Abstract
Beginning in 1970, a committee was constituted under the auspices of the World Health Organization (WHO) to catalog primary immunodeficiencies. Twenty years later, the International Union of Immunological Societies (IUIS) took the remit of this committee. The current report details the categorization and listing of 354 (as of February 2017) inborn errors of immunity. The growth and increasing complexity of the field have been impressive, encompassing an increasing variety of conditions, and the classification described here will serve as a critical reference for immunologists and researchers worldwide.
Keywords: IUIS, primary immune deficiency, immune dysregulation, autoinflammatory disorders
Introduction
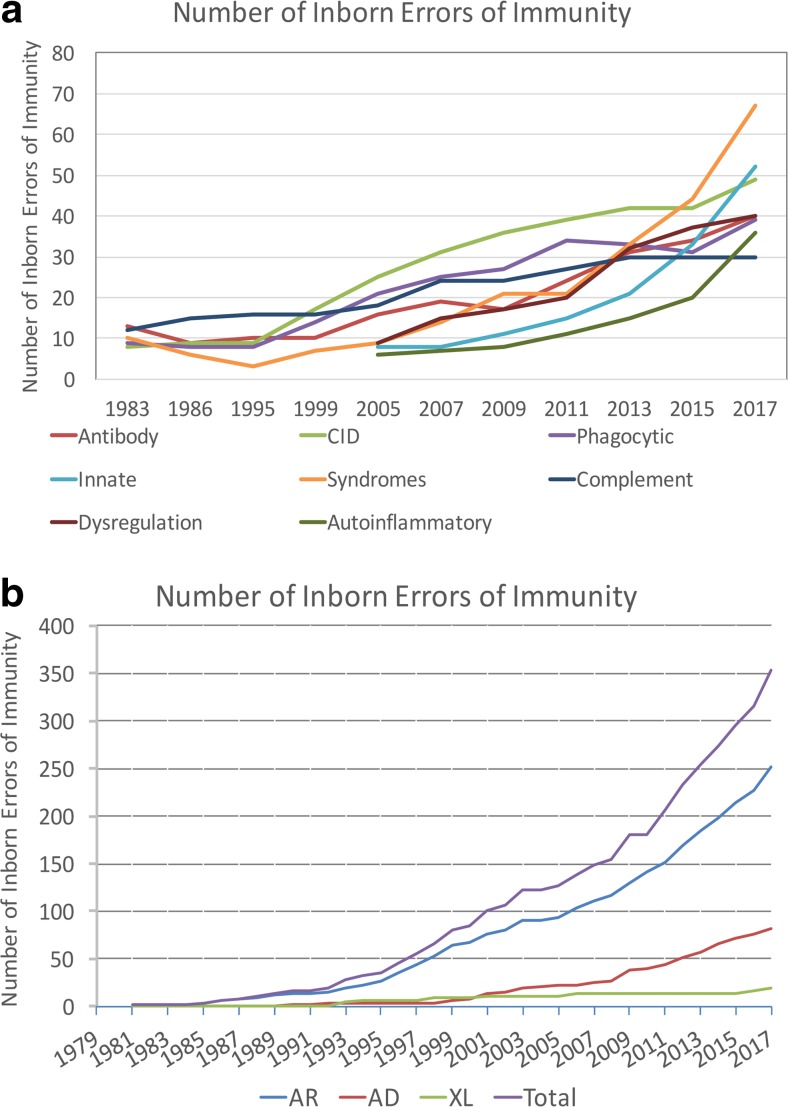
In 1970, Drs. Fudenberg, Good, Hitzig, Kunkel, Roitt, Rosen, Rowe, Seligmann, and Soothill met under the auspices of the World Health Organization to classify the emerging “primary immune deficiencies.” This august group focused on understanding whether immunodeficiencies could be categorized as B cell disorders or T cell disorders [1, 2]. Their initial report identified 16 distinct immunodeficiencies and included the prophetic comment that “the variable immunodeficiency group probably lumps together a series of syndromes…. Included in this group are cases previously classified as ‘congenital’, non-sex linked or sporadic hypogammaglobulinemia, primary ‘dysgammglobulinemia’ of both childhood and adult life, and ‘acquired’ primary hypogammaglobulinemia. It is hoped that careful analysis of such patients…. will result in delineation of several homogeneous syndromes…”. Indeed, the emergence of monogenic causes of hypogammaglobulinemia (Table 3) and disorders with variable immunoglobulin abnormalities associated with immune dysregulation (Table 4) have been the groups of immunodeficiencies most transformed by the advent of new technologies. Another group dramatically impacted by resetting of the clinical radar and new techniques has been the set of disorders associated with a limited spectrum of infectious susceptibility. The graphs in Fig. 1 define the transformation of the field over the interval during which next-generation sequencing came to prominence. The tremendous progress, energy, and enthusiasm in the field currently have led to a greater need than ever for a current cataloging of the disorders.
Table 3.
Predominantly antibody deficiencies
| Disease | Genetic defect | Inheritance | OMIM | Ig | Associated features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Severe reduction in all serum immunoglobulin isotypes with profoundly decreased or absent B cells, agammaglobulinemia | |||||
| BTK deficiency, X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) | BTK | XL | 300300 | All isotypes decreased in majority of patients, some patients have detectable immunoglobulins | Severe bacterial infections, normal numbers of pro-B cells |
| μ heavy chain deficiency | IGHM | AR | 147020 | All isotypes decreased | Severe bacterial infections, normal numbers of pro-B cells |
| λ5 deficiency | IGLL1 | AR | 146770 | All isotypes decreased | Severe bacterial infections, normal numbers of pro-B cells |
| Igα deficiency | CD79A | AR | 112205 | All isotypes decreased | Severe bacterial infections, normal numbers of pro-B cells |
| Igβ deficiency | CD79B | AR | 147245 | All isotypes decreased | Severe bacterial infections, normal numbers of pro-B cells |
| BLNK deficiency | BLNK | AR | 604515 | All isotypes decreased | Severe bacterial infections, normal numbers of pro-B cells |
| PIK3R1 deficiency | PIK3R1 | AR | 171833 | All isotypes decreased | Severe bacterial infections, decreased or absent pro-B cells |
| E47 transcription factor deficiency | TCF3 | AD | 147141 | All isotypes decreased | Recurrent bacterial infections |
| 2. Severe reduction in at least 2 serum immunoglobulin isotypes with normal or low number of B cells, CVID phenotype | |||||
| Common variable immune deficiency with no gene defect specified (CVID) | Unknown | Variable | Low IgG and IgA and/or IgM | Clinical phenotypes vary: most have recurrent infections, some have polyclonal lymphoproliferation, autoimmune cytopenias and/or granulomatous disease | |
| PIK3CD mutation (GOF) | PIK3CD GOF | AD | 602839 | All isotypes decreased | Severe bacterial infections; decreased or absent pro-B cells, EBV |
| PIK3R1 deficiency (LOF) | PIK3R1 | AD | 616005 | All isotypes decreased | Severe bacterial infections, pro-B cells present and low numbers of memory B cells, EBV |
| PTEN Deficiency (LOF) | PTEN | AD | 601728 | Decreased | Lymphoproliferation, autoimmunity |
| CD19 deficiency | CD19 | AR | 107265 | Low IgG and IgA and/or IgM | Recurrent infections, may have glomerulonephritis |
| CD81 deficiency | CD81 | AR | 186845 | Low IgG, low or normal IgA and IgM | Recurrent infections, may have glomerulonephritis |
| CD20 deficiency | MS4A1 | AR | 112210 | Low IgG, normal or elevated IgM and IgA | Recurrent infections |
| CD21 deficiency | CR2 | AR | 120650 | Low IgG, impaired anti-pneumococcal response | Recurrent infections |
| TACI deficiency | TNFRSF13B (TACI) | AD or AR | 604907 | Low IgG and IgA and/or IgM | Variable clinical expression |
| BAFF receptor deficiency | TNFRSF13C (BAFF-R) | AR | 606269 | Low IgG and IgM, | Variable clinical expression |
| TWEAK deficiency | TNFSF12 | AD | 602695 | Low IgM and A, lack of anti-pneumococcal antibody | Pneumonia, bacterial infections, warts, thrombocytopenia. Neutropenia |
| Mannosyl-oligosaccharide glucosidase deficiency (MOGS) | MOGS (GCS1) | AR | 601336 | Severe hypogammaglobulinemia, | Bacterial and viral infections, severe neurologic disease, also known as congenital disorder of glycosylation type IIb (CDG-IIb) |
| TRNT1 deficiency | TRNT1 | AR | 612907 | B cell deficiency and hypogammaglobulinemia | Congenital sideroblastic anemia, deafness, developmental delay |
| TTC37 deficiency | TTC37 | AR | 614649 | Poor antibody response to pneumococcal vaccine | Recurrent bacterial and viral infections, abnormal hair findings: trichorrhexis nodosa |
| NFKB1 deficiency | NFKB1 | AD | 164011 | Normal or low IgG, IgA, IgM, low or normal B cells, low memory B cells | Recurrent sinopulmonary infections, COPD, EBV proliferation, autoimmune cytopenias, alopecia and autoimmune thyroiditis |
| NFKB2 deficiency | NFKB2 | AD | 615577 | Low serum IgG, A and M; low B cell numbers | Recurrent sinopulmonary infections, alopecia, and endorinopathies |
| IKAROS deficiency | IKZF1 | AD | 603023 | Low IgG, IgA, IgM, low or normal B cells, potentially reducing levels with age | Recurrent sinopulmonary infections |
| IRF2BP2 deficiency | IRF2BP2 | AD | 615332 | Hypogammaglobulenia, absent IgA | Recurrent infections, possible autoimmunity and inflammatory disease |
| ATP6AP1 deficiency | ATP6AP1 | XL | 300197 | Variable immunoglobulin findings | Hepatopathy, leukopenia, low copper |
| 3. Severe reduction in serum IgG and IgA with normal/elevated IgM and normal numbers of B cells, hyper IgM | |||||
| AID deficiency | AICDA | AR | 605257 | IgG and IgA decreased, IgM increased | Bacterial infections, enlarged lymph nodes and germinal centers |
| UNG deficiency | UNG | AR | 191525 | IgG and IgA decreased, IgM increased | Enlarged lymph nodes and germinal centers |
| INO80 | INO80 | AR | 610169 | IgG and IgA decreased, IgM increased | Severe bacterial infections |
| MSH6 | MSH6 | AR | 600678 | Variable IgG, defects, increased IgM in some, normal B cells, low switched memory B cells, Ig-class switch recombination and somatic hypermutation defects | Family or personal history of cancer |
| 4. Isotype, light chain, or functional deficiencies with generally normal numbers of B cells | |||||
| Ig heavy chain mutations and deletions | Mutation or chromosomal deletion at 14q32 | AR | One or more IgG and/or IgA subclasses as well as IgE may be absent | May be asymptomatic | |
| Kappa chain deficiency | IGKC | AR | 147200 | All immunoglobulins have lambda light chain | Asymptomatic |
| Isolated IgG subclass deficiency | Unknown | ? | Reduction in one or more IgG subclass | Usually asymptomatic, a minority may have poor antibody response to specific antigens and recurrent viral/bacterial infections | |
| IgG subclass deficiency with IgA deficiency | Unknown | ? | Reduced IgA with decrease in one or more IgG subclass | Recurrent bacterial infections | |
| Selective IgA deficiency | Unknown | ? | Very low to absent IgA with other isotypes normal, normal subclasses and specific antibodies | Bacterial infections, autoimmunity mildly increased | |
| Specific antibody deficiency with normal Ig levels and normal B cells | Unknown | ? | Normal | Reduced ability to produce antibodies to specific antigens | |
| Transient hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy | Unknown | ? | IgG and IgA decreased | Normal ability to produce antibodies to vaccine antigens, usually not associated with significant infections | |
| CARD11 GOF | CARD11 | AD GOF | 607210 | High B cell numbers due to constitutive NF-κB activation | Splenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, poor vaccine response |
| Selective IgM deficiency | Unknown | ? | Absent serum IgM | Pneumococcal / bacterial infections | |
Common variable immunodeficiency disorders (CVID) include several clinical and laboratory phenotypes that may be caused by distinct genetic and/or environmental factors. Some patients with CVID and no known genetic defect have markedly reduced numbers of B cells as well as hypogammaglobulinemia. Identification of causal variants can assist in defining treatment. In addition to monogenic causes on this table, a small minority of patients with XLP (Table 4), WHIM syndrome (Table 6), ICF (Table 2), VOD1 (Table 2), thymoma with immunodeficiency (Good syndrome) or myelodysplasia are first seen by an immunologist because of recurrent infections, hypogammaglobulinemia and normal or reduced numbers of B cells. Total number of disorders in Table 3: 40. New disorders: 7, PTEN, NFKB1, IKZF1, IRF2BP2, ATP6AP1. Selective igA deficiency, selective IgM deficiency
EBV Epstein-Barr virus, COPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, XL X-linked inheritance, AR autosomal recessive inheritance, AD autosomal dominant inheritance, LOF loss-of-function, GOF gain-of-function
Table 4.
Diseases of immune dysregulation
| Disease | Genetic defect | Inheritance | OMIM | Circulating T cells | Circulating B cells | Functional defect | Associated features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (FHL syndromes) | |||||||
| Perforin deficiency (FHL2) | PRF1 | AR | 170280 | Increased activated T cells | Normal | Decreased to absent NK and CTL activities cytotoxicity | Fever, (H)SM, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), cytopenias |
| UNC13D/Munc13-4 deficiency (FHL3) | UNC13D | AR | 608897 | Increased activated T cells | Normal | Decreased to absent NK and CTL activities (cytotoxicity and/or degranulation) | Fever, (H)SM, HLH, cytopenias, |
| Syntaxin 11 deficiency (FHL4) | STX11 | AR | 605014 | Increased activated T cells | Normal | Decreased NK activity (cytotoxicity and/or degranulation) | Fever, (H)SM, cHLH, cytopenias, |
| STXBP2/Munc18-2 deficiency (FHL5) | STXBP2 | AR or AD | 601717 | Increased activated T cells | Normal | Decreased NK and CTL activities (cytotoxicity and/or degranulation) | Fever, (H)SM, cHLH, cytopenias, enteropathy |
| FAAP24 deficiency | FAAP24 | AR | 610884 | Increased activated T cells | Normal | Failure to kill autologous EBV transformed B cells. Normal NK cell function | EBV infection-driven lymphoproliferative disease |
| 2. FHL syndromes with hypopigmentation | |||||||
| Chediak-Higashi syndrome | LYST | AR | 606897 | Increased activated T cells | Normal | Decreased NK and CTL activities (cytotoxicity and/or degranulation) | Partial albinism, recurrent infections, fever, HSM, HLH, giant lysosomes, neutropenia, cytopenias, bleeding tendency, progressive neurological dysfunction |
| Griscelli syndrome, type 2 | RAB27A | AR | 603868 | Normal | Normal | Decreased NK and CTL activities (cytotoxicity and/or degranulation) | Partial albinism, fever, HSM, HLH, cytopenias |
| Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, type 2 | AP3B1 | AR | 603401 | Normal | Normal | Decreased NK and CTL activities (cytotoxicity and/or degranulation) | Partial albinism, recurrent infections, pulmonary fibrosis, increased bleeding, neutropenia, HLH |
| Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome, type 10 | AP3D1 | AR | 617050 | Normal | Normal | Decreased NK and CTL activities (cytotoxicity and/or degranulation) | Oculocutaneous albinism, severe neutropenia, recurrent infections, seizures, hearing loss, and neurodevelopmental delay |
| 3. Regulatory T cell defects | |||||||
| IPEX, immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy X-linked | FOXP3 | XL | 300292 | Normal | Normal | Lack of (and/or impaired function of) CD4+ CD25+ FOXP3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) | Autoimmune enteropathy, early-onset diabetes, thyroiditis hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, eczema, elevated IgE, IgA |
| CD25 deficiency | IL2RA | AR | 147730 | Normal to decreased | Normal | No CD4 + C25+ cells with impaired function of Tregs cells | Lymphoproliferation, autoimmunity, impaired T cell proliferation |
| CTLA4 deficiency (ALPSV) | CTLA4 | AD | 123890 | Decreased | Decreased | Impaired function of Tregs. | Autoimmune cytopenias, enteropathy, interstitial lung disease, extra-lymphoid lymphocytic infiltration recurrent infections |
| LRBA deficiency | LRBA | AR | 606453 | Normal or decreased CD4 numbers, T cell dysregulation | Low or normal numbers of B cells | Reduced I IgG and IgA in most | Recurrent infections, inflammatory bowel disease, autoimmunity, EBV infections |
| STAT3 GOF mutation | STAT3 | AD (GOF) | 102582 | Decreased | Decreased | Enhanced STAT3 signaling, leading to increased Th17 cell differentiation, lymphoproliferation and autoimmunity. Decreased Tregs and impaired function | Lymphoproliferation, solid organ autoimmunity, recurrent infections |
| BACH2 deficiency | BACH2 | AD | 605394 | Progressive T cell lymphopenia | Impaired memory B cell development | Haplosufficiency for a critical lineage specification transcription factor | Lymphocytic colitis, sinopulmonary infections |
| 4. Autoimmunity with or without Lymphoproliferation | |||||||
| APECED (APS-1), autoimmune polyendocrinopathy with candidiasis and ectodermal dystrophy | AIRE | AR or AD | 607358 | Normal | Normal | AIRE serves as check-point in the thymus for negative selection of autoreactive T cells and for generation of Tregs | Autoimmunity: hypoparathyroidism hypothyroidism, adrenal insufficiency, diabetes, gonadal dysfunction and other endocrine abnormalities, chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis, dental enamel hypoplasia, alopecia areata enteropathy, pernicious anemia |
| ITCH deficiency | ITCH | AR | 606409 | Not assessed | Not assessed | Itch deficiency may cause immune dysregulation by affecting both anergy induction in autoreactive effector T cells and generation of Tregs | Early-onset chronic lung disease (interstitial pneumonitis), autoimmunity (thyroiditis, type I diabetes, chronic diarrhea/enteropathy, and hepatitis), failure to thrive, developmental delay, dysmorphic facial features |
| ZAP-70 combined hypomorphic and activation mutations | ZAP70 | AR (LOF/GOF) | 176947 | Decreased CD8, normal or decreased CD4 cells | Normal or decreased | Hyperactive Zap70 kinase | Severe autoimmunity |
| Tripeptidyl-peptidase II deficiency | TPP2 | AR | 190470 | Decreased | Decreased | TPP2 deficiency results in premature immunosenescence and immune dysregulation | Variable lymphoproliferation, severe autoimmune cytopenias, hypergammaglobulinemia, recurrent infections |
| JAK1 GOF | JAK1 | AD GOF | 147795 | Not assessed | Not assessed | Hyperactive JAK1 | HSM, eosinophilia, eosinophilic enteritis, thyroid disease, poor growth, viral infections |
| Prolidase deficiency | PEPD | AR | 613230 | Normal | Normal | Peptidase D | Autoantibodies common, chronic skin ulcers, eczema, infections |
| 5. Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (ALPS, Canale-Smith syndrome) | |||||||
| ALPS-FAS | TNFRSF6 | AD or AR | 134637 | Increased CD4−CD8−TCR α/β-double negative (DN) T cells | Normal, low memory B cells | Apoptosis defect FAS mediated | Splenomegaly, adenopathies, autoimmune cytopenias, increased lymphoma risk, IgG and A normal or increased, elevated serum FasL and IL-10, vitamin B12 |
| ALPS-FASLG | FASLG | AR | 134638 | Increased DN T cells | Normal | Apoptosis defect FAS mediated | Splenomegaly, adenopathies, autoimmune cytopenias, SLE, soluble FasL is not elevated |
| ALPS-caspase 10 | CASP10 | AD | 601762 | Increased DN T cells | Normal | Defective lymphocyte apoptosis | Adenopathies, splenomegaly, autoimmunity |
| ALPS-caspase 8 | CASP8 | AR | 601763 | Slightly increased DN T cells | Normal | Defective lymphocyte apoptosis and activation | Adenopathies, splenomegaly, bacterial and viral infections, hypogammaglobulinemia |
| FADD deficiency | FADD | AR | 602457 | Increased DN T cells | Normal | Defective lymphocyte apoptosis | Functional hyposplenism, bacterial and viral infections, recurrent episodes of encephalopathy and liver dysfunction |
| 6. Immune dysregulation with colitis | |||||||
| IL-10 deficiency | IL10 | AR | 124092 | Normal | Normal | No functional IL-10 secretion | Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), Folliculitis, recurrent respiratory diseases, arthritis, |
| IL-10Ra deficiency | IL10RA | AR | 146933 | Normal | Normal | Leukocytes unresponsive to IL-10 | IBD, Folliculitis, recurrent respiratory diseases, arthritis, lymphoma |
| IL-10Rb deficiency | IL10RB | AR | 123889 | Normal | Normal | Leukocytes unresponsive to IL-10, IL-22, IL-26, IL-28A, IL-28B, and IL-29 | IBD, folliculitis, recurrent respiratory diseases, arthritis, lymphoma |
| NFAT5 haploinsufficiency | NFAT5 | AD | 604708 | Normal | Normal | Decreased memory B cells and plasmablasts | IBD, recurrent sinopulmonary infections |
| 7. Susceptibility to EBV and lymphoproliferative conditions | |||||||
| SH2D1A deficiency (XLP1) | SH2D1A | XL | 300490 | Normal or increased activated T cells | Reduced memory B cells | normal NK cell and CTL cytotoxic activity | Clinical and immunologic features triggered by EBV infection: HLH, lymphoproliferation, aplastic anemia, lymphoma. hypogammaglobulinemia, absent iNKT cells |
| XIAP deficiency (XLP2) | XIAP | XL | 300079 | Normal or Increased activated T cells; low/normal iNKT cells | Normal or reduced memory B cells | Increased T cells susceptibility to apoptosis to CD95 and enhanced activation-induced cell death (AICD) | EBV infection, splenomegaly, lymphoproliferation HLH, colitis, IBD, hepatitis low iNKT cells, hypogammaglobulinemia |
| CD27 deficiency | CD27 | AR | 615122 | Normal | No memory B cells | Low immunoglobulin after EBV infection | Features triggered by EBV infection, HLH, aplastic anemia, low iNKT cells, lymphoma |
| CTPS1 deficiency | CTPS1 | AR | 615897 | Nl to low, poor proliferation to antigen | Nl/low | Nl/high IgG | Recurrent/chronic bacterial and viral infections (EBV, VZV), lymphoproliferation, B cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma |
| RASGRP1 deficiency | RASGRP1 | AR | 603962 | Poor activation, proliferation, motility | Poor activation, proliferation, motility | Normal IgM, IgG, increased IgA | Recurrent pneumonia, herpesvirus infections, EBV associated lymphoma |
| CD70 deficiency | CD70 (TNFSF7) | AR | 602840 | Nl number, low Treg, poor activation and function | Nl number, poor antibody and memory responses | Reduced IgM, IgG, IgA (75%) and reduced Ag-specific Ab responses (50%) | EBV susceptibility, Hodgkin lymphoma |
| RLTPR (CARMIL2) deficiency | RLTPR | AR | 610859 | Nl number, low Treg, high CD4, poor function | Nl number | Nl to low, poor T dependent antibody response | Recurrent bacterial, fungal and mycobacterial infections, viral warts, molluscum and EBV lymphoproliferative and other malignancy, atopy |
| ITK deficiency | ITK | AR | 186973 | Progressive decrease | Normal | Nl to low | EBV associated B cell lymphoproliferation, lymphoma, Nl or low IgG |
| MAGT1 deficiency (XMEN) | MAGT1 | XL | 300853 | Low CD4 Low recent thymic emigrant cells, poor proliferation to CD3 |
Normal | Normal | EBV infection, lymphoma, viral infections, respiratory and GI infections |
| PRKCD deficiency | PRKCD | AR | 176977 | Normal | Low memory B cells, high CD5 B cells | Apoptotic defect in B cells | Recurrent infections, EBV chronic infection, lymphoproliferation, SLE-like autoimmunity (nephrotic and antiphospholipid syndromes), low IgG |
Total number of disorders in Table 4: 40. New disorders: 9, FAAP24, RASGRP1, CD70, RLTPR, ZAP70 (GOF + LOF), AP3D1, BACH2, JAK1 GOF, PEPD. Removed gene: Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome type 9 was removed due to retraction of the defining publication
FHL familial hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, HLH hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, HSM hepatosplenomegaly ((H)SM indicating variable hepatomegaly), DN double negative, SLE systemic lupus erythematous, IBD inflammatory bowel disease, XL X-linked inheritance, AR autosomal recessive inheritance, AD autosomal dominant inheritance, LOF loss-of-function, GOF gain-of-function
Fig. 1.
Each publication of the World Health Organization and IUIS Primary Immunodeficiencies Committee was reviewed for the number of conditions listed and displayed graphically [1–19]. The rapid increase in the twenty-first century relates to improved awareness and increasing use of sequencing. Assuming 20,000 coding genes in the human genome, inborn errors of immunity are implicated through mutations in 1.7% of these genes. There are now 330 specific disorders, 320 monogenic defects, 312 distinct genes (nine genes with both LOF and GOF and C4 deficiency requiring defects in both C4A and C4B). a The categorization of the inborn errors of immunity according the schema in the current manuscript. b The categorization of the inborn errors of immunity according to their inheritance
The new disorders (since 2015 [3]) represent an impressive spectrum of phenotypes. There are 354 distinct disorders with 344 different gene defects listed. The emerging dominance of next-generation sequencing has driven the rapid increase in the number of recognized disorders which has led to two major consequences. Often new inborn errors of immunity are initially described in a single kindred or a small number of kindreds. This may lead to incorrect assumptions about prevalence and phenotype. In fact, for most disorders, we have little idea of the prevalence within even the recognized population with the described phenotype. The second consequence of the rapid rise of next-generation sequencing is a striking expansion of the phenotypic spectrum associated with many diseases. Where once the phenotype of a given disorder was clear, the spectrum of manifestations often extends impressively once the ascertainment is not linked to a preconceived idea [20]. As a community, we recognize the importance of publishing cases and small series and to report specific mutations with clinical findings because publications are used to define likelihood of causality during bioinformatic analysis of next-generation sequencing results.
In 1999, the Committee on Primary Immunodeficiencies came under the auspices of the International Union of Immunological Societies (IUIS). The current committee met on February 23–24, 2017, in London to update the classification of human primary immunodeficiencies. Inclusion in this “master list” requires a body of literature supporting causality of a gene defect and a penetrance indicating clinical relevance [21]. Committee members vote on inclusion of each new disorder and this publications lists those included as of the February 2017 meeting. The landscape is changing so rapidly, and the number of primary immunodeficiencies growing so fast, that two major changes have been implemented. The published list will continue to serve as a reference; however, this list will now be available as a csv file on the IUIS website to enable sorting according to gene, disease name, or clinical/laboratory feature. This file will also include the associated ICD10 codes in order to promote harmonization of utilization. The second major change is to the nomenclature. The term primary immunodeficiency has an important legacy—the abbreviations PID or PIDD are often used by patient organizations and are recognized around the world. However, this terminology does limit the conceptualization of disorders to those in which susceptibility to infection is the main manifestation. The improving recognition of immune dysregulation diseases, including the growing field of autoinflammatory disorders and interferonopathies, has mandated that a more encompassing terminology be used. This manuscript, therefore, utilizes “inborn errors of immunity” as the descriptor for the work and the categorization. In addition to embracing technology to remain updated, the companion publication “Update of the Phenotypical IUIS Classification for Primary Immunodeficiencies” will provide a phenotype-oriented approach to the IUIS categorization of disorders. Moreover, a new free application can be found as “PID phenotypical diagnosis” or “PID classification” from iTunes and Android app stores [22, 23]. Information that is readily accessible is the new standard, and the IUIS Expert Committee on Primary Immunodeficiencies believes that improved access to information will positively impact patient care around the world.
The tables divide disease categories according to common phenotypes for ease of review and searching. Table 1 lists combined immunodeficiencies, Table 2 lists combined immunodeficiencies with syndromic features, Table 3 lists predominantly antibody deficiencies, Table 4 lists diseases of immune dysregulation, Table 5 lists defects of phagocyte number or function, Table 6 lists defects in intrinsic and innate immunity, Table 7 lists autoinflammatory diseases, Table 8 lists complement deficiencies, and Table 9 lists phenocopies of inborn errors of immunity. The division into phenotypes for the purpose of this list does not imply that the presentation is homogeneous. Each disorder is listed only once for the sake of simplicity although distinct modes of inheritance can be listed separately. There are nine genes for which both loss-of-function and gain-of-function variants have been identified: CFB, C3, CARD11, STAT1, STAT3, WAS, JAK1, IFIH1, and ZAP70. For these, the loss-of-function and gain-of-function aspects are listed. Within each table, there are additional sub-tables that segregate into coherent phenotypic sets. At the end of each table, the new disorders, added for this publication, are listed for easy reference. Other features important for navigation of the list include the use of OMIM links [24]. For additional information on a gene, the links can be accessed from within the online publication. For the second time, we also include non-inborn errors of immunity in Table 9, representing phenocopies of inborn errors which might be important to consider diagnostically.
Table 1.
Immunodeficiencies affecting cellular and humoral immunity
| Disease | Genetic defect | Inheritance | OMIM | T cells | B cells | Ig | Associated features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. T-B+ severe combined immune deficiency (SCID) | |||||||
| γc deficiency (common gamma chain SCID, CD132 deficiency) | IL2RG | XL | 308380 | Very low | Normal to high | Low | Low NK |
| JAK3 deficiency | JAK3 | AR | 600173 | Very low | Normal to high | Low | Low NK |
| IL7Rα deficiency | IL7R | AR | 146661 | Very low | Normal to high | Low | Nl NK |
| CD45 deficiency | PTPRC | AR | 151460 | Very low | Normal | Low | Nl γ/δ Τ cells |
| CD3δ deficiency | CD3D | AR | 186790 | Very low | Normal | Low | Nl NK, no γ/δ T cells |
| CD3ε deficiency | CD3E | AR | 186830 | Very low | Normal | Low | Nl NK, no γ/δ T cells |
| CD3ζ deficiency | CD247 | AR | 186780 | Very low | Normal | Low | Nl NK, no γ/δ T cells |
| Coronin-1A deficiency | CORO1A | AR | 605000 | Very low | Normal | Low | Detectable thymus, EBV |
| LAT deficiency | LAT | AR | 602354 | Nl to low number | Nl to low | High | Adenopathy, splenomegaly, recurrent infections, autoimmunity |
| 2. T-B- SCID | |||||||
| RAG1 deficiency | RAG1 | AR | 179615 | Very low | Very low | Decreased | Nl NK |
| RAG2 deficiency | RAG2 | AR | 179616 | Very low | Very low | Decreased | Nl NK |
| DCLRE1C (Artemis) deficiency | DCLRE1C | AR | 605988 | Very low | Very low | Decreased | Nl NK, radiation sensitive |
| DNA PKcs deficiency | PRKDC | AR | 176977 | Very low | Very low | Variable | Nl NK, radiation sensitive, microcephaly |
| Cernunnos/XLF deficiency | NHEJ1 | AR | 611290 | Very low | Very low | Decreased | Nl NK, radiation sensitive, microcephaly |
| DNA ligase IV deficiency | LIG4 | AR | 601837 | Very low | Very low | Decreased | Nl NK, radiation sensitive, microcephaly |
| Reticular dysgenesis | AK2 | AR | 103020 | Very low | Nl to low | Decreased | Granulocytopenia and deafness |
| Adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency | ADA | AR | 608958 | Very low | Low, decreasing | Low, decreasing | Low NK, bone defects, may have pulmonary alveolar proteinosis, cognitive defects |
| 3. Combined immunodeficiencies generally less profound than severe combined immunodeficiency | |||||||
| DOCK2 deficiency | DOCK2 | AR | 603122 | Low | Normal | IgG Nl or low, poor antibody responses | Nl NK cells, but defective function. Poor interferon responses in hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic cells |
| CD40 ligand deficiency (CD154) | CD40LG (TNFSF5) | XL | 300386 | Nl to low | sIgM+, IgD+ cells present, absent sIgG+, IgA+, and IgE+ cells | IgM normal or high, other Ig isotypes low | Neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia, opportunistic infections, biliary tract and liver disease, Cryptosporidium infections |
| CD40 deficiency | CD40 (TNFRSF5) | AR | 109535 | Normal | sIgM+, IgD+ cells present, absent sIgG+, IgA+ and IgE+ cells | IgM normal or high, other Ig isotypes low | Neutropenia, opportunistic infections, gastrointestinal and biliary tract and liver disease, Cryptosporidium infections |
| ICOS deficiency | ICOS | AR | 604558 | Normal | Normal | Low | Recurrent infections, autoimmunity, gastroenteritis, granulomas |
| CD3γ deficiency | CD3G | AR | 186740 | Nl number, but low TCR expression | Normal | Normal | |
| CD8 deficiency | CD8A | AR | 186910 | Absent CD8, nl CD4 | Normal | Normal | Recurrent infections, may be asymptomatic |
| ZAP-70 deficiency (ZAP70 LOF) | ZAP70 | AR | 176947 | Low CD8, Nl CD4 number but poor function | Normal | Normal | May have immune dysregulation, autoimmunity |
| MHC class I deficiency | TAP1 | AR | 170260 | Low CD8, Nl CD4, absent MHC I on lymphocytes | Normal | Normal | Vasculitis, pyoderma gangrenosum |
| MHC class I deficiency | TAP2 | AR | 170261 | Low CD8, Nl CD4, absent MHC I on lymphocytes | Normal | Normal | Vasculitis, pyoderma gangrenosum |
| MHC class I deficiency | TAPBP | AR | 601962 | Low CD8, Nl CD4, absent MHC I on lymphocytes | Normal | Normal | Vasculitis, pyoderma gangrenosum |
| MHC class I deficiency | B2M | AR | 109700 | Low CD8, Nl CD4, absent MHC I on lymphocytes | Normal | Normal | Sinopulmonary infections, cutaneous granulomas. Absent β2m associated proteins MHC I, CD1a, CD1b, CD1c |
| MHC class II deficiency group A | CIITA | AR | 600005 | Low CD4 cells Absent MHC II expression on lymphocytes |
Normal | Nl to low | Respiratory and gastrointestinal infections, liver/biliary tract disease |
| MHC class II deficiency group B | RFXANK | AR | 603200 | Low CD4 cells Absent MHC II expression on lymphocytes |
Normal | Nl to low | Respiratory and gastrointestinal infections, liver/biliary tract disease |
| MHC class II deficiency group C | RFX5 | AR | 601863 | Low CD4 cells Absent MHC II expression on lymphocytes |
Normal | Nl to low | Respiratory and gastrointestinal infections, liver/biliary tract disease |
| MHC class II deficiency group D | RFXAP | AR | 601861 | Low CD4 cells Absent MHC II expression on lymphocytes |
Normal | Nl to low | Respiratory and gastrointestinal infections, liver/biliary tract disease |
| DOCK8 deficiency | DOCK8 | AR | 243700 | Low, poor proliferation, few, poorly functioning Treg | Low, low CD27+ memory B cells Poor peripheral B cell tolerance | Low IgM, Nl to high IgG and IgA, high IgE | Low NK cells with poor function, eosinophilia, recurrent infections, cutaneous viral, fungal and staphylococcal infections, severe atopy, cancer diathesis |
| Rhoh deficiency | RHOH | AR | 602037 | Nl number, low naïve T cells, restricted repertoire, poor proliferation to CD3 | Normal | Normal | HPV infection, lung granulomas, molluscum contagiosum, lymphoma |
| MST1 deficiency | STK4 | AR | 614868 | Low, low terminal differentiated effector memory (TEMRA) cells, low naïve T cells, poor proliferation | Low | High | Intermittent neutropenia, bacterial, viral (HPV), candidal infections, EBV lymphoproliferation, autoimmune cytopenias, lymphoma, congenital heart disease |
| TCRα deficiency | TRAC | AR | 615387 | Absent TCRαβ, all T cells are γδ, poor proliferation | Normal | Normal | Recurrent viral, bacterial, fungal infections, immune dysregulation and autoimmunity, diarrhea |
| LCK deficiency | LCK | AR | 615758 | Low CD4+, low Treg, restricted T cell repertoire, poor TCR signaling | Normal | Nl IgG and IgA, high IgM | Recurrent infections, immune dysregulation, autoimmunity |
| MALT1 deficiency | MALT1 | AR | 615468 | Nl number, poor proliferation | Normal | Nl levels, poor specific antibody response | Bacterial, fungal and viral infections |
| CARD11 deficiency (LOF) | CARD11 | AR | 615206 | Nl number, predominant naïve T cells, poor proliferation | Normal, transitional B cell predominance | Absent/low | Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, bacterial and viral infections |
| BCL10 deficiency | BCL10 | AR | 616098 | Nl number, low memory T and Treg cells, poor antigen and anti-CD3 proliferation | Nl number, decreased memory and switched B cells | Low | Recurrent bacterial and viral infections, candidiasis, gastroenteritis |
| BCL11B deficiency | BCL11B | AD | 617237 | Low, poor proliferation | Normal | Normal | Congenital abnormalities, neonatal teeth, dysmorphic facies, absent corpus callosum, neurocognitive deficits |
| IL-21 deficiency | IL21 | AR | 615767 | Nl number, nl/low function | Low | Low IgG | Severe early-onset colitis, recurrent sinopulmonary infections |
| IL-21R deficiency | IL21R | AR | 615207 | Nl number, low cytokine production, poor antigen proliferation | Normal | Nl number, poor specific antibody responses | Recurrent infections, Pneumocystis jiroveci, Cryptosporidium infections and liver disease |
| OX40 deficiency | TNFRSF4 | AR | 615593 | Nl numbers, low antigen specific memory CD4+ | Nl numbers, low memory B cells | Normal | Impaired immunity to HHV8, Kaposi’s sarcoma |
| IKBKB deficiency | IKBKB | AR | 615592 | Nl number, absent Treg and γ/δ T cells, impaired TCR activation | Nl number, poor function | Low | Recurrent bacterial, viral, fungal infections, opportunistic infections |
| NIK deficiency | MAP3K14 | AR | 604655 | Nl number, poor proliferation to antigen | Low, low switched memory B cells | Low Ig’s | Low NK number and function, recurrent bacterial, viral and Cryptosporidium infections |
| RelB deficiency | RELB | AR | 604758 | Nl number, poor diversity, poor function | Recurrent infections | ||
| Moesin deficiency | MSN | XL | 300988 | Nl number, defective migration, proliferation | Low number | Low Ig’s over time | Recurrent infections with bacteria, varicella, neutropenia |
| TFRC deficiency | TFRC | AR | 616740 | Nl number, poor proliferation | Nl number, low memory B cells | Low | Recurrent infections, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia |
SCID/CID spectrum: Infants with SCID who have maternal T cell engraftment may have T cells in normal numbers that do not function normally; these cells may cause autoimmune cytopenias or graft versus host disease. Hypomorphic mutations in several of the genes that cause SCID may result in Omenn syndrome (OS), or “leaky” SCID, or still less profound combined immunodeficiency (CID) phenotypes. Both OS and leaky SCID can be associated with > 300 autologous T cells/μL of peripheral blood and reduced, rather than absent, proliferative responses when compared with typical SCID caused by null mutations. A spectrum of clinical findings including typical SCID, OS, leaky SCID, CID, granulomas with T lymphopenia, autoimmunity and CD4 T lymphopenia can be found in an allelic series of RAG1 and other SCID-associated genes. Total number of disorders in Table 1: 49 (17 SCID, 32 CID). New disorders: 5, MOESIN, BCL11B, TFRC, RELB, LAT. Removed gene: UNC119 deficiency has been removed. The UNC119 variant reported previously is a benign polymorphism in unaffected individuals
SCID severe combined immunodeficiency, EBV Epstein-Barr virus, MHC major histocompatibility complex, HPV human papillomavirus, Treg T regulatory cell, Nl normal, XL X-linked inheritance, AR autosomal recessive inheritance, AD autosomal dominant inheritance, LOF loss-of-function
Table 2.
Combined immunodeficiencies with associated or syndromic features
| Disease | Genetic defect | Inheritance | OMIM | T cells | B cells | Ig | Associated features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Immunodeficiency with congenital thrombocytopenia | |||||||
| Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS LOF) | WAS | XL | 300392 | Progressive decrease in numbers, abnormal lymphocyte responses to anti-CD3 | Normal numbers | Low IgM and antibody responses to polysaccharides, often high IgA and IgE | Thrombocytopenia with small platelets, recurrent bacterial and viral infections, bloody diarrhea, eczema, lymphoma, autoimmune disease, IgA nephropathy, vasculitis. XL thrombocytopenia is a mild form of WAS, and XL neutropenia is caused by missense mutations in the GTPase binding domain of WASp |
| WIP deficiency | WIPF1 | AR | 602357 | Reduced, defective lymphocyte responses to anti-CD3 | Normal or low | Normal, except for high IgE | Thrombocytopenia with or without small platelets, recurrent bacterial and viral infections, eczema, bloody diarrhea, WAS protein absent |
| ARPC1B deficiency | ARPC1B | AR | 604223 | Normal | Normal numbers | Normal except for high IgA and IgE | Mild thrombocytopenia with normal sized platelets, recurrent invasive infections, colitis, vasculitis, autoantibodies (ANA, ANCA), eosinophilia, defective Arp2/3, filament branching |
| 2. DNA repair defects other than those listed in Table 1 | |||||||
| Ataxia-telangiectasia | ATM | AR | 607585 | Progressive decrease, abnormal proliferation to mitogens | Normal | Often low IgA, IgE and IgG subclasses, increased IgM monomers, antibodies variably decreased | Ataxia, telangiectasia, pulmonary infections, lymphoreticular and other malignancies, increased alpha fetoprotein, increased radiosensitivity, chromosomal instability and chromosomal translocations |
| Nijmegen breakage syndrome | NBS1 | AR | 602667 | Progressive decrease | Variably reduced | Often low IgA, IgE, and IgG subclasses, increased IgM, antibodies variably decreased | Microcephaly, dysmorphic facies, lymphomas, solid tumors, increased radiosensitivity, chromosomal instability |
| Bloom Syndrome | BLM (RECQL3) | AR | 604610 | Normal | Normal | Low | Short stature, dysmorphic facies, sun-sensitive erythema, marrow failure, leukemia, lymphoma, chromosomal instability |
| Immunodeficiency with centromeric instability and facial anomalies, ICF1 | DNMT3B | AR | 602900 | Decreased or normal, responses to PHA may be decreased | Decreased or normal | Hypogammaglobulinemia or agammaglobulinemia, variable antibody deficiency | |
| Immunodeficiency with centromeric instability and facial anomalies, ICF2 | ZBTB24 | AR | 614064 | Decreased or normal, | Decreased or normal | Hypogammaglobulinemia or agammaglobulinemia, variable antibody deficiency | |
| Immunodeficiency with centromeric instability and facial anomalies, ICF3 | CDCA7 | AR | 609937 | responses to PHA may be decreased | Decreased or normal | Hypogammaglobulinemia or agammaglobulinemia, variable antibody deficiency | |
| Immunodeficiency with centromeric instability and facial anomalies, ICF4 | HELLS | AR | 603946 | Decreased or normal | Decreased or normal | Hypogammaglobulinemia or agammaglobulinemia, variable antibody deficiency | |
| PMS2 deficiency | PMS2 | AR | 600259 | Normal | Low B cells, switched and non-switched | Low IgG and IgA, high IgM, abnormal antibody responses | Recurrent infections, café-au-lait spots, lymphoma, colorectal carcinoma, brain tumors |
| RNF168 deficiency (radiosensitivity, immune deficiency, dysmorphic features, learning difficulties [RIDDLE] syndrome) | RNF168 | AR | 612688 | Normal | Normal | Low IgG or IgA | Short stature, mild defect of motor control to ataxia, normal intelligence to learning difficulties, mild facial dysmorphism to microcephaly, increased radiosensitivity |
| MCM4 deficiency | MCM4 | AR | 602638 | Normal | Normal | Normal | NK cells: low number and function. Viral infections (EBV, HSV, VZV), short stature, B cell lymphoma, adrenal failure |
| POLE1 (polymerase ε subunit 1) deficiency (FILS syndrome) | POLE | AR | 174762 | Decreased T cell proliferation | Low memory B cells | Low IgG2 and IgM, lack of antibody to PPS | Recurrent respiratory infections, meningitis, facial dysmorphism, livido, short stature |
| POLE2 (polymerase ε subunit 2) deficiency | POLE2 | AR | 602670 | Lymphopenia, lack of TRECS, absent proliferation in response to antigens | Very low | Hypogammaglobulinemia | Recurrent infections, disseminated BCG infections, autoimmunity (type 1 diabetes, hypothyroidism, facial dysmorphism |
| Ligase I deficiency | LIG1 | AR | 126391 | Lymphopenia, decreased mitogen response | Normal | Low IgA and IgG Reduced antibody responses |
Recurrent respiratory infections, growth retardation, sun sensitivity, lymphoma, radiation sensitivity |
| NSMCE3 deficiency | NSMCE3 | AR | 608243 | Number decreased, poor response to mitogens and antigens | Normal | Normal Decreased Ab responses to PPS normal IgG, IgA, elevated IgM |
Severe lung disease (possibly viral), thymic hypoplasia, chromosomal breakage, radiation sensitivity |
| ERCC6L2 (Hebo deficiency) | ERCC6L2 | AR | 615667 | Lymphopenia | Low | Normal | Facial dysmorphism, microcephaly, bone marrow failure |
| GINS1 deficiency | GINS1 | AR | 610608 | Low or normal | Low or normal | High IgA, low IgM and IgG | Neutropenia, IUGR, NK cells very low |
| 3. Thymic defects with additional congenital anomalies | |||||||
| DiGeorge/velocardiofacial syndrome Chromosome 22q11.2 deletion syndrome (22q11.2DS) |
Large deletion (3 Mb) typically in chromosome 22 | AD | 602054 | Decreased or normal, 5% have < 1500 CD3T cells/μL in neonatal period | Normal | Normal or decreased | Hypoparathyroidism, conotruncal cardiac malformation, velopalatal insufficiency, abnormal facies, intellectual disability |
| DiGeorge/velocardiofacial syndrome | Unknown | Sporadic | Decreased or normal | Normal | Normal or decreased | Hypoparathyroidism, conotruncal cardiac malformation, velopalatal insufficiency, abnormal facies, intellectual disability | |
| TBX1 deficiency | TBX1 | AD | 602054 | Decreased or normal | Normal | Normal or decreased | Hypoparathyroidism, conotruncal cardiac malformation, velopalatal insufficiency, abnormal facies, intellectual disability |
| CHARGE syndrome due to CHD7 deficiency | CHD7 | AD | 608892 | Decreased or normal, response to PHA may be decreased | Normal | Normal or decreased | Coloboma, heart anomaly, choanal atresia, intellectual disability, genital and ear anomalies, CNS malformation, some are SCID-like and have low TRECs |
| CHARGE syndrome due to SEMA3E deficiency | SEMA3E | AD | 608166 | Decreased or normal, response to PHA may be decreased | Normal | Normal or decreased | Coloboma, heart anomaly, choanal atresia, intellectual retardation, genital and ear anomalies, CNS malformation, some are SCID-like and have low TRECs |
| CHARGE syndrome | Unknown | Decreased or normal, response to PHA may be decreased | Normal | Normal or decreased | Coloboma, heart anomaly, choanal atresia, intellectual disability, genital and ear anomalies, CNS malformation, some are SCID-like and have low TRECs | ||
| Winged helix nude FOXN1 deficiency | FOXN1 | AR | 600838 | Very low | Normal | Decreased | Severe infections, abnormal thymic epithelium, immunodeficiency, congenital alopecia, nail dystrophy, neural tube defect |
| Chromosome 10p13-p14 deletion Syndrome (10p13-p14DS) | Del10p13-p14 | AD | 601362 | Normal, rarely lymphopenia and decreased lymphoproliferation to mitogens and antigens, hypolastic thymus may be present | Normal | Normal | Hypoparathyroidism, renal disease, deafness, growth retardation, facial dysmorphism, cardiac defects may be present, recurrent infections +/− |
| 4. Immuno-osseous dysplasias | |||||||
| Cartilage hair hypoplasia (CHH) | RMRP | AR | 157660 | Varies from severely decreased (SCID) to normal, impaired lymphocyte proliferation | Normal | Normal or reduced, antibodies variably decreased | Short-limbed dwarfism with metaphyseal dysostosis, sparse hair, bone marrow failure, autoimmunity, susceptibility to lymphoma and other cancers, impaired spermatogenesis, neuronal dysplasia of the intestine |
| Schimke immuno-osseous dysplasia | SMARCAL1 | AR | 606622 | Decreased | Normal | Normal | Short stature, spondiloepiphyseal dysplasia, intrauterine growth retardation, nephropathy, bacterial, viral, fungal infections, may present as SCID, bone marrow failure |
| MYSM1 deficiency | MYSM1 | AR | 612176 | T cell lymphopenia, reduced naïve T cells | Immature B cells | Hypogammaglobulinemia | Short stature, recurrent infections, congenital bone marrow failure, myelodysplasia, immunodeficiency affecting B cells and granulocytes, skeletal anomalies, cataracts, developmental delay. |
| MOPD1 deficiency | RNU4ATAC | AR | 601428 | Normal | Normal | Normal, specific antibodies variably decreased | Recurrent bacterial infections, lymphadenopathy, spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia, extreme intrauterine growth retardation, retinal dystrophy, facial dysmorphism, may present with microcephaly |
| EXTL3 deficiency | EXTL3 | AR | Reduced | Normal | Variably decreased | Platyspondyly, kyphosis, variable skeletal dysplasias, developmental delay | |
| 5. Hyper IgE syndromes (HIES) | |||||||
| AD-HIES STAT3 deficiency (Job syndrome) |
STAT3 | AD LOF | 102582 | Normal overall, Th-17 and T-follicular helper cells decreased | Normal, reduced switched and non-switched memory B cells, BAFF expression increased | High IgE, specific antibody production decreased | Distinctive facial features (broad nasal bridge), bacterial infections (boils and pulmonary abscesses, pneumatoceles) due to S. aureus, pulmonary aspergillus, Pneumocystis jirovecii, eczema, mucocutaneous candidiasis, hyperextensible joints, osteoporosis and bone fractures, scoliosis, retention of primary teeth, coronary and cerebral aneurysm formation |
| Comel-Netherton syndrome | SPINK5 | AR | 605010 | Normal | Low Switched and non-switched B cells | High IgE and IgA Antibody variably decreased |
Congenital ichthyosis, bamboo hair, atopic diathesis, increased bacterial infections, failure to thrive |
| PGM3 deficiency | PGM3 | AR | 172100 | CD8 and CD4 T cells may be decreased | Low B and memory B cells | Normal or elevated IgG and IgA, most high IgE, eosinophilia | Severe atopy, autoimmunity, bacterial and viral infections, skeletal anomalies dysplasia: short stature, brachydactyly, dysmorphic facial features, and intellectual disability cognitive impairment, hypomyelination |
| 6. Dyskeratosis congenita (DKC), myelodysplasia, short telomeres | |||||||
| XL-DKC due to dyskerin deficiency | DKC1 | XL | 300126 | Progressive decrease | Progressive decrease | Variable hypogammaglobulinemia | Intrauterine growth retardation, microcephaly, nail dystrophy, sparse scalp hair and eyelashes, hyperpigmentation of skin, palmar hyperkeratosis, premalignant oral leukoplakia, pancytopenia, myelodysplasia, +/− recurrent infections. A severe phenotype with developmental delay and cerebellar hypoplasia known as Hoyeraal-Hreidarsson syndrome (HHS) may occur in some DKC patients |
| AR-DKC due to nucleolar protein family A member 2 (NHP2) deficiency | NHP2 | AR | 606470 | Decreased | Variable | Variable | |
| AR-DKC due to nucleolar protein family A member 3 (NHP3) or NOP10 deficiency | NOP10 | AR | 606471 | Decreased | Variable | Variable | |
| AD/AR-DKC due to regulator of telomere elongation (RTEL1) deficiency | RTEL1 | AD or AR | 608833 | Decreased | Variable | Variable | |
| AD-DKC due to TERC deficiency | TERC | AD | 602322 | Variable | Variable | Variable | |
| AD/AR-DKC due to TERT deficiency | TERT | AD or AR | 187270 | Variable | Variable | Variable | |
| AD-DKC due to TINF2 deficiency | TINF2 | AD | 604319 | Variable | Variable | Variable | |
| AD/AR-DKC due to TPP1 deficiency | TPP1 | AD or AR | 609377 | Variable | Variable | Variable | |
| AR-DKC due to DCLRE1B deficiency | DCLRE1B/SNM1/APOLLO: | AR | 609683 | Variable | Variable | Variable | |
| AR-DKC due to PARN deficiency | PARN | AR (AD?) | 604212 | Variable | Variable | Variable | |
| AR-DKC due to WRAP53 deficiency | WRAP53 | AR | 612661 | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | |
| Coats plus syndrome due to STN1 deficiency | STN1 | AR | 613128 | Variable | Variable | Not known | Intrauterine growth retardation, premature aging, pancytopenia, hypocellular bone marrow, gastrointestinal hemorrhage due to vascular ectasia, intracranial calcification, abnormal telomeres |
| Coats plus syndrome due to CTC1 deficiency | CTC1 | AR | 613129 | Normal | Normal | Normal | Intrauterine growth retardation, sparse graying hair, dystrophic nails, trilinear bone marrow failure, osteopenia, gastrointestinal hemorrhage due to vascular ectasia, retinal telangiectasia, intracranial calcification, abnormal telomeres |
| SAMD9 | SAMD9 | AD (GOF) | 617053 | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | IUGR with gonadal abnormalities, adrenal failure, MDS with chromosome 7 aberrations, predisposition to infections, enteropathy, absent spleen |
| SAMD9L | SAMD9L | AD (GOF) | 159550 | Normal | Low | Not reported | Cytopenia, predisposition to MDS with chromosome 7 aberrations, immunodeficiency, and progressive cerebellar dysfunction |
| 7. Defects of vitamin B12 and folate metabolism | |||||||
| Transcobalamin 2 deficiency | TCN2 | AR | 613441 | Normal | Variable | Decreased | Megaloblastic anemia, pancytopenia, if untreated for prolonged periods results in intellectual disability |
| SLC46A1/PCFT deficiency causing hereditary folate malabsorption | SLC46A1 | AR | 229050 | Variable numbers and activation profile | Variable | Decreased | Megaloblastic anemia, if untreated for prolonged periods results in intellectual disability |
| Methylene-tetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase 1 (MTHFD1) deficiency | MTHFD1 | AR | 172460 | Low thymic output, normal in vitro proliferation | Low | Decreased/poor antibody responses to conjugated polysaccharide antigens | Recurrent bacterial infection, Pneumocystis jirovecii, megaloblastic anemia, neutropenia, seizures, intellectual disability, folate-responsive |
| 8. Anhidrotic ectodermodysplasia with immunodeficiency (EDA-ID)) | |||||||
| EDA-ID due to NEMO /IKBKG deficiency (ectodermal dysplasia, immune deficiency) | NEMO (IKBKG) | XL | 300248 | Normal or decreased, TCR activation impaired | Normal Low memory and isotype switched B cells |
Decreased, some with elevated IgA, IgM, poor specific antibody responses, absent antibody to polysaccharide antigens | Anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (in some), various infections (bacteria, mycobacteria, viruses and fungi), colitis, conical teeth, variable defects of skin, hair and teeth, monocyte dysfunction |
| EDA-ID due to IKBA GOF mutation | IKBA (NFKBIA) | AD GOF | 164008 | Normal total T cells, TCR activation impaired | Normal B cell numbers, impaired BCR activation, low memory and isotype switched B cells | Decreased IgG and IgA, elevated IgM, poor specific antibody responses, absent antibody to polysaccharide antigens | Anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia, various infections (bacteria, mycobacteria, viruses and fungi), colitis, variable defects of skin, hair and teeth, T cell and monocyte dysfunction |
| 9. Calcium channel defects | |||||||
| ORAI-1 deficiency | ORAI1 | AR | 610277 | Normal, defective TCR mediated activation | Normal | Normal | Autoimmunity, EDA, non-progressive myopathy |
| STIM1 deficiency | STIM1 | AR | 605921 | Normal, defective TCR mediated activation | Normal | Normal | Autoimmunity, EDA, non-progressive myopathy |
| 10. Other defects | |||||||
| Purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) deficiency | PNP | AR | 164050 | Progressive decrease | Normal | Normal or low | Autoimmune hemolytic anemia, neurological impairment |
| Immunodeficiency with multiple intestinal atresias | TTC7A | AR | 609332 | Variable, but sometimes absent low TRECs | Normal or low | Markedly decreased IgG, IgM, IgA | Bacterial (sepsis), fungal, viral infections, multiple intestinal atresias, often with intrauterine polyhydramnios and early demise, some with SCID phenotype |
| Hepatic veno-occlusive disease with immunodeficiency (VODI) | SP110 | AR | 604457 | Normal (decreased memory T cells) | Normal (decreased memory B cells) | Decreased IgG, IgA, IgM, absent germinal centers and tissue plasma cells | Hepatic veno-occlusive disease, Susceptibility to Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, CMV, candida, thrombocytopenia, hepatosplenomegaly, cerebrospinal leukodystrophy |
| Vici syndrome due to EPG5 deficiency | EPG5 | AR | 615068 | Profound depletion of CD4+ cells | Defective | Decreased (particularly IgG2) | Agenesis of the corpus callosum, cataracts, cardiomyopathy, skin hypopigmentation, intellectual disability, microcephaly, recurrent infections, chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis |
| HOIL1 deficiency | HOIL1 (RBCK1) | AR | 610924 | Normal numbers | Normal, decreased memory B cells | Poor antibody responses to polysaccharides | Bacterial infections, autoinflammation, amylopectinosis |
| HOIP deficiency | RNF31 | AR | 612487 | Normal numbers | Normal, decreased memory B cells | decreased | Bacterial infections, autoinflammation, amylopectinosis, lymphangiectasia |
| Hennekam-lymphangiectasia-lymphedema syndrome due to CCBE1 deficiency | CCBE1 | AR | 612753 | Low/variable | Low/variable | decreased | Lymphangiectasia and lymphedema with facial abnormalities and other dysmorphic features |
| Hennekam-lymphangiectasia-lymphedema syndrome due to FAT4 deficiency | FAT4 | AR | 612411 | Low/variable | Low/variable | decreased | Lymphangiectasia and lymphedema with facial abnormalities and other dysmorphic features |
| STAT5b deficiency | STAT5B | AR | 604260 | Modestly decreased | Normal | Normal | Growth-hormone insensitive dwarfism, dysmorphic features, eczema, lymphocytic interstitial pneumonitis, autoimmunity |
| Kabuki syndrome 1 due to KMT2D deficiency | KMT2D (MLL2) | AD | 602113 | Normal | Normal | Low IgA and occasionally low IgG | Typical facial abnormalities, cleft or high arched palate, skeletal abnormalities, short stature, intellectual disability, congenital heart defects, recurrent infections (otitis media, pneumonia) in 50% of patients. Autoimmunity may be present |
| Kabuki syndrome 2 due to KDM6A deficiency | KDM6A | XL (females may be affected) | 300128 | Normal | Normal | Low IgA and occasionally IgG | |
Pure bone marrow failure syndromes have not been included. Total number of disorders in Table 2: 67. New disorders: 23, ARPC1B, CDCA7, HELLS, POLE2, LIG1, GINS1, NSMCE3, ERCC6L2, TBX1, MYSM1, MOPD1, STN1, CTC1, KMT2D, KDM6A, SAMD9, SAMD9L, EXTL3, WRAP53, FAT4. Unknown cause of DiGeorge syndrome, unknown cause CHARGE, 10p13-14 deletion
IUGR intrauterine growth retardation, HSV herpes simplex virus, VZV varicella zoster virus, BCG Bacillus Calmette-Guerin, XL X-linked inheritance, AR autosomal recessive inheritance, AD autosomal dominant inheritance, LOF loss-of-function, GOF gain-of-function
Table 5.
Congenital defects of phagocyte number or function
| Disease | Genetic defect | Inheritance | OMIM | Affected cells | Affected function | Associated features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Congenital neutropenias | ||||||
| Elastase deficiency (SCN1) | ELANE | AD | 130130 | N | Myeloid differentiation | Susceptibility to MDS/leukemia Severe congenital neutropenia or cyclic neutropenia |
| GFI 1 deficiency (SCN2) | GFI1 | AD | 600871 | N | Myeloid differentiation | B/T lymphopenia |
| HAX1 deficiency (Kostmann disease) (SCN3) | HAX1 | AR | 605998 | N | Myeloid differentiation | Cognitive and neurological defects in patients with defects in both HAX1 isoforms, susceptibility to MDS/leukemia |
| G6PC3 deficiency (SCN4) | G6PC3 | AR | 611045 | N | Myeloid differentiation, chemotaxis, O2 − production | Structural heart defects, urogenital abnormalities, inner ear deafness, and venous angiectasias of trunks and limbs |
| VPS45 deficiency (SCN5) | VPS45 | AR | 610035 | N | Myeloid differentiation, migration | Extramedullary hematopoiesis, bone marrow fibrosis, nephromegaly |
| Glycogen storage disease type 1b | G6PT1 | AR | 602671 | N + M | Myeloid differentiation, chemotaxis, O2 − production | Fasting hypoglycemia, lactic acidosis, hyperlipidemia, hepatomegaly |
| X-linked neutropenia/myelodysplasia WAS GOF | WAS | XL | 300392 | N | Differentiation, mitosis | Neutropenia, myeloid maturation arrest, monocytopenia, variable lymphoid anomalies |
| P14/LAMTOR2 deficiency | LAMTOR2 | AR | 610389 | N + M | Endosomal biogenesis | Neutropenia Hypogammaglobulinemia ↓CD8 cytotoxicity, partial albinism, growth failure |
| Barth syndrome (3-methylglutaconic aciduria type II) | TAZ | XL | 300394 | N + L Mel | Mitochondrial function | Cardiomyopathy, myopathy, growth retardation, neutropenia |
| Cohen syndrome | VPS13B | AR | 607817 | N | Myeloid differentiation | Dysmorphism, mental retardation, obesity, deafness, neutropenia |
| Clericuzio syndrome (poikiloderma with neutropenia) | USB1 | AR | 613276 | N | Myeloid differentiation | Retinopathy, developmental delay, facial dysmorphisms, poikiloderma |
| JAGN1 deficiency | JAGN1 | AR | 616012 | N | Myeloid differentiation | Myeloid maturation arrest, osteopenia |
| 3-Methylglutaconic aciduria | CLPB | AR | 616254 | N | Myeloid differentiation Mitochondrial protein |
Neurocognitive developmental aberrations, microcephaly, hypoglycemia, hypotonia, ataxia, seizures, cataracts, IUGR |
| G-CSF receptor deficiency | CSF3R | AR | 138971 | N | Stress granulopoiesis disturbed | |
| SMARCD2 deficiency | SMARCD2 | AR | 601736 | N | Chromatin remodeling, myeloid differentiation and neutrophil functional defect | Neutropenia, developmental aberrations, skeletal abnormalities, hematopoietic stem cells, myelodysplasia |
| HYOU1 deficiency | HYOU1 | AR | 601746 | N | Unfolded protein response | Hypoglycemia, inflammatory complications |
| 2. Defects of motility | ||||||
| Leukocyte adhesion deficiency type 1 (LAD1) | ITGB2 | AR | 600065 | N + M +L + NK | Adherence, chemotaxis, endocytosis, T/NK cytotoxicity | Delayed cord separation, skin ulcers, periodontitis, leukocytosis |
| Leukocyte adhesion deficiency type 2 (LAD2) | SLC35C1 | AR | 605881 | N + M | Rolling, chemotaxis | Mild LAD type 1 features with hh-blood group, growth retardation, developmental delay |
| Leukocyte adhesion deficiency type 3 (LAD3) | FERMT3 | AR | 607901 | N + M + L + NK | Adherence, chemotaxis | LAD type 1 plus bleeding tendency |
| Rac 2 deficiency | RAC2 | AD | 602049 | N | Adherence, chemotaxis O2 − production | Poor wound healing, leukocytosis |
| β actin deficiency | ACTB | AD | 102630 | N + M | Motility | Mental retardation, short stature |
| Localized juvenile periodontitis | FPR1 | AR | 136537 | N | Formylpeptide induced chemotaxis | Periodontitis only |
| Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome | CTSC | AR | 602365 | N + M | Chemotaxis | Periodontitis, palmoplantar hyperkeratosis in some patients |
| Specific granule deficiency | CEBPE | AR | 189965 | N | Chemotaxis | Neutrophils with bilobed nuclei |
| Shwachman-Diamond syndrome | SBDS | AR | 607444 | N | Chemotaxis | Pancytopenia, exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, chondrodysplasia |
| WDR1 deficiency | WDR1 | AR | 604734 | N | Spreading, survival, chemotaxis | Mild neutropenia, poor wound healing, severe stomatitis, neutrophil nuclei herniate |
| Cystic fibrosis | CFTR | AR | 602421 | M only | Chemotaxis | Respiratory infections, pancreatic insufficiency, elevated sweat chloride |
| Schwachman Diamond syndrome due to DNAJC21 deficiency | DNAJC21 | AR | 617048 | N | Motility, ribosome biogenesis | Metaphyseal changes, short stature, developmental delay, pancreatic dysfunction, bone marrow failure |
| Neutropenia with combined immune deficiency due to MKL1 deficiency | MKL1 | AR | 606078 | N + M +L + NK | Impaired expression of cytoskeletal genes | Mild thrombocytopenia |
| 3. Defects of respiratory burst | ||||||
| X-linked chronic granulomatous disease (CGD), gp91phox | CYBB | XL | 300481 | N + M | Killing (faulty O2 − production) | Infections, autoinflammatory phenotype, IBD McLeod phenotype in patients with deletions extending into the contiguous Kell locus |
| Autosomal recessive CGD p22phox | CYBA | AR | 608508 | N + M | Killing (faulty O2 − production) | Infections, autoinflammatory phenotype |
| Autosomal recessive CGD p47phox | NCF1 | AR | 608,512 | N + M | Killing (faulty O2 − production) | Infections, autoinflammatory phenotype |
| Autosomal recessive CGD p67phox | NCF2 | AR | 608515 | N + M | Killing (faulty O2 − production) | Infections, autoinflammatory phenotype |
| Autosomal recessive CGD p40phox | NCF4 | AR | 601488 | N + M | Killing (faulty O2 − production) | Infections, autoinflammatory phenotype |
| G6PD deficiency class I | G6PD | XL | 305900 | N | Reduced O2 − production | Infections |
| 4. Other non-lymphoid defects | ||||||
| GATA2 deficiency (MonoMac syndrome) | GATA2: loss of stem cells | AD | 137295 | Monocytes + peripheral DC | Multi lineage cytopenias | Susceptibility to mycobacteria, HPV, histoplasmosis, alveolar proteinosis, MDS/AML/CMMoL, lymphedema |
| Congenital pulmonary alveolar proteinosis due to CSF2RB mutations | CSF2RB | AR | 138981 | Alveolar macrophages | GM-CSF signaling | Alveolar proteinosis |
| Congenital pulmonary alveolar proteinosis due to CSF2RA mutations | CSF2RA | XL (pseudoautosomal) | 306250 | Alveolar macrophages | GM-CSF signaling | Alveolar proteinosis |
Total number of disorders in Table 5: 39. New disorders: 9, WDR1, CFTR, SMARCD2, JAGN1, HYOU1, MKL1, DNAJC21, G6PD, CSF2RB. Removed: cyclic neutropenia was merged with elastase deficiency
MDS myelodysplastic syndrome, IUGR intrauterine growth retardation, LAD leukocyte adhesion deficiency, AML acute myelogenous leukemia, CMML chronic myelomonocytic leukemia, N neutrophil, M monocyte, MEL melanocyte, L lymphocyte, NK natural killer, XL X-linked inheritance, AR autosomal recessive inheritance, AD autosomal dominant inheritance, GOF gain-of-function
Table 6.
Defects in intrinsic and innate immunity
| Disease | Genetic defect | Inheritance | OMIM | Affected cells | Affected function | Associated features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial disease (MSMD) | ||||||
| IL-12 and IL-23 receptor β1 chain deficiency | IL12RB1 | AR | 601604 | L + NK | IFN-γ secretion | Susceptibility to mycobacteria and Salmonella |
| IL-12p40 (IL-12 and IL-23) deficiency | IL12B | AR | 161561 | M | IFN-γ secretion | Susceptibility to mycobacteria and Salmonella |
| IFN-γ receptor 1 deficiency | IFNGR1 | AR/AD | 107470 | M + L | IFN-γ binding and signaling | Susceptibility to mycobacteria and Salmonella |
| IFN-γ receptor 2 deficiency | IFNGR2 | AR | 147569 | M + L | IFN-γ signaling | Susceptibility to mycobacteria and Salmonella |
| STAT1 deficiency (AD LOF) | STAT1 | AD | 600555 | M + L | IFN-γsignaling | Susceptibility to mycobacteria, Salmonella |
| Macrophage gp91 phox deficiency | CYBB | XL | 300481 | Macrophage only | Killing (faulty O2 − production) | Isolated susceptibility to mycobacteria |
| IRF8 deficiency (AD) | IRF8 | AD | 601565 | CD1c+ MDC | Differentiation of CD1c+ MDC subgroup | Susceptibility to mycobacteria |
| IRF8 deficiency (AR) | IRF8 | AR | 601565 | CD1c+ MDC | Differentiation of CD1c+ MDC subgroup | Susceptibility to mycobacteria and multiple other infectious agents |
| Tyk2 deficiency | TYK2 | AR | 176941 | Normal, but multiple cytokine signaling defect | Normal | Susceptibility to intracellular bacteria (mycobacteria, Salmonella), viruses, +/− elevated IgE |
| ISG15 deficiency | ISG15 | AR | 147571 | IFNγ production defect | Susceptibility to mycobacteria (BCG), brain calcification | |
| RORc deficiency | RORC | AR | 602943 | L + NK | Lack of functional RORγT protein, IFNγ production defect, complete absence of IL-17A/F-producing T cells | Susceptibility to mycobacteria and candida |
| JAK1 (LOF) | JAK1 | AR | 147795 | N + L | IFNγ production | Susceptibility to mycobacteria and viruses, urothelial carcinoma |
| 2. Epidermodysplasia verruciformis (HPV) | ||||||
| EVER1 deficiency | TMC6 | AR | 605828 | Keratinocytes and leukocytes | EVER proteins may be involved in the regulation of cellular zinc homeostasis in lymphocytes | Human papillomavirus (HPV) (group B1) infections and cancer of the skin (typical EV) |
| EVER2 deficiency | TMC8 | AR | 605829 | Keratinocytes and leukocytes | EVER proteins may be involved in the regulation of cellular zinc homeostasis in Ly | HPV (group B1) infections and cancer of the skin (typical EV) |
| WHIM (warts, hypogammaglobulinemia, infections, myelokathexis) syndrome | CXCR4 | AD GOF | 162643 | Granulocytes + lymphocytes | Increased response of the CXCR4 chemokine receptor to its ligand CXCL12 (SDF-1) | Warts, neutropenia, low B cell number, hypogammaglobulinemia |
| 3. Predisposition to severe viral infection | ||||||
| STAT1 deficiency (AR LOF) | STAT1 | AR | 600555 | T and NK cells and monocytes | STAT1-dependent IFN-α, β, and γ response | Severe viral infections, mycobacterial infection |
| STAT2 deficiency | STAT2 | AR | 600556 | T and NK cells | STAT2-dependent IFN-α, β, and γ response | Severe viral infections (disseminated vaccine-strain measles) |
| IRF7 deficiency | IRF7 | AR | 605047 | Leukocytes, plasmacytoid dendritic cells, non-hematopoietic cells | IFN-α, β, and γ production and IFN-λ production | Severe influenza disease |
| IFNAR2 deficiency | IFNAR2 | AR | 602376 | Broadly expressed | No response to IFN-α | Severe viral infections (disseminated vaccine-strain measles, HHV6) |
| CD16 deficiency | FCGR3A | AR | 146740 | NK cells | Altered NK cells function | Severe herpes viral infections, particularly VZV, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), and (HPV) |
| MDA5 deficiency (LOF) | IFIH1 | AR | 606951 | Somatic and hematopoietic | Viral recognition | Rhinovirus and other RNA viruses |
| 4. Herpes simplex encephalitis (HSE) | ||||||
| TLR3 deficiency | TLR3 | AD or AR | 603029 | Central nervous system (CNS) resident cells and fibroblasts | TLR3-dependent IFN-α, β, and γ response | Herpes simplex virus 1 encephalitis (incomplete clinical penetrance for all etiologies listed here) |
| UNC93B1 deficiency | UNC93B1 | AR | 608204 | CNS resident cells and fibroblasts | UNC-93B-dependent IFN-α, β, and γ response | Herpes simplex virus 1 encephalitis |
| TRAF3 deficiency | TRAF3 | AD | 601896 | CNS resident cells and fibroblasts | TRAF3-dependent IFN-α, β, and γ response | Herpes simplex virus 1 encephalitis |
| TRIF deficiency | TICAM1 | AD or AR | 607601 | CNS resident cells and fibroblasts | TRIF-dependent IFN-α, β, and γ response | Herpes simplex virus 1 encephalitis |
| TBK1 deficiency | TBK1 | AD | 604834 | CNS resident cells and fibroblasts | TBK1-dependent IFN-α, β, and γ response | Herpes simplex virus 1 encephalitis |
| IRF3 deficiency | IRF3 | AD | 616532 | CNS resident cells and fibroblasts | Low IFN-α/β production in response to HSV1 and decreased IRF3 phosphorylation | Herpes simplex virus 1 encephalitis |
| 5. Predisposition to invasive fungal diseases | ||||||
| CARD9 deficiency | CARD9 | AR | 607212 | Mononuclear phagocytes | CARD9 signaling pathway | Invasive candidiasis infection, deep dermatophytoses, other invasive fungal infections |
| 6. Predisposition to mucocutaneous candidiasis | ||||||
| IL-17RA deficiency | IL17RA | AR | 605461 | Epithelial cells, fibroblasts, mononuclear phagocytes | IL-17RA signaling pathway | CMC, folliculitis |
| IL-17RC deficiency | IL17RC | AR | 610925 | Epithelial cells, fibroblasts, mononuclear phagocytes | IL-17RC signaling pathway | CMC |
| IL-17F deficiency | IL17F | AD | 606496 | T cells | IL-17F-containing dimers | CMC, folliculitis |
| STAT1 GOF | STAT1 | AD GOF | 600555 | T cells, B cells, monocytes | Gain-of-function STAT1 mutations that impair the development of IL-17-producing T cells | CMC, various fungal, bacterial and viral (HSV) infections, autoimmunity (thyroiditis, diabetes, cytopenias), enteropathy |
| ACT1 deficiency | TRAF3IP2 | AR | 607043 | T cells, fibroblasts | Fibroblasts fail to respond to IL-17A and IL-17F, and their T cells to IL-17E | CMC, blepharitis, folliculitis and macroglossia |
| 7. TLR signaling pathway deficiency with bacterial susceptibility | ||||||
| IRAK-4 deficiency | IRAK4 | AR | 606883 | Lymphocytes + granulocytes + monocytes | TIR-IRAK4 signaling pathway | Bacterial infections (pyogens) |
| MyD88 deficiency | MYD88 | AR | 602170 | Lymphocytes + granulocytes + monocytes | TIR-MyD88 signaling pathway | Bacterial infections (pyogens) |
| IRAK1 deficiency | IRAK1 | XL | Not yet attributed | Lymphocytes + granulocytes + monocytes | TIR-IRAK1 signaling pathway | Bacterial infections, X-linked MECP2 deficiency-related syndrome due to a large de novo Xq28 chromosomal deletion encompassing both MECP2 and IRAK1 |
| TIRAP deficiency | TIRAP | AR | 614382 | Lymphocytes + granulocytes+ monocytes | TIRAP- signaling pathway, TLR1/2, TLR2/6, and TLR4 agonists were impaired in the fibroblasts and leukocytes | Staphylococcal disease during childhood |
| 8. Other inborn errors of immunity related to non-hematopoietic tissues | ||||||
| Isolated congenital asplenia (ICA) due to RPSA deficiency | RPSA | AD | 271400 | No spleen | RPSA encodes ribosomal protein SA, a component of the small subunit of the ribosome | Bacteremia (encapsulated bacteria) |
| Isolated congenital asplenia (ICA) due to HMOX deficiency | HMOX | AR | 141250 | Macrophages | HO-1 regulates iron recycling and heme-dependent damage occurs | Hemolysis, nephritis, inflammation |
| Trypanosomiasis | APOL1 | AD | 603743 | Somatic | Lipid | Trypanosomiasis |
| Acute liver failure due to NBAS deficiency | NBAS | AR | 608025 | Somatic and hematopoietic | ER stress | Fever induces liver failure |
| Acute necrotizing encephalopathy | RANBP2 | AD | 601181 | Ubiquitous expression | Nuclear pore | Fever induces acute encephalopathy |
| CLCN7 deficiency associated osteopetrosis | CLCN7 | AR | 602727 | Osteoclasts | Secretory lysosomes | Osteopetrosis with hypocalcemia, neurologic features |
| SNX10 deficiency associated osteopetrosis | SNX10 | AR | 614780 | Osteoclasts | Secretory lysosomes | Osteopetrosis with visual impairment |
| OSTM1 deficiency associated osteopetrosis | OSTM1 | AR | 607649 | Osteoclasts | Secretory lysosomes | Osteopetrosis with hypocalcemia, neurologic features |
| PLEKHM1 deficiency associated osteopetrosis | PLEKHM1 | AR | 611466 | Osteoclasts | Secretory lysosomes | Osteopetrosis |
| TCIRG1 deficiency associated osteopetrosis | TCIRG1 | AR | 604592 | Osteoclasts | Secretory lysosomes | Osteopetrosis with hypocalcemia |
| TNFRSF11A deficiency associated osteopetrosis | TNFRSF11A | AR | 603499 | Osteoclasts | Osteoclastogenesis | Osteopetrosis |
| TNFSF11 deficiency associated osteopetrosis | TNFSF11 | AR | 602642 | Stromal | Osteoclastogenesis | Osteopetrosis with severe growth retardation |
| NCSTN deficiency hidradenitis suppurativa | NCSTN | AD | 605254 | Epidermis | Gamma-secretase in hair follicle regulates keratinization | Hidradenitis suppurativa with acne |
| PSEN deficiency hidradenitis suppurativa | PSEN | AD | 104311 | Epidermis | Gamma-secretase in hair follicle regulates keratinization | Hidradenitis suppurative with cutaneous hyperpigmentation |
| PSENEN deficiency hidradenitis suppurativa | PSENEN | AD | 607632 | Epidermis | Gamma-secretase in hair follicle regulates keratinization | Hidradenitis suppurativa |
Total number of disorders in Table 6: 52. New genes: 19, IFNAR 2, IRF3, JAK1, IRAK1, TIRAP, IFIH1, HMOX, NBAS, RANBP2, CLCN7, SNX10, OSTM1, PLEKHM1, TCIRG1, TNFRSF11A, TNFSF11, NCSTN, PSEN, PSENEN
NF-κB nuclear factor kappa B, TIR Toll and interleukin-1 receptor, IFN interferon, TLR Toll-like receptor, MDC myeloid dendritic cell, CNS central nervous system, CMC chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis, HPV human papillomavirus, VZV varicella zoster virus, EBV Epstein-Barr virus, HHV6 human herpesvirus 6, XL X-linked inheritance, AR autosomal recessive inheritance, AD autosomal dominant inheritance, LOF loss-of-function, GOF gain-of-function
Table 7.
Autoinflammatory disorders
| 1. Type 1 interferonopathies | |||||||
| Disease | Genetic defect | Inheritance | OMIM | T cells | B cells | Functional defect | Associated features |
| TREX1 deficiency, Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome 1 (AGS1) | TREX1 | AR or AD | 606609 | Not assessed | Not assessed | Intracellular accumulation of abnormal ss DNA species leading to increased type I IFN production | Classical AGS, SLE, FCL |
| RNASEH2B deficiency, AGS2 | RNASEH2B | AR | 610326 | Not assessed | Not assessed | Intracellular accumulation of abnormal RNA-DNA hybrid species leading to increased type I IFN production | Classical AGS, SP |
| RNASEH2C deficiency, AGS3 | RNASEH2C | AR | 610330 | Not assessed | Not assessed | Intracellular accumulation of abnormal RNA-DNA hybrid species leading to increased type I IFN production | Classical AGS |
| RNASEH2A deficiency, AGS4 | RNASEH2A | AR | 606034 | Not assessed | Not assessed | Intracellular accumulation of abnormal RNA-DNA hybrid species leading to increased type I IFN production | Classical AGS |
| SAMHD1 deficiency, AGS5 | SAMHD1 | AR | 606754 | Not assessed | Not assessed | Controls dNTPs in the cytosol, failure of which leads to increased type I IFN production | Classical AGS, FCL |
| ADAR1 deficiency, AGS6 | ADAR1 | AR | 146920 | Not assessed | Not assessed | Catalyzes the deamination of adenosine to inosine in dsRNA substrates, failure of which leads to increased type I IFN production | Classical AGS, BSN, SP |
| Aicardi-Goutieres syndrome 7 (AGS7) | IFIH1 (GOF) | AD | 606951 | Not assessed | Not assessed | IFIH1 gene encodes a cytoplasmic viral RNA receptor that activates type I interferon signaling through the MAVS adaptor molecule | Classical AGS, SLE, SP, SMS |
| Spondyloenchondro-dysplasia with immune dysregulation (SPENCD) | ACP5 | AR | 171640 | Not assessed | Not assessed | Upregulation of IFN through mechanism possibly relating to pDCS | Short stature, SP, ICC, SLE, thrombocytopenia and autoimmune hemolytic anemia, possibly recurrent bacterial and viral infections |
| STING-associated vasculopathy, infantile-onset | TMEM173 | AR | 612374 | Not assessed | Not assessed | STING activates both the NF-kappa-B and IRF3 transcription pathways to induce expression of IFN | Skin vasculopathy, inflammatory lung disease, systemic autoinflammation and ICC, FCL |
| X-linked reticulate pigmentary disorder | POLA1 | XL | 301220 | Not assessed | Not assessed | POLA1 is required for synthesis of cytosolic RNA:DNA and its deficiency leads to increase production of type I interferon | Hyperpigmentation, characteristic facies, lung and GI involvement |
| USP18 deficiency | USP18 | AR | 607057 | Not assessed | Not assessed | Defective negative regulation of ISG15 leading to increased IFN | TORCH like syndrome |
| CANDLE (chronic atypical neutrophilic dermatitis with lipodystrophy) | PSMB8 a | AR and AD | 256040 | Not assessed | Not assessed | Mutations cause increased IFN signaling through an undefined mechanism | Contractures, panniculitis, ICC, fevers |
| Singleton-Merten syndrome | DDX58 | AD | 609631 | Not assessed | Not assessed | Recognizes double stranded RNA | Dental dysplasia), calcifications in the aorta, osteoporosis, especially in the hands and feet |
| 2. Defects affecting the inflammasome | |||||||
| Disease | Genetic defect | Inheritance | OMIM | Affected cells | Functional defects | Associated features | |
| Familial Mediterranean fever | MEFV | AR or AD | 249100 134610 |
Mature granulocytes, cytokine-activated monocytes | Decreased production of pyrin permits ASC-induced IL-1 processing and inflammation following subclinical serosal injury, macrophage apoptosis decreased | Recurrent fever, serositis and inflammation responsive to colchicine. Predisposes to vasculitis and inflammatory bowel disease | |
| Mevalonate kinase deficiency (Hyper IgD syndrome) | MVK | AR | 260920 | Somatic and hemaotpoietic | Affecting cholesterol synthesis, pathogenesis of disease unclear | Periodic fever and leukocytosis with high IgD levels | |
| Muckle-Wells syndrome | NLRP3 (also called NALP3 CIAS1 or PYPAF1) | AD GOF | 191900 | PMNs Monocytes | Defect in cryopyrin, involved in leukocyte apoptosis and NFkB signaling and IL-1 processing | Urticaria, SNHL, amyloidosis | |
| Familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome 1 | NLRP3 | AD GOF | 120100 | PMNs, monocytes | As above | Non-pruritic urticaria, arthritis, chills, fever and leukocytosis after cold exposure | |
| Familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome 2 | NLRP12 | AD GOF | 611762 | PMNs, monocytes | As above | Non-pruritic urticaria, arthritis, chills, fever and leukocytosis after cold exposure | |
| Neonatal onset multisystem inflammatory disease (NOMID) or chronic infantile neurologic cutaneous and articular syndrome (CINCA) | NLRP3 | AD GOF | 607115 | PMNs, chondrocytes | As above | Neonatal onset rash, chronic meningitis, and arthropathy with fever and inflammation | |
| NLRC4-MAS (macrophage activating syndrome) or familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome 4 | NLRC4 | AD GOF | 616050 616115 |
PMNs monocytes macrophages | Gain-of-function mutation in NLRC4 results in elevated secretion of IL-1β and IL-18 as well as macrophage activation | Severe enterocolitis and macrophage activation syndrome | |
| PLAID (PLCγ2 associated antibody deficiency and immune dysregulation) or familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome 3 or APLAID (c2120A>C) | PLCG2 | AD GOF | 614468 | B cells, NK, mast cells | Mutations cause activation of IL-1 pathways | Cold urticaria hypogammaglobulinemia, autoinflammation | |
| NLRP1 deficiency | NLRP1 | AR | 606579 | Leukocytes | Systemic elevation of IL-18 and caspase 1, suggesting involvement of NLRP1 inflammasome | Dyskeratosis, autoimmunity and arthritis | |
| 3. Non-inflammasome-related conditions | |||||||
| Disease | Genetic defect | Inheritance | OMIM | Affected cells | Functional defects | Associated Features | |
| TNF receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS) | TNFRSF1A | AD | 142680 | PMNs, monocytes | Mutations of 55-kD TNF receptor leading to intracellular receptor retention or diminished soluble cytokine receptor available to bind TNF | Recurrent fever, serositis, rash, and ocular or joint inflammation | |
| Pyogenic sterile arthritis, pyoderma gangrenosum, acne (PAPA) syndrome, hyperzincemia, and hypercalprotectinemia | PSTPIP1 (also called C2BP1) | AD | 604416 | Hematopoietic tissues, upregulated in activated T cells | Disordered actin reorganization leading to compromised physiologic signaling during inflammatory response | Destructive arthritis, inflammatory skin rash, myositis | |
| Blau syndrome | NOD2 (also called CARD15) | AD | 186580 | Monocytes | Mutations in nucleotide binding site of CARD15, possibly disrupting interactions with lipopolysaccharides and NF-kB signaling | Uveitis, granulomatous synovitis, camptodactyly, rash and cranial neuropathies, 30% develop Crohn colitis | |
| ADAM17 deficiency | ADAM17 | AR | 614328 | Leukocytes and epithelial cells | Defective TNFα production | Early-onset diarrhea and skin lesions | |
| Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis and congenital dyserythropoietic anemia (Majeed syndrome) | LPIN2 | AR | 609628 | Neutrophils, bone marrow cells | Undefined | Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis, transfusion-dependent anemia, cutaneous inflammatory disorders | |
| DIRA (deficiency of the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist) | IL1RN | AR | 612852 | PMNs, Monocytes | Mutations in the IL-1 receptor antagonist allow unopposed action of interleukin-1 | Neonatal onset of sterile multifocal osteomyelitis, periostitis and pustulosis | |
| DITRA (deficiency of IL-36 receptor antagonist) | IL36RN | AR | 614204 | Keratinocytes, leukocytes | Mutations in IL-36RN leads to increase IL-8 production | Pustular psoriasis | |
| SLC29A3 mutation | SLC29A3 | AR | 602782 | Leukocytes, bone cells | Hyperpigmentation hypertrichosis, histiocytosis-lymphadenopathy plus syndrome | ||
| CAMPS (CARD14 mediated psoriasis) | CARD14 | AD | 602723 | Mainly in keratinocytes | Mutations in CARD14 activate the NF-kB pathway and production of IL-8 | Psoriasis | |
| Cherubism | SH3BP2 | AD | 118400 | Stroma cells, bone cells | Hyperactived macrophage and increase NF-kB | Bone degeneration in jaws | |
| COPA defect | COPA | AD | 6011924 | PMN and tissue specific cells | Defective intracellular transport via the coat protein complex I (COPI) | Autoimmune inflammatory arthritis and interstitial lung disease with Th17 dysregulation and autoantibody production | |
| Otulipenia/ORAS | OTULIN | AR | 615712 | Leukocytes | Increase LUBAC induction of NF-KB activation leading to high proinflammatory cytokines levels | Fever, diarrhea, dermatitis | |
| A20 deficiency | TNFAIP3 | AD LOF | 616744 | Lymphocytes | Defective inhibition of NF-KB signaling pathway | Arthralgia, mucosal ulcers, ocular inflammation | |
| ADA2 deficiency | CECR1 | AR | 607575 | Lymphocytes | ADAs deactivate extracellular adenosine and terminate signaling through adenosine receptors | Polyarteritis nodosa, childhood-onset, early-onset recurrent ischemic stroke and fever | |
| AP1S3 deficiency | AP1S3 | AR | 615781 | Keratinocytes | Disrupted TLR3 translocation | Pustular psoriasis | |
Total number of disorders in Table 7: 37. New disorders: 7, DDX58, POLA1, USP18, NLRP1, OTULIN, TNFAIP3, AP1S3
IFN interferon; HSM hepatosplenomegaly; CSF cerebrospinal fluid; SLE systemic lupus erythematosus; TORCH toxoplasmosis, other, rubella, cytomegalovirus, and herpes infections; SNHL sensorineural hearing loss; AGS Aicardi-Goutières syndrome; BSN bilateral striatal necrosis; FCL familial chilblain lupus; ICC intracranial calcification; IFN interferon type I; pDCs plasmacytoid dendritic cells; SP spastic paraparesis; SMS Singleton-Merten syndrome; ss single-stranded DNA; XL X-linked inheritance; AR autosomal recessive inheritance; AD autosomal dominant inheritance; LOF loss-of-function; GOF gain-of-function
aVariants in PSMB4, PSMB9, PSMA3, and POMP have been proposed to cause a similar CANDLE phenotype in monogenic and digenic models
Table 8.
Complement deficiencies
| 1. Complement deficiencies | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disease | Genetic defect | Inheritance | Gene OMIM | Laboratory features | Associated features |
| C1q deficiency due to defects in C1QA | C1QA | AR | 120550 | Absent CH50 hemolytic activity, defective activation of the classical pathway, diminished clearance of apoptotic cells | SLE, infections with encapsulated organisms |
| C1q deficiency due to defects in C1QB | C1QB | AR | 120570 | Absent CH50 hemolytic activity, Defective activation of the classical pathway, diminished clearance of apoptotic cells | SLE, infections with encapsulated organisms |
| C1q deficiency due to defects in C1QC | C1QC | AR | 120575 | Absent CH50 hemolytic activity, Defective activation of the classical pathway, diminished clearance of apoptotic cells | SLE, infections with encapsulated organisms |
| C1r deficiency | C1R | AR | 613785 | Absent CH50 hemolytic activity, defective activation of the classical pathway | SLE, infections with encapsulated organisms, Ehlers-Danlos phenotype |
| C1s deficiency | C1S | AR | 120580 | Absent CH50 hemolytic activity, defective activation of the classical pathway | SLE, infections with encapsulated organisms, Ehlers-Danlos phenotype |
| Complete C4 deficiency | C4A + C4B | AR | 120810 | Absent CH50 hemolytic activity, defective activation of the classical pathway, complete deficiency requires biallelic mutations/deletions/conversions of both C4A and C4B | SLE, infections with encapsulated organisms, partial deficiency is common (either C4A or C4B) and appears to have a modest effect on host defense |
| C2 deficiency | C2 | AR | 217000 | Absent CH50 hemolytic activity, defective activation of the classical pathway | SLE, infections with encapsulated organisms, atherosclerosis |
| C3 deficiency (LOF) | C3 | AR | 120700 | Absent CH50 and AH50 hemolytic activity, defective opsonization, defective humoral immune response | Infections, glomerulonephritis, atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome with GOF mutations |
| C3 GOF | C3 | AD | 120700 | Increased activation of complement | Atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome |
| C5 deficiency | C5 | AR | 120900 | Absent CH50 and AH50 hemolytic activity Defective bactericidal activity | Disseminated neisserial infections |
| C6 deficiency | C6 | AR | 217050 | Absent CH50 and AH50 hemolytic activity, defective bactericidal activity | Disseminated neisserial infections |
| C7 deficiency | C7 | AR | 217070 | Absent CH50 and AH50 hemolytic activity, defective bactericidal activity | Disseminated neisserial infections |
| C8α deficiency | C8A | AR | 120950 | Absent CH50 and AH50 hemolytic activity, defective bactericidal activity | Disseminated neisserial infections |
| C8γ deficiency | C8G | AR | 120930 | Absent CH50 and AH50 hemolytic activity, defective bactericidal activity | Disseminated neisserial infections |
| C8β-deficiency | C8B: | AR | 120960 | Absent CH50 and AH50 hemolytic activity, defective bactericidal activity | Disseminated neisserial infections |
| C9 deficiency | C9 | AR | 120940 | Reduced CH50 and AP50 hemolytic activity, deficient bactericidal activity | Mild susceptibility to disseminated neisserial infections |
| MASP2 deficiency | MASP2 | AR | 605102 | Deficient activation of the lectin activation pathway | Pyogenic infections, inflammatory lung disease, autoimmunity |
| Ficolin 3 deficiency | FCN3 | AR | 604973 | Absence of complement activation by the Ficolin 3 pathway. | Respiratory infections, abscesses |
| C1 inhibitor deficiency | SERPING1 | AD | 606860 | Spontaneous activation of the complement pathway with consumption of C4/C2, spontaneous activation of the contact system with generation of bradykinin from high molecular weight kininogen | Hereditary angioedema |
| Factor B GOF | CFB | AD | 138470 | Gain-of-function mutation with increased spontaneous AH50 | Atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome |
| Factor B LOF | CFB | AR | 138470 | Deficient activation of the alternative pathway | Infections with encapsulated organisms |
| Factor D deficiency | CFD | AR | 134350 | Absent AH50 hemolytic activity | Neisserial infections |
| Properdin deficiency | CFP | XL | 300383 | Absent AH50 hemolytic activity | Neisserial infections |
| Factor I deficiency | CFI | AR | 217030 | Spontaneous activation of the alternative complement pathway with consumption of C3 | Infections, disseminated neisserial infections, atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome, preeclampsia |
| Factor H deficiency | CFH | AR or AD | 134370 | Spontaneous activation of the alternative complement pathway with consumption of C3 | Infections, disseminated neisserial infections, atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome, preeclampsia |
| Factor H-related protein deficiencies | CFHR1-5 | AR or AD | 134371, 600889, 605336, 605337, 608593 | Normal CH50, AH50, autoantibodies to factor H, linked deletions of one or more CFHR genes leads to susceptibility autoantibody-mediated aHUS | Older onset atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome, disseminated neisserial infections |
| Thrombomodulin deficiency | THBD | AD | 188040 | Normal CH50, AH50 | Atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome |
| Membrane cofactor protein (CD46) deficiency | CD46 | AD | 120920 | Inhibitor of complement alternate pathway, decreased C3b binding | Atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome, infections, preeclampsia |
| Membrane attack Complex inhibitor (CD59) deficiency | CD59 | AR | 107271 | Erythrocytes highly susceptible to complement-mediated lysis | Hemolytic anemia, polyneuropathy |
| CD55 deficiency (CHAPEL disease) | CD55 | AR | 125240 | Hyperactivation of complement on endothelium | Protein losing enteropathy, thrombosis |
Total number of disorders in Table 8: 30. New disorders: 1, CD55
MAC membrane attack complex, SLE systemic lupus erythematosus, XL X-linked inheritance, AR autosomal recessive inheritance, AD autosomal dominant inheritance, LOF loss-of-function, GOF gain-of-function
Table 9.
Phenocopies of inborn errors of immunity
| 1. Phenocopies of inborn errors of immunity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disease | Genetic defect/presumed pathogenesis | Circulating T cells | Circulating B cells | Serum Ig | Associated features/similar PID |
| Associated with somatic mutations | |||||
| Autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (ALPS–SFAS) | Somatic mutation in TNFRSF6 | Increased CD4−CD8− double negative (DN) T alpha/beta cells | Normal, but increased number of CD5+ B cells | Normal or increased | Splenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, autoimmune cytopenias, defective lymphocyte apoptosis/ALPS–FAS (=ALPS type Im) |
| RAS-associated autoimmune leukoproliferative disease (RALD) | Somatic mutation in KRAS (GOF) | Normal | B cell lymphocytosis | Normal or increased | Splenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, autoimmune cytopenias, granulocytosis, monocytosis/ALPS-like |
| RAS-associated autoimmune leukoproliferative disease (RALD) | Somatic mutation in NRAS (GOF) | Increased CD4−CD8− double negative (DN) T alpha/beta cells | Lymphocytosis | Normal or increased | Splenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, autoantibodies/ALPS-like |
| Cryopyrinopathy, (Muckle-Wells/CINCA/NOMID-like syndrome) | Somatic mutation in NLRP3 | Normal | Normal | Normal | Urticaria-like rash, arthropathy, neurological signs |
| Hypereosinophilic syndrome due to somatic mutations in STAT5b | Somatic mutation in STAT5b (GOF) | Normal | Normal | Normal | Eosinophilia, atopic dermatitis, urticarial rash, diarrhea |
| Large granular lymphocytosis | Somatic mutations in STAT3 (GOF) | Clonal expansion of large T cells | Normal | Normal | Anemia, neutropenia, splenomegaly |
| Associated with autoantibodies | |||||
| Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis (isolated or with APECED syndrome) | Germline mutation in AIRE AutoAb to IL-17 and/or IL-22 | Normal | Normal | Normal | Endocrinopathy, chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis/CMC |
| Adult-onset immunodeficiency with susceptibility to mycobacteria | AutoAb to IFNγ | Decreased naive T cells | Normal | Normal | Mycobacterial, fungal, Salmonella VZV infections/MSMD, or CID |
| Recurrent skin infection | AutoAb to IL-6 | Normal | Normal | Normal | Staphylococcal infections/STAT3 deficiency |
| Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis | AutoAb to GM-CSF | Normal | Normal | Normal | Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis, cryptococcal meningitis, disseminated nocardiosis/CSF2RA deficiency |
| Acquired angioedema | AutoAb to CI inhibitor | Normal | Normal | Normal | Angioedema/C1 INH deficiency (hereditary angioedema) |
| Atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome | AutoAb to complement factor H | Normal | Normal | Normal | aHUS = spontaneous activation of the alternative complement pathway |
| Thymoma with hypogammaglobulinemia (Good syndrome) | AutoAb to various cytokines | Increased CD8+ T cells | No B cells | Decreased | Invasive bacterial, viral or opportunistic infections, autoimmunity, PRCA, lichen planus, cytopenia, colitis, chronic diarrhea |
Total number of conditions for Table 9: 12
aHUS atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome, GOF gain-of-function, PRCA pure red cell aplasia
The goal of the IUIS Expert Committee on Primary Immunodeficiencies is to increase awareness, facilitate recognition, promote optimal treatment, and support research in the field of immune deficiency disorders. Thus, the “IUIS PID Committee Report on Inborn Errors of Immunity” and “Update of the Phenotypical IUIS Classification for Primary Immunodeficiencies” publications are important resources for clinicians and researchers. In addition, these tables form the basis of lists used for sequencing panels and are used to monitor health utilization which will influence health services funding by federal or state governments and/or insurance companies in various global settings. The addition of ICD10 codes for the online version will promote a harmonization between the diagnostic tables and coding items that will facilitate bioinformatics research going forward.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Dawn Westerfer for the expert secretarial support and Ulrika Smrekova for the administrative support.
Compliance with Ethical Standards
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Fudenberg H, Good RA, Goodman HC, Hitzig W, Kunkel HG, Roitt IM, Rosen FS, Rowe DS, Seligmann M, Soothill JR. Primary immunodeficiencies. Report of a World Health Organization Committee. Pediatrics. 1971;47:927–946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fudenberg HH, Good RA, Hitzig W, Kunkel HG, Roitt IM, Rosen FS, Rowe DS, Seligmann M, Soothill JR. Classification of the primary immune deficiencies: WHO recommendation. N Engl J Med. 1970;283:656–657. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197009172831211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Picard C, Al-Herz W, Bousfiha A, Casanova JL, Chatila T, Conley ME, Cunningham-Rundles C, Etzioni A, Holland SM, Klein C, Nonoyama S, Ochs HD, Oksenhendler E, Puck JM, Sullivan KE, Tang ML, Franco JL, Gaspar HB. Primary immunodeficiency diseases: an update on the classification from the International Union of Immunological Societies Expert Committee for Primary Immunodeficiency 2015. J Clin Immunol. 2015;35:696–726. doi: 10.1007/s10875-015-0201-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Anonymous Primary immunodeficiency diseases. Report of a WHO scientific group. Clin Exp Immunol. 1997;109(Suppl 1):1–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chandra R, Cooper M, Hitzig W, Rosen F, Seligmann M, Soothill JF, Terry R. WHO scientific group on immunodeficiencies. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1979;13:296–359. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(79)90075-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gatti R. On the classification of patients with primary immunodeficiency disorders. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1974;3:243–247. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(74)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cooper M, Faulk W, Fudenberg H, Good R, Hitzig W, Kunkel H, Roitt I, Rosen F, Seligmann M, Soothill J. Meeting report of the second international workshop on primary immunodeficiency diseases in man. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1974;2:416–445. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(74)90059-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Anonymous Primary immunodeficiency diseases. Report of an IUIS Scientific Committee. International Union of Immunological Societies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1999;118(Suppl 1):1–28. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00109.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Immunodeficiency WSGo: meeting report primary immunodeficiency diseases. Clinical Immunology and Immunopathology 28: 450–475, 1983. [PubMed]
- 10.Rosen F, Wedgewood R, Eibl M. Primary immunodeficiency diseases. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986;40:166–196. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90082-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Bousfiha A, Jeddane L, Al-Herz W, Ailal F, Casanova JL, Chatila T, Conley ME, Cunningham-Rundles C, Etzioni A, Franco JL, Gaspar HB, Holland SM, Klein C, Nonoyama S, Ochs HD, Oksenhendler E, Picard C, Puck JM, Sullivan KE, Tang ML. The 2015 IUIS phenotypic classification for primary immunodeficiencies. J Clin Immunol. 2015;35:727–738. doi: 10.1007/s10875-015-0198-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bousfiha AA, Jeddane L, Ailal F, Al Herz W, Conley ME, Cunningham-Rundles C, Etzioni A, Fischer A, Franco JL, Geha RS, Hammarstrom L, Nonoyama S, Ochs HD, Roifman CM, Seger R, Tang ML, Puck JM, Chapel H, Notarangelo LD, Casanova JL. A phenotypic approach for IUIS PID classification and diagnosis: guidelines for clinicians at the bedside. J Clin Immunol. 2013;33:1078–1087. doi: 10.1007/s10875-013-9901-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Primary immunodeficiency diseases. Report of an IUIS Scientific Committee. International Union of Immunological Societies. Clin Exp Immunol 118 Suppl 1: 1–28, 1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 14.Notarangelo L, Casanova JL, Fischer A, Puck J, Rosen F, Seger R, Geha R, International Union of Immunological Societies Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases Classification C Primary immunodeficiency diseases: an update. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;114:677–687. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2004.06.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Notarangelo L, Casanova JL, Conley ME, Chapel H, Fischer A, Puck J, Roifman C, Seger R, Geha RS, International Union of Immunological Societies Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases Classification C Primary immunodeficiency diseases: an update from the International Union of Immunological Societies Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases Classification Committee Meeting in Budapest, 2005. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117:883–896. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2005.12.1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Geha RS, Notarangelo LD, Casanova JL, Chapel H, Conley ME, Fischer A, Hammarstrom L, Nonoyama S, Ochs HD, Puck JM, Roifman C, Seger R, Wedgwood J, International Union of Immunological Societies Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases Classification C Primary immunodeficiency diseases: an update from the International Union of Immunological Societies Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases Classification Committee. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;120:776–794. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2007.08.053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.International Union of Immunological Societies Expert Committee on Primary I. Notarangelo LD, Fischer A, Geha RS, Casanova JL, Chapel H, Conley ME, Cunningham-Rundles C, Etzioni A, Hammartrom L, Nonoyama S, Ochs HD, Puck J, Roifman C, Seger R, Wedgwood J. Primary immunodeficiencies: 2009 update. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;124:1161–1178. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.10.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Al-Herz W, Bousfiha A, Casanova JL, Chapel H, Conley ME, Cunningham-Rundles C, Etzioni A, Fischer A, Franco JL, Geha RS, Hammarstrom L, Nonoyama S, Notarangelo LD, Ochs HD, Puck JM, Roifman CM, Seger R, Tang ML. Primary immunodeficiency diseases: an update on the classification from the international union of immunological societies expert committee for primary immunodeficiency. Front Immunol. 2011;2:54. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2011.00054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Primary immunodeficiency diseases. Report of a WHO Scientific Group. Clin Exp Immunol 99 Suppl 1: 1–24, 1995. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 20.Stray-Pedersen A, Sorte HS, Samarakoon P, Gambin T, Chinn IK, Coban Akdemir ZH, Erichsen HC, Forbes LR, Gu S, Yuan B, Jhangiani SN, Muzny DM, Rodningen OK, Sheng Y, Nicholas SK, Noroski LM, Seeborg FO, Davis CM, Canter DL, Mace EM, Vece TJ, Allen CE, Abhyankar HA, Boone PM, Beck CR, Wiszniewski W, Fevang B, Aukrust P, Tjonnfjord GE, Gedde-Dahl T, Hjorth-Hansen H, Dybedal I, Nordoy I, Jorgensen SF, Abrahamsen TG, Overland T, Bechensteen AG, Skogen V, Osnes LT, Kulseth MA, Prescott TE, Rustad CF, Heimdal KR, Belmont JW, Rider NL, Chinen J, Cao TN, Smith EA, Caldirola MS, Bezrodnik L, Lugo Reyes SO, Espinosa Rosales FJ, Guerrero-Cursaru ND, Pedroza LA, Poli CM, Franco JL, Trujillo Vargas CM, Aldave Becerra JC, Wright N, Issekutz TB, Issekutz AC, Abbott J, Caldwell JW, Bayer DK, Chan AY, Aiuti A, Cancrini C, Holmberg E, West C, Burstedt M, Karaca E, Yesil G, Artac H, Bayram Y, Atik MM, Eldomery MK, Ehlayel MS, Jolles S, Flato B, Bertuch AA, Hanson IC, Zhang VW, Wong LJ, Hu J, Walkiewicz M, Yang Y, Eng CM, Boerwinkle E, Gibbs RA, Shearer WT, Lyle R, Orange JS, Lupski JR. Primary immunodeficiency diseases: genomic approaches delineate heterogeneous Mendelian disorders. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017;139:232–245. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.05.042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Casanova JL, Conley ME, Seligman SJ, Abel L, Notarangelo LD. Guidelines for genetic studies in single patients: lessons from primary immunodeficiencies. J Exp Med. 2014;211:2137–2149. doi: 10.1084/jem.20140520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Boufiha A, Phenotypical classification of PIDD. 2017. https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.horiyasoft.pidclassification.
- 23.Bousfiha A, Phenotypical classification of PIDD, iTunes. 2017. https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/pid-phenotypical-diagnosis/id1160729399?mt=8.
- 24.OMIM Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/omim.