Figure 1.
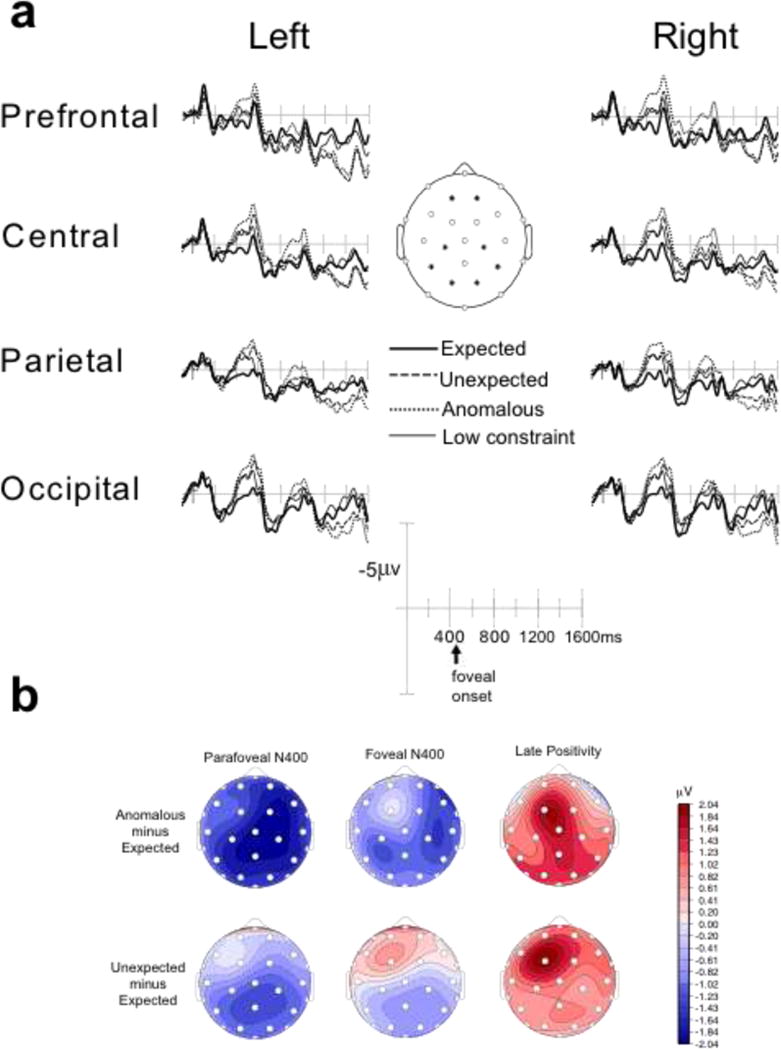
(a) Grand average event-related brain potentials at representative electrode sites. The time window encompasses both parafoveal and foveal viewing for high constraint sentences with expected, unexpected, and anomalous target words and target words in low constraint contexts. Time 0 indicates when the critical target appeared in parafoveal vision. This is followed at 450 ms by the subsequent triad, in which the target appeared in foveal vision, marked in the diagram as “foveal onset”. (B) Scalp distribution of the effect of expectancy (unexpected – expected) and congruity (anomalous – expected) violations on parafoveal and foveal N400 responses and on the late positivity following foveal viewing.
