Figure 2.
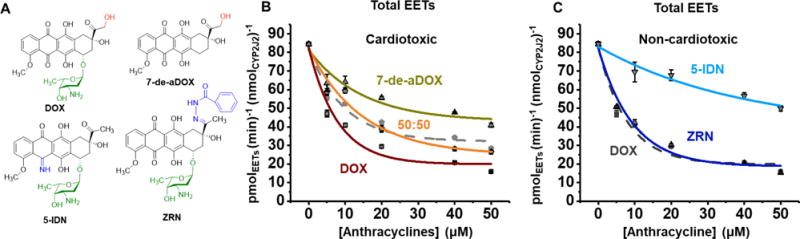
AA Inhibition by DOX, 7-de-aDOX, and the non-toxic analogues ZRN and 5-IDN. (A) Structures of the anthracyclines doxorubicin (DOX), 7-deoxydoxorubicin aglycone (7-de-aDOX), 5-iminodaunorubicin (5-IDN), and zorubicin (ZRN). (B) Rate of epoxidation of 100 μM AA to EETs by CYP2J2-CPr in the presence of increasing concentrations of cardiotoxic DOX, 7-de-aDOX, or a 50:50 mixture of DOX:7-de-aDOX. The theoretical fit based on the linear combination of DOX and 7-de-aDOX is shown as a grey, dashed line to demonstrate the overlap of the theoretical fit to the experimental (see Results for details). (C) Rate of epoxidation in the presence of non-cardiotoxic analogues, zorubicin (ZRN) and 5-iminodaunorubicin (5-IDN) with the DOX data from panel (B) shown in grey for comparison. 100 μM of AA was used in all experiments. Concentrations of anthracyclines represent the total amount of anthracyclines present. All inhibition data fit to eq S1. Error represents the SEM of 3 experiments.
