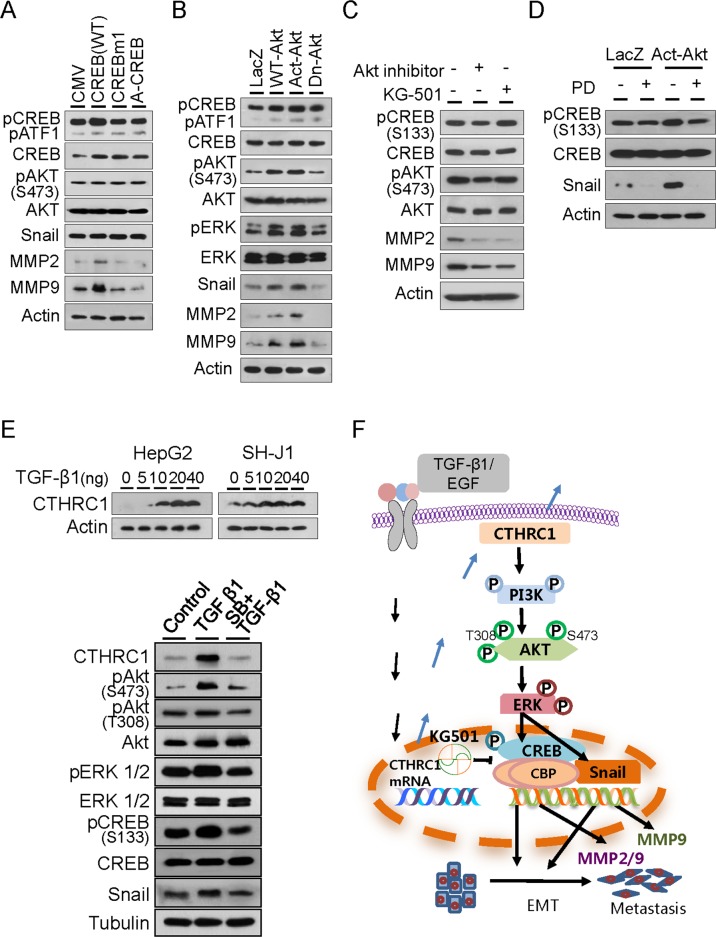
Figure 7. Downstream signaling of CTHRC1.
(A) Immunoblot analysis of phospho-Akt, phospho-CREB, snail, MMP2 and MMP9 levels in HepG2 cells transiently transfected with control plasmid CMV, WT-CREB, CREBm1, or A-CREB. (B) Immunoblot analysis of phospho-Akt, phospho-ERK, phospho-CREB, Snail, MMP2 and MMP9 levels in HepG2 cells transiently transfected with LacZ, WT-Akt, Act-Akt, or Dn-Akt. (C) Phospho-Akt, phospho-CREB, Snail, MMP2 and MMP9 expression were measured after treatment with an Akt inhibitor or CREB inhibitor KG501 in SH-J1 cells. (D) CREB activation and Snail expression were measured after treatment with vehicle or ERK inhibitor PD98059 (PD) in HepG2 cells. (E) TGF-β1-induced CTHRC1 expression in HepG2 and SH-J1 cells. Cells were treated with TGF-β1 at the indicated concentrations for 4 days (upper panels). SB431542 suppressed TGF-β1-mediated activation of the CTHRC1/CREB (Snail) signaling pathway. HepG2 cells were treated with TGF-β1 (20 ng/ml) alone or in combination with SB431542 (SB, 10 μM) for 3 days (lower panels). (F) Schematic model of growth factor-mediated CTHRC1 expression. Invasiveness and metastasis of cancer cells are promoted through activation of the PI3K/Akt/ERK/CREB (Snail) signaling pathway, which induced EMT change and MMP2/MMP9 expression.