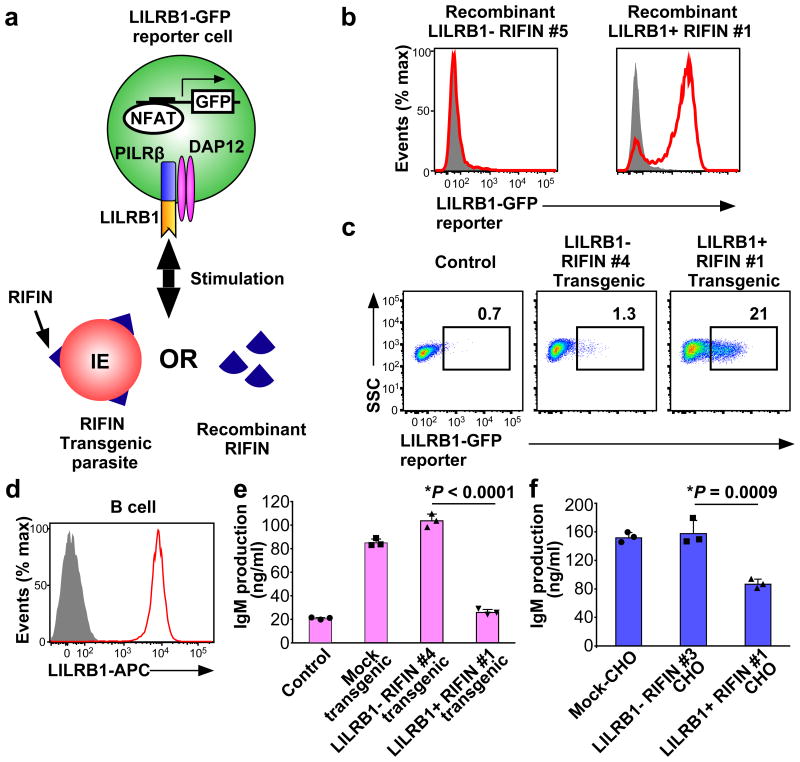
Figure 3. Inhibition of LILRB1-expressing B cells by RIFIN.
a, Diagram of the LILRB1 NFAT-GFP reporter assay. b, GFP expression in LILRB1-reporter cells upon treatment with recombinant RIFIN. Red histograms indicate treatment with recombinant LILRB1+ RIFIN#1 or LILRB1− RIFIN#5. Shaded histogram areas represent medium alone. c, GFP expression in LILRB1-reporter cells upon treatment with IEs expressing the LILRB1+ RIFIN #1 or LILRB1− RIFIN #4 transgene. Percentages of GFP-expressing cells are shown. SSC: Side-scattered light. d, Red and shaded histograms indicate staining of primary human B cells from a healthy donor with an anti-LILRB1 antibody and control, respectively. e, Inhibition of human immunoglobulin M (IgM) production in PBMCs by IEs. Human PBMCs were co-cultured with IEs, and IgM was measured in culture supernatants (mean ± s.d.). Transgenic malarial parasites expressing LILRB1+ RIFIN #1, LILRB1− RIFIN #4 or mock (GFP) are shown. Control indicates PBMCs alone. n = 3 technically independent samples. f, Inhibition of human IgM production by RIFIN-transfected CHO cells. PBMCs were co-cultured with CHO cells expressing LILRB1+ RIFIN #1, LILRB1− RIFIN #3 and an unrelated gene (MDA5). Data represent the mean ± s.d. (n = 3 technically independent samples). *P< 0.05 (one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc test). Data represent at least three independent experiments, and the variability of data presented in c is shown in Extended Data Fig.2d.