ABSTRACT
Orientia tsutsugamushi, an obligate intracellular bacterium that is auxotrophic for the aromatic amino acids and histidine, causes scrub typhus, a potentially deadly infection that threatens 1 billion people. O. tsutsugamushi growth is minimal during the first 24 to 48 h of infection but its growth becomes logarithmic thereafter. How the pathogen modulates cellular functions to support its growth is poorly understood. The unfolded protein response (UPR) is a cytoprotective pathway that relieves endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress by promoting ER-associated degradation (ERAD) of misfolded proteins. Here, we show that O. tsutsugamushi invokes the UPR in the first 48 h and benefits from ER stress in an amino acid-dependent manner. O. tsutsugamushi also impedes ERAD during this time period. By 72 h, ER stress is alleviated and ERAD proceeds unhindered. Sustained inhibition of ERAD using RNA interference results in an O. tsutsugamushi growth defect at 72 h that can be rescued by amino acid supplementation. Thus, O. tsutsugamushi temporally stalls ERAD until ERAD-derived amino acids are needed to support its growth. The O. tsutsugamushi effector Ank4 is linked to this phenomenon. Ank4 interacts with Bat3, a eukaryotic chaperone that is essential for ERAD, and is transiently expressed by O. tsutsugamushi during the infection period when it inhibits ERAD. Ectopically expressed Ank4 blocks ERAD to phenocopy O. tsutsugamushi infection. Our data reveal a novel mechanism by which an obligate intracellular bacterial pathogen modulates ERAD to satisfy its nutritional virulence requirements.
KEYWORDS: ER stress, ERAD, intracellular bacterium, Orientia, Rickettsia, ankyrin repeat, bacterial effector, host-pathogen interaction, unfolded protein response
INTRODUCTION
Microbial acquisition of host nutrients is essential for the development of infectious disease. This is especially true for obligate intracellular bacterial pathogens, which are auxotrophic for essential metabolites. Scrub typhus is a neglected and potentially fatal infection caused by the obligate intracellular bacterium Orientia tsutsugamushi. The disease is endemic throughout areas of southeastern Asia and northern Australia, where it is a leading cause of nonmalarial febrile illness and estimated to afflict 1 million people annually (1). The geographic range of scrub typhus is expanding, with case reports in Africa (2, 3) and Chile (4, 5), and a new etiologic species, Orientia chuto, has been identified from the United Arab Emirates (6). Untreated scrub typhus carries a median mortality rate of 6%, but can reach as high as 70% (7). O. tsutsugamushi infects and replicates in the cytosol of diverse mammalian cell types (1). The bacterium's obligate reliance on host cells derives, in part, from its auxotrophism for histidine and aromatic amino acids (8). During the first 24 to 48 h following invasion, growth of the intracellular O. tsutsugamushi population is minimal, followed by a logarithmic replication phase that persists for days (9). The host cellular processes that the pathogen modulates and the effectors it employs to support its expansive growth are poorly defined.
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) plays an important role in maintaining cellular homeostasis by controlling the processing and folding of newly synthesized proteins. Accumulation of misfolded proteins induces physiologic stress on the ER. The unfolded protein response (UPR) is an evolutionarily conserved cytoprotective pathway that is invoked by and relieves ER stress by inhibiting mRNA translation, increasing ER protein folding capacity, and facilitating ER-associated degradation (ERAD) (10). With ERAD, newly synthesized proteins that are unsuccessfully targeted to the ER lumen or fail to attain their native conformation are recognized and trafficked to the 26S proteasome for degradation (11, 12). The resulting short peptides are rapidly degraded to amino acids by cytosolic aminopeptidases (13–15). Viruses have long been known to exert stress on the ER and induce the UPR (16). Recently, a small number of bacterial and protozoan pathogens, most of which live in vacuoles that interface with the ER, have been shown to induce or inhibit the UPR (10). The responsible microbial factors and their associated mechanisms are largely undefined. Even less is known about the interactions of cytosolic bacteria with the ER and UPR. As ER stress and the UPR also contribute to the development of other health disorders, including cancer, diabetes, and inflammatory diseases and have been therapeutically targeted in some of these contexts (17–25), dissecting the interplay between microbes, the ER, and the UPR is a burgeoning area of microbial pathogenesis research that could ultimately have an impact that extends beyond infectious disease.
The ankyrin repeat is one of the most common protein-protein interaction motifs in nature (26). Ankyrin repeat-containing proteins (Anks) are emerging as key virulence factors of intracellular bacteria and viruses for interacting with host cell proteins to coopt cellular processes (27). O. tsutsugamushi encodes one of the largest known Ank repertoires of any microbe (26). Most O. tsutsugamushi Anks also carry an F-box domain that is capable of interacting with SKP1 of the SCF1 ubiquitin ligase complex (28, 29), which normally functions in eukaryotic cells to tag proteins for degradation by the 26S proteasome (30). The O. tsutsugamushi Ikeda strain, originally isolated from a patient in Japan (31), encodes 20 full-length Ank genes, 12 of which are single copy and 8 of which exist as 26 identical or nearly identical paralogs (32). The Anks are type 1 secretion system substrates, and their importance to O. tsutsugamushi is underscored by the fact that the bacterium transcribes all 20 during infection (32). When ectopically expressed, 14 of the 20 Anks localize to the ER (32). This finding, together with the bacterium's intracellular tropism for the ER-proximal perinuclear region and its ability to inhibit the host cell secretory pathway (33, 34), suggest that O. tsutsugamushi-ER interactions and Ank modulation of ER-associated processes might be critical aspects of the organism's pathobiology.
In this study, we report that O. tsutsugamushi temporally modulates the UPR and stalls ERAD until the amino acids that it yields are needed to support the bacterium's growth. The O. tsutsugamushi effector Ank4 is linked to this phenomenon. Ank4 is expressed only during the UPR induction/ERAD inhibition period in infected cells and, when ectopically expressed, both interacts with the ERAD chaperone Bat3 and inhibits ERAD. We reveal a novel mechanism by which a bacterial pathogen manipulates ERAD to facilitate its intracellular parasitism.
RESULTS
O. tsutsugamushi induces the UPR.
In O. tsutsugamushi infected cells, the ER is slightly distended and protein secretion is inhibited (34, 35). Because these phenomena can indicate ER stress (36), we examined if O. tsutsugamushi infection invokes the UPR. ATF4 (activating transcription factor 4) and XBP1 (X-box-binding protein 1) are two transcription factors that are upregulated in response to ER stress and activate expression of UPR genes. ATF4 directly drives expression of UPR genes involved in amino acid transport and oxidative resistance and indirectly promotes expression of genes that lead to the induction of apoptosis (37, 38). XPB1 induces expression of ER-resident chaperones and protein-folding enzymes (39). Upon being transcribed, xbp1u (unspliced mRNA) is spliced to yield xbp1s (spliced mRNA), from which active XPB1 is translated (40). Both ATF4 and XBP1 upregulate factors involved in ERAD (10, 41). Quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR) revealed that at 24 h, atf4, xbp1u, and xbp1s mRNA levels were significantly higher in O. tsutsugamushi-infected cells than in mock-infected cells (Fig. 1A). At 48 h, atf4 and xbp1s transcript levels were still elevated, while xbp1u expression had returned to that of control cells. This suggests that while ER stress and the UPR were still occurring at this time point, XPB1 activity had likely begun to wane, as the pool of unspliced transcripts available to generate the active form of the transcription factor was considerably reduced. By 72 h, mRNA levels of atf4, xbp1u, and xbp1s in mock-infected cells were comparable to or lower than those in control cells. An early event in the UPR that occurs upstream of the induction of atf4 and xbp1 transcription is phosphorylation of the ER-localized protein IRE1α (inositol-requiring enzyme 1α) (37). Western blot analysis confirmed that levels of phosphorylated IRE1α, but not total IRE1α, were significantly elevated in O. tsutsugamushi-infected cells at 24 but not 72 h (Fig. 1B to D). Taken together, these results indicate that O. tsutsugamushi infection temporally invokes the UPR during the first 24 to 48 h of infection, but that the UPR is no longer activated at 72 h.
FIG 1.
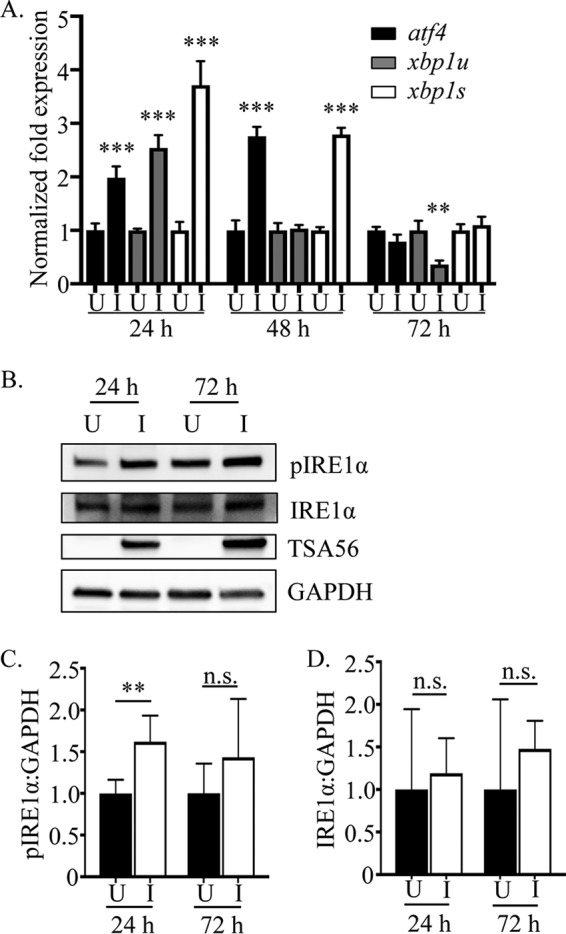
O. tsutsugamushi induces and benefits from ER stress in an amino acid-dependent manner. (A) O. tsutsugamushi infection induces UPR gene expression. Total RNAs isolated from O. tsutsugamushi-infected HeLa cells were subjected to qRT-PCR using primers targeting transcripts of ER stress-regulated genes. Relative mRNA levels of atf4, xbp1s, and xbp1u in infected samples (I) were normalized to gapdh gene transcript levels using the 2−ΔΔCT method. These values were normalized to those of mock-infected (U) samples at each respective time point. Results are representative of at least three separate experiments performed in triplicate. (B) Whole-cell lysates of mock-infected or O. tsutsugamushi-infected cells were analyzed by Western blotting and screened with antibodies specific for phosphorylated IRE1α, IRE1α, TSA56, or GADPH. (C and D) Densitometry was performed on blots from six separate experiments. Statistically significant values are indicated: **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; n.s., not significant.
ER stress benefits O. tsutsugamushi growth in an amino acid-dependent manner.
To examine if the UPR benefits O. tsutsugamushi intracellular replication, HeLa cells were infected in the presence of the ER stress inducers tunicamycin and thapsigargin or the ER stress inhibitor tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA). Tunicamycin promotes the accumulation of misfolded proteins by inhibiting N-linked glycosylation (42), while thapsigargin blocks sarco-ER calcium ATPases to deplete ER calcium stores (43). Treatment with either tunicamycin or thapsigargin activates the UPR pronouncedly more than O. tsutsugamushi, as indicated by phosphorylated IRE1α Western blotting (Fig. 2A). TUDCA is a chemical chaperone that enhances the ER folding capacity to alleviate ER stress and block the UPR (44–46). Bacterial DNA loads in chemical-treated cells, determined using qPCR, were normalized to those of vehicle control-treated cells per time point. The O. tsutsugamushi load was significantly higher in tunicamycin- and thapsigargin-treated cells at 48 h and 3- to 4-fold higher by 72 h (Fig. 2B and C). TUDCA reduced the bacterial load by approximately two-thirds at 24 h and prevented any increase at subsequent time points (Fig. 2D).
FIG 2.
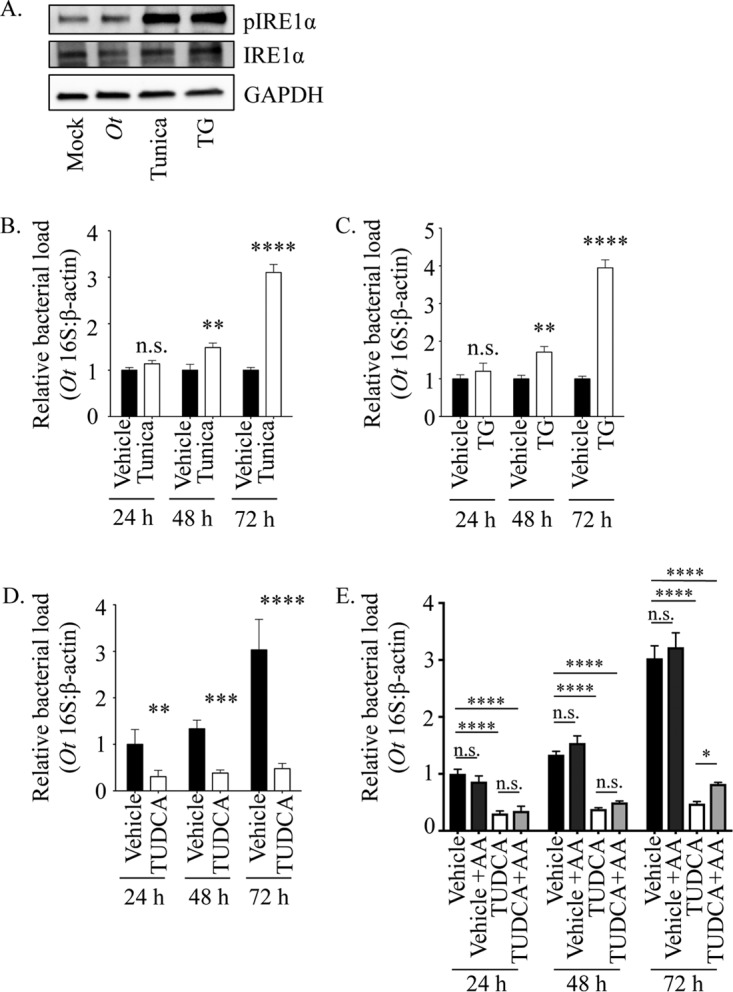
O. tsutsugamushi benefits from ER stress in an amino acid-dependent manner. (A) Whole-cell lysates of HeLa cells that were mock infected, O. tsutsugamushi infected (Ot), or treated with tunicamycin (Tunica) or thapsigargin (TG) were analyzed by Western blotting and screened with antibodies specific for phosphorylated IRE1α, IRE1α, or GADPH. (B to D) HeLa cells were treated with tunicamycin (B), TG (C), TUDCA (D), or vehicle for 1 h prior to and throughout infection with O. tsutsugamushi. Total DNA isolated at 24, 48, and 72 h was analyzed by qPCR. Relative levels of the O. tsutsugamushi 16S rRNA gene were normalized to the relative levels of β-actin by using the 2−ΔΔCT method. Resulting relative levels per treatment were normalized to those of the respective vehicle controls at each time point. (E) The TUDCA experiment was performed as described for panel D, except that an additional sample was included in which vehicle- or TUDCA-treated O. tsutsugamushi-infected HeLa cells were grown in medium containing amino acids (+AA). Statistically significant values are indicated: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001; n.s., not significant. Results are representative of at least three separate experiments performed in triplicate.
O. tsutsugamushi is a cytosolic pathogen that is auxotrophic for histidine and the aromatic amino acids (8), which necessitates that it parasitize them from its host cell. The bacterium also induces and benefits from the UPR, a cellular process that ultimately leads to the dispersal of ERAD-derived amino acids into the cytosol (8, 10, 13–15). Therefore, to determine if the UPR favors O. tsutsugamushi growth by providing amino acids, the TUDCA experiment was repeated, except that the host cells were cultivated in medium containing essential and nonessential amino acids beginning at time zero of infection. Amino acid supplementation partially rescued the TUDCA-induced bacterial growth defect but did not do so until 72 h (Fig. 2E). These data suggest that the UPR benefits O. tsutsugamushi intracellular replication in an amino acid-dependent manner and, conspicuously, the bacterium does not utilize amino acids for growth until 72 h.
O. tsutsugamushi temporally impedes ERAD.
The UPR leads to ERAD, which in turn yields amino acids in the cytosol (11, 12). Because O. tsutsugamushi induces and benefits from the UPR in an amino acid-dependent manner, the ability of cells infected with the pathogen to perform ERAD was examined. The T-cell antigen receptor (TCR), a hetero-oligomeric membrane complex composed of several transmembrane polypeptide chains, is a model for the assembly and degradation of integral membrane proteins in the ER (47). Unassembled TCRα chains are rapidly degraded by ERAD and are therefore model substrates for its study (48). HEK-293T cells, which do not naturally express the TCR, have proven useful for TCRα-based ERAD assays (49). HEK-293T cells stably expressing yellow fluorescent protein (YFP)-tagged TCRα chain (YFP-TCRα) were infected with O. tsutsugamushi for 24 or 72 h and treated with the eukaryotic protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide for 3 h prior to being assayed. Cycloheximide, which has no effect on bacterial protein synthesis, was used to verify whether ERAD was inhibited. Cells in which ERAD proceeded normally would have lower YFP-TCRα amounts post-cycloheximide treatment, because the resulting lack of translation would not replenish that which had been degraded. YFP-TCRα was efficiently degraded in mock-infected control cells, as the amount of the substrate was reduced by 63 to 82% following cycloheximide treatment (Fig. 3). Strikingly, YFP-TCRα levels were relatively unchanged in cells that had been infected for 24 h and cycloheximide treated but were reduced 3-fold in cells that had been infected for 72 h and treated with cycloheximide. These results indicate that O. tsutsugamushi impairs ERAD at 24 h but not at 72 h.
FIG 3.
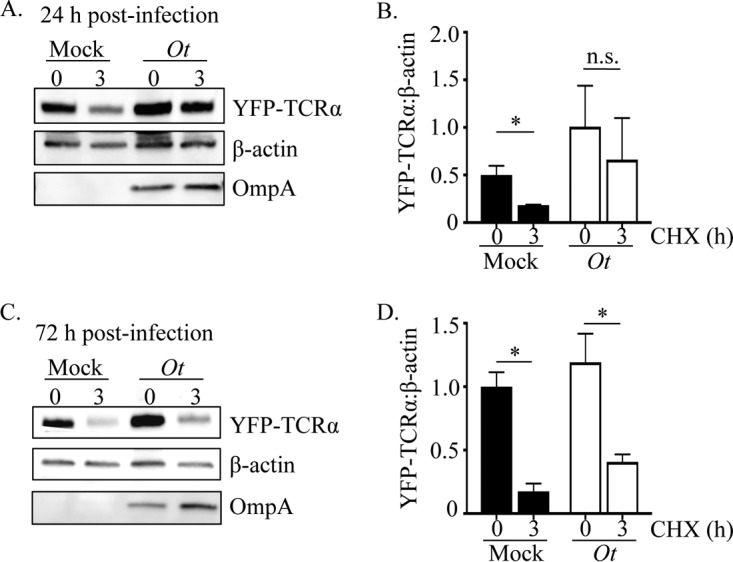
ERAD is impeded in O. tsutsugamushi-infected cells. HEK-293T cells expressing YFP-TCRα were infected with O. tsutsugamushi (Ot) for 24 (A and B) or 72 h (C and D). The cells were treated with cycloheximide for 0 or 3 h, lysed, analyzed by Western blotting, and screened with antibodies against GFP (detecting YFP), β-actin, and O. tsutsugamushi OmpA. Densitometry was performed on blots resulting from two separate experiments (B and D). Statistically significant values are indicated: *, P < 0.05; n.s., not significant.
The timing of O. tsutsugamushi-mediated ERAD inhibition is critical for bacterial growth.
O. tsutsugamushi population growth during the first 24 to 48 h of infection is minimal, but this is followed by logarithmic expansion (9). It is reasonable to presume that the bacterial demand for amino acids is initially low during the first 24 h but increases when the pathogen population prepares for/enters log-phase growth that initiates at or after 48 h. Coincident with such timing, O. tsutsugamushi induces the UPR and simultaneously inhibits ERAD during the first 48 h, which would stall production of ERAD-derived amino acids. By 72 h, when ERAD is no longer inhibited and amino acids generated by the degradative process would be present, the bacterium grows expansively (9). Moreover, amino acid supplementation restores O. tsutsugamushi growth in TUDCA-treated cells, but this complementation effect does not occur until 72 h. We therefore hypothesized that O. tsutsugamushi transiently inhibits ERAD during the first 24 h, when the pathogen does not require a large pool of amino acids, but it utilizes ERAD-derived amino acids to benefit its growth beginning between 48 and 72 h.
To test this hypothesis, we examined if sustaining ERAD inhibition beyond 48 h hindered O. tsutsugamushi growth. RNA interference was used to target Bat3 (HLA-B-associated transcript 3), also known as BAG6 or Scythe, a cytosolic chaperone that is essential for ERAD. Bat3 binds and mediates the translocation of misfolded/aggregation-prone transmembrane proteins and newly synthesized polypeptides with exposed hydrophobic stretches from ER exit sites to the 26S proteasome (11, 50). First, it was confirmed by Western blotting that Bat3 levels are unchanged in O. tsutsugamushi-infected HeLa cells (Fig. 4A and B). Next, the relative amounts of bacterial DNA were measured in HeLa cells that had been treated with Bat3 or nontargeting small interfering RNA (siRNA). Bat3 knockdown was confirmed by Western blotting (Fig. 4C). The O. tsutsugamushi DNA load in Bat3 knockdown cells was reduced by approximately 22, 46, and 53% at 24, 48, and 72 h, respectively (Fig. 4D). In support of our hypothesis, free amino acid supplementation restored bacterial growth in Bat3 knockdown cells at 48 h and 72 h but not at 24 h.
FIG 4.
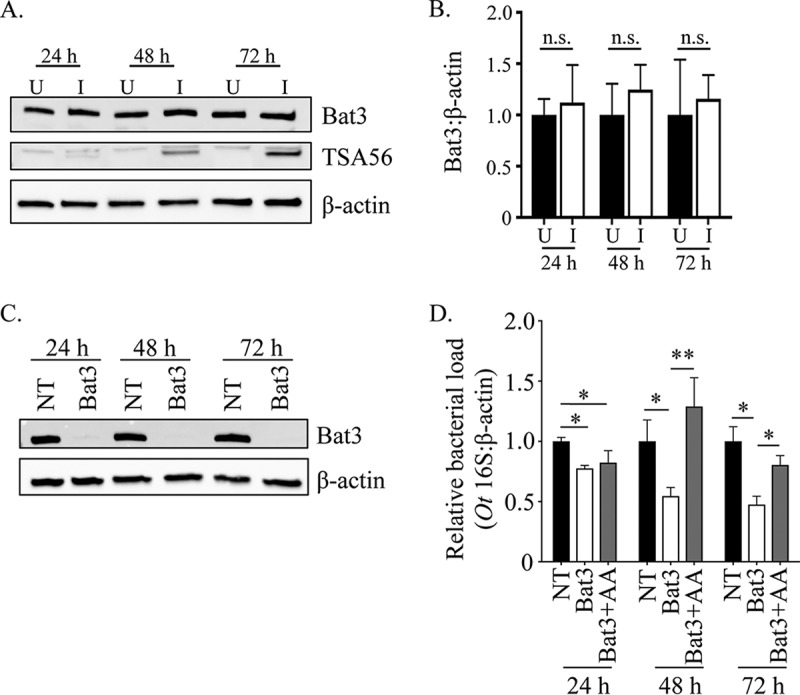
The timing of O. tsutsugamushi-mediated ERAD inhibition is important for bacterial growth. (A and B) O. tsutsugamushi infection does not alter Bat3 cellular levels. (A) Whole-cell lysates of O. tsutsugamushi infected (I) or uninfected (U) HeLa cells were subjected to Western blotting using Bat3, TSA56, and β-actin antibodies. (B) Densitometry was performed on blots from three separate experiments. (C and D) Inhibition of O. tsutsugamushi growth resulting from siRNA-mediated knockdown of Bat3 can be rescued by free amino acid supplementation. HeLa cells were treated with Bat3-targeting (Bat3) or nontargeting (NT) siRNA for 48 h, followed by infection with O. tsutsugamushi. Bat3-targeting siRNA-treated cells were cultivated in media that were either supplemented with amino acids (+AA) or not, while nontargeting siRNA-treated infected cultures were grown in medium alone. At 24, 48, and 72 h postinfection, total DNA was isolated or whole-cell lysate was generated from each sample. (C) Western blotting of whole-cell lysates of treated and control cells were screened with antibody against Bat3 or host β-actin to confirm knockdown. (D) Relative levels of the O. tsutsugamushi 16S rRNA gene were normalized to levels of β-actin by using the 2−ΔΔCT method. Resulting relative levels per treatment were normalized to those of the respective vehicle control at each time point. Statistically significant values are indicated: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; n.s., not significant. Results are representative of at least three separate experiments performed in triplicate.
O. tsutsugamushi Ank4 interacts with host Bat3.
Simultaneous with our studies that revealed that O. tsutsugamushi modulates ERAD, we performed a series of yeast two-hybrid screens to identify potential interacting partners of various ER-tropic Anks, one of which was Ank4. The O. tsutsugamushi strain Ikeda Ank4 is a 45-kDa protein that is 392-amino acids in length, carries 7 ankyrin repeats arranged in tandem and a C-terminal F-box domain that we confirmed to interact with SKP1 and nucleate the SCF1 ubiquitin ligase complex (28, 51). The Ikeda strain genome carries two identical ank4 copies (51). As determined using the BLASTP algorithm, Ikeda Ank4 is conserved among O. tsutsugamushi strains Boryong, Gilliam, and Woods which were isolated from scrub typhus patients in Korea, Burma, and Australia, respectively (Table 1) (52–54). Several prey proteins in the Ank4 screen had high predicted biological (PDB) scores, an indication of the probability that the interaction was valid (Table 2) (55). One such candidate was SKP1, which, given our previous study results (28, 51), further strengthened confidence in the validity of the interactions. Notable among the other high-PDB-scoring candidates was Bat3. Because genetic manipulation of O. tsutsugamushi at a specific locus is not possible, the putative Ank4-Bat3 interaction was validated by coimmunoprecipitation. Immunoprecipitating Flag-tagged versions of Ank4, Ank4 lacking the F-box (Ank4ΔF-box), and the negative control, bacterial alkaline phosphatase (BAP), from transfected HeLa cells and screening the resulting Western blots with Bat3 antibody demonstrated that Flag-Ank4 and Flag-Ank4ΔF-box coimmunoprecipitated Bat3 (Fig. 5A). Despite having an F-box, Ank4 did not appear to alter the electrophoretic mobility or promote degradation of Bat3, as no difference in the apparent molecular weight or band intensity level of Bat3 coimmunoprecipitated by Flag-Ank4 versus Flag-Ank4ΔF-box was apparent. Quantifying Bat3 levels in HeLa cells expressing Flag-BAP, Flag-Ank4, and Flag-Ank4ΔF-box by using Western blotting and densitometry confirmed that its levels were similar in all three transfected cell populations (Fig. 5B and C). Thus, Ank4 interacts with Bat3 in an F-box-independent manner but does not alter its cellular levels or electrophoretic mobility.
TABLE 1.
Ank4 sequence conservation in O. tsutsugamushi strains
| Strain | Ank4 homologue | Conservation with Ikeda Ank4 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % coverage | % nucleotide identity | % amino acid identity | ||
| Boryong | WP_011944711.1 | 100 | 90.4 | 81.7 |
| WP_011944257.1 | 100 | 74.6 | 62.5 | |
| Gilliam | WP_047220544.1 | 100 | 84.9 | 72.2 |
| WP_047220972.1 | 100 | 63 | ||
| Woods | Genome annotation not published | 75.6 | 84.9 | 74.2 |
TABLE 2.
Ank4 candidate interacting partners identified via yeast two-hybrid analysis
| Candidate | Name and function | PBSa | No. of positive clones/total XX |
|---|---|---|---|
| SKP1 | S-phase kinase-associated protein 1; binds F-box in the SCF1 ubiquitin ligase complex | A | 22/197 |
| Bat3 | HLA-B-associated transcript 3 (also known as Bag6 and Scythe); ERAD chaperone, regulator of p53, HSP70, and apoptosis | C | 2/197 |
| HSP90AB1 | Heat shock protein 90-kDa alpha (cytosolic), class B member 1; role in protein folding and signal transduction | A | 28/197 |
| HIF1AN | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha subunit inhibitor; functions as oxygen sensor | A | 6/197 |
| VCPIP | Valosin-containing protein p97/p47 complete interacting protein 1; deubiquitinating enzyme, involved in postmitosis Golgi complex reassembly | C | 2/197 |
The predicted biological score (PBS) was calculated for each candidate protein to assess the reliability of each interaction, ranging from the highest probability of specificity (score of A) to the lowest probability of specificity (score of E) between two proteins.
FIG 5.
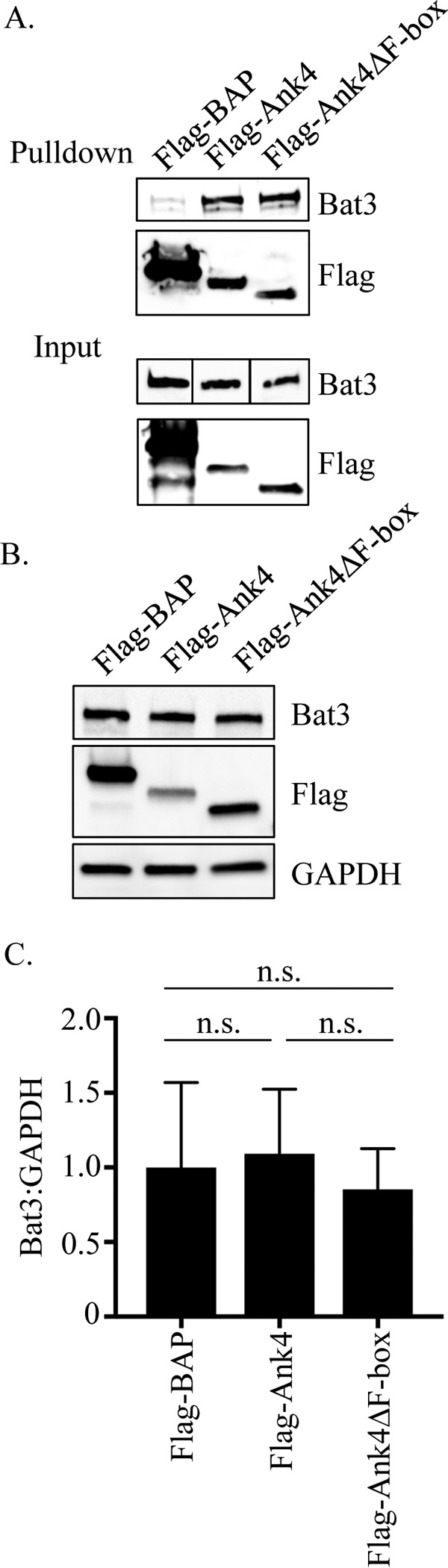
Ectopically expressed Ank4 precipitates endogenous Bat3 but does not alter Bat3 cellular levels. (A) Flag-Ank4 precipitates Bat3 in an F-box-independent manner. Whole-cell lysates of transfected HeLa cells expressing Flag-tagged BAP, Ank4, or Ank4ΔF-box were incubated with Flag affinity resin to precipitate Flag-tagged proteins and coprecipitate interacting proteins. Eluted proteins were analyzed by Western blotting and screened with Bat3 antibody. Input samples corresponding to 3% of each lysate used for precipitation were also probed. Vertical lines between the lanes in the input samples indicate that irrelevant lanes of the blot were removed. Flag protein expression and pulldown were confirmed by stripping and reprobing the blots with Flag antibody. (B and C) Flag-Ank4 does not alter endogenous Bat3 cellular levels. Whole-cell lysates of HeLa cells transfected to express Flag-BAP, Flag-Ank4, or Flag-Ank4ΔF-box were subjected to Western blotting using Bat3, Flag tag, and GADPH antibodies (B). The means ± standard deviations of the ratios of Bat3 to GADPH densitometric signals from three separate experiments were determined (C). Data are representative of three experiments with similar results.
O. tsutsugamushi temporally expresses Ank4 early during infection.
In our previous report, ank4 transcript was detected by RT-PCR in L929 cells that had been infected with O. tsutsugamushi strain Ikeda for several days and in which the infection had become asynchronous (32). Whether the bacterium temporally expresses ank4, particularly within the 72-h window examined for infection experiments here, was unknown. To fill this knowledge gap, total RNA isolated at 2, 4, 8, 12, 24, 48, and 72 h from infected HeLa cells was analyzed by qRT-PCR for ank4 expression normalized to that of O. tsutsugamushi 16S rRNA. Whereas 16S rRNA expression was detected at all time points (Fig. 6A), ank4 expression was detected only at 8 and 12 h, the latter time point being when it was in the greatest abundance (Fig. 6B). Thus, O. tsutsugamushi expresses ank4 only during the initial hours of infection.
FIG 6.
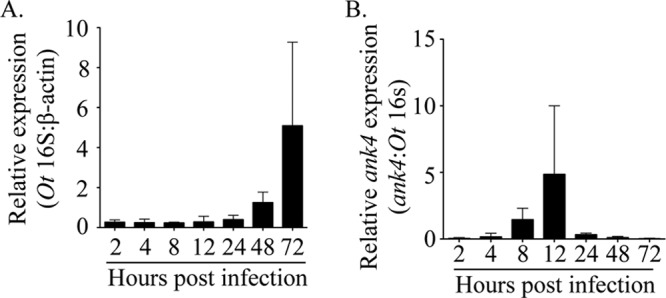
Ank4 is expressed early in infection. HeLa cells were infected with O. tsutsugamushi. At the postinfection time points indicated, total RNA was isolated and subjected to qRT-PCR analysis using primers targeting O. tsutsugamushi ank4 and 16S rRNA and human β-actin. The 2−ΔΔCT method was used to determine the relative 16S rRNA expression level normalized to that of β-actin (A), and the relative ank4 expression level was normalized to that of 16S rRNA (B). Results shown are representative of three experiments with similar results.
Ectopically expressed Ank4 phenocopies O. tsutsugamushi infection by impairing ERAD.
Because O. tsutsugamushi temporally blocks ERAD and transcriptionally expresses Ank4 in the period when it does so, Ank4 itself was directly assessed for the ability to impede ERAD. HEK-293T cells stably expressing YFP-TCRα were transfected to also express Flag-tagged Ank4, Ank4ΔF-box, or BAP. YFP-TCRα levels in cells expressing Flag-Ank4 were approximately 50% higher than in cells expressing Flag-BAP (Fig. 7A and B). The difference in YFP-TCRα levels in cells expressing Flag-Ank4ΔF-box was not statistically significantly different from levels in cells expressing either Flag-BAP or Flag-Ank4. These data confirm that Ank4 impairs ERAD, and they imply a possible contributory role of its F-box motif in its ability to do so.
FIG 7.
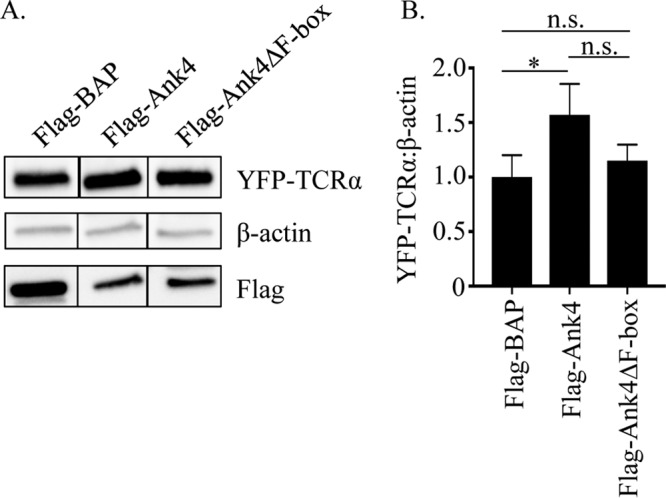
ERAD is impeded in cells ectopically expressing Ank4. (A) Western blots of lysates from HEK-293T cells stably expressing YFP-TCRα transfected to also express Flag-tagged BAP, Ank4, or Ank4ΔF-box were screened with antibodies that recognize YFP, β-actin, and the Flag tag. Vertical lines between the lanes indicate that irrelevant lanes of the blot were removed. (B) Densitometry was performed on blots resulting from three separate experiments. Statistically significant values are indicated: *, P < 0.05; n.s., not significant.
DISCUSSION
Microbial acquisition of host nutrients is essential for the development of infectious disease. This is especially true for obligate intracellular bacteria, which are auxotrophic for essential metabolites. Bacterial, viral, and protozoan pathogens induce ER stress, and for some the ensuing UPR supports their intracellular replication. Until this report, however, the molecular events downstream of the UPR that these organisms orchestrate to enable their growth were undefined. We identified O. tsutsugamushi as the first example of an intracellular pathogen that modulates ERAD to time the availability of ERAD-derived amino acids it parasitizes for growth. By inducing the UPR and inhibiting ERAD in the first 24 to 48 h of infection, O. tsutsugamushi creates a stockpile of misfolded proteins in the ER that is not degraded until 48 to 72 h, when the bacterium allows for ERAD to proceed. This model is supported by the following observations. Tunicamycin and thapsigargin, which induce the UPR by distinct mechanisms (42, 43), enhance O. tsutsugamushi replication, while TUDCA inhibits it. The TUDCA-associated growth defect is partially rescued by the addition of amino acids at 0 h, but the complementation does not occur until 72 h. O. tsutsugamushi infection inhibits ERAD of YFP-TCRα at 24 h, but not 72 h. Sustained inhibition of ERAD via knockdown of Bat3 at 72 h reduces O. tsutsugamushi replication, and this growth defect is also rescued by free amino acid supplementation.
Sustained Bat3 knockdown does not abolish O. tsutsugamushi growth, which could be due to compensatory actions of uncharacterized mechanisms that the pathogen utilizes to meet its nutritional virulence requirements. O. tsutsugamushi elicits but is not cleared by autophagy (56, 57), autophagy is induced by and decreases ER stress (58), and amino acids resulting from autophagy benefit the intracellular growth of Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Ehrlichia chaffeensis (59, 60), which are obligate intracellular bacteria that are in the order Rickettsiales with O. tsutsugamushi. Amino acids resulting from the autophagy response to O. tsutsugamushi-induced ER stress might enable the bacterium to grow, albeit less efficiently, when ERAD is inhibited in Bat3 knockdown cells.
Given the proximity of O. tsutsugamushi to the ER, Ank4 translocated by the bacterium's type 1 secretion system during infection would have easy access to Bat3, which is recruited to the cytosolic face of the ER membrane during the UPR (11). Moreover, the ability of O. tsutsugamushi to modulate ERAD is linked, at least in part, to Ank4 interacting with Bat3. In addition to the Ank4-Bat3 interaction identified via yeast two-hybrid analysis, ectopically expressed Ank4 pulls down endogenous Bat3, and the bacterium expresses ank4 only during the period when it inhibits ERAD. During the first 24 to 48 h of O. tsutsugamushi infection, when ERAD is inhibited, xbp1 and xbp1s mRNA levels are increased, but not at 72 h when ERAD is no longer hindered. Ank9, an O. tsutsugamushi effector that traffics in the retrograde direction from the Golgi complex to the ER, invokes the UPR and inhibits the secretory pathway (34). Therefore, the pathogen minimally employs Ank9 to invoke ER stress while also utilizing Ank4 to modulate the ensuing UPR and ERAD to bolster its growth. Other intracellular bacterial effectors, including Brucella species TcpB and Listeria monocytogenes listeriolysin O, and extracellular bacterial toxins, such as Vibrio cholerae cholera toxin and Escherichia coli subtilase and Shiga toxin 1, induce the UPR and/or ER morphological changes (10, 61–71). To our knowledge, Ank4 stands unique as the only bacterial protein identified thus far that modulates ERAD.
Ank4 is not the only bacterial protein that interacts with Bat3. Effectors LegU1 and Lpg2160 of the facultative intracellular bacterial pathogen Legionella pneumophila nonexclusively associate with Bat3. Like LegU1, Ank4 is an F-box-containing protein that binds Bat3 in an F-box-independent manner (72). Unlike LegU1, Ank4 likely does not polyubiquitinate Bat3, as the apparent molecular weight and cellular level of Bat3 are unchanged in cells infected with O. tsutsugamushi compared to uninfected cells and in cells ectopically expressing Ank4 versus Ank4-ΔFbox. Rather than stimulate the UPR, L. pneumophila suppresses the UPR by multiple mechanisms, including blocking xbp1u splicing and inhibiting translation of BiP and CHOP (73, 74). In addition to being a chaperone for ERAD, Bat3 regulates apoptosis, Hsp70 stability, and p53-related expression (75–78). Thus, even though O. tsutsugamushi and L. pneumophila both target Bat3, they might do so for different purposes.
The abilities of Ank4 and LegU1 to bind both Bat3 and SKP1 reflect an emerging theme of individual bacterial effectors interacting with two distinct host cell proteins to interface with two distinct cellular processes. O. tsutsugamushi Ank9, like Ank4 and LegU1, bears a C-terminal F-box (28, 72). In addition to binding SKP1 and nucleating the SCF complex in an F-box-dependent manner, Ank9 binds COPB2, which directs in the retrograde direction from the Golgi complex to the ER (28, 34). Yet another F-box-containing Ank is L. pneumophila AnkX, which exploits SKP1 to mediate ubiquitination and subsequent proteosomal degradation of unknown host cell protein substrates to ultimately yield free amino acids that are essential for the bacterium's intracellular growth (79, 80). AnkX exploits another eukaryotic process, farnesylation, to mediate its association with the Legionella-containing vacuole (81). Finally, Coxiella burnetii AnkG binds both host p32 and importin-α1 in order to traffic into the nucleus and inhibit apoptosis (82, 83).
Deciphering themes in the nutritional virulence strategies of intracellular pathogens will not only advance understanding of microbial pathogenesis, but also may lead to novel treatments for infectious diseases. TUDCA is being evaluated in humans as a treatment for UPR-related metabolic syndromes (84, 85). Here, we demonstrated that TUDCA inhibits O. tsutsugamushi growth, a result that phenocopies the inhibition achieved by extended Bat3 knockdown and thereby supports our model that the bacterium nutritionally benefits from temporally modulating the UPR and ERAD. Likewise, TUDCA prevents intracellular replication of B. abortus, B. suis vaccine strain 2, tick-borne encephalitis virus, and influenza A virus, each of which invoke and benefit from the UPR (61, 63, 86, 87). Perhaps like O. tsutsugamushi these pathogens stimulate the UPR to support their growth in an ERAD-dependent manner. Due to its excellent safety profile and low cost, TUDCA has been recommended as a possible therapeutic treatment against brucellosis (61). TUDCA could be considered a potential nonantibiotic treatment of scrub typhus, especially because the intracellular lifestyle of O. tsutsugamushi makes it naturally resistant to many antibiotics, and tetracycline- and chloramphenicol-resistant cases of scrub typhus have been reported (88, 89).
In summary, we identified a novel strategy used by an obligate intracellular bacterium to finely modulate cellular homeostatic processes to facilitate its replication. This may be a common strategy employed by diverse intracellular pathogens and for the first time offers an explanation as to why such bacteria benefit from invoking the UPR: the amino acids generated by ERAD support their growth. Finally, this study identified the UPR and ERAD pathways that O. tsutsugamushi modulates as possible pharmacologic targets for treating scrub typhus.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cultivation of uninfected and O. tsutsugamushi-infected host cells.
HeLa cells (CCL-2; American Type Culture Collection, Manassas, VA) were maintained as previously described (15). HEK-293T cells expressing YFP-TCRα (88), kindly provided by Yihong Ye (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD) were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM; Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Gemini Bio-Products), 2 mM l-glutamine, 1× MEM nonessential amino acids (Invitrogen), and 15 mM HEPES and maintained at 37°C in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. Infection with the O. tsutsugamushi Ikeda strain was maintained in HeLa cells by the addition of O. tsutsugamushi organisms recovered from heavily infected cells that had been mechanically disrupted using glass beads and incubated at 35°C in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. Mock infections corresponded to the addition of mechanically disrupted uninfected host cells to recipient cells.
Plasmid constructs.
The p3XFLAG-CMV-7-BAP control plasmid was purchased from Sigma-Alrich (St. Louis, MO). pFlag-Ank4, previously designated pFlag-Ank4_01, has been described elsewhere (15). pFlag-Ank4ΔF-box was generated as described previously (11).
Antibodies.
Antibodies used were sera from a scrub typhus patient (a kind gift from Wei-Mei Ching, Naval Medical Research Center, Silver Spring, MD), rat anti-O. tsutsugamushi OmpA serum (11), rabbit anti-TSA56 (34), rabbit anti-reticulon 4 (LifeSpan Biosciences, Seattle, WA), mouse anti-Bat3 (Abcam, Cambridge, UK), rabbit anti-phospho-IRE1α (Abcam), goat anti-IRE1α (Abcam), mouse anti-β-actin (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA), rabbit anti-green fluorescent protein (anti-GFP; Santa Cruz Biotechnology), mouse anti-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (anti-GAPDH; Santa Cruz Biotechnology), fluorescein-conjugated rat anti-human IgG (a kind gift from Wei-Mei Ching, Naval Medical Research Center, Silver Spring, MD), Alexa Fluor 594-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (Invitrogen), Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (Invitrogen), Alexa Fluor 405-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG (Invitrogen), horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated horse anti-rabbit IgG (Cell Signaling Technology), HRP-conjugated horse anti-mouse IgG (Cell Signaling Technology), HRP-conjugated goat anti-rat IgG (Thermo Scientific, Rockford, IL), and HRP-conjugated rabbit anti-goat IgG (Millipore Sigma, Burlington, MA).
Immunofluorescence microscopy.
HeLa cells grown on coverslips were incubated with O. tsutsugamushi organisms at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 10 for 2 h, followed by washing, and replacement of the medium. An MOI of 10 was selected because it is reflective of the number of O. tsutsugamushi organisms observed within leukocytes in the eschars of human scrub typhus patients (90). At various time points postinfection, the cells were fixed and screened with TSA56 antibody, followed by incubation with Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG and staining with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI).
qRT-PCR and qPCR.
HeLa cells were infected with O. tsutsugamushi, and the inoculum was removed at 1 h. At 2, 4, 8, 12, 24, 48, and 72 h postinfection, total RNA was isolated using the RNeasy minikit (Qiagen, Germantown, MD). Genomic DNA was removed by treatment with amplification-grade DNase (Invitrogen). cDNA synthesis was performed with 1 μg of each RNA sample by using the iScript Supermix cDNA synthesis kit (Bio-Rad). Oligonucleotide primers used in these studies are listed in Table 3. RNA was confirmed to be free of contaminating DNA by PCR using O. tsutsugamushi 16S rRNA gene-specific and β-actin gene-specific primers. qRT-PCR analysis of each sample was performed using SsoFast EvaGreen supermix (Bio-Rad). Relative O. tsutsugamushi 16S rRNA gene levels were normalized to the those of β-actin by using the 2−ΔΔCT method (90). Relative ank4 levels were normalized to the transcript levels of the O. tsutsugamushi 16S rRNA gene by using the 2−ΔΔCT method. To determine the effect of ER stress on the O. tsutsugamushi DNA load, confluent HeLa cell cultures in 6-well plates were treated with 500 μg/ml TUDCA (Sigma-Aldrich), 2.5 μg/ml tunicamycin (Sigma-Aldrich), 1 μM thapsigargin (Sigma-Aldrich), or vehicle for 1 h. The cells were then incubated with O. tsutsugamushi organisms at an MOI of 10 for 2 h. The inoculum was removed, the cells were washed with phosphate-buffered saline, and fresh medium containing each ER stress modulator or vehicle was added. Medium containing drug or vehicle was replaced every 24 h. DNA was isolated at 24, 48, and 72 h by using the DNeasy blood and tissue kit (Qiagen). One hundred nanograms of each DNA sample was analyzed in triplicate with primers specific for O. tsutsugamushi 16S rRNA and host cell β-actin genes. In some cases, TUDCA-treated cultures were cultivated in media containing essential and nonessential amino acids (Sigma-Aldrich).
TABLE 3.
Oligonucleotides used in this study
| Designationa | Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| β-Actin F | AGAGGGAAATCGTGCGTGAC |
| β-Actin R | CAATAGTGATGACCTGGCCGT |
| Ot 16S-911F | GTGGAGCATGCGGTTTAATTCGATGATC |
| Ot 16S-1096R | TAAGAATAAGGGTTGCGCTCGTTGC |
| ank4-1F | AATAACGGTAATTTATTACAT |
| ank4-122F | CATGAGGGTGGCTTTAGTCTTGCTG |
| ank4-287F | ATGCAAATATGGTCATGCTTTTGTT |
| ank4-349R | CGTCTGTACATGGTACATTGACATTAGCTCC |
| ank4-1176R | GAGATAATAGTGGTAAAATTCCTGCACAT |
| atf4 F | CAACAACAGCAAGGAGGATG |
| atf4 R | AATTGGGTTCACCGTCTGG |
| xbp1s F | TCCGCAGCAGGTGCAGGC |
| xbp1s R | GAAAGGGAGGCTGGTAAGG |
| xbp1u F | TCCGCAGCACTCAGACTAC |
| xbp1u R | TCCAAGTTGTCCAGAATGCC |
| gapdh F | ACATCATCCCTGCCTCTACTGG |
| gapdh R | TCCGACGCCTGCTTCACC |
F and R refer to primers that bind to the sense or antisense strand, respectively.
Analysis of ank4 conservation among O. tsutsugamushi strains.
Genomic DNAs from O. tsutsugamushi strain Gilliam and strain Woods were used as the templates for PCR, using O. tsutsugamushi strain Ikeda ank4 gene-specific primers (Table 3). Primer pair ank4-1F and ank4-1176R, which targets Ikeda ank4 nucleotides 1 to 1176, was used to generate an amplicon from Gilliam DNA. Primer pair ank4-287F and ank4-1176R, which targets Ikeda ank4 nucleotides 287 to 1176 of ank4, was used to generate an amplicon from strain Woods DNA, as PCR using ank4-1F did not amplify DNA. The PCR products were purified using a QIAquick gel extraction kit (Qiagen, Germantown, MD) and cloned into pcDNA3.1 (Invitrogen) as instructed by the manufacturer. Insert integrity was verified by nucleotide sequence analysis. Alignments of the nucleotide and translated protein sequences with those of strain Ikeda were performed using Clustal W (http://www.ch.embnet.org/software/ClustalW.html). The sequences were then searched against the nucleotide collection and nonredundant protein sequences databases by using nucleotide and protein BLAST analysis (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool) (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi).
Yeast two-hybrid analysis.
ULTImate yeast two-hybrid analysis was performed by Hybrigenics Services (Paris, France). The coding sequence for mammalian codon-optimized O. tsutsugamushi strain Ikeda ank4 (amino acids 4 to 392) was PCR amplified and cloned into the pB27 construct as an N-terminal fusion with LexA (N-LexA-Ank4-C). After confirming sequence fidelity, the construct was introduced into yeast as bait and screened by mating with yeast bearing a randomly primed human placental cDNA library (prey). Because O. tsutsugamushi infects multiple mammalian host cell types, the placental library offered the best representation of the human proteome for identifying potential Ank4 interactions. Positively selected clones were isolated, and the corresponding prey fragments were PCR amplified, sequenced, and identified using the NCBI GenBank Database with BLASTP. A predicted biological score (PBS) was calculated for each candidate to assess the reliability of each interaction, ranging from the highest probability of specificity (score of A) to the lowest probability of specificity (score of E) between two proteins (53).
Flag pulldown assays.
Precipitation of Flag-tagged proteins and Western blot analyses of the resulting eluates were performed exactly as described previously (34).
Analysis of Bat3 protein levels in Ank4-expressing and O. tsutsugamushi-infected cells.
HeLa cells in 25-cm2 flasks were transfected with 4 μg of plasmid to express Flag-BAP, Flag-Ank4, or Flag-Ank4ΔF-box for 18 to 24 h. Cells were collected and lysed in radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer, and 15 μg of each cell lysate was analyzed by Western blotting using Bat3 and GAPDH antibodies for protein-level analysis or Flag antibody to confirm the expression of the Flag-tagged proteins of interest. In some cases, mock- or O. tsutsugamushi-infected HeLa cells were assessed via Western blotting at 24, 48, or 72 h postinfection using Bat3, β-actin, and O. tsutsugamushi TSA56 antibodies.
Bat3 siRNA knockdown.
HeLa cells were transfected with Bat3 or nontargeting ON-TARGETplus SMARTpool siRNA (GE Dharmacon, Lafayette, CO). After 48 h, the medium was replaced and the cells were infected with O. tsutsugamushi at an MOI of 10. In some experiments, infected cells were cultivated in medium containing amino acids. Isolated DNA was subjected to qPCR to assess the bacterial DNA load, and whole-cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting to confirm knockdown.
ERAD assay.
HEK-293T cells expressing YFP-TCRα were transfected with pFlag-BAP, pFlag-Ank4, or pFlag-Ank4ΔF-box for 18 h. Mock- or O. tsutsugamushi-infected HEK-293T cells expressing YFP-TCRα were incubated for 24 or 72 h. Duplicate samples were treated with 50 μg/ml cycloheximide or ethanol vehicle control for 3 h, followed by Western blotting.
Statistical analyses.
Statistical analyses were performed using the Prism 5.0 software package (GraphPad, San Diego, CA). One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey's post hoc test was used to test for significant differences among groups. For the experiment in which the O. tsutsugamushi DNA load was assessed in infected HeLa cells treated with TUDCA with or without amino acid supplementation, relative bacterial loads were log transformed and then subjected to ANOVA with a Tukey's HSD post hoc analysis. The Student t test was used to test for a significant difference among pairs. Statistical significance was set at a P value of < 0.05.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Yihong Ye (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD) for providing the YFP-TCRα-expressing HEK293T cell line, Wei-Mei Ching (U.S. Medical Research Center, Silver Spring, MD) for providing O. tsutsugamushi antiserum and fluorescein-conjugated rat anti-human IgG, George Belov (University of Maryland, College Park, MD) for providing the pCMV-GLuc plasmid, Haley E. Adcox (Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA) for technical assistance, and Margaret Park (University of South Florida, Tampa, FL) for assistance with statistical analyses.
This work was funded by the National Institutes of Health (grants AI123346 and AI128152 to Jason A. Carlyon), American Heart Association (grant 13GRNT16810009 to Jason A. Carlyon and grant 13PRE16840032 to Lauren VieBrock), the U.S. Military Infectious Diseases Research Program (grant A1230 to Allen L. Richards), and Virginia Commonwealth University (Presidential Research Quest Fund grant to Jason A. Carlyon). LSCM was performed at the VCU Microscopy Facility, which is supported in part by funding from NIH-NCI Cancer Center grant P30 CA016059.
The views expressed in this presentation are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official policy or position of the Department of the Navy, Department of Defense, U.S. Government.
REFERENCES
- 1.Paris DH, Shelite TR, Day NP, Walker DH. 2013. Unresolved problems related to scrub typhus: a seriously neglected life-threatening disease. Am J Trop Med Hyg 89:301–307. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.13-0064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ghorbani RP, Ghorbani AJ, Jain MK, Walker DH. 1997. A case of scrub typhus probably acquired in Africa. Clin Infect Dis 25:1473–1474. doi: 10.1086/516990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Osuga K, Kimura M, Goto H, Shimada K, Suto T. 1991. A case of Tsutsugamushi disease probably contracted in Africa. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 10:95–96. doi: 10.1007/BF01964418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Balcells ME, Rabagliati R, Garcia P, Poggi H, Oddo D, Concha M, Abarca K, Jiang J, Kelly DJ, Richards AL, Fuerst PA. 2011. Endemic scrub typhus-like illness, Chile. Emerg Infect Dis 17:1659–1663. doi: 10.3201/eid1709.100960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Weitzel T, Dittrich S, Lopez J, Phuklia W, Martinez-Valdebenito C, Velasquez K, Blacksell SD, Paris DH, Abarca K. 2016. Endemic scrub typhus in South America. N Engl J Med 375:954–961. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1603657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Izzard L, Fuller A, Blacksell SD, Paris DH, Richards AL, Aukkanit N, Nguyen C, Jiang J, Fenwick S, Day NP, Graves S, Stenos J. 2010. Isolation of a novel Orientia species (O. chuto sp. nov.) from a patient infected in Dubai. J Clin Microbiol 48:4404–4409. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01526-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Taylor AJ, Paris DH, Newton PN. 2015. A systematic review of mortality from untreated scrub typhus (Orientia tsutsugamushi). PLoS Negl Trop Dis 9:e0003971. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Min CK, Yang JS, Kim S, Choi MS, Kim IS, Cho NH. 2008. Genome-based construction of the metabolic pathways of Orientia tsutsugamushi and comparative analysis within the Rickettsiales order. Comp Funct Genomics 2008:623145. doi: 10.1155/2008/623145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Giengkam S, Blakes A, Utsahajit P, Chaemchuen S, Atwal S, Blacksell SD, Paris DH, Day NP, Salje J. 2015. Improved quantification, propagation, purification and storage of the obligate intracellular human pathogen Orientia tsutsugamushi. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 9:e0004009. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Celli J, Tsolis RM. 2015. Bacteria, the endoplasmic reticulum and the unfolded protein response: friends or foes? Nat Rev Microbiol 13:71–82. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro3393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kawahara H, Minami R, Yokota N. 2013. BAG6/BAT3: emerging roles in quality control for nascent polypeptides. J Biochem 153:147–160. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvs149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ruggiano A, Foresti O, Carvalho P. 2014. Quality control: ER-associated degradation: protein quality control and beyond. J Cell Biol 204:869–879. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201312042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Saric T, Graef CI, Goldberg AL. 2004. Pathway for degradation of peptides generated by proteasomes: a key role for thimet oligopeptidase and other metallopeptidases. J Biol Chem 279:46723–46732. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406537200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Reits E, Griekspoor A, Neijssen J, Groothuis T, Jalink K, van Veelen P, Janssen H, Calafat J, Drijfhout JW, Neefjes J. 2003. Peptide diffusion, protection, and degradation in nuclear and compartments before antigen presentation by MHC class I. Immunity 18:97–108. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(02)00511-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Falk K, Rotzschke O, Rammensee HG. 1990. Cellular peptide composition governed by major histocompatibility complex class I molecules. Nature 348:248–251. doi: 10.1038/348248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Byun H, Gou Y, Zook A, Lozano MM, Dudley JP. 2014. ERAD and how viruses exploit it. Front Microbiol 5:330. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hasnain SZ, Prins JB, McGuckin MA. 2016. Oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress in beta-cell dysfunction in diabetes. J Mol Endocrinol 56:R33–R54. doi: 10.1530/JME-15-0232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Engin F. 2016. ER stress and development of type 1 diabetes. J Investig Med 64:2–6. doi: 10.1097/JIM.0000000000000229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kharabi Masouleh B, Chevet E, Panse J, Jost E, O'Dwyer M, Bruemmendorf TH, Samali A. 2015. Drugging the unfolded protein response in acute leukemias. J Hematol Oncol 8:87. doi: 10.1186/s13045-015-0184-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Rivas A, Vidal RL, Hetz C. 2015. Targeting the unfolded protein response for disease intervention. Expert Opin Ther Targets 19:1203–1218. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2015.1053869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Jiang D, Niwa M, Koong AC. 2015. Targeting the IRE1α-XBP1 branch of the unfolded protein response in human diseases. Semin Cancer Biol 33:48–56. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2015.04.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kato H, Nishitoh H. 2015. Stress responses from the endoplasmic reticulum in cancer. Front Oncol 5:93. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2015.00093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Dandekar A, Mendez R, Zhang K. 2015. Cross talk between ER stress, oxidative stress, and inflammation in health and disease. Methods Mol Biol 1292:205–214. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2522-3_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Guo B, Li Z. 2014. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in hepatic steatosis and inflammatory bowel diseases. Front Genet 5:242. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nagelkerke A, Bussink J, Sweep FC, Span PN. 2014. The unfolded protein response as a target for cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1846:277–284. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2014.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jernigan KK, Bordenstein SR. 2014. Ankyrin domains across the Tree of Life. PeerJ 2:e264. doi: 10.7717/peerj.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Voth DE. 2011. ThANKs for the repeat: intracellular pathogens exploit a common eukaryotic domain. Cell Logist 1:128–132. doi: 10.4161/cl.1.4.18738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Beyer AR, VieBrock L, Rodino KG, Miller DP, Tegels BK, Marconi RT, Carlyon JA. 2015. Orientia tsutsugamushi strain Ikeda ankyrin repeat-containing proteins recruit SCF1 ubiquitin ligase machinery via poxvirus-like F-box motifs. J Bacteriol 197:3097–3109. doi: 10.1128/JB.00276-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Min CK, Kwon YJ, Ha NY, Cho BA, Kim JM, Kwon EK, Kim YS, Choi MS, Kim IS, Cho NH. 2014. Multiple Orientia tsutsugamushi ankyrin repeat proteins interact with SCF1 ubiquitin ligase complex and eukaryotic elongation factor 1 alpha. PLoS One 9:e105652. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lee EK, Diehl JA. 2014. SCFs in the new millennium. Oncogene 33:2011–2018. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Ohashi N, Koyama Y, Urakami H, Fukuhara M, Tamura A, Kawamori F, Yamamoto S, Kasuya S, Yoshimura K. 1996. Demonstration of antigenic and genotypic variation in Orientia tsutsugamushi which were isolated in Japan, and their classification into type and subtype. Microbiol Immunol 40:627–638. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1996.tb01120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.VieBrock L, Evans SM, Beyer AR, Larson CL, Beare PA, Ge H, Singh S, Rodino KG, Heinzen RA, Richards AL, Carlyon JA. 2014. Orientia tsutsugamushi ankyrin repeat-containing protein family members are Type 1 secretion system substrates that traffic to the host cell endoplasmic reticulum. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 4:186. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2014.00186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kim SW, Ihn KS, Han SH, Seong SY, Kim IS, Choi MS. 2001. Microtubule- and dynein-mediated movement of Orientia tsutsugamushi to the microtubule organizing center. Infect Immun 69:494–500. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.1.494-500.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Beyer AR, Rodino KG, VieBrock L, Green RS, Tegels BK, Oliver LD Jr, Marconi RT, Carlyon JA. 3 February 2017. Orientia tsutsugamushi Ank9 is a multifunctional effector that utilizes a novel GRIP-like Golgi localization domain for Golgi-to-endoplasmic reticulum trafficking and interacts with host COPB2. Cell Microbiol doi: 10.1111/cmi.12727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Yang L, Zhao Z, Li B, Liu Y, Feng Y. 2008. Electron-microscopic observation of mouse spleen tissue infected with Orientia tsutsugamushi isolated from Shandong, China. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo) 57:169–174. doi: 10.1093/jmicro/dfn017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Schuck S, Prinz WA, Thorn KS, Voss C, Walter P. 2009. Membrane expansion alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress independently of the unfolded protein response. J Cell Biol 187:525–536. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200907074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Urra H, Dufey E, Lisbona F, Rojas-Rivera D, Hetz C. 2013. When ER stress reaches a dead end. Biochim Biophys Acta 1833:3507–3517. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.07.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Harding HP, Zhang Y, Zeng H, Novoa I, Lu PD, Calfon M, Sadri N, Yun C, Popko B, Paules R, Stojdl DF, Bell JC, Hettmann T, Leiden JM, Ron D. 2003. An integrated stress response regulates amino acid metabolism and resistance to oxidative stress. Mol Cell 11:619–633. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(03)00105-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Lee AH, Iwakoshi NN, Glimcher LH. 2003. XBP-1 regulates a subset of endoplasmic reticulum resident chaperone genes in the unfolded protein response. Mol Cell Biol 23:7448–7459. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.21.7448-7459.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lee K, Tirasophon W, Shen X, Michalak M, Prywes R, Okada T, Yoshida H, Mori K, Kaufman RJ. 2002. IRE1-mediated unconventional mRNA splicing and S2P-mediated ATF6 cleavage merge to regulate XBP1 in signaling the unfolded protein response. Genes Dev 16:452–466. doi: 10.1101/gad.964702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Adachi Y, Yamamoto K, Okada T, Yoshida H, Harada A, Mori K. 2008. ATF6 is a transcription factor specializing in the regulation of quality control proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell Struct Funct 33:75–89. doi: 10.1247/csf.07044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ruddock LW, Molinari M. 2006. N-glycan processing in ER quality control. J Cell Sci 119:4373–4380. doi: 10.1242/jcs.03225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Lytton J, Westlin M, Hanley MR. 1991. Thapsigargin inhibits the sarcoplasmic or endoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase family of calcium pumps. J Biol Chem 266:17067–17071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ozcan U, Yilmaz E, Ozcan L, Furuhashi M, Vaillancourt E, Smith RO, Gorgun CZ, Hotamisligil GS. 2006. Chemical chaperones reduce ER stress and restore glucose homeostasis in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Science 313:1137–1140. doi: 10.1126/science.1128294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.de Almeida SF, Picarote G, Fleming JV, Carmo-Fonseca M, Azevedo JE, de Sousa M. 2007. Chemical chaperones reduce endoplasmic reticulum stress and prevent mutant HFE aggregate formation. J Biol Chem 282:27905–27912. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M702672200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Xie Q, Khaoustov VI, Chung CC, Sohn J, Krishnan B, Lewis DE, Yoffe B. 2002. Effect of tauroursodeoxycholic acid on endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced caspase-12 activation. Hepatology 36:592–601. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2002.35441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Klausner RD, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Bonifacino JS. 1990. The T cell antigen receptor: insights into organelle biology. Annu Rev Cell Biol 6:403–431. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.002155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Lippincott-Schwartz J, Bonifacino JS, Yuan LC, Klausner RD. 1988. Degradation from the endoplasmic reticulum: disposing of newly synthesized proteins. Cell 54:209–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90553-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Xu Y, Liu Y, Lee JG, Ye Y. 2013. A ubiquitin-like domain recruits an oligomeric chaperone to a retrotranslocation complex in endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation. J Biol Chem 288:18068–18076. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.449199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Lee JG, Ye Y. 2013. Bag6/Bat3/Scythe: a novel chaperone activity with diverse regulatory functions in protein biogenesis and degradation. Bioessays 35:377–385. doi: 10.1002/bies.201200159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Nakayama K, Yamashita A, Kurokawa K, Morimoto T, Ogawa M, Fukuhara M, Urakami H, Ohnishi M, Uchiyama I, Ogura Y, Ooka T, Oshima K, Tamura A, Hattori M, Hayashi T. 2008. The whole-genome sequencing of the obligate intracellular bacterium Orientia tsutsugamushi revealed massive gene amplification during reductive genome evolution. DNA Res 15:185–199. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsn011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Jiang J, Paris DH, Blacksell SD, Aukkanit N, Newton PN, Phetsouvanh R, Izzard L, Stenos J, Graves SR, Day NP, Richards AL. 2013. Diversity of the 47-kD HtrA nucleic acid and translated amino acid sequences from 17 recent human isolates of Orientia. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 13:367–375. doi: 10.1089/vbz.2012.1112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Sunyakumthorn P, Paris DH, Chan TC, Jones M, Luce-Fedrow A, Chattopadhyay S, Jiang J, Anantatat T, Turner GD, Day NP, Richards AL. 2013. An intradermal inoculation model of scrub typhus in Swiss CD-1 mice demonstrates more rapid dissemination of virulent strains of Orientia tsutsugamushi. PLoS One 8:e54570. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kelly DJ, Fuerst PA, Ching WM, Richards AL. 2009. Scrub typhus: the geographic distribution of phenotypic and genotypic variants of Orientia tsutsugamushi. Clin Infect Dis 48(Suppl 3):S203–S230. doi: 10.1086/596576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Rain JC, Selig L, De Reuse H, Battaglia V, Reverdy C, Simon S, Lenzen G, Petel F, Wojcik J, Schachter V, Chemama Y, Labigne A, Legrain P. 2001. The protein-protein interaction map of Helicobacter pylori. Nature 409:211–215. doi: 10.1038/35051615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Ko Y, Choi JH, Ha NY, Kim IS, Cho NH, Choi MS. 2013. Active escape of Orientia tsutsugamushi from cellular autophagy. Infect Immun 81:552–559. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00861-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Choi JH, Cheong TC, Ha NY, Ko Y, Cho CH, Jeon JH, So I, Kim IK, Choi MS, Kim IS, Cho NH. 2013. Orientia tsutsugamushi subverts dendritic cell functions by escaping from autophagy and impairing their migration. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 7:e1981. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Grootjans J, Kaser A, Kaufman RJ, Blumberg RS. 2016. The unfolded protein response in immunity and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol 16:469–484. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Niu H, Xiong Q, Yamamoto A, Hayashi-Nishino M, Rikihisa Y. 2012. Autophagosomes induced by a bacterial beclin 1 binding protein facilitate obligatory intracellular infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:20800–20807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1218674109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Lin M, Liu H, Xiong Q, Niu H, Cheng Z, Yamamoto A, Rikihisa Y. 2016. Ehrlichia secretes Etf-1 to induce autophagy and capture nutrients for its growth through RAB5 and class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Autophagy 12:2145–2166. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2016.1217369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Smith JA, Khan M, Magnani DD, Harms JS, Durward M, Radhakrishnan GK, Liu YP, Splitter GA. 2013. Brucella induces an unfolded protein response via TcpB that supports intracellular replication in macrophages. PLoS Pathog 9:e1003785. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Taguchi Y, Imaoka K, Kataoka M, Uda A, Nakatsu D, Horii-Okazaki S, Kunishige R, Kano F, Murata M. 2015. Yip1A, a novel host factor for the activation of the IRE1 pathway of the unfolded protein response during Brucella infection. PLoS Pathog 11:e1004747. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Wang X, Lin P, Li Y, Xiang C, Yin Y, Chen Z, Du Y, Zhou D, Jin Y, Wang A. 2016. Brucella suis vaccine strain 2 induces endoplasmic reticulum stress that affects intracellular replication in goat trophoblast cells in vitro. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 6:19. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Myeni S, Child R, Ng TW, Kupko JJ 3rd, Wehrly TD, Porcella SF, Knodler LA, Celli J. 2013. Brucella modulates secretory trafficking via multiple type IV secretion effector proteins. PLoS Pathog 9:e1003556. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Cho JA, Lee AH, Platzer B, Cross BC, Gardner BM, De Luca H, Luong P, Harding HP, Glimcher LH, Walter P, Fiebiger E, Ron D, Kagan JC, Lencer WI. 2013. The unfolded protein response element IRE1α senses bacterial proteins invading the ER to activate RIG-I and innate immune signaling. Cell Host Microbe 13:558–569. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.03.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 66.de Jong MF, Starr T, Winter MG, den Hartigh AB, Child R, Knodler LA, van Dijl JM, Celli J, Tsolis RM. 2013. Sensing of bacterial type IV secretion via the unfolded protein response. mBio 4:e00418-12. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00418-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Bischof LJ, Kao CY, Los FC, Gonzalez MR, Shen Z, Briggs SP, van der Goot FG, Aroian RV. 2008. Activation of the unfolded protein response is required for defenses against bacterial pore-forming toxin in vivo. PLoS Pathog 4:e1000176. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Morinaga N, Yahiro K, Matsuura G, Moss J, Noda M. 2008. Subtilase cytotoxin, produced by Shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli, transiently inhibits protein synthesis of Vero cells via degradation of BiP and induces cell cycle arrest at G1 by downregulation of cyclin D1. Cell Microbiol 10:921–929. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.01094.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Wolfson JJ, May KL, Thorpe CM, Jandhyala DM, Paton JC, Paton AW. 2008. Subtilase cytotoxin activates PERK, IRE1 and ATF6 endoplasmic reticulum stress-signalling pathways. Cell Microbiol 10:1775–1786. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2008.01164.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Lee SY, Lee MS, Cherla RP, Tesh VL. 2008. Shiga toxin 1 induces apoptosis through the endoplasmic reticulum stress response in human monocytic cells. Cell Microbiol 10:770–780. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2007.01083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Paton AW, Beddoe T, Thorpe CM, Whisstock JC, Wilce MC, Rossjohn J, Talbot UM, Paton JC. 2006. AB5 subtilase cytotoxin inactivates the endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP. Nature 443:548–552. doi: 10.1038/nature05124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Ensminger AW, Isberg RR. 2010. E3 ubiquitin ligase activity and targeting of BAT3 by multiple Legionella pneumophila translocated substrates. Infect Immun 78:3905–3919. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00344-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Hempstead AD, Isberg RR. 2015. Inhibition of host cell translation elongation by Legionella pneumophila blocks the host cell unfolded protein response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:E6790–E6797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1508716112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Treacy-Abarca S, Mukherjee S. 2015. Legionella suppresses the host unfolded protein response via multiple mechanisms. Nat Commun 6:7887. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Corduan A, Lecomte S, Martin C, Michel D, Desmots F. 2009. Sequential interplay between BAG6 and HSP70 upon heat shock. Cell Mol Life Sci 66:1998–2004. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-9198-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Tsukahara T, Kimura S, Ichimiya S, Torigoe T, Kawaguchi S, Wada T, Yamashita T, Sato N. 2009. Scythe/BAT3 regulates apoptotic cell death induced by papillomavirus binding factor in human osteosarcoma. Cancer Sci 100:47–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2008.00991.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Sasaki T, Gan EC, Wakeham A, Kornbluth S, Mak TW, Okada H. 2007. HLA-B-associated transcript 3 (Bat3)/Scythe is essential for p300-mediated acetylation of p53. Genes Dev 21:848–861. doi: 10.1101/gad.1534107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Desmots F, Russell HR, Lee Y, Boyd K, McKinnon PJ. 2005. The reaper-binding protein scythe modulates apoptosis and proliferation during mammalian development. Mol Cell Biol 25:10329–10337. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.23.10329-10337.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Price CT, Al-Khodor S, Al-Quadan T, Santic M, Habyarimana F, Kalia A, Kwaik YA. 2009. Molecular mimicry by an F-box effector of Legionella pneumophila hijacks a conserved polyubiquitination machinery within macrophages and protozoa. PLoS Pathog 5:e1000704. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Price CT, Al-Quadan T, Santic M, Rosenshine I, Abu Kwaik Y. 2011. Host proteasomal degradation generates amino acids essential for intracellular bacterial growth. Science 334:1553–1557. doi: 10.1126/science.1212868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Price CT, Al-Quadan T, Santic M, Jones SC, Abu Kwaik Y. 2010. Exploitation of conserved eukaryotic host cell farnesylation machinery by an F-box effector of Legionella pneumophila. J Exp Med 207:1713–1726. doi: 10.1084/jem.20100771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Eckart RA, Bisle S, Schulze-Luehrmann J, Wittmann I, Jantsch J, Schmid B, Berens C, Luhrmann A. 2014. Antiapoptotic activity of Coxiella burnetii effector protein AnkG is controlled by p32-dependent trafficking. Infect Immun 82:2763–2771. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01204-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Schafer W, Eckart RA, Schmid B, Cagkoylu H, Hof K, Muller YA, Amin B, Luhrmann A. 15 July 2016. Nuclear trafficking of the anti-apoptotic Coxiella burnetii effector protein AnkG requires binding to p32 and Importin-alpha1. Cell Microbiol doi: 10.1111/cmi.12634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Engin F, Hotamisligil GS. 2010. Restoring endoplasmic reticulum function by chemical chaperones: an emerging therapeutic approach for metabolic diseases. Diabetes Obes Metab 12(Suppl 2):S108–S115. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2010.01282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Kars M, Yang L, Gregor MF, Mohammed BS, Pietka TA, Finck BN, Patterson BW, Horton JD, Mittendorfer B, Hotamisligil GS, Klein S. 2010. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid may improve liver and muscle but not adipose tissue insulin sensitivity in obese men and women. Diabetes 59:1899–1905. doi: 10.2337/db10-0308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Yu C, Achazi K, Niedrig M. 2013. Tick-borne encephalitis virus triggers inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1) and transcription factor 6 (ATF6) pathways of unfolded protein response. Virus Res 178:471–477. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2013.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Hassan IH, Zhang MS, Powers LS, Shao JQ, Baltrusaitis J, Rutkowski DT, Legge K, Monick MM. 2012. Influenza A viral replication is blocked by inhibition of the inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1) stress pathway. J Biol Chem 287:4679–4689. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.284695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Rosenberg R. 1997. Drug-resistant scrub typhus: paradigm and paradox. Parasitol Today 13:131–132. doi: 10.1016/S0169-4758(97)01020-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Watt G, Chouriyagune C, Ruangweerayud R, Watcharapichat P, Phulsuksombati D, Jongsakul K, Teja-Isavadharm P, Bhodhidatta D, Corcoran KD, Dasch GA, Strickman D. 1996. Scrub typhus infections poorly responsive to antibiotics in northern Thailand. Lancet 348:86–89. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)02501-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Paris DH, Phetsouvanh R, Tanganuchitcharnchai A, Jones M, Jenjaroen K, Vongsouvath M, Ferguson DP, Blacksell SD, Newton PN, Day NP, Turner GD. 2012. Orientia tsutsugamushi in human scrub typhus eschars shows tropism for dendritic cells and monocytes rather than endothelium. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 6:e1466. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


