Abstract
Inhaled corticosteroids (ICSs) are used as first-line drugs for asthma, and various novel antiasthma drugs targeting type 2 immune mediators are now under development. However, molecularly targeted drugs are expensive, creating an economic burden on patients. We and others previously found pendrin/SLC26A4 as a downstream molecule of IL-13, a signature type 2 cytokine critical for asthma, and showed its significance in the pathogenesis of asthma using model mice. However, the molecular mechanism of how pendrin causes airway inflammation remained elusive. We have recently demonstrated that hypothiocyanite (OSCN−) produced by the pendrin/DUOX/peroxidase pathway has the potential to cause airway inflammation. Pendrin transports thiocyanate (SCN−) into pulmonary lumens at the apical side. Peroxidases catalyze SCN− and H2O2 generated by DUOX into OSCN−. Low doses of OSCN− activate NF-κB in airway epithelial cells, whereas OSCN− in high doses causes necrosis of the cells, inducing the release of IL-33 and accelerating inflammation. OSCN− production is augmented in asthma model mice and possibly in some asthma patients. Heme peroxidase inhibitors, widely used as antithyroid agents, diminish asthma-like phenotypes in mice, indicating the significance of this pathway. These findings suggest the possibility of repositioning antithyroid agents as antiasthma drugs.
1. Introduction
Asthma is a common and chronic respiratory disease characterized by variable symptoms and features―wheezing, shortness of breath, cough, and expiratory airflow limitation [1]. Asthma is estimated to affect at least 300 million people worldwide, making it a significant medical and social problem. Inhaled corticosteroids (ICSs) are used as first-line drugs for asthma. Although ICSs are very effective, 5–10% of asthma patients are estimated as having severe asthma characterized by difficulty to achieve disease control despite high-dose ICSs plus long-acting β2-agonists or oral corticosteroids, which accounts for about 50% of the total costs for treating asthma [2, 3]. It is known that type 2 inflammation is dominant in the pathogenesis of asthma [4]. Based on this immunological background, various novel antiasthma drugs targeting type 2 immune mediators―interleukin- (IL-) 4, IL-5, IL-13, TSLP, IL-33, and CRTH2―are now under development [5]. However, molecularly targeted drugs, mostly biologics, are expensive, creating an economic burden on patients. Therefore, it is of great importance to elucidate the pathogenesis of severe asthma to help identify therapeutic strategies that will be more affordable for these patients.
It has been sporadically reported that IL-4 and/or IL-13, signature type 2 cytokines, influence anion transport in airway tissues [6]. However, the underlying mechanism of how anion transport in airway tissues leads to inflammation has not been sufficiently explained. We and others previously found that pendrin/SLC26A4, an anion transporter located at the apical side of airway epithelial cells, is a downstream molecule of the IL-4/IL-13 signals that plays an important role in the pathogenesis of asthma [7, 8]. We then investigated how pendrin causes airway inflammation, pinpointing the significance of the hypothiocyanite (OSCN−) production via the pendrin/DUOX/peroxidase pathway [9, 10]. These results have revealed for the first time the involvement of anion or its derivative in the pathogenesis of asthma. Moreover, these findings suggest to us that we can apply antithyroid agents, pan-heme peroxidase inhibitors, to drug repositioning for antiasthma drugs.
In this article, we describe how we started our research and how we have arrived at these findings.
2. Discovery of Pendrin as a Downstream Molecule of the IL-4/IL-13 Signals
IL-4 and IL-13 are signature cytokines of type 2 inflammation produced by TH2 cells, follicular helper T cells, group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2), eosinophils, mast cells, and basophils [11–14]. A number of analyses using asthma model mice have established the significance of IL-4 and/or IL-13, particularly the latter, in the pathogenesis of asthma [11, 15–17]. Based on these findings, several IL-4 or IL-13 signaling antagonists such as tralokinumab and dupilumab are now under clinical development as antiasthma drugs [18, 19]. To identify a novel mediator involved in asthma pathogenesis downstream of the IL-13 signals, we and others previously used DNA microarray to search for IL-13-induced molecules in human airway epithelial cells, finding that the SLC26A4 gene encoding pendrin is a downstream molecule of IL-13 [7, 20, 21]. Moreover, Pedemonte et al. found that IL-4 increases thiocyanate (SCN−) transport in human airway epithelial cells independently of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) [22]. They found that among the investigated transporters, the SLC26A4 gene was significantly induced by IL-4 and that pendrin is responsible for the SCN−/Cl− exchange. Thus, pendrin appears to be an IL-4- or IL-13-inducible molecule.
In agreement with the in vitro experiments, we and others have demonstrated that pendrin is highly expressed in the lungs of asthma model mice such as ovalbumin-inhaled, IL-13-inhaled, and IL-13 transgenic mice [7, 20–23]. We showed that pendrin is expressed in the apical side of airway epithelial cells in ovalbumin-inhaled mice [7]. Nonciliated airway epithelial cells are likely the main pendrin-expressing cells when stimulated by IL-4/IL-13, because pendrin expression is upregulated in the IL-13-overexpressing mice, in which STAT6 is expressed only in nonciliated airway epithelial cells [21]. Moreover, pendrin expression was enhanced in model mice of both acute and chronic asthma [23].
Since the SLC26A4 gene is an IL-4/IL-13-inducible molecule, it was reasonable to think that STAT6, a transcriptional factor critical for the IL-4/IL-13 signals, regulates the expression of the SLC26A4 gene. Nofziger et al. found that there exist two consensus binding sites for STAT6 (TTC(N4)GAA) at −3472 to −3463 (motif 1) and −1812 to −1803 (motif 2) of the 5′-flanking region of the SLC26A4 gene [24, 25]. Vanoni et al. showed that although both consensus sequences can bind STAT6 following IL-4 exposure, IL-4- or IL-13-inducible pendrin expression requires only motif 2 [25]. These results suggest that IL-4 or IL-13 induces expression of the SLC26A4 gene in a cis-regulating manner.
It has been thereafter demonstrated that in addition to IL-4 and IL-13, pendrin expression in lung tissues or airway epithelial cells can have other causes. These include various cytokines, such as IL-1β [22, 26] and IL-17A [27–29]. Also possible are various environmental stimuli such as silica [30], welding fumes [31], C60 fullerene [32], and single-wall carbon nanotubes [33]. In addition, pathogenic microbes or microbe-derived molecules―pertussis toxin [27, 34] and a combination of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and rhinovirus [8]―can be a cause. These findings expand the potential of pathophysiological roles of pendrin. It is of note that the combination of IL-13 and IL-17A enhances pendrin expression in airway epithelial cells [29]. Since expression of IL-17A is a hallmark of severe asthma correlated with infiltration of neutrophils [35], pendrin may be maximally expressed in severe asthma patients.
3. The Pathological Roles of Pendrin in Asthma
Using model mice, we and Nakagami et al. have previously demonstrated the significance of pendrin in the pathogenesis of airway allergic inflammation [7, 8]. Overexpression of pendrin in bronchial tissues leads to mucus hyperproduction, enhanced airway hyperreactivity (AHR), and upregulation of chemokine expression followed by infiltration of neutrophils [7]. Reciprocally, ovalbumin challenge for pendrin-deficient mice decreases airway reactivity and infiltration of inflammatory cells, including eosinophils in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), although systemic IgE production, mucus production, and the production of type 2 cytokines do not change [8]. Accordingly, it has been reported that pendrin expression was enhanced in asthma patients compared to control subjects [36], although there is a contradictory report [21]. Moreover, it has been shown that pendrin is highly expressed in the nasal mucosa of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) and allergic rhinitis (AR) [29, 37]. It is known that the existence of eosinophilic CRS in asthma patients is a risk factor for worsening asthma and that the presence of concomitant AR can affect the severity of asthma [38]. These results support the pathogenic significance of pendrin in both upper and lower respiratory allergic inflammation.
The involvement of pendrin in the pathogenesis of airway inflammation has been expanded into COPD and pertussis disease. We found that pendrin expression was enhanced in the lung tissues of esterase-inhaled mice mimicking COPD [7]. In COPD model mice, pendrin is expressed at the apical side of epithelial cells, as it is in asthma model mice, followed by expression of Muc5ac and Muc5b. Since it is known that expression of IL-17A and IL-13 is enhanced in COPD patients [39–41], the combination of these cytokines may induce pendrin expression in COPD. Scanlon et al., moreover, have demonstrated that Bordetella pertussis induces pendrin expression in an IL-17A-dependent manner and that pendrin deficiency improves Bordetella pertussis-induced inflammation but does not affect bacteria colonization [27].
4. The Role of Pendrin in Airway Surface Liquid (ASL)
Airway surfaces are covered by a thin layer of fluid, ASL, whose composition and volume are critical to ensure proper mucociliary clearance and maintain innate defense systems [6]. The amount and composition of ASL are regulated by the balance between fluid secretion and absorption coordinated by several ion channels and transporters, including pendrin. Nakagami et al. and Lee et al. showed that ASL is thickened in pendrin-deficient tracheal cells stimulated by IL-13 and deaf patients carrying pendrin mutations, probably because of dysregulated anion transport [8, 42]. This suggests the possibility that thickened ASL can enhance mucus clearance and improve airway function, which may at least partially explain how periostin deficiency improves asthma-like phenotypes. Increased pendrin expression following allergen challenges may lead to ASL dehydration and then to airway inflammation and obstruction, thereby exacerbating asthma.
5. The Pathological Role of the Pendrin/DUOX/Peroxidase Pathway in Asthma
The finding that pendrin is important for the onset of airway inflammation suggested to us that anions transported by pendrin, or their derivatives, could play an important role in asthma.
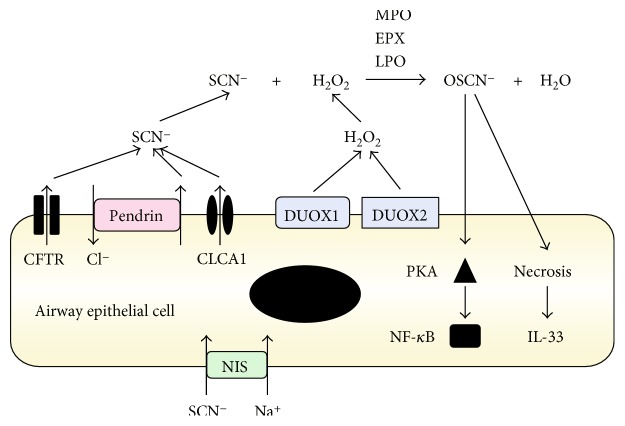
Among various anions, we focused on SCN−, because pendrin can transport SCN− into the apical side of airway epithelial cells [22] and OSCN− derived from SCN− plays a critical role in the innate defense of mucosal surfaces [43–45]. SCN− is incorporated from the basal side into airway epithelial cells by the Na+I− symporter (NIS)/SLC5A5 and then is actively transported into pulmonary lumens at the apical side by CFTR and pendrin (Figure 1). In contrast, DUOX1 and/or DUOX2, members of the NOX/DUOX family, generate hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in pulmonary lumens. SCN− and H2O2 are catalyzed into OSCN− by three peroxidases—myeloperoxidase (MPO), eosinophil peroxidase (EPX), and lactoperoxidase (LPO)—expressed in neutrophils, eosinophils, and epithelial cells, respectively, in the lung tissue. OSCN− has potent antimicrobial properties against bacteria, viruses, and fungi, as seen in cystic fibrosis patients, whose susceptibility to chronic respiratory infections increases in proportion to impaired CFTR function [46].
Figure 1.
Schematic model of OSCN− production via the pendrin/DUOX/peroxidase pathway in airway epithelial cells (modified from [9]). In airway epithelial cells, SCN− is actively transported into pulmonary lumens via NIS/SLC5A5 at the basal side and via several anion transporters including CFTR and pendrin/SLC26A4 at the apical side. SCN− together with H2O2 generated by Duox1 and Duox2 is catalyzed by peroxidases into OSCN−. Three peroxidases including MPO, EPX, and LPO are involved in this reaction. A low dose of OSCN− activates NF-κB via PKA, whereas a high dose of OSCN− causes necrosis followed by release of IL-33 in airway epithelial cells. It is of note that if peroxidases are inhibited, it would protect airway epithelial cells against inflammation.
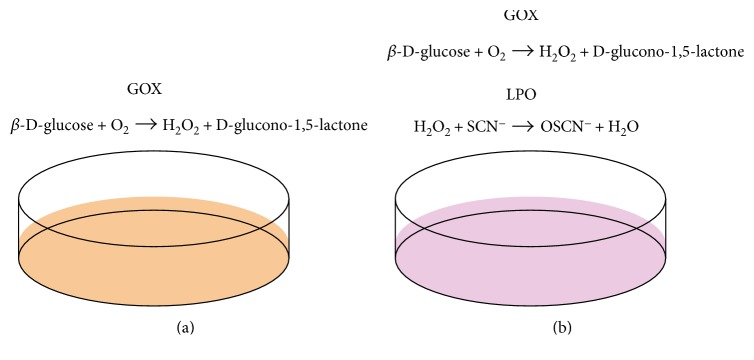
We examined whether the production of OSCN− leads to inflammation in airway epithelial cells (H292 cells) using an in vitro OSCN− production system [9]. In this system, when we added only β-D-glucose and glucose oxidase (GOX) in the reaction mixture, H2O2 was generated by GOX using β-D-glucose and oxygen (Figure 2(a)). When SCN− and LPO were furthermore added in the mixture, OSCN− was generated by LPO via the oxidation of SCN− with H2O2 (Figure 2(b)). Using this system, we compared the ability of H2O2 and OSCN− to activate NF-κB, finding that OSCN−, but not H2O2, activated NF-κB (Figure 1). Activation of NF-κB in airway epithelial cells is important for production of chemokines and inflammatory cytokines as well as for expression of adhesion molecules accelerating type 2 immunity [47]. OSCN− was sensed by protein kinase A (PKA) followed by the dimerization of PKA. The regulatory subunit of type I PKA is dimerized through a disulfide bond followed by increased affinity for the substrates, demonstrating that oxidative stress is changed to intracellular signaling through PKA, independently of cAMP [48]. The stronger oxidative ability of OSCN− compared to H2O2 may be due to the existence of a detoxifying system for H2O2, mainly by catalase in airway epithelial cells. Furthermore, OSCN− in high doses caused necrosis of the cells, inducing release of IL-33, which acts on several immune cells—ILC2, mast cells, basophils, eosinophils, and TH2 cells accelerating type 2 inflammation [49]. To our knowledge, OSCN− is the first anion to activate NF-κB in epithelial cells. Thus, we have shown that OSCN− produced by the pendrin/DUOX/peroxidase pathway potentially plays an important role in the pathogenesis of asthma.
Figure 2.
In vitro OSCN− production system (modified from [9]). When only β-D-glucose and glucose oxidase (GOX) are added into the system using airway epithelial cells (H292 cells), H2O2 is generated (a). When more SCN− and LPO are added, H2O2 is catalyzed into OSCN− (b). Thus, in this system, the oxidative activities of H2O2 and OSCN− can be estimated with or without addition of SCN− and LPO.
6. Enhancement of the OSCN− Production System in Asthma
We next examined whether OSCN− production via the pendrin/DUOX/peroxidase pathway is enhanced in asthma model mice (Table 1) [10]. Expression of pendrin was significantly enhanced, as shown in a previous study [7], whereas expression of CFTR did not change. Expression of all three heme peroxidases (Mpo, Epx, and Lpo) together with peroxidase activities in BALFs was enhanced in allergen-challenged mice. Moreover, the expression of DUOX1, but not DUOX2, was also significantly enhanced in allergen-challenged mice, consistent with a previous report showing that IL-4 can induce DUOX1 [50]. These results suggest that the OSCN− production machinery is enhanced in asthma model mice. We then investigated whether expression of the heme peroxidases was enhanced in the bronchial tissues of mild to moderate asthma patients well controlled with inhaled corticosteroids [50]. The peroxidase activities and the expression levels of LPO were not statistically enhanced. However, some patients showed distinctly high peroxidase activities and LPO expression. The clinical severity of their asthma, modified treatment for these patients, and/or heterogeneity among asthma patients may affect airway peroxidase expression, although the precise factor causing the difference is unclear at this moment. Expression of neither EPO nor MPO was detected. These results confirm that OSCN− production via pendrin/DUOX/peroxidase is augmented in asthma model mice and possibly in some asthma patients.
Table 1.
Change of the machineries of the OSCN− production system in asthma model mice and asthma patients.
| Molecule | Asthma model mouse | Asthma patient |
|---|---|---|
| Pendrin | ↑ | ↑/→∗ |
| CFTR | → | |
| Heme peroxidase | ||
| Myeloperoxidase | ↑ | ND |
| Eosinophil peroxidase | ↑ | ND |
| Lactoperoxidase | ↑ | ↑/→ |
| DUOX1 | ↑ | → |
| DUOX2 | → | ↑/→ |
To define the pathological roles of peroxidase in bronchial asthma, we applied heme peroxidase inhibitors to an asthma mouse model [10]. We examined the effects of 2-mercapto-1-methylimidazole (methimazole) and 6-propyl-2-thiouracil (PTU), which are agents that inhibit all peroxidases and are widely used as antithyroid agents targeting thyroid peroxidase. The long administration of methimazole (orally every day from the start of sensitization (day 0)) completely inhibited airway inflammation―enhanced AHR, infiltration of inflammatory cells in BALF, and histological changes (Table 2). Short administration (from two days before the start of the allergen airway challenge (day 20)) inhibited inflammation less so, yet significantly. Another peroxidase-inhibiting antithyroid agent, PTU, showed effects similar to but weaker than those of methimazole. These results strongly suggest that heme peroxidase activities are critical for the onset of allergic airway inflammation in these model mice. Our results appear consistent with the findings of several reports showing that accidental administration of antithyroid agents provided beneficial effects to asthma patients [51, 52], although there is one conflicting report [53]. It is of note that in most patients, bronchial asthma was exacerbated by discontinuing or tapering off antithyroid agents [51, 52].
Table 2.
Effects of peroxidase inhibitor and genetic deficiency of each peroxidase on asthma model mice (referred from [10]).
| Phenotype | Met-L | Met-S | Lpo − | Epx − | Mpo − |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AHR | ↓↓↓ | ↓↓ | ↓ | ↓ | → |
| BALF | |||||
| Eosinophil | ↓↓↓ | ↓↓ | ↓↓ | → | → |
| T cell | ↓↓↓ | ↓ | ↓↓ | ↓ | → |
| Neutrophil | ↓↓↓ | ↓↓ | ↓ | → | → |
| Macrophage | → | → | ↓ | → | → |
Effects of the long (Met-L) or short (Met-S) administration of methimazole or genetic deficiency of Lpo (Lpo−), Epx (Epx−), and Mpo (Mpo−) on enhanced AHR and the numbers of eosinophils, T cells, neutrophils, and macrophages in BALF of asthma model mice are depicted.
Next, we examined which peroxidase dominantly contributes to the onset of allergic airway inflammation using mice deficient in each of the three peroxidases (Mpo, Epx, and Lpo) [10]. Epx- and Lpo-deficient mice showed a nominal but not statistically significant decrease of AHR compared to their control littermates, whereas the Mpo-deficient mice showed no change of AHR (Table 2). Furthermore, infiltration of eosinophils and T cells was decreased in the BALF of the Lpo-deficient mice, whereas there was no change in infiltration in the Mpo- or Epx-deficient mice. These results suggest that the contributions of the three peroxidases are redundant in the onset of allergic airway inflammation. However, Lpo appears to be dominant among the peroxidases.
Taking these results together, we assume that whereas the OSCN− production system may be an innate host defense mechanism in the lung, this misplaced production of OSCN− is likely to contribute to pulmonary inflammation, causing deleterious effects in response to airway allergen provocation.
7. Clinical Application of the Pathological Significance of the Pendrin/DUOX/Peroxidase Pathway to Asthma
The findings showing the importance of the OSCN− production via the pendrin/DUOX/peroxidase pathway in asthma indicate that all of the machineries of the OSCN− production system can be viewed as potential novel therapeutic targets for asthma. It is of note that we have confirmed that heme peroxidase inhibitors widely used as antithyroid agents are efficacious for inhibiting allergic airway inflammation in mice. This suggests that we can apply antithyroid agents to drug repositioning for antiasthma drugs. Drug repositioning, which is the process of finding new therapeutic indications for existing drugs, is now seen as a less expensive alternative to drug discovery and development [54, 55]. The use of antithyroid agents could be the first example of drug repositioning for asthma. Various antiasthma drugs targeting type 2 immune mediators, such as IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, TSLP, IL-33, and CRTH2, are now under development [5]. However, to develop novel drugs, particularly biologics, huge investments of time and money are required, and safety risks are involved. Moreover, most molecularly targeted drugs for asthma under development are biologics, which are relatively expensive. Clearly, drug repositioning in asthma can potentially decrease the economic burden on asthma patients.
Moreover, the importance of the OSCN− by the pendrin/DUOX/peroxidase pathway in asthma can be applied to airway inflammation in smokers. Plasma SCN− levels in smokers are almost three times higher than in nonsmokers (130–140 μM versus 40–50 μM) [56, 57]. It is well known that smoking is associated with poor control, decrease of lung function, and enhanced corticosteroid resistance in asthma [58, 59]. However, no deleterious effects of SCN− or OSCN− derived from tobacco on the lungs have yet been reported. The findings suggest the possible involvement of the OSCN− production system in how smoking affects asthma or other smoking-related pulmonary diseases, giving us clues on how best to treat asthma patients who smoke.
8. Conclusion
After showing that pendrin/SLC26A4 is a downstream molecule of IL-13 and that it is actively involved in the pathogenesis of airway allergic inflammation, we investigated the underlying molecular mechanism of how this occurs. As a result, we have demonstrated the significance of OSCN− production via the pendrin/DUOX/peroxidase pathway in allergic airway inflammation. The most important clinical point of this finding is that it suggests the possibility of using antithyroid agents, pan-heme peroxidase inhibitors, as repositioned antiasthma drugs. If we can apply this strategy to asthma patients, it should greatly reduce the cost of treating asthma.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Dovie R. Wylie for the critical review of this manuscript. The authors also thank their colleagues and collaborators as follows for contributing to the present work: Isao Nakao, Sachiko Kanaji, Shoichiro Ohta, Kazuhiko Arima, Hiroshi Shiraishi, Shuji Toda, Hiroki Yoshida (Saga Medical School), Noriko Yuyama (Genox Research Inc.), Katsutoshi Nakayama (Tohoku University), Tomoaki Hoshino (Kurume University), Hiroyuki Tanaka (Gifu Pharmaceutical University), Yutaka Nakamura (Iwate Medical University School of Medicine), Yasuaki Aratani (Yokohama City University), Shigeru Kakuta, Yoichiro Iwakura (The University of Tokyo), and James J. Lee (Mayo Clinic Arizona).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there is no competing interest associated with the present study.
References
- 1.Global Initiative for Asthma. 2017 GINA Report, global strategy for asthma management and prevention. http://ginasthma.org/2017-gina-report-global-strategy-for-asthma-management-and-prevention.
- 2.Adcock I. M., Lane S. J. Corticosteroid-insensitive asthma: molecular mechanisms. Journal of Endocrinolology. 2003;178(3):347–355. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1780347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hekking P. P., Wener R. R., Amelink M., Zwinderman A. H., Bouvy M. L., Bel E. H. The prevalence of severe refractory asthma. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2015;135(4):896–902. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.08.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Peters M. C., Mekonnen Z. K., Yuan S., Bhakta N. R., Woodruff P. G., Fahy J. V. Measures of gene expression in sputum cells can identify TH2-high and TH2-low subtypes of asthma. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2014;133(2):388–394.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.07.036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Izuhara K., Matsumoto H., Ohta S., Ono J., Arima K., Ogawa M. Recent developments regarding periostin in bronchial asthma. Allergology International. 2015;64:S3–S10. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2015.04.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Izuhara K., Suzuki S., Nofziger C., et al. The Role of Pendrin in Health and Disease. Cham: Springer; 2017. The role of pendrin in the airways: links with asthma and COPD; pp. 141–154. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nakao I., Kanaji S., Ohta S., et al. Identification of pendrin as a common mediator for mucus production in bronchial asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Journal of Immunology. 2008;180(9):6262–6269. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.9.6262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Nakagami Y., Favoreto S., Jr., Zhen G., et al. The epithelial anion transporter pendrin is induced by allergy and rhinovirus infection, regulates airway surface liquid, and increases airway reactivity and inflammation in an asthma model. Journal of Immunology. 2008;181(3):2203–2210. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.3.2203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Suzuki S., Ogawa M., Ohta S., et al. Induction of airway allergic inflammation by hypothiocyanite via epithelial cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2016;291(53):27219–27227. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.746909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Suzuki S., Ogawa M., Ohta S., et al. The potential for repositioning antithyroid agents as antiasthma drugs. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2016;138(5):1458–1461.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.04.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Izuhara K., Arima K., Kanaji S., Ohta S., Kanaji T. IL-13: a promising therapeutic target for bronchial asthma. Current Medicinal Chemistry. 2006;13(19):2291–2298. doi: 10.2174/092986706777935140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kubo M. T follicular helper and TH2 cells in allergic responses. Allergology International. 2017;66(3):377–381. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2017.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kabata H., Moro K., Koyasu S., Asano K. Group 2 innate lymphoid cells and asthma. Allergology International. 2015;64(3):227–234. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2015.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Miyake K., Karasuyama H. Emerging roles of basophils in allergic inflammation. Allergology International. 2017;66(3):382–391. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2017.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wills-Karp M., Luyimbazi J., Xu X., et al. Interleukin-13: central mediator of allergic asthma. Science. 1998;282(5397):2258–2261. doi: 10.1126/science.282.5397.2258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Grünig G., Warnock M., Wakil A. E., et al. Requirement for IL-13 independently of IL-4 in experimental asthma. Science. 1998;282(5397):2261–2263. doi: 10.1126/science.282.5397.2261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zhu Z., Homer R. J., Wang Z., et al. Pulmonary expression of interleukin-13 causes inflammation, mucus hypersecretion, subepithelial fibrosis, physiologic abnormalities, and eotaxin production. The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 1999;103(6):779–788. doi: 10.1172/JCI5909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Brightling C. E., Chanez P., Leigh R., et al. Efficacy and safety of tralokinumab in patients with severe uncontrolled asthma: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet Respiratory Medicine. 2015;3(9):692–701. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(15)00197-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wenzel S., Castro M., Corren J., et al. Dupilumab efficacy and safety in adults with uncontrolled persistent asthma despite use of medium-to-high-dose inhaled corticosteroids plus a long-acting β2 agonist: a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled pivotal phase 2b dose-ranging trial. Lancet. 2016;388(10039):31–44. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zhen G., Park S. W., Nguyenvu L. T., et al. IL-13 and epidermal growth factor receptor have critical but distinct roles in epithelial cell mucin production. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology. 2007;36(2):244–253. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2006-0180OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kuperman D. A., Lewis C. C., Woodruff P. G., et al. Dissecting asthma using focused transgenic modeling and functional genomics. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2005;116(2):305–311. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2005.03.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pedemonte N., Caci E., Sondo E., et al. Thiocyanate transport in resting and IL-4-stimulated human bronchial epithelial cells: role of pendrin and anion channels. Journal of Immunology. 2007;178(8):5144–5153. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.8.5144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Di Valentin E., Crahay C., Garbacki N., et al. New asthma biomarkers: lessons from murine models of acute and chronic asthma. The American Journal of Physiology - Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology. 2009;296(2):L185–L197. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.90367.2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Nofziger C., Vezzoli V., Dossena S., et al. STAT6 links IL-4/IL-13 stimulation with pendrin expression in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 2011;90(3):399–405. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2011.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Vanoni S., Nofziger C., Dossena S., et al. The human pendrin promoter contains two N4 GAS motifs with different functional relevance. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry. 2013;32(7):238–248. doi: 10.1159/000356642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hogmalm A., Bry M., Strandvik B., Bry K. IL-1β expression in the distal lung epithelium disrupts lung morphogenesis and epithelial cell differentiation in fetal mice. The American Journal of Physiology - Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology. 2014;306(1):L23–L34. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00154.2013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Scanlon K. M., Gau Y., Zhu J., et al. Epithelial anion transporter pendrin contributes to inflammatory lung pathology in mouse models of Bordetella pertussis infection. Infection and Immunity. 2014;82(10):4212–4221. doi: 10.1128/IAI.02222-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Adams K. M., Abraham V., Spielman D., et al. IL-17A induces pendrin expression and chloride-bicarbonate exchange in human bronchial epithelial cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(8, article e103263) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Seshadri S., Lu X., Purkey M. R., et al. Increased expression of the epithelial anion transporter pendrin/SLC26A4 in nasal polyps of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 2015;136(6):1548–1558.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.05.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sellamuthu R., Umbright C., Roberts J. R., et al. Molecular insights into the progression of crystalline silica-induced pulmonary toxicity in rats. Journal of Applied Toxicology. 2013;33(4):301–312. doi: 10.1002/jat.2733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Oh J. H., Yang M. J., Heo J. D., et al. Inflammatory response in rat lungs with recurrent exposure to welding fumes: a transcriptomic approach. Toxicology and Industrial Health. 2012;28(3):203–215. doi: 10.1177/0748233711410906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Fujita K., Morimoto Y., Endoh S., et al. Identification of potential biomarkers from gene expression profiles in rat lungs intratracheally instilled with C60 fullerenes. Toxicology. 2010;274(1-3):34–41. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2010.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Fujita K., Fukuda M., Fukui H., et al. Intratracheal instillation of single-wall carbon nanotubes in the rat lung induces time-dependent changes in gene expression. Nanotoxicology. 2015;9(3):290–301. doi: 10.3109/17435390.2014.921737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Connelly C. E., Sun Y., Carbonetti N. H. Pertussis toxin exacerbates and prolongs airway inflammatory responses during Bordetella pertussis infection. Infection and Immunity. 2012;80(12):4317–4332. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00808-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Linden A., Dahlen B. Interleukin-17 cytokine signalling in patients with asthma. The European Respiratory Journal. 2014;44(5):1319–1331. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00002314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yick C. Y., Zwinderman A. H., Kunst P. W., et al. Transcriptome sequencing (RNA-Seq) of human endobronchial biopsies: asthma versus controls. The European Respiratory Journal. 2013;42(3):662–670. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00115412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ishida A., Ohta N., Suzuki Y., et al. Expression of pendrin and periostin in allergic rhinitis and chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergology International. 2012;61(4):589–595. doi: 10.2332/allergolint.11-OA-0370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Okano M., Kariya S., Ohta N., Imoto Y., Fujieda S., Nishizaki K. Association and management of eosinophilic inflammation in upper and lower airways. Allergology International. 2015;64(2):131–138. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2015.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Caramori G., Adcock I. M., Di Stefano A., Chung K. F. Cytokine inhibition in the treatment of COPD. International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. 2014;9(9):397–412. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S42544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Halwani R., Al-Muhsen S., Hamid Q. T helper 17 cells in airway diseases: from laboratory bench to bedside. Chest. 2013;143(2):494–501. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-0598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Bel E. H., Ten Brinke A. New anti-eosinophil drugs for asthma and COPD: targeting the trait! Chest. 2017 doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2017.05.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lee H. J., Yoo J. E., Namkung W., et al. Thick airway surface liquid volume and weak mucin expression in pendrin-deficient human airway epithelia. Physiological Reports. 2015;3(8, article e12480) doi: 10.14814/phy2.12480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ratner A. J., Prince A. Lactoperoxidase. New recognition of an “old” enzyme in airway defenses. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology. 2000;22(6):642–644. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.22.6.f186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hawkins C. L. The role of hypothiocyanous acid (HOSCN) in biological systems. Free Radical Research. 2009;43(12):1147–1158. doi: 10.3109/10715760903214462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Barrett T. J., Hawkins C. L. Hypothiocyanous acid: benign or deadly? Chemical Research in Toxicology. 2012;25(2):263–273. doi: 10.1021/tx200219s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Moskwa P., Lorentzen D., Excoffon K. J., et al. A novel host defense system of airways is defective in cystic fibrosis. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2007;175(2):174–183. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200607-1029OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Schuliga M. NF-κB signaling in chronic inflammatory airway disease. Biomolecules. 2015;5(3):1266–1283. doi: 10.3390/biom5031266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Brennan J. P., Bardswell S. C., Burgoyne J. R., et al. Oxidant-induced activation of type I protein kinase A is mediated by RI subunit interprotein disulfide bond formation. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2006;281(31):21827–21836. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M603952200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Cayrol C., Girard J. P. IL-33: an alarmin cytokine with crucial roles in innate immunity, inflammation and allergy. Current Opinion in Immunology. 2014;31:31–37. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2014.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Harper R. W., Xu C., Eiserich J. P., et al. Differential regulation of dual NADPH oxidases/peroxidases, Duox1 and Duox2, by Th1 and Th2 cytokines in respiratory tract epithelium. FEBS Letters. 2005;579(21):4911–4917. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Settipane G. A., Schoenfeld E., Hamolsky M. W. Asthma and hyperthyroidism. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 1972;49(6):348–355. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(72)90133-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Nakazawa T., Kobayashi S. Influence of antithyroidal therapy on asthma symptoms in the patients with both bronchial asthma and hyperthyroidism. Journal of Asthma. 1991;28(2):109–116. doi: 10.3109/02770909109082735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Grembiale R. D., Naty S., Iorio C., Crispino N., Pelaia G., Tranfa C. M. Bronchial asthma induced by an antithyroid drug. Chest. 2001;119(5):1598–1599. doi: 10.1378/chest.119.5.1598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Tobinick E. L. The value of drug repositioning in the current pharmaceutical market. Drug News and Perspectives. 2009;22(2):119–125. doi: 10.1358/dnp.2009.22.2.1343228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Li Y. Y., Jones S. J. Drug repositioning for personalized medicine. Genome Medicine. 2012;4(3):p. 27. doi: 10.1186/gm326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Husgafvel-Pursiainen K., Sorsa M., Engstrom K., Einisto P. Passive smoking at work: biochemical and biological measures of exposure to environmental tobacco smoke. International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health. 1987;59(4):337–345. doi: 10.1007/BF00405277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Saloojee Y., Vesey C. J., Cole P. V., Russell M. A. Carboxyhaemoglobin and plasma thiocyanate: complementary indicators of smoking behaviour? Thorax. 1982;37(7):521–525. doi: 10.1136/thx.37.7.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Tamimi A., Serdarevic D., Hanania N. A. The effects of cigarette smoke on airway inflammation in asthma and COPD: therapeutic implications. Respiratory Medicine. 2012;106(3):319–328. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2011.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Polosa R., Thomson N. C. Smoking and asthma: dangerous liaisons. The European Respiratory Journal. 2013;41(3):716–726. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00073312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]