Abstract
Objectives
To compare the quality of care—using unplanned acute hospital readmissions as a quality measure—among patients treated at private for-profit hospitals (PFPs), private non-profit hospitals (PNPs) and public hospitals (PUBs) in Norway.
Design
A retrospective comparative study using the Norwegian Patient Register. Readmissions were evaluated by logistic regressions both using adjustment for various patient-level and other covariates, and a two-stage model using distance as an instrumental variable.
Setting
The Norwegian healthcare system.
Population
All publicly financed patients having primary total hip (37 897 patients) or primary total knee arthroplasty (25 802 patients) at one of the three hospital types from 2009 to 2014.
Primary outcome measure
30-day unplanned acute hospital readmission rate.
Results
We found highest readmission rates among PUBs and lowest among PFPs, for both procedures. However, the patients were on average more than 2 years younger at PFPs. PFPs also treated the least severe patients, while PUBs treated the most severe. Using adjustment for various patient-level and other covariates, compared to PUBs, both PFPs and PNPs had lower odds of readmission following both procedures. However, using the instrumental variable method, the only significant difference found was a lower odds of readmission at PNPs among hip patients when compared with PUBs. No patients in our data set were readmitted to PFPs, those originally treated at PFPs were readmitted to either PNPs or PUBs, and PUBs received most of the readmitted patients across hospital types.
Conclusions
Quality differences between hospital types were small; however, PNPs had significantly lower readmission rates compared with PUBs among patients having total hip arthroplasty. PUBs received the larger part of the readmitted patients across hospital types and thus play an essential role in the care of more complex patients and for readmissions, regardless of any quality differences.
Keywords: Health outcomes research, private hospitals, public hospitals, readmission, case mix
Strengths and limitations of this study.
The study of the free choice of hospital system enables comparisons between private for-profit, private non-profit and public hospitals in a universal healthcare system.
The use of data from a large and comprehensive nationwide register allows the population of publicly financed patients to be most accurately represented.
The study’s recentness gives timely indications of current clinical and hospital practice.
Patients who were financed out of pocket or by voluntary private health insurance were not included in this study.
Introduction
In recent decades, countries with tax-based universal healthcare systems have experienced increasing attention from private healthcare providers.1 This trend is a result of growing policy challenges centred around containing healthcare costs while retaining universal access to health services and further improving quality of care.2 However, knowledge about the effects of the expansion of private hospitals in universal health systems is limited.2 3 In Norway’s tax-based universal healthcare system, services are largely provided through public hospitals (PUBs). However, private non-profit hospitals (PNPs) and private for-profit hospitals (PFPs) have become important health service providers. The expanded use of private hospitals has raised several concerns—for example, regarding maintaining quality of care. The aim of the present study was therefore to compare the quality of care among PUBs, PNPs and PFPs measured by acute readmission rates. In addition, we analysed whether patients were readmitted to the same type of hospital as where they had their initial procedure or at a different hospital type, hypothesising that PUBs would ultimately be responsible for complicated patients requiring readmission even when their primary surgeries took place at other types of hospitals.
All major PUBs and PNPs in Norway are funded by the Regional Health Authorities (RHAs) through a combination of risk-adjusted capitation and activity-based financing (ABF) based on DRGs.4 As in many other countries, PNPs were forerunners in healthcare delivery. In contrast, the first Norwegian PFP was established in 1985, and PFPs had only modest activity until early 2000. Three major changes in Norwegian secondary care services led to an expansion in the number of PFPs and PFP activity1: the introduction of ABF in 1997, the Hospital Reform of 2002 and the Patients’ Rights Act (implemented in 2001 and expanded in 2004). In this new system, a patient with a referral for secondary care services from a general practitioner had a right to choose any hospital owned by, or under contract with, the RHAs for the same copay.4 The patient was also given the right to examination and, potentially, treatment within a specific time limit. If this time limit was exceeded, the responsible RHA was obligated to cover the costs and provide the services at another hospital in Norway or abroad.5 The newly formed state-owned RHAs were given the authority to organise procurement competitions among PFPs1; after winning a contract, the PFP was included in Norway’s ‘free hospital choice system’ (FHCS).6 PFPs also served patients whose care was financed out of pocket or by voluntary private health insurance (VPHI).7
We focus on two surgical procedures to assess quality of care: total hip arthroplasty (THA) and total knee arthroplasty (TKA) due to osteoarthritis. In addition to the projected growth of THA and TKA surgeries,8 these procedures were performed at all three hospital types and at high enough volumes such that complications leading to hospital readmissions—our primary outcome measure—may occur with sufficient frequency so that differences between hospital types could be detected. The use of 30-day readmission rates at facility level is a widely used quality measure in Europe, including Norway,9 and in the USA; the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), for example, chose a 30-day readmission rate following THA or TKA as an initial measure of quality after reviewing several National Quality Forum metrics.10 Hospital readmissions have also been cited in The US Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act as an important quality measure for total joint arthroplasty.11–13 Since our aim was to compare hospital types in the Norwegian health system, where increased use of private hospitals—whose organisation and tasks performed differ considerably from what is found in PUBs—is frequently discussed as a policy option, we assessed average quality (based on these standard measures) and differences across hospital types. There are considerable costs associated with hospital readmissions,13 and understanding these patterns may help Norwegian decision makers improve the use of resources and health outcomes. Since the FHCS includes PUBs, PNPs and PFPs, quality of care among all three is crucial for policymakers and patients. However, empirical literature comparing quality of care between the three in a universal health system is limited and inconclusive. Comparisons targeting countries with healthcare systems different from that of Norway also differ in their conclusions.14–17 All three hospital types were financed via a prospective payment system and thus had substantial incentives to deliver high-quality care to attract patients. However, since quality measures were often used as criteria by the RHAs when new contracts with PFPs and PNPs were being evaluated and, since Norwegian PFPs and PNPs in general are more specialised in their services compared to PUBs, it was hypothesised that there would be lower odds of readmission following surgery at PFPs or PNPs compared with PUBs.
Methods and statistics
Study population and data sources
The study cohort was identified using the Norwegian Patient Register (NPR), which contains data on all publicly financed patients treated at any Norwegian hospital. We included patients having primary hip or knee replacement due to osteoarthritis coded with the ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases) and NCSP (NOMESCO Classification of Surgical Procedures) combinations included in the online supplementary appendix table A1. The Norwegian Arthroplasty Register (NAR) uses the same NCSP codes in their annual report for both primary THA and primary TKA*. The NPR and NAR have previously been merged and found valid and reliable.18 19 Even though most PFPs report all their patients to the NPR, the register only fully captures the publicly financed patients; patients financed out of pocket or by VPHI are therefore not included in this study. We also excluded all patients financed under the time limit violation arrangement, as those patients could receive treatment at hospitals not included in the FHCS for that specific procedure.
bmjopen-2016-015771supp001.pdf (270.6KB, pdf)
Variable definitions
We treated readmission at any hospital within 30 days as a binary outcome. Only readmissions registered as acute were included, and patients readmitted with a classified cancer diagnosis registered as main cause of readmission were excluded. Independent variables included age group, gender, comorbidity using the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) and the sum of inpatient days at any hospital within 365 days prior to the date of the surgical procedure (length of hospital stay in the previous year; LOSPY). The CCI was calculated from recorded main diagnosis or secondary diagnoses20 at any hospital stay within 365 days prior to the date of the procedure, and is previously found to be associated with a higher readmission rate following orthopaedic surgery, arthroplasties included.21
Analytical approach and statistical methods
In Norway, all citizens are given a personal identification number which we used to trace the patient at any hospital, both public and private. We performed all analyses using the statistical software SAS V.9.4 † . Mean, SD and frequencies were used for descriptive purposes and logistic regressions ‡ were used to compare PNPs to PUBs and PFPs to PUBs. We adjusted for case-mix differences when comparing quality differences by hospital type. The first approach we used was adjustment for various patient-level and other covariates. The second approach was a two-stage method using instrumental variable (IV). We used distance to hospital as an IV22—that is, a variable associated with a specific treatment pattern, but not otherwise related to the underlying patient characteristics and not directly affecting the variable of interest.22 23 Distance in kilometres to the nearest hospital type—whether PFP, PNP or PUB—was measured from the centre of the patient’s home municipality to the centre of the municipality in which the hospital was located. If the patient used a hospital in the patient’s home municipality, distances were set to 2 km, which reflects the average density and hence travel distance that patients in urban areas of Norway face. In the first stage, we used distance to hospital as an IV together with other relevant variables to model the odds of choosing a hospital of a particular type (online supplementary appendix tables A2 and A3). In the second stage, we included predicted odds from the first stage as an independent variable for the hospital type, in addition to the above-mentioned risk adjusters. Logistic regressions were used in both stages § . All variables, including the four RHAs and year, were treated as fixed effects. The OR and a 95% CI were calculated, and we reported per cent concordant (%C) and Akaike information criterion as goodness-of-fit measures. Lastly, taking advantage of each patient’s unique identification number at any hospital, we performed a flow analysis to investigate to what extent readmitted patients were readmitted to the same type of hospital as where they had the surgical procedure, or if they were readmitted to a different type of hospital.
Results
Patients and hospital characteristics
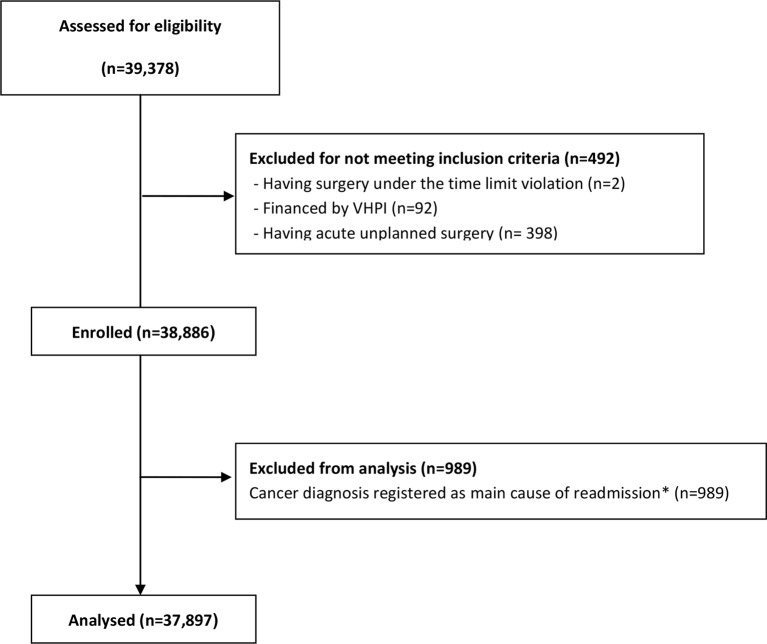
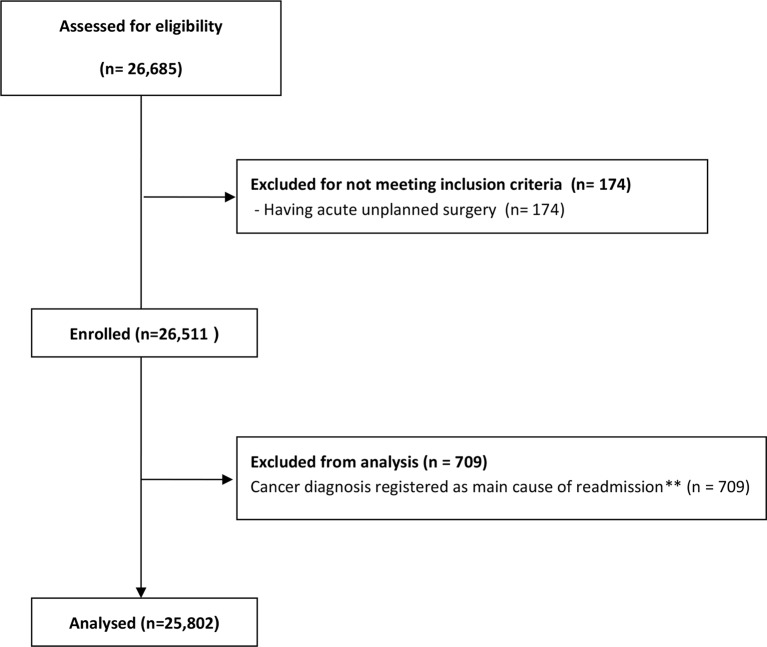
After applying our exclusion criteria, we had 37 897 THA patients and 25 802 TKA patients for analysis (figures 1 and 2). Descriptive statistics about the patient sample included in the study and readmission rates among the three different hospital types for the THA and TKA patients are reported in table 1.
Figure 1.
Analysed and excluded total hip arthroplasty patients. *Both new and pre-existing cancers. VPHI, voluntary private health insurance.
Figure 2.
Analysed and excluded total knee arthroplasty patients. **Both new and pre-existing cancers.
Table 1.
Descriptive statistics for publicly funded FHCS patients 2009–2014
| Total hip arthroplasty | Total knee arthroplasty | |||||||||||
| Private for-profit | Private non-profit | Public | Private for-profit | Private non-profit | Public | |||||||
| Number of hospitals | 5 | 6 | 40 | 5 | 6 | 37 | ||||||
| Number of patients | 422 | 7871 | 29 604 | 488 | 5847 | 19 467 | ||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| 30-day readmission rate | 0.038 | 0.191 | 0.049 | 0.217 | 0.080 | 0.272 | 0.053 | 0.225 | 0.053 | 0.225 | 0.085 | 0.279 |
| Share of men | 0.360 | 0.481 | 0.310 | 0.463 | 0.357 | 0.479 | 0.480 | 0.500 | 0.344 | 0.475 | 0.394 | 0.489 |
| Age (average years) | 66.071 | 10.186 | 68.638 | 10.552 | 68.268 | 11.209 | 65.451 | 9.152 | 68.133 | 9.473 | 68.022 | 9.734 |
| LOSPY (average number of days)* | 0.481 | 1.931 | 0.944 | 3.621 | 1.375 | 5.301 | 0.607 | 2.289 | 1.021 | 3.797 | 1.322 | 4.526 |
| Number of comorbidities | 0.097 | 0.381 | 0.212 | 0.569 | 0.233 | 0.630 | 0.100 | 0.406 | 0.208 | 0.549 | 0.235 | 0.614 |
| CCI (average score)† | 0.116 | 0.434 | 0.217 | 0.718 | 0.263 | 0.798 | 0.115 | 0.543 | 0.212 | 0.663 | 0.265 | 0.763 |
| Distance to closest PUB (average kilometres) | 24.282 | 29.186 | 17.980 | 27.749 | 33.634 | 44.650 | 28.482 | 38.214 | 18.744 | 29.351 | 34.766 | 46.175 |
| Distance to closest PNP (average kilometres) | 93.036 | 218.871 | 65.096 | 204.742 | 345.343 | 447.294 | 157.228 | 392.503 | 83.185 | 254.448 | 378.062 | 480.400 |
| Distance to closest PFP (average kilometres) | 97.320 | 229.045 | 125.409 | 246.765 | 427.123 | 430.707 | 164.873 | 401.589 | 146.843 | 286.431 | 457.198 | 459.316 |
*Sum of inpatient days at any hospital within 365 days prior to the date of the surgical procedure.
†Registered from recorded main diagnosis or secondary diagnoses at any hospital stay within 365 days prior to the date of the procedure.
CCI, Charlson Comorbidity Index; FHCS, free hospital choice system; LOSPY, length of hospital stay in the previous year; PFP, private for-profit hospital; PNP, private non-profit hospital; PUB, public hospital.
For both procedures, the 30-day readmission rate was lowest among PFPs and highest among PUBs. The share of men who had THA and TKA ranged from 31% to 36% and 34.4% to 48%, respectively, and the share of men was highest at PFPs for both procedures. The mean age was lowest in PFPs and the mean age for patients treated by PUBs and PNPs was approximately 2 years higher. Patients who had surgery at PFPs had the shortest average length of stay in hospitals the previous year, the on average fewest number of comorbidities and the lowest average CCI. Respectively, patients at PUBs had more than twice the average LOSPY, number of comorbidities and CCI. PUBs were the hospitals closest to patients on average regardless of where they had surgery (ranging from 18 to 34 km among THA and 19 to 35 km among TKA), and PFPs were generally the furthest (ranging from 97 to 427 km among THA and 147 to 457 km among TKA).
Regression analyses
Using the method of adjustment for various patient-level and other covariates, we found that patients who had THA or TKA surgery at PNPs or PFPs had lower odds of unplanned acute readmissions compared to otherwise similar patients having surgery at PUBs. The effects are sizeable, with approximately 50% lower odds of readmission (table 2). Using the two-stage IV method, PNPs still had lower odds of readmission among THA patients. Among TKA patients, the point estimate was 0.89, suggesting somewhat lower odds of readmission among patients having surgery at PNPs than those having surgery at PUBs, but the difference was not significant. For patients having surgery at PFPs, the estimate for both procedures was no longer significant, indicating no detectable differences when compared with patients having surgery at PUBs. Results from the first stage of the IV method and their interpretation are shown in the online supplementary appendix.
Table 2.
(a) Readmission risk among THA patients. ORs (CIs). (b) Readmission risk among TKA patients. ORs (CIs)
| PNP versus PUB (ref) | PFP versus PUB (ref) | |||||||
| Without IV | With IV | Without IV | With IV | |||||
| OR | CI | OR | CI | OR | CI | OR | CI | |
| (a) Readmission risk among THA patients. ORs (CIs) | ||||||||
| PNP | 0.568 | 0.506 to 0.637 | – | – | – | |||
| PNP (IV) | – | 0.674 | 0.527 to 0.861 | – | – | |||
| PFP | – | – | 0.46 | 0.278 to 0.762 | – | |||
| PFP (IV) | – | – | – | 0.701 | 0.090 to 5.444 | |||
| Male | 1.324 | 1.207 to 1.452 | 1.329 | 1.211 to 1.458 | 1.327 | 1.199 to 1.468 | 1.327 | 1.199 to 1.469 |
| Age group 18–49 years* | 0.761 | 0.611 to 0.947 | 0.763 | 0.613 to 0.950 | 0.793 | 0.627 to 1.004 | 0.793 | 0.627 to 1.003 |
| Age group 50–59 years | 0.672 | 0.570 to 0.791 | 0.674 | 0.572 to 0.793 | 0.675 | 0.564 to 0.807 | 0.674 | 0.563 to 0.806 |
| Age group 60–69 years | 0.799 | 0.713 to 0.895 | 0.799 | 0.713 to 0.895 | 0.813 | 0.717 to 0.921 | 0.813 | 0.717 to 0.921 |
| Age group 70–79 years | Ref | – | Ref | – | Ref | Ref | ||
| Age group ≥80 years | 1.562 | 1.386 to 1.761 | 1.561 | 1.386 to 1.759 | 1.527 | 1.337 to 1.745 | 1.532 | 1.337 to 1.755 |
| CCI | 1.094 | 1.042 to 1.148 | 1.093 | 1.042 to 1.147 | 1.096 | 1.039 to 1.155 | 1.096 | 1.040 to 1.156 |
| LOSPY | 1.013 | 1.006 to 1.020 | 1.013 | 1.006 to 1.020 | 1.013 | 1.005 to 1.020 | 1.013 | 1.005 to 1.020 |
| Fixed effects | RHA/year | RHA/year | RHA/year | RHA/year | ||||
| Per cent concordant | 61.3 | 59.8 | 59.4 | 59.3 | ||||
| AIC | 14 712.063 | 14 803.935 | 11 844.369 | 11 855.8 | ||||
| (b) Readmission risk among TKA patients. ORs (CIs) | ||||||||
| PNP | 0.580 | 0.508 to 0.662 | – | – | – | |||
| PNP (IV) | – | 0.894 | 0.656 to 1.216 | – | – | |||
| PFP | – | – | 0.576 | 0.379 to 0.875 | – | |||
| PFP (IV) | – | – | – | 1.935 | 0.399 to 9.395 | |||
| Male | 1.261 | 1.130 to 1.408 | 1.284 | 1.150 to 1.434 | 1.288 | 1.140 to 1.455 | 1.276 | 1.128 to 1.443 |
| Age group 18–49 years* | 1.082 | 0.809 to 1.447 | 1.093 | 0.818 to 1.461 | 1.082 | 0.786 to 1.489 | 1.077 | 0.783 to 1.483 |
| Age group 50–59 years | 0.959 | 0.809 to 1.136 | 0.961 | 0.811 to 1.139 | 0.967 | 0.801 to 1.166 | 0.949 | 0.785 to 1.147 |
| Age group 60–69 years | 0.851 | 0.745 to 0.971 | 0.845 | 0.740 to 0.964 | 0.858 | 0.741 to 0.994 | 0.847 | 0.730 to 0.982 |
| Age group 70–79 years | Ref | Ref | Ref | Ref | ||||
| Age group ≥80 years | 1.276 | 1.079 to 1.509 | 1.276 | 1.079 to 1.508 | 1.188 | 0.981 to 1.439 | 1.204 | 0.993 to 1.460 |
| CCI | 1.135 | 1.065 to 1.208 | 1.139 | 1.070 to 1.213 | 1.134 | 1.057 to 1.217 | 1.142 | 1.064 to 1.226 |
| LOSPY | 1.017 | 1.007 to 1.027 | 1.018 | 1.008 to 1.028 | 1.015 | 1.004 to 1.027 | 1.016 | 1.005 to 1.027 |
| Fixed effects | RHA/year | RHA/year | RHA/year | RHA/year | ||||
| Per cent concordant | 59.9 | 57.7 | 57.2 | 57.2 | ||||
| AIC | 10 007.277 | 10 071.436 | 7862.441 | 7864.188 | ||||
*Age was divided into five groups: patients aged 18–49 years, patients aged 50–59 years, and then 10-year interval groups until the last group (aged 80 years and above).
AIC, Akaike information criterion; CCI, Charlson Comorbidity Index; IV, instrumental variable; LOSPY, length of hospital stay in the previous year; PFP, private for-profit hospital; PNP, private non-profit hospital; PUB, public hospital; RHA, Regional Health Authorities; THA, total hip arthroplasty; TKA, total knee arthroplasty.
With both the adjustment for various patient-level and other covariates method and the two-stage IV method, we found that men, and patients with a high comorbidity index (CCI) or longer LOSPY, had a significantly higher odds of readmission compared to the reference groups. We also found that younger THA patients (18–49 years, 50–59 years and 60–69 years) had lower odds of readmissions than the reference group (who ranged from 70 to 79 years), while older THA patients (≥80 years) had higher odds of readmission. Among TKA patients, the age group of 60 to 69-year-olds had significantly lower odds of readmission than the reference group. Lastly, in the analysis comparing PNPs and PUBs, the oldest patients (≥80 years) had significantly higher odds of readmission.
Readmission flow
The clear majority of readmissions were made to PUBs regardless of where patients received their initial surgery. No readmissions (per our criteria) were found at PFPs in the Norwegian Patients Register ¶ , across procedures (table 3). Among patients having surgery at PFPs, 81.25% of the THA readmissions and 96.15% of the TKA readmissions were readmitted to a PUB. Among patients having surgery at PNPs, 59.64% of the THA readmissions and 57.05% of the TKA readmissions were readmitted to a PUB. Among readmitted patients having surgery at a PUB, 99.16% of the THA readmissions and 99.21% of the TKA readmissions were readmitted to a PUB.
Table 3.
Flow of patient readmissions from index hospital—THA and TKA
| Index hospital | Receiving hospital | |||
| THA | PFP | PNP | PUB | Total |
| PFP | 0 | 3 (18.75%) | 13 (81.25%) | 16 |
| PNP | 0 | 157 (40.36%) | 232 (59.64%) | 389 |
| PUB | 0 | 20 (0.84%) | 2357 (99.16%) | 2377 |
| TKA | ||||
| PFP | 0 | 1 (3.85%) | 25 (96.15%) | 26 |
| PNP | 0 | 134 (42.95%) | 178 (57.05%) | 312 |
| PUB | 0 | 13 (0.79%) | 1640 (99.21%) | 1653 |
Share of readmissions from index hospital within parentheses.
PFP, private for-profit hospital; PNP, private non-profit hospital; PUB, public hospital; THA, total hip arthroplasty; TKA, total knee arthroplasty.
Discussion
Principal findings
In terms of quality of care as measured by readmissions for THA and TKA, we found little significant difference between the various hospital types. While adjusting for various patient-level and other covariates, we found some significant quality differences. These were greatly attenuated using the IV approach, whose advantage is that it permits adjustment for both observed and unobserved confounders in observational data.22 24–26 Using this method, we compared patient groups that differ in the likelihood of receiving a treatment at different hospital types as opposed to comparing patients with respect to the actual treatment received (which may be biased). Thus, we adjusted for unobserved confounders that we could not adjust for by simply including patient-level and other covariates—for example, patient compliance, which may explain some observed quality differences between hospital types. The use of thromboprophylaxis, recommended by the national Norwegian guidelines the first 10 postoperative days following primary THA and TKA** †† , is found to prevent venous thrombosis27 28 and better patient compliance has previously been found to result in lower readmission rates.29 The additional finding that PUBs received the major share of hospital readmissions while PFPs received none, indicates that regardless of any quality differences, PUBs play an essential role in the care of more complex patients and for readmissions.
Strengths and weaknesses
The primary strength of our study is access to the NPR, which contains information on all publicly financed patients who have received treatment at all public and private hospitals in Norway. The academic literature covering quality of care in PUBs, PNPs and PFPs in the Nordic countries using register data is almost non-existent. Compared to many studies on hospital readmission carried out on a limited group of patients, this large and thorough data set represents the Norwegian population in the most robust way. Additionally, the recent time range of our study, 2009–2014, provides indications of current clinical practice that will be relevant for policy and decision makers. Our results from comparing the hospital groups are obviously only valid for the two procedures analysed. However, despite not being generalisable to all activities in the various hospital groups, the increasing importance and prevalence of these, now classic, procedures make them particularly interesting to understand in universal health systems such as the Norwegian. In many of the countries with comparable health systems, these two procedures represent a large share of the elective inpatient surgeries performed at private hospitals and are thus among the procedures offered at all hospital groups in these countries. A limitation is that our study does not include patients at PFPs financed out of pocket or by VPHI, which caused the relatively small number of patients at PFPs to be even smaller. An implication of this limitation is that given the small number of observations in the PFP category, the study’s power to detect differences between PFPs and PUBs is lower than desired. Another limitation is that the register does not contain all clinical variables that one may want when differentiating patient subgroups, such as various anatomical variables and the American Society of Anesthesiologists score.
Discussing important differences in the results
Studies on quality differences between private and public hospitals from England’s comparable taxed-based National Health System (NHS) report mixed results. Chard et al, for example, found that although private providers tended to provide hip or knee replacements to healthier patients, they had better outcomes when compared to public providers even after adjustment for preoperative differences; however, there were no significant differences in quality of care among patients having surgery for hernias or varicose veins.30 Zaidi et al found no significant differences in 12-month reoperation rates between Independent Treatment Centres and NHS hospitals among patients with primary ankle replacements.31 Browne et al, however, reported better patient-reported outcomes for cataract surgeries and hip replacements in PFPs, but worse patient-reported outcomes for hernia repair.32 Furthermore, Sanjay et al found no significant differences in postoperative complications following inguinal hernia repair in private versus public hospitals.33
Many of the Norwegian PNPs fit into the definition of a specialty hospital, as defined by Schneider et al34 as hospitals that treat patients with specific medical conditions or in need of specific medical or surgical procedures, a possible explanation to why PNPs can provide higher quality of care than PUBs. Cram et al,35 using generalised estimating equation models on CMS data and accounting for hospital level clustering, compared the quality of total hip and knee replacement in specialty and general hospitals in the USA, and found, after adjusting for patient characteristics using Elixhauser’s method and hospital volume, that specialty hospitals had significantly lower odds of adverse outcomes for both primary joint replacement and revision joint replacement. We also speculate that many PNPs have a relatively high hospital volume, often divided between relatively few surgeons, resulting in a high surgeon volume. Katz et al studied the association between hospital and surgeon volume and the outcomes of total hip replacement and found better outcomes among both high-volume hospitals and high-volume surgeons36; in a later study the same pattern was found for total knee replacement.37 Lastly, some PNPs provide relatively limited medical training for doctors, resulting in more experienced surgeons. Singh et al found significantly more errors among trainees, when compared to their non-trainee counterparts, due to lack of technical competence or knowledge, and the trainee errors appeared more complex than non-trainee errors.38 Gawande et al reported that the most commonly cited system factors contributing to errors among the teaching hospitals studied were inexperience/lack of competence in a surgical task.39
Conclusions and policy implications
Among the publicly financed patients having THA or TKA surgery between 2009 and 2014 in Norway, quality differences between hospital types were small. Still, both using adjustment for various patient-level and other covariates and a two-stage model using distance as an IV—the most robust method—we found significantly lower odds of readmission when patients had THA at PNPs compared to PUBs. However, PUBs received the majority of the readmissions for patients having had surgery across hospital types and no readmissions were registered at PFPs. PUBs thus play an essential role in the care of more complex patients and for readmissions, regardless of any quality differences. These findings indicate that Norway’s use of both PNPs and PFPs does not compromise quality of care among THA and TKA patients, but since there are considerable costs associated with hospital readmissions, these patterns require further study to help decision makers in their resource allocation efforts.
Supplementary Material
Footnotes
SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC, USA
Applying the SAS PROC LOGISTIC
Applying the SAS PROC LOGISTIC
PFPs are required to report all hospital admissions among publicly financed patients.
Prevention of VTE in Orthopedic Surgery Patients: A Norwegian adaptation of the 9th ed. of the ACCP Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines.
Contributors: Both authors conceptualised and designed the study as well as analysed the data. GHH drafted the manuscript. TPH contributed to the background. Both authors reviewed drafts of the article.
Funding: The present study was funded by the Research Council of Norway, Grant No. 238133.
Competing interests: None declared.
Ethics approval: Norwegian Regional Committees for Medical and Health Research Ethics.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data sharing statement: Access to the register data can be sought from the Norwegian Regional Committees for Medical and Health Research Ethics and the Norwegian Data Protection Authority.
References
- 1. Hagen TP, Holom GH, Amayu KN. Outsourcing day surgery to private for-profit hospitals: the price effects of competitive tendering. Health Econ Policy Law 2017:1–18. 10.1017/S1744133117000019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Maarse H. The privatization of health care in Europe: an eight-country analysis. J Health Polit Policy Law 2006;31:981–1014. 10.1215/03616878-2006-014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Ovretveit J. Nordic privatization and private healthcare. Int J Health Plann Manage 2003;18:233–46. 10.1002/hpm.712 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Hagen TP, Kaarbøe OM. The Norwegian hospital reform of 2002: central government takes over ownership of public hospitals. Health Policy 2006;76:320–33. 10.1016/j.healthpol.2005.06.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Molven O, Ferkis J. Healthcare, welfare and law: health legislation as a mirror of the norwegian welfare state, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 6. Vrangbaek K, Ostergren K. Patient empowerment and the introduction of hospital choice in Denmark and Norway. Health Econ Policy Law 2006;1:371–94. 10.1017/S1744133106005032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Alexandersen N, Anell A, Kaarboe O, et al. . The development of voluntary private health insurance in the nordic countries, 2016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Zmistowski B, Restrepo C, Hess J, et al. . Unplanned readmission after total joint arthroplasty: rates, reasons, and risk factors. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2013;95:1869–76. 10.2106/JBJS.L.00679 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Hansen TM, Kristoffersen DT, Tomic O, et al. . Kvalitetsindikatoren 30 dagers reinnleggelse etter sykehusopphold. Resultater for sykehus og kommuner 2015 The quality indicator 30‐day readmission after hospitalisation – results for Norwegian hospitals and municipalities 2015. Oslo: Norwegian Institute of Public Health, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 10. Pugely AJ, Callaghan JJ, Martin CT, et al. . Incidence of and risk factors for 30-day readmission following elective primary total joint arthroplasty: analysis from the ACS-NSQIP. J Arthroplasty 2013;28:1499–504. 10.1016/j.arth.2013.06.032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Schairer WW, Sing DC, Vail TP, et al. . Causes and frequency of unplanned hospital readmission after total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2014;472:464–70. 10.1007/s11999-013-3121-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Schairer WW, Vail TP, Bozic KJ. What are the rates and causes of hospital readmission after total knee arthroplasty? Clin Orthop Relat Res 2014;472:181–7. 10.1007/s11999-013-3030-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Saucedo JM, Marecek GS, Wanke TR, et al. . Understanding readmission after primary total hip and knee arthroplasty: who’s at risk? J Arthroplasty 2014;29:256–60. 10.1016/j.arth.2013.06.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Herrera CA, Rada G, Kuhn-Barrientos L, et al. . Does ownership matter? An overview of systematic reviews of the performance of private for-profit, private not-for-profit and public healthcare providers. PLoS One 2014;9:e93456 10.1371/journal.pone.0093456 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Irvin RA. Quality of care differences by ownership in United States renal dialysis facilities. Asaio J 2000;46:775–8. 10.1097/00002480-200011000-00023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Currie G, Donaldson C, Lu M. What does Canada profit from the For-Profit debate on Health Care? Can Public Policy 2003;29:227–51. 10.2307/3552457 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Eggleston K, Shen YC, Lau J, et al. . Hospital ownership and quality of care: what explains the different results in the literature? Health Econ 2008;17:1345–62. 10.1002/hec.1333 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Arthursson AJ, Furnes O, Espehaug B, et al. . Validation of data in the Norwegian Arthroplasty Register and the Norwegian Patient Register: 5,134 primary total hip arthroplasties and revisions operated at a single hospital between 1987 and 2003. Acta Orthop 2005;76:823–8. 10.1080/17453670510045435 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Espehaug B, Furnes O, Havelin LI, et al. . Registration completeness in the Norwegian Arthroplasty Register. Acta Orthop 2006;77:49–56. 10.1080/17453670610045696 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Quan H, Li B, Couris CM, et al. . Updating and validating the Charlson comorbidity index and score for risk adjustment in hospital discharge abstracts using data from 6 countries. Am J Epidemiol 2011;173:676–82. 10.1093/aje/kwq433 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Voskuijl T, Hageman M, Ring D. Higher Charlson Comorbidity Index Scores are associated with readmission after orthopaedic surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2014;472:1638–44. 10.1007/s11999-013-3394-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Newhouse JP, McClellan M. Econometrics in outcomes research: the use of instrumental variables. Annu Rev Public Health 1998;19:17–34. 10.1146/annurev.publhealth.19.1.17 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Ryan JW, Peterson ED, Chen AY, et al. . Optimal timing of intervention in non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndromes: insights from the CRUSADE (Can Rapid risk stratification of Unstable angina patients Suppress ADverse outcomes with Early implementation of the ACC/AHA guidelines) Registry. Circulation 2005;112:3049–57. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.582346 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Kahn JM, Ten Have TR, Iwashyna TJ. The relationship between hospital volume and mortality in mechanical ventilation: an instrumental variable analysis. Health Serv Res 2009;44:862–79. 10.1111/j.1475-6773.2009.00959.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Venkitachalam L, Lei Y, Magnuson EA, et al. . Survival benefit with drug-eluting stents in observational studies: fact or artifact? Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 2011;4:587–94. 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.111.960971 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Verbeek M. A guide to modern econometrics: John Wiley & Sons, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 27. Geerts WH, Pineo GF, Heit JA, et al. . Prevention of venous thromboembolism: the Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and thrombolytic therapy. CHEST Journal 2004;126:338S–400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Bergqvist D, Benoni G, Björgell O, et al. . Low-molecular-weight heparin (enoxaparin) as prophylaxis against venous thromboembolism after total hip replacement. N Engl J Med 1996;335:696–700. 10.1056/NEJM199609053351002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Frankl SE, Breeling JL, Goldman L. Preventability of emergent hospital readmission. Am J Med 1991;90:667–74. 10.1016/S0002-9343(05)80053-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Chard J, Kuczawski M, Black N, et al. . Outcomes of elective surgery undertaken in independent sector treatment centres and NHS providers in England: audit of patient outcomes in surgery. BMJ 2011;343:d6404 10.1136/bmj.d6404 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Zaidi R, Macgregor AJ, Goldberg A. Quality measures for total ankle replacement, 30-day readmission and reoperation rates within 1 year of surgery: a data linkage study using the NJR data set. BMJ Open 2016;6:e011332 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-011332 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Browne J, Jamieson L, Lewsey J, et al. . Case-mix & patients’ reports of outcome in Independent Sector Treatment Centres: Comparison with NHS providers. BMC Health Serv Res 2008;8:1 10.1186/1472-6963-8-78 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Sanjay P, Marioud A, Woodward A. Anaesthetic preference and outcomes for elective inguinal hernia repair: a comparative analysis of public and private hospitals. Hernia 2013;17:745–8. 10.1007/s10029-012-1011-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Schneider JE, Miller TR, Ohsfeldt RL, et al. . The economics of specialty hospitals. Med Care Res Rev 2008;65:531–53. 10.1177/1077558708316687 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Cram P, Vaughan-Sarrazin MS, Wolf B, et al. . A comparison of total hip and knee replacement in specialty and general hospitals. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2007;89:1675–84. 10.2106/00004623-200708000-00002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Katz JN, Losina E, Barrett J, et al. . Association between hospital and surgeon procedure volume and outcomes of total hip replacement in the United States medicare population. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2001;83-A:1622–9. 10.2106/00004623-200111000-00002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Katz JN, Barrett J, Mahomed NN, et al. . Association between hospital and surgeon procedure volume and the outcomes of total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2004;86-A:1909–16. 10.2106/00004623-200409000-00008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Singh H, Thomas EJ, Petersen LA, et al. . Medical errors involving trainees: a study of closed malpractice claims from 5 insurers. Arch Intern Med 2007;167:2030–6. 10.1001/archinte.167.19.2030 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Gawande AA, Zinner MJ, Studdert DM, et al. . Analysis of errors reported by surgeons at three teaching hospitals. Surgery 2003;133:614–21. 10.1067/msy.2003.169 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
bmjopen-2016-015771supp001.pdf (270.6KB, pdf)