-S321 are dose-dependently neuroprotective, improve general health, and attenuate premature death associated with PTX.
(A–C) AUCs to mechanical (A) and cold (B) stimulation and IENF densities (C) showing the dose-dependent neuroprotective effects of P7C3-A20 and P7C3-S321. Horizontal lines represent mean AUC ±SEM calculated from individual rat AUC values shown as small circles. ****p<0.0001, ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05 vs. Veh/PTX by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-hoc test, n = 5–17 rats/group. (D and E). Correlation analyses between individual rat IENF density and their respective mechanical (D) or cold (E) AUC (Pearson, two-tailed, p<0.0001). Black lines are linear regression curves with 95% confidence bands. Colors reflect treatment group as defined in Figure 3A–C. (F) Study attrition by treatment group. For each behavioral experiment, the number of rats removed due to >20% wt loss or death was divided by the total number of rats per treatment group. Data represent mean ± SEM, n = 1–4 independent experiments. (G) Survival curves showing attrition of rats treated only with PTX (red line) typically occurred between days 8–11, which was abolished by P7C3-A20 treatment. *p=0.0206 (χ2=13.32) by the Mantel-Cox log-rank test.