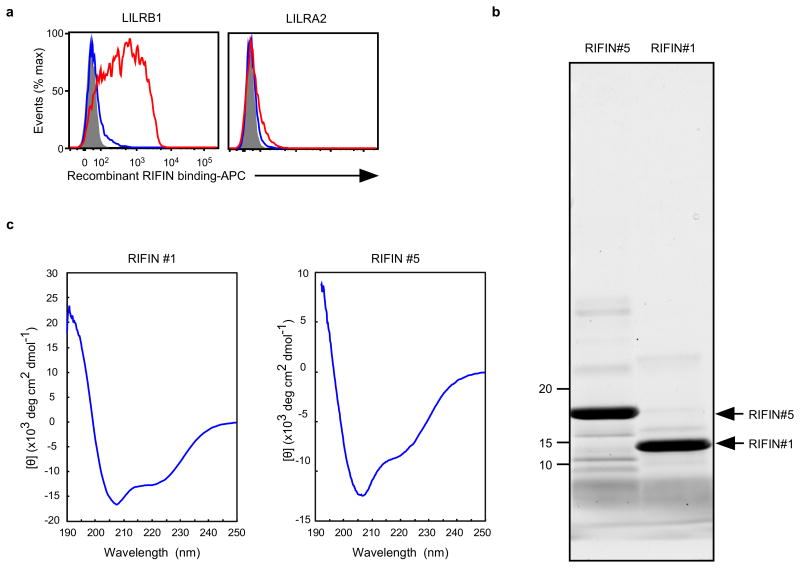
Extended Data Figure 6. Recombinant RIFINs.
a, Binding of recombinant RIFINs to LILRB1 that was produced using a wheat germ cell-free protein expression system. 293T cells expressing transfected LILRB1 or LILRA2 were stained with recombinant His-tagged RIFINs that were produced using a wheat germ cell-free protein expression system. LILRA2 is an activating counterpart of LILRB1 and was used as a control. Red and blue histograms indicate binding of LILRB1+RIFIN #1 and LILRB1−RIFIN #5, respectively. The shaded histogram represents an unstained control. The experiments were replicated at least twice. b, Production of recombinant RIFINs in Escherichia coli.N-terminal-His-tagged variable regions of RIFINs were expressed in E. coli and purified using TALON metal-affinity chromatography. Recombinant RIFINs were analysed using SDS-PAGE and Oriole staining. LILRB1+RIFIN #1 and LILRB1−RIFIN #5 are shown on the right and left, respectively. The experiments were replicated at least twice. c, Circular dichroism (CD) spectra of recombinant RIFINs. Refolded and purified recombinant RIFIN #1 and #5 were subjected to CD spectral analysis. The spectra are shown as the mean residue ellipticity after subtracting the solvent background. RIFINs #1 and #5 exhibited CD spectra typical for well-folded proteins with α-helix (208 nm +222 nm) and β-sheet (215 nm) structures. Prediction of the secondary structures of each RIFIN using the BeStSel server (http://bestsel.elte.hu/index.php) yielded α/β values of ∼30%/∼10% and ∼30%/∼20% for RIFINs #1 and #5, respectively. The experiment was performed once.