Abstract
Invasive fungal infections are still an important cause of morbidity and mortality in immunocompromised patients such as patients suffering from hematological malignancies or patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantion. In addition, other populations such as human immunodeficiency virus-patients are at higher risk for invasive fungal infection. Despite the availability of new antifungal compounds and better supportive care measures, the fatality rate of invasive fungal infection remained unacceptably high. It is therefore of major interest to improve our understanding of the host–pathogen interaction to develop new therapeutic approaches such as adoptive immunotherapy. As experimental methodologies have improved and we now better understand the complex network of the immune system, the insight in the interaction of the host with the fungus has significantly increased. It has become clear that host resistance to fungal infections is not only associated with strong innate immunity but that adaptive immunity (e.g., T cells) also plays an important role. The antifungal activity of natural killer (NK) cells has been underestimated for a long time. In vitro studies demonstrated that NK cells from murine and human origin are able to attack fungi of different genera and species. NK cells exhibit not only a direct antifungal activity via cytotoxic molecules but also an indirect antifungal activity via cytokines. However, it has been show that fungi exert immunosuppressive effects on NK cells. Whereas clinical data are scarce, animal models have clearly demonstrated that NK cells play an important role in the host response against invasive fungal infections. In this review, we summarize clinical data as well as results from in vitro and animal studies on the impact of NK cells on fungal pathogens.
Keywords: natural killer cell, invasive fungal infection, Aspergillus, Candida, mucormycete, Cryptococcus, antifungal host response
Introduction
Invasive fungal infections are still associated with significant morbidity and mortality. For example, a retrospective cohort study in the US demonstrated that as compared to patients without invasive aspergillosis, patients suffering from the infection had a significant longer hospital stay, caused significantly higher costs, and, most importantly, had a significant higher mortality (1). A population-based analysis of invasive fungal infections in France revealed that between 2001 and 2010, the incidence of invasive fungal disease due to Candida spp., Aspergillus spp., and mucormycetes increased by 7.8, 4.4, and 7.3% per year, respectively, which was highly significant for each pathogen (2). In contrast to cryptococcosis, which often occurs in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-patients, the population at high risk for candidemia, invasive aspergillosis, and mucormycosis includes in particular patients with hematological malignancies, patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) and solid organ recipients (2–6). These patient populations are characterized by the impairment of multiple arms of the immune system (7, 8), such as of natural barriers, the phagocyte system, innate immunity, and lymphocytes, all of which may increase the risk for an invasive fungal infection. Therefore, it is not surprising that the mortality rate of invasive fungal disease is extremely high in these patient populations, exceeding 70% in HSCT recipients suffering from invasive aspergillosis or mucormycosis (4).
It is well known that the recovery of the immune system has a major impact on the outcome of invasive fungal infection in an immunocompromised patient (9, 10). Unfortunately, to date, immunomodulation using cytokine and growth factor therapies, as well as adoptive immunotherapeutic strategies such as granulocyte transfusions or the administration of Aspergillus-specific T-cells did not significantly improve the prognosis of immunocompromised patients with invasive fungal disease (11). It is therefore of major interest to improve our understanding of the host–pathogen interaction to develop new therapeutic strategies for immunocompromised individuals suffering from fungal infection. This review will summarize available clinical data as well as results from in vitro and animal studies on the impact of natural killer (NK) cells on fungal pathogens.
The Host Response to Fungal Infection
Over the last decades, we could witness major advances not only in the understanding of the complexity of the immune system but also in our knowledge on the immunopathogenesis of invasive fungal infections. The host response to a fungal pathogen includes, but is not restricted to various cells of the innate and adaptive immunity such as monocytes, neutrophils, dendritic cells (DCs), T and B lymphocytes, as well as multiple soluble molecules such as collectins, defensins, cytokines including interferons (IFNs) (12, 13). Although it is known for a long time that severe and prolonged neutropenia (e.g., absolute neutrophil count ≤500/μl and duration of neutropenia ≥10 days) is the single most important risk factor for invasive aspergillosis, invasive Candida infection, and mucormycosis in patients receiving cytotoxic chemotherapy or undergoing allogeneic HSCT (9, 14), recent studies refined our understanding how neutrophils are controlling in particular the early stages of invasive fungal infection. Neutrophils are attracted by cytokines released by endothelial cells and macrophages and are able to quickly migrate to a focus of infection. In addition to recruiting and activating other immune cells by the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, neutrophils may attack as front-line defense invading pathogens by phagocytosis, the production of reactive oxygen intermediates, and the release antimicrobial enzymes to the formation of complex extracellular traps (NETs) that help in the elimination of the fungus (15). DCs transport fungal antigens to the draining lymph nodes, where they orchestrate T cell activation and differentiation (16). A number of lymphocyte subsets have an important impact in the antifungal immunity, such as Th1 cells (important for inflammation and fungal clearance), Th17 cells (neutrophil recruitment, defensins), Th22 cells (defensins, tissue homeostasis), and Treg cells (immunosuppression). In addition, a number of cytokines play important roles in the complex crosstalk between different cells of the immune system, which modify and regulate innate and adaptive immune responses, such as the induction of proliferation and differentiation, as well as the activation or suppression of different target cells (11–13). Still, many open questions have to be resolved, including the influence of the genetic background in the delicate interplay of immune cells, the interaction of the innate and adaptive immune system in balancing protection and immunopathology in fungal infections (12), and the influence of fungal microbiota or “mycobiota” on health and disease (17). More importantly, we have to learn how to modify the immune system in the combat against invasive fungal infections, in particular in the immunocompromised host, which includes not only the activation of the immune response to eliminate the pathogen but also its suppression to avoid collateral tissue damage.
NK Cell Biology
Human NK cells, which originate from the bone marrow, represent up to 15% of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. They are characterized by the expression of CD56 and by the absence of the T cell marker CD3. According to the surface expression density of CD56 and CD16, NK cells can be subdivided in two main subpopulations, namely the cytotoxic CD56dimCD16bright and the immune regulatory CD56brightCD16dim subsets (18). Although NK cells were originally considered as cells of innate immunity, they demonstrate qualities of the adaptive immunity such as immunological memory (19–22). In this regard, animal models and human studies indicate that NK cells are able to develop long-lasting antigen-specific memory (23–26). It has been demonstrated that memory-like NK cells display a less differentiated phenotype in CD56dim NK cells, which were CD94+NKG2A+ but CD57−KIR− (27). The name “natural killer cell” originally came from their ability to kill tumor cells in vitro and in vivo without previous stimulation (22, 28–31). Their antitumor activity includes activity against acute lymphoblastic leukemia (32), acute myeloid leukemia (33), and neuroblastoma (34, 35). In addition to their antitumor activity, NK cells play an important role in the host response against various pathogens which includes viruses such as cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein–Barr virus (23, 36–38), or hepatitis B and C virus (37, 39, 40), and Gram-positive, Gram-negative, and intracellular bacteria, such as Salmonella typhi, Escherichia coli (41), or Listeria monocytogenes (42).
Natural killer cells eliminate their potential targets either by directly using cytotoxic molecules such as perforin or granzyme B, which are stored in granules, or by death receptor-mediated apoptosis (36). In addition, CD16 (FcγRIII) triggers antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity on opsonized target cells (36). Education and differentiation are considered to be important mechanisms for both direct and antibody-dependent functionality of NK cells (43–45). Several models have been developed to explain the process of “education” (43, 45–49). In general, the expression of self-recognizing inhibitory receptors (SRIR) results in the development of NK cells toward fully functional mature form, which has been termed as “licensing” process (50). In contrast, the “disarming” model describes NK cells lacking SRIR that become anergic due to chronic activation (51). The more dynamic “rheostat model” has been used to describe that stronger inhibitory signaling through more SRIR interactions results in a greater functional responsiveness of NK cells (52, 53). Importantly, cytokine stimulation can prime SRIR-deficient NK cells to a functional state (50), and uneducated cells are also able to combat viral infections, as SRIR-deficient NK cells strongly respond toward murine CMV (54).
In addition to the direct cytotoxic abilities, NK cells have recently been classified closely to group 1 innate lymphoid cells, which are characterized by the production of IFN-γ, whereas type 2 cytokines are not produced (55). Via the release of chemokines and cytokines such as IFN-γ, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), or chemokine ligand 5 (CCL5) [regulated upon activation, normal T-cell expressed, and secreted (RANTES)], NK cells modulate the activity of various immune cells including neutrophils, DCs, and T cells (46, 56), which complements their direct anti-pathogen and antibody-mediated activities.
NK Cells and Invasive Fungal Infection: Clinical Observations
Although clinical data suggest the importance of NK cells in the risk and outcome of invasive fungal infection, the exact role of NK cells is difficult to determine as multiple cells are involved in the antifungal host response, and as these cells interact in a complex network with both positive and negative feedback mechanisms (7, 8). A recent study analyzed 51 patients undergoing allogeneic HSCT, among them 9 patients in whom proven or probable invasive aspergillosis occurred (10). The study evaluated both the quantitative and qualitative reconstitution of immune cells including polymorphonuclear cells, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, and NK cells, and the authors reported two important observations: first, transplant recipients suffering from invasive aspergillosis displayed insufficient NK cell recovery with cell counts remaining less than 200/μl as well as lower reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Second, HSCT transplant recipients who were cured from invasive aspergillosis had significantly higher ROS production and higher NK cell counts as compared to those patients who had a poor outcome of the invasive fungal infection. As both cell count and ROS production were altered in each of the analyses, the importance of the NK cell count as single risk and single prognostic factor for invasive aspergillosis remains unresolved. Another study evaluated 396 patients undergoing solid organ transplantation (57). A total of 304 patients were kidney and 92 patients were liver transplant recipients, and median followed-up time was 504.5 days after transplantation. The analysis demonstrated that 1 month after transplantation, patients who did not develop invasive fungal disease at a later time point had significantly higher mean NK cell count as compared with those patients who developed fungal disease. In the non-transplant setting, larger clinical studies on the impact of NK cell-mediated immunity on fungal infections are lacking. Although it was observed that patients suffering from chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis (CMCC) have a decrease of both NK cell number and cytotoxic activity (58–60), the exact impact of NK cells in the pathogenesis of the infection or in the progression of the disease is hard to define, in particular as cell-mediated immunity is also impaired in patients with CMCC. Although it may very well be that the pathologic NK cell findings are a risk factor for CMCC, other possible explanations for the decreased NK cell count and NK cell activity include that the fungus had a negative impact on originally normal NK cells, or that the observation is an epiphenomenon only. Similarly, it was reported that a patient developed a Trichophyton rubrum infection during corticosteroid treatment for systemic lupus erythematosus (61). Although immunosuppressive therapy was stopped, the infection remained. Further evaluation demonstrated that both numbers and activity of NK cells were reduced. The authors speculated that the impairment of the NK cells was causing the infection, but again, one could also argue that the infection resulted in a decreased NK cell number and NK cell activity in this individual patient.
NK Cells Damage Various Fungi In Vitro
Multiple studies published over the last three decades demonstrate that both murine and human NK cells exhibit antifungal activity in vitro against various fungal pathogens, such as Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus niger, Candida albicans, Cryptococcus neoformans, Paracoccidioides brasiliensis, Rhizopus oryzae, and other mucormycetes including Lichthemia ramosa or Absidia corymbifera (62–70) (Figure 1). NK cells damage the hyphal form of A. fumigatus and R. oryzae, but are not able to exhibit fungicidal activity toward conidia (62, 63, 65). In C. albicans, human NK cell are cytotoxic against germ tubes and additionally are able to phagocyte C. albicans yeasts (8 ± 0.5% of C. albicans yeasts were phagocytosed by NK cells within the first 2 h of interaction) (70). The lack of antifungal activity against conidia may be explained by the fact that conidia are often protected by capsules, by pigments such as melanin, or by hydrophobic layers, all of which may prevent recognition by various immune cells (71–74). For example, the rodlet/hydrophobin layer on dormant A. fumigatus conidia masks the recognition by the immune system and thus prevents an host immune response, whereas the genetical removal the rodlet/hydrophobin layer in dormant conidia of the ΔrodA mutant resulted in the induction of maturation and activation of human DCs (71). Similarly, the lack of a capsule in the strain CAP67 of the yeast-like fungus C. neoformans leads to a higher expression of the cytotoxic molecule perforin by NK cells as compared to the encapsulated strain B3501 (75).
Figure 1.
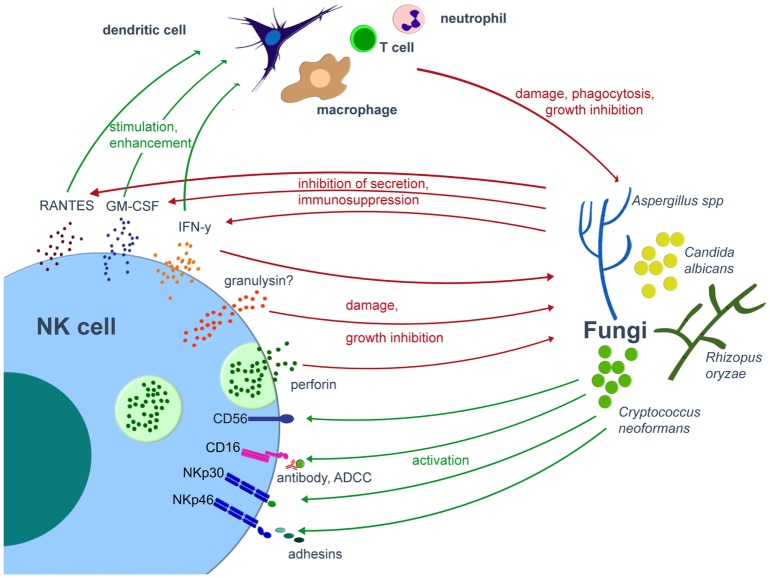
Interplay of NK cells and fungal pathogens. Various fungal pathogens are able to activate NK cells. Once activated, NK cells directly damage fungi by cytotoxic molecules such as perforin or release cytokines, by which they modulate the antifungal host response via various immune cells. On the other hand, the fungus may compromise the host immune system. Green arrows indicate activation/stimulation, red arrows inhibition/damage. ADCC, antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity; IFN, interferon; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; NK, natural killer.
Recognition of Fungi by NK Cells
Over the last years, there were major advances in the identification and characterization of receptors by which NK cells recognize fungal pathogens (Figure 1, Table 1). NK cells express unique activating receptors on their surface, which are called natural cytotoxicity receptors (NCR) 1–3 (NKp46, NKp44, and NKp30; CD335–CD337). Studies using blocking antibodies and siRNA to knockdown the NKp30 expression on the surface of the cell line YT demonstrated that NK cells are able to directly recognize C. albicans and C. neoformans by the NKp30 receptor, which further mediates killing of these fungi (68). However, polymorphonuclear neutrophils and granulocyte myeloid-derived suppressor cells may decrease the NKp30 expression on NK cells, which results in reduced cytotoxicity toward A. fumigatus and a decrease in IFN-γ secretion (76). Recently, the NKp46 receptor and its mouse ortolog NCR1 were identified to play an important role in the NK cell-mediated killing of C. glabrata (77). It was speculated whether NKp46/NCR1 may be a novel type of pattern recognition receptor, as these receptors not only recognize the C. glabrata adhesins Epa1, Epa6, and Epa7 but also bind viral adhesion receptors (77). The importance of the receptor is underlined by the observation that NCR1-deficient mice were unable to clear C. glabrata systemic infection (77). Because several fungi including Aspergillus, Cryptococcus, and Coccidioides express adhesins (78), further studies have to evaluate whether and to what extent these fungal adhesins are recognized by which of the NK cell receptors (79).
Table 1.
Natural killer (NK) cell receptors in antifungal response.
| Receptor | Origin | Ligand | Fungus | Remarks | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NKp30 | Human, YT cell line | Undefined pathogen-associated molecular pattern | Candida albicans, Cryprococcus neoformans |
|
Li et al. (68) |
| NKp46 | Human | Fungal adhesins Epa1, Epa6, Epa7 | Candida glabrata | Human NKp46 and mouse ortholog NCR1 bind C. glabrata in vitro | Vitenshtein et al. (77) |
| NCR1 | Mouse | Clearing of systemic C. glabrata infection in vivo depends on recognition of fungal adhesins by NCR1 | |||
| CD56 | Human | Unknown | Aspergillus fumigatus | Blocking of CD56 by inhibitory antibodies reduces fungal-mediated NK cell activation and inhibits amount of secreted cytokines in vitro | Ziegler et al. (80) |
| CD16 | Mouse | Cryptococcal polysaccharide | Cryptococcus neoformans | Purified IgG fraction of rabbit anticryptococcal antibody augments growth inhibitory activity of murine splenic NK cells in vitro | Nabavi and Murphy (81) |
Recent studies suggested CD56 as pathogen recognition receptor, as it was demonstrated by flow cytometry that the fluorescence positivity of the surface receptor significantly decreased upon fungal contact (80). The authors could visualize the direct interaction of NK cells and A. fumigatus via CD56, which was re-organized and accumulated at this interaction site time dependently. Importantly, blocking of CD56 surface receptor reduced fungal-mediated NK cell activation and reduced cytokine secretion. Earlier studies have demonstrated that the low-affinity Fc-receptor CD16 [FcγRIIIa (CD16a) and FcγRIIIb (CD16b)] is also involved in the antifungal activity of NK cells, as NK cells inhibited the growth of Cryptococci more effectively in the presence of anti-cryptococcal IgG antibodies than in the presence of normal rabbit serum or medium (81). However, it is important to note that primary and pre-activated NK cells downregulate CD16 after contact with C. albicans, which has also been described for the cellular adhesin CD56 and immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif-bearing receptors NKG2D (CD314) and NKp46 (CD335) (70). Taken together, we just begin to understand the complexity how NK cells are being activated by fungal pathogens.
Direct Damage of Fungal Pathogens by NK Cells
Various mechanisms are described by which NK cells directly kill tumor cells, which include the release of soluble cytotoxic molecules such as perforin or granzyme, or the induction of apoptosis by the Fas–FasL or the TNF pathway. Regarding fungal pathogens, several studies reported on the importance of lytic granules released by NK cells. For example, the use of monensin, which inhibits granule secretion, partially abrogated the growth inhibition of C. neoformans by human NK cells [reviewed in Ref. (79)]. It further became clear that mainly perforin and granulysin mediate the direct NK cell cytotoxicity toward fungal pathogens (67, 82). When pretreating human NK cells with concanamycin A (ConA), which induces accelerated perforin degradation via an increase of pH in the lytic granules, significantly less damage of A. fumigatus and R. oryzae hyphae can be observed as compared to the addition of untreated NK cells to the fungus (62, 63, 83). Other studies used purified perforin and reported on fungal damage of A. fumigatus hyphae (62), the inhibition of filamentation of C. albicans (84), and the inhibition of the metabolic activity of C. albicans and R. oryzae in a dose-dependent manner (63, 70). The fact that ConA did not totally abrogate NK cell-mediated fungal damage suggests that other molecules than perforin also participate in the antifungal activity of human NK cells, as reported for A. fumigatus, C. albicans, and R. oryzae. Interestingly, inhibition of perforin by ConA or by small interfering RNA decreased NK cell anti-cryptococcal activity, whereas inhibition of granulysin did not alter the antifungal effect (67). However, it has been shown that the defective anti-cryptococcal activity of NK cells from HIV-patients can be corrected by ex vivo treatment with interleukin (IL)-12 (68), as IL-12 restores the lower perforin expression in NK cells from HIV-infected patients as well as the defective granule polarization in response to C. neoformans (85). In tumor cells, perforin perforates the membrane of the target, which leads to an influx of water and a loss of intracellular molecules, resulting in cell lysis (86, 87). Similarly, granulysin disrupts the target cell membrane, which results in higher intracellular calcium and lower intracellular potassium concentrations, both of which ultimately activate caspases and programmed cell death (apoptosis) (88–92). However, it is important to note that the mechanisms of the antifungal effect of perforin and granulysin have not fully been elucidated to date.
There is an ongoing controversy on the direct antifungal effect of IFN-γ. One study reported on a direct IFN-γ-mediated antifungal activity of NK cells against Aspergillus, which was independent of degranulation of NK cells and their cytotoxic molecules (65). The authors suggested as explanation that “IFN-γ might cooperate with fungal ribotoxins, (…), transforming them into suicide molecules for fungus” (65). Similarly, it was demonstrated that IFN-γ at a concentration of 32 pg/ml exhibited a small but significant antifungal effect on A. fumigatus, A. flavus, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and inhibited the growth by 6, 11, and 17%, respectively (93). As higher concentrations of IFN-γ, e.g., 50 or 100 pg/ml, did not increase antifungal activity, and IFN-γ serum levels of 18 ± 30 pg/ml can be detected in healthy individuals (94), the importance of the direct antifungal effect in vivo is questionable. Corroborating the data of another report (70), no significant antifungal effects of IFN-γ were detected in Candida and C. neoformans (93). However, it is important to note that a combination of amphotericin B at a concentration of 1 µg/ml and IFN-γ at 32 pg/ml increased the efficacy of amphotericin B against A. fumigatus, which might be important for immunotherapeutic strategies.
Inducing apoptosis via the Fas–FasL or the TNF pathway is another mechanism by which NK cells are able to kill a target and has been described for various tumor cells as well as for pathogen infected cells (95, 96). Whereas data on apoptosis are missing for molds, apoptosis in yeast cells has been reported, but molecular mechanisms at the core of apoptotic execution is still unknown (97, 98). One recent study reported that blocking the death receptor ligands FasL and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis inducing ligand on the surface of human NK cells by antibodies did not have any impact on the antifungal activity (70). In addition, phagocytosis may be another mechanism of direct fungal damage by NK cells, which has been reported for C. albicans yeast (70). Notably, the IgG fraction of rabbit anti-cryptococcal serum enhanced the anti-cryptococcal activity of NK cells via their CD16 receptor (81).
Modulation of the Antifungal Host Response by NK Cells
Upon stimulation, NK cells produce various cytokines, all of which modulate the host immunity against fungi. IFN-γ is one of the key molecules in the antifungal host response and is constitutively produced by NK cells (99). IFN-γ exhibits multiple effects on various immune cells. For example, IFN-γ is able to stimulate migration, adherence, phagocytosis, as well as oxidative killing by neutrophils and macrophages. Conditioned medium from co-incubation of NK cells and C. albicans enhanced polymorphonuclear neutrophil activation (70). In addition, data of a murine model demonstrated the pivotal role of IFN-γ-producing NK cells in inducing the phagocytic activity of splenic macrophages, thus mediating protection against systemic infection with C. albicans (100). As NK cells are the main source of IFN-γ in neutropenic mice suffering from aspergillosis, depletion of NK cells resulted in diminished IFN-γ levels in the lungs followed by an increased fungal load (101). Interestingly, the fungal load could be reduced by the transfer of wild-type IFN-γ producing NK cells, whereas this was not seen when transferring NK cells from IFN-γ-deficient mice. Because IFN-γ also enhances maturation of DCs and plays a pivotal role in the protective TH1 cell response (11, 12, 102), the molecule was used as immunotherapy in invasive fungal disease. Whereas the administration of IFN-γ to mice with invasive aspergillosis was leading to reduced fungal burden and increased survival (103), available clinical data are inconclusive and do not allow a final conclusion on the usefulness of this strategy (11).
In addition to IFN-γ, NK cells produce soluble molecules such as GM-CSF and RANTES, both of which augment the host immune response via the stimulation of phagocytes and T cells, respectively (104–106).
Interplay of NK Cells and Fungi
Fungi have developed strategies to counteract the complex and sophisticated antifungal immune response of the host. For example, A. fumigatus galactosaminogalactan induces apoptosis of polymorphonuclear neutrophils (107). Shedding of this molecule results in NK cell activation, which, in turn, leads to a Fas-dependent apoptosis-promoting signal in polymorphonuclear neutrophils (108). Galactosaminogalactan also induces IL-1 receptor antagonist, which leads to the suppression of IL-17 and IL-22 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (109), and similar effects were observed with Aspergillus chitin (110). In addition, mycotoxins such as gliotoxin or aflatoxin (111) inhibit the phagocytic activity of macrophages, induce the apoptosis of monocytes, decrease the activation of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase in neutrophils, and impair functional T cell responses (112–116), all of which hampers the host immune response toward the pathogen.
When NK cells are co-incubated with A. fumigatus or R. oryzae, lower levels of IFN-γ, GM-CSF, and RANTES are detected in the supernatant as compared to NK cells incubated alone (62, 63). Surprisingly, A. fumigatus increases the gene expression of IFN-γ in NK cells, but inhibits its release, thus leading to intracellular accumulation and decreased extracellular availability (117). Similarly, various mucormycetes affect the IFN-γ release by human NK cells (64). In contrast, earlier studies report that C. neoformans downregulates of the production of GM-CSF and TNF-α in unstimulated human NK cells, as assessed by gene expression and supernatant protein levels (118).
When looking at the fungal pathogen, it has been demonstrated that co-incubation of NK cells with A. fumigatus upregulated the expression of several stress-related fungal genes (117). This has been demonstrated for the heat shock protein hsp90 or the ferric reductase freB (117). In A. fumigatus, Hsp90 plays an important role in the compensatory repair mechanisms of the cell wall in response to stress induced by antifungals, and Hsp90 has been described as a trigger for resistance to high concentrations of caspofungin, known as the paradoxical effect (119). FreB has recently been identified as an important enzyme in filamentous fungi which helps the fungus to adapt to iron starvation (120). Similarly, perforin-induced reduction of iron availability leads to the upregulation of the gene expression of CSA2 in C. albicans, which is involved in the uptake of iron of human hemoglobin (84). Further characterization of specific interactions of the host immune system and fungal pathogens might identify novel targets for the antifungal armamentarium, e.g., the disruption of Hsp90 circuitry by Hsp90 inhibitors or anti-calcineurin drugs.
NK Cells and Invasive Fungal Infection: Animal Studies
The few data of animal models clearly support the in vitro findings that NK cells play an important role in the antifungal host immune response. An early study in mice infected with A. niger demonstrated the association of the proliferation of NK cells and the inhibition of fungal growth (69). In addition, depletion of NK cells in mice inoculated with C. neoformans resulted in a considerably higher fungal load in the lungs as compared to untreated animals (121). In addition, antibody-mediated depletion of NK cells also decreased the phagocytosis of C. albicans by splenic macrophages as compared to controls (5.2 versus 21.5%) (100), and depletion of NK cells in mice via anti-asialo GM1 antibody resulted in enhanced susceptibility to Histoplasma capsulatum (122). Interestingly, in neutropenic mice, antibody-mediated depletion of NK cells also resulted in impaired clearance of the pathogen from the lungs and in a greater than twofold increase in mortality as compared to neutropenic mice with NK cells (123).
Importantly, the adoptive transfer of NK cells in mice lacking these cells can restore antifungal resistance. For example, in cyclophosphamide-pretreated mice suffering from cryptococcosis, the adoptive transfer of NK cell-enriched cell populations resulted in an enhanced clearance of the fungus as compared to controls receiving NK cell-depleted grafts (124, 125). As noted above, NK cell-derived IFN-γ plays an important role in the antifungal host response. NK cell depletion in neutropenic mice with invasive aspergillosis was leading to reduced lung IFN-γ levels and increased pulmonary fungal load, which was independent of T and B cell lymphocytes (101). However, the transfer of activated NK cells from wild-type, but not from IFN-γ-deficient mice resulted in better clearance of A. fumigatus from the lungs of both IFN-γ-deficient and wild-type recipients. Based on these findings, future studies have to assess in which clinical circumstances the adoptive transfer of NK cells to an immunocomoromised host suffering from an invasive fungal infection will be of benefit.
Conclusion and Perspectives
There is increasing evidence that NK cells play an important role in the antifungal host response. In vitro data show that multiple fungal pathogens are able to activate NK cells, and further research will hopefully shed more light in the characterization of the complex interplay of NK cell receptors and fungal ligands. Once activated, NK cells directly damage the fungus by soluble cytotoxic molecules such as perforin, whereas the role of other mechanisms such as the induction of apoptosis via different pathways is still relatively unclear. In addition to the direct fungal damage, NK cells release multiple cytokines and IFNs by which they modulate the immune system, e.g., via neutrophils and T cells. As cure from an infectious complication not only depends on the successful activation of the immune system but also from a timely downregulation and resolution of the inflammatory process, further research needs to characterize the release of pro- and anti-inflammatory molecules. How and to what extent the fungus itself alters its gene expression profile in the presence of NK cells remains another research gap. In this regard, we have to learn how the fungus compromises the host immune system, which might offer new targets in our combat against the pathogen. In addition, animal studies will help to clarify the benefit and potential risks of using NK cells as adoptive preventive or therapeutic strategy, which may be a significant step toward decreasing morbidity and mortality of invasive fungal infection in the clinical setting.
Author Contributions
All authors were involved in the concept of the manuscript, search and analysis of the references, and writing the manuscript; read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
ADCC, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity; CD, cluster of differentiation; SRIR, self-recognizing inhibitory receptors; EBV, Epstein–Barr virus; CMV, cytomegalovirus; ALL, acute lymphoblastic leukemia; AML, acute myeloid leukemia; IFN, interferon; ILC, innate lymphoid cell; DCs, dendritic cells; RANTES, regulated upon activation, normal T-cell expressed, and secreted; CCL5, chemokine ligand 5; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; HSCT, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; ROS, reactive oxygen species; CMCC, chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; IL, interleukin; TRAIL, tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis inducing ligand; IgG, immunoglobulin G; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; Hsp, heat shock protein; NCR, natural cytotoxicity receptors; Gr-MDSC, granulocyte myeloid-derived suppressor cell; ITAM, immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif.
References
- 1.Zaoutis TE, Heydon K, Chu JH, Walsh TJ, Steinbach WJ. Epidemiology, outcomes, and costs of invasive aspergillosis in immunocompromised children in the United States, 2000. Pediatrics (2006) 117:e711–6. 10.1542/peds.2005-1161 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bitar D, Lortholary O, Le Strat Y, Nicolau J, Coignard B, Tattevin P, et al. Population-based analysis of invasive fungal infections, France, 2001–2010. Emerg Infect Dis (2014) 20:1149–55. 10.3201/eid2007.140087 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.McNeil MM, Nash SL, Hajjeh RA, Phelan MA, Conn LA, Plikaytis BD, et al. Trends in mortality due to invasive mycotic diseases in the United States, 1980-1997. Clin Infect Dis (2001) 33:641–7. 10.1086/322606 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kontoyiannis DP, Marr KA, Park BJ, Alexander BD, Anaissie EJ, Walsh TJ, et al. Prospective surveillance for invasive fungal infections in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients, 2001-2006: overview of the transplant-associated infection surveillance network (TRANSNET) database. Clin Infect Dis (2010) 50:1091–100. 10.1086/651263 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Horn DL, Fishman JA, Steinbach WJ, Anaissie EJ, Marr KA, Olyaei AJ, et al. Presentation of the PATH Alliance® registry for prospective data collection and analysis of the epidemiology, therapy, and outcomes of invasive fungal infections. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis (2007) 59:407–14. 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2007.06.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Azie N, Neofytos D, Pfaller M, Meier-Kriesche HU, Quan SP, Horn D. The PATH (prospective antifungal therapy) Alliance® registry and invasive fungal infections: update 2012. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis (2012) 73:293–300. 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2012.06.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lehrnbecher T, Koehl U, Wittekindt B, Bochennek K, Tramsen L, Klingebiel T, et al. Changes in host defence induced by malignancies and antineoplastic treatment: implication for immunotherapeutic strategies. Lancet Oncol (2008) 9:269–78. 10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70071-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lehrnbecher T, Foster C, Vázquez N, Mackall CL, Chanock SJ. Therapy-induced alterations in host defense in children receiving therapy for cancer. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol (1997) 19:399–417. 10.1097/00043426-199709000-00001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bodey GP. Infectious complications of acute leukemia. Med Times (1966) 94:1076–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Stuehler C, Kuenzli E, Jaeger VK, Baettig V, Ferracin F, Rajacic Z, et al. Immune reconstitution after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and association with occurrence and outcome of invasive aspergillosis. J Infect Dis (2015) 212:959–67. 10.1093/infdis/jiv143 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lehrnbecher T, Kalkum M, Champer J, Tramsen L, Schmidt S, Klingebiel T. Immunotherapy in invasive fungal infection – focus on invasive aspergillosis. Curr Pharm Des (2013) 19:3689–712. 10.2174/1381612811319200010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Romani L. Immunity to fungal infections. Nat Rev Immunol (2004) 4:1–23. 10.1038/nri1255 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Romani L. Immunity to fungal infections. Nat Rev Immunol (2011) 11:275–88. 10.1038/nri2939 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fisher BT, Robinson PD, Lehrnbecher T, Steinbach WJ, Zaoutis TE, Phillips B, et al. Risk factors for invasive fungal disease in pediatric cancer and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a systematic review. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc (2017). 10.1093/jpids/pix030 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cunha C, Kurzai O, Löffler J, Aversa F, Romani L, Carvalho A. Neutrophil responses to aspergillosis: new roles for old players. Mycopathologia (2014) 178:387–93. 10.1007/s11046-014-9796-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Borghi M, Renga G, Puccetti M, Oikonomou V, Palmieri M, Galosi C, et al. Antifungal Th immunity: growing up in family. Front Immunol (2014) 5:506. 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00506 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Limon JJ, Skalski JH, Underhill DM. Commensal fungi in health and disease. Cell Host Microbe (2017) 22:156–65. 10.1016/j.chom.2017.07.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cooper MA, Fehniger TA, Caligiuri MA. The biology of human natural killer-cell subsets. Trends Immunol (2001) 22:633–40. 10.1016/S1471-4906(01)02060-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sun JC, Lopez-Verges S, Kim CC, DeRisi JL, Lanier LL. NK cells and immune “memory”. J Immunol (2011) 186:1891–7. 10.4049/jimmunol.1003035 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Narni-Mancinelli E, Vivier E, Kerdiles YM. The “T-cell-ness” of NK cells: unexpected similarities between NK cells and T cells. Int Immunol (2011) 23:427–31. 10.1093/intimm/dxr035 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kleinnijenhuis J, Quintin J, Preijers F, Joosten LAB, Jacobs C, Xavier RJ, et al. BCG-induced trained immunity in NK cells: role for non-specific protection to infection. Clin Immunol (2014) 155:213–9. 10.1016/j.clim.2014.10.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kiessling R, Klein E, Wigzell H. “Natural” killer cells in the mouse. I. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Specificity and distribution according to genotype. Eur J Immunol (1975) 5:112–7. 10.1002/eji.1830050208 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lam VC, Lanier LL. NK cells in host responses to viral infections. Curr Opin Immunol (2017) 44:43–51. 10.1016/j.coi.2016.11.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Arase H, Mocarski ES, Campbell AE, Hill AB, Lanier LL. Direct recognition of cytomegalovirus by activating and inhibitory NK cell receptors. Science (2002) 296:1323–6. 10.1126/science.1070884 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Adams EJ, Juo ZS, Venook RT, Boulanger MJ, Arase H, Lanier LL, et al. Structural elucidation of the m157 mouse cytomegalovirus ligand for Ly49 natural killer cell receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2007) 104:10128–33. 10.1073/pnas.0703735104 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kielczewska A, Kim H-S, Lanier LL, Dimasi N, Vidal SM. Critical residues at the Ly49 natural killer receptor’s homodimer interface determine functional recognition of m157, a mouse cytomegalovirus MHC class I-like protein. J Immunol (2007) 178:369–77. 10.4049/jimmunol.178.1.369 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Romee R, Schneider SE, Leong JW, Chase JM, Keppel CR, Sullivan RP, et al. Cytokine activation induces human memory-like NK cells. Blood (2012) 120:4751–60. 10.1182/blood-2012-04-419283 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Malmberg K-J, Carlsten M, Björklund A, Sohlberg E, Bryceson YT, Ljunggren H-G. Natural killer cell-mediated immunosurveillance of human cancer. Semin Immunol (2017) 31:20–9. 10.1016/j.smim.2017.08.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Herberman RR, Ortaldo JR, Bonnard GD. Augmentation by interferon of human natural and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Nature (1979) 277:221–3. 10.1038/277221a0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ortaldo JR, Bonnard GD, Kind PD, Herberman RB. Cytotoxicity by cultured human lymphocytes: characteristics of effector cells and specificity of cytotoxicity. J Immunol (1979) 122:1489–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Biron CA, Welsh RM. Activation and role of natural killer cells in virus infections. Med Microbiol Immunol (1982) 170:155–72. 10.1007/BF02298196 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Liu LL, Béziat V, Oei VYS, Pfefferle A, Schaffer M, Lehmann S, et al. Ex vivo expanded adaptive NK cells effectively kill primary acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Cancer Immunol Res (2017) 5:654–65. 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-16-0296 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Schlegel P, Ditthard K, Lang P, Mezger M, Michaelis S, Handgretinger R, et al. NKG2D signaling leads to NK cell mediated lysis of childhood AML. J Immunol Res (2015) 2015:473175. 10.1155/2015/473175 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Castriconi R, Dondero A, Corrias MV, Lanino E, Pende D, Moretta L, et al. Natural killer cell-mediated killing of freshly isolated neuroblastoma cells: critical role of DNAX accessory molecule-1-poliovirus receptor interaction. Cancer Res (2004) 64:9180–4. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2682 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kloess S, Huenecke S, Piechulek D, Esser R, Koch J, Brehm C, et al. IL-2-activated haploidentical NK cells restore NKG2D-mediated NK-cell cytotoxicity in neuroblastoma patients by scavenging of plasma MICA. Eur J Immunol (2010) 40:3255–67. 10.1002/eji.201040568 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Vivier E, Tomasello E, Baratin M, Walzer T, Ugolini S. Functions of natural killer cells. Nat Immunol (2008) 9:503–10. 10.1038/ni1582 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Béziat V, Dalgard O, Asselah T, Halfon P, Bedossa P, Boudifa A, et al. CMV drives clonal expansion of NKG2C+ NK cells expressing self-specific KIRs in chronic hepatitis patients. Eur J Immunol (2012) 42:447–57. 10.1002/eji.201141826 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Saghafian-Hedengren S, Sohlberg E, Theorell J, Carvalho-Queiroz C, Nagy N, Persson J-O, et al. Epstein-Barr virus coinfection in children boosts cytomegalovirus-induced differentiation of natural killer cells. J Virol (2013) 87:13446–55. 10.1128/JVI.02382-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Shabani Z, Bagheri M, Zare-Bidaki M, Hassanshahi G, Arababadi MK, Mohammadi Nejad M, et al. NK cells in hepatitis B virus infection: a potent target for immunotherapy. Arch Virol (2014) 159:1555–65. 10.1007/s00705-013-1965-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Werner JM, Heller T, Gordon AM, Sheets A, Sherker AH, Kessler E, et al. Innate immune responses in hepatitis C virus-exposed healthcare workers who do not develop acute infection. Hepatology (2013) 58:1621–31. 10.1002/hep.26353 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Garcia-Peñarrubia P, Koster FT, Kelley RO, McDowell TD, Bankhurst AD. Antibacterial activity of human natural killer cells. J Exp Med (1989) 169:99–113. 10.1084/jem.169.1.99 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Wherry JC, Schreiber RD, Unanue ER. Regulation of gamma interferon production by natural killer cells in scid mice: roles of tumor necrosis factor and bacterial stimuli. Infect Immun (1991) 59:1709–15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Anfossi N, André P, Guia S, Falk CS, Roetynck S, Stewart CA, et al. Human NK cell education by inhibitory receptors for MHC class I. Immunity (2006) 25:331–42. 10.1016/j.immuni.2006.06.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Parsons MS, Zipperlen K, Gallant M, Grant M. Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL1 licenses CD16-mediated effector functions of natural killer cells. J Leukoc Biol (2010) 88:905–12. 10.1189/jlb.1009687 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Horowitz A, Djaoud Z, Nemat-Gorgani N, Blokhuis J, Hilton HG, Béziat V, et al. Class I HLA haplotypes form two schools that educate NK cells in different ways. Sci Immunol (2016) 1:eaag1672. 10.1126/sciimmunol.aag1672 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Campbell KS, Hasegawa J. NK cell biology: an update and future directions. J Allergy Clin Immunol (2013) 132:536–44. 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.07.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Yawata M, Yawata N, Draghi M, Little A-M, Partheniou F, Parham P. Roles for HLA and KIR polymorphisms in natural killer cell repertoire selection and modulation of effector function. J Exp Med (2006) 203:633–45. 10.1084/jem.20051884 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Yawata M, Yawata N, Draghi M, Partheniou F, Little A-M, Parham P. MHC class I-specific inhibitory receptors and their ligands structure diverse human NK-cell repertoires toward a balance of missing self-response. Blood (2008) 112:2369–80. 10.1182/blood-2008-03-143727 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Horowitz A, Strauss-Albee DM, Leipold M, Kubo J, Nemat-Gorgani N, Dogan OC, et al. Genetic and environmental determinants of human NK cell diversity revealed by mass cytometry. Sci Transl Med (2013) 5:208ra145. 10.1126/scitranslmed.3006702 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kim S, Poursine-Laurent J, Truscott SM, Lybarger L, Song Y-J, Yang L, et al. Licensing of natural killer cells by host major histocompatibility complex class I molecules. Nature (2005) 436:709–13. 10.1038/nature03847 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Fernandez NC, Treiner E, Vance RE, Jamieson AM, Lemieux S, Raulet DH. A subset of natural killer cells achieves self-tolerance without expressing inhibitory receptors specific for self-MHC molecules. Blood (2005) 105:4416–23. 10.1182/blood-2004-08-3156 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Brodin P, Lakshmikanth T, Johansson S, Kärre K, Höglund P. The strength of inhibitory input during education quantitatively tunes the functional responsiveness of individual natural killer cells. Blood (2009) 113:2434–41. 10.1182/blood-2008-05-156836 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Joncker NT, Fernandez NC, Treiner E, Vivier E, Raulet DH. NK cell responsiveness is tuned commensurate with the number of inhibitory receptors for self-MHC class I: the rheostat model. J Immunol (2009) 182:4572–80. 10.4049/jimmunol.0803900 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Orr MT, Murphy WJ, Lanier LL. “Unlicensed” natural killer cells dominate the response to cytomegalovirus infection. Nat Immunol (2010) 11:321–7. 10.1038/ni.1849 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Spits H, Artis D, Colonna M, Diefenbach A, Di Santo JP, Eberl G, et al. Innate lymphoid cells – a proposal for uniform nomenclature. Nat Rev Immunol (2013) 13:145–9. 10.1038/nri3365 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Orange JS, Ballas ZK. Natural killer cells in human health and disease. Clin Immunol (2006) 118:1–10. 10.1016/j.clim.2005.10.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Fernández-Ruiz M, López-Medrano F, San Juan R, Allende LM, Paz-Artal E, Aguado JM. Low natural killer cell counts and onset of invasive fungal disease after solid organ transplantation. J Infect Dis (2016) 213:873–4. 10.1093/infdis/jiv552 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Palma-Carlos AG, Palma-Carlos ML. Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis revisited. Allerg Immunol (Paris) (2001) 33:229–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Chiu S-J, Tsao C-H, Chen L-C, Kao C-C, Lue K-H, Huang J-L. Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis in a 6-year-old boy. J Microbiol Immunol Infect (2004) 37:196–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.De Moraes-Vasconcelos D, Orii NM, Romano CC, Iqueoka RY, Duarte AJS. Characterization of the cellular immune function of patients with chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. Clin Exp Immunol (2001) 123:247–53. 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01430.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Akiba H, Motoki Y, Satoh M, Iwatsuki K, Kaneko F. Recalcitrant trichophytic granuloma associated with NK-cell deficiency in a SLE patient treated with corticosteroid. Eur J Dermatol (2001) 11:58–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Schmidt S, Tramsen L, Hanisch M, Latgé J-P, Huenecke S, Koehl U, et al. Human natural killer cells exhibit direct activity against Aspergillus fumigatus hyphae, but not against resting conidia. J Infect Dis (2011) 203:430–5. 10.1093/infdis/jiq062 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Schmidt S, Tramsen L, Perkhofer S, Lass-Florl C, Hanisch M, Roger F, et al. Rhizopus oryzae hyphae are damaged by human natural killer (NK) cells, but suppress NK cell mediated immunity. Immunobiology (2013) 218:939–44. 10.1016/j.imbio.2012.10.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Schmidt S, Schneider A, Demir A, Lass-Flörl C, Lehrnbecher T. Natural killer cell-mediated damage of clinical isolates of mucormycetes. Mycoses (2016) 59:34–8. 10.1111/myc.12431 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Bouzani M, Ok M, McCormick A, Ebel F, Kurzai O, Morton CO, et al. Human NK cells display important antifungal activity against Aspergillus fumigatus, which is directly mediated by IFN-γ release. J Immunol (2011) 187:1369–76. 10.4049/jimmunol.1003593 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Hidore MR, Nabavi N, Reynolds CW, Henkart PA, Murphy JW. Cytoplasmic components of natural killer cells limit the growth of Cryptococcus neoformans. J Leukoc Biol (1990) 48:15–26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Ma LL, Wang CLC, Neely GG, Epelman S, Krensky AM, Mody CH. NK cells use perforin rather than granulysin for anticryptococcal activity. J Immunol (2004) 173:3357–65. 10.4049/jimmunol.173.5.3357 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Li SS, Kyei SK, Timm-McCann M, Ogbomo H, Jones GJ, Shi M, et al. The NK receptor NKp30 mediates direct fungal recognition and killing and is diminished in NK cells from HIV-infected patients. Cell Host Microbe (2013) 14:387–97. 10.1016/j.chom.2013.09.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Benedetto N, Sabatini P, Sellitto C, Romano Carratelli C. Interleukin-2 and increased natural killer activity in mice experimentally infected with Aspergillus niger. Microbiologica (1988) 11:339–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Voigt J, Hünniger K, Bouzani M, Jacobsen ID, Barz D, Hube B, et al. Human natural killer cells acting as phagocytes against Candida albicans and mounting an inflammatory response that modulates neutrophil antifungal activity. J Infect Dis (2014) 209:616–26. 10.1093/infdis/jit574 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Aimanianda V, Bayry J, Bozza S, Kniemeyer O, Perruccio K, Elluru SR, et al. Surface hydrophobin prevents immune recognition of airborne fungal spores. Nature (2009) 460:1117–21. 10.1038/nature08264 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Chai LYA, Netea MG, Sugui J, Vonk AG, van de Sande WWJ, Warris A, et al. Aspergillus fumigatus conidial melanin modulates host cytokine response. Immunobiology (2010) 215:915–20. 10.1016/j.imbio.2009.10.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Kozel TR, Gotschlich EC. The capsule of Cryptococcus neoformans passively inhibits phagocytosis of the yeast by macrophages. J Immunol (1982) 129:1675–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Rappleye CA, Goldman WE. Fungal stealth technology. Trends Immunol (2008) 29:18–24. 10.1016/j.it.2007.10.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Marr KJ, Jones GJ, Zheng C, Huston SM, Timm-McCann M, Islam A, et al. Cryptococcus neoformans directly stimulates perforin production and rearms NK cells for enhanced anticryptococcal microbicidal activity. Infect Immun (2009) 77:2436–46. 10.1128/IAI.01232-08 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Mueller-Leisse J, Brueggemann S, Bouzani M, Schmitt A-L, Einsele H, Loeffler J. Polymorphonuclear neutrophils and granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells inhibit natural killer cell activity toward Aspergillus fumigatus. Med Mycol (2015) 53:622–9. 10.1093/mmy/myv030 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Vitenshtein A, Charpak-Amikam Y, Yamin R, Bauman Y, Isaacson B, Stein N, et al. NK cell recognition of Candida glabrata through binding of NKp46 and NCR1 to fungal ligands Epa1, Epa6, and Epa7. Cell Host Microbe (2016) 20:527–34. 10.1016/j.chom.2016.09.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.de Groot PWJ, Bader O, de Boer AD, Weig M, Chauhan N. Adhesins in human fungal pathogens: glue with plenty of stick. Eukaryot Cell (2013) 12:470–81. 10.1128/EC.00364-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Ogbomo H, Mody CH. Granule-dependent natural killer cell cytotoxicity to fungal pathogens. Front Immunol (2017) 7:692. 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00692 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Ziegler S, Weiss E, Schmitt A-L, Schlegel J, Burgert A, Terpitz U, et al. CD56 is a pathogen recognition receptor on human natural killer cells. Sci Rep (2017) 7:6138. 10.1038/s41598-017-06238-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Nabavi N, Murphy JW. Antibody-dependent natural killer cell-mediated growth inhibition of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun (1986) 51:556–62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Obata-Onai A, Hashimoto S, Onai N, Kurachi M, Nagai S, Shizuno K, et al. Comprehensive gene expression analysis of human NK cells and CD8(+) T lymphocytes. Int Immunol (2002) 14:1085–98. 10.1093/intimm/dxf086 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Kataoka T, Shinohara N, Takayama H, Takaku K, Kondo S, Yonehara S, et al. Concanamycin A, a powerful tool for characterization and estimation of contribution of perforin- and Fas-based lytic pathways in cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J Immunol (1996) 156:3678–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Hellwig D, Voigt J, Bouzani M, Löffler J, Albrecht-Eckardt D, Weber M, et al. Candida albicans induces metabolic reprogramming in human NK cells and responds to perforin with a zinc depletion response. Front Microbiol (2016) 7:750. 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00750 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Kyei SK, Ogbomo H, Li S, Timm-mccann M, Xiang RF, Huston SM. Mechanisms by which interleukin-12 corrects defective NK cell anticryptococcal activity in HIV-infected patients. MBio (2016) 7:e00878–16. 10.1128/mBio.00878-16 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Duke RC, Persechini PM, Chang S, Liu C-C, Cohen JJ, Young JD. Purified perforin induces target cell lysis but not DNA fragmentation. J Exp Med (1989) 170:1451–6. 10.1084/jem.170.4.1451 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Law RHP, Lukoyanova N, Voskoboinik I, Caradoc-Davies TT, Baran K, Dunstone MA, et al. The structural basis for membrane binding and pore formation by lymphocyte perforin. Nature (2010) 468:447–51. 10.1038/nature09518 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Ernst WA, Thoma-Uszynski S, Teitelbaum R, Ko C, Hanson DA, Clayberger C, et al. Granulysin, a T cell product, kills bacteria by altering membrane permeability. J Immunol (2000) 165:7102–8. 10.4049/jimmunol.165.12.7102 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Gamen S, Hanson DA, Kaspar A, Naval J, Krensky AM, Anel A. Granulysin-induced apoptosis. I. Involvement of at least two distinct pathways. J Immunol (1998) 161:1758–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Kaspar AA, Okada S, Kumar J, Poulain FR, Drouvalakis KA, Kelekar A, et al. A distinct pathway of cell-mediated apoptosis initiated by granulysin. J Immunol (2001) 167:350–6. 10.4049/jimmunol.167.1.350 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Krensky AM, Clayberger C. Biology and clinical relevance of granulysin. Tissue Antigens (2009) 73:193–8. 10.1111/j.1399-0039.2008.01218.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Okada S, Li Q, Whitin JC, Clayberger C, Krensky AM. Intracellular mediators of granulysin-induced cell death. J Immunol (2003) 171:2556–62. 10.4049/jimmunol.171.5.2556 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.El-Khoury M, Ligot R, Mahoney S, Stack CM, Perrone GG, Morton CO. The in vitro effects of interferon-gamma, alone or in combination with amphotericin B, tested against the pathogenic fungi Candida albicans and Aspergillus fumigatus. BMC Res Notes (2017) 10:364. 10.1186/s13104-017-2696-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Katti MK. Assessment of serum IL-1, IL-2 and IFN-γ levels in untreated pulmonary tuberculosis patients: role in pathogenesis. Arch Med Res (2011) 42:199–201. 10.1016/j.arcmed.2011.04.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Screpanti V, Wallin RPA, Grandien A, Ljunggren HG. Impact of FASL-induced apoptosis in the elimination of tumor cells by NK cells. Mol Immunol (2005) 42:495–9. 10.1016/j.molimm.2004.07.033 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Guerra C, Johal K, Morris D, Moreno S, Alvarado O, Gray D, et al. Control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis growth by activated natural killer cells. Clin Exp Immunol (2012) 168:142–52. 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2011.04552.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Madeo F, Herker E, Wissing S, Jungwirth H, Eisenberg T, Fröhlich KU. Apoptosis in yeast. Curr Opin Microbiol (2004) 7:655–60. 10.1016/j.mib.2004.10.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Fröhlich KU, Fussi H, Ruckenstuhl C. Yeast apoptosis – from genes to pathways. Semin Cancer Biol (2007) 17:112–21. 10.1016/j.semcancer.2006.11.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Mah AY, Cooper MA. Metabolic regulation of natural killer cell IFN-γ production. Crit Rev Immunol (2016) 36:131–47. 10.1615/CritRevImmunol.2016017387 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Algarra I, Ortega E, Serrano MJ, Alvarez de Cienfuegos G, Gaforio JJ. Suppression of splenic macrophage Candida albicans phagocytosis following in vivo depletion of natural killer cells in immunocompetent BALB/c mice and T-cell-deficient nude mice. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol (2002) 33:159–63. 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2002.tb00586.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Park SJ, Hughes MA, Burdick M, Strieter RM, Mehrad B. Early NK cell-derived IFN-y is essential to host defense in neutropenic invasive aspergillosis. J Immunol (2009) 182:4306–12. 10.4049/jimmunol.0803462 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Boehm U, Klamp T, Groot M, Howard JC. Cellular responses to interferon-gamma. Annu Rev Immunol (1997) 15:749–95. 10.1146/annurev.immunol.15.1.749 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Nagai H, Guo J, Choi H, Kurup V. Interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha protect mice from invasive aspergillosis. J Infect Dis (1995) 172:1554–60. 10.1093/infdis/172.6.1554 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Homey B, Müller A, Zlotnik A. Chemokines: agents for the immunotherapy of cancer? Nat Rev Immunol (2002) 2:175–84. 10.1038/nri748 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Richardson MD, Brownlie CE, Shankland GS. Enhanced phagocytosis and intracellular killing of Candida albicans by GM-CSF-activated human neutrophils. J Med Vet Mycol (1992) 30:433–41. 10.1080/02681219280000591 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Roilides E, Holmes A, Blake C, Venzon D, Pizzo PA, Walsh TJ. Antifungal activity of elutriated human monocytes against Aspergillus fumigatus hyphae: enhancement by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interferon-gamma. J Infect Dis (1994) 170:894–9. 10.1093/infdis/170.4.894 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Fontaine T, Delangle A, Simenel C, Coddeville B, van Vliet SJ, van Kooyk Y, et al. Galactosaminogalactan, a new immunosuppressive polysaccharide of Aspergillus fumigatus. PLoS Pathog (2011) 7:e1002372. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002372 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Robinet P, Baychelier F, Fontaine T, Picard C, Debré P, Vieillard V, et al. A polysaccharide virulence factor of a human fungal pathogen induces neutrophil apoptosis via NK cells. J Immunol (2014) 192:5332–42. 10.4049/jimmunol.1303180 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Gresnigt MS, Bozza S, Becker KL, Joosten LAB, Abdollahi-Roodsaz S, van der Berg WB, et al. A polysaccharide virulence factor from Aspergillus fumigatus elicits anti-inflammatory effects through induction of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. PLoS Pathog (2014) 10:e1003936. 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003936 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Becker KL, Aimanianda V, Wang X, Gresnigt MS, Ammerdorffer A, Jacobs CW, et al. Aspergillus cell wall chitin induces anti- and proinflammatory cytokines in human PBMCs via the Fc-γ receptor/Syk/PI3K pathway. MBio (2016) 7:e01823–15. 10.1128/mBio.01823-15 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Abad A, Fernández-Molina JV, Bikandi J, Ramírez A, Margareto J, Sendino J, et al. What makes Aspergillus fumigatus a successful pathogen? Genes and molecules involved in invasive aspergillosis. Rev Iberoam Micol (2010) 27:155–82. 10.1016/j.riam.2010.10.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Müllbacher A, Eichner RD. Immunosuppression in vitro by a metabolite of a human pathogenic fungus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (1984) 81:3835–7. 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3835 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Sutton P, Newcombe NR, Waring P, Mullbacher A. In vivo immunosuppressive activity of gliotoxin, a metabolite produced by human pathogenic fungi. Infect Immun (1994) 62:1192–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Stanzani M, Orciuolo E, Lewis R, Kontoyiannis DP, Martins SLR, St. John LS, et al. Aspergillus fumigatus suppresses the human cellular immune response via gliotoxin-mediated apoptosis of monocytes. Blood (2005) 105:2258–65. 10.1182/blood-2004-09-3421 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Tsunawaki S, Yoshida LS, Nishida S, Kobayashi T. Fungal metabolite gliotoxin inhibits assembly of the human respiratory burst NADPH oxidase fungal metabolite gliotoxin inhibits assembly of the human respiratory burst NADPH oxidase. Infect Immun (2004) 72:3373–82. 10.1128/IAI.72.6.3373-3382.2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Yamada A, Kataoka T, Nagai K. The fungal metabolite gliotoxin: immunosuppressive activity on CTL-mediated cytotoxicity. Immunol Lett (2000) 71:27–32. 10.1016/S0165-2478(99)00155-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Schneider A, Blatzer M, Posch W, Schubert R, Lass-Flörl C, Schmidt S, et al. Aspergillus fumigatus responds to natural killer (NK) cells with upregulation of stress related genes and inhibits the immunoregulatory function of NK cells. Oncotarget (2016) 7:71062–71. 10.18632/oncotarget.12616 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Murphy JW, Zhou A, Wong SC. Direct interactions of human natural killer cells with Cryptococcus neoformans inhibit granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and tumor necrosis factor alpha production. Infect Immun (1997) 65:4564–71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Lamoth F, Juvvadi PR, Steinbach WJ. Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90): a novel antifungal target against Aspergillus fumigatus. Crit Rev Microbiol (2014) 42:1–12. 10.3109/1040841X.2014.947239 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Blatzer M, Binder U, Haas H. The metalloreductase FreB is involved in adaptation of Aspergillus fumigatus to iron starvation. Fungal Genet Biol (2011) 48:1027–33. 10.1016/j.fgb.2011.07.009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Lipscomb MF, Alvarellos T, Toews GB, Tompkins R, Evans Z, Koo G, et al. Role of natural killer cells in resistance to Cryptococcus neoformans infections in mice. Am J Pathol (1987) 128:354–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Tewari RP, Von Behren LA. Immune responses in histoplasmosis, a prototype of respiratory mycoses. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci (2000) 42:265–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Morrison BE, Park SJ, Mooney JM, Mehrad B. Chemokine-mediated recruitment of NK cells is a critical host defense mechanism in invasive aspergillosis. J Clin Invest (2003) 112:1862–70. 10.1172/JCI18125 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Hidore MR, Murphy JW. Natural cellular resistance of beige mice against Cryptococcus neoformans. J Immunol (1986) 137:3624–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Hidore MR, Murphy JW. Correlation of natural killer cell activity and clearance of Cryptococcus neoformans from mice after adoptive transfer of splenic nylon wool-nonadherent cells. Infect Immun (1986) 51:547–55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]