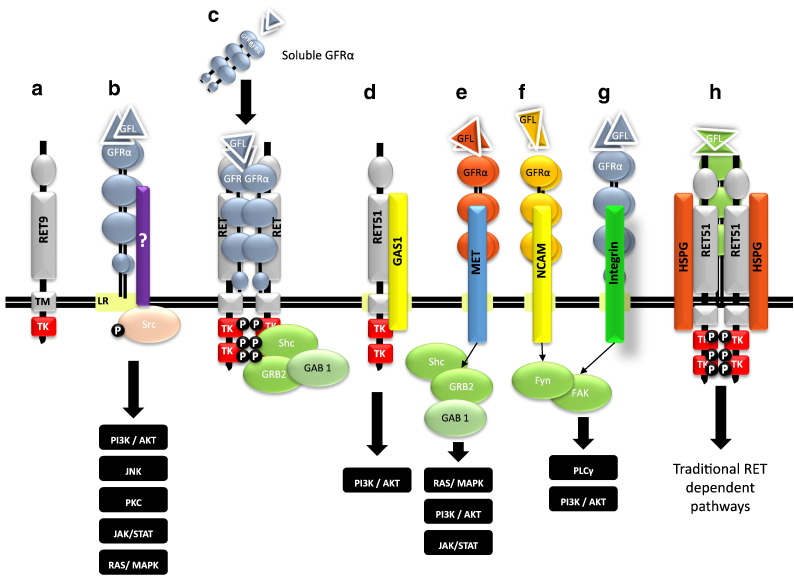
Figure 2.
Alternative signaling pathways of GFLs. In addition to the traditional GFL:GFRα:RET51 pathway, several other novel pathways have been discovered to modulate GFL signaling [from left to right]. (a) Alternative RET isoforms, e.g., RET9 (ret proto-oncogene isoforms c); (b) activated Src (v-src sarcoma viral oncogene homolog) signaling associated with lipid rafts (LR) by means of yet an unknown transmembrane protein; (c) soluble GFRα responsible for RET activation outside lipid rafts; (d) GAS1 (growth arrest-specific 1), a recent GFRα alternative receptor; (e) MET (met proto-oncogene); (f) NCAM (neural cell adhesion molecule); (g) integrins; and (h) HSPGs (heparan sulfate proteoglycans) are essential for RET activity.
TM, transmembrane domain; TK, tyrosine kinase domain; Fyn, p59fyn kinase; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; GAB1, GRB2 associated binding protein 1;GRB2, growth receptor binding protein 2; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase; AKT, protein kinase B; JAK, Janus kinase; STAT, signal transducer and activator of transcription; SHC, Src homology 2 domain containing.