Abstract
Background:
Over the last century, human life style and food habits have drastically changed which lead to various chronic diseases. Diabetes mellitus is one such disease which is causing serious problems to human health. Allopathic drugs are not much effective in handling the disease and its complications. Hence focus has been turned towards the traditional system of medicine. Medicinal plants play an important role in the management of diabetes mellitus.
Methods:
Experimental studies conducted on species of Artemisia on diabetic animal models and human published since the year 2000 until April, 2017 were reviewed. Each article was critically appraised by two independent reviewers for their methodological quality using the JBIMAStARI tool.
Result:
A total of 14 studies were included in this review and the blood glucose data obtained from these critically reviewed studies clearly showed that both the aqueous and alcoholic extracts of species of Artemisia produced significant hypoglycemic effects in alloxan, Streptozotocin and high fat diet induced diabetic animals and diabetic humans with different mechanisms of action as compared to standard antidiabetic medications.
Discussion and Conclusion:
The antidiabetic effect of single or multiple doses of aqueous and alcoholic extracts of Artemisia species was due to the active compounds of these plants and they all are effective in lessening the blood glucose level in all of those experimental studies. Despite the presence of known antidiabetic medicines in the pharmaceutical market, therapeutic remedies from these medicinal plants have been utilized with success to treat this disorder and its complications with a relatively less side effects.
Keywords: Artemisia, diabetes mellitus, review
Introduction
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a complex and a fast growing medical problem throughout the globe, in both developed and developing countries. World health organization (WHO) defines diabetes as a multifaceted group of disorders that impairs the metabolism of carbohydrates, fat and protein; caused by lack of insulin secretion and/or reduced sensitivity of the tissue to insulin.[1]
The metabolic dysregulation associated with DM causes secondary pathophysiological changes in multiple organ systems that impose a tremendous burden on the individual with diabetes and on health care systems.[2] Diabetes mellitus is a global health crisis, which has been persistently affecting humanity, irrespective of the socioeconomic profile and geographic location of the population.[3,4] Despite advances in understanding and management of this metabolic disorder, the rate of morbidity and mortality due to this disorder is increasing every year. Globally, an estimated 415 million adults were living with DM in 2015 and this figure is expected to increase to 642 million by the year 2040.[5]
World Health Organization (WHO) estimates report that densely populated Asian countries such as India and China’s expenditure is going to be more than US$1 trillion annually for treating this disease and its complications due to huge increase of diabetic cases by 2030.[6]
Current therapeutic measures to treat this disorder include use of insulin and other agents such as amylin analogues, alpha glycosidase inhibitors, sulphonylureas, and biguanides. These drugs also have certain adverse effects such as causing hypoglycemia at higher doses, liver problems, lactic acidosis and diarrhea.[7] Apart from these available therapeutic options, many herbal medicines have been recommended for the treatment of diabetes. Traditional herbal medicines are used throughout the world. Herbal drugs are prescribed widely because of their effectiveness, lesser side effects and relatively lower cost.[8]
Management of DM with medicinal plants along with dietary restrictions has caught the attention of most researchers. Even today, natural sources form the basis for a large number of modern drugs and one or more active ingredients from them is to be found in 25% of all prescriptions.[9] There is a dire need for other strategies to complement the current modern pharmacotherapy of DM. Herbal drugs comprise a significant amount of conventional medicine and literature reveals anti-diabetic activity exhibited by more than 400 plant species.[10]
Plants are very common in use in our daily either as nutrients or as sources of food and are being consumed by patients as well as healthy people.[11] Easy availability, raw consumption, lesser side effects and low cost makes the herbal preparations desirable among available therapies.[12]
In Western and African folk medicine, several species of the genus Artemisia are used for their claimed healing properties and for the cure of specific ailments. Among those, more than 400 species have been reported to show antidiabetic activity, some species of the genus Artemisia are widely used in traditional medicine as medicinal plants to treat patients with DM.[13] This review is aimed to identify, critically appraise and provide summarized evidence of experimental studies that justify the traditional claim of Artemisia species for treatment of DM.
Methods
The objective of this review is to systematically identify, appraise and synthesize the best available evidence on the effectiveness of species of Artemisia for DM. The review includes studies conducted on different species of Artemisia and their antidiabetic effects on diabetic animals and humans published since the year 2000. A three staged search strategy was used to identify all relevant published literature in English language. Databases searched were PubMed, CINAHl, PopLine, LILACS, MedNar, and MEDLINE. Secondary search was carried out using Google Scholar and Elsevier’s Scirus, to identify articles that are not indexed well in traditional bibliographic databases. The search strategy used or modified for the various databases and search engines was with initial keywords/search terms: [“Antidiabetic Agents” OR “Hypoglycemics” OR “Hypoglycemic Effects” OR “Hypoglycemic Effect” OR “Hypoglycemic Drugs” OR “Antihyperglycemics” OR “Antihyperglycemic Agents” OR “Antidiabetics” OR “Antidiabetic Drugs”] AND [“Artemisia”]. Studies done on animals and humans using alloxan, Streptozotocin and high fat diet as diabetic inducing agents, articles with clear objectives and methodologies; articles published up to April 2017; and articles published in English language were included in this review. All papers selected for inclusion in the review were subjected to a rigorous, independent appraisal by two reviewers prior to inclusion in the review using standardized critical appraisal instruments from the Joanna Briggs Institute.[14]
Result
A total of 156 relevant papers were identified in the literature search from databases, majority of these were duplicates, and hence 61 papers were left after removing duplication. All of them were retrieved for preliminary evaluation. Following review of titles and abstracts against the review objectives and inclusion criteria, 25 articles were excluded. The entire texts of the remaining 36 studies were retrieved for detailed evaluation, after which, 19 of them were excluded. The remaining 17 studies were assessed for methodological quality using the JBI-MAStARI critical appraisal tool and, subsequently, 14 studies were included in the review while 3 studies were deemed to be of insufficient methodological quality and did not meet inclusion criteria and were excluded from the review [Figure 1]. Table 1 shows characteristics of articles included in this review.
Figure 1.
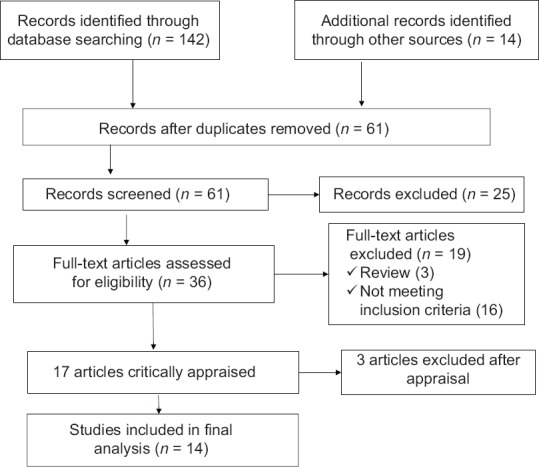
Flow chart for selection process of articles
Table 1.
Summary of characteristics of studies included in the review
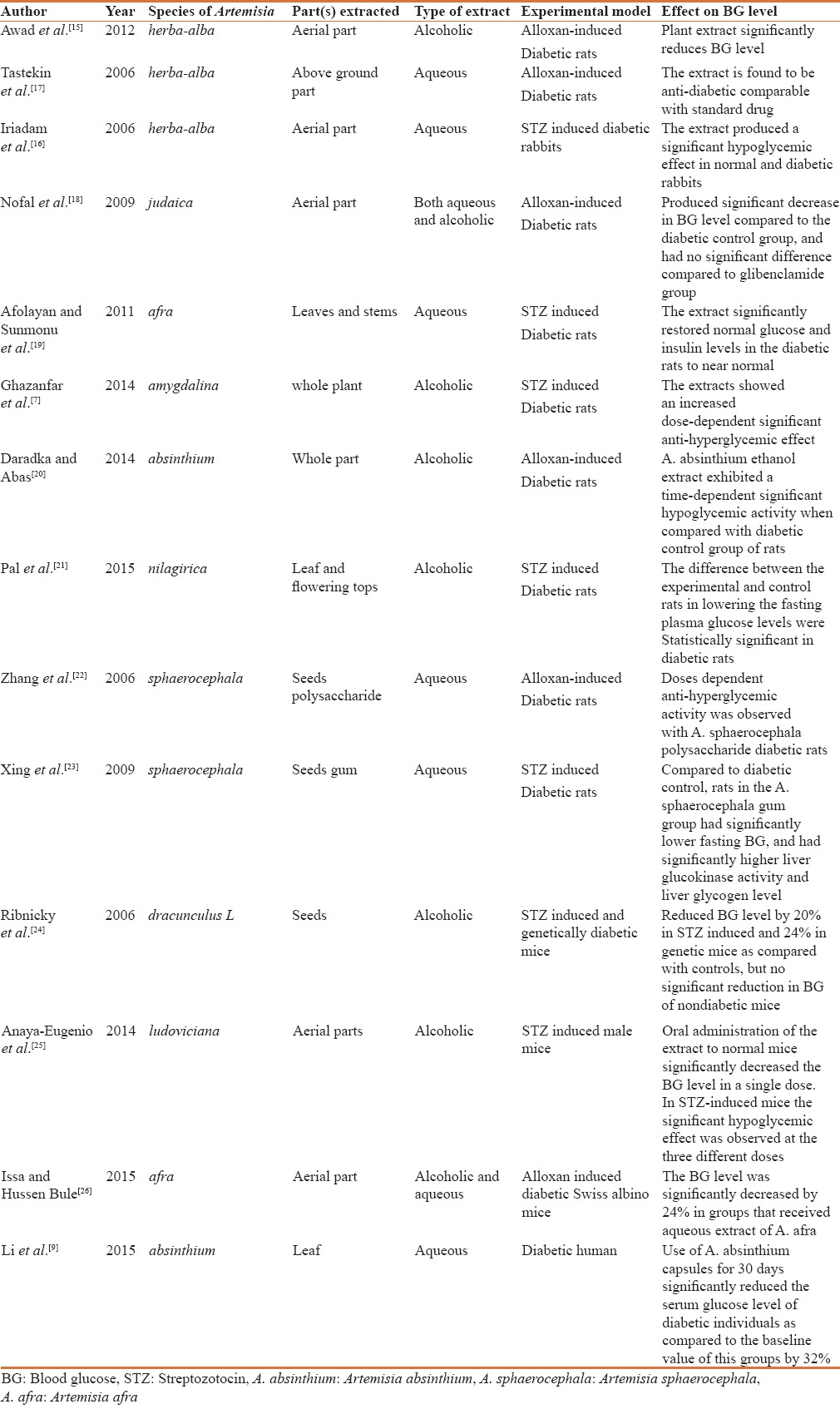
This review included studies conducted on nine species of Artemisia (A. herba-alba, A. judaica, A. afra, A. amygdalina, A. dracunculus, A. ludoviciana, A. absinthium, A. nilagirica and A. sphaerocephala). Only one study was done on humans; the remaining used experimental animal models. In those studies, investigators treated diabetic animals and humans with plant extracts for a duration ranging from 7 to 60 days. Except for two studies,[15,16] all included standard antidiabetic medications as reference to compare the effect of extract with those drugs. Glibenclamide was the most commonly used reference drug. Nine studies employed multiple dosage regimens to assess dose dependent hypoglycaemic effect of extracts while five studies used single dosage regimen of extracts throughout the study period [Table 2].
Table 2.
Detailed description of study characteristics included in the review
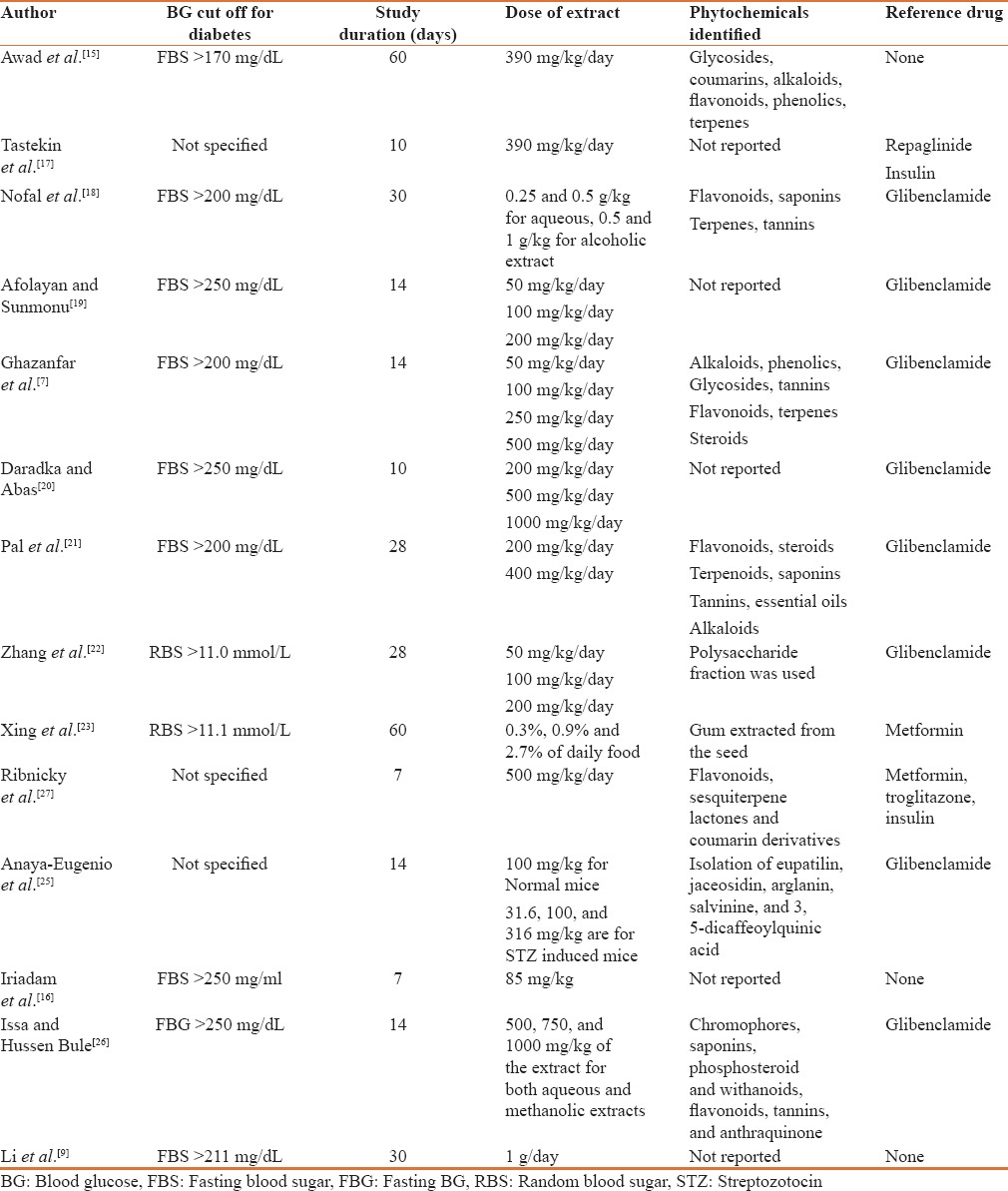
Among studies that reported phytochemicals identified from the extract, flavonoids were the most common secondary metabolites followed by alkaloids and glycosides. Two studies used polysaccharides extracted from A. sphaerocephala seeds.
Discussion
Even in the era of highly advanced bio medicine, herbal medicines are area of focus for researchers around the world to complement modern drugs and as sources for development of novel drugs. The mechanism of most of the herbs used has not been scientifically determined. Many traditional plants and their derived bioactive compounds are used for treatments of diabetes through various mechanisms of actions[28] and, there has been increased scientific interest in medicinal plants research that has been reported to be used traditionally to manage diabetes. This is due to increase efficacy of new plant derived drugs, growing interest in natural products, and the presence of serious side effects, high cost and poor availability of modern antidiabetic drugs for many rural populations particularly in developing countries.[29]
The finding of this review is consistent with results of studies conducted on the species of Artemisia across many regions with different experimental animals and humans.[28,29,30] The blood glucose data obtained from these critically reviewed studies clearly indicate that both the aqueous and alcoholic extracts of species of Artemisia produced significant hypoglycemic effects in alloxan, Streptozotocin and high fat diet induced diabetic animals with different mechanisms of action. Their Hypoglycemic effect was comparable with that of the usual hypoglycemic drugs repaglinide, insulin, metformin and glibenclamide.[7,15,19,20] However, as can be seen from the study of some of those species of Artemisia, such as Artemisia herba-alba have a greater potency in decreasing the serum glucose level and animals treated with this plant showed only mild visible undesirable clinical symptoms whereas the synthetic oral hypoglycemic agents can produce serious side effects.[15]
The significant anti-hyperglycemic activity of ethanolic and aqueous extraction of A. absinthium may be due to the presence of active components such as α-and ß-thujones, thujyl alcohol, azulenes, bisabolene, cadinene, sabinene, pinene, and phellandrene.[31] Whereas, the antidiabetic effects of the plants Artemisia afra, Artemisia judaica and Artemisia amygdalana may be due to the presence of active compounds such as flavonoids and saponins[18,26,32] and also the active ingredients such as tannins, flavonoids, terpenes, steroids and alkaloids in Artemisia niagirica and Artemisia sphaerocephala and the substance apigenin in the Artemisia herba-alba probably make them have a nature of decreasing the serum glucose level.[21,23,33]
The exact molecular mechanisms of action of most of these components to reduce blood glucose is not clearly known. But, it is hypothesized that the reduction in blood glucose level may be due to the presence of thujone, a major component of these medicinal herbs, which had an effect in insulin-sensitizing action. Thujone can increase free insulin-stimulated glucose transporter by activation of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase.[20] A reported data about the hypoglycemic activities of flavonoids, tannins and apigenin proved that they increase insulin secretion and have insulinomimetic effect.[34] The main function of flavonoids are antioxidant activity.[35] Supplementation of antioxidants may be a protective factor against free radical induced beta cell damage, thus preventing and ameliorating diabetes mellitus.
Moreover, the safety and efficacy of these plants were assessed through the administration of both the aqueous and ethanolic extracts of these species which attenuated the elevated activities of all investigated enzymes in diabetic animals comparable to the control. This may be an indication of the relatively nontoxic nature and protective action of the extracts in the primary organs of the body which are commonly affected by toxic insults.[11,32,36,37,38,39]
Conclusion and Recommendation
In this systematic review, we can conclude that the antidiabetic effect of single or multiple doses of aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Artemsia species were due to the active compounds of these plants and they all are effective in decreasing the blood glucose level in all of those experimental studies. Despite the presence of known antidiabetic medicines in the pharmaceutical market, therapeutic remedies from these medicinal plants have been used with success to treat this disorder and its ramifications with relatively lesser side effects. According to WHO recommendation, antihyperglycemic agents of natural plant origin used in traditional medicine are important. Therefore it may be better to consider these species in assessing of their general toxic profile and formulation of antidiabetic drugs.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.World Health Organization. Definition, Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus and its Complications. Geneva: WHO Department of Noncommunicable Diseases Surveillance; 1999. [Last accessed on 2017 May 30]. Available from: http://www.apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/66040/1/WHO_NCD_NCS_99.2.pdf . [Google Scholar]
- 2.Anderson ZL, Scopelliti EM, Trompeter JM, Havrda DE. Management of prediabetes: A comparison of the treatment approaches utilized by a family practice clinic and an internal medicine/endocrinology practice. J Pharm Pract. 2015;28:86–92. doi: 10.1177/0897190013514089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.World Health Organization. Global Report on Diabetes. Geneva: WHO; 2016. [Last accessed on 2017 May 30]. Available from: http://www.apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/204871/1/9789241565257_eng.pdf . [Google Scholar]
- 4.International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 7th ed. IDF; 2015. [Last accessed on 2017 May 30]. Available from: http://www.diabetesatlas.org/component/attachments/?task=download&id=116 . [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ogurtsova K, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Huang Y, Linnenkamp U, Guariguata L, Cho NH, et al. IDF diabetes atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2017;128:40–50. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2017.03.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes: Estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1047–53. doi: 10.2337/diacare.27.5.1047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ghazanfar K, Ganai BA, Akbar S, Mubashir K, Dar SA, Dar MY, et al. Antidiabetic activity of Artemisia amygdalina decne in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:185676. doi: 10.1155/2014/185676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Korkmaz H, Gürdal A. Effect of Artemisia santonicum L. on blood glucose in normal and alloxan-induced diabetic rabbits. Phytother Res. 2002;16:675–6. doi: 10.1002/ptr.943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Li Y, Zheng M, Zhai X, Huang Y, Khalid A, Malik A, et al. Effect of-Gymnema Sylvestre Citrullus colocynthis and Artemisia absinthium on blood glucose and lipid profile in diabetic human. Acta Pol Pharm. 2015;72:981–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tahraoui A, El-Hilaly J, Israili ZH, Lyoussi B. Ethnopharmacological survey of plants used in the traditional treatment of hypertension and diabetes in South-Eastern Morocco (Errachidia province) J Ethnopharmacol. 2007;110:105–17. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2006.09.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Aziz S, Saha K, Sultana N, Nur HP, Ahsan MD, Ahmed S, et al. Comparative studies of elemental composition in leaves and flowers of Catharanthus roseus growing in Bangladesh. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2016;6:50–4. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sahu U, Tiwari SP, Roy A. Comprehensive notes on anti diabetic potential of medicinal plants and polyherbal formulation. UK J Pharm Biosci. 2015;3:57–64. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Eshetu N, Afework M, Makonnen E, Debella A, Ergete W, Tolesssa T. Evaluation of the acute and sub-chronic toxic effects of aqueous leaf extracts of Artemisia afra on liver, kidney and some blood parameters in Wistar rats. J Biomed Eng Sci. 2016;1:1–9. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Joanna Briggs Institute for Evidence Based Practice [JBI] Reviewers’Manual. 2014. [Last accessed on 2017 Nov 01]. p. 197. Available from: https://www.joannabriggs.org/assets/.../reviewersHandbook/JBI-ReviewersManual-2014.pdf .
- 15.Awad NE, Seida AA, Shaffie ZE, El-Aziz AM, Awad NE. Hypoglycemic activity of Artemisia herba-alba (Asso) used in Egyptian traditional medicine as Hypoglycemic remedy. J Appl Pharm Sci. 2012;2:30–9. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Iriadam M, Musa D, Gümüflhan H, Baba F. Effects of two Turkish medicinal plants Artemisia herba-alba and Teucrium polium on blood glucose levels and other biochemical parameters in rabbits. J Cell Mol Biol. 2006;5:19–24. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tastekin D, Atasever M, Adiguzel G, Keles M, Tastekin A. Hypogycaemic effect of Artemisia Herb-alba in experimental hyperglycaemic rats. Bull Vet Inst Pulawy. 2006;50:235–8. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Nofal SM, Mahmoud SS, Ramadan A, Soliman GA, Fawzy R. Anti-diabetic effect of Artemisia judaica Extracts. Res J Med Med Sci. 2009;4:42–8. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Afolayan AJ, Sunmonu TO. Artemisia afra Jacq. Ameliorates oxidative stress in the pancreas of streptozotocin-induced diabetic Wistar rats. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2011;75:2083–6. doi: 10.1271/bbb.100792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Daradka HM, Abas MM. Antidiabetic effect of Artemisia absinthium extracts on alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Comp Clin Pathol. 2014;23:1733–42. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pal P, Sharma A, Mehra M, Choudhary A, Ghosh AK, Praveen S. Antidiabetic and antihyperlipidimic activity of Ethanolic extract of Artemisia nilagirica (clark) in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Indo Am J Pharm Sci. 2015;2:1256–63. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhang J, Huang Y, Hou T, Wang Y. Hypoglycaemic effect of Artemisia sphaerocephala Krasch seed polysaccharide in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Swiss Med Wkly. 2006;136:529–32. doi: 10.4414/smw.2006.11348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Xing XH, Zhang ZM, Hu XZ, Wu RQ, Xu C. Antidiabetic effects of Artemisia sphaerocephala Krasch. Gum, a novel food additive in China, on streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2009;125:410–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2009.07.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ribnicky DM, Poulev A, Watford M, Cefalu WT, Raskin I. Antihyperglycemic activity of Tarralin, an ethanolic extract of Artemisia dracunculus L. Phytomedicine. 2006;13:550–7. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2005.09.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Anaya-Eugenio GD, Rivero-Cruz I, Rivera-Chávez J, Mata R. Hypoglycemic properties of some preparations and compounds from Artemisia ludoviciana Nutt. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;155:416–25. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.05.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Issa IA, Hussen Bule M. Hypoglycemic effect of aqueous and methanolic extract of Artemisia afra on alloxan induced diabetic swiss albino mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:752486. doi: 10.1155/2015/752486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ribnicky DM, Kuhn P, Poulev A, Logendra S, Zuberi A, Cefalu WT, et al. Improved absorption and bioactivity of active compounds from an anti-diabetic extract of Artemisia dracunculus L. Int J Pharm. 2009;370:87–92. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2008.11.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mahabir D, Gulliford MC. Use of medicinal plants for diabetes in Trinidad and Tobago. Rev Panam Salud Publica. 1997;1:174–9. doi: 10.1590/s1020-49891997000300002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mohammed SA, Yaqub AG, Sanda KA, Nicholas AO, Arastus W, Muhammad M, et al. Review on diabetes, synthetic drugs and glycemic effects of medicinal plants. J Plants Res. 2013;7:2628–37. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lakshmi MS, Rani SK, Reddy UK. A review on diabetes mellitus and herbal plants used for its treatment. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2012;5:15–21. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ene AC, Atawodi SE, Ameh DA, Kwanashie HO, Agomo PU. In vivo antiplasmodial effect of chloroform extracts of Artemisia maciverae Linn and Artemisia maritima Linn. Afr J Biotechnol. 2009;8:6612–6. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sunmonu TO, Afolayan AJ. Evaluation of antidiabetic activity and associated toxicity of artemisia afra aqueous extract in Wistar rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:929074. doi: 10.1155/2013/929074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.al-Shamaony L, al-Khazraji SM, Twaij HA. Hypoglycaemic effect of Artemisia herba alba. II. Effect of a valuable extract on some blood parameters in diabetic animals. J Ethnopharmacol. 1994;43:167–71. doi: 10.1016/0378-8741(94)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hanrahan JR, Chebib M, Johnston GA. Flavonoid modulation of GABA(A) receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 2011;163:234–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01228.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ribnicky DM, Poulev A, O’Neal J, Wnorowski G, Malek DE, Jäger R, et al. Toxicological evaluation of the ethanolic extract of Artemisia dracunculus L. for use as a dietary supplement and in functional foods. Food Chem Toxicol. 2004;42:585–98. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2003.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Abdel Jaleel GA, Abdallah HM, Gomaa NE. Pharmacological effects of ethanol extract of Egyptian Artemisia herba-alba in rats and mice. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2016;6:44–9. [Google Scholar]
- 37.El-Sharabasy HM. Acaricidal activities of Artemisia judaica L. extracts against Tetranychus urticae Koch and its predator Phytoseiulus persimilis athias henriot (Tetranychidae: Phytoseiidae) J Biopestic. 2010;3:514–9. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mubashir K, Ganai BA, Ghazanfar K, Akbar S, Malik AH, Masood A, et al. Evaluation of Artemisia amygdalina D. For anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory potential. ISRN Inflamm. 2013;2013:483646. doi: 10.1155/2013/483646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Muto T, Watanabe T, Okamura M, Moto M, Kashida Y, Mitsumori K, et al. Thirteen-week repeated dose toxicity study of wormwood (Artemisia absinthium) extract in rats. J Toxicol Sci. 2003;28:471–8. doi: 10.2131/jts.28.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


