Abstract
Tumor-associated fibroblasts (TAFs) are often essential for solid tumor growth. However, few genetic or epigenetic alterations have been found in TAFs during the progression of solid tumors. Employing a tumor-stromal cell co-injection model, we adapted here retroviral-insertional mutagenesis to stromal cells to identify novel tumor-associated genes in TAFs. We successfully identified 20 gene candidates that might modulate tumor growth if altered in TAFs at genomic level. To validate our finding, the function of one of the candidate genes, tubulin tyrosine ligase (Ttl), was further studied in TAFs from fibrosarcoma, colon, breast and hepatocarcinoma. We demonstrated that down-regulated TTL expression in TAFs indeed promoted tumor growth in mice. Interestingly, decreased expression of TTL in tumor stromal cells also correlated with poor outcome in human colon carcinoma. Thus, the co-injection model of tumor cells with retrovirus-modified fibroblasts proved a valid method to identify tumor-modulating genes in TAFs, allowing for a deeper insight into the role of the stroma for tumor development.
Keywords: Tumor-associated fibroblasts, retrovirus-insertional mutagenesis, tumor-promoting gene, co-injection model, Ttl
INTRODUCTION
Spontaneous genetic or epigenetic aberrations are hallmarks of tumor cells, but are also discovered in some stromal cells [1, 2]. Heterozygosity is often lost in stromal cells that surround tumor cells in human epithelial tumor tissues [3–6]. Some studies argue for rare genetic aberrations in stromal cells [7] that might originate from tumor cells after epithelial–mesenchymal transition [8]. It is widely acknowledged that co-evolution with tumor cells favors genetically or epigenetically abnormal tumor stromal cells [1, 9]. Most aberrations were found in fibroblast-like stromal cells, also known as tumor-associated fibroblasts (TAFs). Altered genes including Pten[10], Tgfbr2[11], Tp53[3], Sqstm1[12], Ereg[13], Ifngr[14], Hif1a and Vegfa[15] were identified from genetically engineered mice that limit a technically complicated and time-consuming attempt to only one gene per strain. Using artificial tumor microenvironments, gene expression profiling of fibroblasts co-cultured with tumor cells [16], or growth factor induced TAFs [17], also revealed altered genes in TAFs that functionally associated with tumor growth, such as IDH3α[17]. We here aim for a strategy that systematically identifies multiple functional tumor-associated genes in TAFs from dynamic tumor progression in vivo.
Retroviral genomes naturally insert into a cell genome during phylogenesis and ontogenesis [18] where it can activate oncogenes or inactivate tumor-associated genes [19]. The so called retrovirus-insertional mutagenesis has been widely applied to screen tumor-associated genes in tumor cells [19–22]. The tumor-stromal cell co-injection model helped to identify functions of tumor-associated genes in TAFs in vivo, for the convenience of genetically manipulating TAFs without altering the tumor cells themselves [23, 24]. Our previous study demonstrated that mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) upon co-injection mainly differentiated into TAFs [14], making MEFs suitable for this system [14, 20, 23, 25–27]. Combining the advantages of retrovirus-insertional mutagenesis to produce shotgun-mutated MEF libraries and co-injecting them with different tumor cell types into mice, we established a new method to identify multiple functional tumor-associated genes in TAFs. This strategy effectively models complex tumor-stroma interaction in vivo. We successfully discovered 20 tumor-associated candidate genes and subsequently confirmed Ttl, the gene for tubulin tyrosine ligase as tumor-suppressor gene in TAFs within different mouse tumor models. Strikingly, low TTL expression in tissues of human colon cancer or hepatocarcinoma correlated with poor prognosis. These results demonstrate the power of our new strategy to identify relevant tumor-associated genes in TAFs.
RESULTS
Establishment of the co-injection model of tumor cells with a fibroblast library containing shotgun gene mutations
We hypothesized that during in-vivo tumor progression from co-injected tumor cells and a pool of MEFs mutated by retroviral insertion that we call retro-MEFs, only the subsets of retro-MEFs with tumor-promoting potential survive, proliferate and enrich in the tumor stroma. The retroviral integration sites in the genome DNA of this retro-MEF progeny, further called TA-MEFs and considered equivalent to TAFs, can be identified and will provide the information on tumor-associated genes within the tumor stroma. We first tested the feasibility of all steps of our strategy.
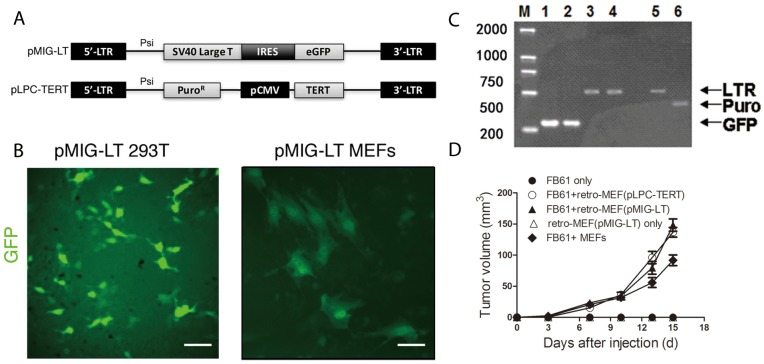
To estimate the infection efficiency and ensure ample numbers of retro-MEFs for use in the mouse model, we infected freshly prepared MEFs with retrovirus produced by a packaging cell line 293T that was transfected with the pMIG-LT vector (Figure 1A and 1C). After 72 hours, about 30% of the retro-MEFs were GFP+ (Figure 1B) and retrovirus-specific LTR amplicons from MEFs’ genomic DNA demonstrated successful integration (Figure 1C). In our previous study, the proportion of GFP+ TAFs in the tumor established by the co-injection of GFP+ MEFs with tumor cells became less than 2% after 16 days [14]. So, it was technically challenging to purify these GFP+ MEFs. We tested a pLPC-TERT retrovirus containing a puromycin-resistance gene (Figure 1A) and found it successfully integrating into the genome of infected MEFs too (Figure 1C). These MEFs were easily enriched by puromycin selection that effectively eliminated e.g. contaminating tumor cells or host fibroblasts. We next investigated the capacity of retro-MEFs to support tumor development. If co-injected with FB61 fibrosarcoma cells, MEFs infected with pMIG-LT or pLPC-TERT retrovirus, equally supported FB61 tumor growth (Figure 1D). Therefore, the pLPC-TERT retrovirus was used in the following study.
Figure 1. Production of a fibroblast library with shotgun gene mutations (retro-MEFs).
(A) Schema of the retroviral insertion sequences from the plasmids pMIG-LT and pLPC-TERT. (B) 293T cells (left panel) and freshly prepared MEFs (right panel) were transfected with pMIG-LT and cultured on slide for 24 h. Green fluorescence was assessed by fluorescence microscopy. Scale bars, 50 μm; data are representative of two independent experiments. (C) Agarose-gel images showing successful transfection. pMIG-LT was used to transfect 293T cells (lanes 1,3) or MEFs (lane 2,4); pLPC-TERT for MEFs (lanes 5,6). Inserted retroviral sequences were assessed by RT-PCR specific for GFP (amplicon size: 278 bp; lanes 1-2), retroviral LTR (amplicon size: 512 bp; lanes 3,4,5) or the puromycin-resistance gene (amplicon size: 441 bp; lane 6). M, marker. (D) Retro-MEFs were prepared by infecting MEFs with pMIG-LT (LT-GFP) or pLPC-TERT (TERT-puro) retrovirus. FB61 tumor cells were injected alone or in combination with retro-MEFs as indicated. Injection of retro-MEFs with pMIG-LT retroviral particles served as control. Tumor volumes were monitored over time as indicated. Mean ± SEM, **P< 0.01, two-way ANOVA, n=4 per group; data are representative of two independent experiments.
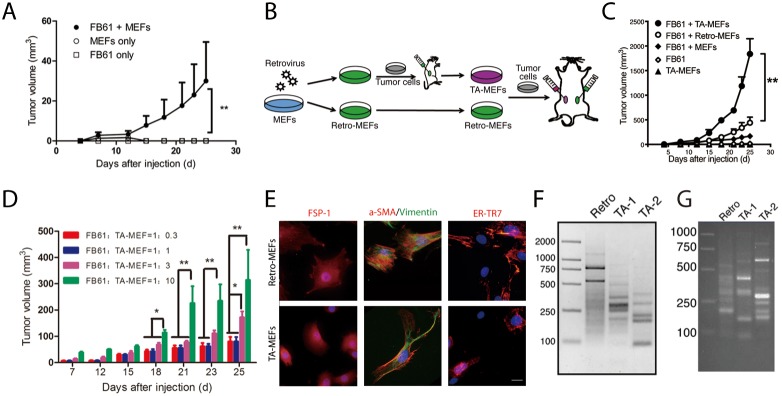
Addressing cell-dose dependencies and specificity in the co-injection model, we started with FB61 cells in combination with non-mutated MEFs. Tumors were successfully established after subcutaneous injection of MEFs (1×105) combined with low numbers of FB61 cells (2×104), while MEFs or FB61 cells alone did not establish tumors (Figure 2A). We further co-injected FB61 cells with parental retro-MEFs or TA-MEFs, and injected very large numbers of TA-MEFs (5×106) alone to test their tumorigenicity (Figure 2B). Tumor-derived TA-MEFs were not only superior to retro-MEFs or normal MEFs in supporting tumor development (Figure 2C), but dose-dependently augmented tumor growth (Figure 2D). During TA-MEF purification from tumor tissues, the efficiency of puromycin selection was routinely assessed by parallel in-vitro culture of FB61 tumor cells in the presence of puromycin (see Supplementary Figure 1). To ensure absent tumor cell contamination in the TA-MEF preparations, the selective pressure of puromycin was kept in the TA-MEFs cultures for an additional week. Final TA-MEFs preparations did not contain cells with the hematopoietic or endothelial cell markers CD45 and CD31 (not shown). All cells expressed the mesenchymal cell markers vimentin, α-smooth muscle actin (SMA), fibroblast-specific protein (FSP)-1 and ER-TR7 (Figure 2E). The staining result is consistent with our previous finding that the progeny of MEFs in such co-injection models mostly displayed an appearance of fibroblasts. Our experimental setup did not exclude that a small proportion of co-injected MEFs might have differentiated into other cell types [14]. Since these were not tumor cells, we assumed them negligible for the overall effects. The products of LAM-PCR from retro-MEFs out of FB61 and TS/A tumor tissues appear as continuum of amplicon length, whereas a decreased diversity of retroviral integration sites in the TA-MEFs is represented by defined bands with very high intensity against a reduced background of amplicon length (Figure 2F-2G).
Figure 2. In vivo discovery of tumor-associated genes in TA-MEFs.
(A) BALB/c mice were subcutaneously injected with MEFs in combination with FB61 tumor cells. Injection of FB61 tumor cells or MEFs alone served as control. Tumor volumes were monitored over time as indicated. Mean ± SEM, **P< 0.01, two-way ANOVA, n = 6 per group; data are representative of three independent experiments. (B) Schema for the functional development of TA-MEFs from shotgun transduced MEFs (retro-MEFs) via primary tumor passage. (C) BALB/c mice were subcutaneously injected with MEFs, retro-MEFs or TA-MEFs in combination with FB61 tumor cells. Injection of FB61 tumor cells or larger number of TA-MEFs (5×106) alone served as control. Tumor volumes were monitored over time as indicated. Mean ± SEM, **P< 0.01, two-way ANOVA, n=6 per group; data are representative of three independent experiments. (D) FB61 cells were mixed with TA-MEFs at different ratios as indicated before co-injection into BALB/c mice. Tumor volumes were monitored over time as indicated. Mean ± SEM, *P< 0.05, **P< 0.01, two-way ANOVA, n=5 per group; data are representative of two independent experiments. (E) TA-MEFs isolated from tumors established by co-injection of retro-MEFs and FB61 tumor cells were stained for FSP-1, α-SMA/vimentin or ER-TR7 and assessed by confocal microscopy. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Scale bars, 20 μm; data are representative of two independent experiments. (F, G) LAM-PCR was performed for retro-MEFs and TA-MEFs isolated from FB61 (F) and TS/A (G) tumors. TA-1 and TA-2 were two different batches of TA-MEFs isolated from two different tumors. Data are representative of three independent experiments.
Taken together, TA-MEFs were able to support substantial tumor growth with 2×104 co-injected tumor cells, an amount that was used in all following experiments. Fulfilling a prerequisite condition for our screening strategy, selective enrichment of limited numbers of LTR-containing amplicons during tumor progression indicated that the TA-MEFs derived from retro-MEFs indeed functioned as TAFs.
Identification of retrovirus integration sites
Twelve batches of TA-MEFs re-isolated from co-injection models with FB61 (6/12), TS/A (4/12) and MCA-205 (2/12) were subjected to LAM-PCR. For each batch, the three most abundant bands were cloned and sequenced. We obtained sequence data from 68/144 colonies from the FB61-tumor model whereas 55 of them contained LAM-PCR adaptor and retroviral LTR sequences. DNA sequences between LAM adaptor and retroviral LTR were compared to mouse genomic DNA sequences, 16/55 showed similarities higher than 95%. These numbers suggested valid amplification of TAF genomic DNA adjacent to the insertion site and successful identification of retrovirus insertion sites. Increasing the confidence in the identified integration sites, only sites located within, or up/down-stream of a gene within a window size of 30 kb were considered further. Finally, the FB61 model revealed 7 different insertion sites while an altered Ttl gene was found twice. Using the same screening strategy, we identified 5 and 2 additional insertion sites from the TS/A and MCA-205 model, respectively.
Totally, our co-injection strategy identified 20 tumor-associated candidate genes from TAFs that located in 14 retroviral insertion sites (Table 1). We reanalyzed four published GSE datasets (GEO: GSE40595, GSE38666, GSE45001, GSE26910) [28–32] from the NCBI GEO database that focused on gene expression differences between tumor stroma and normal stroma, using the online shinyGEO tool [33] (http://bioinformatics.easternct.edu/shinyGEO/). Underlining the high relevance of our identified gene candidates for tumor development, 16/20 genes including Ttl were found significantly altered (Table 2, detailed information in Supplementary Table 1).
Table 1. Summary of retroviral insertion sites in the genome and tumor-associated candidate genes in TAFs from three mouse tumor models.
| Tumor model | Insertion ID | Symbol | Subclones identified | Retroviral insertion | Summary of function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FB-61 | FB-1 | Ttl | 2 | Exon 4 | Post-translational tyrosination of the detyrosinated α-tubulin |
| FB-2 | Hist1h4m | 4 | Exon 1 | Transcription regulation | |
| FB-3 | Coro2b | 2 | Intron 7 | Binds to F-actin and to vinculin | |
| FB-4 | Slc43a2 | 1 | Exon 7 | Large neutral amino acids transportation | |
| FB-5 | Fcho2 | 2 | Intron 1 | Imposing and stabilizing particular membrane curvatures | |
| FB-6 | Cct3 | 4 | 19.9 kb up | Chaperonin | |
| FB-6 | Rhbg | 4 | 22.8 kb up | Ammonium transporter | |
| FB-7 | Zfx | 1 | 28.9 kb up | Potential transcriptional activator | |
| MCA-205 | M-1 | Bmx | 2 | 11.8 kb up | Intracellular signaling cascade |
| M-1 | Pir | 2 | Intron 1 | NFI/CTF1 cofactor | |
| M-2 | Tex13 | 2 | 24.2 kb up | Unknown | |
| TS/A | TS-1 | Stat3 | 1 | 0.5 kb up | STAT transcription factor |
| TS-2 | Stab1 | 5 | Exon 6 | Scavenger receptor | |
| TS-3 | Abt1 | 2 | 8.2 kb up | Transcription co-activator | |
| TS-3 | Btn1a1 | 2 | 29.2 kb down | Functions in the secretion of milk-fat droplets | |
| TS-4 | S100a2 | 4 | 2.0 kb down | Ca2+-binding S100 protein | |
| TS-4 | S100a3 | 4 | 7.9 kb up | Ca2+-binding S100 protein | |
| TS-4 | S100a4 | 4 | 11.5 kb up | Ca2+-binding S100 protein(Fibroblast specific protein) | |
| TS-5 | Hnrpl | 2 | 21.2 kb up | Nucleic acid and nucleotide binding | |
| TS-5 | Nfkbib | 2 | 22.2 kb up | NF-kappa B inhibitor |
Table 2. Appearance of tumor-associated candidate genes from TAFs identified in this study in published datasets comparing tumor stroma (TAF) and normal stroma (NF) from human tissues.
| Symbol | GSE accessions | FC = TAF/NF* | p-value | Tissue type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PIR | GSE26910 | 0.45 | 0.003 | Breast |
| S100A4 | GSE26910 | 0.33 | 0.002 | Prostate |
| SLC43A2 | GSE38666 | 4.00 | 0.009 | Ovary |
| S100A2 | GSE38666 | 20.00 | <0.001 | Ovary |
| STAB1 | GSE38666 | 9.09 | <0.001 | Ovary |
| S100A4 | GSE38666 | 8.33 | 0.001 | Ovary |
| TTL | GSE40595 | 0.26 | <0.001 | Ovary |
| S100A4 | GSE40595 | 9.55 | <0.001 | Ovary |
| CCT3 | GSE40595 | 9.61 | <0.001 | Ovary |
| FCHO2 | GSE40595 | 2.49 | 0.003 | Ovary |
| STAT3 | GSE40595 | 5.43 | <0.001 | Ovary |
| S100A2 | GSE40595 | 3.94 | <0.001 | Ovary |
| STAB1 | GSE40595 | 4.47 | <0.001 | Ovary |
| BMX | GSE45001 | 0.15 | <0.001 | Bile duct |
| S100A3 | GSE45001 | 9.34 | <0.001 | Bile duct |
| S100A2 | GSE45001 | 4.88 | 0.003 | Bile duct |
*Genes with fold change (FC) values >2.0 or <0.5 and p <0.01 were considered significantly up- or down-regulated.
The location of retrovirus integration suggests the direction of regulation of the candidate genes. Four gene candidates (Ttl, Hist1h4m, Slc43a2, Stab1) inserted in an exon with putative loss-of-function. Asking for the biological relevance of our findings in TAFs, we focused the following study on the functional role of Ttl that encodes an enzyme catalyzing posttranslational tyrosination of α-tubulin [34]. Lafanechere et al. showed a tumor-suppressor role for Ttl in NIH-3T3 fibroblasts [35], but considered these cell solely as tumor cells. Their study does not reflect on Ttl as a tumor-suppressor gene from the non-tumorous cell compartment within the tumor microenvironment as we specifically do here [14].
Ttl is a tumor suppressor gene in stromal cells during tumor progression
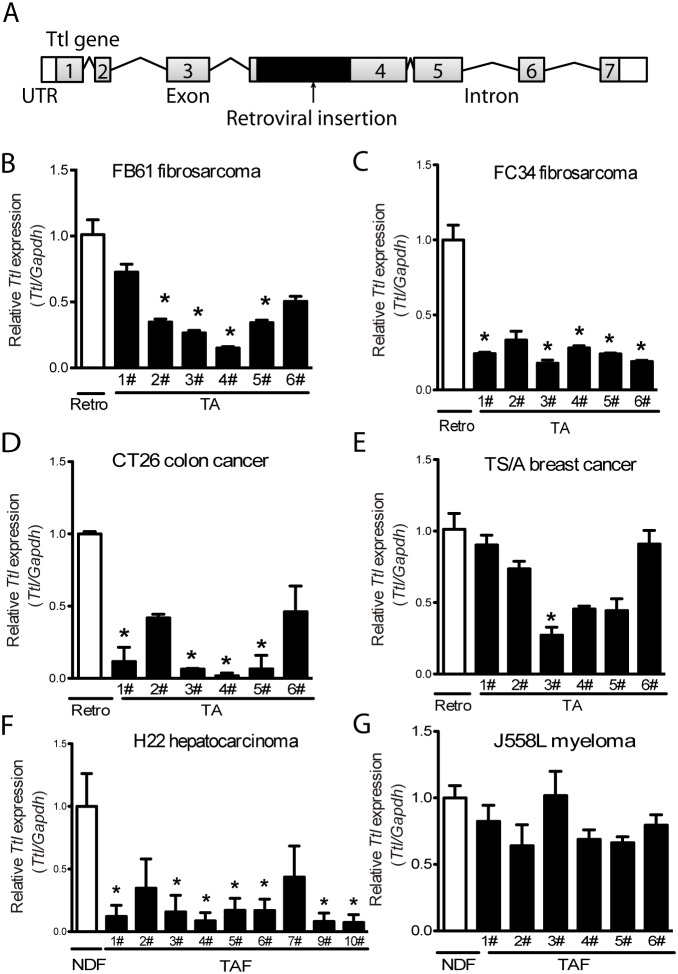
We next studied the tumor-suppressing capacity of Ttl in TAFs. The retrovirus insertion site within the exon 4 of Ttl indicated suppression of the Ttl expression (Figure 3A). Indeed, Ttl mRNA levels of TA-MEFs from the FB61 model were significantly lower compared with parental retro-MEFs (Figure 3B) - a finding repeated in TA-MEFs from most FC34, CT26 tumors and one TS/A tumor (Figure 3C-3E). To exclude extraneous effects of fibroblasts, host TAFs from H22 and J558L tumors without MEFs co-injection were isolated. In H22 TAFs, Ttl-mRNA levels were lower than that in normal dermal fibroblasts (Figure 3F). Notably, Ttl was not suppressed in the majority of the TA-MEFs from the TS/A tumors (Figure 3E) or J558L host TAFs (Figure 3G).
Figure 3. Suppressed stromal Ttl expression in different mouse tumor models.
(A) Schema of the retroviral integration site in the Ttl gene. Grey boxes with numbers represent the exons. Lines represent introns. Black boxes indicate the inserted retroviral genome. White boxes indicate untranslated regions (UTR). (B-E) Ttl mRNA levels in retro-MEFs and TA-MEFs (TA) isolated from (B) FB61, (C) FC34, (D) CT26, or (E) TS/A tumors. (F-G) Ttl mRNA levels in normal dermal fibroblasts (NDFs) and tumor-associated fibroblasts (TAFs) isolated from the subcutaneously transplanted (F) H22, n=10, and (G) J558L tumors, n=6. (B-G) Each bar indicates RT-PCR replicates of one batch of stromal cells re-isolated from a distinct tumor. Mean ± SEM, *P< 0.05, Student’s t test, n=6 per model; data are representative of two independent experiments.
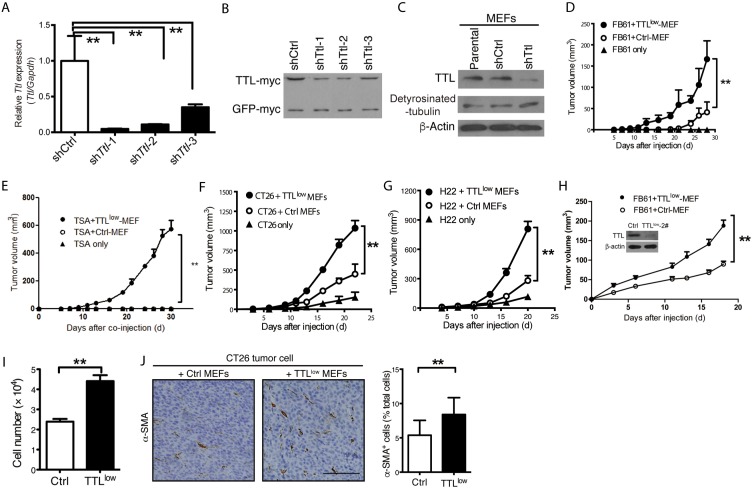
To investigate whether TAFs with reduced Ttl expression favor tumor growth, we suppressed Ttl expression exclusively in MEFs by anti-Ttl shRNA (TTLlow MEFs) before co-injection (Figure 4A-4C). Very low doses of TTLlow MEFs generated by shTtl-1 significantly promoted the in vivo growth of FB61, TS/A, CT26 and H22 tumors (Figure 4D-4G). A similar phenomenon was observed if ten times larger numbers of FB61 tumor cells were co-injected at the same ratio with TTLlow MEFs transduced with shTtl-2. We concluded that the effect on tumor growth of TTLlow MEFs neither depended on the inactivating Ttl sequence nor on the tumor cell number (Figure 4H). We hypothesized that tumor-promoting gene alterations increase proliferation of TAFs enabling them to enrich in a tumor. Indeed, TTLlow MEFs proliferated stronger than control MEFs in vitro (Figure 4I) and the α-SMA+ proportion in vivo in CT26 tumors containing TTLlow MEFs was moderately increased (Figure 4J). Taken together, these results pointed to tumor-type dependent Ttl suppression in TAFs that might be sufficient to promote the growth of certain tumor types independent of TAF proliferation.
Figure 4. Promoted tumor growth by suppressed stromal Ttl expression.
(A-C) Knock-down of Ttl in MEFs by three shTtl sequences. Three shTtl sequences were cloned into pSUPER.retro.puro plasmid. The 293T cells were transfected with either shTtl or non-targeting shCtrl vectors, together with a plasmid that carries murine Ttl and GFP cDNA with independent myc-tags for the expression of murine Ttl in the 293T cells, which is human origin. The efficacy of shTtl was determined after 24 hours. (A) Real time RT-PCR. Mean ± SEM, **P< 0.01, Student’s t test, n=3 RT-PCR replicates; data are representative of two independent experiments. (B) Western-blot analysis using an antibody specific for the myc-tag to show TTL-myc (∼45 kDa) in comparison to GFP-myc (∼27 kDa) as control for transfection efficiency. Data are representative of two independent experiments. (C) MEFs were transduced with shTtl-1 (shTtl) or shCtrl retroviral particles. Western-blot analysis using antibodies specific to TTL (∼45 kDa) and detyrosinated α-tubulin (detyrosinated-tubulin; ∼50 kDa). β-actin (∼ 42 kDa) served as loading control. Data are representative of three independent experiments. (D-G) TTLlow MEFs (transduced with shTtl-1) or Ctrl MEFs were co-injected with 2×104 (D) FB61, (E) TS/A, (F) CT26, or (G) H22 tumor cells. As a control, 2×104 tumor cells were injected alone. Tumor volumes were monitored over time as indicated. Mean ± SEM, **P< 0.01, two-way ANOVA, n = 6 per group; data are representative of two of three independent experiments. (H) 1×106 TTLlow MEFs (transduced with shTtl-2) or control MEFs were co-injected with 2×105 FB61 tumor cells. Tumor volumes were monitored over time. Mean ± SEM, *P < 0.05, two-way ANOVA, n=3; data are representative of two independent experiments. Insert: Western-blot analysis for Ttl and β-actin in MEFs transduced with shTtl-2 as described for Figure 4C. (I) Aormazan-based assay were used for cell proliferation analysis of TTLlow MEFs or control MEFs. Mean ± SEM, **P < 0.01, Student’s t-test, n = 6 culture replicates; data are representative of three independent experiments. (J) CT26 tumor cells were co-injected into mice with either TTLlow or control MEFs. Tumor sections were stained with α-SMA (brown). (Left) Representative images for the staining are shown. Scale bar, 50 μm. (Right) The proportion of α-SMA+ cells in the total cells was calculated (counted with nuclear numbers) from 5-6 visual fields (35 visual fields in total) of 3 sections of each tumor. Mean ± SEM, **P < 0.01, Student’s t-test, n=6 tumors per group; data are representative of three independent experiments.
Low TTL expression correlates with poor prognosis of human tumors
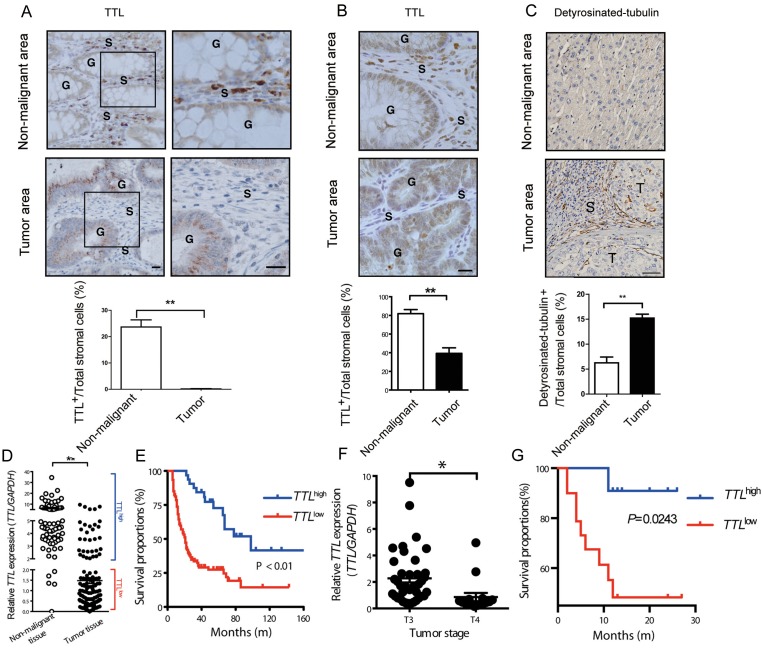
To investigate whether TTL is relevant in human tumors besides neuroblastoma [36], we examined TTL expression levels in human colon carcinoma and hepatocarcinoma tissues. In colon, TTL was highly expressed in the non-glandular stromal cells of non-malignant areas, but drastically decreased in the TAF-like stromal cells within tumor areas (Figure 5A). A similar phenotype was observed in inflammation induced mouse colon tumors (AOM/DSS, Figure 5B). Detyrosinated α-tubulin was accumulated in stromal cells of human hepatocarcinoma tissues, indicating a TTLlow-like phenotype (Figure 5C). Underlining this, TTL-mRNA levels in colon tumor tissues were significantly lower than that in non-malignant colon tissues (Figure 5D). To evaluate the clinical significance of TTL, patients with colon tumors were grouped into TTLhigh and TTLlow based on the relative TTL mRNA-levels within the tumor. Eighty months post-surgery, patients in the TTLhigh group showed better overall survival compared to the TTLlow group (Figure 5E), and multivariate survival analysis showed that such grouping based on TTL levels significantly impacted survival of patients (Supplementary Table 2). Although TTL levels did not correlate with size or metastasis of colon tumors (Supplementary Table 3), the average TTL levels in T4-stage tumor tissues was significantly lower than that in T3 stage (Figure 5F). Similarly, low TTL levels were also associated with shorter survival times of hepatocarcinoma patients (Figure 5G). However, due to the limited samples, the multivariate survival analysis here did not show such grouping significantly impacted the survival of patients, just as parameters like age, tumor stage and size as well as the degree of liver fibrosis (Supplementary Table 4). Together, the results indicated that low TTL levels in human tumors might be a novel indicator of poor prognosis.
Figure 5. Suppressed TTL expression in stromal cells of human colon and liver cancer tissues.
(A) Paraffin-embedded tissue samples ± 1 cm from the boundary of a tumor nodule (tumor area) or more than 2 cm away from tumor nodules (non-malignant areas) of human colon carcinoma were stained by immunohistochemistry for TTL (brown). (Upper left panel) Representative images from colon areas of one patient; boxed areas enlarged next to original (upper right panel); G, colonic glands; S, stroma; scale bars, 20 μm. (B) Representative images of TTL+ cells (brown) stained in non-malignant and adenoma areas of the colon tissues from a mouse model of intestinal inflammation-induced carcinogenesis (AOM/DSS). G, colonic glands; S, stromal surrounding the colonic glands; scale bars, 20 μm. (C) Tumor and non-tumor areas as described in (A) from human hepatocarcinoma tissues were stained for detyrosinated-tubulin (abbreviated as “Glu-tublin”, brown). Representative images from liver tissue areas from one patient. T, tumor nests; S, stroma. Bars, 50 μm. (A-C, lower panels) Proportions of TTL+ or detyrosinated-tubulin+ stromal cells were calculated by counting TTL+ or detyrosinated-tubulin+ stromal cells and all nuclei within the stroma from 35 visual fields (AOM/DSS induced), or 6 visual fields (human colon or liver) tissue sample. Mean ± SEM, **P< 0.01, Student’s t test, n=6 tumors per group. (D) Human TTL mRNA levels in non-malignant colon tissues (n = 72) and colon tumor tissues (n = 77). Scatter plot and mean, **P < 0.0001, Student’s t test. Cut-off value for definition of TTLhigh samples set as 2.0. (E) TTLlow and TTLhigh expression in colon tumor tissue was correlated to the overall survival of the colon tumor patients after surgery. P < 0.01, log-rank test, n = 72. (F) The TTL expression levels in colon tumor tissues from T3 (n = 42) and T4 stage (n = 16) were compared. Scatter plot and mean, *P= 0.012, Student’s t test. (G) TTLlow and TTLhigh expression in liver tumor tissues was defined as described in (D) and correlated to the overall survival times of the hepatocarcinoma patients after surgery. P= 0.0243, log-rank test, n = 31.
DISCUSSION
More and more studies demonstrated that tumor stroma, especially TAFs are essential in tumor progression. We here for the first time, applied retrovirus insertional mutagenesis to MEFs (TAF precursors) and used them in an in vivo tumor-stroma co-injection model to identify tumor-associated genes in TAFs. This strategy successfully identified 20 putative tumor-associated candidate genes in TAFs; some were previously reported as tumor-associated in TAFs, such as Stat3[37], Stab1[38], and Nfkbib[39]. We deliberately choose Ttl to underline the biological relevance of the findings using this method and validated the tumor-promoting ability of Ttl in TAFs. Differential expression of other candidate genes like Pir and Bmx between tumor stroma and normal stroma [28–31], indicated the power of the method to address TAFs functions.
Taking in account that the number of processed retroviral insertion sites was relatively limited, we here used a strategy based on cloned LAM-PCR amplicons [40]. This approach enabled the identification of insertion sites that were most abundant in the TAF population, and, as we assumed, the most likely to be functional in TAFs for tumor growth. Confirming known functional tumor-associated genes in stromal cells such as Stat3[37] and the proof that the found altered Ttl indeed is another tumor-suppressor gene in TAFs supports the strength of this assumption. Of course, this selective approach has some drawbacks. It misses less-enriched insertions and does not allow statistical analysis among the candidate genes or between different tumor models. These questions can be addressed in further studies by deep sequencing.
So far, abnormal Ttl expression in the epithelial component of tumors is much better studied than in stromal cells [35, 36, 41–45]. Germline deletion of Ttl gene results in perinatal death of mouse [44]. High frequencies (20%) of TTL alterations has been found in prostate adenocarcinoma [46]. Ttl loss-of-function occurs in different tumor cells, and correlates with tumor progression [35, 36, 41–45]. Most of these tumor cells are the epithelial component of tumor, and only a few studies made mention of varied Ttl expression in the stromal components of a tumor, especially in TAFs [41]. Even if Ttl levels assessed at mRNA level from whole tumor tissues acceptably substantiates the prognostic value of TTL expression in human tumor tissues, our study suggests that it is much more accurate to address it at protein level in stromal compartment e.g. by immunohistochemistry for TTL or detyrosinated tubulin.
Lafanechere et al. elegantly investigated Ttl suppression in NIH-3T3 fibroblasts using these fibroblasts as tumor cells [35], while we explicitly focused on the function of Ttl in tumor stromal cells. Knock-down of Ttl promoted the proliferation of MEFs in in-vitro culture. However, in our new in vivo model of co-injecting tumor cells and retro-MEFs, promoted tumor growth was not mainly due to the increased TAF numbers or proliferation. Last but not least, injection of only small numbers of tumor cell (2×104) or MEFs alone did not establish tumor in mice. At these cell doses, the mixture of both tumor cells and MEFs was required. All this is in line with our previous work with normal MEFs where arresting proliferation by gamma-radiation did not affect the tumor-promoting capacity of MEFs in vivo, in a similar tumor-stroma co-injection model [14]. Therefore, we concluded that promoting TAF proliferation in general is only a minor factor for tumor growth.
Having demonstrated Ttl to be a “driver” gene of the tumor-promoting capacity of TAFs, we cannot fully exclude that our strategy identifies proliferation-related genes without tumor-associated function, so called “passenger” genes. Thus, subsequent functional validation of the candidate gene from TAFs during tumor progression is mandatory to confirm its “driver” gene function, as exemplified by Ttl here. Notably, with Ttl, S100a4, Zfx, Cct3, Stat3, Stab1 and Bmx, 7/20 found candidate genes have been reported as proliferation-related in tumor cells too [27, 35, 47–53]. We hypothesize that tumor-promoting gene alterations supporting TAFs proliferation and segregation within the tumor stroma enabled the enrichment of these TAFs and made them accessible. The current retrovirus-insertional mutagenesis is limited by non-random integration and low efficiency. We anticipate that less biased mutation systems such as the Sleeping Beauty transposon will improve the sensitivity of our model.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patient samples and ethics
Archived formaldehyde-fixed, paraffin-embedded and frozen tumor tissue were obtained the Peking University People’s Hospital and Henan Tumor Hospital samples. Tumor tissue was defined within these samples by the tumor nodules and areas ± 1 cm from the boundary of a tumor nodule. Non-malignant colon tissue was defined from the same samples as areas more than 2 cm distant from any tumor nodule. Fresh colon tissues from surgery that used for RNA preparation were from 77 colon cancer patients, as well as from 72 age- and sex-matched non-tumor patients of the Henan Tumor Hospital. Fresh surgical liver tissues from 31 hepatocarcinoma cancer patients were obtained from the Peking University People’s Hospital. Protocols concerning clinical sample use were approved by the Ethics Committee of Henan Tumor Hospital or Peking University People’s Hospital. Protocols concerning animal use were approved by the Institution of the Animal Care and Use Committee of Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (SYXK2013-36).
Mouse strains, MEFs and tumor cell lines
BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice were purchased from Vital River (China). Age matched (6-8 weeks) female mice were used in all experiments and randomly allocated to experimental and control groups. MEFs were prepared from E13.5 mouse embryos as described [14]. The following cell lines were used: 293T human embryonic kidney, CT26 undifferentiated colon carcinoma (ATCC, LGC Standards), FB61 and FC34 fibrosarcoma (BALB/c)[54], MCA-205 fibrosarcoma (C57BL/6)[55], TS/A mammary adenocarcinoma [56, 57] and J558L myeloma [56, 57]. H22 mouse hepatocarcinoma cells were kindly provided by Dr. Yingxin Xu (The General Hospital of People’s Liberation Army, Beijing, China). If not noted otherwise, cell lines were of murine origin. Cells were cultured in DMEM (293T, CT26) or RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with 10% newborn calf serum and 100 IU/mL penicillin/streptomycin (all from Gibco).
Plasmids
The pMIG-LT plasmid contained the a green fluorescent protein (GFP) and SV40 large-T fragment from LoxP-HyTK-SV40Tag [58] subcloned to the pMIG vector [59]. Vectors for expressing myc-tagged murine Ttl or GFP based on pcDNA4-myc (Invitrogen) were kindly provided by Dr. Guangxia Gao (Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China). Oligonucleotides specific for mouse Ttl and non-targeting sequences were cloned into pSUPER.retro.puro (Oligo Engine) to produce shTtl-retroviral particles.
Retrovirus production and transfection
The 293T cells were transfected with pMIG-LT or pLPC-TERT (Clontech) (Figure 1A) in combination with the pCL–10A1 packaging vector (Imgenex). MEFs were repeatedly infected with freshly prepared retrovirus-containing cell-culture supernatant [60]. We later refered to these cells as retro-MEFs. The 293T cells were transfected with the retroviral vectors pMIG-LT, pLPC-TERT (Clontech) or pSUPER.retro.puro-based shTtl/Ctrl in combination with the pCL–10A1 packaging vector (Imgenex) using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen). After 48 and 72 hours of culture, supernatants were collected, filtered (pore size: 0.45 μm; Millipore) and used immediately. To construct retro-MEFs, retrovirus-containing 293T supernatant was mixed with equal volumes of fresh culture medium, supplemented with 8 μg/mL polybrene (Sigma-Aldrich) and added to 3×105 MEFs in a 6-well plate The plate was spun at 1,500×g and 31 °C for 1 hour. After 6 hours at 37 °C, medium was replaced for fresh culture medium. Increasing the infection efficiency, the whole procedure was repeated three times [60].
To knock-down Ttl expression in MEFs or in 293T cells co-transfected to express myc-tagged murine Ttl and myc-tagged GFP, 1 mL retrovirus-containing 293T supernatant supplemented with 4 μg/mL polybrene was added to 2×104 MEFs or 293T cells. Cells were incubated at 37 °C for 12 hours before the medium was replaced for fresh culture medium. At 36 hours post infection, cells were collected to determine mouse Ttl expression. The following sequences specific for the mouse Ttl gene and a non-targeting control sequence were synthesized:
shTtl-1, 5’-gCATTCAgAAAGAgTACTC-3’;
shTtl-2, 5’-ggCAACgTTTggATTgCAA-3’;
shTtl-3: 5’-AgTATAATATCTACCTCTA-3’;
shCtrl: 5’-AAgCTgACCCTgAAg-3’.
Tumor transplantation
Exponentially growing tumor cells from standard culture were harvested, washed twice with PBS and subcutaneously injected into the abdominal region of the mice. In the co-injection model, mice received 2×104 tumor cells and 1×105 retro-MEFs (passages 3-6). Tumor volumes were measured and calculated by (length × width × width)/2 over time.
Isolation of tumor stromal cells and fibroblasts
Sixteen days after co-injecting tumor cells and retro-MEFs, tumors were surgically removed, cut into small fragments about 3×3×3 mm and digested with 0.48 U/mL collagenase NB4 (Serva) for 30 min at 37 °C. Single-cell suspensions were cultured in fibroblast medium consisting of DMEM supplemented with 10% newborn calf serum and 3 μg/mL puromycin. After <14 days in vitro, genomic DNA was extracted. Retro-MEFs subjected to the same in-vitro selection procedure served as controls. J558L and H22 tumor cells (1×105) were injected into mice as described above. Twenty days later, cells from the tumors were isolated, cultured in fibroblast medium before suspension-tumor cells were removed by washing the cell layers with fresh fibroblast medium the following day. The remaining adherent TAFs were passaged and identified by immunostaining for the fibroblasts markers α-smooth muscle actin (SMA) and ER-TR7. Normal dermal fibroblasts were isolated from mice with the same genetic background as the host mice of TAFs, as described before [61].
Linear amplification-mediated (LAM)-PCR
LAM-PCR was performed as described earlier [40]. Briefly, genomic DNA from TA-MEFs was digested with the NlaIII restriction enzyme and subsequently amplified using a biotinylated primer LTRI (BT-LTRI, 5’-Bio-gTTCgCTTCTCgCTTCTgTTCgC-3’). Amplification products were purified with streptavidin-coated Dynabeads M-280 (Invitrogen) and ligated to a linker cassette. Non-biotinylated strands denatured by NaOH (100 mM) served as templates for the subsequent nested PCR with the following primers:
LTRII: 5’-CTCAATAAAAgAgCCCACAACCCCT-3’;
LTRIII: 5’-ACTTgTggTCTCgCTgTTCCTTg-3’.
LAM-PCR Products were separated on 2% agarose gels and purified using MiniElute columns (Qiagen). For each sample, 3 most clearly and brightly enriched gel bands were purified and sub-cloned into the pMD19-T vector (Takara). E. coli TOP10 (Invitrogen) were transformed with the resulting plasmids. Plasmids were purified and sequenced using the M13 primer sites. Sequences adjacent to retroviral long terminal repeats (LTR) were blasted against the mouse genome (NCBI) [40]. The sequences of cloning primers were as follows:
Forward: 5'-CCggAAgATCTgCCACCATggATAAAgTTTTAAACAgAg-3';
Reverse: 5'-ggATCCggAATTCTTATgTTTCAggTTCAggg-3'.
All oligonucleotides used within this study were purchased from Sangon Biotech (Shanghai, China).
Real-time RT-PCR
Total RNA from 1×106 murine fibroblasts or from clinical samples was extracted using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen) and 2 μg RNA was reversely transcribed by M-MLV reverse transcriptase (Promega). Expression levels of Ttl were determined in relation to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (Gapdh) using the iQTM SYBR Green Supermix on MyiQTM system (Bio-Rad). The specific primers for real-time PCR were:
Western-blot analysis
Cells were lysed by RIPA solution before proteins were separated and transferred to nitrocellulose membrane (GE Healthcare) as described before [54]. Briefly, cells were lysed by RIPA solution (50 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 150 mM NaCl, 1.0% Nonidet P-40, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% sodium dodecyl sulfate, 1 mM EDTA) supplemented with 100 μM phenylmethanesulfonyl fluoride, 25 μg/mL aprotinin, 1 mM sodium orthovanadate, and 50 mM NaF [54]. Proteins from cell extracts were separated using homogenous 10% SDS-PAGE and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane (GE Healthcare) on a semi-dry transfer device (Bio-Rad). Binding of mouse-specific primary antibodies for TTL (1:2,000, SAB1103321, Sigma-Aldrich), β-actin (1:8,000, a5441, Sigma-Aldrich), rabbit polyclonal detyrosinated α-tubulin (1:2,000, ab3201, Millipore), and myc tag (1,000 clone 9E10, Thermo) were visualized using peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies (Thermo). The following peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies were used: goat anti-rabbit (1:15,000, 32460, Thermo) and goat anti-mouse (1:10,000, 31430, Thermo). Membranes were incubated with a chemiluminescent substrate (Thermo) for 5 minutes and exposed to X-ray film (Kodak).
| Mouse | Ttl | Sense: 5’-TgTAgACCATgTAgTTgAggT-3’ Anti-sense: 5’-TACgACTCggggAACCATgAg-3’ |
| Gapdh | Sense: 5’-AggTCggTgTgAACggATTTg-3’ Anti-sense: 5’-TgTAgACCATgTAgTTgAggT-3’ |
|
| Human | TTL | Sense: 5’-CAgCTCTTCggCTTTgACTT-3’ Anti-sense: 5’-GCTgTgggCTggATAAAgAg-3’ |
| GAPDH | Sense: 5’-AAgAAggTggTgAAgCAggC-3’ Anti-sense: 5’-TCCACCACCCTgTTgCTgTA-3’ |
Proliferation assay
The cell proliferation was determined using the Cell Counting Kit-8 (Sigma-Aldrich) according to the manufacturers’ instructions. In brief, MEFs were plated in a 96-well plate with the density of 2×104 cells/well, and cultured for 68 hours before the addition of CCK-8 solution. To each well, 10 μL CCK-8 solution were added and cells were cultured for additional 4 hours. The absorbance of the water soluble formazan product was measured at a wavelength of 450 nm using a microplate reader (Bio-rad).
Immunofluorescent staining and immunohistochemistry
Cells (8×103) were seeded on 10×10 mm coverslips and cultured for 12 hours before staining. Primary antibodies included: rat anti-mouse ER-TR7 (ab51824, Abcam); rabbit anti-mouse CD31 (ab28364, Abcam), vimentin (ab45939, Abcam), FSP-1 (ab27957, Abcam) and CD45 (550539, BD Biosciences); and mouse monoclonal antibody α-SMA (ab5694, Abcam). Secondary antibodies were conjugated with Alexa Fluor 555 or Alexa Fluor 488 (Invitrogen) and nuclei counterstained with 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (Sigma-Aldrich). Slides were assessed by confocal microscopy (FV1000) and images analyzed using the FV10-ASW1.7 Viewer software (both Olympus). Paraffin sections of mouse or human tissues were stained with rabbit anti-mouse TTL (SAB1103321, Sigma-Aldrich) or detyrosinated α-tubulin (ab3201, Millipore) using diaminobenzidine histochemistry kits (Invitrogen). Slides were assessed by brightfield microscopy (DP71, Olympus) and images analyzed using the Image-Pro Plus software (Media Cybernetics).
Statistical analysis
All data are from two to three independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using the GraphPad Prism software (GraphPad). P-values <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
CONCLUSION
For the first time, we successfully established a method to identify tumor-associated genes in TAFs in vivo by applying retrovirus insertional mutagenesis to MEFs in a tumor-stroma co-injection model. TA-MEFs re-isolated from tumors after co-injection exhibit augmented tumor-promoting capacity. Exemplified by suppressed Ttl expression, we show new evidence supporting the hypothesis that TAFs containing tumor-promoting genetic/epigenetic changes are selected in the tumor microenvironment. Taken together, we provide a proof of concept how insertional mutagenesis can be used as a novel strategy to identify tumor-associated genes in TAFs.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS FIGURE AND TABLES
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Ulrike Erben for comments and improvements of the manuscript, and Dr. Shu Xing for providing AOM/DSS-induced mouse colon adenoma sections.
Abbreviations
- α-SMA
α-smooth muscle actin
- GAPDH
glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- GFP
green-fluorescent protein
- LAM-PCR
linear amplification-mediated PCR
- LTR
long terminal repeat
- MEF
mouse embryonic fibroblast
- TAF
tumor-associated fibroblast
- TA-MEF
tumor-associated MEF
- TERT
telomerase reverse transcriptase
- Ttl
tubulin tyrosine ligase
Author contributions
Zhihai Qin, Lijie Rong, and Shubai Liu designed experiments; Lijie Rong, Shubai Liu, Xiaoman Liu, Xiao Li, Haiyang Liu, Jinxue Zhou, Jirun Peng, Henghui Zhang, and Hongsong Chen performed experiments; Lijie Rong, Yangyang Bian, and Shubai Liu analyzed data; Lijie Rong, Yangyang Bian, Shubai Liu, and Zhihai Qin wrote the paper. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
FUNDING
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [81630068, 31670881, 81600046, 81030049, 31071261, 81001328 and 81261130024].
REFERENCES
- 1.Hu M, Yao J, Cai L, Bachman KE, van den Brule F, Velculescu V, Polyak K. Distinct epigenetic changes in the stromal cells of breast cancers. Nat Genet. 2005;37:899–905. doi: 10.1038/ng1596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Eng C, Leone G, Orloff MS, Ostrowski MC. Genomic alterations in tumor stroma. Cancer Res. 2009;69:6759–64. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-0985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hill R, Song Y, Cardiff RD, Van Dyke T. Selective evolution of stromal mesenchyme with p53 loss in response to epithelial tumorigenesis. Cell. 2005;123:1001–11. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.09.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kurose K, Gilley K, Matsumoto S, Watson PH, Zhou XP, Eng C. Frequent somatic mutations in PTEN and TP53 are mutually exclusive in the stroma of breast carcinomas. Nat Genet. 2002;32:355–7. doi: 10.1038/ng1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Patocs A, Zhang L, Xu Y, Weber F, Caldes T, Mutter GL, Platzer P, Eng C. Breast-cancer stromal cells with TP53 mutations and nodal metastases. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:2543–51. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa071825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ashida S, Orloff MS, Bebek G, Zhang L, Zheng P, Peehl DM, Eng C. Integrated analysis reveals critical genomic regions in prostate tumor microenvironment associated with clinicopathologic phenotypes. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:1578–87. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Qiu W, Hu M, Sridhar A, Opeskin K, Fox S, Shipitsin M, Trivett M, Thompson ER, Ramakrishna M, Gorringe KL, Polyak K, Haviv I, Campbell IG. No evidence of clonal somatic genetic alterations in cancer-associated fibroblasts from human breast and ovarian carcinomas. Nat Genet. 2008;40:650–5. doi: 10.1038/ng.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Shipitsin M, Campbell LL, Argani P, Werernowicz S, Bloushtain-Qimron N, Yao J, Nikolskaya T, Serebryiskaya T, Beroukhim R, Hu M, Halushka MK, Sukumar S, Parker LM, et al. Molecular definition of breast tumor heterogeneity. Cancer Cell. 2007;11:259–73. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2007.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Polyak K, Haviv I, Campbell IG. Co-evolution of tumor cells and their microenvironment. Trends Genet. 2009;25:30–8. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2008.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Trimboli AJ, Cantemir-Stone CZ, Li F, Wallace JA, Merchant A, Creasap N, Thompson JC, Caserta E, Wang H, Chong JL. Pten in stromal fibroblasts suppresses mammary epithelial tumours. Nature. 2009;461:1084–91. doi: 10.1038/nature08486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bhowmick NA, Chytil A, Plieth D, Gorska AE, Dumont N, Shappell S, Washington MK, Neilson EG, Moses HL. TGF-beta signaling in fibroblasts modulates the oncogenic potential of adjacent epithelia. Science. 2004;303:848–51. doi: 10.1126/science.1090922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Valencia T, Kim JY, Abu-Baker S, Moscat-Pardos J, Ahn CS, Reina-Campos M, Duran A, Castilla EA, Metallo CM, Diaz-Meco MT, Moscat J. Metabolic reprogramming of stromal fibroblasts through p62-mTORC1 signaling promotes inflammation and tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 2014;26:121–35. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.05.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Neufert C, Becker C, Tureci O, Waldner MJ, Backert I, Floh K, Atreya I, Leppkes M, Jefremow A, Vieth M, Schneider-Stock R, Klinger P, Greten FR, et al. Tumor fibroblast-derived epiregulin promotes growth of colitis-associated neoplasms through ERK. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:1428–43. doi: 10.1172/JCI63748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lu Y, Yang W, Qin C, Zhang L, Deng J, Liu S, Qin Z. Responsiveness of stromal fibroblasts to IFN-gamma blocks tumor growth via angiostasis. J Immunol. 2009;183:6413–21. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kim JW, Evans C, Weidemann A, Takeda N, Lee YS, Stockmann C, Branco-Price C, Brandberg F, Leone G, Ostrowski MC, Johnson RS. Loss of fibroblast HIF-1alpha accelerates tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2012;72:3187–95. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-0534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Fromigue O, Louis K, Dayem M, Milanini J, Pages G, Tartare-Deckert S, Ponzio G, Hofman P, Barbry P, Auberger P, Mari B. Gene expression profiling of normal human pulmonary fibroblasts following coculture with non-small-cell lung cancer cells reveals alterations related to matrix degradation, angiogenesis, cell growth and survival. Oncogene. 2003;22:8487–97. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zhang D, Wang Y, Shi Z, Liu J, Sun P, Hou X, Zhang J, Zhao S, Zhou BP, Mi J. Metabolic reprogramming of cancer-associated fibroblasts by IDH3α downregulation. Cell Rep. 2015;10:1335–48. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sciamanna I, Vitullo P, Curatolo A, Spadafora C. Retrotransposons, reverse transcriptase and the genesis of new genetic information. Gene. 2009;448:180–6. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2009.07.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Vogt PK. Retroviral oncogenes: a historical primer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12:639–48. doi: 10.1038/nrc3320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Uren AG, Kool J, Berns A, van Lohuizen M. Retroviral insertional mutagenesis: past, present and future. Oncogene. 2005;24:7656–72. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Touw IP, Erkeland SJ. Retroviral insertion mutagenesis in mice as a comparative oncogenomics tool to identify disease genes in human leukemia. Mol Ther. 2007;15:13–9. doi: 10.1038/sj.mt.6300040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Qin ZH, Schuller I, Richter G, Diamantstein T, Blankenstein T. The interleukin-6 gene locus seems to be a preferred target site for retrotransposon integration. Immunogenetics. 1991;33:260–6. doi: 10.1007/BF00230504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Scherz-Shouval R, Santagata S, Mendillo ML, Sholl LM, Ben-Aharon I, Beck AH, Dias-Santagata D, Koeva M, Stemmer SM, Whitesell L, Lindquist S. The reprogramming of tumor stroma by HSF1 is a potent enabler of malignancy. Cell. 2014;158:564–78. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.05.045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Augsten M, Hagglof C, Olsson E, Stolz C, Tsagozis P, Levchenko T, Frederick MJ, Borg A, Micke P, Egevad L, Ostman A. CXCL14 is an autocrine growth factor for fibroblasts and acts as a multi-modal stimulator of prostate tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:3414–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0813144106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kiaris H, Chatzistamou I, Trimis G, Frangou-Plemmenou M, Pafiti-Kondi A, Kalofoutis A. Evidence for nonautonomous effect of p53 tumor suppressor in carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2005;65:1627–30. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lafkas D, Trimis G, Papavassiliou AG, Kiaris H. P53 mutations in stromal fibroblasts sensitize tumors against chemotherapy. Int J Cancer. 2008;123:967–71. doi: 10.1002/ijc.23546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Grum-Schwensen B, Klingelhofer J, Berg CH, El-Naaman C, Grigorian M, Lukanidin E, Ambartsumian N. Suppression of tumor development and metastasis formation in mice lacking the S100A4 (mts1) gene. Cancer Res. 2005;65:3772–80. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Yeung TL, Leung CS, Wong KK, Samimi G, Thompson MS, Liu J, Zaid TM, Ghosh S, Birrer MJ, Mok SC. TGF-β modulates ovarian cancer invasion by upregulating CAF-derived versican in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2013;73:5016–28. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-0023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lili LN, Matyunina LV, Walker L, Benigno BB, McDonald JF. Molecular profiling predicts the existence of two functionally distinct classes of ovarian cancer stroma. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:846387. doi: 10.1155/2013/846387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sulpice L, Rayar M, Desille M, Turlin B, Fautrel A, Boucher E, Llamas-Gutierrez F, Meunier B, Boudjema K, Clément B. Molecular profiling of stroma identifies osteopontin as an independent predictor of poor prognosis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology. 2013;58:1992–2000. doi: 10.1002/hep.26577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Planche A, Bacac M, Provero P, Fusco C, Delorenzi M, Stehle JC, Stamenkovic I. Identification of prognostic molecular features in the reactive stroma of human breast and prostate cancer. PLoS One. 2011;6:e18640. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sulpice L, Desille M, Turlin B, Fautrel A, Boudjema K, Clement B, Coulouarn C. Gene expression profiling of the tumor microenvironment in human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Genom Data. 2016;7:229–32. doi: 10.1016/j.gdata.2016.01.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Dumas J, Gargano MA, Dancik GM. shinyGEO: a web-based application for analyzing gene expression omnibus datasets. Bioinformatics. 2016;32:3679–3681. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Erck C, Frank R, Wehland J. Tubulin-tyrosine ligase, a long-lasting enigma. Neurochem Res. 2000;25:5–10. doi: 10.1023/a:1007523028834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lafanechère L, Courtay-Cahen C, Kawakami T, Jacrot M, Rudiger M, Wehland J, Job D, Margolis RL. Suppression of tubulin tyrosine ligase during tumor growth. J Cell Sci. 1998;111:171–81. doi: 10.1242/jcs.111.2.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kato C, Miyazaki K, Nakagawa A, Ohira M, Nakamura Y, Ozaki T, Imai T, Nakagawara A. Low expression of human tubulin tyrosine ligase and suppressed tubulin tyrosination/detyrosination cycle are associated with impaired neuronal differentiation in neuroblastomas with poor prognosis. Int J Cancer. 2004;112:365–75. doi: 10.1002/ijc.20431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Mace TA, Ameen Z, Collins A, Wojcik S, Mair M, Young GS, Fuchs JR, Eubank TD, Frankel WL, Bekaii-Saab T, Bloomston M, Lesinski GB. Pancreatic cancer-associated stellate cells promote differentiation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in a STAT3-dependent manner. Cancer Res. 2013;73:3007–18. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bacac M, Provero P, Mayran N, Stehle JC, Fusco C, Stamenkovic I. A mouse stromal response to tumor invasion predicts prostate and breast cancer patient survival. PLoS One. 2006;1:e32. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Tchou J, Kossenkov AV, Chang L, Satija C, Herlyn M, Showe LC, Pure E. Human breast cancer associated fibroblasts exhibit subtype specific gene expression profiles. BMC Med Genomics. 2012;5:39. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-5-39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Schmidt M, Schwarzwaelder K, Bartholomae C, Zaoui K, Ball C, Pilz I, Braun S, Glimm H, von Kalle C. High-resolution insertion-site analysis by linear amplification-mediated PCR (LAM-PCR) Nat Methods. 2007;4:1051–7. doi: 10.1038/nmeth1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Mialhe A, Lafanechere L, Treilleux I, Peloux N, Dumontet C, Bremond A, Panh MH, Payan R, Wehland J, Margolis RL, Job D. Tubulin detyrosination is a frequent occurrence in breast cancers of poor prognosis. Cancer Res. 2001;61:5024–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Soucek K, Kamaid A, Phung AD, Kubala L, Bulinski JC, Harper RW, Eiserich JP. Normal and prostate cancer cells display distinct molecular profiles of alpha-tubulin posttranslational modifications. Prostate. 2006;66:954–65. doi: 10.1002/pros.20416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Whipple RA, Balzer EM, Cho EH, Matrone MA, Yoon JR, Martin SS. Vimentin filaments support extension of tubulin-based microtentacles in detached breast tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2008;68:5678–88. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Erck C, Peris L, Andrieux A, Meissirel C, Gruber AD, Vernet M, Schweitzer A, Saoudi Y, Pointu H, Bosc C, Salin PA, Job D, Wehland J. A vital role of tubulin-tyrosine-ligase for neuronal organization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:7853–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409626102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Whipple RA, Matrone MA, Cho EH, Balzer EM, Vitolo MI, Yoon JR, Ioffe OB, Tuttle KC, Yang J, Martin SS. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition promotes tubulin detyrosination and microtentacles that enhance endothelial engagement. Cancer Res. 2010;70:8127–37. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Cancer Genome Atlas Research N The Molecular Taxonomy of Primary Prostate Cancer. Cell. 2015;163:1011–25. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.10.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Debidda M, Wang L, Zang H, Poli V, Zheng Y. A role of STAT3 in Rho GTPase-regulated cell migration and proliferation. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:17275–85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413187200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Fang J, Yu Z, Lian M, Ma H, Tai J, Zhang L, Han D. Knockdown of zinc finger protein, X-linked (ZFX) inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 2012;360:301–7. doi: 10.1007/s11010-011-1069-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Han HJ, Russo J, Kohwi Y, Kohwi-Shigematsu T. SATB1 reprogrammes gene expression to promote breast tumour growth and metastasis. Nature. 2008;452:187–93. doi: 10.1038/nature06781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Wu S, Lao XY, Sun TT, Ren LL, Kong X, Wang JL, Wang YC, Du W, Yu YN, Weng YR. Knockdown of ZFX inhibits gastric cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo via downregulating the ERK-MAPK pathway. Cancer Lett. 2013;337:293–300. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.04.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Zhang Y, Wang Y, Wei Y, Wu J, Zhang P, Shen S, Saiyin H, Wumaier R, Yang X, Wang C. Molecular chaperone CCT3 supports proper mitotic progression and cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma Cells. Cancer Lett. 2016;372:101–9. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.12.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Sherry MM, Reeves A, Wu JK, Cochran BH. STAT3 is required for proliferation and maintenance of multipotency in glioblastoma stem cells. Stem Cells. 2009;27:2383–92. doi: 10.1002/stem.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Chau CH, Chen KY, Deng HT, Kim KJ, Hosoya KI, Terasaki T, Shih HM, Ann DK. Coordinating Etk/Bmx activation and VEGF upregulation to promote cell survival and proliferation. Oncogene. 2002;21:8817–29. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Zhao X, Rong L, Zhao X, Li X, Liu X, Deng J, Wu H, Xu X, Erben U, Wu P, Syrbe U, Sieper J, Qin Z. TNF signaling drives myeloid-derived suppressor cell accumulation. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:4094–104. doi: 10.1172/JCI64115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Asher AL, Mule JJ, Kasid A, Restifo NP, Salo JC, Reichert CM, Jaffe G, Fendly B, Kriegler M, Rosenberg SA. Murine tumor cells transduced with the gene for tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Evidence for paracrine immune effects of tumor necrosis factor against tumors. J Immunol. 1991;146:3227–34. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Nanni P, de Giovanni C, Lollini PL, Nicoletti G, Prodi G. TS/A: a new metastasizing cell line from a BALB/c spontaneous mammary adenocarcinoma. Clin Exp Metastasis. 1983;1:373–80. doi: 10.1007/BF00121199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Hock H, Dorsch M, Kunzendorf U, Qin Z, Diamantstein T, Blankenstein T. Mechanisms of rejection induced by tumor cell-targeted gene transfer of interleukin 2, interleukin 4, interleukin 7, tumor necrosis factor, or interferon gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90:2774–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Li LP, Schlag PM, Blankenstein T. Transient expression of SV 40 large T antigen by Cre/LoxP-mediated site-specific deletion in primary human tumor cells. Hum Gene Ther. 1997;8:1695–700. doi: 10.1089/hum.1997.8.14-1695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Pear WS, Miller JP, Xu L, Pui JC, Soffer B, Quackenbush RC, Pendergast AM, Bronson R, Aster JC, Scott ML, Baltimore D. Efficient and rapid induction of a chronic myelogenous leukemia-like myeloproliferative disease in mice receiving P210 bcr/abl-transduced bone marrow. Blood. 1998;92:3780–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Westermann J, Aicher A, Qin Z, Cayeux Z, Daemen K, Blankenstein T, Dorken B, Pezzutto A. Retroviral interleukin-7 gene transfer into human dendritic cells enhances T cell activation. Gene Ther. 1998;5:264–71. doi: 10.1038/sj.gt.3300568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Zhang J, Chen L, Xiao M, Wang C, Qin Z. FSP1+ fibroblasts promote skin carcinogenesis by maintaining MCP-1-mediated macrophage infiltration and chronic inflammation. Am J Pathol. 2011;178:382–90. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2010.11.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.