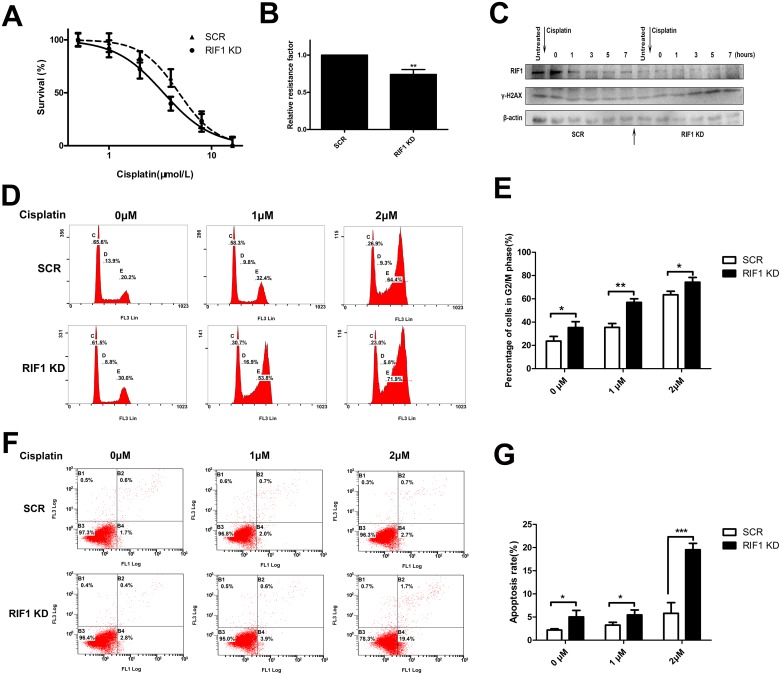
Figure 5. RIF1 knockdown increases cisplatin sensitivity, cisplatin-induced G2/M phase arrest, apoptosis and leads to defects in DNA repair.
(A) Concentration-dependent growth inhibition in response to cisplatin in RIF1-silenced and scrambled control HeLa cells. (B) Half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) was calculated by Graphpad 5 from 3 independent experiments. Relative resistance factor (RRF) of cisplatin was calculated by dividing the IC50 of the control cells and by that of the cells with RIF1 knockdown. (C) HeLa cells were treated with cisplatin for 1 h, washed free of cisplatin (0 time point) and then harvested at various time points. Total cell lysate was immunoblotted for γ-H2AX antibody, which is a marker for damaged DNA not repaired yet. (D, E) RIF1 knockdown increases cisplatin induced G2/M phase arrest in a concentration-dependent manner compared with scrambled control. (F, G) Annexin V/PI staining showed that RIF1 knockdown HeLa cells enhanced cisplatin-induced apoptosis rate compared with scrambled control in a concentration-dependent manner. Data were presented as means ± SD of three independent experiments. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, *** P<0.001.