Abstract
Introduction
Children of alcoholic parents are at increased risk for lifetime depression. However, little is known about how this risk may change in magnitude across age, especially in mid-adulthood and beyond.
Methods
We used a nationally representative sample (N = 36,057) of US adults from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions, wave III. After adjusting for demographic characteristics, we examined the relationship between parental alcoholism and outcomes of 1) major depressive disorder, Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-5th edition (DSM-5) and 2) DSM-5 persistent depressive disorder. To examine continuous moderation of this relationship across participants’ age, we used time-varying effect models.
Results
Parental alcoholism was associated in general with a higher risk for both major depressive disorder (odds ratio [OR], 1.98, 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.85–2.11; P < .001) and persistent depressive disorder (OR, 2.28, 95% CI, 2.04–2.55; P < .001). The association between parental alcoholism and major depressive disorder was stable and positive across age, but the association with persistent depressive disorder significantly declined among older adults; respondents older than 73 years old were not at increased risk for persistent depressive disorder.
Conclusions
Findings from this study show that the risk of parental alcoholism on depression is significant and stable among individuals of a wide age range, with the exception of a decline in persistent depressive risk among older adults. These findings highlight the importance of screening for depression among adults with parental alcoholism.
MEDSCAPE CME.
Medscape, LLC, is pleased to provide online continuing medical education (CME) for this journal article, allowing clinicians the opportunity to earn CME credit.
 In support of improving patient care, this activity has been planned and implemented by Medscape, LLC, and Preventing Chronic Disease. Medscape, LLC, is jointly accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME), the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education (ACPE), and the American Nurses Credentialing Center (ANCC), to provide continuing education for the healthcare team.
In support of improving patient care, this activity has been planned and implemented by Medscape, LLC, and Preventing Chronic Disease. Medscape, LLC, is jointly accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME), the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education (ACPE), and the American Nurses Credentialing Center (ANCC), to provide continuing education for the healthcare team.
Medscape, LLC, designates this Journal-based CME activity for a maximum of 1.00 AMA PRA Category 1 Credit(s)™. Physicians should claim only the credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity.
All other clinicians completing this activity will be issued a certificate of participation. To participate in this journal CME activity: (1) review the learning objectives and author disclosures; (2) study the education content; (3) take the post-test with a 75% minimum passing score and complete the evaluation at http://www.medscape.org/journal/pcd; (4) view/print certificate.
Release date: December 14, 2017; Expiration date: December 14, 2018
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this activity, participants will be able to:
Evaluate risk for lifetime major depressive disorder among children of alcoholic parents, based on a national database study using the National Epidemiological Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions, wave III
Determine risk for lifetime persistent depressive disorder among children of alcoholic parents, based on a national database study using the National Epidemiological Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions, wave III
Assess clinical implications regarding risk for lifetime depression among children of alcoholic parents, based on a national database study using the National Epidemiological Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions, wave III
EDITOR
Camille Martin, RD, LD
Editor, Preventing Chronic Disease
Disclosure: Camille Martin, RD, LD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
CME AUTHOR
Sunita Thapa, MPH
Department of Health Policy, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, Tennessee
Disclosure: Sunita Thapa, MPH, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
AUTHORS
Arielle S. Selya, PhD
Master of Public Health Program, Department of Population Health, University of North Dakota, Grand Forks, North Dakota
Disclosure: Arielle S. Selya, PhD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received grants for clinical research from: Sanford Research
Yvonne Jonk, PhD
Master of Public Health Program, Department of Population Health, University of North Dakota, Grand Forks, North Dakota
Disclosure: Yvonne Jonk, PhD, has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
Introduction
Parental alcoholism has various negative physical, mental, and social consequences. Chief among these is depression; offspring of alcoholics are at heightened risk of depressive mood symptoms (1,2). The evidence for heightened depression among those exposed to parental alcoholism is particularly strong among young, college-aged adults (3,4).
Much of the research on the association between parental alcoholism and depression focuses on the question of resilience among adult children of alcoholics; that is, whether these individuals are ever able to overcome the challenges of parental alcoholism. Although some evidence suggests that older adults (those in their late 20s and early 30s) are more resilient than are young adults (those aged 18 through their early 20s) (5), there is little research on the effects of parental alcoholism among offspring of alcoholics in mid- to late adulthood, making their longer-term resilience unknown. Furthermore, the question of increased resilience at older ages assumes that the magnitude of the effect of parental alcoholism changes with increasing age; however, such age-varying effects have not yet been examined.
This study examined 1) the association between parental alcoholism and lifetime outcomes of both major depressive disorder (MDD) and persistent depressive disorder (PDD) among a full range of adults after controlling for demographic characteristics and 2) the age-varying effects of these associations (ie, how they may change in strength across participants’ ages). We used data from wave III of the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions (NESARC-III), a large nationally representative data set.
Methods
NESARC-III was sponsored, designed, and directed by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) and conducted during 2012–2013. NESARC-III is a nationally representative sample of the civilian noninstitutionalized population of the United States aged 18 years or older; it had a 61.1% response rate and an original sample size of 36,309. The NIAAA collected information via questionnaires on alcohol and drug use and disorders, related risk factors, and associated physical and mental disabilities on the basis of NIAAA’s Alcohol Use Disorder and Associated Disabilities Interview Schedule. This study excluded respondents with missing information on parental alcoholism; the final sample size for this study was 36,057. We used existing data from human participants in NESARC, and the study was approved by the University of North Dakota institutional review board. We completed the final analyses in May of 2016.
Measures
Parental alcoholism
Parental alcoholism was based on the self-reported answer to the question “Before you were 18, parent/other adult living in home was a problem drinker/alcoholic?” as a binary response variable (yes or no).
Depression
We analyzed 2 depressive disorders, lifetime MDD and lifetime PDD, as separate outcomes. Each outcome was derived from detailed self-reported responses to questionnaire items on the basis of corresponding criteria from the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th edition (DSM-5)(6). Briefly, lifetime MDD is characterized by one or more discrete episodes of at least 2 weeks during which respondents had either a depressed mood or a loss of interest in nearly all activities at some time during their adult lives (6). Lifetime PDD is a milder but more chronic form of depression and can be diagnosed when the mood disturbance continues for at least 2 years at some time during an adult’s life (6). Both MDD and PDD exclude mood or anxiety disorders that are either substance-induced or due to a general medical condition.
Demographic characteristics
Age and sex were self-reported. Race/ethnicity was self-reported as white, black, Hispanic, American Indian, or Asian. Full-time employment was self-reported as working 35 or more hours per week or less than 35 hours per week.
Marital status was self-reported according to 6 response options, which were re-categorized as currently married (ie, married or living with someone as if married), not currently married (ie, widowed, divorced, or separated), and never married.
Education was self-reported with 14 response levels ranging from “no formal schooling” to “completed Master’s degree or higher,” and we re-categorized these into 3 levels: less than a high school diploma, high school diploma, and some college or more.
Annual household income was self-reported with 21 response categories ranging from less than $5,000 to $200,000 or more. We recoded these into a new numeric variable on the basis of midpoints of each category up to level 20; level 21 (≥$200,000) was recoded as $250,000, which is approximately the median income among households earning $200,000 or more (7).
Statistical analyses
We conducted weighted regressions using the statistical software R (The R Foundation) and its survey package to examine the association between parental alcoholism and outcomes of MDD and PDD, after adjusting for demographic characteristics.
We used time-varying effect models (TVEMs), an extension of regression modeling that allows coefficients to vary continuously over time (8), to assess how the association between parental alcoholism and depression outcomes varied across age of participants. In other words, TVEMs examine moderation across some continuous measure of time (eg, historical time, age, time from event). TVEMs are spline-based regression models, which estimate a lower-order polynomial trend within equal intervals on the basis of user-specified number of knots, k. On the basis of established standards for this methodology (9), 10 knots were specified, and P-spline estimation, which automatically finds the most parsimonious model (k ≤10), was used. We ran separate logistic TVEM models for outcomes of MDD and PDD after controlling for demographic characteristics. Each model included a time-varying intercept (to adjust for the overall prevalence of depression across age) and the time-varying predictor of age (to examine continuous moderation of the effect of parental alcoholism across ages). We performed TVEM analyses in SAS 9.3 (SAS Institute Inc) using a publicly available SAS macro (9), version 3.1.0. TVEM analyses were interpreted with respect to 1) overall significance of the effect at a given value of age (ie, whether the confidence bands overlap the odds ratio (OR) of 1.0), and 2) the change in the effect across different ages (ie, whether the confidence bands exclude each other at different ages). Although these methods of establishing significance are more conservative than conventional significance tests, we did this because P values were available only for time-invariant covariates.
Results
Approximately 23% of respondents (n = 8,407) reported parental alcoholism. Respondents who reported parental alcoholism were significantly more likely than adults who did not report parental alcoholism to meet DSM-5 criteria for both MDD (29.6% vs 17.7%, P < .001) and PDD (9.3% vs 4.4%, P < .001) (Table). People who reported parental alcoholism were slightly but significantly younger (mean age, 44.8 y vs 45.9 y, P < .001); were more likely to be female (59.4% vs 55.4%, P < .001); had lower annual household incomes (median $32,500 vs $37,500, P < .001); were less likely to be never married (25.8% vs 28.4%, P < .001); were more likely to be not currently married (27.6% vs 25.4%, P < .001); were more likely to be white (57.8% vs 51.4%) or American Indian (2.1% vs 1.2%); and were less likely to be black (18.2% vs 22.3%) or Asian (1.9% vs 5.9%). The 2 groups did not significantly differ by education level (approximately 15% had <high school diploma, 22% high school diploma, and 62% some college or more), or full-time employment status (approximately 43%).
Table. Descriptive Statistics of Sample (N = 36,057), Study on Effects of Parental Alcoholism on Depression, National Epidemiological Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions, Wave III, 2012–2013.
| Measure | Parental Alcoholisma
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | |
| Major depressive disorderb | 29.6 | 17.7 |
| Persistent depressive disorderb | 9.3 | 4.4 |
| Median (IQR), age, yc | 44.0 (32–56) | 44.0 (30–59) |
| Sexb | ||
| Female | 59.4 | 55.4 |
| Male | 40.6 | 44.6 |
| Education | ||
| <High school diploma | 15.7 | 14.8 |
| High school diploma | 22.4 | 22.7 |
| Some college or more | 61.9 | 62.4 |
| Median (IQR) annual household income, $c | 32,500 (17,500–65,000) | 37,500 (17,500–65,000) |
| Full-time employment (≥35 h/wk) | 43.2 | 44.2 |
| Marital status | ||
| Currently married | 46.6 | 46.2 |
| Not currently marriedb | 27.6 | 25.4 |
| Never marriedb | 25.8 | 28.4 |
| Race/ethnicity | ||
| Whiteb | 57.8 | 51.4 |
| Blackb | 18.2 | 22.3 |
| American Indianb | 2.1 | 1.2 |
| Asianb | 1.9 | 5.9 |
| Hispanic | 19.9 | 19.2 |
Abbreviation: IQR, interquartile range.
Numeric variables presented as median (IQR), and categorical variables presented as percentages.
χ2 significant in parental alcoholism status at P < .05. MDD is characterized by discrete episodes of at least 2 weeks during which respondents experienced either depressed mood or a loss of interest in nearly all activities in adults at some time in their lives. Lifetime PDD is a milder but more chronic form of depression and can be diagnosed when the mood disturbance continues for at least 2 years in adults at some time in their lives (6).
Analysis of variance significant in parental alcoholism status at P < .05.
Additionally, compared with respondents who did not report parental alcoholism, those who reported parental alcoholism were slightly but significantly younger when they first had the first episode of MDD (median age, 27.8 y vs 30.5 y, P < .001) and PDD (median age, 27.9 y vs 30.6 y, P < .001) and had a significantly higher number of MDD episodes (median no., 4.6 vs 3.5, P < .001) and a nonsignificantly higher number of PDD episodes (median no., 2.1 vs 1.9). Respondents who reported parental alcoholism also talked to any health professional or therapist significantly more often to help improve their mood caused by MDD (63% vs 58%, P < .001) and nonsignificantly more often to help improve their mood caused by PDD (68% vs 64%) compared with respondents who did not report parental alcoholism. Respondents who reported parental alcoholism were significantly more likely to have symptoms of suicidal ideation (13% vs 8%, P < .001) and also meet DSM-5 criteria for other mental comorbidities such as anxiety (21% vs 11%, P < .001), personality disorders (27% vs 12%, P < .001), eating disorders (3% vs 1.5%, P < .001), substance use disorders (57% vs 37%, P < .001), and posttraumatic stress (12% vs 5%, P < .001).
Weighted regression analyses showed that parental alcoholism was associated with an approximately twofold increase in the odds of both MDD (OR, 1.84; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.72–1.96; P < .001) and PDD (OR, 2.11; 95% CI, 1.88–2.37; P < .001), after controlling for demographics.
Parental alcoholism had a positive and stable effect on MDD across individuals throughout most of the age range of respondents aged 18 to 85 years (Figure 1). Participants between these ages were approximately 2 times as likely to have MDD as were participants who reported no parental alcoholism. Because of the small sample size of participants older than 85 years and the resulting widening of the confidence band (ie, the lower limit of the confidence band is less than the OR of 1), the relationship was no longer significant among these individuals, even though the point estimate remained stable.
Figure 1.
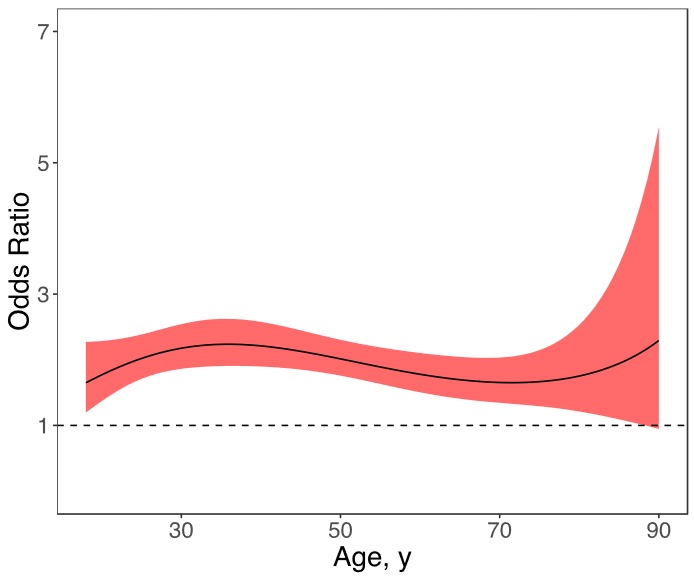
Age-varying effects of parental alcoholism on lifetime major depressive disorder for respondents aged 18–90 years, National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions, Wave III, 2012–2013. Age-varying effects are presented as odds ratios (ORs) across ages; the solid line represents the OR point estimates, and the surrounding shading represents 95% confidence intervals. The horizontal line represents an OR of 1.00.
| Age, y | Parental Alcoholism Lower Limit | Parental Alcoholism Upper Limit | Parental Alcoholism Estimate (Odds Ratio) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18.0 | 1.195427179 | 2.272260309 | 1.648126734 |
| 18.7272727 | 1.260284189 | 2.275778416 | 1.69355471 |
| 19.4545455 | 1.323772899 | 2.280927531 | 1.737650728 |
| 20.1818182 | 1.385351709 | 2.287849951 | 1.780302458 |
| 20.9090909 | 1.444477368 | 2.296690058 | 1.821405175 |
| 21.6363636 | 1.500622699 | 2.307580984 | 1.860862275 |
| 22.3636364 | 1.553300166 | 2.320625326 | 1.898585711 |
| 23.0909091 | 1.60209056 | 2.335870551 | 1.934496358 |
| 23.8181818 | 1.646673787 | 2.353282051 | 1.968524287 |
| 24.5454545 | 1.686856114 | 2.37271941 | 2.000608968 |
| 25.2727273 | 1.722586815 | 2.393922902 | 2.030699393 |
| 26.0 | 1.753958399 | 2.416515995 | 2.05875412 |
| 26.7272727 | 1.781188888 | 2.440025357 | 2.084741244 |
| 27.4545455 | 1.804590073 | 2.463914416 | 2.108638304 |
| 28.1818182 | 1.824529489 | 2.487622715 | 2.130432116 |
| 28.9090909 | 1.841394202 | 2.510602989 | 2.150118552 |
| 29.6363636 | 1.85556197 | 2.532350392 | 2.167702259 |
| 30.3636364 | 1.867381868 | 2.552421807 | 2.183196327 |
| 31.0909091 | 1.877163724 | 2.570445928 | 2.196621918 |
| 31.8181818 | 1.885174314 | 2.586126186 | 2.208007849 |
| 32.5454545 | 1.891638012 | 2.599238875 | 2.217390145 |
| 33.2727273 | 1.896739946 | 2.609628446 | 2.224811569 |
| 34.0 | 1.900630285 | 2.617201424 | 2.230321118 |
| 34.7272727 | 1.903428782 | 2.621919841 | 2.23397352 |
| 35.4545455 | 1.905229075 | 2.623794732 | 2.235828708 |
| 36.1818182 | 1.906102546 | 2.622879964 | 2.235951291 |
| 36.9090909 | 1.906101639 | 2.619266515 | 2.234410033 |
| 37.6363636 | 1.905262677 | 2.613077218 | 2.231277324 |
| 38.3636364 | 1.903608223 | 2.604461965 | 2.226628666 |
| 39.0909091 | 1.901149081 | 2.593593312 | 2.220542173 |
| 39.8181818 | 1.897886019 | 2.580662423 | 2.213098084 |
| 40.5454545 | 1.893811306 | 2.565875303 | 2.204378293 |
| 41.2727273 | 1.888910167 | 2.549449243 | 2.194465902 |
| 42.0 | 1.883162224 | 2.531609402 | 2.183444799 |
| 42.7272727 | 1.876543032 | 2.512585464 | 2.17139926 |
| 43.4545455 | 1.869025779 | 2.492608297 | 2.158413575 |
| 44.1818182 | 1.8605832 | 2.471906558 | 2.144571709 |
| 44.9090909 | 1.851189775 | 2.45070322 | 2.129956981 |
| 45.6363636 | 1.840824171 | 2.429212002 | 2.114651785 |
| 46.3636364 | 1.829471908 | 2.40763378 | 2.098737326 |
| 47.0909091 | 1.817128103 | 2.386153072 | 2.082293401 |
| 47.8181818 | 1.803800135 | 2.364934788 | 2.065398192 |
| 48.5454545 | 1.789509965 | 2.344121462 | 2.048128101 |
| 49.2727273 | 1.774295891 | 2.323831223 | 2.030557606 |
| 50.0 | 1.758213466 | 2.304156723 | 2.012759145 |
| 50.7272727 | 1.741335442 | 2.285165178 | 1.994803027 |
| 51.4545455 | 1.723750686 | 2.266899561 | 1.976757363 |
| 52.1818182 | 1.705562128 | 2.249380853 | 1.958688029 |
| 52.9090909 | 1.686883971 | 2.232611154 | 1.940658643 |
| 53.6363636 | 1.667838406 | 2.216577355 | 1.922730569 |
| 54.3636364 | 1.648552156 | 2.201255072 | 1.904962938 |
| 55.0909091 | 1.629153115 | 2.186612553 | 1.887412687 |
| 55.8181818 | 1.609767297 | 2.17261433 | 1.87013462 |
| 56.5454545 | 1.590516228 | 2.159224489 | 1.853181478 |
| 57.2727273 | 1.571514848 | 2.146409484 | 1.836604033 |
| 58.0 | 1.552869893 | 2.134140499 | 1.820451189 |
| 58.7272727 | 1.534678724 | 2.122395428 | 1.804770098 |
| 59.4545455 | 1.517028509 | 2.111160516 | 1.789606295 |
| 60.1818182 | 1.499995669 | 2.100431798 | 1.775003831 |
| 60.9090909 | 1.4836455 | 2.090216384 | 1.761005432 |
| 61.6363636 | 1.468031882 | 2.08053371 | 1.74765266 |
| 62.3636364 | 1.453197003 | 2.07141681 | 1.734986081 |
| 63.0909091 | 1.439171043 | 2.062913685 | 1.723045455 |
| 63.8181818 | 1.42597177 | 2.055088813 | 1.711869923 |
| 64.5454545 | 1.413604026 | 2.048024841 | 1.701498211 |
| 65.2727273 | 1.402059091 | 2.041824467 | 1.69196884 |
| 66.0 | 1.391313947 | 2.03661252 | 1.683320351 |
| 66.7272727 | 1.381330494 | 2.032538193 | 1.675591533 |
| 67.4545455 | 1.372054796 | 2.029777369 | 1.668821672 |
| 68.1818182 | 1.363416488 | 2.028534933 | 1.663050803 |
| 68.9090909 | 1.355328512 | 2.029046931 | 1.658319981 |
| 69.6363636 | 1.347687402 | 2.031582382 | 1.654671563 |
| 70.3636364 | 1.340374316 | 2.036444577 | 1.652149511 |
| 71.0909091 | 1.333257058 | 2.043971681 | 1.650799706 |
| 71.8181818 | 1.326193189 | 2.054536565 | 1.650670288 |
| 72.5454545 | 1.319034267 | 2.068545902 | 1.651812013 |
| 73.2727273 | 1.311631011 | 2.086438791 | 1.654278641 |
| 74.0 | 1.303839047 | 2.10868534 | 1.658127342 |
| 74.7272727 | 1.295524668 | 2.135785855 | 1.663419147 |
| 75.4545455 | 1.286570012 | 2.168271365 | 1.670219421 |
| 76.1818182 | 1.276877083 | 2.206706168 | 1.678598384 |
| 76.9090909 | 1.266370228 | 2.25169296 | 1.688631673 |
| 77.6363636 | 1.254996934 | 2.303880859 | 1.700400957 |
| 78.3636364 | 1.242727071 | 2.363976434 | 1.713994606 |
| 79.0909091 | 1.229550899 | 2.432757678 | 1.729508424 |
| 79.8181818 | 1.21547627 | 2.511090838 | 1.747046458 |
| 80.5454545 | 1.200525457 | 2.599950042 | 1.766721884 |
| 81.2727273 | 1.184731956 | 2.700439852 | 1.788657985 |
| 82.0 | 1.168137532 | 2.813821052 | 1.812989238 |
| 82.7272727 | 1.150789662 | 2.941540212 | 1.839862513 |
| 83.4545455 | 1.132739419 | 3.085263815 | 1.869438403 |
| 84.1818182 | 1.11403981 | 3.246917982 | 1.901892713 |
| 84.9090909 | 1.094744514 | 3.42873509 | 1.937418109 |
| 85.6363636 | 1.07490697 | 3.633308915 | 1.976225968 |
| 86.3636364 | 1.054579739 | 3.86366024 | 2.01854844 |
| 87.0909091 | 1.03381408 | 4.123315369 | 2.064640764 |
| 87.8181818 | 1.012659698 | 4.416400501 | 2.114783865 |
| 88.5454545 | 0.991164591 | 4.747755626 | 2.16928727 |
| 89.2727273 | 0.969375 | 5.123072466 | 2.228492399 |
| 90.0 | 0.947335398 | 5.549062135 | 2.292776262 |
Similarly, parental alcoholism had a positive effect on PDD across a wide age range (Figure 2). Participants aged 18 to 73 years were approximately 2 times as likely to have PDD as were participants who reported no parental alcoholism. The association was nonsignificant for those aged 74 years and older. Additionally, the effect of parental alcoholism among older individuals (eg, OR of 0.8 for participants aged 80 y) was significantly weaker than the effect among younger individuals (eg, OR of 2.3 for participants aged 60 y).
Figure 2.
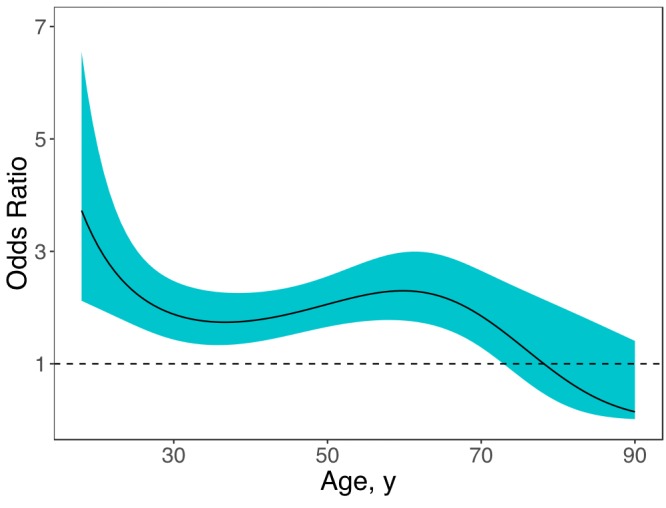
Age-varying effects of parental alcoholism on lifetime persistent depressive disorder for respondents aged 18–90 years, National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions, Wave III, 2012–2013. Age-varying effects are presented as odds ratios (ORs) across ages; the solid line represents the OR point estimates, and the surrounding shading represents 95% confidence intervals. The horizontal line represents an OR of 1.00.
| Age | Parental Alcoholism Lower Limit | Parental Alcoholism Upper Limit | Parental Alcoholism Estimate (Odds Ratio) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18.0 | 2.121333968 | 6.551176806 | 3.727899394 |
| 18.7272727 | 2.075574017 | 5.860781704 | 3.487762352 |
| 19.4545455 | 2.029848789 | 5.283819956 | 3.274958861 |
| 20.1818182 | 1.984035647 | 4.800238575 | 3.086072657 |
| 20.9090909 | 1.938049696 | 4.39400751 | 2.91818521 |
| 21.6363636 | 1.891863229 | 4.052213687 | 2.768796503 |
| 22.3636364 | 1.84552654 | 3.764360941 | 2.635759478 |
| 23.0909091 | 1.799186017 | 3.521828612 | 2.517225614 |
| 23.8181818 | 1.753093756 | 3.317455994 | 2.411599342 |
| 24.5454545 | 1.707603271 | 3.145230146 | 2.317499792 |
| 25.2727273 | 1.663149306 | 3.000060743 | 2.233729828 |
| 26.0 | 1.620212854 | 2.877621024 | 2.159249539 |
| 26.7272727 | 1.579278657 | 2.774236703 | 2.093153796 |
| 27.4545455 | 1.540794475 | 2.686804367 | 2.034653121 |
| 28.1818182 | 1.505138875 | 2.612721855 | 1.98305553 |
| 28.9090909 | 1.4726045 | 2.549829007 | 1.937753769 |
| 29.6363636 | 1.443395174 | 2.496351313 | 1.898215329 |
| 30.3636364 | 1.417631989 | 2.450842872 | 1.86397244 |
| 31.0909091 | 1.395365259 | 2.412132959 | 1.834613456 |
| 31.8181818 | 1.376588712 | 2.379277958 | 1.80977545 |
| 32.5454545 | 1.361253018 | 2.351518978 | 1.789137308 |
| 33.2727273 | 1.349275107 | 2.328241584 | 1.77241034 |
| 34.0 | 1.34054929 | 2.308950615 | 1.759335701 |
| 34.7272727 | 1.334956119 | 2.293250066 | 1.749682316 |
| 35.4545455 | 1.332367535 | 2.280824388 | 1.74324306 |
| 36.1818182 | 1.332650157 | 2.271423676 | 1.739831348 |
| 36.9090909 | 1.335667115 | 2.264852012 | 1.739278112 |
| 37.6363636 | 1.341277836 | 2.260956984 | 1.741428003 |
| 38.3636364 | 1.349333336 | 2.259616451 | 1.746131668 |
| 39.0909091 | 1.359678241 | 2.260738268 | 1.753247453 |
| 39.8181818 | 1.372151379 | 2.264258285 | 1.76264152 |
| 40.5454545 | 1.386584443 | 2.270136172 | 1.77418587 |
| 41.2727273 | 1.402800706 | 2.278351648 | 1.787756499 |
| 42.0 | 1.420613986 | 2.288900855 | 1.803231701 |
| 42.7272727 | 1.439825989 | 2.301790321 | 1.820488266 |
| 43.4545455 | 1.46021974 | 2.3170262 | 1.839393214 |
| 44.1818182 | 1.481565837 | 2.334616571 | 1.859808634 |
| 44.9090909 | 1.503626278 | 2.354567875 | 1.881592446 |
| 45.6363636 | 1.52615736 | 2.376878206 | 1.904597114 |
| 46.3636364 | 1.548913488 | 2.401529913 | 1.928668471 |
| 47.0909091 | 1.571651669 | 2.428481794 | 1.953644662 |
| 47.8181818 | 1.594132997 | 2.457658161 | 1.979351907 |
| 48.5454545 | 1.616121257 | 2.488935549 | 2.005597579 |
| 49.2727273 | 1.637394377 | 2.522142752 | 2.032176755 |
| 50.0 | 1.657749164 | 2.557057044 | 2.058873278 |
| 50.7272727 | 1.677002996 | 2.593401109 | 2.085459525 |
| 51.4545455 | 1.694993838 | 2.630842419 | 2.111696401 |
| 52.1818182 | 1.711578621 | 2.668995055 | 2.13733359 |
| 52.9090909 | 1.726627828 | 2.707421364 | 2.162107553 |
| 53.6363636 | 1.740019732 | 2.745634607 | 2.185739782 |
| 54.3636364 | 1.751641031 | 2.783109656 | 2.20794227 |
| 55.0909091 | 1.761383135 | 2.819292424 | 2.228419648 |
| 55.8181818 | 1.769137897 | 2.853610183 | 2.246871139 |
| 56.5454545 | 1.774793588 | 2.885483038 | 2.262992884 |
| 57.2727273 | 1.778231237 | 2.914336455 | 2.276480643 |
| 58.0 | 1.779321666 | 2.939615161 | 2.28703322 |
| 58.7272727 | 1.777923295 | 2.960796734 | 2.294356007 |
| 59.4545455 | 1.773879747 | 2.977405156 | 2.298164203 |
| 60.1818182 | 1.767017848 | 2.989025971 | 2.298186729 |
| 60.9090909 | 1.757146192 | 2.995321497 | 2.294170386 |
| 61.6363636 | 1.74405449 | 2.996045392 | 2.285884165 |
| 62.3636364 | 1.727514047 | 2.99105584 | 2.273123617 |
| 63.0909091 | 1.70727983 | 2.980326367 | 2.255715207 |
| 63.8181818 | 1.683095655 | 2.963954754 | 2.233521741 |
| 64.5454545 | 1.65470297 | 2.942168241 | 2.206448396 |
| 65.2727273 | 1.621849546 | 2.915316254 | 2.174443456 |
| 66.0 | 1.584304069 | 2.883859212 | 2.13750085 |
| 66.7272727 | 1.541875679 | 2.848350404 | 2.095662715 |
| 67.4545455 | 1.494437512 | 2.809410365 | 2.049021287 |
| 68.1818182 | 1.441952684 | 2.767695097 | 1.997720044 |
| 68.9090909 | 1.384500016 | 2.723860792 | 1.941953993 |
| 69.6363636 | 1.322295886 | 2.678528746 | 1.881969059 |
| 70.3636364 | 1.255708302 | 2.632254659 | 1.818060513 |
| 71.0909091 | 1.18525999 | 2.585505937 | 1.750570405 |
| 71.8181818 | 1.111619045 | 2.538649444 | 1.679884243 |
| 72.5454545 | 1.035577447 | 2.491949854 | 1.606426801 |
| 73.2727273 | 0.958018876 | 2.445576339 | 1.530656165 |
| 74.0 | 0.879880702 | 2.399616068 | 1.453057422 |
| 74.7272727 | 0.802113889 | 2.35409105 | 1.374135775 |
| 75.4545455 | 0.725644318 | 2.308975503 | 1.294409113 |
| 76.1818182 | 0.651338299 | 2.264211802 | 1.214400208 |
| 76.9090909 | 0.579974061 | 2.219723938 | 1.134628709 |
| 77.6363636 | 0.512220104 | 2.175428095 | 1.055603148 |
| 78.3636364 | 0.448620673 | 2.13124046 | 0.977813137 |
| 79.0909091 | 0.389588073 | 2.087082647 | 0.901721968 |
| 79.8181818 | 0.335401273 | 2.042885183 | 0.827759803 |
| 80.5454545 | 0.286210024 | 1.99858954 | 0.756317632 |
| 81.2727273 | 0.242043585 | 1.954149091 | 0.687742141 |
| 82.0 | 0.202823099 | 1.909529338 | 0.62233163 |
| 82.7272727 | 0.168376606 | 1.864707633 | 0.560333063 |
| 83.4545455 | 0.138455714 | 1.819672597 | 0.501940305 |
| 84.1818182 | 0.112752985 | 1.774423347 | 0.44729356 |
| 84.9090909 | 0.090919169 | 1.728968626 | 0.396479999 |
| 85.6363636 | 0.07257957 | 1.683325891 | 0.349535504 |
| 86.3636364 | 0.057348922 | 1.637520403 | 0.306447434 |
| 87.0909091 | 0.044844346 | 1.591584332 | 0.267158301 |
| 87.8181818 | 0.034696095 | 1.545555889 | 0.231570192 |
| 88.5454545 | 0.026555975 | 1.499478512 | 0.199549778 |
| 89.2727273 | 0.020103438 | 1.453400077 | 0.170933726 |
| 90.0 | 0.015049499 | 1.407372163 | 0.145534345 |
Discussion
This study examined how the relationship between parental alcoholism and depression outcomes may change across individuals of different ages. Respondents who reported being exposed to parental alcoholism as children had approximately twice the risk of meeting criteria for lifetime MDD and PDD. Parental alcoholism had a positive and stable effect on the odds of lifetime MDD throughout most of the age range of the participants, although this association was no longer significant for those aged 85 years old or older. However, although the association with PDD was positive and stable across individuals in early and late adulthood, it significantly decreased in strength for those older than 73, such that parental alcoholism was no longer associated with a heightened risk for PDD.
Results of this study also showed that 23% of adults had a parent with alcohol problems before the age of 18; the 1988 National Health Interview Survey estimated that 18.1% of adults had a parent with alcohol problems before the age of 18 (10). Although there is a large gap in timeline, the prevalence of adults growing up with a parent with alcohol problems seems comparable. Although current data on the prevalence of adults who grew up with a parent with alcohol problems are not available, it is estimated that an annual average of 7.5 million US children (10.5% of all children) live with a parent who had an alcohol use disorder in the past year (11). Although this figure is lower than we report here, it includes only past-year alcohol use disorder, a severe form of problem drinking. Hence, assuming that this prevalence will increase under NESARC’s inclusion of other, less severe forms of problem drinking, the current prevalence rates are more consistent with those of previous reports.
Our findings confirm those of previous research that established that parental alcoholism is associated with an increased risk of depression among offspring (2,12,13). This study also extends this research in 2 important ways, given that many previous studies are limited to younger adults (2,3). Here, we examined the effects of parental alcoholism on depression among adults across a wide age range, and we rigorously examined the age-varying effects of parental alcoholism, showing that its effect is largely stable across individuals from early to late adulthood.
This study has limitations. First, the measure of parental alcoholism is limited in several ways. The single question that assessed parental alcoholism was proxy-reported by offspring. As a result, both the timing and the nature of the question may have created recall bias, in which those with depression are more likely to remember the drinking of their parents as problematic than those with no depression. Additionally, the wording of the question included parents as well as non-parental adults living in the household, although most participants reported living only with one or more biological parents. Thus, the wording of this question may have affected the results in unknown ways. Second, this study used cross-sectional data and thus cannot conclude that parental alcoholism causes depression among offspring.
Third, because we used cross-sectional data, the findings do not distinguish between true age and cohort when considering the age-varying effect of parental alcoholism. A true age-varying effect would capture data on the change in the effect of parental alcoholism as an individual ages, but these analyses examined the effect across individuals of different ages. This analysis introduces a cohort effect: the association between parental alcoholism and depression may change across individuals born in different years as a result of differences across time periods in, for example, the prevalence of parental alcoholism, the threshold at which participants consider alcohol consumption “problem drinking,” the prevalence of depression, or other associated risk and protective factors. It is likely that both an age effect (5) and a cohort effect (14,15) contribute to our findings, but this study cannot distinguish between them. Thus, the findings should not be interpreted as effects for a given individual across time. Future studies using longitudinal data are needed to separate true age-varying effects from cohort effects.
Strengths of this study include the large, nationally representative sample, the use of rigorous and well-validated DSM-5 measures of MDD and PDD, and the use of TVEMs, an innovative methodology for examining continuous moderation across age.
Parental alcoholism is stably associated with depression outcomes among offspring across a range of ages from early to late adulthood, with a decline in PDD among older adults. This finding implies that the effect of parental alcoholism on PDD may weaken among older adults (aged ≥60 y), making them more resilient than middle-aged and younger adults for PDD. Conversely, we found no evidence of resilience to MDD, as shown by a similar effect across ages. Despite this long-term effect of parental alcoholism, many adults with depression do not seek treatment because of a desire for self-reliance and the perceived stigma of mental health difficulties (16). Children of alcoholics often desire secrecy about their parents’ alcoholism (17), and this additional stigma may further compound the lack of treatment seeking among adult offspring of alcoholics. Our findings highlight the importance of screening for depression among offspring of alcoholics in health care settings to provide them with services and support to ultimately manage this mental health burden.
Acknowledgments
The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) sponsored the National Epidemiologic Surveys on Alcohol and Related Conditions. We acknowledge the contribution of NIAAA funding support and support of the intramural program, NIAAA, National Institutes of Health. The manuscript for this article was prepared using a limited access dataset obtained from NIAAA and does not reflect the opinions or views of NIAAA or the US government.
Post-Test Information
To obtain credit, you should first read the journal article. After reading the article, you should be able to answer the following, related, multiple-choice questions. To complete the questions (with a minimum 75% passing score) and earn continuing medical education (CME) credit, please go to http://www.medscape.org/journal/pcd. Credit cannot be obtained for tests completed on paper, although you may use the worksheet below to keep a record of your answers.
You must be a registered user on http://www.medscape.org. If you are not registered on http://www.medscape.org, please click on the “Register” link on the right hand side of the website.
Only one answer is correct for each question. Once you successfully answer all post-test questions, you will be able to view and/or print your certificate. For questions regarding this activity, contact the accredited provider, CME@medscape.net. For technical assistance, contact CME@medscape.net. American Medical Association’s Physician’s Recognition Award (AMA PRA) credits are accepted in the US as evidence of participation in CME activities. For further information on this award, please go to https://www.ama-assn.org. The AMA has determined that physicians not licensed in the US who participate in this CME activity are eligible for AMA PRA Category 1 Credits™. Through agreements that the AMA has made with agencies in some countries, AMA PRA credit may be acceptable as evidence of participation in CME activities. If you are not licensed in the US, please complete the questions online, print the AMA PRA CME credit certificate, and present it to your national medical association for review.
Post-Test Questions
Study Title: Time-Varying Effects of Parental Alcoholism on Depression
CME Questions
-
Your patient is a 37-year-old man with a history of maternal alcoholism. On the basis of the national database study using the National Epidemiological Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions, wave III, by Thapa and colleagues, which one of the following statements about risk for lifetime major depressive disorder (MDD) among children of alcoholic parents is correct?
Parental alcoholism was associated with nearly twice the risk for MDD (OR, 1.98; 95% CI, 1.85-2.11; P < .001)
The association between parental alcoholism and MDD declined with increasing age above 50 years
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th edition (DSM-5), criteria for MDD were met by 15% of those who reported parental alcoholism and by 6% of those who did not
Age at first episode of MDD was not significantly different between those who reported parental alcoholism and those who did not
-
According to the national database study using the National Epidemiological Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions, wave III, by Thapa and colleagues, which one of the following statements about risk for lifetime persistent depressive disorder (PDD) among children of alcoholic parents is correct?
Parental alcoholism was not associated with a significantly higher risk for PDD
The association with PDD significantly declined among older adults, with those older than 73 years no longer at increased risk for PDD
DSM-5 criteria for PDD were met by 12% of those who reported parental alcoholism and by 3% of those who did not
Age at first episode of PDD was not significantly different between those who reported parental alcoholism and those who did not
-
According to the national database study using the National Epidemiological Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions, wave III, by Thapa and colleagues, which one of the following statements about clinical implications regarding risk for lifetime depression among children of alcoholic parents would be correct?
The study proves that parental alcoholism causes depression among offspring
Given the low prevalence of parental alcoholism, it is unlikely to cause a significant public health burden in the offspring
Adult offspring of alcoholics are more likely to seek treatment for depression than those without this family history
The findings support the need to screen adults with parental alcoholism for depression to provide them with services and support to manage this mental health burden
Footnotes
The opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the opinions of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions.
Suggested citation for this article: Thapa S, Selya AS, Jonk Y. Time-Varying Effects of Parental Alcoholism on Depression. Prev Chronic Dis 2017;14:170100. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5888/pcd14.170100.
References
- 1. Christensen HB, Bilenberg N. Behavioural and emotional problems in children of alcoholic mothers and fathers. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2000;9(3):219–26. 10.1007/s007870070046 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Kelley ML, Braitman A, Henson JM, Schroeder V, Ladage J, Gumienny L. Relationships among depressive mood symptoms and parent and peer relations in collegiate children of alcoholics. Am J Orthopsychiatry 2010;80(2):204–12. 10.1111/j.1939-0025.2010.01024.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Chassin L, Pitts SC, DeLucia C, Todd M. A longitudinal study of children of alcoholics: predicting young adult substance use disorders, anxiety, and depression. J Abnorm Psychol 1999;108(1):106–19. 10.1037/0021-843X.108.1.106 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Kelley ML, Pearson MR, Trinh S, Klostermann K, Krakowski K. Maternal and paternal alcoholism and depressive mood in college students: parental relationships as mediators of ACOA-depressive mood link. Addict Behav 2011;36(7):700–6. 10.1016/j.addbeh.2011.01.028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Jennison KM, Johnson KA. Parental alcoholism as a risk factor for DSM-IV-defined alcohol abuse and dependence in American women: the protective benefits of dyadic cohesion in marital communication. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse 2001;27(2):349–74. 10.1081/ADA-100103714 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, fifth edition (DSM-5). Arlington (VA): American Psychiatric Association; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 7. US Census Bureau. Current population survey (CPS) annual social and economic (ASEC) supplement table HINC-06: income distribution to $250,000 or more for households 2014; 2015.
- 8. Tan X, Shiyko MP, Li R, Li Y, Dierker L. A time-varying effect model for intensive longitudinal data. Psychol Methods 2012;17(1):61–77. 10.1037/a0025814 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Li R, Dziak JD, Tan X, Huang L, Wagner AT, Yang J. TVEM (time-varying effect modeling) SAS macro users’ guide (version 3.1.0). University Park (PA): The Methodology Center, Penn State; updated 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 10. Schoenborn CA. Exposure to alcoholism in the family: United States, 1988. Adv Data 1991;(205):1–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. Data spotlight: more than 7 million children live with a parent with alcohol problems; 2012.
- 12. Klostermann K, Chen R, Kelley ML, Schroeder VM, Braitman AL, Mignone T. Coping behavior and depressive symptoms in adult children of alcoholics. Subst Use Misuse 2011;46(9):1162–8. 10.3109/10826080903452546 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Sher KJ. Psychological characteristics of children of alcoholics: overview of research methods and findings. In: M. Galanter, H. Begleiter, R. Deitrich, et al, editors. New York (NY): Plenum Press; 1991. p. 301–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Hasin D, Link B. Age and recognition of depression: implications for a cohort effect in major depression. Psychol Med 1988;18(3):683–8. 10.1017/S0033291700008369 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Rice JP, Neuman RJ, Saccone NL, Corbett J, Rochberg N, Hesselbrock V, et al. Age and birth cohort effects on rates of alcohol dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 2003;27(1):93–9. 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2003.tb02727.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Jennings KS, Cheung JH, Britt TW, Goguen KN, Jeffirs SM, Peasley AL, et al. How are perceived stigma, self-stigma, and self-reliance related to treatment-seeking? A three-path model. Psychiatr Rehabil J 2015;38(2):109–16. 10.1037/prj0000138 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Haverfield MC, Theiss JA. A theme analysis of experiences reported by adult children of alcoholics in online support forums. J Fam Stud 2014;20(2):166–84. 10.1080/13229400.2014.11082004 [DOI] [Google Scholar]


