Adherence to prescribed medications is associated with improved clinical outcomes for chronic disease management and reduced mortality from chronic conditions (1). Conversely, nonadherence is associated with higher rates of hospital admissions, suboptimal health outcomes, increased morbidity and mortality, and increased health care costs (2). In the United States, 3.8 billion prescriptions are written annually (3). Approximately one in five new prescriptions are never filled, and among those filled, approximately 50% are taken incorrectly, particularly with regard to timing, dosage, frequency, and duration (4). Whereas rates of nonadherence across the United States have remained relatively stable, direct health care costs associated with nonadherence have grown to approximately $100–$300 billion of U.S. health care dollars spent annually (5,6). Improving medication adherence is a public health priority and could reduce the economic and health burdens of many diseases and chronic conditions (7).
Understanding Medication Nonadherence
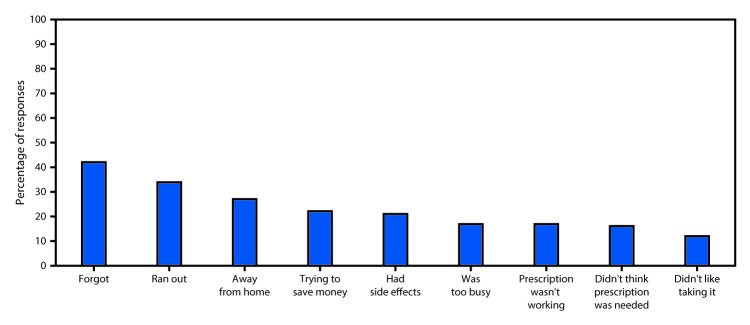
Medication adherence is a complex behavior influenced by factors along the continuum of care, relating to the patient, providers, and health systems (8). Patient-related factors include unintentional factors, which often worsen with increasingly complex medication regimens (e.g., forgetting to take medication or obtain refills, or inadequate understanding of dose or schedules); and intentional factors (e.g., active decision to stop or modify a treatment regimen based on ability to pay, beliefs and attitudes about their disease, medication side effects, and expectations for improvement) (9) (Figure). Additional patient-related barriers include lack of engagement in treatment decisions, impaired cognition (e.g., related to aging or disease), substance abuse, depression, and other mental health conditions. Provider-related factors include barriers to communicating with patients and their caregivers, complex dosing regimens, and limited coordination of care among multiple providers. Health care system and service delivery factors include limited access to an appropriate provider for prescriptions or refills, restricted drug coverage, high costs and copayments, unclear medication labeling and instructions, limited availability of culturally appropriate patient education materials, and inadequate provider time to review benefits, risks, and alternatives to prescribed medications.
FIGURE.
Self-reported reasons* for nonadherence to recommended medication regimens — United States, 2013
Source: Medication Adherence in America: A National Report 2013. Adapted with permission. https://www.ncpanet.org/pdf/reportcard/AdherenceReportCard_Abridged.pdf.
* Participants could provide more than one response, and as such, categories are not mutually exclusive.
Innovative Strategies to Improve Medication Adherence for Chronic Disease Management
Successful efforts to improve rates of adherence often incorporate multiple strategies across the continuum of care. A proven cost-effective strategy to reducing unintentional nonadherence is the use of pillboxes and blister packs to organize medication regimens in clear and simple ways (10). Combining the ease of packaging with effective behavioral prompts, such as electronic pill monitors that can remind patients to take their medication and provide messages to health care providers when a scheduled drug-dose is missed, supports increased medication adherence (11).
Interventions that include team-based or coordinated care have been shown to increase adherence rates. In a recent study, patients assigned to team-based care, including pharmacist-led medication reconciliation and tailoring; pharmacist-led patient education; collaborative care between pharmacist and primary care provider or cardiologist; and two types of voice messaging (educational and medication refill reminder calls) were significantly more adherent with their medication regimen 12 months after hospital discharge (89%) compared with patients not receiving team-based care (74%). Patients reported that team-based care improved their comfort in asking clarifying questions, raising concerns about their medication regimen, and collaborating in developing their treatment plan (12,13).
Lowering economic barriers to prescribed medications also improves adherence rates. In 2007, Pitney-Bowes Corporation employees and beneficiaries with diabetes or vascular disease increased their medication adherence rates increased by 3%–4% after the company eliminated or reduced health plan copays for cholesterol-lowering statins and the antiplatelet medication, clopidogrel (used to prevent heart attacks and strokes), compared with beneficiaries insured by another health plan with the same third-party prescription drugs administrator that did not reduce or eliminate copays for the same medications. These improvements, while modest, could result in significant cost savings in the prevention of acute events (e.g., hospitalizations) and progression of major chronic conditions if scaled to larger populations (14).
System-based strategies that address health disparities can improve clinical goals or reduce disease burden. For example, medication adherence is crucial for persons infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), because treatment lowers the amount of virus circulating in the blood, which improves the patient’s health and reduces the risk of transmitting HIV to others by >90% (15). Interventions, such as CDC’s Data to Care (16) strategy, that identify and re-engage nonadherent patients in care by linking them through the health department, their care providers, or both, improve the health of the individual and achieve the public health benefit of reducing HIV transmission (17).
Advances in health information technology can also improve medication adherence. In a 2011 study, providers using electronic prescribing (e-prescribing) increased first-fill medication adherence by 10% compared with those using paper prescriptions (18). Some e-prescribing software can monitor prescriptions dispensed or unfilled in near real-time, as well as send patients prompts when a new or refill prescription is available. These data allow providers to review current medication use with patients during office visits, identify gaps or barriers to adherence, and discuss workable solutions.
Health information technology can also be used to show real-time impact of medication use on chronic conditions. Reliant Medical Group, a multispecialty group practice in Massachusetts, provided home blood pressure monitors to 200 of its patients. Patients uploaded blood pressure readings into their electronic health record. At office visits, providers were able to display trends of patients’ blood pressure, discuss barriers if blood pressure was not controlled and patients were not adherent, or add alternative drugs or lifestyle changes if pharmacy data indicated patients were adherent but their blood pressure was still poorly controlled. In addition, health information technology systems enabled providers to view medication coverage by insurer and choose lower cost medications. Reliant also made complex prescribing algorithms easier to follow by establishing and incorporating treatment protocols for hypertension into the electronic health record. Using these and other strategies (Box), Reliant improved its hypertension control rate from 68% in 2011 to 79% in 2014 and was recognized as a Million Hearts Hypertension Control Champion in 2015 (19).
BOX. Strategies used by Reliant Medical Group (Massachusetts) to improve adherence to blood pressure medication and increase hypertension control rates.
Ensure that patient understands the benefits
Educate about harms of uncontrolled hypertension and benefits of controlling hypertension
Make culturally appropriate education materials available
Automatically print educational information in the After-Visit Summary if patient has diagnosis of hypertension
Show patients graphs of their blood pressure trends during office visits and online electronic health record (EHR) portal. Use graphs to demonstrate challenges and successes with treatment regimens
Choose lower cost medications
Use step-therapy protocols that are developed by a multidisciplinary team and are standardized across the organization
Control access to pharmaceutical marketing
Make the patient’s payer-specific formulary available in the EHR to inform medication selection
Use generic medication substitution
Provide assistance in paying for medications (e.g., RxAssist.org)
Consult social workers to assist with adherence barriers
Minimize medication complexity
Choose once-a-day and combination medications
Engage in dialogue about costs versus convenience (e.g., pill-splitting can reduce cost but increase inconvenience)
Monitor side effects
-
Be creative in addressing concerns
e.g., if concerned about swollen feet, use a diuretic, if appropriate
e.g., if concerned about medication causing abnormal potassium level, use a combined angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor and a diuretic to normalize potassium
-
When to monitor side effects
At visits
At prescription renewals, using a standard documentation template
After hospital discharge: automated alerts for new medications
-
Consult pharmacists
For complex medication regimens or side effects
After hospital discharge regarding patients who are on high-risk medications
Show effectiveness of the medications in lowering blood pressure
Empower patient to record blood pressure readings at home
Provide booklets to record readings
For patients with financial hardships, provide free home blood pressure monitors
Offer free blood pressure clinics
Automatically upload blood pressure readings into the EHR
Monitor medication adherence
Encourage patients to document their medication-taking behavior
Use EHR systems that can show medication fill history
Automate adherence monitoring using payer medication claims
Review adherence information during visits. Patients’ knowing that a clinician is monitoring adherence is at least as important as a patient seeing the results
Opportunities in Medication Adherence Outcomes
Although a range of interventions have demonstrated improved medication adherence and health outcomes during the study period, few studies have shown that these benefits were maintained over time (20). Interventions that can sustain patient medication adherence are needed. One priority for developing sustainable strategies to improve medication adherence includes standardizing research methodology for both clinic and research settings. Currently, studies use a variety of measurement methods. Varying study methodologies prevents comparability across interventions, hinders wide application into clinical practice, and limits efforts that focus on patients with the greatest burden and need. Standardization might also help to understand both the dose-response and effectiveness of interventions over a longer time, increasing sustainability and reducing a waning effect at follow-up time points (21).
In addition, patient-specific tailored approaches to identifying reasons for nonadherence and aligning intervention efforts to address identified needs are needed. Outcomes might also be improved by recognizing populations at increased risk for nonadherence and addressing the broader reasons for their nonadherence, such as low health literacy. Health literacy is lower among the elderly, racial and ethnic minorities, and persons living in poverty (22). Interventions to improve medication adherence could be more effective if patient’s health literacy, cultural background, and language preference and proficiency are taken into account when designing communication and patient education materials.
Conclusion and Comments
Medication adherence is critical to improving chronic disease outcomes and reducing health care costs. Successful strategies to improve medication adherence include 1) ensuring access to providers across the continuum of care and implementing team-based care; 2) educating and empowering patients to understand the treatment regimen and its benefits; 3) reducing barriers to obtaining medication, including cost reduction and efforts to retain or re-engage patients in care; and 4) use of health information technology tools to improve decision-making and communication during and after office visits. Understanding root causes of medication nonadherence and cost-effective approaches that are applicable in diverse patient populations is essential to increasing adherence and improving long-term health impact.
Conflict of Interest: Dr. Ho reports grants from Veterans Health Administration during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Janssen, Inc., personal fees from American Heart Association, outside the submitted work. Dr. Garber reports grants from Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality during the conduct of the study.
References
- 1.Vrijens B, De Geest S, Hughes DA, et al. ; ABC Project Team. A new taxonomy for describing and defining adherence to medications. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2012;73:691–705. 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2012.04167.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.DiMatteo MR. Variations in patients’ adherence to medical recommendations: a quantitative review of 50 years of research. Med Care 2004;42:200–9. 10.1097/01.mlr.0000114908.90348.f9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cutler DM, Everett W. Thinking outside the pillbox—medication adherence as a priority for health care reform. N Engl J Med 2010;362:1553–5. 10.1056/NEJMp1002305 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Osterberg L, Blaschke T. Adherence to medication. N Engl J Med 2005;353:487–97. 10.1056/NEJMra050100 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Iuga AO, McGuire MJ. Adherence and health care costs. Risk Manag Healthc Policy 2014;7:35–44 . 10.2147/RMHP.S19801 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Viswanathan M, Golin CE, Jones CD, et al. Interventions to improve adherence to self-administered medications for chronic diseases in the United States: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med 2012;157:785–95. 10.7326/0003-4819-157-11-201212040-00538 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.National Center for Health Statistics. National health expenditures, average annual percent change, and percent distribution, by type of expenditure: United States, selected years 1960–2014. Hyattsville, MD: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC, National Center for Health Statistics; 2015. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/hus/2015/094.pdf
- 8.Gellad WF, Grenard K, McGlynn EA. A review of barriers to medication adherence: a framework for driving policy options. Santa Monica, CA: RAND; 2009. https://www.rand.org/content/dam/rand/pubs/technical_reports/2009/RAND_TR765.pdf [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lehane E, McCarthy G. Intentional and unintentional medication non-adherence: a comprehensive framework for clinical research and practice? A discussion paper. Int J Nurs Stud 2007;44:1468–77. 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2006.07.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ruppar TM, Delgado JM, Temple J. Medication adherence interventions for heart failure patients: a meta-analysis. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs 2015;14:395–404. 10.1177/1474515115571213 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Checchi KD, Huybrechts KF, Avorn J, Kesselheim AS. Electronic medication packaging devices and medication adherence: a systematic review. JAMA 2014;312:1237–47. 10.1001/jama.2014.10059 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lambert-Kerzner A, Havranek EP, Plomondon ME, et al. Perspectives of patients on factors relating to adherence to post-acute coronary syndrome medical regimens. Patient Prefer Adherence 2015;9:1053–9. 10.2147/PPA.S84546 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ho PM, Lambert-Kerzner A, Carey EP, et al. Multifaceted intervention to improve medication adherence and secondary prevention measures after acute coronary syndrome hospital discharge: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern Med 2014;174:186–93. 10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.12944 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Choudhry NK, Fischer MA, Avorn J, et al. At Pitney Bowes, value-based insurance design cut copayments and increased drug adherence. Health Aff (Millwood) 2010;29:1995–2001. 10.1377/hlthaff.2010.0336 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cohen MS, Chen YQ, McCauley M, et al. ; HPTN 052 Study Team. Antiretroviral therapy for the prevention of HIV-1 transmission. N Engl J Med 2016;375:830–9. 10.1056/NEJMoa1600693 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.CDC. Data to care. Using HIV surveillance data to support the HIV care continuum. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC; 2017. https://effectiveinterventions.cdc.gov/en/HighImpactPrevention/PublicHealthStrategies/DatatoCare.aspx
- 17.Crepaz N, Dong X, Chen M, Hall HI. Examination of HIV infection through heterosexual contact with partners who are known to be HIV infected in the United States. AIDS 2017;31:1641–4. 10.1097/QAD.0000000000001526 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Surescripts. The national progress report on e-prescribing and interoperable health care. Arlington, VA: Surescripts; 2011.
- 19.Million Hearts. Reliant Medical Group strategizes for the road to success. Empowering patients to control hypertension. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC, Million Hearts; 2017. https://millionhearts.hhs.gov/files/Champions-SS-Reliant.pdf
- 20.Demonceau J, Ruppar T, Kristanto P, et al. ; ABC project team. Identification and assessment of adherence-enhancing interventions in studies assessing medication adherence through electronically compiled drug dosing histories: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Drugs 2013;73:545–62. 10.1007/s40265-013-0041-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bosworth HB, Granger BB, Mendys P, et al. Medication adherence: a call for action. Am Heart J 2011;162:412–24. 10.1016/j.ahj.2011.06.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lewey J, Shrank WH, Bowry AD, Kilabuk E, Brennan TA, Choudhry NK. Gender and racial disparities in adherence to statin therapy: a meta-analysis. Am Heart J 2013;165:665–78. 10.1016/j.ahj.2013.02.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]