Abstract
The data presented in this article provide supporting information to the related research article “Comparison of ten different DNA extraction procedures with respect to their suitability for environmental samples” (Kuhn et al., 2017) [1]. In that article, we compared the suitability of ten selected DNA extraction methods based on DNA quality, purity, quantity and applicability to universal PCR. Here we provide the data on the specific DNA gel sample load, all unreported gel images of crude DNA and PCR results, and the complete cost analysis for all tested extraction procedures and in addition two commercial DNA extraction kits for soil and water.
Keywords: Cost analysis, DNA sample load, Gel electrophoresis
Specifications Table
| Subject area | Biology |
| More specific subject area | Molecular Biology |
| Type of data | Tables, figures, equations |
| How data was acquired | Bio View Biostep transilluminator |
| Data format | Raw and analyzed |
| Experimental factors | Sample were preserved at −20 °C before DNA extraction |
| Experimental features | DNA extraction, universal PCR, DNA visualization, cost analysis |
| Data source location | Cottbus, Germany |
| Data accessibility | Data is within this article |
Value of the data
-
•
The data on the gel sample load are valuable to serve as indirect control for DNA quantification with fluorescence stain called PicoGreen.
-
•
This data provide additional gel images of crude DNA and PCR of the tested DNA extraction procedures.
-
•
The cost analysis of the DNA extraction procedures provided are valuable for further economical comparison.
1. Data
Table 1 presents the DNA sample load (in µL) necessary to visualize the crude DNA on the agarose gels. Different DNA loads were used in order to achieve comparable DNA concentrations ranging between 250 and 300 ng on the gel. Higher DNA loads were necessary for visualization on the agarose gels, especially for the crude DNA extracts from the Havel River sediment (procedure A, D, F, G, and H).
Table 1.
Sample load in µL on the agarose gel for visualization of crude DNA extracts.
| Extraction protocol according to first author | Origin of samples |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activated sludge | Havel River sediment | Anaerobic digestion sludge | Nitrifying sludge | ||
| A | Bourrain | 4 | 15 | 5 | 8 |
| B | Gabor harsh | 2 | 8 | 5 | 8 |
| C | Garbor soft | 2 | 8 | 5 | 15 |
| D | Shan | 4 | 12 | 10 | 20 |
| E | Orsini/Spica | 4 | 8 | 6 | 15 |
| F | Singka | 4 | 12 | 15 | 15 |
| G | Soya method | 1 | 20 | 3 | 15 |
| H | Tabatabaei | 2 | 10 | 12 | 8 |
| I | Tresse | 1 | 6 | 6 | 10 |
| J | Wilson | 2 | 4 | 12 | 8 |
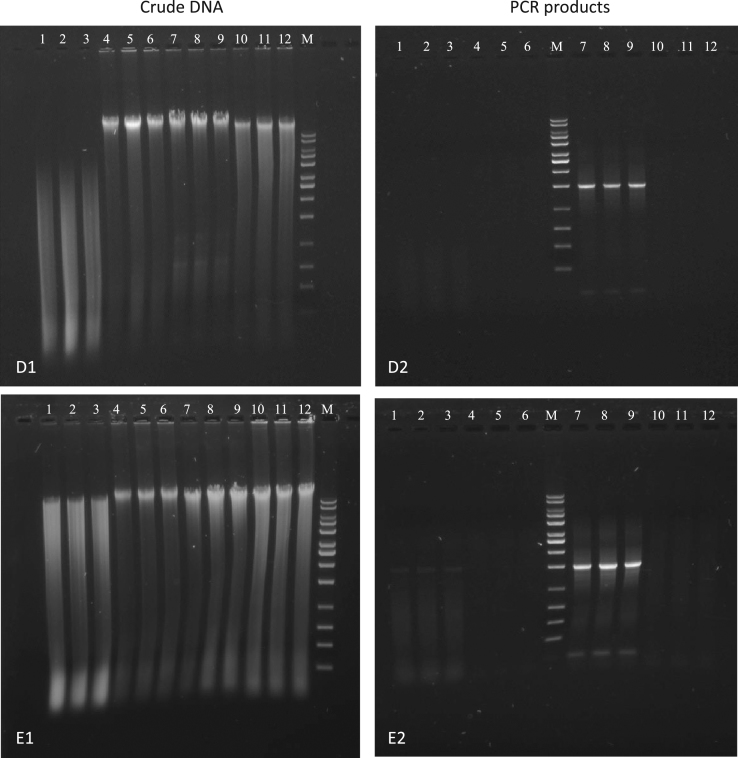
The visual DNA quality control of crude DNA extracts and PCR of procedures B, C, D, E, H, I and J is presented in Fig. 1, Fig. 2, Fig. 3, Fig. 4. The results for crude DNA extracts and PCR amplification of procedure B and C (method according to [2]) were almost similar. In both cases, intensive fragmentation was found for crude DNA extracts of the activated sludge and no distinct genomic DNA band was visible (Fig. 1, D1 & E1). The crude DNA of the sediment and anaerobic digestion sludge indicated a good quality with lower content of impurities, while the quality of the crude DNA for the nitrifying sludge was lower. A higher content of impurities was visible on both gel images. Positive PCR amplification was only feasible for the anaerobic digestion sludge and showed a very good quality of the amplicon (Fig. 1, D2 & E2).
Fig. 1.
Agarose gel electrophoresis of crude DNA (D1 & E1) and universal PCR (D2 & E2) using universal primer set 27f and 1525r. D1 & D2: Procedure B (Gabor harsh). E1 & E2: Procedure C (Gabor soft). Lane declaration for all crude DNA and universal PCR gel images: lane 1 to 3 activated sludge; lane 4 to 6 Havel River sediment; lane 7 to 9 anaerobic digestion sludge; lane 10 to 12 nitrifying sludge; M in all gel images: 10 kb MassRuler DNA ladder.
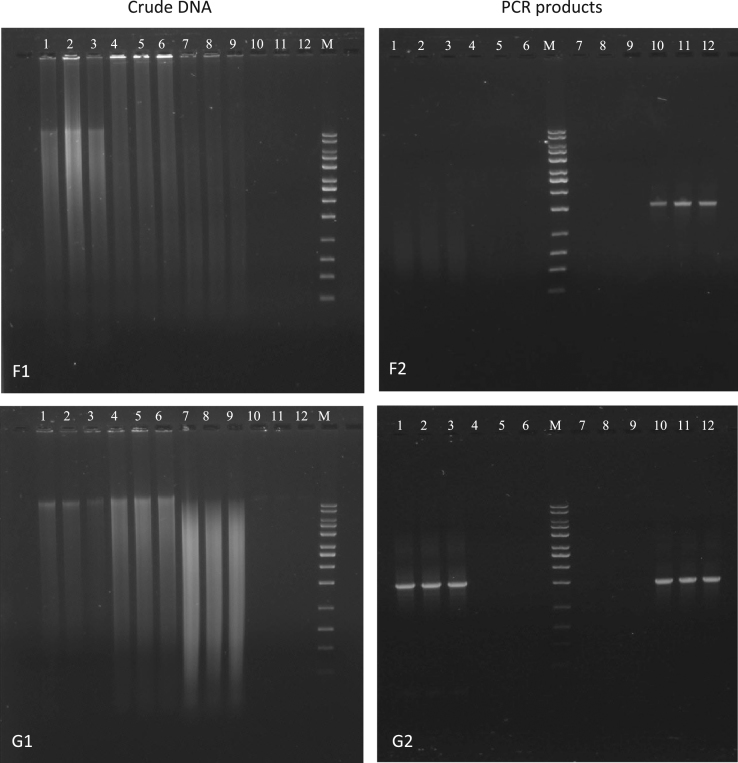
Fig. 2.
Agarose gel electrophoresis of crude DNA (F1 & G1) and universal PCR (F2 & G2) using universal primer set 27f and 1525r. F1 & F2: Procedure D (Shan). G1 & G2: Procedure E (Orsini & Romano-Spica). Lane declaration for all crude DNA and universal PCR gel images: lane 1 to 3 activated sludge; lane 4 to 6 Havel River sediment; lane 7 to 9 anaerobic digestion sludge; lane 10 to 12 nitrifying sludge; M in all gel images: 10 kb MassRuler DNA ladder.
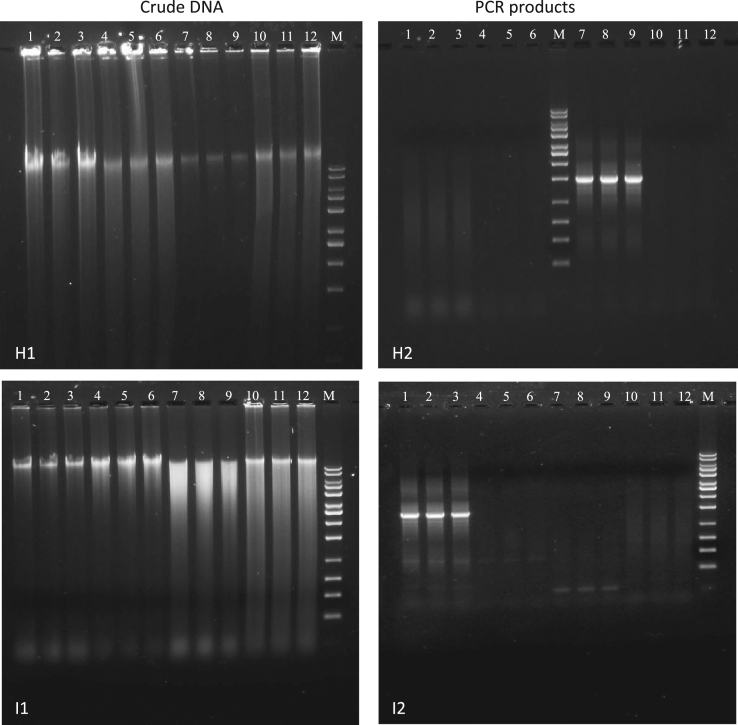
Fig. 3.
Agarose gel electrophoresis of crude DNA (H1, I1) and universal PCR (H2, I2) using universal primer set 27f and 1525r. H1 & H2: Procedure H (Tabatabaei). I1 & I2: Procedure I (Tresse). Lane declaration for all crude DNA and universal PCR gel images: lane 1 to 3 activated sludge; lane 4 to 6 Havel River sediment; lane 7 to 9 anaerobic digestion sludge; lane 10 to 12 nitrifying sludge; M in all gel images: 10 kb MassRuler DNA ladder.
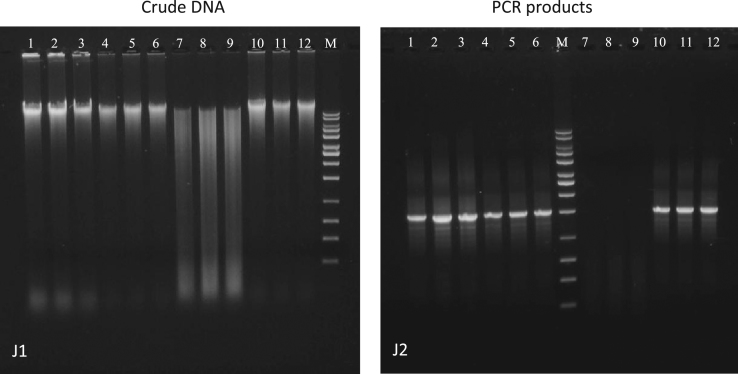
Fig. 4.
Agarose gel electrophoresis of crude DNA (J1) and universal PCR (J2) using universal primer set 27f and 1525r. G1 & G2: Procedure J (Wilson). Lane declaration for all crude DNA and universal PCR gel images: lane 1 to 3 activated sludge; lane 4 to 6 Havel River sediment; lane 7 to 9 anaerobic digestion sludge; lane 10 to 12 nitrifying sludge; M in all gel images: 10 kb MassRuler DNA ladder.
The results for the crude DNA extracts of procedure D and E (method according to [3], [4]) were also almost similar (Fig. 2, F1 & G1). For procedure D, no distinct genomic DNA band was visible on the agarose gel but instead, fragmentation and higher content of undefined impurities (Fig. 2, F1). The pattern for the nitrifying sludge, especially, indicated complete failure of the extraction procedure. The gel image of the crude DNA extraction for procedure E occurred almost similar to procedure D with one exception. The crude DNA extract of the activated sludge showed a slight distinct genomic DNA band, however, the background staining indicated the presence of impurities (Fig. 2, G1). Nevertheless, positive PCR amplification was obtained for the crude DNA extract from activated sludge for procedure E (Fig. 2, G2). Surprisingly, positive amplification of the nitrifying sludge was also obtained for both procedure D and E (Fig. 2, F2).
The results of the crude DNA extracts of procedure H and I (method according to [5], [6]) are presented in Fig. 3. All crude DNA extracts of procedure H indicate a slight distinct genomic DNA band and higher content of impurities through background staining (Fig. 3, H1). Positive PCR amplification was only obtained for the crude DNA extract of the anaerobic digestion sludge. PCR amplification of the crude DNA extracts of the activated sludge, Havel River sediment and nitrifying sludge failed (Fig. 3, H2). The quality of crude DNA extracts of procedure I was different between the four environmental samples (Fig. 3, I1). A distinct genomic DNA band without higher content of visible impurities was obtained for the activated sludge. The degree of increased impurities occurred slightly for the crude DNA extracts of the Havel River sediment, but a distinct genomic DNA band was still good visible on the gel image. The crude DNA extract of the anaerobic digestion sludge showed higher content of DNA fragmentation as well as possible impurities in the background of the gel. Besides a distinct DNA band higher background smearing was also visible for the crude DNA extract of the nitrifying sludge. Positive PCR amplification was only obtained for the crude DNA extract of the activated sludge (Fig. 3, I2).
The results of the crude DNA extracts of procedure J are presented in Fig. 4 (method according to [7]). The gel image indicated distinct genomic DNA bands with lower content of background smearing for the activated sludge, Havel River sediment and the nitrifying sludge. A higher degree of possible DNA fragmentation and/or background impurities were observed for the crude DNA extract of the anaerobic digestion sludge (Fig. 4, J1). Positive PCR amplification was obtained from the activated sludge, Havel River sediment and the nitrifying sludge, while the amplification for the anaerobic digestion sludge failed (Fig. 4, J2).
The cost analysis of the ten DNA extraction procedures and the two commercial DNA extraction kits is presented in detail in Table 2, Table 3, Table 4, Table 5, Table 6, Table 7, Table 8, Table 9, Table 10, Table 11, Table 12, Table 13. Our cost analysis is based on cost estimation. Therefore a cost range between lowest and highest prices is presented. We assumed that the real extraction price will be in this cost range. The presented results show that every extraction procedure has its specific cost range, which is mainly dependent on the extraction time and therefore also on the cost of the laboratory staff. We calculated the lowest laboratory staff cost ranging between 3.65 € and 5.10 € for procedure J (Table 11), and the highest ranging between 8.68 and 12.15 for procedure A (Table 2). We calculated the lowest cost for the chemicals needed ranging between 0.13 € to 0.31 € for procedure D (Table 5) and the highest cost ranging between 0.47 € to 0.96 € for procedure I (Table 10). The cost for the other consumables such as gloves, tubes and tips were almost similar for all analyzed extraction procedures and extraction kits.
Table 2.
Cost analysis for DNA extraction procedure A (according to Bourrain et al., 1999).
| Consumables | Volumes | Units | Concentration | Volumes | /Weight |
High costs |
Low costs |
Low cost | High cost | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount | Unit | Fix cost (€) | Amount | Unit | Fix cost (€) | per prep (€) | per prep (€) | ||||||
| Gloves (any size) | 1 | pair | – | – | – | 50 | pair | 8.20 | 50 | pair | 4.50 | 0.090 | 0.1640 |
| Tubes | 5 | – | – | 2.0 | mL | 500 | pieces | 11.9 | 1000 | pieces | 21.90 | 0.1095 | 0.1190 |
| Tips | 12 | – | – | 1000 | µL | 500 | pieces | 5.08 | 1000 | pieces | 7.70 | 0.0924 | 0.1218 |
| Tips | 1 | – | – | 200 | µL | 500 | pieces | 5.40 | 1000 | pieces | 8.19 | 0.0082 | 0.0108 |
| Lysozyme buffer | 0.75 | mL | 0.15 M NaCl | 6,6 | mg | 500 | g | 15.84 | 1000 | g | 24.19 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 |
| 0.1 M Na2EDTA | 27.9 | mg | 100 | g | 23.50 | 1000 | g | 59.70 | 0.0017 | 0.0066 | |||
| 15 mg mL-1 Lysozyme | 15.0 | mg | 1.0 | g | 23.89 | 10 | g | 96.04 | 0.1441 | 0.3584 | |||
| SDS solution | 0.75 | mL | 0.1 M NaCl | 4.4 | mg | 500 | g | 15.84 | 1000 | g | 24.19 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 |
| 0.5 M Tris–HCl | 45.4 | mg | 500 | g | 93.40 | 1000 | g | 128.00 | 0.0058 | 0.0085 | |||
| w/v 10% SDS | 0.075 | mg | 100 | g | 16.56 | 1000 | g | 56.48 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | |||
| Tris–HCl saturated phenol | 1.0 | mL | 0.1 M Tris–HCl | 12.1 | mg | 500 | g | 93.40 | 1000 | g | 128.00 | 0.0016 | 0.0023 |
| Phenol | 1.0 | g | 100 | g | 18.00 | 1000 | g | 64.40 | 0.0644 | 0.1800 | |||
| Phenol:Chloroform:Isoamyl | 1.0 | mL | 25′ Phenol | 0.5 | g | 100 | g | 18.00 | 1000 | g | 64.40 | 0.0322 | 0.0900 |
| (25:24:1 v/v) | 24′ Chloroform | 0.48 | mL | 500 | mL | 50.62 | 2500 | mL | 100.66 | 0.0193 | 0.0486 | ||
| 1′ Isoamyl | 0.02 | mL | 25 | mL | 13.92 | 1000 | mL | 108.00 | 0.0022 | 0.0111 | |||
| Chloroform:Isoamyl | 1.0 | mL | 24′ Chloroform | 0.96 | mL | 500 | mL | 50.62 | 2500 | mL | 100.66 | 0.0387 | 0.0972 |
| (24:1 v/v) | 1′ Isoamyl | 0.04 | mL | 25 | mL | 13.92 | 1000 | mL | 108.00 | 0.0043 | 2.2E-05 | ||
| Isopropanol | 1.0 | mL | 100% | 2.0 | mL | 1000 | mL | 30.30 | 2500 | mL | 61.70 | 0.0494 | 6.1E-02 |
| TE buffer | 0.1 | mL | 10 mM Tris–HCl | 0.12 | mg | 500 | g | 93.40 | 1000 | g | 128.00 | 1.6E-05 | 2.3E-05 |
| 1 mM EDTA | 0.03 | mg | 100 | g | 34.08 | 1000 | g | 245.23 | 7.2E-06 | 1.0E-05 | |||
| RNaseA treatment | 5.0 | µL | 0.2 µg µL-1 | 1.0 | µg | 250 | mg | 94.40 | 1000 | mg | 292.00 | 0.0003 | 3.8E-04 |
| Extracted samples | 12 | – | – | – | – | – | – | ||||||
| Extraction time | 250 | min | – | – | – | – | – | – | |||||
| Lab staff (per hour) | – | 35.00 | – | 25.00 | – | – | |||||||
| Lab staff (€/extraction) | 8.68 | 12.15 | |||||||||||
| Chemicals (€/extraction) | 0.36 | 0.86 | |||||||||||
| Gloves, tubes, tips (€/extraction) | 0.30 | 0.42 | |||||||||||
| Final price per extraction including extraction time, lab staff and all consumables (€) | 9.34 | 13.43 | |||||||||||
Table 3.
Cost analysis for DNA extraction procedure B (according to Gabor et al. [2]; harsh method).
| Consumables | Volumes | Units | Concentration | Volumes | /Weight |
High costs |
Low costs |
Low cost | High cost | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount | Unit | Fix cost (€) | Amount | Unit | Fix cost (€) | per Prep (€) | per Prep (€) | ||||||
| Gloves (any size) | 1 | pair | – | – | – | 50 | pair | 8.20 | 50 | pair | 4.50 | 0.0900 | 0.1640 |
| Tubes | 3 | – | – | 2.0 | mL | 500 | pieces | 11.90 | 1000 | pieces | 21.90 | 0.0657 | 0.0714 |
| Tips | 10 | 1000 | µL | 500 | pieces | 5.08 | 1000 | pieces | 7.70 | 0.0770 | 0.1015 | ||
| Tips | 4 | 200 | µL | 500 | pieces | 5.40 | 1000 | pieces | 8.19 | 0.0328 | 0.0432 | ||
| Tips | 1 | 10 | µL | 1000 | pieces | 27.14 | 2000 | pieces | 43.42 | 0.0217 | 0.0271 | ||
| Silica beads | 0.1 | mm | – | 700 | mg | 1000 | g | 24.30 | 25000 | g | 202.00 | 0.0057 | 0.0170 |
| Lysozyme buffer | 1.25 | mL | 100 mM Tris | 15.1 | mg | 500 | g | 93.40 | 1000 | g | 128.00 | 0.0019 | 0.0028 |
| mL | 100 mM sodium EDTA | 46.5 | mg | 100 | g | 23.50 | 1000 | g | 59.70 | 0.0028 | 0.0109 | ||
| 100 M NaCl | 109.6 | mg | 500 | g | 15.84 | 1000 | g | 24.19 | 0.0027 | 0.0035 | |||
| 1% w/v CTAB | 12.5 | µg | 100 | g | 22.64 | 1000 | g | 89.11 | 0.0011 | 0.0028 | |||
| Lysozyme | 0.04 | mL | 50 mg mL−1 | 2.0 | mg | 1.0 | g | 23.89 | 10 | g | 96.04 | 0.0192 | 0.0478 |
| Proteinase K | 0.01 | mL | 10 mg mL−1 | 0.1 | mg | 0.1 | g | 67.68 | 0.5 | g | 259.62 | 0.0519 | 0.0677 |
| SDS | 0.2 | mL | w/v 20% | 0.04 | mg | 100 | g | 16.56 | 1000 | g | 56.48 | 2.3E-06 | 6.6E-06 |
| Chloroform (1:1 v/v) | 1.0 | mL | 100% | 1.0 | mL | 500 | mL | 50.62 | 2500 | mL | 100.66 | 0.0403 | 0.1012 |
| Isopropanol (0.6:1 v/v) | 0.6 | mL | 100% | 0.6 | mL | 1000 | mL | 30.30 | 2500 | mL | 61.70 | 0.0148 | 0.0182 |
| Ethanol | 0.5 | mL | 70% | 0.375 | mL | 250 | mL | 47.56 | 2500 | mL | 246.58 | 0.0345 | 0.0666 |
| TE buffer | 0.1 | mL | 10 mM Tris–HCl | 0.12 | mg | 500 | g | 93.40 | 1000 | g | 128.00 | 1.6E-05 | 2.3E-05 |
| 1 mM EDTA | 0.03 | mg | 100 | g | 34.08 | 1000 | g | 245.23 | 7.2E-06 | 1.0E-05 | |||
| Extracted samples | 12 | – | – | – | – | – | – | ||||||
| Extraction time | 235 | min | – | – | – | – | – | – | |||||
| Lab staff (per hour) | – | 35.00 | – | 25.00 | – | – | |||||||
| Lab staff (€/extraction) | 8.16 | 11.42 | |||||||||||
| Chemicals (€/extraction) | 0.17 | 0.34 | |||||||||||
| Gloves, tubes, tips (€/extraction) | 0.29 | 0.41 | |||||||||||
| Final price per extraction including extraction time, lab staff and all consumables (€) | 8.62 | 12.17 | |||||||||||
Table 4.
Cost analysis for DNA extraction procedure C (according to Gabor et al. [2]; soft method).
| Consumables | Volumes | Units | Concentration | Volumes | /Weight |
High costs |
Low costs |
Low cost | High Cost | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount | Unit | Fix cost (€) | Amount | Unit | Fix cost (€) | per Prep (€) | per Prep (€) | ||||||
| Gloves (any size) | 1 | pair | – | – | – | 50 | pair | 8.20 | 50 | pair | 4.50 | 0.090 | 0.164 |
| Tubes | 3 | – | – | 2.0 | mL | 500 | pieces | 11.90 | 1000 | pieces | 21.90 | 0.066 | 0.071 |
| Tips | 10 | 1000 | µL | 500 | pieces | 5.08 | 1000 | pieces | 7.70 | 0.077 | 0.102 | ||
| Tips | 4 | 200 | µL | 500 | pieces | 5.40 | 1000 | pieces | 8.19 | 0.033 | 0.043 | ||
| Tips | 1 | 10 | µL | 1000 | pieces | 27.14 | 2000 | pieces | 43.42 | 0.022 | 0.027 | ||
| Silica beads | 0.1 | mm | ID | 700 | mg | 1000 | g | 24.30 | 25000 | g | 202.00 | 0.0057 | 0.0170 |
| Lysozyme buffer | 1.25 | mL | 100 mM Tris | 15.1 | mg | 500 | g | 93.40 | 1000 | g | 128.00 | 0.0019 | 0.0028 |
| mL | 100 mM sodium EDTA | 46.5 | mg | 100 | g | 23.50 | 1000 | g | 59.70 | 0.0028 | 0.0109 | ||
| 100 M NaCl | 109.6 | mg | 500 | g | 15.84 | 1000 | g | 24.19 | 0.0027 | 0.0035 | |||
| 1% w/v CTAB | 12.5 | µg | 100 | g | 22.64 | 1000 | g | 89.11 | 0.0011 | 0.0028 | |||
| Lysozyme | 0.04 | mL | 50 mg mL-1 | 2.0 | mg | 1.0 | g | 23.89 | 10 | g | 96.04 | 0.0192 | 0.0478 |
| Proteinase K | 0.01 | mL | 10 mg mL-1 | 0.1 | mg | 0.1 | g | 67.68 | 0.5 | g | 259.62 | 0.0519 | 0.0677 |
| SDS | 0.2 | mL | w/v 20% | 0.04 | mg | 100 | g | 16.56 | 1000 | g | 56.48 | 2.3E-06 | 6.6E-06 |
| Chloroform (1:1 v/v) | 1.0 | mL | 100% | 1.0 | mL | 500 | mL | 50.62 | 2500 | mL | 100.66 | 0.0403 | 0.1012 |
| Isopropanol (0.6:1 v/v) | 0.6 | mL | 100% | 0.6 | mL | 1000 | mL | 30.30 | 2500 | mL | 61.70 | 0.0148 | 0.0182 |
| Ethanol | 0.5 | mL | 70% | 0.375 | mL | 250 | mL | 47.56 | 2500 | mL | 246.58 | 0.0345 | 0.0666 |
| TE buffer | 0.1 | mL | 10 mM Tris–HCl | 0.12 | mg | 500 | g | 93.40 | 1000 | g | 128.00 | 1.6E-05 | 2.3E-05 |
| 1 mM EDTA | 0.03 | mg | 100 | g | 34.08 | 1000 | g | 245.23 | 7.2E-06 | 1.0E-05 | |||
| Extracted samples | 12 | – | – | – | – | – | – | ||||||
| Extraction time | 230 | min | – | – | – | – | – | – | |||||
| Lab staff (per hour) | – | 35.00 | – | 25.00 | – | – | |||||||
| Lab staff (€/extraction) | 7.99 | 11.18 | |||||||||||
| Chemicals (€/extraction) | 0.17 | 0.34 | |||||||||||
| Gloves, tubes, tips (€/extraction) | 0.29 | 0.41 | |||||||||||
| Final price per extraction including extraction time, lab staff and all consumables (€) | 8.45 | 11.93 | |||||||||||
Table 5.
Cost analysis for DNA extraction procedure D (according to Shan et al. [3]).
| Consumables | Volumes | Units | Concentration | Volumes | /Weight |
High costs |
Low costs |
Low cost | High cost | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount | Unit | Fix cost (€) | Amount | Unit | Fix cost (€) | per Prep (€) | per Prep (€) | ||||||
| Gloves (any size) | 1 | pair | – | – | – | 50 | pair | 8.20 | 50 | pair | 4.50 | 0.0900 | 0.1640 |
| Tubes | 3 | – | – | 2.0 | mL | 500 | pieces | 11.90 | 1000 | pieces | 21.90 | 0.0657 | 0.0714 |
| Tips | 8 | 1000 | µL | 500 | pieces | 5.08 | 1000 | pieces | 7.70 | 0.0616 | 0.0812 | ||
| Tips | 2 | 200 | µL | 500 | pieces | 5.40 | 1000 | pieces | 8.19 | 0.0164 | 0.0216 | ||
| Tips | 1 | 10 | µL | 1000 | pieces | 27.14 | 2000 | pieces | 43.42 | 0.0217 | 0.0271 | ||
| TENP Puffer | 0.4 | mL | 50 mM Tris | 2.42 | mg | 500 | g | 93.40 | 1000 | g | 128.00 | 0.0003 | 0.0005 |
| 20 mM EDTA | 2.34 | mg | 100 | g | 34.08 | 1000 | g | 245.23 | 0.0006 | 0.0008 | |||
| 100 mM NaCl | 2.34 | mg | 500 | g | 15.84 | 1000 | g | 24.19 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | |||
| 10 mg mL-1 PVP | 4.00 | mg | 100 | g | 45.30 | 1000 | g | 224.00 | 0.0009 | 0.0018 | |||
| SDS | 50 | µL | w/v 20% | 10.0 | µg | 10]0 | g | 16.56 | 1000 | g | 56.48 | 5.6E-07 | 1.7E-06 |
| CTAB Puffer | 0.5 | mL | 0,7 M NaCl | 20.5 | mg | 500 | g | 15.84 | 1000 | g | 24.19 | 0.0005 | 0.0006 |
| 10% CTAB | 50.0 | µg | 100 | g | 22.64 | 1000 | g | 89.11 | 4.5E-06 | 1.1E-05 | |||
| KH2PO4 | 0.25 | mL | 240 mM | 8.16 | mg | 250 | g | 19.66 | 1000 | g | 56.66 | 4.6E-07 | 0.0006 |
| Phenol:Chloroform:Isoamyl | 1.0 | mL | 100 mM Tris | 12.1 | mg | 500 | g | 93.40 | 1000 | g | 128.00 | 0.0016 | 0.0023 |
| (25:24:1 v/v) | Phenol | 0.50 | g | 100 | g | 18.00 | 1000 | g | 64.40 | 0.0322 | 0.0900 | ||
| Chloroform | 0.48 | mL | 500 | mL | 50.62 | 2500 | mL | 100.66 | 0.0193 | 0.0486 | |||
| Isoamyl | 0.02 | mL | 25 | mL | 13.92 | 1000 | mL | 108.00 | 0.0022 | 0.0111 | |||
| Chloroform:Isoamyl | 1.0 | mL | Chloroform | 0.96 | mL | 500 | mL | 50.62 | 2500 | mL | 100.66 | 0.0387 | 0.0972 |
| (24:1 v/v) | Isoamyl | 0.04 | mL | 25 | mL | 13.92 | 1000 | mL | 108.00 | 0.0043 | 0.0223 | ||
| Isopropanol | 1.0 | mL | 100% | 1.0 | mL | 1000 | mL | 30.30 | 2500 | mL | 61.70 | 0.0247 | 0.0303 |
| TE buffer | 0.1 | mL | 10 mM Tris–HCl | 0.12 | mg | 500 | g | 93.40 | 1000 | g | 128.00 | 1,6E-05 | 2.3E-05 |
| 1.0 mM EDTA | 0.03 | mg | 100 | g | 34.08 | 1000 | g | 245.23 | 7.2E-06 | 1.0E-05 | |||
| Extracted samples | 12 | – | – | – | – | – | |||||||
| Extraction time | 210 | min | – | – | – | – | – | – | |||||
| Lab staff (per hour) | – | 35.00 | – | 25.00 | – | – | |||||||
| Lab staff (€/extraction) | 7.29 | 10.21 | |||||||||||
| Chemicals (€/extraction) | 0.13 | 0.31 | |||||||||||
| Gloves, tubes, tips (€/extraction) | 0.26 | 0.37 | |||||||||||
| Final price per extraction including extraction time, lab staff and all consumables (€) | 7.67 | 10.88 | |||||||||||
Table 6.
Cost analysis for DNA extraction procedure E (according to Orsini and Romano-Spica [4]).
| Consumables | Volumes | Units | Concentration | Volumes | /Weight |
High costs |
Low costs |
Low cost | High cost | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount | Unit | Fix cost (€) | Amount | Unit | Fix cost (€) | per Prep (€) | per Prep (€) | ||||||
| Gloves (any size) | 1 | pair | – | – | – | 50 | pair | 8.20 | 50 | pair | 4.50 | 0.0900 | 0.1640 |
| Tubes | 2 | – | – | 2.0 | mL | 500 | pieces | 11.90 | 1000 | pieces | 21.90 | 0.0438 | 0.0476 |
| Tips | 9 | – | 1000 | µL | 500 | pieces | 5.08 | 1000 | pieces | 7.70 | 0.0693 | 0.0914 | |
| Tips | 3 | – | 200 | µL | 500 | pieces | 5.40 | 1000 | pieces | 8.19 | 0.0246 | 0.0324 | |
| Tips | 0 | – | 10 | µL | 1000 | pieces | 27.14 | 2000 | pieces | 43.42 | 0,0000 | 0.0000 | |
| Wash solution | 1.0 | mL | 50 mM Tris–HCl | 6.1 | mg | 500 | g | 93.40 | 1000 | g | 128.00 | 0.0008 | 0.0011 |
| 25 mM EDTA | 7.3 | mg | 100 | g | 34.08 | 1000 | g | 245.23 | 0.0018 | 0.0025 | |||
| 0.1% w/v SDS | 1.0 | µg | 100 | g | 16.56 | 1000 | g | 56.48 | 5.6E-08 | 1.7E-07 | |||
| 0.1% w/v PVP | 1.0 | µg | 100 | g | 45.30 | 1000 | g | 224.00 | 2.2E-07 | 4.5E-07 | |||
| Lysis buffer | 0.1 | mL | 50 mM Tris–HCl | 0.61 | mg | 500 | g | 93.40 | 1000 | g | 128.00 | 7.8E-05 | 1.1E-04 |
| 25 mM EDTA | 0.73 | mg | 100 | g | 34.08 | 1000 | g | 245.23 | 1.8E-04 | 2.5E-04 | |||
| 3% w/v SDS | 30.0 | µg | 100 | g | 16.56 | 1000 | g | 56.48 | 1.7E-06 | 5.0E-06 | |||
| 1.2% w/v PVP | 12.0 | µg | 100 | g | 45.30 | 1000 | g | 224.00 | 2.7E-06 | 5.4E-06 | |||
| Extraction buffer | 0.8 | mL | 10 mM Tris–HCl | 9.7 | mg | 500 | g | 93.40 | 1000 | g | 128.00 | 0.0012 | 0.0018 |
| 1 mM EDTA | 0.23 | mg | 100 | g | 34.08 | 1000 | g | 245.23 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | |||
| 0.3 M NaOAc | 19.7 | mg | 250 | g | 22.47 | 1000 | g | 56.30 | 0.0011 | 0.0018 | |||
| 1.2% PVP | 9.6 | µg | 100 | g | 45.30 | 1000 | g | 224.00 | 2.2E-06 | 4.3E-06 | |||
| Phenol:Chloroform | 1.0 | mL | Phenol | 0.5 | g | 100 | g | 18.00 | 1000 | g | 64.40 | 0.0322 | 0.0900 |
| (1:1 v/v) | Chloroform | 0.5 | mL | 500 | mL | 50.62 | 2500 | mL | 100.66 | 0.0201 | 0.0506 | ||
| Sodiumacetate | 0.08 | mL | 3 M | 19.7 | mg | 250 | g | 22.47 | 1000 | g | 56.30 | 0.0011 | 0.0018 |
| Isopropanol | 0.9 | mL | 100% | 0.9 | mL | 1000 | mL | 30.30 | 2500 | mL | 61.70 | 0.0222 | 0.0273 |
| Ethanol | 2.0 | mL | 70% | 1.4 | mL | 250 | mL | 47.56 | 2500 | mL | 246.58 | 0.1381 | 0.2663 |
| TE buffer | 0.1 | mL | 10 mM Tris–HCl | 0.12 | mg | 500 | g | 93.40 | 1000 | g | 128.00 | 1.6E-05 | 2.3E-05 |
| 1.0 mM EDTA | 0.03 | mg | 100 | g | 34.08 | 1000 | g | 245.23 | 7.2E-06 | 1.0E-05 | |||
| Extracted samples | 12 | – | – | – | – | – | – | ||||||
| Extraction time | 150 | min | – | – | – | – | – | – | |||||
| Lab staff (per hour) | – | 35.00 | – | 25.00 | – | – | |||||||
| Lab staff (€/extraction) | 5.21 | 7.29 | |||||||||||
| Chemicals (€/extraction) | 0.22 | 0.44 | |||||||||||
| Gloves, tubes, tips (€/extraction) | 0.23 | 0.34 | |||||||||||
| Final price per extraction including extraction time, lab staff and all consumables (€) | 5.65 | 8.07 | |||||||||||
Table 7.
Cost analysis for DNA extraction procedure F (according to Singka et al., 2012).
| Consumables | Volumes | Units | Concentration | Volumes | /Weight |
High costs |
Low costs |
Low cost | High cost | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount | Unit | Fix cost (€) | Amount | Unit | Fix cost (€) | per Prep (€) | per Prep (€) | ||||||
| Gloves (any size) | 1 | pair | – | – | – | 50 | pair | 8.20 | 50 | pair | 4.50 | 0,.900 | 0.1640 |
| Tubes | 4 | – | – | 1.5 | mL | 500 | pieces | 8.20 | 1000 | pieces | 14.90 | 0.0596 | 0.0656 |
| Tips | 12 | – | 1000 | µl | 500 | pieces | 5.08 | 1000 | pieces | 7.70 | 0.0924 | 0.1218 | |
| Tips | 2 | – | 200 | µL | 500 | pieces | 5.40 | 1000 | pieces | 8.19 | 0.0164 | 0.0216 | |
| Glass beads 0.1 mm | 0.5 | g | – | 5.0 | g | 1000 | g | 24.30 | 25000 | g | 202.00 | 0.0404 | 0.1215 |
| CTAB extraction buffer | 0.5 | mL | 0.7 M NaCl | 10.2 | mg | 500 | g | 15.84 | 1000 | g | 24.19 | 0.0002 | 0.0003 |
| (1:1 v/v) 10% w/v (CTAB in NaCl) | 10% w/v CTAB | 2,5 | µg | 100 | g | 22.64 | 1000 | g | 89.11 | 2.2E-07 | 5.7E-07 | ||
| to KH2PO4 | 240 mM KH2PO4 | 8.2 | mg | 250 | g | 19.66 | 1000 | g | 56.66 | 0.0005 | 0.0006 | ||
| Phenol:Chloroform:Isoamyl | 1.0 | mL | 25′ Phenol | 0.5 | g | 100 | g | 18.00 | 1000 | g | 64.40 | 0.0322 | 0.0900 |
| (25:24:1 v/v) | 24′ Chloroform | 0.48 | mL | 500 | mL | 50.62 | 2500 | mL | 100.66 | 0.0193 | 0.0486 | ||
| 1′ Isoamyl | 0.02 | mL | 25 | mL | 13.92 | 1000 | mL | 108.00 | 0.0022 | 0.0111 | |||
| Chloroform:Isoamyl | 0.5 | mL | 24' Chloroform | 0.48 | mL | 500 | mL | 50.62 | 2500 | mL | 100.66 | 0.0193 | 0.0486 |
| (24:1 v/v) | 1′ Isoamyl | 0.02 | mL | 25 | mL | 13.92 | 1000 | mL | 108.00 | 0.0022 | 0.0111 | ||
| Sodium acetate (0.1:1 v/v) | 0.05 | mL | 3 M | 12.3 | mg | 250 | g | 22.47 | 1000 | g | 56.30 | 0.0007 | 0.0011 |
| Isopropanol (0.6: 1 v/v) | 0.3 | mL | 100% | 0.3 | mL | 1000 | mL | 30.30 | 2500 | mL | 61.70 | 0.0074 | 0.0091 |
| Ethanol | 1.5 | mL | 70% | 1.05 | mL | 250 | mL | 47.56 | 2500 | mL | 246.58 | 0.1036 | 0.1998 |
| TE buffer | 0.1 | mL | 10 mM Tris–HCl | 0.12 | mg | 500 | g | 93.40 | 1000 | g | 128.00 | 1.6E-05 | 2.3E-05 |
| 1 mM EDTA | 0.03 | mg | 100 | g | 34.08 | 1000 | g | 245.23 | 7.2E-06 | 1.0E-05 | |||
| Extracted samples | 12 | – | – | – | – | ||||||||
| Extraction time | 195 | min | – | – | – | – | – | – | |||||
| Lab staff (per hour) | – | 35.00 | – | 25.00 | – | – | |||||||
| Lab staff (€/extraction) | 6.77 | 9.48 | |||||||||||
| Chemicals (€/extraction) | 0.19 | 0.42 | |||||||||||
| Gloves, tubes, tips (€/extraction) | 0.30 | 0.49 | |||||||||||
| Final price per extraction including extraction time, lab staff and all consumables (€) | 7.26 | 10.39 | |||||||||||
Table 8.
Cost analysis for DNA extraction procedure G (according to Saxony State Method).
| Consumables | Volumes | Units | Concentration | Volumes | /Weight |
High costs |
Low costs |
Low cost | High Cost | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount | Unit | Fix cost (€) | Amount | Unit | Fix cost (€) | per Prep (€) | per Prep (€) | ||||||
| Gloves (any size) | 1 | pair | – | – | – | 50 | pair | 8.20 | 50 | pair | 4.50 | 0.0900 | 0.1640 |
| Tubes | 3 | – | – | 2.0 | mL | 500 | pieces | 11.90 | 1000 | pieces | 21.90 | 0.0657 | 0.0714 |
| 1 | – | – | 1.5 | mL | 500 | pieces | 8.20 | 1000 | pieces | 14.90 | 0.0149 | 0.0164 | |
| Tips | 13 | – | 1000 | µL | 500 | pieces | 5.08 | 1000 | pieces | 7.70 | 0.1001 | 0.1320 | |
| Tips | 1 | – | 200 | µL | 500 | pieces | 5.40 | 1000 | pieces | 8.19 | 0.0082 | 0.0108 | |
| Tips | 1 | – | 10 | µL | 1000 | pieces | 27.14 | 2000 | pieces | 43.42 | 0.0217 | 0.0271 | |
| Extraction buffer | 1.0 | mL | 2% w/v CTAB | 20.0 | µg | 100 | g | 22.64 | 1000 | g | 89.11 | 1.8E-06 | 4.5E-06 |
| 0.1 M Tris–HCl | 12.1 | mg | 500 | g | 93.40 | 1000 | g | 128.00 | 0.0016 | 0.0023 | |||
| 0.02 M EDTA | 5.8 | mg | 100 | g | 34.08 | 1000 | g | 245.23 | 0.0014 | 0.0020 | |||
| 1.4 M NaCl | 81.8 | mg | 500 | g | 15.84 | 1000 | g | 24.19 | 0.0020 | 0.0026 | |||
| RNase A | 0.02 | mL | 20 mg mL-1 | 0.4 | mg | 250 | mg | 94.40 | 1000 | mg | 292.00 | 0.1168 | 0.1510 |
| Chloroform | 0.75 | mL | 100% | 0.75 | mL | 500 | mL | 50.62 | 2500 | mL | 100.66 | 0.0302 | 0.0759 |
| Precipitation solution | 1.0 | mL | 0.5% w/v CTAB | 0.5 | µg | 100 | g | 22.64 | 1000 | g | 89.11 | 4.5E-08 | 1.1E-07 |
| 40 mM NaCL | 2.3 | mg | 500 | g | 15.84 | 1000 | g | 24.19 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | |||
| NaCl | 0.35 | mL | 1.2 M NaCl | 24.5 | mg | 500 | g | 15.84 | 1000 | g | 24.19 | 0.0006 | 0.0008 |
| Chloroform | 0.35 | mL | 100% | 0.35 | mL | 500 | mL | 50.62 | 2500 | mL | 100.66 | 0.0141 | 0.0354 |
| Isopropanol (0.6:1 v/v) | 0.15 | mL | 100% | 0.15 | mL | 250 | mL | 47.56 | 2500 | mL | 246.58 | 0.0148 | 0.0285 |
| Ethanol | 1.5 | mL | 70% | 1.05 | mL | 250 | mL | 47.56 | 2500 | mL | 246.58 | 0.1036 | 0.1998 |
| TE buffer | 0.1 | mL | 10 mM Tris–HCl | 0.12 | mg | 500 | g | 93.40 | 1000 | g | 128.00 | 1.6E-05 | 2.3E-05 |
| 1.0 mM EDTA | 0.03 | mg | 100 | g | 34.08 | 1000 | g | 245.23 | 7.2E-06 | 1.0E-05 | |||
| Extracted samples | 12 | – | – | – | – | – | – | ||||||
| Extraction time | 175 | min | – | – | – | – | – | – | |||||
| Lab staff (per hour) | – | 35.00 | – | 25.00 | – | – | |||||||
| Lab staff (€/extraction) | 6.08 | 8.51 | |||||||||||
| Chemicals (€/extraction) | 0.29 | 0.50 | |||||||||||
| Gloves, tubes, tips (€/extraction) | 0.30 | 0.42 | |||||||||||
| Final price per extraction including extraction time, lab staff and all consumables (€) | 6.66 | 9.43 | |||||||||||
Table 9.
Cost analysis for DNA extraction procedure H (according to Tabatabaei et al. [5]).
| Consumables | Volumes | Units | Concentration | Volumes | /Weight |
High costs |
Low costs |
Low cost | High cost | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount | Unit | Fix cost (€) | Amount | Unit | Fix cost (€) | per Prep (€) | per Prep (€) | ||||||
| Gloves (any size) | 1 | pair | – | – | – | 50 | pair | 8.20 | 50 | pair | 4.50 | 0.0900 | 0.1640 |
| Tubes | 3 | – | – | 2.0 | mL | 500 | pieces | 11.90 | 1000 | pieces | 21.90 | 0.0657 | 0.0714 |
| Tips | 12 | – | 1000 | µL | 500 | pieces | 5.08 | 1000 | pieces | 7.70 | 0.0924 | 0.1218 | |
| Tips | 1 | – | 200 | µL | 500 | pieces | 5.40 | 1000 | pieces | 8.19 | 0.0082 | 0.0108 | |
| Tips | 0 | – | 10 | µL | 1000 | pieces | 27.14 | 2000 | pieces | 43.42 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | |
| EDTA | 0.4 | mL | 0.5 EDTA | 58.4 | mg | 100 | g | 34.08 | 1000 | g | 245.23 | 0.0143 | 0.0199 |
| Lysis buffer | 0.4 | mL | 10 mM Tris | 0.48 | mg | 500 | g | 93.40 | 1000 | g | 128.00 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 |
| 1 mM EDTA | 0.12 | mg | 100 | g | 34.08 | 1000 | g | 245.23 | 3.E-05 | 4.E-05 | |||
| 2 mg mL-1 Lysozyme | 0.80 | mg | 1,0 | g | 23.89 | 10 | g | 96.04 | 0.0077 | 0.0191 | |||
| SDS | 0.05 | mL | 10% w/v | 0.005 | mg | 100 | g | 16.56 | 1000 | g | 56.48 | 2.8E-07 | 8.3E-07 |
| Phenol:Chloroform | 0.8 | mL | Phenol | 0.4 | g | 100 | g | 18.00 | 1000 | g | 64.40 | 0.0258 | 0.0720 |
| (1:1 v/v) | Chloroform | 0.4 | mL | 500 | mL | 50.62 | 2500 | mL | 100.66 | 0.0161 | 0.0405 | ||
| Sodium acetate | 0.08 | mL | 3 M | 19.7 | mg | 250 | g | 22.47 | 1000 | g | 56.30 | 0.0011 | 0.0018 |
| Isopropanol | 0.9 | mL | 100% | 0.9 | mL | 1000 | mL | 30.30 | 2500 | mL | 61.70 | 0.0222 | 0.0273 |
| Ethanol | 1.5 | mL | 70% | 1.05 | mL | 250 | mL | 47.56 | 2500 | mL | 246.58 | 0.1036 | 0.1998 |
| TE buffer | 0.1 | mL | 10 mM Tris–HCl | 0.12 | mg | 100 | g | 34.08 | 1000 | g | 245.23 | 3.0E-05 | 4.1E-05 |
| 1.0 mM EDTA | 0.03 | mg | 500 | g | 93.40 | 1000 | g | 128.00 | 3.7E-06 | 5.5E-06 | |||
| Extracted samples | 12 | – | – | – | – | – | |||||||
| Extraction time | 210 | min | – | – | – | – | – | – | |||||
| Lab staff (per hour) | – | 35.00 | – | 25,00 | – | – | |||||||
| Lab staff (€/extraction) | 7.29 | 10.21 | |||||||||||
| Chemicals (€/extraction) | 0.19 | 0.38 | |||||||||||
| Gloves, tubes, tips (€/extraction) | 0.26 | 0.37 | |||||||||||
| Final price per extraction (€) | 7.74 | 10.96 | |||||||||||
Table 10.
Cost analysis for DNA extraction procedure I (according to Tresse et al. [6]).
| Consumables | Volumes | Units | Concentration | Volumes | /Weight |
High costs |
Low costs |
Low cost | High cost | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount | Unit | Fix cost (€) | Amount | Unit | Fix cost (€) | per Prep (€) | per Prep (€) | ||||||
| Gloves (any size) | 1 | pair | – | – | – | 50 | pair | 8.20 | 50 | pair | 4.50 | 0.0900 | 0.1640 |
| Tubes | 3 | – | – | 2.0 | mL | 500 | pieces | 11.90 | 1000 | pieces | 21.90 | 0.0657 | 0.0714 |
| 4 | – | – | 1.5 | mL | 500 | pieces | 8.20 | 1000 | pieces | 14.90 | 0.0596 | 0.0656 | |
| Tips | 14 | – | 1000 | µL | 500 | pieces | 5.08 | 1000 | pieces | 7.70 | 0.1078 | 0.1421 | |
| Tips | 4 | – | 200 | µL | 500 | pieces | 5.40 | 1000 | pieces | 8.19 | 0.0328 | 0.0432 | |
| Tips | 1 | – | 10 | µL | 1000 | pieces | 27.14 | 2000 | pieces | 43.42 | 0.0217 | 0.0271 | |
| TEN buffer | 0.7 | mL | 100 mM Tris | 8.48 | mg | 500 | g | 93.40 | 1000 | g | 128.00 | 0.0011 | 0.0016 |
| 100 mM EDTA | 20.45 | mg | 100 | g | 34.08 | 1000 | g | 245.23 | 0.0050 | 0.0070 | |||
| 100 mM NaCl | 4.09 | mg | 500 | g | 15.84 | 1000 | g | 24.19 | 9.9E-05 | 1.3E-04 | |||
| 5 mg mL-1 Lysozyme | 3.5 | mg | 1.0 | g | 23.89 | 10 | g | 96.04 | 0.0336 | 0.0836 | |||
| SDS | 0.035 | mL | 20% w/v | 0.007 | mg | 100 | g | 16.56 | 1000 | g | 56.48 | 4.0E-07 | 1.2E-06 |
| Proteinase K | 0.01 | mL | 20 mg mL-1 | 0.2 | mg | 100 | mg | 67.68 | 500 | mg | 259.62 | 0.1038 | 0.1354 |
| Silica beads | – | ID 0.1 mm | 250 | mg | 1000 | g | 24.30 | 25000 | g | 202.00 | 2.0E-03 | 0.0061 | |
| Silica beads | – | ID 0.5 mm | 250 | mg | 1000 | g | 25.23 | 20000 | g | 227.18 | 0.0028 | 0.0063 | |
| Silica beads | 2 | beads | ID 6.0 mm | 69 | mg | 500 | g | 34.20 | 1000 | g | 12.35 | 0.0009 | 0.0047 |
| Ammoniumacetate | 0.145 | mL | 10 M | 111.8 | mg | 250 | g | 15.30 | 1000 | g | 45.29 | 0.0051 | 0.0068 |
| RNase A | 0.005 | mL | 1 mg mL-1 | 0.005 | mg | 250 | mg | 94.40 | 1000 | mg | 292.00 | 0.0015 | 0.0019 |
| Phenol:Chloroform:Isoamyl | 1.5 | mL | 25' Phenol | 0.75 | g | 100 | g | 18.00 | 1000 | g | 64.40 | 0.0483 | 0.1350 |
| (25:24:1 v/v) | 24' Chloroform | 0.72 | mL | 500 | mL | 50.62 | 2500 | mL | 100.66 | 0.0290 | 0.0729 | ||
| 1' Isoamyl | 0.03 | mL | 25 | mL | 13.92 | 1000 | mL | 108.00 | 0.0032 | 0.0167 | |||
| Chloroform:Isoamyl | 0.7 | mL | 24' Chloroform | 0.672 | mL | 500 | mL | 50.62 | 2500 | mL | 100.66 | 0.0271 | 0.0680 |
| (24:1 v/v) | 1' Isoamyl | 0.028 | mL | 25 | mL | 13.92 | 1000 | mL | 108.00 | 0.0030 | 0.0156 | ||
| Sodiumaceate (1:10 v/v) | 0.07 | mL | 3 M | 17.2 | mg | 250 | g | 22.47 | 1000 | g | 56.30 | 0.0010 | 0.0015 |
| Ethanol (2:1 v/v) | 1.4 | mL | 98% | 1.37 | mL | 250 | mL | 47.56 | 2500 | mL | 246.58 | 0.1353 | 0.2610 |
| Ethanol | 1.0 | mL | 70% | 0.7 | mL | 250 | mL | 47.56 | 2500 | mL | 246.58 | 0.0690 | 0.1332 |
| TE buffer | 0.1 | mL | 10 mM Tris–HCl | 0.12 | mg | 100 | g | 34.08 | 1000 | g | 245.23 | 3.0E-05 | 4.1E-05 |
| 1.0 mM EDTA | 0.03 | mg | 500 | g | 93.40 | 1000 | g | 128.00 | 3.7E-06 | 5.5E-06 | |||
| Extracted samples | 12 | – | – | – | – | – | |||||||
| Extraction time | 170 | min | – | – | – | – | – | – | |||||
| Lab staff (per hour) | – | 35.00 | – | 25.00 | – | – | |||||||
| Lab staff (€/extraction) | 5.90 | 8.26 | |||||||||||
| Chemicals (€/extraction) | 0.47 | 0.96 | |||||||||||
| Gloves, tubes, tips (€/extraction) | 0.38 | 0.51 | |||||||||||
| Final price per extraction including extraction time, lab staff and all consumables (€) | 6.75 | 9.73 | |||||||||||
Table 11.
Cost analysis for DNA extraction procedure J (according to Wilson [7]).
| Consumables | Volumes | Units | Concentration | Volumes | /Weight |
High costs |
Low costs |
Low cost | High cost | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount | Unit | Fix cost (€) | Amount | Unit | Fix cost (€) | per Prep (€) | per Prep (€) | ||||||
| Gloves (any size) | 1 | pair | – | – | – | 50 | pair | 8.20 | 50 | pair | 4.50 | 0.0900 | 0.1640 |
| Tubes | 3 | – | – | 2.0 | mL | 500 | pieces | 11.90 | 1000 | pieces | 21.90 | 0.0657 | 0.0714 |
| Tips | 9 | – | 1000 | µL | 500 | pieces | 5.08 | 1000 | pieces | 7.70 | 0.0693 | 0.0914 | |
| Tips | 4 | – | 200 | µL | 500 | pieces | 5.40 | 1000 | pieces | 8.19 | 0.0328 | 0.0432 | |
| Tips | 1 | – | 10 | µL | 1000 | pieces | 27.14 | 2000 | pieces | 43.42 | 0.0217 | 0.0271 | |
| TE buffer | 0.567 | mL | 10 mM Tris | 0.69 | mg | 100 | g | 34.08 | 1000 | g | 245.23 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 |
| 10 mM EDTA | 1.66 | mg | 500 | g | 93.40 | 1000 | g | 128.00 | 0,0002 | 0.0003 | |||
| SDS | 0.03 | mL | 10% w/v | 0.003 | mg | 100 | g | 16.56 | 1000 | g | 56.48 | 1.7E-07 | 5.0E-07 |
| Proteinase K | 0.003 | mL | 20 mg mL-1 | 0.06 | mg | 100 | mg | 67.68 | 500 | mg | 259.62 | 0.0312 | 0.0406 |
| NaCl | 0.1 | mL | 5 M | 29.22 | mg | 500 | g | 15.84 | 1000 | g | 24.19 | 7.1E-04 | 9.3E-04 |
| CTAB/NaCl | 0.08 | mL | 0,7 M NaCl | 3,3 | mg | 500 | g | 15.84 | 1000 | g | 24.19 | 0.0001 | 0.1037 |
| 10% w/v CTAB | 0.008 | mg | 100 | g | 22.64 | 1000 | g | 89.11 | 7.1E-07 | 1.8E-06 | |||
| Chloroform:Isoamyl | 1.0 | mL | 24' Chloroform | 0.96 | mL | 500 | mL | 50.62 | 2500 | mL | 100.66 | 0.0387 | 0.0972 |
| (24:1 v/v) | 1' Isoamyl | 0.04 | mL | 25 | mL | 13.92 | 1000 | mL | 108.00 | 0.0043 | 0.0223 | ||
| Phenol:Chloroform:Isoamyl | 0.9 | mL | 25' Phenol | 0.45 | g | 100 | g | 18.00 | 1000 | g | 64.40 | 0.0290 | 0.0810 |
| (25:24:1 v/v) | 24' Chloroform | 0.432 | mL | 500 | mL | 50.62 | 2500 | mL | 100.66 | 0.0174 | 0.0437 | ||
| 1' Isoamyl | 0.018 | mL | 25 | mL | 13.92 | 1000 | mL | 108.00 | 0.0019 | 0.0100 | |||
| Isopropanol (0.6: 1 v/v) | 0.3 | mL | 100% | 0.3 | mL | 1000 | mL | 30.30 | 2500 | mL | 61.70 | 0.0074 | 0.0091 |
| Ethanol | 0.5 | mL | 70% | 0.35 | mL | 250 | mL | 47.56 | 2500 | mL | 246.58 | 0.0345 | 0.0666 |
| TE buffer | 0.1 | mL | 10 mM Tris–HCl | 0.12 | mg | 100 | g | 34.08 | 1000 | g | 245.23 | 3.0E-05 | 4.1E-05 |
| 1.0 mM EDTA | 0.03 | mg | 500 | g | 93.40 | 1000 | g | 128.00 | 3.7E-06 | 5.5E-06 | |||
| Extracted samples | 12 | – | – | – | – | – | – | ||||||
| Extraction time | 105 | min | – | – | – | – | – | – | |||||
| Lab staff (per hour) | – | 35.00 | – | 25.00 | – | – | |||||||
| Lab staff (€/extraction) | 3.65 | 5.10 | |||||||||||
| Chemicals (€/extraction) | 0.17 | 0.48 | |||||||||||
| Gloves, tubes, tips (€/extraction) | 0.28 | 0.40 | |||||||||||
| Final price per extraction including extraction time, lab staff and all consumables (€) | 4.09 | 5.98 | |||||||||||
Table 12.
Cost analysis for FastDNA SPIN Kit for Soil.
| Consumables | Volumes | Units | Concentration | Volumes | /Weight |
High costs |
Low costs |
Low cost | High cost | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount | Unit | Fix cost (€) | Amount | Unit | Fix cost (€) | per Prep (€) | per Prep (€) | ||||||
| Gloves (any size) | 1 | pair | – | – | – | 50 | pair | 8.20 | 50 | pair | 4.50 | 0.090 | 0.164 |
| Tips | 12 | 1000 | µl | 500 | pieces | 5.08 | 1000 | pieces | 7.70 | 0.092 | 0.122 | ||
| Tips | 4 | 200 | µL | 500 | pieces | 5.40 | 1000 | pieces | 8.19 | 0.033 | 0.043 | ||
| Tips | 1 | 10 | µl | 1000 | pieces | 27.14 | 2000 | pieces | 43.42 | 0.022 | 0.027 | ||
| Test Kit | 50 | extractions | 390.00 | 100 | extractions | 820.00 | 8.20 | 7.80 | |||||
| Extracted samples | 12 | – | – | ||||||||||
| Extraction time | 45 | min | – | – | – | – | |||||||
| lab staff (per hour) | 35.00 | 25.00 | 1.56 | 2.19 | |||||||||
| Lab staff (€/extraction) | 1.56 | 2.19 | |||||||||||
| Chemicals (€/extraction) | 8.20 | 7.80 | |||||||||||
| Gloves, tubes, tips (€/extraction) | 0.24 | 0.36 | |||||||||||
| Final price per extraction including extraction time, lab staff and all consumables (€) | 10.00 | 10.34 | |||||||||||
Table 13.
Cost analysis for DNeasy power water kit.
| Consumables | Volumes | Units | Concentration | Volumes | /Weight | Amount |
High costs |
Low costs |
Low cost | High cost | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | Fix cost (€) | Amount | Unit | Fix cost (€) | per Prep (€) | per Prep (€) | |||||||
| Gloves (any size) | 1 | pair | – | – | – | 50 | pair | 8.20 | 50 | pair | 4.50 | 0.090 | 0.164 |
| Tips | 12 | 1000 | µl | 500 | pieces | 5.08 | 1000 | pieces | 7.70 | 0.092 | 0.122 | ||
| Tips | 4 | 200 | µL | 500 | pieces | 5.40 | 1000 | pieces | 8.19 | 0.033 | 0.043 | ||
| Tips | 1 | 10 | µl | 1000 | pieces | 27.14 | 2000 | pieces | 43.42 | 0.022 | 0.027 | ||
| Test Kit | 50 | extractions | 558.61 | 100 | extractions | 1062.9 | 10.63 | 11.17 | |||||
| Extracted samples | 12 | – | – | ||||||||||
| Extraction time | 40 | min | – | – | – | – | |||||||
| lab staff (per hour) | 35.00 | 25.00 | 1.39 | 1.94 | |||||||||
| Lab staff (€/extraction) | 1.39 | 1.94 | |||||||||||
| Chemicals (€/extraction) | 10.63 | 11.17 | |||||||||||
| Gloves, tubes, tips (€/extraction) | 0.24 | 0.36 | |||||||||||
| Final price per extraction including extraction time, lab staff and all consumables (€) | 12.25 | 13.47 | |||||||||||
2. Experimental design, materials and methods
The sample preservation, DNA extraction, PCR performance and gel electrophoresis were described elsewhere [1]. For the cost analysis, a cost range was estimated ranging between minimum and maximum prices for all needed consumables. The number of required tubes and tips per extraction was counted. In all equations that follow, an index was included identifying low or high cost calculations, respectively. For clarification, the letter x represents all low cost calculations and the letter y represents all high cost calculations. The individual cost per chemical needed for every DNA extraction was calculated either with Eqs. (1) or (2), where mextraction is the chemical weight required for a single DNA extraction and mtotal,fix cost is the total weight corresponding to the fix cost. The individual cost for additional consumables such as gloves, tubes and/or tips was calculated either with Eqs. (3) or (4).
| (1) |
| (2) |
| (3) |
| (4) |
The cost for the lab staff was calculated either with Eqs. (5) or (6). The calculation is based on a total of 12 extractions per staff and the individual extraction time of the tested extraction procedures.
| (5) |
| (6) |
The sum of total costs of chemicals was calculated either with Eqs. (7) or (8). The total costs of all additional consumables needed per extraction was calculated either with Eqs. (9) or (10). The final price per preparation was then calculated either with Eqs. (11) or (12) considering the cost for the lab staff, for all chemicals and additional consumables needed.
| (7) |
| (8) |
| (9) |
| (10) |
| (11) |
| (12) |
2.1. Cost analysis
See Table 2, Table 3, Table 4, Table 5, Table 6, Table 7, Table 8, Table 9, Table 10, Table 11, Table 12, Table 13.
Footnotes
Transparency document associated with this article can be found in the online version at doi:10.1016/j.dib.2017.11.082.
Transparency document. Supplementary material
Supplementary material
References
- 1.Kuhn R., Böllmann J., Krahl K., Bryant I.M., Martienssen M. Comparison of ten different DNA extraction procedures with respect to their suitability for environmental samples. J. Microbiol. Methods. 2017;143:78–86. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2017.10.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gabor M.E., de Vries E.J., Janssen D.B. Efficient recovery of environmental DNA for expression cloning by indirect extraction methods. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2003;44:153–163. doi: 10.1016/S0168-6496(02)00462-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Shan G., Jin W., Lam E.K., Xing X. Purification of total DNA extracted from activated sludge. J. Environ. Sci. 2008;20:80–87. doi: 10.1016/s1001-0742(08)60012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Orsini M., Romano-Spica V. A microwave-based method for nucleic acid isolation from environmental samples. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2001;33:17–20. doi: 10.1046/j.1472-765x.2001.00938.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tabatabaei M., Zakaria M.R., Rahim R.A., Abdullah N., Wright D.G., Shirai Y., Shamsara M., Sakai K., Hassan M.A. Comparative study of methods for extraction and purification of environmental DNA from high-strength wastewater sludge. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010;9:4926–4937. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tresse O., Lorrain M.J., Roh D. Population dynamics of free-floating and attached bacteria in a styrene-degrading biotrickling filter analyzed by denaturating gradient gel electrophoresis. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2002;59:585–590. doi: 10.1007/s00253-002-1039-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wilson K. Preparation of genomic DNA from bacteria. Curr. Proced. Mol. Biol. 2001 doi: 10.1002/0471142727.mb0204s56. 00:I:2.4:2.4.1–2.4.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary material