Abstract
Discrepancies in the response to drugs are partially due to polymorphisms in genes involved in drug metabolism and transport. The frequency, pattern and impact of these polymorphisms vary among populations. In the present study, the pharmacokinetics and pharmacogenetics of atorvastatin (ATV) in a Mexican population were investigated. The study cohort exhibited differing ATV metabolizing phenotypes, and in subsequent allelic discrimination assays, single nucleotide polymorphisms in the angiotensinogen, angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AGTR1) and bradykinin B2 receptor (BDKRB2) genes were genotyped and their effects on the pharmacokinetic parameters of ATV were assessed. Additionally, association studies were performed to test for a correlation between metabolizing phenotypes and genetic variants. It was observed that carriers of the genotypes A/C and C/T in AGTR1 and BDKRB2 had higher area under the plasma concentration-time curve values from time 0 to the time of the last measurement and from time 0 extrapolated to infinity, and lower values of clearance of the fraction dose absorbed compared with homozygous carriers (P<0.05). Only the C/C genotype of BDKRB2 was associated with the fast metabolizer phenotype. These data suggest that AGTR1 and BDKRB2 are involved in ATV pharmacokinetics; a novel finding that requires confirmation in further studies.
Keywords: angiotensin II type 1 receptor, bradykinin B2 receptor, atorvastatin, drug metabolism, Mexican population
Introduction
The prevalence of chronic degenerative diseases has increased in the adult Mexican population (1,2). In Mexico, cardiovascular disease (CVD) was a leading cause of death in 2015 (3), while hypercholesterolemia, a major risk factor for CVD, was the most prevalent type of dyslipidemia in the Mexican population between 2003 and 2005 (4). Statins are cholesterol-lowering drugs, and in 2012, atorvastatin (ATV) was the most frequently prescribed statin in Mexico (5). Within liver cells, ATV disrupts cholesterol biosynthesis by blocking 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase, which reduces the amount of cholesterol released into the blood. As a consequence, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol uptake by liver cells increases and blood cholesterol levels diminish (6). However, in clinical trials of ATV, pharmacokinetic parameters including maximum plasma concentration (Cmax), time to reach Cmax (Tmax), area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) from time 0 to the time of last measurement (AUC0-t), AUC from time 0 extrapolated to infinity (AUC0-∞), apparent clearance of the fraction dose absorbed (Cl/F), elimination rate constant in the terminal drug phase (Ke) and the half-life in the terminal drug phase (T1/2) are variable (7). This reflects the underlying variability in the absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (ADME) processes of ATV, which may affect the pharmacological response (8). Although in general, genetic factors influence ~30% of variation in drug disposition and response (9,10), recent results have indicated that genetic variability may contribute to >90% of the variance in ATV plasma concentrations (11). These differences in the ADME characteristics of ATV have been attributed to polymorphisms in genes associated with drug pharmacokinetics, particularly those encoding enzymes and transporters (7,10,11).
The anti-inflammatory effect of statins has been investigated (12). The angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AGTR1) blocks the angiotensin II pathway and has been associated with the development of atherosclerosis (12). In addition, polymorphisms in AGTR1 have been associated with muscle toxicity in patients treated with statins (13). In addition to AGTR1, angiotensinogen (AGT) is part of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (14). An improved response to diuretics has been observed in the presence of the AGTR1 A1166C and AGT G-6A polymorphisms in African-American women and a Chinese population (15,16).
The kallikrein-kinin system is also involved in multiple cardiovascular events; it modulates the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, promotes vasodilation, modulates neovascularization and stimulates the inflammatory response (17). Genetic variants in the bradykinin B2 receptor (BDKRB2) and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) genes have been associated with CVD risk (18,19). Notably, the BDKRB2 C(−58)T polymorphism has been associated with hypertension in an Asian population; carriers of the C/C genotype had an increased risk, whereas carriers of the T/T genotype had a decreased risk. However, in Asian heterozygous carriers, Americans and Europeans, no association has been identified (20), though an improved response to enalapril for the treatment of hypertension has been observed in individuals with the C/C genotype (21).
Although polymorphisms in the AGTR1, AGT and BDKRB2 genes have been described, there is a lack of studies on their frequency and effect on ATV pharmacokinetics. Therefore, the present study aimed to: i) Identify novel polymorphic variants influencing the pharmacokinetic parameters of ATV; and ii) associate genotypes with metabolizing phenotypes.
Materials and methods
Design
A randomized clinical study was conducted in 60 healthy volunteers of Mexican origin to assess the bioequivalence of a single oral dose (80 mg) of ATV (coated tablets; Pfizer, Inc., New York, NY, USA) (7). The study was performed according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki (22), of Tokyo for Good Clinical Practice Standards (23), and to Mexican regulations for studies of bioavailability and bioequivalence (24). The clinical protocol was approved by the Research and Ethics Committee of the Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology Center, Ipharma S.A. (Monterrey, Mexico), and the pharmacogenetic procedure was approved by the Ethics, Research and Biosecurity Committees of the University of Monterrey (Monterrey, Mexico). The study was registered with the Federal Commission for Protection Against Health Risks under code Atorvastatina/A95-10Bis and in the Register of Clinical Trials of Australia and New Zealand (registration no. ACTRN12614000851662). Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects.
Study population
As described in our preliminary pilot study (7), a total of 60 healthy male volunteers of Mexican origin were included in the study from January 2011 to February 2011, with a mean age of 24.01±4.35 years. The inclusion criteria were as follows: Non-smoker; 18–45 years old; weight, ≥50 kg; body mass index, 20–26 kg/m2; availability to complete the study and normal health status (free from disease). Health status was assessed based on physical examination, medical history and clinical and biochemical tests. Insufficiency in any requirement (abnormal laboratory results, drug abuse, ingestion of alcohol 1 week prior to the study, prescription or over-the-counter medication prior to enrollment and reluctance to complete the study) was reason for exclusion from the study. Women were excluded as ATV is classified as a pregnancy category X drug (25). All subjects were informed of the aims of the study.
Sampling
ATV administration and blood sampling were performed as described in the pilot study (7). Briefly, peripheral blood (4 ml) was collected in K2EDTA-coated BD Vacutainers® (BD Diagnostics, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) at different time points: Prior to drug administration (time 0) and at 17 time points (0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, 4, 5, 6, 8, 12, 24, 36 and 48 h) after drug administration. The plasma was used for pharmacokinetic analysis and DNA was isolated from blood cells using an alkaline lysis method (26). Genomic DNA was quantified by UV absorbance using a Nanodrop 1000 Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA). An absorbance 260/280 ratio between 1.8 and 2 was considered of adequate quality for subsequent use. The DNA concentration was adjusted to 10 ng/µl and stored at −20°C until analysis.
Pharmacokinetic analysis
ATV plasma concentrations were measured by high-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry with an Agilent 1100 system (Agilent Technologies, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA) using a method validated by Ipharma S.A. (7,27,28). The Cmax and Tmax parameters were obtained from the concentration-time data of the plasma. Pharmacokinetic parameters including AUC0-t, AUC0-∞, Cl/F, Ke, and T1/2, were calculated with a non-compartmental method (29) using WinNonlin® software v5.3 (Pharsight Corp., Mountain View, CA, USA) as described in the pilot study (7).
Metabolic phenotype classification
The metabolizer phenotypes were determined according to the results of a multivariate analysis of the combined pharmacokinetic parameters Cmax and AUC0-t (7). First, Cmax and AUC0-t were standardized to minimize the effect of scale differences, and a distance matrix was made from the combined standardized Cmax and AUC0-t values. Subsequently, hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) using the Ward linkage method (30) was performed on individual Cmax and AUC0-t values. Finally, the interindividual Manhattan distances were computed. Minitab 16 software (Minitab Inc., State College, PA, USA) was used for standardization and HCA.
Pharmacogenetic tests
DNA samples were genotyped for the polymorphisms AGT-rs699, AGTR1-rs5186 and BDKRB2-rs1799722 using real-time polymerase chain reaction and Taqman® probes (Applied Biosystems; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Three quality controls thresholds were applied: A genotype call rate equal to 1.0, a Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) test with P>0.05, and a minor allele frequency of >0.01.
Statistical analysis
The HWE was determined by comparing the genotype frequencies with the expected values using the maximum likelihood method (31). All statistical analysis was performed with SPSS v20 software (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). To assess the effects of polymorphisms on the ATV pharmacokinetic parameters, comparisons between two and three groups were made. The Student's t-test and one-way analysis of variance were used for parametric distributions, while Mann-Whitney U and Kruskal-Wallis H tests were used for nonparametric distributions. To confirm the contribution of genetic factors to the variability of pharmacokinetic parameters, linear regression analysis was performed. Possible associations of genotypes or combinations of genotypes with phenotypes were evaluated using χ2 and Fisher's exact tests. Linear regression and associations were assessed under three different models (dominant, over-dominant and recessive) (32). The odds ratio (OR) was estimated with a 95% confidence interval (95% CI). All P-values were two-tailed. Corrected P-values (Pc) were obtained using the Bonferroni correction for exclusion of spurious associations. P<0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance.
Results
Metabolic phenotype classification
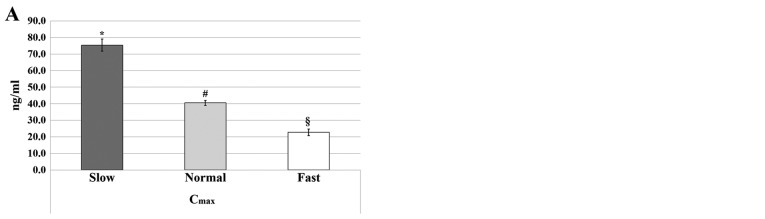
As reported in our previous study (7), the classification of metabolizer phenotypes, based on the combination of the Cmax and AUC0-t parameters, identified three ATV metabolizer phenotypes: Slow metabolizers (30.00%), normal metabolizers (41.66%) and fast metabolizers (28.33%). The Cmax and AUC0-t parameters used for the classification were significantly different between the three phenotypes (7); the parameters were significantly higher for the slow phenotype compared with the normal and fast phenotypes, and significantly higher for the normal phenotype compared with the fast phenotype (P<0.05; Fig. 1). None of the subjects reported any side effects (7).
Figure 1.
Metabolizer phenotypes based on atorvastatin pharmacokinetics. (A) Metabolizer phenotypes based on Cmax values; (B) metabolizer phenotypes based on AUC0-t values. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error. *P<0.05 vs. normal; #P<0.05 vs. fast; §P<0.05 vs. slow. Cmax, maximum plasma concentration; AUC0-t, area under the plasma concentration-time curve from time 0 to the time of last measurement.
Pharmacogenetic tests
Allele frequencies of the genetic polymorphisms were consistent with HWE (P>0.05). All genetic polymorphisms satisfied the quality control tests.
Association between genotypes and ATV pharmacokinetics
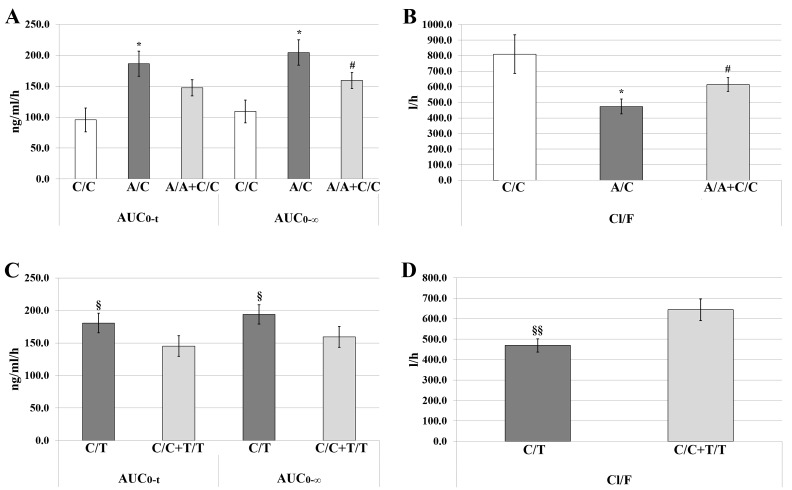
There was no significant effect of the AGT-rs699 polymorphism on ATV pharmacokinetic parameters (Table I). Conversely, AUC0-t and AUC0-∞ values were significantly higher in individuals with the heterozygous genotype (A/C) of the AGTR1-rs5186 polymorphism when compared with the C/C genotype (P<0.05). In addition, the AUC0-∞ of the A/C genotype was increased compared with that observed for the combination of the homozygous wild-type and homozygous variant alleles (A/A+C/C; P<0.05). In heterozygous carriers, Cl/F values were significantly lower than those observed for homozygous variant allele carriers (C/C) and for the combination of homozygous alleles (A/A+C/C; P<0.05; Table I and Fig. 2A and B).
Table I.
Effect of polymorphisms on the pharmacokinetic parameters of atorvastatin.
| Genotypes | N | Cmax (ng/ml) | AUC0-t (ng/ml/h) | AUC0-∞ (ng/ml/h) | Cl/F (l/h) | Ke | T1/2 (h) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGT-rs699 | A/A | 4 | 45.72±11.03 | 109.72±38.89 | 121.44±43.81 | 729.06±266.90 | 0.05±0.02 | 14.97±9.68 |
| A/G | 29 | 43.21±21.06 | 141.98±51.00 | 159.05±56.37 | 588.08±279.10 | 0.07±0.04 | 12.43±7.99 | |
| G/G | 27 | 51.20±26.65 | 189.40±11.65 | 200.34±110.61 | 516.63±246.52 | 0.08±0.02 | 9.22±3.25 | |
| A/A+A/G | 33 | 43.51±20.00 | 138.07±50.32 | 154.49±55.82 | 605.17±277.53 | 0.07±0.04 | 12.74±8.09 | |
| AGTR1-rs5186 | A/A | 34 | 44.14±22.86 | 155.21±83.44 | 166.63±81.73 | 585.92±269.36 | 0.08±0.03 | 9.78±5.53 |
| A/C | 21 | 54.80±23.47 | 186.44±92.45a | 204.55±94.76a | 473.67±220.44a | 0.06±0.03 | 13.49±8.12 | |
| C/C | 5 | 33.36±18.79 | 95.57±43.10 | 109.28±40.84 | 810.19±275.81 | 0.07±0.02 | 10.72±3.30 | |
| A/A+C/C | 39 | 42.76±22.46 | 147.56±81.54 | 159.28±79.71b | 614.68±277.11b | 0.08±0.03 | 9.90±5.27 | |
| BDKRB2-rs1799722 | C/C | 24 | 44.00±27.21 | 151.53±103.77 | 163.00±102.00 | 649.67±316.78 | 0.09±0.02 | 8.78±3.27 |
| C/T | 27 | 51.80±20.93 | 180.66±78.48c | 194.17±77.38d | 469.55±168.36e | 0.07±0.04 | 12.64±7.21 | |
| T/T | 9 | 40.40±17.73 | 128.38±42.26 | 150.31±66.35 | 627.71±287.80 | 0.06±0.02 | 13.05±9.53 | |
| C/C+T/T | 33 | 43.02±24.76 | 145.22±91.08 | 159.54±92.80 | 643.68±304.85 | 0.08±0.02 | 9.94±5.84 |
Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation.
P =0.015 (A/C vs. C/C)
P =0.040 (A/A+C/C vs. A/C)
P =0.021 (C/C+T/T vs. C/T)
P =0.023 (C/C+T/T vs. C/T)
P =0.007 (C/C+T/T vs. C/T). AGT, AGTR1, angiotensin II type 1 receptor; BDKRB2, bradykinin B2 receptor; Cmax, maximum plasma concentration; AUC, area under the plasma concentration-time curve; AUC0-t, AUC from time 0 to the time of last measurement; AUC0-∞, AUC from time 0 extrapolated to infinity; Cl/F, apparent clearance of the fraction dose absorbed; Ke, elimination rate constant in the terminal drug phase; T1/2, half-life in the terminal drug phase.
Figure 2.
AGTR1 and BDKRB2 genotypes based on atorvastatin pharmacokinetics. (A) Mean values of AUC0-t and AUC0-∞ for the genotypes and genotype combinations of AGTR1-rs5186; (B) mean values of Cl/F for the genotypes and genotype combinations of AGTR1-rs5186; (C) mean values of AUC0-t and AUC0-∞ for the genotypes and genotype combinations of BDKRB2-rs1799722; (D) mean values of Cl/F for the genotypes and genotype combinations of BDKRB2-rs1799722. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error. *P<0.05 vs. C/C; #P<0.05 vs. A/C; §P<0.05 and §§P<0.01 vs. C/C+T/T. AGTR1, angiotensin II type 1 receptor; BDKRB2, bradykinin B2 receptor; AUC, area under the plasma concentration-time curve; AUC0-t, AUC from time 0 to the time of last measurement; AUC0-∞, AUC from time 0 extrapolated to infinity; Cl/F, apparent clearance of the fraction dose absorbed.
For BDKRB2-rs1799722, carriers of the heterozygous genotype (C/T) were identified to have significantly higher values of AUC0-t (P=0.021) and AUC0-∞ (P=0.023) and lower values of Cl/F (P=0.007) compared with those obtained for the combination of homozygous alleles (C/C+T/T; Table I and Fig. 2C and D).
The linear regression analysis under the over-dominant genetic model indicated that the AGTR1-rs5186 polymorphism significantly affected the values of T1/2 (adjusted R2=0.053, P=0.043); however, on comparison of the means by genotype, no significant differences were observed. Similarly, the BDKRB2-rs1799722 polymorphism significantly affected the Cl/F values (adjusted R2=0.093, P=0.01; data not shown).
Association between genotypes and metabolizer phenotypes
Of the two polymorphisms with an effect on ATV pharmacokinetics, BDKRB2-rs1799722 was associated with fast metabolism when considering genetic models; association analysis using the dominant model identified that the C/C genotype of BDKRB2-rs1799722 was associated with the fast metabolizer phenotype (OR, 0.47; 95% CI, 0.26–0.83), whereas the C/T+T/T combination was associated with the normal and slow phenotypes (OR, 1.98; 95% CI, 1.01–3.88; P=0.014). When using the over-dominant model, the C/C+T/T combination was associated with the fast metabolizer phenotype (OR, 0.68; 95% CI, 0.40–0.92) and C/T was associated with the normal and slow phenotypes (OR, 2.27; 95% CI, 0.92–5.60; P=0.036). However, following Bonferroni's correction, only the associations under the dominant model remained statistically significant (Pc=0.03; Table II).
Table II.
Association between genotypes and metabolizer phenotypes.
| Gene | Polymorphism | Model | OR (95% CI) | P-value | Pc-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDKRB2 | rs1799722 | Dominant (C/C vs. C/T+T/T) | C/C: Fast metabolizers | 0.014 | 0.03 |
| 0.47 (0.26–0.83) | |||||
| C/T+T/T: Normal/slow metabolizers | |||||
| 1.98 (1.01–3.88) | |||||
| BDKRB2 | rs1799722 | Over-dominant (C/C+T/T vs. C/T) | C/C+T/T: Fast metabolizers | 0.036 | 0.07 |
| 0.68 (0.40–0.92) | |||||
| C/T: Normal/slow metabolizers | |||||
| 2.27 (0.92–5.60) |
BDKRB2, bradykinin B2 receptor; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; Pc, Bonferroni-corrected P-values.
Discussion
The pharmacokinetic parameters of ATV, namely Cmax and AUC, may vary by >10-fold (7,33). Following analysis of pharmacokinetic discrepancies, three major metabolizer phenotypes of ATV have been identified in Chinese and Mexican populations (7,33). This variation has been associated with polymorphisms in genes encoding drug metabolizing enzymes and transporters (34). However, differences in allele frequencies and their effect on quantitative parameters including cholesterol levels, arterial pressure and pharmacokinetic parameters, and associations of genotypes with drug metabolism and response have been documented across various populations (7,33,35,36).
In the current study, the effect on ATV pharmacokinetics of three polymorphic variants in genes related to drug metabolism and response were evaluated. AGT-rs699 had no significant effect on pharmacokinetic parameters. However, to the best of our knowledge, the study is the first to identify an effect of AGTR1-rs5186 and BDKRB2-rs1799722 on ATV pharmacokinetics.
Heterozygous carriers of rs5186 (A/C) exhibited higher AUC0-t and AUC0-∞ values, while having lower Cl/F values, than homozygous carriers (C/C), which thus indicates a diminished clearance activity and longer permanence of ATV in heterozygous carriers. The effect of the AGTR1 polymorphism on T1/2 was consistent with this interpretation. This decreased clearance and longer exposure to ATV may lead to an improved response to drug therapy, or to an adverse effect. By contrast, carriers of homozygous genotypes (A/A or C/C) had increased clearance, and thus may have a poorer response to treatment. However, there was no association between the A/A or C/C genotypes with the fast metabolizer phenotype. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report on the influence of rs5186 on ATV pharmacokinetics, though the rs5186 polymorphism has previously been associated with lipid levels (37), and ATV, as a statin, has lipid-lowering effects (38). Consistent with the present results, the C/C genotype has been related to higher levels of triglycerides in a healthy Malayan population (37). Additionally, in a case-control study conducted in a Northern Indian population, the C/C genotype was associated with essential hypertension and higher gene expression of AGTR1 (39). Regarding the anti-inflammatory effect of statins, ATV may affect activation of the angiotensin pathway through AGTR1 by attenuating the activity of angiotensin II (ANG II), as observed in rats, whereby ATV modulated ANG II-induced expression of inflammatory and fibrogenic genes in the liver (40); however there is a lack of data regarding the association of AGTR1-rs5186 with the anti-inflammatory response.
Regarding BDKRB2-rs1799722, significant differences in the AUC0-t, AUC0-∞ and Cl/F parameters were identified between heterozygous carriers (C/T) and homozygous carriers (C/C or T/T). The current results suggest that the BDKRB2-rs1799722 polymorphism affects ATV clearance activity. This effect was demonstrated by linear regression and association analyses under over-dominant and dominant models. Notably, it was indicated that the C allele promotes fast metabolism, while accumulation of the T allele leads to a shift towards slower metabolism. However, the pharmacokinetic parameters of the T/T homozygous carriers did not differ significantly compared with heterozygous carriers. To the best of our knowledge, BDKRB2-rs1799722 has not previously been associated with statin metabolism. However, a meta-analysis identified that the C allele of rs1799722 increased the risk of hypertension in Asian and African-American populations (20). A pharmacogenetic study conducted in a Brazilian population revealed that carriers of the C allele responded to Enalapril, an antihypertensive drug that serves as an inhibitor of angiotensin-converting enzyme (21). The statins are also established for their antihypertensive effects in hypercholesterolemic patients (41). Nonetheless, there is a lack of studies into the effect of BDKRB2-rs1799722 on the metabolism or response of patients to statins.
Although a number of polymorphisms have been suggested as candidate responsible for the pharmacokinetic variability of ATV, the present study is the first to indicate the involvement of AGTR1-rs5186 and BDKRB2-rs1799722. The inclusion of these biomarkers in future studies may improve the prediction of the pharmacokinetic variability of ATV or decrease the number of variants required for prediction (7,11). While the current study demonstrated the contribution of genetic polymorphisms to ATV pharmacokinetics, there were a number of limitations. Firstly, there was a lack of data, such as cholesterol levels at one month post-treatment, for complete analysis of polymorphism effect on response. Secondly, in some cases the number of subjects per genotype was small, and thus associations may have been lost following correction. To validate the results, further studies should be performed in a larger population. In addition, the influence of other genes may explain the lack of association with the slow metabolizer phenotype.
In conclusion, a significant effect of AGTR1-rs5186 and BDKRB2-rs1799722 on ATV pharmacokinetics was detected. The present findings suggest that the A/C genotype of AGTR1-rs5186 is associated with slow ATV metabolism, while the C/C or A/A+C/C genotypes are associated with fast metabolism. Additionally, the C/T genotype of BDKRB2-rs1799722 may be associated with the slow metabolizer phenotype, while the homozygous genotypes may be associated with the fast metabolizer phenotype. These novel findings increase the panel of potential genetic biomarkers associated with ATV metabolism, and should be verified in future pharmacogenetic studies in larger populations with different genetic backgrounds.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the University of Monterrey, Italy, for funding the current study (grant no. UIN15009) and Dr Irene Meester from the University of Monterrey for reviewing and improving the manuscript.
References
- 1.Valdez Morales M, Medina Godoy S, Chacón López MA, Espinosa Alonso LG. Comprehensive approach of diet importance on health status of the Mexican population. Biotecnia. 2016;18:10. doi: 10.18633/bt.v18i1.247. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kuri-Morales PA. La transición en salud y su impacto en la demanda de servicios. Gac Med Mex. 2011;147:451–454. (In Spanish) [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.National Institute of Statistics and Geography (INEGI), corp-author http://www.beta.inegi.org.mx/contenidos/proyectos/registros/vitales/mortalidad/doc/presentacion.pdf. [Jun 15;2016 ];Mortality Statistics. INEGI, Mexico City. 2015 (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- 4.Escobedo-de la Peña J, de Jesús-Pérez R, Schargrodsky H, Champagne B. Prevalence of dyslipidemias in Mexico city and Its relation to other cardiovascular risk factors. Results from the CARMELA study. Gac Med Mex. 2014;150:128–136. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- 5.Canalizo-Miranda E, Favela-Pérez EA, Salas-Anaya JA, Gómez-Díaz R, Jara-Espino R, Del Pilar Torres-Arreola L, Viniegra-Osorio A. Clinical practice guideline. Diagnosis and treatment of dyslipidemia. Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc. 2013;51:700–709. (In Spanish) [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.McFarland AJ, Anoopkumar-Dukie S, Arora DS, Grant GD, McDermott CM, Perkins AV, Davey AK. Molecular mechanisms underlying the effects of statins in the central nervous system. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15:20607–20637. doi: 10.3390/ijms151120607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.León-Cachón RBR, Ascacio-Martínez JA, Gamino-Peña ME, Cerda-Flores RM, Meester I, Gallardo-Blanco HL, Gómez-Silva M, Piñeyro-Garza E, Barrera-Saldaña HA. A pharmacogenetic pilot study reveals MTHFR, DRD3, and MDR1 polymorphisms as biomarker candidates for slow atorvastatin metabolizers. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:74. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2062-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.León-Cachón RBR, Ascacio-Martínez JAI, Gómez-Silva M, Piñeyro-Garza E, González-González JG, Pogue G, Simón-Buela L, Barrera-Saldaña HA. Application of genomic technologies in clinical pharmacology research. Rev Inves Clin. 2015;67:212–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.US Food and Drug Administration, corp-author. Draft guidance on atorvastatin calcium and ezetimibe. US Department of Health and Human Services; Silver Spring, MD: 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 10.León-Cachón RB1, Ascacio-Martínez JA, Barrera-Saldaña HA. Individual response to drug therapy: Bases and study approaches. Rev Invest Clin. 2012;64:364–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cruz-Correa OF, León-Cachón RB, Barrera-Saldaña HA, Soberón X. Prediction of atorvastatin plasmatic concentrations in healthy volunteers using integrated pharmacogenetics sequencing. Pharmacogenomics. 2017;18:121–131. doi: 10.2217/pgs-2016-0072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ma Y, Chen Z, Zou Y, Ge J. Atorvastatin represses the angiotensin 2-induced oxidative stress and inflammatory response in dendritic cells via the PI3K/Akt/Nrf 2 pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014:148798. doi: 10.1155/2014/148798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ruaño G, Thompson PD, Windemuth A, Smith A, Kocherla M, Holford TR, Seip R, Wu AH. Physiogenomic analysis links serum creatine kinase activities during statin therapy to vascular smooth muscle homeostasis. Pharmacogenomics. 2005;6:865–872. doi: 10.2217/14622416.6.8.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Peters BJ, Klungel OH, de Boer A, Ch Stricker BH, Maitland-van der Zee AH. Pharmacogenetics of cardiovascular drug therapy. Clin Cases Miner Bone Metab. 2009;6:55–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Frazier L, Turner ST, Schwartz GL, Chapman AB, Boerwinkle E. Multilocus effects of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system genes on blood pressure response to a thiazide diuretic. Pharmacogenomics J. 2004;4:17–23. doi: 10.1038/sj.tpj.6500215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jiang X, Sheng HH, Lin G, Li J, Lu XZ, Cheng YL, Huang J, Xiao HS, Zhan YY. Effect of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system gene polymorphisms on blood pressure response to antihypertensive treatment. Chin Med J (Engl) 2007;120:782–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Bryant JW, Shariat-Madar Z. Human plasma kallikrein-kinin system: Physiological and biochemical parameters. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2009;7:234–250. doi: 10.2174/187152509789105444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bentley JP, Asselbergs FW, Coffey CS, Hebert PR, Moore JH, Hillege HL, van Gilst WH. Cardiovascular risk associated with interactions among polymorphisms in genes from the renin-angiotensin, bradykinin, and fibrinolytic systems. PLoS One. 2010;5:e12757. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pal GK, Adithan C, Umamaheswaran G, Pal P, Nanda N, Indumathy J, Syamsunder AN. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene polymorphisms are associated with cardiovascular risks in prehypertensives. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2016;10:865–872. doi: 10.1016/j.jash.2016.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Luo K, Kang W, Xu G. The risk of bradykinin B2 receptor-58T/C gene polymorphism on hypertension: A meta-analysis. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8:19917–19927. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Silva PS, Fontana V, Luizon MR, Lacchini R, Silva WA, Jr, Biagi C, Tanus-Santos JE. eNOS and BDKRB2 genotypes affect the antihypertensive responses to enalapril. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;69:167–177. doi: 10.1007/s00228-012-1326-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.World Medical Association, corp-author. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA. 2013;310:2191–2194. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.281053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.World Medical Association, corp-author. WMA Declaration of Tokyo - Guidelines for physicians concerning torture and other cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment in relation to detention and imprisonment; 29th WMA General Assembly; Tokyo, Japan. 1975. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Solorzano-Flores LI. Official Mexican Standard NOM-177-SSA1-1998, establishing tests and procedures to demonstrate that a drug is interchangeable. Requirements must be subject to third party authorized to perform the tests. Secretaria de Salud, Mexico. 1999 [Google Scholar]
- 25.Briggs GG, Freeman RK, Towers CV, Forinash AB. Drugs in Pregnancy and Lactation. 11th. Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA: 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sambrook J, Russell DW. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. 3rd. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; New York, NY: 2001. Preparation and analysis of eukaryotic genomic DNA. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ahmed T, Kollipara S, Gautam A, Gigras R, Kothari M, Saha N, Batra V, Paliwal J. Bioavailability and interaction potential of atorvastatin and losartan on co-administration in healthy human subjects. J Bioequiv Availab. 2009;1:18–27. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Stanisz B, Kania L. Validation of HPLC method for determination of atorvastatin in tablets and for monitoring stability in solid phase. Acta Pol Pharm. 2006;63:471–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rowland M, Tozer TN. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics: Concepts and Applications. 4th. Williams & Willkins; Philadelphia, PA: 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ward JH., Jr Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. J Am Stat Assoc. 1963;58:236–244. doi: 10.1080/01621459.1963.10500845. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Reed TE, Schull WJ. A general maximum likelihood estimation program. Am J Hum Genet. 1968;20:579–580. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Horita N, Kaneko T. Genetic model selection for a case-control study and a meta-analysis. Meta Gene. 2015;5:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.mgene.2015.04.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Huang Q, Aa J, Jia H, Xin X, Tao C, Liu L, Zou B, Song Q, Shi J, Cao B, et al. A Pharmacometabonomic approach to predicting metabolic phenotypes and pharmacokinetic parameters of atorvastatin in healthy volunteers. J Proteome Res. 2015;14:3970–3981. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b00440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Niemi M. Transporter pharmacogenetics and statin toxicity. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2010;87:130–133. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2009.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kadam P, Ashavaid TF, Ponde CK, Rajani RM. Genetic determinants of lipid-lowering response to atorvastatin therapy in an Indian population. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2016;41:329–333. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.12369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Prado Y, Zambrano T, Salazar LA. Transporter genes ABCG2 rs2231142 and ABCB1 rs1128503 polymorphisms and atorvastatin response in Chilean subjects. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2017 Aug 19; doi: 10.1111/jcpt.12607. (Epub ahead of print) [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Yap RWK, Shidoji Y, Yap WS, Masaki M. Association and interaction effect of AGTR1 and AGTR2 gene polymorphisms with dietary pattern on metabolic risk factors of cardiovascular disease in Malaysian adults. Nutrients. 2017;9:E853. doi: 10.3390/nu9080853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Isley WL, Miles JM, Patterson BW, Harris WS. The effect of high-dose simvastatin on triglyceride-rich lipoprotein metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Lipid Res. 2006;47:193–200. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M500387-JLR200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Chandra S, Narang R, Sreenivas V, Bhatia J, Saluja D, Srivastava K. Association of angiotensin II type 1 receptor (A1166C) gene polymorphism and its increased expression in essential hypertension: A case-control study. PLoS One. 2014;9:e101502. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0101502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Moreno M, Ramalho LN, Sancho-Bru P, Ruiz-Ortega M, Ramalho F, Abraldes JG, Colmenero J, Dominguez M, Egido J, Arroyo V, et al. Atorvastatin attenuates angiotensin II-induced inflammatory actions in the liver. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009;296:G147–G156. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00462.2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Morgado M, Rolo S, Macedo AF, Castelo-Branco M. Association of statin therapy with blood pressure control in hypertensive hypercholesterolemic outpatients in clinical practice. J Cardiovasc Dis Res. 2011;2:44–49. doi: 10.4103/0975-3583.78596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]