Abstract
ESBL-producing bacteria are present in wildlife and the environment might serve as a resistance reservoir. Wild gulls have been described as frequent carriers of ESBL-producing E. coli strains with genotypic characteristics similar to strains found in humans. Therefore, potential dissemination of antibiotic resistance genes and bacteria between the human population and wildlife need to be further investigated. Occurrence and characterization of ESBL-producing E. coli in Swedish wild gulls were assessed and compared to isolates from humans, livestock and surface water collected in the same country and similar time-period. Occurrence of ESBL-producing E. coli in Swedish gulls is about three times higher in gulls compared to Swedish community carriers (17% versus 5%) and the genetic characteristics of the ESBL-producing E. coli population in Swedish wild gulls and Swedish human are similar. ESBL-plasmids IncF- and IncI1-type carrying ESBL-genes blaCTX-M-15 or blaCTX-M-14 were most common in isolates from both gulls and humans, but there was limited evidence of clonal transmission. Isolates from Swedish surface water harbored similar genetic characteristics, which highlights surface waters as potential dissemination routes between wildlife and the human population. Even in a low-prevalence country such as Sweden, the occurrence of ESBL producing E. coli in wild gulls and the human population appears to be connected and the occurrence of ESBL-producing E. coli in Swedish gulls is likely a case of environmental pollution.
Introduction
Escherichia coli producing extended-spectrum betalactamases (ESBL) and/or carbapenemases are of great concern globally in patients and a threat to all modern healthcare. Further, community carriage of ESBL-producing E. coli, the emergence of ESBL-producing E. coli in the livestock population as well as multiple reports of ESBL-producing E. coli in wildlife show that transmission and persistence of such bacteria also occurs outside of clinical settings [1]. However, the extent to which, and how, transmission of ESBL- and carbapenemase-producing E. coli occur between the different sectors is under current investigation and debate in the scientific community [1, 2]. Several studies have reported occurrence of ESBL- and carbapenemase-producing E. coli in wild animals, primarily in wild birds. ESBL-producing E. coli in wildlife has been proposed to be a spill-over form of environmental pollution from human influenced settings and exposure to ESBL-producing E. coli from livestock through spreading of manure [1]. ESBL- and carbapenemase-producing E. coli found in wild birds often display phenotypic and genetic characteristics similar to strains in humans and thus, birds have been postulated as environmental indicators, reservoirs and possible spreaders of antibiotic resistance [3, 4]. Waterfowl and birds of prey appear to carry ESBL-producing E. coli more frequently compared to other groups of birds, possibly due to exposure to contaminated water and feed [1].
In recent years, ESBL-producing E. coli in gulls (Laridae spp) have been particularly studied due to their exposure to human influenced environments, migratory behavior and vast global distribution [5]. Gulls have been found to carry ESBL-producing E. coli in several studies from Europe, North America, South America and Asia and the isolates often harbor genes commonly found in strains that cause severe infections in humans [5–8]. This highlights the need to further investigate dissemination of these bacteria between gulls and human sources. Even more worrisome is that the global emergence of carbapenemase-producing E. coli is also becoming apparent in nature and such strains have recently been isolated from gulls in Spain, France and Australia [8–10].
Provided that dissemination of ESBL- or carbapenamase-producing E. coli occurs between wildlife and other sectors, the mechanism of dissemination needs to be assessed. The entire bacterium harboring resistance may be transmitted, i.e. clonal transfer. Alternatively, the genes mediating antimicrobial resistance could be transferred via plasmids or other mobile genetic elements from bacteria in one sector to bacteria more suitable to a specific host in the other sector [2].
The main objective of this study was to determine the occurrence of, and to characterize, ESBL-producing E. coli in wild gulls inhabiting urban environments in Sweden. In addition, to assess transmission we studied genetic relatedness of ESBL-producing E. coli strains found in wild gulls and compared them to strains detected in other sectors in Sweden. The current study was conducted in conjunction with a large Swedish national study reported by Börjesson et al. [11], investigating the dissemination of ESBL-producing E. coli in community carriers, bloodstream infection and livestock. Furthermore, a study on ESBL-producing E. coli in Swedish surface water was conducted during the same time period by Egervärn et al. [12]. However, there was one important difference between the current study and the other mentioned Swedish studies, (Börjesson et al. 2016, Egervärn et al. 2017) plasmid-mediated AmpC (pAmpC) betalactamase-producing E. coli were not included in the current study. The comparison of ESBL-producing E. coli isolates from wild gulls to isolates from humans, livestock and water sampled during a similar time-period and the same country is a unique feature of this study.
Materials and methods
Sample collection
Sample collection was performed in May-June 2013 by swirling a sterile cotton swab in freshly deposited feces from a variety of Gulls (Larus marinus, Larus argentatus, Larus canus and Croicocephalus ridibundus) (n = 96) in Malmö (Lat 55.6° Long 13.0°) and Black-headed Gulls (Croicocephalus ridibundus) (n = 74) in Gothenburg (Lat 57.7° Long 11.9°). Swabs were placed in cryovials containing Luria Berthani broth and glycerol (20%) and stored frozen at -80°C until further analyses was performed. The sampling did not require a field permit.
Isolation and verification of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli
Fecal samples were enriched in Brain Heart Infusion broth with 16 mg/L Vancomycin and subsequently cultivated on chromIDR ESBL bacterial plates (Biomerieux). Species identity of presumptive E. coli was assessed using MALDI-TOF (Biotyper, Bruker Corporation, The Netherlands). To confirm ESBL phenotype, isolates were prepared and spread on Muller-Hinton agar (Linnaeus University in Kalmar) according to EUCAST disc diffusion method for antimicrobial susceptibility testing and five antibiotic discs—amoxicillin/clavulanic acid 30/1 μg, cefotaxime 5 μg, ceftazidime 10 μg, cefepime 30 μg, and cefoxitin 30 μg–were placed on the plate. Specific inhibition of bacterial growth around the antibiotic discs was used to identify ESBL phenotypes [13, 14].
Characterization of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli
ESBL-genes were identified using the Check-MDR microarray system (CT-101 or -103) (Checkpoint BV, Wageningen, the Netherlands) and sequenced using Sanger sequencing [15]. All isolates were subjected to multilocus sequence typing (MLST) according to protocols at the University of Warwick web site (http://mlst.warwick.ac.uk/mlst/dbs/Ecoli). Alleles and STs were determined using BioNumerics 7.0 MLST Plug-in (Applied Maths, Gent, Belgium).
All isolates were tested for susceptibility to additional 13 antibiotics by disc diffusion according to EUCAST disc diffusion method for antimicrobial susceptibility testing and/or using VetMIC GN-mo panels according to the manufacturer (SVA, Uppsala) (Table 1), with the exception of fosfomycin were susceptibility was determined by Etest (bioMérieux, Sweden). Epidemiological cut-off values for resistance according to EUCAST (www.eucast.org) were used. Isolates with decreased susceptibility to ≥ 3 antibiotic classes in including beta-lactam antibiotics were classified as multiresistant.
Table 1. Characteristics of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli in wild gulls habituating in Swedish urban environments in 2012.
Susceptibility to ampicillin (Am), ciprofloxacin (Ci), nalidixic acid (Nal), gentamycin (Gm), streptomycin (Sm), tetracycline (Tc), flophenicol (Ff), colistin (Cs), sulfamethoxazole (Su), trimethoprime (Tm), chloramphenicol (Cm), kanamycin (Km), cefotaxim (Ctx) and ceftazidime (Caz), and was determined by microdilution. Susceptibility to, cefoxitin (Fox), tobramycin (Nn), piperacillin/Tazobactam (Tzp), amoxicillin/Clavulanic acid (AmC), tigecycline (Tgc), nitrofurantoin, meropenem, amikacin, Ertapenem and imipenem was determined by disc diffusion. Susceptibility to fosfomycin was determined by E-test. Epidemiological cut-off values for resistance according to EUCAST (www.eucast.org). All isolates were resistant to ampicillin and cefotaxime.
| City | β-lactamase gene | MLST type | Antibiotic resistance | Replicon type | Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (pMLST of IncI1) | transformants e | ||||
| Malmö | blaCTX-M-32 | ST681 | AmC, Caz | a | |
| Malmö | blaCTX-M-27 | Tc, Sm, Su, Tm | IncFIB/FII | Tc, Su, Su, Tm | |
| Malmö | blaCTX-M15 | ST10 | Ci, Tc | a | |
| Malmö | blaSHV-12 | ST10 | Ci, Tm, Nal, Tc | IncI1 (pST3) | - |
| Malmö | blaCTX-M-15 | ST10 | Ci, Tc, Caz | a | |
| Malmö | blaCTX-M-15 | ST3268 | Ci, Sm, Su, AmC, Caz | b | Ci, Su, Tm |
| Malmö | blaCTX-M-15 | ST540 | Ci, Sm, Su, Tm, Tc, AmC, Caz | b | - |
| Malmö | blaCTX-M-15 | ST93 | Ci, Tm, Nal, Tc, Caz | IncFIA, IncFIB | Tc, Tm |
| Malmö | blaCTX-M-32 | ST681 | AmC, Caz | a | |
| Malmö | blaCTX-M-55 | ST58 | Nal, Tc, Gm, Nn, Ci, AmC, Caz | IncFIA/FIB/FII | Ci, Gm, Tc |
| Malmö | blaCTX-M-55 | ST58 | Ci, Nal, Tc, Gm, AmC, Caz | IncFIA/FIB/FII | Ci, Gm, Tc |
| Malmö | blaCTX-M-1 | ST10 | - | a | |
| Malmö | blaCTX-M-1 | ST10 | Nal, Tc, Gm, Caz | a | |
| Gothenburg | blaCTX-M-15 | ST617 | Ci, Su, Tm, Nal, AmC, Caz | a | |
| Gothenburg | blaCTX-M-55 | ST155 | Ci, Ff, Sm, Su, Km, Tm, Nal, Tc, Cm, Gm, Nn, AmC, Caz | IncFIB/FII | Gm, Tc, Su, Tm |
| Gothenburg | blaCTX-M-14 | Ci, Ff, Su, Tgc, Tc, Cm, Gm, AmC | IncHI1 | Ci, Ff, Gm, Tc, Su, Cm | |
| Gothenburg | blaCTX-M-15 | ST767 | Ci, Sm, Su, Km, Tm, Nal, Tc, Cm, Gm, AmC, Caz | IncI1 (pST175) | - |
| Gothenburg | blaSHV-12 | ST540 | Ci, Sm, Su, Tm, Tc, AmC | b | Ci |
| Gothenburg | blaCTX-M-15 | ST155 | Ci, Caz | IncK | Ci |
| Gothenburg | blaSHV-12 | Ci, Su, Cm, AmC | b | Ci, Su, Cm | |
| Gothenburg | blaCTX-M-15 | ST10 | Ci, Km, Nal, Gm, Nn, Fox, Caz, Tzp, AmC | b | - |
| Gothenburg | blaCTX-M-14 | ST10 | Ci, Su, Tm, Nal, Tc, AmC | IncBO | - |
| Gothenburg | blaCTX-M-15 | ST131 | Ci, Sm, Su, Km, Tm, Nal, Tc, Gm, Nn, AmC, Caz | a | |
| Gothenburg | blaCTX-M-15 | ST38 | Ci, Sm, Su, Tm, Nal, AmC, Caz | a | |
| Gothenburg | blaCTX-M-14 | ST38 | Ci, Sm, Su, Tm, Nal, AmC | a | |
| Gothenburg | blaCTX-M-15 | Tm, Nal, Tc, Cm, Gm, Nn, Tzp, AmC, Caz d | c | ||
| Gothenburg | blaCTX-M-15 | ST636 | Tm, Nal, Tc, AmC, Caz d | c | |
| Gothenburg | blaCTX-M-14 | ST58 | Nal, AmC, Caz d | c | |
| Gothenburg | blaCTX-M-14 | ST155 | Tc, Cm, Gm, AmC d | c |
aNon-transferable with transformation.
bNon-typable using PCR-based plasmid replicon typing.
cTransformation and replicon typing was not performed.
dMicrodilution was not performed.
eThe recipient cell ElektroMax ™ DH108 ™ (Gibco Invitrogen) naturally resistant to streptomycin.
Transformation and characterization of plasmids carrying ESBL-producing E. coli-genes
On a subset of randomly selected isolates, transfer of plasmids carrying ESBL-producing E. coli-genes was assessed by electroporation to ElectroMax DH10B cells (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and transformation was confirmed by detection of the same genes as previously described [16]. All transformants positive for an ESBL gene were tested for plasmid replicon types using the Diatheva PBRT-kit (Fano, Italy). For transformants positive for incompatibility group incI1, the plasmid was subjected to plasmid MLST (pMLST) according to the Plasmid MLST database (http://pubmlst.org/plasmid/).
Transformants and corresponding donor cells were also tested for susceptibility to 14 antibiotics by microdilution according to CLSI standard [16] using VetMIC GN-mo panels (SVA, Uppsala) (Table 1).
Results
Occurrence of ESBL-producing E. coli in wild gulls
ESBL-producing E. coli were detected in 13 out of 96 sample collected from Malmö and 16 out of 74 samples collected from Gothenburg, yielding occurrence frequencies of 14% and 22% respectively and 17% combined. None of the 29 isolates were resistant to carbapenems.
Characteristics of ESBL-producing E. coli in wild gulls
All 29 ESBL-producing E. coli isolates were characterized regarding MLST-type, ESBL-genotype and susceptibility to antibiotics (Table 1). ESBL-producing E. coli-isolates belonged to 13 different MLST-types: ST10 (n = 7), ST58 (n = 3), ST155 (n = 3), ST38 (n = 2), ST540 (n = 2), ST131 (n = 1), ST681 (n = 1), ST3268 (n = 1), ST93 (n = 1), ST681 (n = 1), ST617 (n = 1), ST676 (n = 1), ST636 (n = 1) and non-typable (n = 4). The genotypic characterization revealed seven different genes encoding for ESBLs; blaCTX-M-15 (n = 13), blaCTX-M-14 (n = 5), blaCTX-M-55 (n = 3), blaSHV-12 (n = 3), blaCTX-M-1 (n = 2), blaCTX-M-32 (n = 2) and blaCTX-M-27 (n = 1). The isolate of MLST-type ST131 carried the blaCTX-M-15 gene.
Out of the 29 isolates, 25 isolates were subjected to gene transfer and subsequently replicon typing. Plasmid transfer and replicon typing were achieved in 10 isolates (40%) (Table 1). The non-transferrable isolates harboured blaCTX-M-15 (n = 5), blaCTX-M-1 (n = 2), blaCTX-M-32 (n = 2) and blaCTX-M-14, (n = 1). Isolates resulting in unsuccessful plasmid replicon typing harboured blaCTX-M-15 (n = 3) and blaSHV-12 (n = 2). Two genes, one blaCTX-M-15 and one blaSHV-12, were identified on an IncI1 plasmid, these two were further characterized regarding plasmid-MLST and belonged to pST175 and pST3 respectively.
Susceptibility to 10 antibiotic classes was assessed and 83% of ESBL-producing E. coli-isolates were classified as multiresistant, i.e. resistant to ≥ 3 classes of antibiotics. Resistance to fluoroquinolones, aminoglycosides, tetracycline, trimethoprim and sulfa-methoxazole were common characteristics. All isolates were susceptible to amikacin, colistin, fosfomycin, nitrofurantoin, ertapenem, meropenem and imipenem.
Comparison to other sectors
The characteristics of the isolates from the current study (Table 1) were compared to isolates from two other studies conducted in the same year in Sweden; a large Swedish national study reported by Börjesson et al [11], investigating the dissemination of ESBL-producing in community carriers, bloodstream infection and livestock as well as a study by Egervärn et al [12] investigating ESBL-producing E. coli in Swedish surface water. Comparisons were made at the level of ESBL gene, plasmid replicon type, MLST and the combinations of all mentioned.
ESBL-producing E. coli genes
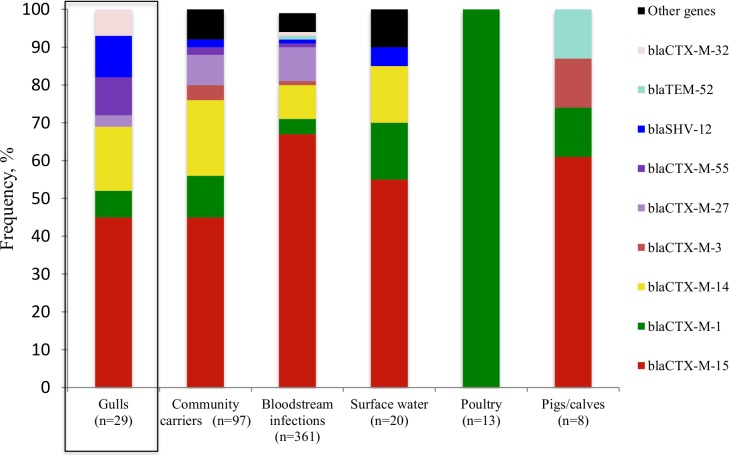
In Fig 1, the frequency of ESBL-producing E. coli genes in different sectors is visualized. The vast majority, 89%, of identified genes in gulls were of CTX-M-type and 11% were of SHV-type. The dominating gene in Swedish gulls, blaCTX-M-15, was detected in 45% of the isolates and blaCTX-M-14 was the second most common gene, detected in 17% of isolates. blaCTX-M-15 and blaCTX-M-14 were the most prevalent genes isolated from community carriers and bloodstream infections [11] and blaCTX-M-15 was the most common gene in Swedish surface water [12]. ESBL-producing E. coli isolates from poultry were exclusively of blaCTX-M-1 type and isolates from pigs/calves carried genes similar to the human and environmental sectors.
Fig 1. Frequency of overlapping ESBL genes in Swedish gulls (current study), community carriers, bloodstream infections, poultry, pigs/calves (Börjesson et al. [11]) and surface waters (Egervärn et al. [12]).
Plasmids and combinations of plasmids and genes
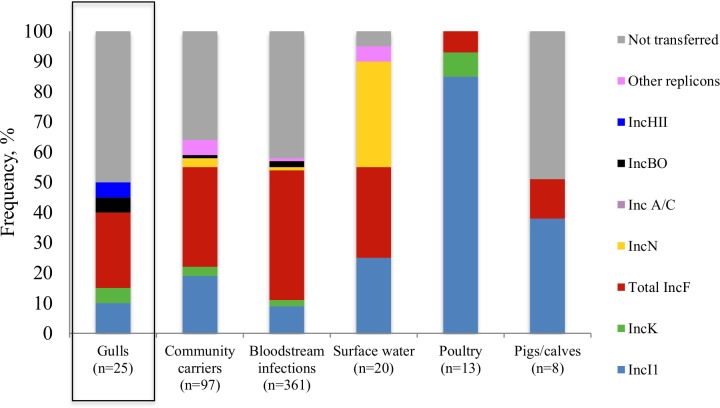
In Fig 2, the frequency of plasmid replicon type connected with plasmid carrying ESBL-producing E. coli genes in different sectors is visualized. ESBL genes identified in E. coli isolates from gulls were mainly connected to plasmids belonging to different IncF replicon types and IncI1. The distribution of plasmid types in gulls was similar to the distribution of plasmid types in community carriers and bloodstream infections. A high percentage of plasmids from gulls (50%), community carriers (36%), bloodstream infections (42%) and pigs/calves (50%) could not be transferred.
Fig 2. Frequency of overlapping plasmid replicon types containing ESBL genes in Swedish gulls (current study), community carriers, bloodstream infections, poultry, pigs/calves (Börjesson et al. [11]) and surface waters (Egervärn et al. [12]).
Eight isolates from gulls were successfully assigned a replicon type and genotype, out of which six isolates displayed combinations of plasmid replicon types and genes that were found in healthy human carriers and/or bloodstream infection in the same year; IncI1-blaCTX-M-15, IncFIA/B-blaCTX-M-15, incK-blaCTX-M-15, incB/O-blaCTX-M-14, IncBO-blaCTX-M-14 and incFIB/II-blaCTX-M-55 (Table 2). Three isolates from gulls had identical plasmid/gene combinations to isolates found in Swedish surface water. Only one isolate from pigs/calves had a combination of plasmid/gene that was identical to one isolate found in gulls, IncI1-blaCTX-M-15. Isolates from poultry displayed no plasmid/gene overlap when compared to isolates from gulls. To further characterize a selected proportion of isolates, plasmids of IncI1 type (n = 2) were subjected to pMLST. IncI1-pST3 carried the blaSHV-12 gene and IncI1-pST175 carried the blaCTX-M-15 gene. These two combinations of pMLST, plasmid replicon type and gene were not found among isolates from other sectors.
Table 2. Number (%) of overlap plasmid-replicon type /gene combination in ESBL-producing E. coli isolates from Swedish gulls (current study), community carriers, bloodstream infections, poultry, pigs/calves (Börjesson et al. [11]) and surface water (Egervärn et al. [12]).
| Plasmid | Gene variant in plasmid | Swedish gulls (n = 25) | Community carriers (n = 97) | Bloodstream infections (n = 361) | Swedish surface water (n = 27) | Swedish calf/pig (n = 8) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IncI1 | blaCTX-M-15 | 1 (4) | 8 (8) | 13 (3) | 2 (7) | 1 (9) |
| blaSHV-12 | 1 (4) | - | - | 2 (7) | - | |
| IncFIA/B | blaCTX-M-15 | 1 (4) | 6 (6) | 44 (11) | 1 (4) | - |
| IncK | blaCTX-M-15 | 1 (4) | 1 (1) | 2 (0.5) | - | - |
| IncBO | blaCTX-M-14 | 1 (4) | - | 5 (1) | - | - |
| IncFIB/II | blaCTX-M-27 | 1 (4) | 8 (8) | 31 (8) | - | - |
| IncFIB/II | blaCTX-M-55 | 1 (4) | - | 3 (1) | - | - |
ST-types and combinations of ST-types, plasmids and genes
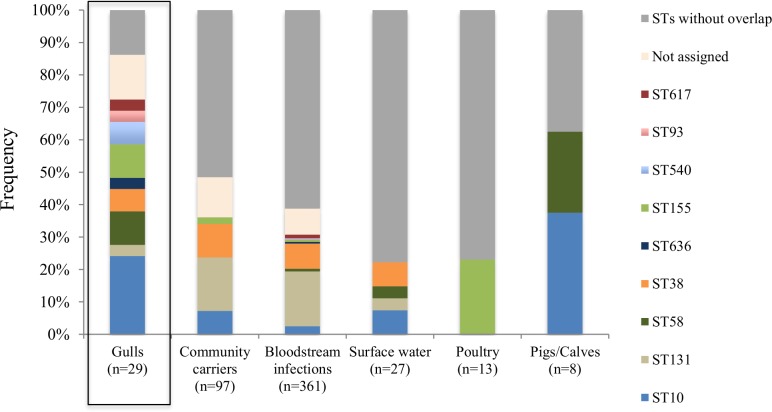
Nine out of twelve ST-types identified from gulls were detected in Swedish community carriers and/or bloodstream infections in the same year (Fig 3). Four out of the overlapping nine ST-types were also found in Swedish surface water in the same year [12]. ST10 and ST58 were found in Swedish calves and ST155 in Swedish poultry sampled in the same year [11]. The combination ST131-blaCTX-M-15 was found in one gull in this study. This combination was very common in bloodstream infections where ST131-blaCTX-M-15 was found in 31% of all isolates. When comparing clonal distributions, defined as identical ST, plasmid, and gene, of E. coli isolates from the different sectors, no overlapping combinations could be identified.
Fig 3. Frequency of multi-locus sequence types (MLST) in ESBL producing E. coli isolates from Swedish gulls (current study), community carriers, bloodstream infections, poultry, pigs/calves (Börjesson et al. [11]) and surface waters (Egervärn et al. [12]).
Discussion
In this study, we found that the genetic characteristics of ESBL-producing E. coli in Swedish wild gulls mirrors those found in humans living in Sweden. The two most common ESBL genes identified in E. coli isolates from Swedish gulls were blaCTX-M-15 and blaCTX-M-14, which are the same genes most frequently observed in isolates from community carriers and bloodstream infections in Sweden. Furthermore, isolates from Swedish gulls and humans carried ESBL-plasmids belonging to IncF- and IncI1-types, and in both populations, a large proportion of genes belonging to blaCTX-M-15 could not be transferred. The unsuccessful transfer of blaCTX-M-15 genes could be due either to a non-transferrable plasmid, or that the gene was chromosomally located, the latter have previously been described to be relatively common in ESBL-producing E. coli harbouring blaCTX-M-15 [17]. The genes blaCTX-M-15/blaCTX-M-14 and plasmids IncF/IncI1 were also common in isolates from surface water and healthy pigs/calves, previously recognized as groups carrying ESBL-producing E. coli strains with characteristics similar to strains carried by humans [11, 12]. The genetic characteristics of ESBL-producing E. coli in gulls and humans were generally different to the characteristics of poultry isolates. In Swedish poultry, isolated ESBL-producing E. coli carried blaCTX-M-1 genes. However, the clear majority of cephalosporin resistant E. coli in Swedish poultry are of pAmpC-type and harbour blaCMY-2 genes [18]. No blaCMY-2 genes were detected in Swedish gulls in this study, implying that genetic transfer between the wild bird population and the poultry population is limited. It should nevertheless be noted that the current study used chromID ESBL agar plates, which are primarily selective for ESBL-producing isolates. It is therefore likely that we underestimated the occurrence of blaCMY-2 and other pAmpCs. Though if strains carrying blaCMY-2 had been common in Swedish gulls it is highly likely that at least a fraction would have been detected using our methodology. In concordance with our findings, most previous studies have also reported a dominance of blaCTX-M-type genes in gulls [6, 19–21], but blaCMY-2 has been identified from gulls in Spain and Florida [22, 23]. Our study shows that Swedish gulls carry isolates showing genetic similarities to isolates from humans in Sweden; this indicates that the migratory Swedish gull population is domestically infected. However, the genetic characteristics of the bacteria from Swedish gulls and humans are also similar to those found in other European countries, prompting a cautious interpretation. For example, the most common ESBL-genes in Swedish gulls and humans, blaCTX-M-15 and blaCTX-M-14, are also common in human isolates from Germany [24, 25], France [26], Switzerland [27] and the Netherlands [28]. While in European farm animals, blaCTX-M-1 appears to be the most common ESBL gene in cattle, pigs and poultry, and in poultry the pAmpC gene blaCMY-2 also appears to be widespread [29].
There was a high heterogeneity of STs found in gulls in this study. All of the STs have previously been detected in isolates from humans (MLST Database of Warwick, 2017-04-01), and a majority of them were detected in isolates from Swedish humans in the same year [30]. The similarities in genetic characteristics in isolates from gulls and humans indicate transmission of ESBL-producing E. coli between the two groups. However, despite the overlapping sequence types, ESBL-genes and ESBL-carrying plasmids in gulls and humans, there was no evidence of clonal spread due to the absence of identical combinations of sequence type/gene/plasmid. Although one should be aware that the lack of direct overlap between the different sector could also be due to the small sample size in the current study. The fact that only one isolate was collected per sample in each of the studies, likely also influenced the outcome. However, the absent evidence of clonal spread and heterogeneity of ST-types could also suggest dissemination of genes encoding ESBLs rather than clonal transmission of resistant bacteria. ESBL-genes are transferred easily between bacteria through mobile genetic elements, primarily via horizontal transfer of plasmids [31]. A high diversity of ESBL-producing E. coli in communities is a common finding in previous studies, especially pronounced in CTX-M-type ESBL-producing E. coli [32]. On the contrary, two findings from our study could be consistent with clonal transfer–firstly, one of the gull isolates from Gothenburg might be derived from the successful sub-clone of blaCTX-M-15 -producing Escherichia coli ST131. This sub-clone has spread as a pandemic among humans, often identified as the pathogen in severe bloodstream infections [33]. Secondly, ST617, ST38 and ST10, found in one, two and seven gulls respectively, are also sequence types with clinical importance in human medicine [34–37]. A recent study also described high relatedness of clinical isolates of ST38 from UK and one isolate of ST38 isolated from a Mongolian wild bird [36]. In that study it was also shown that the ST38 isolates carried the genes blaCTX-M-14 and blaCTX-M-15 chromosomally, and in the current study these same two genes in ST38 were non-transferable with transformation (Table 1).
In our study, ESBL-producing E. coli occurred in 14% and 22% of gulls sampled in the Swedish cities Malmö and Gothenburg, respectively, 17% combined. This is slightly higher than the reported occurrence in gulls sampled in Stockholm in 2010, 9% [38], but at a similar level as gulls sampled in the Swedish city Hudiksvall in 2009, 21% [5]. Thus, it appears the occurrence frequency in Swedish gulls is relatively stable the last few years, although one should be careful in making direct comparisons due to small sample sizes (200–300) and different sampling locations and to some extent species of gulls. Interestingly enough the occurrence of ESBL-producing E. coli in wild gulls was therefore more than three times higher than that described in Swedish human carriers [30]. This finding is also in concordance with studies performed in other European countries, but with the difference that the ratio of ESBL-producing E. coli in gulls versus humans is often even higher [5]. This difference in carriages might be due to a higher degree of exposure and possible accumulation of resistant bacteria of the gulls; e.g. proximity to human activity has been identified as a risk factor for occurrence of antibiotic resistant bacteria in wild animals in several studies [39–42]. One such human activity could be wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) which have been recognized as hotspots for the accumulation, selection, and spread of antibiotic resistance to the environment [43]. This as gulls are often observed in connection to open WWTP basins containing untreated faecal material from entire cities. After sewage treatment in WWTPs, bacterial load is reduced by approximately 99%, but ESBL-producing E. coli are still frequently detected in rivers downstream of WWTPs and exemplifies a direct influx of antibiotic resistance from humans to the environment [44]. In this study, the isolates from gulls and humans showed high similarities to those originating from Swedish surface waters, suggesting WWTPs as one possible source. Comparable a recent Norwegian study described that ST131, ST10 and ST38 carrying the genes blaCTX-M-1, blaCTX-M-14 and blaCTX-M-15 were frequently identified from surface waters, wastewaters and human UTIs [37]. The same gene and MLST combinations were also frequent in Swedish gulls, humans and surface waters (Table 1, Fig 1, Fig 3).
There is evidence supporting a human-to-wild bird directed transmission of antibiotic resistant bacteria/antibiotic resistant genetic elements, but an important question is whether birds can also transmit antibiotic resistance to the human population? As pointed out by Guenther et al [1], in contrast to the human population, there is no sewage system for bird feces and droppings are shed directly into the environment, potentially exposing human and animal populations to resistant bacteria. Interestingly, wild birds have been found to transmit Campylobacter to crops of peas which led to an outbreak of Campylobacteriosis in humans in Alaska [45] and Campylobacter from wild birds have been isolated from children´s playground in New Zealand [46]. Furthermore, a case of bovine salmonellosis in a Japanese dairy farm was associated with Salmonella enterica Typhimurium in wild sparrows habituating near the farm [47]. As pointed out earlier, the ESBL-producing E. coli isolates from Swedish gulls resemble isolates from Swedish surface water used as drinking water sources. Wild gulls are waterfowls that feed and defecate in the water, and these settings could potentially serve as a dissemination route of ESBL-producing E. coli from wild birds back to humans. One can also not rule out other settings such as faeces-contaminated agricultural land fields and playgrounds for small children as transmission routes to humans.
Conclusions
The genetic similarities to human isolates and high occurrence frequency of ESBL-producing E. coli in gulls suggest that ESBL-producing E. coli are a form of environmental pollution. The results of the study support the hypothesis that gulls can function as environmental reservoirs and as indicators of environmental contamination of ESBL genes. In addition, the results suggest that gulls could be used as indicators of what types of antibiotic resistance are circulating in a human population. Our findings highlight the need for efforts to minimize the risk of exposing wildlife to human waste and sewage to prevent further contamination and dissemination of antibiotic resistance.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by Research Council of South East Sweden (FORSS). We appreciate the help of Martin Wintersparv Stervander, Andreas Eriksson, Johan Stedt, Kenneth Bengtsson and Sara Larsson, for sampling logistic and primary isolation of gull samples. We also thank Maria Finn, Stina Englund and Maj Anttila Ringman with practical laboratory help and interpretation of data and Professor Dan Andersson for comments on the manuscript.
Data Availability
All relevant data are within the manuscript.
Funding Statement
This work was supported by the Swedish Civil Contingency Agency (https://www.msb.se/en/?ResetTargetNavigation=true) to SN, SBo, SBy and by Forskningsrådet i Sydöstra Sverige (FORSS) (https://www.researchweb.org/is/en/forss), FORSS-234221, FORSS-391161, FORSS-314151 to JB. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Guenther S, Ewers C, Wieler LH. Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamases Producing E. coli in Wildlife, yet Another Form of Environmental Pollution? Front Microbiol. 2011;2:246 doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2011.00246 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3244693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lazarus B, Paterson DL, Mollinger JL, Rogers BA. Do human extraintestinal Escherichia coli infections resistant to expanded-spectrum cephalosporins originate from food-producing animals? A systematic review. Clinical infectious diseases: an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. 2015;60(3):439–52. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciu785 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Allen HK, Donato J, Wang HH, Cloud-Hansen KA, Davies J, Handelsman J. Call of the wild: antibiotic resistance genes in natural environments. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010;8(4):251–9. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2312 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bonnedahl J, Jarhult JD. Antibiotic resistance in wild birds. Ups J Med Sci. 2014;119(2):113–6. doi: 10.3109/03009734.2014.905663 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4034547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Stedt J, Bonnedahl J, Hernandez J, Waldenstrom J, McMahon BJ, Tolf C, et al. Carriage of CTX-M type extended spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs) in gulls across Europe. Acta Vet Scand. 2015;57:74 doi: 10.1186/s13028-015-0166-3 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4629291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bonnedahl J, Hernandez J, Stedt J, Waldenstrom J, Olsen B, Drobni M. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases in Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in Gulls, Alaska, USA. Emerg Infect Dis. 2014;20(5):897–9. doi: 10.3201/eid2005.130325 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4012786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hasan B, Melhus A, Sandegren L, Alam M, Olsen B. The gull (Chroicocephalus brunnicephalus) as an environmental bioindicator and reservoir for antibiotic resistance on the coastlines of the Bay of Bengal. Microb Drug Resist. 2014;20(5):466–71. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2013.0233 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Baez J, Hernandez-Garcia M, Guamparito C, Diaz S, Olave A, Guerrero K, et al. Molecular characterization and genetic diversity of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli colonizing the migratory Franklin's gulls (Leucophaeus pipixcan) in Antofagasta, North of Chile. Microb Drug Resist. 2015;21(1):111–6. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2014.0158 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dolejska M, Masarikova M, Dobiasova H, Jamborova I, Karpiskova R, Havlicek M, et al. High prevalence of Salmonella and IMP-4-producing Enterobacteriaceae in the silver gull on Five Islands, Australia. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016;71(1):63–70. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkv306 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4681372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Vittecoq M, Laurens C, Brazier L, Durand P, Elguero E, Arnal A, et al. VIM-1 carbapenemase-producing Escherichia coli in gulls from southern France. Ecol Evol. 2017;7(4):1224–32. doi: 10.1002/ece3.2707 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC5305998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Börjesson S, Ny S, Egervarn M, Bergstrom J, Rosengren A, Englund S, et al. Limited Dissemination of Extended-Spectrum beta-Lactamase- and Plasmid-Encoded AmpC-Producing Escherichia coli from Food and Farm Animals, Sweden. Emerg Infect Dis. 2016;22(4):634–40. doi: 10.3201/eid2204.151142 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4806949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Egervarn M, Englund S, Ljunge M, Wiberg C, Finn M, Lindblad M, et al. Unexpected common occurrence of transferable extended spectrum cephalosporinase-producing Escherichia coli in Swedish surface waters used for drinking water supply. Sci Total Environ. 2017;587–588:466–72. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.157 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Jarlier V, Nicolas MH, Fournier G, Philippon A. Extended broad-spectrum beta-lactamases conferring transferable resistance to newer beta-lactam agents in Enterobacteriaceae: hospital prevalence and susceptibility patterns. Rev Infect Dis. 1988;10(4):867–78. . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Polsfuss S, Bloemberg GV, Giger J, Meyer V, Bottger EC, Hombach M. Practical approach for reliable detection of AmpC beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. J Clin Microbiol. 2011;49(8):2798–803. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00404-11 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3147735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Brolund A. Overview of ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae from a Nordic perspective. Infect Ecol Epidemiol. 2014;4 doi: 10.3402/iee.v4.24555 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4185132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Börjesson S, Jernberg C, Brolund A, Edquist P, Finn M, Landen A, et al. Characterization of plasmid-mediated AmpC-producing E. coli from Swedish broilers and association with human clinical isolates. Clinical microbiology and infection: the official publication of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. 2013;19(7):E309–11. doi: 10.1111/1469-0691.12192 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Price LB, Johnson JR, Aziz M, Clabots C, Johnston B, Tchesnokova V, et al. The epidemic of extended-spectrum-beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli ST131 is driven by a single highly pathogenic subclone, H30-Rx. MBio. 2013;4(6):e00377–13. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00377-13 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3870262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Nilsson O, Börjesson S, Landen A, Bengtsson B. Vertical transmission of Escherichia coli carrying plasmid-mediated AmpC (pAmpC) through the broiler production pyramid. The Journal of antimicrobial chemotherapy. 2014;69(6):1497–500. doi: 10.1093/jac/dku030 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pinto L, Radhouani H, Coelho C, Martins da Costa P, Simoes R, Brandao RM, et al. Genetic detection of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-containing Escherichia coli isolates from birds of prey from Serra da Estrela Natural Reserve in Portugal. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010;76(12):4118–20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02761-09 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC2893492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hernandez J, Johansson A, Stedt J, Bengtsson S, Porczak A, Granholm S, et al. Characterization and comparison of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) resistance genotypes and population structure of Escherichia coli isolated from Franklin's gulls (Leucophaeus pipixcan) and humans in Chile. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e76150 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076150 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3786981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bonnedahl J, Stedt J, Waldenstrom J, Svensson L, Drobni M, Olsen B. Comparison of Extended-Spectrum beta-Lactamase (ESBL) CTX-M Genotypes in Franklin Gulls from Canada and Chile. PLoS One. 2015;10(10):e0141315 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141315 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4619735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Poirel L, Potron A, De La Cuesta C, Cleary T, Nordmann P, Munoz-Price LS. Wild coastline birds as reservoirs of broad-spectrum-beta-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in Miami Beach, Florida. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012;56(5):2756–8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05982-11 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3346599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Alcala L, Alonso CA, Simon C, Gonzalez-Esteban C, Oros J, Rezusta A, et al. Wild Birds, Frequent Carriers of Extended-Spectrum beta-Lactamase (ESBL) Producing Escherichia coli of CTX-M and SHV-12 Types. Microb Ecol. 2016;72(4):861–9. doi: 10.1007/s00248-015-0718-0 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Valenza G, Nickel S, Pfeifer Y, Eller C, Krupa E, Lehner-Reindl V, et al. Extended-spectrum-beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli as intestinal colonizers in the German community. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(2):1228–30. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01993-13 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3910888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pietsch M, Eller C, Wendt C, Holfelder M, Falgenhauer L, Fruth A, et al. Molecular characterisation of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Escherichia coli isolates from hospital and ambulatory patients in Germany. Vet Microbiol. 2017;200:130–7. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2015.11.028 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nicolas-Chanoine MH, Gruson C, Bialek-Davenet S, Bertrand X, Thomas-Jean F, Bert F, et al. 10-Fold increase (2006–11) in the rate of healthy subjects with extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli faecal carriage in a Parisian check-up centre. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2013;68(3):562–8. doi: 10.1093/jac/dks429 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Geser N, Stephan R, Korczak BM, Beutin L, Hachler H. Molecular identification of extended-spectrum-beta-lactamase genes from Enterobacteriaceae isolated from healthy human carriers in Switzerland. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012;56(3):1609–12. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05539-11 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3294945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.van Hoek AH, Schouls L, van Santen MG, Florijn A, de Greeff SC, van Duijkeren E. Molecular characteristics of extended-spectrum cephalosporin-resistant Enterobacteriaceae from humans in the community. PLoS One. 2015;10(6):e0129085 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129085 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4451282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ewers C, Bethe A, Semmler T, Guenther S, Wieler LH. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing and AmpC-producing Escherichia coli from livestock and companion animals, and their putative impact on public health: a global perspective. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2012;18(7):646–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2012.03850.x . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ny S, Lofmark S, Börjesson S, Englund S, Ringman M, Bergstrom J, et al. Community carriage of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli is associated with strains of low pathogenicity: a Swedish nationwide study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017;72(2):582–8. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkw419 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Brolund A, Sandegren L. Characterization of ESBL disseminating plasmids. Infect Dis (Lond). 2016;48(1):18–25. doi: 10.3109/23744235.2015.1062536 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Woerther PL, Burdet C, Chachaty E, Andremont A. Trends in human fecal carriage of extended-spectrum beta-lactamases in the community: toward the globalization of CTX-M. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2013;26(4):744–58. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00023-13 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3811232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Nicolas-Chanoine MH, Blanco J, Leflon-Guibout V, Demarty R, Alonso MP, Canica MM, et al. Intercontinental emergence of Escherichia coli clone O25:H4-ST131 producing CTX-M-15. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2008;61(2):273–81. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkm464 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Day MJ, Rodriguez I, van Essen-Zandbergen A, Dierikx C, Kadlec K, Schink AK, et al. Diversity of STs, plasmids and ESBL genes among Escherichia coli from humans, animals and food in Germany, the Netherlands and the UK. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016;71(5):1178–82. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkv485 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Schaufler K, Semmler T, Wieler LH, Wohrmann M, Baddam R, Ahmed N, et al. Clonal spread and interspecies transmission of clinically relevant ESBL-producing Escherichia coli of ST410—another successful pandemic clone? FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2016;92(1). doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiv155 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Guenther S, Semmler T, Stubbe A, Stubbe M, Wieler LH, Schaufler K. Chromosomally encoded ESBL genes in Escherichia coli of ST38 from Mongolian wild birds. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2017;72(5):1310–3. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkx006 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Jorgensen SB, Soraas AV, Arnesen LS, Leegaard TM, Sundsfjord A, Jenum PA. A comparison of extended spectrum beta-lactamase producing Escherichia coli from clinical, recreational water and wastewater samples associated in time and location. PLoS One. 2017;12(10):e0186576 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186576 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC5645111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Wallensten A, Hernandez J, Ardiles K, Gonzalez-Acuna D, Drobni M, Olsen B. Extended spectrum beta-lactamases detected in Escherichia coli from gulls in Stockholm, Sweden. Infect Ecol Epidemiol. 2011;1 doi: 10.3402/iee.v1i0.7030 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3426345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Skurnik D, Ruimy R, Andremont A, Amorin C, Rouquet P, Picard B, et al. Effect of human vicinity on antimicrobial resistance and integrons in animal faecal Escherichia coli. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006;57(6):1215–9. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkl122 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Allen SE, Boerlin P, Janecko N, Lumsden JS, Barker IK, Pearl DL, et al. Antimicrobial resistance in generic Escherichia coli isolates from wild small mammals living in swine farm, residential, landfill, and natural environments in southern Ontario, Canada. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011;77(3):882–8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01111-10 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3028733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Atterby C, Ramey AM, Hall GG, Jarhult J, Börjesson S, Bonnedahl J. Increased prevalence of antibiotic-resistant E. coli in gulls sampled in Southcentral Alaska is associated with urban environments. Infect Ecol Epidemiol. 2016;6:32334 doi: 10.3402/iee.v6.32334 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC5030259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Gomez P, Lozano C, Camacho MC, Lima-Barbero JF, Hernandez JM, Zarazaga M, et al. Detection of MRSA ST3061-t843-mecC and ST398-t011-mecA in white stork nestlings exposed to human residues. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2016;71(1):53–7. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkv314 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Michael I, Rizzo L, McArdell CS, Manaia CM, Merlin C, Schwartz T, et al. Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for the release of antibiotics in the environment: a review. Water Res. 2013;47(3):957–95. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2012.11.027 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Korzeniewska E, Harnisz M. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL)-positive Enterobacteriaceae in municipal sewage and their emission to the environment. J Environ Manage. 2013;128:904–11. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.06.051 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kwan PS, Xavier C, Santovenia M, Pruckler J, Stroika S, Joyce K, et al. Multilocus sequence typing confirms wild birds as the source of a Campylobacter outbreak associated with the consumption of raw peas. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014;80(15):4540–6. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00537-14 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC4148789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.French NP, Midwinter A, Holland B, Collins-Emerson J, Pattison R, Colles F, et al. Molecular epidemiology of Campylobacter jejuni isolates from wild-bird fecal material in children's playgrounds. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009;75(3):779–83. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01979-08 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC2632120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Yukino TI U; Kiyoshi T; Yoshinori N; Hidemasa I; Tatsufumi T and Naoya K. A case study on Salmonellaenterica serovar Typhimurium at a dairy farm associated with massive sparrow death. Acta Vet Scand. 2015;58(23). doi: 10.1186/s13028-016-0205-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are within the manuscript.