Figure 7. IFNγ increases the rate of proteasome-dependent HO-1 degradation.
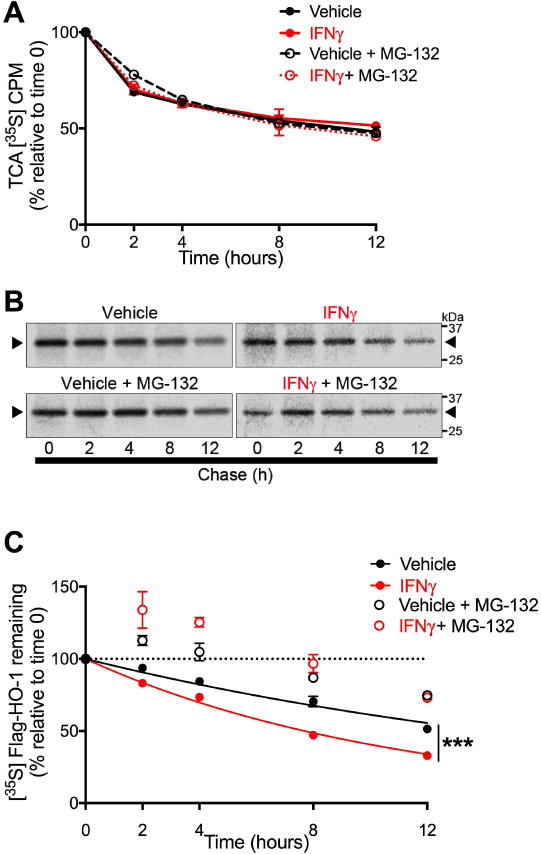
U251 cells transiently expressing FLAG-HO-1 and exposed to IFNγ (10 ng/mL) for 3 days were used in pulse chase assays to measure HO-1 degradation. Cells were pulse labeled with [35S]methionine/cysteine and chased for indicated time points. Degradation mediated by proteasome activity was assessed by treating cells 2 hours prior to labeling with the proteasome inhibitor MG-132 (5 μM) or DMSO (vehicle). (A) Intracellular protein degradation was determined by [35S] liquid scintillation counting of TCA-precipitable lysate fractions. Radioactivity was measured as counts per minute (CPM) and are expressed as a percentage relative to time 0 within each independent experiment (n=3). Data represent mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis of treatment conditions at each time point was performed by two-way RM-ANOVA with post-hoc Holm-Sidak test. (B) Representative phosphorimage used for densitometric quantification of radiolabeled FLAG-HO-1. Black arrows indicate radiolabeled FLAG-HO-1. (C) Degradation of HO-1 protein was determined by densitometric quantification of radiolabeled FLAG-HO-1 and are expressed as a percentage relative to time 0 within each independent experiment (n=3). Data represent mean ± SEM. Protein half-life in vehicle and IFNγ conditions (closed circles) was determined by one-phase exponential decay and rate of decay (k) was compared by Extra sum of squares F test. ***P < 0.001. The effects of MG-132 at each time point was analyzed by two-way RM-ANOVA with post hoc Holm-Sidak test (significance not shown in figure). IFNγ vs. IFNγ+MG-132: P < 0.001 at all time points. PBS vs. PBS + MG-132: P < 0.01 at 8hr; P < 0.001 at 2, 4, and 12 hr.
