Abstract
The role of canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling in postnatal bone growth has not been fully defined. In the present studies, we generated β-catenin conditional knockout (KO) mice and deleted β-catenin in Col2-expressing chondrocytes and mesenchymal progenitor cells. Findings from analyzing the β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice revealed severe bone destruction and bone loss phenotype in epiphyseal bone, probably due to the increase in osteoclast formation and the accumulation of adipocytes in this area. In addition, we also found bone destruction and bone loss phenotype in vertebral bone in β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice. These findings indicate that β-catenin signaling plays a critical role in postnatal bone remodeling. Our study provides new insights into the regulation of epiphyseal bone homeostasis at postnatal stage.
Keywords: Epiphysis, Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling, Postnatal Bone Growth, Osteoarthritis
Introduction
Epiphysis is the terminal section of a growing long bone in mammals. It is separated from the bone shaft (diaphysis) by cartilage. New bone is produced on the side of the cartilage facing the diaphysis, while new cartilage is produced on the other side of the cartilage plate. At the joint, the epiphysis is covered with articular cartilage and a zone of subchondral bone is located below articular cartilage. In young animals, the epiphyses of long bones grow by chondrogenesis within the articular cartilage. A better understanding of the molecular mechanisms that regulate the growth of articular cartilage may give insight into the antecedents of joint disease, such as osteonecrosis 1, 2.
Canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling plays a critical role in skeletal development and postnatal bone growth 3-7. During skeletal development, activation of β-catenin signaling in limb mesenchymal cells inhibits cartilage development and promotes osteoblast differentiation 3, 4. β-catenin also induces growth plate chondrocyte differentiation 5. In mature osteoblasts, β-catenin promotes osteoblast differentiation and inhibits osteoclast formation 6. Our previous studies indicate that β-catenin expressed in Col2-expressing cells interacts with osteoclast precursor cells and regulates osteoclast formation at the postnatal stage 7.
Recent lineage tracing studies revealed that cells expressing Cre-recombinases driven by the Col2 promoter/enhancer and their descendants contributed to, in addition to chondrocytes, early perichondrial precursor cells 8. Similarly, a recent study also demonstrated that hypertrophic chondrocytes can become an osteoblast and contribute to the osteogenic lineage cells 9. In these studies, a cell-specific tamoxifen-inducible genetic recombination approach was utilized to track the fate of murine hypertrophic chondrocytes and the study showed that hypertrophic chondrocytes can survive the cartilage-to-bone transition and become osteogenic cells during embryonic and postnatal skeletal development and persist into adulthood 9. These studies provide new insights into the function and signaling mechanisms in Col2- (or Col10-) expressing cells.
Using Col2-CreER transgenic mice to specifically delete β-catenin in Col2-expressing mesenchymal progenitor cells and chondrocytes, in the present studies we demonstrated that these β-cateninCol2CreER knockout (KO) mice display severe defects in epiphyseal bone, including increased osteoclast formation and accumulation of adipocytes in the marrow cavity. In addition, we also found adipocyte accumulation in the bone marrow underneath the growth plate. We also observed the destruction and bone loss in vertebral bone in β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice. Our studies provide additional evidence of β-catenin signaling in postnatal bone remodeling and bone homeostasis.
Materials and Methods
Animals
Col2-CreERT2 transgenic mice were generated in our lab 10-12 and ROSAmT/mG and ROSA26R reporter mice 13 were obtained from Jackson Laboratories (Bar Harbor, ME, USA). β-cateninflox/flox mice were originally reported by Brault et al. 14 (obtained from Jackson lab) and we have used these mice in our previous studies 7. β-cateninCol2CreERmice were generated by breeding β-cateninflox/flox mice with Col2-CreERT2 transgenic mice. Tamoxifen (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) was administered into 2-week-old β-cateninCol2CreERand Cre-negative control mice by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection (1 mg/l0 g body weight for 5 consecutive days) and mice were sacrificed when they are 3-month-old. The animal protocol of this study has been approved by the IACUC of the Rush University and all experimental methods and procedures were carried out in accordance with the approved guidelines.
Cre-Recombination Efficiency
Col2-CreERT2mice were bred with ROSAmT/mG and ROSA26R reporter mice to generate Col2-CreERT2; ROSAmT/mG and Col2-CreERT2; ROSA26R mice. Tamoxifen was administered into 2-week-old mice by i.p. injection (1 mg/l0 g body weight for 5 days). Long bones were dissected after the mice were sacrificed at 4-week-old, fixed in 0.2 % glutaraldehyde at 4°C for 2 days, followed by washing three times with phosphate buffered saline (PBS). Samples were decalcified in 14% EDTA for 3 weeks, cryo-protected in 30% sucrose at 4°C for 3 days, and then embedded and processed for frozen sections. Three μm thick sections were used for lacZ staining.
Micro-CT Analysis
In 3-month-old Col2-CreERT2and Cre-negative control mice, quantitative μCT analysis was performed on a VivaCT 40 Scanner (Scanco Medical) at a resolution of 10 μm. Briefly, scanning in the femur/tibia began approximately at the proximal femur, and then extended proximally for 600 slices (10-μm thickness for each slice). Morphometric analysis was performed on 100 slices extending proximally. The 3-dimensional structure and morphometry were reconstructed and analyzed.
Histologic and Histomorphometric Analyses
We dissected long bones from β-cateninCol2CreERmice, and their corresponding Cre-negative control mice. Samples were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin (VWR, Radnor, PA, USA) for 3 days, decalcified with formic acid (Decal Chemical Corp., Suffern, NY, USA) for 14 days. Samples were processed and embedded in paraffin. Three μm thick mid-sagittal sections at 3 different levels (50 μm apart) were cut from the medial compartment of the long bone. The sections were stained with Safranin O/fast green (SO/FG), Alcian blue/H&E Orange G (AB/H&E-OG) and tartrate resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) for morphologic analysis. Three slides per mouse, 6 mice per group, were analyzed in the experiment. Histomorphometric analysis was performed using the OsteoMeasure system (OsteoMetrics, Decatur, GA).
Bone Marrow Stromal Cell Culture
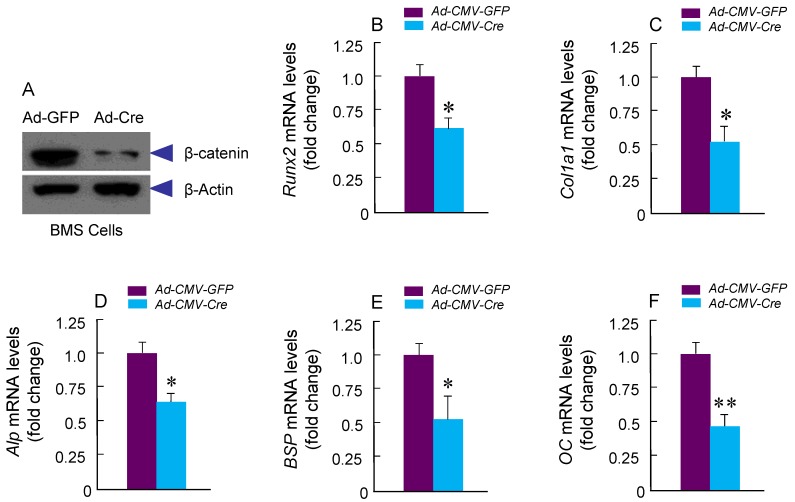
Bone marrow stromal (BMS) cells were isolated from 3-month-old Cre-negative control and β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice or from 3-month-old β-cateninflox/flox mice which were infected with Ad-CMV-Cre or Ad-CMV-GFP (control virus), as described previously 15, 16. The BMS cells were cultured with osteoblast differentiation medium for 3 days and β-catenin protein levels and mRNA expression of osteoblast marker genes, such as Runx2, Col1a1, alkaline phosphatase (Alp), bone sialoprotein (BSP) and osteocalcin (OC) was analyzed by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis. The cells were also cultured with adipocyte differentiation medium for 3 days and expression of adipocyte marker genes, such as PPAR-γ and cEBP-α, was also analyzed by real-time PCR analysis. Total RNA was prepared using a PureLink RNA Mini kit (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's protocol.
Statistical Analysis
The values are presented as mean ± standard error. Statistical difference between groups was evaluated by Student's t-test with SPSS13.0 statistical software. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 were considered as significant difference between groups.
Results
High Cre-Recombination Efficiency of Col2-CreERT2 mice to Target Articular Chondrocytes, Growth Plate Chondrocytes and Bone Marrow Cells below the Growth Plate
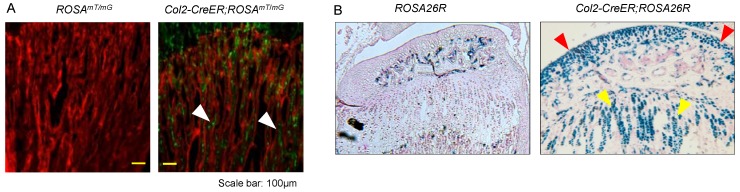
To evaluate targeting efficiency of Col2-CreERT2 mice in epiphyseal area, we first bred Col2a1-CreERT2 mice with ROSAmT/mG reporter mice and generated Col2-CreERT2; ROSAmT/mGmice. Tamoxifen was administered when the mice were at 2-week-old and long bone samples were harvested at 4-week-old. Significant amounts of Col2-CreERT2 targeting cells were detected in bone marrow stromal (BMS) cells below the growth plate (Fig. 1A, white arrowheads). We also bred Col2a1-CreERT2 mice with ROSA26R reporter mice to generate Col2-CreERT2; ROSA26R mice. Similarly, tamoxifen was given to the mice at 2-week-old and bone samples were collected at 4-week-old. The results of lacZ staining revealed no recombination was found in growth plate and articular chondrocytes in Cre-negative mice (Fig. 1B, left panel). The blue-labelled chondrocytes in Col2-CreERT2; ROSA26R mice showed Col2-expressing cells in articular cartilage and growth plate cartilage (Fig. 1B, right panel). The role of β-catenin in epiphyseal bone was first investigated by X-ray radiographic analysis in β-cateninCol2CreERmice. Tamoxifen was given to 2-week-old mice and the mice were analyzed by X-ray at 3 months of age. The size of β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice was similar to Cre-negative control mice (data not shown), suggesting that β-catenin has no significant effect on bone growth at postnatal stage.
Figure 1.
Col2a1-CreERT2 mice efficiently target articular chondrocytes and growth plate chondrocytes and bone marrow stromal (BMS) cells near growth plate. Col2a1-CreERT2 mice were bred with ROSAmTmG and ROSA26R reporter mice. Tamoxifen was given to 2-week-old mice. Analysis of fluorescence images and lacZ staining were performed in 4-week-old Col2-CreERT2; ROSAmTmG mice and Col2-CreERT2; ROSA26R mice. Col2a1-CreERT2 targeting cells were detected in BMS cells underneath the growth plate (A, white arrowheads). LacZ-positive cells were also detected in articular chondrocytes (red arrowheads) and growth plate chondrocytes (yellow arrowheads) in Col2-CreERT2; ROSA26R mice.
Specific Deletion of β-Catenin in Col2-Expressing Cells Leads to Defects of Epiphyseal Bone
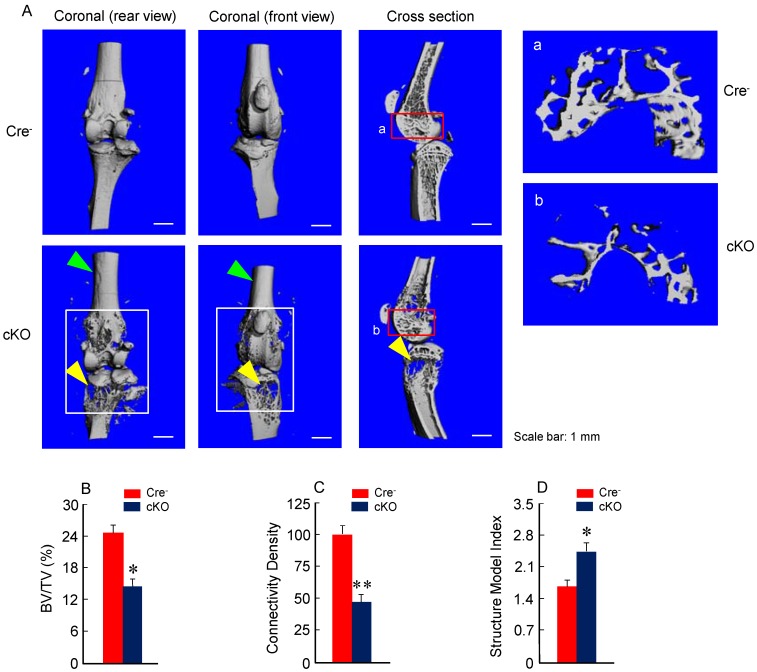
Micro-CT analysis revealed significant bone loss and marked bone destruction in the epiphyseal area in 3-month-old β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice (Fig. 2A, yellow arrowheads). In comparison to Cre-negative control mice, bone volume (%, BV/TV) was significantly reduced in β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice (*P < 0.05; n = 6) (Fig. 2B). Consistent results were also obtained when other bone structure parameters were analyzed by μCT. The connectivity density was significantly reduced (Fig. 2C) (**P < 0.01; n = 6) and structural model index was significantly increased in β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice (*P < 0.05; n = 6) (Fig. 2D).
Figure 2.
Bone mass is reduced in β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice. (A) The μCT images displayed the bone loss in the epiphysis of distal femur and proximal tibia in 3-month-old β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice compared to Cre-negative control mice. Tamoxifen was given to 2-week-old mice. Bone loss and bone destruction appear in the epiphysis area (yellow arrowheads) but not the diaphysis area (green arrowheads) of long bone. (B-D) Bone volume (%, BV/TV), connectivity density and structural model index in the epiphysis of distal femur were analyzed by μCT. The quantification of these parameters showed significantly reduced bone volume (% BV/TV) and connectivity density and significantly increased structural model index. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, unpaired Student's t-test, n=6. Values are means ± SD.
Deletion of β-Catenin in Col2-Expressing Cells Leads to Increased Osteoclast and Adipocyte Formation
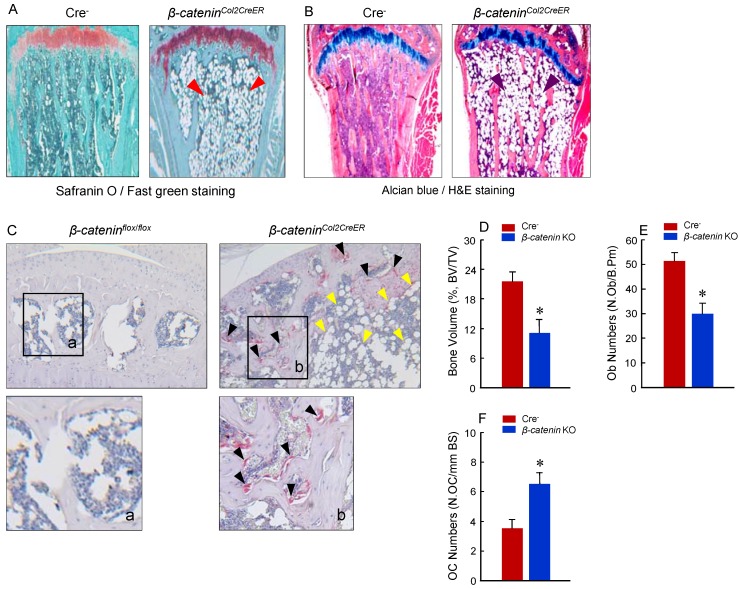
To determine the mechanism of bone loss in epiphyseal area of β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice, we performed histological analysis using histology sections derived from 3-month-old β-cateninCol2CreER KO and Cre-negative control mice. Histological analysis of Safranin O/fast green (SO/FG) and Alcian/H&E Orange G (AB/HE-OG) stained sections showed a significant bone loss and accumulation of adipocytes in bone marrow, especially in the area below the growth plate (Fig. 3A and B). To determine changes in osteoclast formation, we performed TRAP staining and found that TRAP-positive osteoclast formation was significantly increased in β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice (Fig. 3C). Black arrowheads marked TRAP-positive osteoclasts and yellow arrowheads marked adipocytes. Consistent with the μCT findings, results of histomorphometric analysis also showed a significantly reduced bone volume and osteoblast numbers in β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice (Fig. 3D and E). In contrast, osteoclast numbers were significantly increased in β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice (Fig. 3F).
Figure 3.
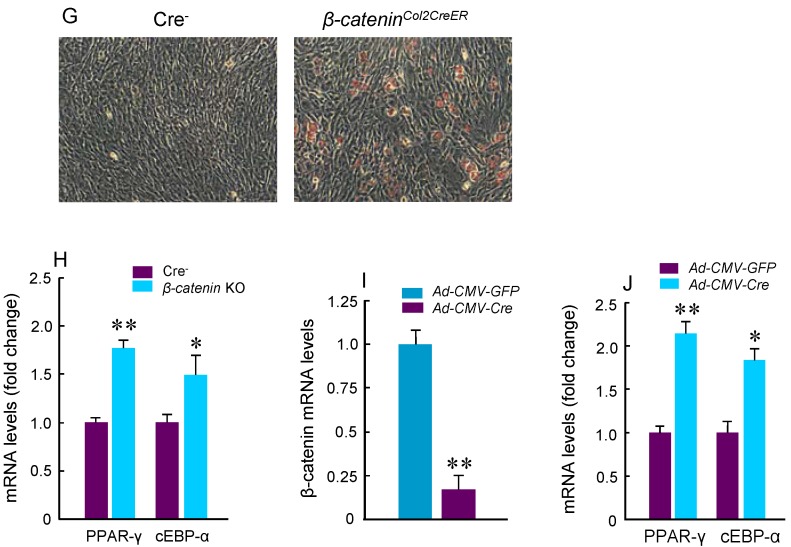
Adipocyte and osteoclast formation was increased in β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice. (A and B) Histologic analysis showed that significant bone loss and accumulation of adipocytes in bone marrow stromal (BMS) cells in 3-month-old β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice. (C) TRAP staining results showed that TRAP-positive osteoclasts (indicated by black arrowheads) and adipocytes (indicated by yellow arrowheads) were significantly increased in 3-month-old β-cateninCol2CreERKO mice. (D-F) Results of histomorphometric analysis showed that bone volume (%, BV/TV) and osteoblast numbers (N.Ob) were significantly reduced and osteoclast numbers (N.OC) was significantly increased in β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice. (G and H) We isolated BMS cells from 3-month-old β-cateninCol2CreER KO and Cre-negative mice and cultured these cells with adipocyte differentiation medium for 3 days. Results of Oil red O staining and expression of adipocyte marker genes, including PPAR-γ and cEBP-α, showed that adipocyte formation was increased in β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice. (I and J) We further isolated BMS cells from β-cateninflox/flox mice and infected these cells with Ad-CMV-Cre or Ad-CMV-GFP (control virus). β-catenin levels were significantly reduced and expression of adipocyte marker genes was significantly increased in β-catenin deficient BMS cells.
To further analyze adipocyte formation, we isolated BMS cells and cultured these cells in the presence of adipocyte differentiation medium. We found that more adipocytes were formed in cultured cells derived from β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice (Fig. 3G). Expression of PPAR-γ and cEBP-α, two adipocyte differentiation markers, was significantly increased in the cells derived from β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice (Fig. 3H). We then isolated BMS cells from β-cateninflox/flox mice and infected these cells with Ad-CMV-Cre. In the BMS cells with β-catenin in vitro deletion, β-catenin levels were very low and expression of PPAR-γ and cEBP-α was much higher in β-catenin deficient cells (Fig. 3I and J).
Deletion of β-Catenin in Col2a1-Expressing Cells Leads to Defects of Vertebrae
In addition to long bone, we also analyzed changes in vertebral bone in β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice using μCT technique. Similar to the results found in epiphyseal bone, bone destruction and bone loss phenotype was found in L4-5 of vertebral bones of β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice (Fig. 4, right panel, red and yellow arrowheads).
Figure 4.
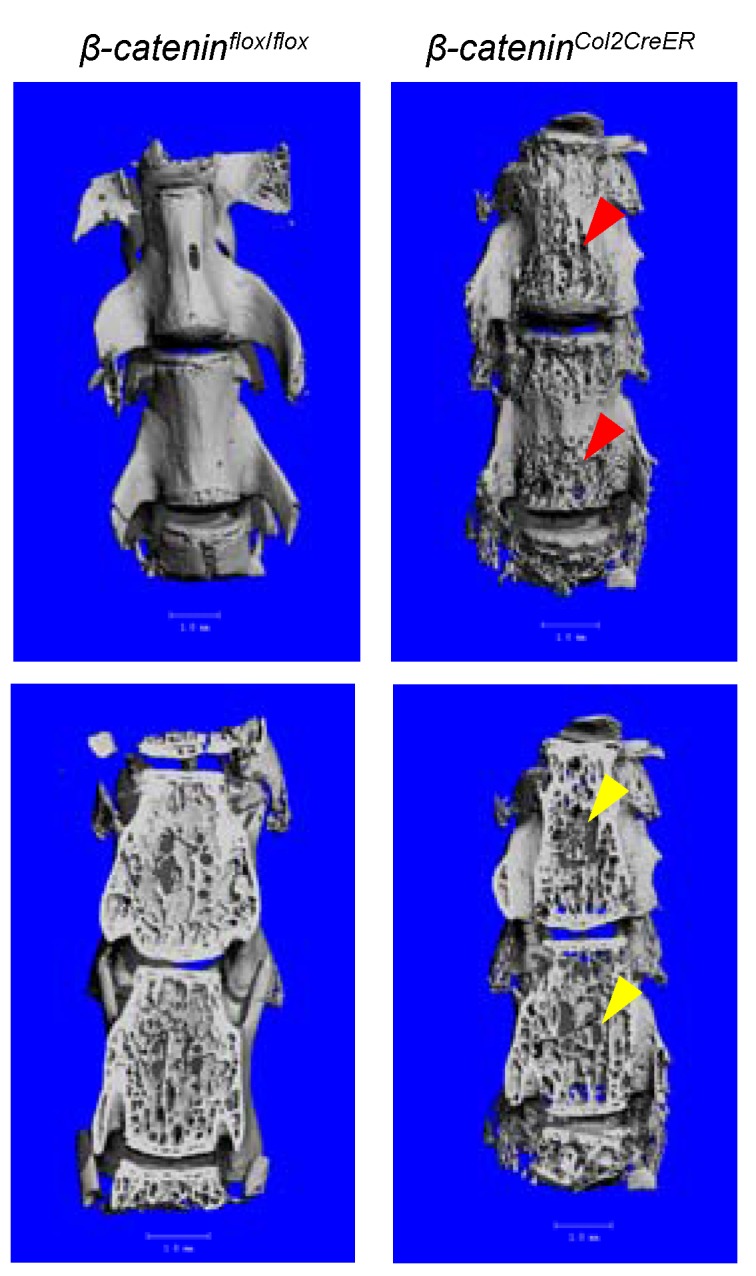
Bone structure and bone mass were altered in vertebrae of β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice. Tamoxifen was given to 2-week-old β-cateninCol2CreERand Cre-negative control mice. The μCT images showed significant bone loss (red and yellow arrowheads) in vertebrae (L4-5) of 3-month-old β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice.
Specific Deletion of β-Catenin in Col2a1-Expressing Cells Inhibited Osteoblast Differentiation
To determine if osteoblast differentiation is altered in β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice, we isolated BMS and examined ALP staining and expression of osteoblast marker genes. No significant changes in ALP activity and expression of osteoblast marker genes were found in β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice (data not shown). To further determine the effects of β-catenin in Col2-expressing cells, we isolated BMS cells from β-cateninflox/flox mice and infected these cells with Ad-CMV-Cre or Ad-CMV-GFP (control virus). We found that β-catenin protein levels were significantly decreased (Fig. 5A). Expression of osteoblast marker genes, including Runx2, Col1a1, alkaline phosphatase (Alp), bone sialoprotein (BSP) and osteocalcin (OC) was significantly decreased in β-catenin deficient BMS cells (Fig. 5 B-F), suggesting that osteoblast differentiation was inhibited by deletion of β-catenin.
Figure 5.
Osteoblast differentiation in was inhibited in β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice. Bone marrow stromal (BMS) cells were isolated from 3-month-old β-cateninflox/flox mice. The cells were infected with Ad-Cre or Ad-GFP (control virus) and cultured for 3 days in the presence of osteoblast differentiation medium. β-catenin protein levels and mRNA expression of osteoblast marker genes, including Runx2, type I collagen (Col1a1), alkaline phosphatase (Alp), bone sialoprotein (BSP) and osteocalcin (OC) were analyzed. In β-catenin deficient BMS cells, expression of osteoblast marker genes was significantly decreased.
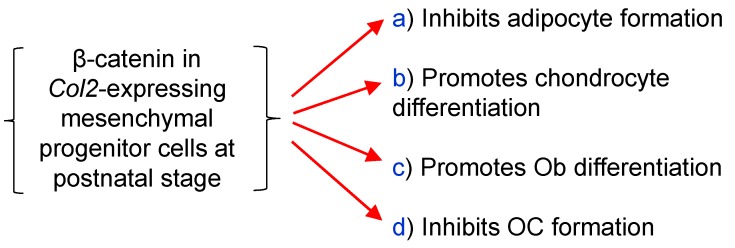
To summarize the effects of β-catenin in epiphyseal bone, we found that β-catenin inhibits osteoclast and adipocyte formation and promotes osteoblast differentiation (Fig. 6).
Figure 6.
The diagram showed β-catenin in Col2a1-expressing cells inhibits osteoclast and adipocyte formation and promotes chondrocyte and osteoblast differentiation.
Discussion
In this study, we generated β-cateninCol2CreER mouse model and demonstrated that deletion of β-catenin in Col2-expressing cells leads to severe defects in epiphyseal bone in β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice. Based on our studies and studies reported by other groups, the Col2-expressing cells not only include chondrocytes but also include mesenchymal progenitor cells 10-12, 8. It has been reported that β-catenin plays a critical role in directing mesenchymal cell differentiation into different lineages of cells 3, 4. Our previous 7 and current studies indicate that β-catenin promotes chondrocyte differentiation and inhibits adipocyte differentiation. Inhibition of β-catenin signaling in Col2-expressing progenitor cells leads to accumulation of adipocytes in bone marrow cavity. In addition, Col2-expressing progenitor cells could directly interact with osteoclast precursor cells. Inhibition of β-catenin signaling triggers osteoclast formation in epiphyseal area, suggesting that β-catenin in Col2-expressing cells plays a critical in regulation of osteoclast formation and is responsible for bone destruction under disease conditions.
Osteonecrosis is bone death caused by poor blood supply. It is most common in the hip and shoulder, but can affect other large joints such as the knee, elbow, wrist and ankle. After long period of lacking blood supply, the bone can collapse. If osteonecrosis is not treated, the joint deteriorates, leading to severe arthritis. Osteonecrosis can be caused by disease or by severe trauma, such as a fracture or dislocation that affects the blood supply to the bone. In osteonecrosis bone, increased osteoclast formation can be observed which leads to bone destruction 17. However, administration of anti-bone resorption drugs, such as bisphosphonates, has also been shown often causing osteonerosis of the Jaw 18, 19. Accumulation of adipocytes in subchondral area of epiphyseal bone is also observed in patients with osteonecrosis 20, 21. Although the mechanism of β-catenin signaling in the pathogenesis of osteonecrosis has not been fully defined, it has already shown that activation of β-catenin signaling by Lithium chloride could relieve osteonecrosis of femoral head by promoting osteoblast differentiation and inhibiting adipocyte formation 22, 23.
In addition to the effects on long bone, β-catenin KO mice also showed severe defects in vertebral bone, suggesting that β-catenin also plays a role in vertebral bone remodeling. Our previous study indicates that Col2-expressing cells are mainly located in the inner annulus fibrosus cells and growth plate cartilage cells in the intervertebral disc tissue 24. It is possible that Col2-expressing cells in growth plate cartilage area in disc tissues could migrate into the vertebral bone and transdifferentiate into osteoblast lineage cells, similar to the Col2-expressing cells in growth plate of long bone. The bone loss phenotype observed in vertebral bone may be due to the β-catenin deficiency in these cells.
In β-cateninCol2CreER KO mice, Rankl expression was increased and Opg expression was decreased in Col2-expressing cells 7. β-catenin could directly act on Opg gene and regulate Opg transcription 6. β-catenin also regulates Rankl expression through a glucocorticoid receptor (GR)-dependent mechanism 7. Changes in osteoclast formation observed in the present studies could be due to the combination of up-regulation of RANKL and down-regulation of OPG 7.
In summary, our study demonstrates that inhibition of β-catenin signaling in Col2-expressing cells could lead to severe defects in long bone, especially in the epiphyseal region and in intervertebral disc, suggesting that β-catenin signaling plays an important role in bone remodeling and bone homeostasis at postnatal stage and in bone and joint diseases.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to Ms. Lily Yu for her help on processing and staining histological samples. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grants, R01 AR054465 and R01 AR070222 to DC. This work was also partially supported by the grants of Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (grant # 81371999 to DC and grants # 81301531 and 81572104 to TW). This work was also partially supported by the grant from Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Committee, China (grant # JCYJ20160331114205502) to DC and the grant from Shenzhen Development and Reform Committee, China for Shenzhen Engineering Laboratory of Orthopaedic Regenerative Technologies to DC.
Author contributions
Tingyu Wang and Di Chen contributed to the experimental design, data interpretation and manuscript preparation and revision. Tingyu Wang, Jun Li, Yue Zhao and Baoli Wang carried out experiments. Guang-Qian Zhou and Peter Ma contributed to the data interpretation and manuscript revision.
References
- 1.Lui JC, Chau M, Chen W, Cheung CS, Hanson J, Rodriguez-Canales J, Nilsson O, Baron J. Spatial regulation of gene expression during growth of articular cartilage in juvenile mice. Pediatr Res. 2015;77(3):406–15. doi: 10.1038/pr.2014.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Xing W, Cheng S, Wergedal J, Mohan S. Epiphyseal chondrocyte secondary ossification centers require thyroid hormone activation of Indian hedgehog and osterix signaling. J Bone Miner Res. 2014;29(10):2262–75. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Day TF, Guo X, Garrett-Beal L, Yang Y. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in mesenchymal progenitors controls osteoblast and chondrocyte differentiation during vertebrate skeletogenesis. Dev Cell. 2005;8(5):739–50. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.03.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kolpakova E, Olsen BR. Wnt/β-catenin-a canonical tale of cell-fate choice in the vertebrate skeleton. Dev Cell. 2005;8(5):626–7. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.04.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Akiyama H, Lyons JP, Mori-Akiyama Y, Yang X, Zhang R, Zhang Z, Deng JM, Taketo MM, Nakamura T, Behringer RR, McCrea PD, de Crombrugghe B. Interactions between Sox9 and beta-catenin control chondrocyte differentiation. Genes Dev. 2004;18(9):1072–87. doi: 10.1101/gad.1171104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Glass DA 2nd, Bialek P, Ahn JD, Starbuck M, Patel MS, Clevers H, Taketo MM, Long F, McMahon AP, Lang RA, Karsenty G. Canonical Wnt signaling in differentiated osteoblasts controls osteoclast differentiation. Dev Cell. 2005;8(5):751–64. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.02.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wang B, Jin H, Zhu M, Li J, Zhao L, Zhang Y, Tang D, Xiao G, Xing L, Boyce BF, Chen D. Chondrocyte β-catenin signaling regulates postnatal bone remodeling through modulation of osteoclast formation in a murine model. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(1):107–120. doi: 10.1002/art.38195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ono N, Ono W, Nagasawa T, Kronenberg HM. A subset of chondrogenic cells provides early mesenchymal progenitors in growing bones. Nat Cell Biol. 2014;16(12):1157–67. doi: 10.1038/ncb3067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Yang L, Tsang KY, Tang HC, Chan D, Cheah KS. Hypertrophic chondrocytes can become osteoblasts and osteocytes in endochondral bone formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111(33):12097–102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1302703111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chen M, Lichtler AC, Sheu T, Xie C, Zhang X, O'Keefe RJ, Chen D. Generation of a transgenic mouse model with chondrocyte-specific and tamoxifen-inducible expression of Cre recombinase. Genesis. 2007;45:44–50. doi: 10.1002/dvg.20261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zhu M, Chen M, Lichtler AC, O'Keefe RJ, Chen D. Tamoxifen-inducible Cre-recombination in articular chondrocytes of adult Col2a1CreERT2 transgenic mice. Osteoarthr Cartilage. 2008;16:129–130. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2007.08.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chen M, Li S, Xie W, Wang B, Chen D. Col2-CreERT2, a mouse model for a chondrocyte-specific and inducible gene deletion. Eur Cell Mater. 2014;28:236–245. doi: 10.22203/ecm.v028a16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Friedrich G, Soriano P. Promoter traps in embryonic stem cells: A genetic screen to identify and mutate developmental genes in mice. Genes Dev. 1991;5(9):1513–23. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Brault V, Moore R, Kutsch S, Ishibashi M, Rowitch DH, McMahon AP. et al. Inactivation of the β-catenin gene by Wnt1-Cremediated deletion results in dramatic brain malformation and failure of craniofacial development. Development. 2001;128:1253–64. doi: 10.1242/dev.128.8.1253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yan Y, Tang D, Chen M, Huang J, Xie R, Jonason JH, Tan X. et al. Axin2 controls bone remodeling through the β-catenin-BMP signaling pathway in adult mice. J Cell Sci. 2009;122:3566–3578. doi: 10.1242/jcs.051904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Oh C-D, Yasuda H, Zhou W, Henry SP, Zhang Z, Xue M. et al. Sox9 directly regulates CTGF/CCN2 transcription in growth plate chondrocytes and in nucleus pulposus cells of intervertebral disc. Sci Rep. 2015;6:29916. doi: 10.1038/srep29916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wang C, Wang X, Xu XL, Yuan XL, Gou WL, Wang AY. et al. Bone microstructure and regional distribution of osteoblast and osteoclast activity in the osteonecrotic femoral head. PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e96361. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Endo Y, Kumamoto H, Nakamura M, Sugawara S, Takano-Yamamoto T, Sasaki K, Takahashi T. Underlying Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies for Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (BRONJ) Biol Pharm Bull. 2017;40(6):739–750. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b16-01020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Vermeer JA, Renders GA, Everts V. Osteonecrosis of the Jaw-a Bone Site-Specific Effect of Bisphosphonates. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2016;14(5):219–25. doi: 10.1007/s11914-016-0318-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wang Y, Li Y, Mao K, Li J, Cui Q, Wang GJ. Alcohol-induced adipogenesis in bone and marrow: a possible mechanism for osteonecrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003 May;(410):213–24. doi: 10.1097/01.blo.0000063602.67412.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yin L, Li YB, Wang YS. Dexamethasone-induced adipogenesis in primary marrow stromal cell cultures: mechanism of steroid-induced osteonecrosis. Chin Med J (Engl) 2006;119(7):581–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yu Z, Fan L, Li J, Ge Z, Dang X, Wang K. Lithium chloride attenuates the abnormal osteogenic/adipogenic differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells obtained from rats with steroid-related osteonecrosis by activating the β-catenin pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2015;36(5):1264–72. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yu Z, Fan L, Li J, Ge Z, Dang X, Wang K. Lithium prevents rat steroid-related osteonecrosis of the femoral head by β-catenin activation. Endocrine. 2016;52(2):380–90. doi: 10.1007/s12020-015-0747-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jin H, Shen J, Wang B, Wang M, Shu B, Chen D. TGF-β signaling plays an essential role in the growth and maintenance of intervertebral disc tissue. FEBS Lett. 2011;585(8):1209–15. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2011.03.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]