Fig. 1.
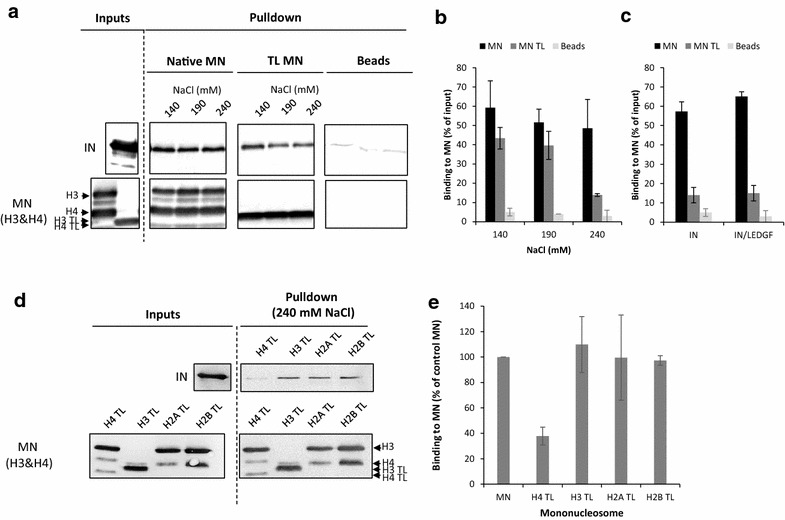
Functional interaction between HIV-1 IN and native or tailless mononucleosomes. Pull-down experiments were performed using WT IN (10 pmol) and either recombinant 601 native mononucleosomes (Native MN) or tailless MNs (TL MN) (125 ng in DNA) at 140, 190 and 240 mM NaCl concentration (lanes 140, 190 and 240). Precipitated IN was detected by western blotting using a polyclonal anti-IN antibody (IN), MNs were detected using a mixture of anti-histone H3 or H4 antibodies (MN H3&H4) (see representative pull down assay in a). The bound IN was quantified and reported as the percentage of input precipitated under each condition. Interactions between IN and native or tailless MN at 140–240 ranged NaCl concentration are reported in (b). Interactions between the IN/LEDGF complex (10 pmol of IN) and the native or tailless MN at 240 mM NaCl are reported in (c). Interactions between IN and the MN deleted either for their H4, H3, H2A or H2B tail (lanes H4 TL, H3 TL, H2A TL and H2B TL) are shown in (d) and quantification in (e). All values are shown as the mean ± standard deviation (error bars) of three independent sets of experiments. Unspecific interactions between IN or IN/LEDGF complex and beads without MN are also reported (a–c)
