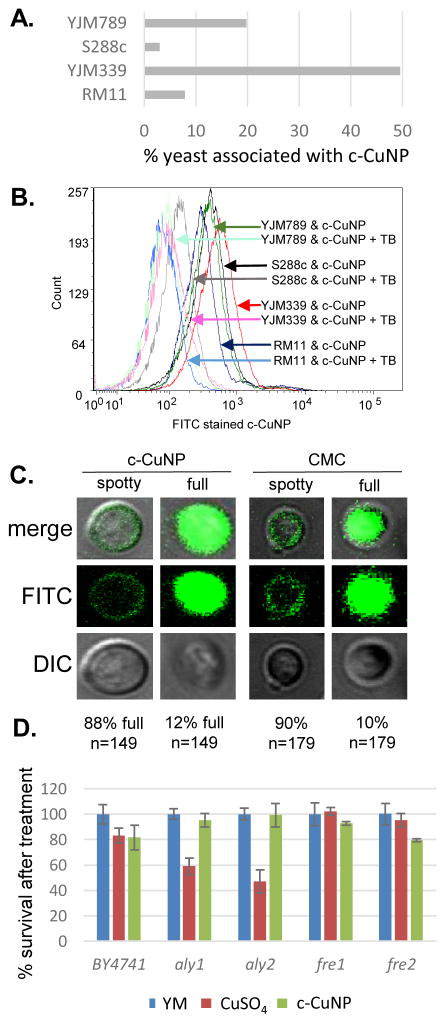
Fig 4. Physical interaction of copper nanoparticle and yeast cells.
A. Flow cytometry measuring interaction between FITC stained c-CuNP and Rhodamine B stained yeast strains, YJM789 (YJM789K5a), S288c (GSY147), RM11 and YJM339. 157 μM. Dual stained c-CuNP and yeast are graphed as percentage. Yeast were stained with Rhodamine B. c-CuNP and yeast were then incubated for two hours. B. Flow cytometry of FITC stained c-CuNP associated with yeast were quenched with trypan blue (TB). Arrows point to peaks as they shift in fluorescence. The number of cells measured is on the x-axis as count. Light lines represent yeast with c-CuNP and solid lines represent yeast and c-CuNP treated with trypan blue. C. Confocal microscopy of yeast (GSY147) and FITC stained c-CuNP. D. Cellular viability of yeast knockouts in the BY4741 (S288c) background normalized to yeast grown in YM supplemented with required amino acids treated with 400 μM CuSO4 or 157 μM c-CuNP.