Abstract
Objectives
Patients with Ebstein’s anomaly of the tricuspid valve (EA) are at risk of tachyarrhythmia, congestive heart failure and sudden cardiac death. We sought to determine the value of cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) for predicting these outcomes.
Methods
Seventy-nine consecutive adult patients (aged 37±15 years) with unrepaired EA underwent CMR and were followed prospectively for a median 3.4 (range 0.4–10.9) years for clinical outcomes, namely major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs: sustained ventricular tachycardia/heart failure hospital admission/cardiac transplantation/death) and first-onset atrial tachyarrhythmia (AT).
Results
CMR-derived variables associated with MACE (n=6) were right ventricular (RV) or left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction (EF) (HR 2.06, 95% CI 1.168 to 3.623, p=0.012 and HR 2.35, 95% CI 1.348 to 4.082, p=0.003, respectively), LV stroke volume index (HR 2.82, 95% CI 1.212 to 7.092, p=0.028) and cardiac index (HR 1.71, 95% CI 1.002 to 1.366, p=0.037); all remained significant when tested solely for mortality. History of AT (HR 11.16, 95% CI 1.30 to 95.81, p=0.028) and New York Heart Association class >2 (HR 7.66, 95% CI 1.54 to 38.20, p=0.013) were also associated with MACE; AT preceded all but one MACE, suggesting its potential role as an early marker of adverse outcome (p=0.011).
CMR variables associated with first-onset AT (n=17; 21.5%) included RVEF (HR 1.55, 95% CI 1.103 to 2.160, p=0.011), total R/L volume index (HR 1.18, 95% CI 1.06 to 1.32, p=0.002), RV/LV end diastolic volume ratio (HR 1.55, 95% CI 1.14 to 2.10, p=0.005) and apical septal leaflet displacement/total LV septal length (HR 1.03, 95% CI 1.00 to 1.07, p=0.041); the latter two combined enhanced risk prediction (HR 6.12, 95% CI 1.67 to 22.56, p=0.007).
Conclusion
CMR-derived indices carry prognostic information regarding MACE and first-onset AT among adults with unrepaired EA. CMR may be included in the periodic surveillance of these patients.
Keywords: Ebstein’s anomaly, arrhythmia, sudden cardiac death, cardiovascular magnetic resonance
Introduction
Mortality in Ebstein’s anomaly (EA) of the tricuspid valve relates to ventricular tachyarrhythmia, congestive heart failure and sudden cardiac death. Several predictors of adverse outcomes have been reported such as age at presentation, anatomic severity, grade of tricuspid regurgitation, cyanosis, male gender, increased cardiothoracic ratio (CTR), prolonged/fragmented QRS, reduced exercise capacity and New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class have been reported.1–7 The onset of atrial tachyarrhythmia (AT) in adults is associated with significant morbidity.8 9 Cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) is used to image adults with Ebstein’s anomaly due to unrestricted views of heart structures and its place as the gold standard for quantification of left ventricular (LV) and right ventricular (RV) volumes and function without geometrical assumption.10–13 Recent studies correlated CMR-derived measures in EA with known heart failure markers and/or exercise capacity,14 15 but its value to guide prognosis is not reported. We aimed to study the prognostic significance of CMR for significant adverse cardiac events in a large, prospective, single-centre and contemporary cohort of adult patients with unrepaired EA.
Methods
Patients and study design
Eighty-six consecutive patients with unrepaired EA underwent protocolised CMR and were prospectively followed for events from November 2002 until July 2014. Seven patients were lost to follow-up, thus the final study cohort consisted of 79 patients including 4 patients with prior atrial septal defect closure (surgical n=2, catheter n=2). EA was defined as apical displacement of the septal leaflet of the tricuspid valve by at least 8 mm/m2 body surface area in relation to the insertion of the anterior mitral valve leaflet. Patients with permanent pacemaker/automated implantable defibrillator (n=10/2) were not included in this study due to relative contraindication to CMR.
The prespecified clinical endpoint of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) consisted of new-onset clinically documented sustained ventricular tachyarrhythmia/heart failure hospital admission/transplantation or death. Ventricular tachyarrhythmia was defined as ventricular tachycardia (VT) associated with presyncope/syncope, sustained VT (≥30 s) or ventricular fibrillation. Heart failure admission was defined as admission for diuresis of fluid overload not secondary to acute arrhythmia presentation. Follow-up started from CMR study and was continued until the first MACE or to surgical repair (patients were censored at surgery; n=31; 39%) or to the last clinical visit for the remainder of patients. All events during follow-up were recorded including AT for all patients, censored or not for the MACE endpoint.
A separate analysis for first-onset AT was conducted on a subset of the original study cohort excluding patients with AT prior to study inclusion, with exception for prior AT due to accessory atrioventricular pathways and Mahaim fibres (atrioventricular re-entry tachycardia (AVRT)). Only first-onset AT defined as new clinically documented sustained focal AT, atrioventricular nodal re-entry tachycardia, atrial flutter or atrial fibrillation during follow-up contributed to subsequent analysis.
Baseline data including demographics, previously documented arrhythmia, NYHA class, ECG, CTR and cardiovascular exercise testing data were obtained from medical records and clinical attendances. Mortality data from the Office for National Statistics, which registers all UK deaths, was complete for all 79 patients.
CMR acquisition and analysis
Retrospective ECG-gated balanced steady-state free precession cine images were acquired from the atrioventricular ring to the apex for measurement of LV volumes and from the diaphragm to the aortic arch for measurement of RV and atrial volumes at 1.5 T CMR. Biventricular and biatrial volumetric and functional analyses were performed by manual planimetry (CMR tools, Cardiovascular Imaging Solutions, London, UK). Native (RA) and functional right atrial and atrialised (aRV) and functional RV volumes were measured as described previously16 (figure 1). In short, the functional RV was defined as the aspect of the ventricle distal to the attachment points of the tricuspid valve leaflets and limited by the pulmonary valve. The malformed tricuspid valve was traced in detail to demarcate the border between the functional RV and aRV. With the aim of simple quantification of the degree of paradoxical LV motion, the magnitude of apical displacement of the septal leaflet of the tricuspid valve (defined as the distance from the atrioventricular ring to the attachment of the septal leaflet) was indexed to LV septal length measured in ventricular diastole and expressed as a percentage (figure 1). Total right/left-volume index was calculated using the equation (RA+aRV+RV)/(LA+LV) in end diastole15 and severity index using the equation (RA+aRV)/(RV+LA+LV).16 Phase contrast flow acquisitions were performed in the ascending aorta and pulmonary trunk. Cardiac output was calculated from aortic flow measurement and cardiac shunt as the ratio of pulmonary and aortic flows. Tricuspid regurgitant fraction was calculated using antegrade and retrograde flow through the pulmonary artery (PAante and PAretro) and functional RV stroke volume (RVSV) using the equation [(RVSV–PAante)/(RVSV–PAretro)] x100.16 LV non-compaction was defined as the end diastolic ratio of non-compacted to compacted (NC:C) myocardium >2.3:1.17 A single experienced observer made all measurements. Twelve random patients were remeasured by the same observer (minimum 6-month interval) as well as a second blinded observer for intraobserver and interobserver variability.
Figure 1.
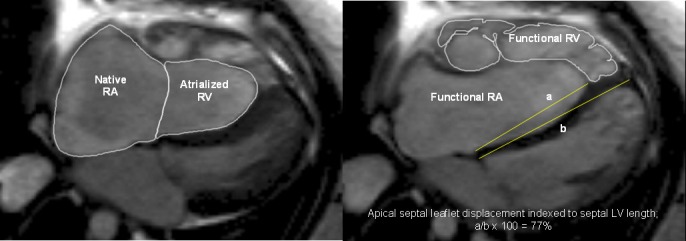
Measurements of native right atrial (RA) and atrialised right ventricular (RV) volumes, functional RV volumes and apical septal leaflet displacement/left ventricular (LV) septal length (A/B*100%). Steady-state free precession sequence and axial stack were used.
Other investigations
Cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPEX) was performed using a symptom-limited graded treadmill exercise within 6 months of the CMR study. Peak oxygen uptake (peak VO2), the per cent of predicted peak VO2 (peak VO2%), peak VO2 pulse, ratio of minute ventilation to carbon dioxide production (VE/VCO2), heart rate reserve (HRR; peak minus resting pulse rate) and anaerobic threshold were recorded. Tests were excluded from subsequent analysis if the respiratory quotient value was <1 (n=5). Venous blood was taken for brain natriuretic peptides (BNP; monoclonal antibody assay, Shionoria, Schering, West Sussex, England) at the time of the CMR examination. CPEX and BNP were performed as a part of the clinical care and were therefore not available for all patients. NYHA classification and QRS duration/QRS fractionation from standard 12-lead ECG were collected at the time point of the CMR exam. Chest X-ray within 1 month of the CMR study was included for measurement of CTR.
Statistical methods
Continuous data are presented as mean (±SD) or median (first and third quartiles) as appropriate. Comparisons between groups were made using t-test, Mann-Whitney test and Fisher’s exact test as appropriate. Correlation was tested with Pearson’s coefficient or Spearman’s r. The association between variables and event-free survival was tested using a Cox proportional hazards model and survival curves were constructed to illustrate the impact of impaired ventricular function, RV to LV volume ratio and apical septal leaflet displacement/LV septal length based on the results of the analyses. The proportional hazards assumption was verified using generalised linear regression analysis, testing for a non-zero slope of the scaled Schoenfeld residuals in addition to visual inspection of the graphs of the regression. Due to the relatively small number of outcome events, we focused on univariable analyses. Variability was expressed as the mean per cent error, derived as the absolute difference between two sets of observations, divided by the mean of the two sets of observations. All tests were two-sided and a p value of <0.05 was considered significant. Analysis was performed using SPSS V.22.
Results
Patient characteristics
Seventy-nine patients with EA (mean age 37.1±15.1 years, 36 males) were prospectively followed for a median 3.4 (range 0.4–10.9) years (table 1). Mean systolic and diastolic blood pressures were 118±16 mm Hg and 77±11 mm Hg, respectively. Resting oxygen saturation was ≤90% in 5% and plasma BNP levels were increased in 76% (>5 pmol/L). The QRS duration was prolonged in 14% (>110 ms). In total, 45 patients (57%) had severe and 23 (29%) moderate tricuspid regurgitation, respectively. Eighty-six per cent of patients (68/79) had increased functional RV end diastolic volume index (>100 mL/m2) clearly above the range for normal RV,18 whereas cardiac index was impaired in 16% (<2.3 L/min/m2).19 No significant difference was found in the tested variables presented in table 1 between patients with data available from CPEX and BNP (n=50 for both) compared with patients without these data. No difference in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) or stroke volume, or right ventricular ejection fraction (RVEF) was seen when patients with LV non-compaction (n=15) were compared with the reminder. LVEF correlated with RVEF (r=0.58, p<0.001) and inversely with NYHA class, aRV indexed volume (rs=−0.37, p=0.001 for both) and functional RV end systolic volume (rs=−0.36, p=0.001). RVEF and LV stroke volume both related inversely with NYHA class (rs=−0.38, p=0.001 and rs=−0.44, p<0.001, respectively). All cardiac events during follow-up are presented in table 2. Patients referred for surgery on clinical grounds during follow-up (n=31; 39%) differed significantly from those without surgery (table 1). Post surgery there was no difference in RVEF (45.0±5.7 vs 44.3±8.0, p=0.743), but LVEF and peak VO2 ameliorated (52.2±6.2 vs 65.7±8.9, p<0.001 and 19.5±6.0 vs 22.8±5.3, p=0.003, respectively).
Table 1.
Patient characteristics for the whole cohort, and for patients with surgery versus patients without surgery during the follow-up
| All patients (n=79) | Patients with surgery* (n=31) | Patients without surgery (n=48) | p Value† | |
| Clinical status | ||||
| Age at CMR, years | 37.1±15.1 | 35.1±15.5 | 38.3±15.0 | 0.361 |
| Male gender, n (%) | 36 (46) | 13 (42) | 23 (48) | 0.602 |
| Body surface area, m2 | 1.68±0.12 | 1.68±0.12 | 1.69±0.12 | 0.630 |
| NYHA functional class 1/2/3, n (%) | 30 (38)/39 (49)/10 (13) | 4 (13)/24 (77)/3 (10) | 26 (54)/15 (31)/7 (15) | <0.001 |
| Atrial septal defect/patent foramen ovale, n (%) | 25 (32)/24 (30) | 15 (48)/12 (39) | 10 (21)/12 (25) | <0.001 |
| Sinus rhythm, n (%)‡ | 73 (92) | 29 (94) | 40 (83) | 0.363 |
| QRS duration, ms | 130.4±26.1 | 140.9±24.5 | 120.5±24.0 | 0.002 |
| QRS fractionation, n (%) | 32 (49) | 23 (72) | 9 (27) | <0.001 |
| Accessory pathway, n (%) | 12 (15) | 4 (13) | 8 (17) | 0.649 |
| Oxygen saturations at rest in room air (%) | 97 (96–98) | 96 (94–98) | 98 (96–98) | 0.023 |
| Previously documented arrhythmia, n (%) | 19 (24) | 7 (23) | 12 (25) | 0.806 |
| AVRT (WPW)/AT/paroxysmal AF, n (%) | 11 (14)/5 (6)/3 (4) | 3 (10)/4 (13)/0 (0) | 8 (17)/1 (2)/3 (6) | – |
| LV non-compaction, n (%)§ | 15 (19) | 12 (39) | 3 (6) | 0.090 |
| Cardiothoracic ratio (n=71) | 0.57±0.08 | 0.58±0.04 | 0.56±0.09 | 0.463 |
| Brain natriuretic peptide, pmol/L (n=50) | 10.5 (5.8–20.8) | 15.0 (8.0–27.0) | 7.0 (5.0–15.0) | 0.017 |
| Peak VO2, mL/kg/min (n=50) | 22.0±7.5 | 19.5±6.0 | 24.0±8.0 | 0.032 |
| Peak VO2% (n=50) | 67.3±22.1 | 58.7±17.2 | 74.0±23.5 | 0.014 |
| CMR | ||||
| Qp:Qs | 1.0±0.2 | 1.0±0.2 | 1.1±0.3 | 0.579 |
| Cardiac index (L/min/m2) | 3.3±1.3 | 2.9±0.9 | 3.6±1.5 | 0.021 |
| Functional RA volume index, mL/m2 | 147.5 (104.7–214.5) | 211.8 (173.7–246.3) | 123.1 (98.8–160.0) | 0.001 |
| Native RA volume index, mL/m2 | 112.5 (83.6–172.6) | 160.3 (114.7–185.1) | 100.5 (81.1–133.3) | <0.001 |
| Atrialised RV volume index, mL/m2 | 40.7 (25.8–69.3) | 63.0 (45.4–92.5) | 33.5 (25.1–53.1) | 0.001 |
| Tricuspid regurgitant fraction, % | 33.7 (24–56) | 51.8 (30–61) | 26.3 (23–36) | 0.004 |
| Apical septal leaflet displacement, mm | 46.6±15.4 | 53.0±17.3 | 42.9±12.8 | 0.004 |
| Apical septal leaflet displacement indexed, % | 53.5±18.6 | 60.0±19.9 | 49.4±16.8 | 0.013 |
| Functional RV end diastolic volume index, mL/m2 | 120.2 (92.5–162.7) | 152.9 (120.0–189.1) | 108.7 (86.0–126.7) | <0.001 |
| Functional RV end systolic volume index, mL/m2 | 63.9 (46.2–87.5) | 86.9 (65.0–105.1) | 51.6 (41.1–66.3) | <0.001 |
| Functional RV stroke volume index, mL/m2 | 57.4 (46.0–78.0) | 74.2 (55.6–85.3) | 50.2 (41.9–65.9) | <0.001 |
| Functional RV ejection fraction, % | 46.5±7.1 | 45.0±5.7 | 47.4±7.8 | 0.144 |
| Functional RV/LV end diastolic indexed volume ratio | 1.58 (1.21–2.32) | 2.32 (1.72–2.90) | 1.34 (1.06–1.71) | <0.001 |
| LV end diastolic volume index, mL/m2 | 81.8 (67.5–93.6) | 72.8 (65.2–83.7) | 85.7 (73.9–101.9) | 0.004 |
| LV end systolic volume index, mL/m2 | 38.1 (31.3–45.5) | 35.4 (26.5–43.3) | 39.9 (31.8–48.4) | 0.117 |
| LV stroke volume index, mL/m2 | 41.2 (35.2–50.9) | 38.8 (32.9–46.9) | 44.5 (36.2–53.9) | 0.014 |
| LV ejection fraction, % | 53.6±7.4 | 52.2±6.2 | 54.5±8.0 | 0.392 |
| Total R/L volume index | 2.7 (1.9–4.4) | 4.4 (2.9–6.0) | 2.1 (1.8–3.2) | <0.001 |
| Severity index | 0.70 (0.46–0.92) | 0.89 (0.70–1.01) | 0.62 (0.42–0.83) | 0.010 |
*Tricuspid valve replacement (bioprosthesis/mechanic n=20/1), tricuspid valve repair (n=11), RV/RA plication (n=20/16), Patent Foramen Ovale(PFO)/Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) closure (n=10/12), ASD enlargement (n=1), MACE/cryoablation (n=5/13). Selection for surgery was based on clinical symptoms including exercise intolerance.
†Mann-Whitney/t-test/χ2.
‡Sinus rhythm in 73 and established AF in 6.
§Non-compacted to compacted myocardium (NC/C) ratio >2.3.
AF, atrial fibrillation; AT, atrial tachycardia; AVRT, atrioventricular re-entry tachycardia; CMR, cardiovascular magnetic resonance; LV, left ventricular; MACE, major adverse cardiovascular event; NYHA, New York Heart Association; Qp:Qs, ratio of pulmonary to aortic flow; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricular; WPW, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
Statistically significant p values are displayed in bold format.
Table 2.
Clinical outcomes of unrepaired Ebstein’s anomaly patients at median 3.4 (range 0.4–10.9) years follow-up
| All cardiac events during follow-up | Patients (n=79) |
| Death (sudden in all), n (%)* | 4 (5%) |
| Cardiac transplantation | 1 |
| Congestive heart failure, n (%)† | 3 (4%) |
| New-onset VT after CMR, n (%) | 12 (15%) |
| Sustained VT, n | 3 |
| Non-sustained VT, n | 9 |
| First-onset atrial tachyarrhythmia after CMR, n (%) | 17 (22%) |
| Atrial tachycardia | 10 |
| Atrial fibrillation | 7 |
Patients experiencing death/sustained VT/heart failure/cardiac transplantation; NYHA class ≥3 n=3, chronic atrial fibrillation n=2, accessory pathway n=3, QRS duration ≥120 ms n=5, exercise intolerance n=2, decreased right ventricular ejection fraction n=6, decreased left ventricular ejection fraction n=4.
Following a MACE, three patients went on for tricuspid valve surgery, one for cardiac transplantation.
*Two confirmed cardiac deaths, two unknown causes but sudden.
†One patient required hospital admission for diuresis and two patients deteriorated to NYHA class 4.
CMR, cardiovascular magnetic resonance; MACE, major adverse cardiovascular event; NYHA, New York Heart Association; VT, ventricular tachycardia.
Association of CMR-derived variables with MACE
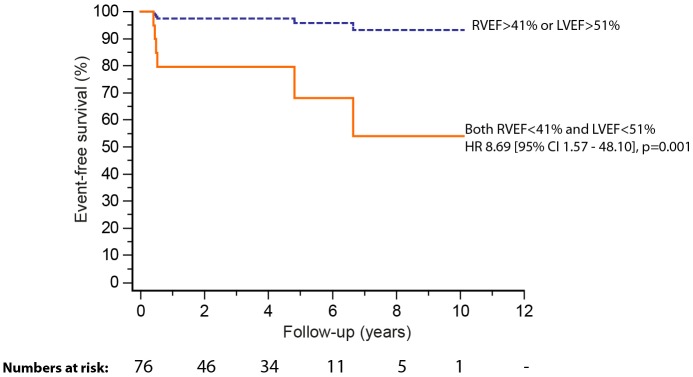
At latest follow-up, six (7.6%) patients had reached the composite endpoint (median time to event of 3.4 years). Events contributing to the composite endpoint were three sustained VT and three sudden deaths; one patient that presented with VT was later hospitalised for heart failure and died 2 years after heart transplantation (table 2). MACEs were preceded by clinically documented AT in all but one patient (p=0.011). Univariable predictors of MACE are summarised in table 3. Survival analysis showed an almost ninefold higher rate of MACE during follow-up in patients with biventricular impairment compared with RV or LV impairment only (lower quartile RVEF; <41% and LVEF; <51%; HR 8.69, 95% CI 1.57 to 48.10, p=0.001) (figure 2). RVEF and LVEF were significantly related (r=0.58, p<0.001). When tested solely for mortality, all univariable predictors with the exception of previous documented AT remained significant. The presence of LV non-compaction was not associated with outcome. No MACE occurred in patients post surgery.
Table 3.
Association of clinical features, cardiopulmonary exercise and CMR with MACE (ventricular tachycardia/heart failure/transplant/death) in unrepaired Ebstein’s anomaly patients during 3.5±2.6 years follow-up
| Patient factors (n=79) | Per* | HR | 95% CI | p Value† |
| Clinical features | ||||
| Age at inclusion | ↑1 year | 0.964 | 0.908 to 1.024 | 0.236 |
| Male gender | – | 0.407 | 0.074 to 2.228 | 0.300 |
| NYHA class>2 | – | 7.659 | 1.535 to38.204 | 0.013 |
| Previous atrial tachyarrhythmia | – | 11.155 | 1.299 to95.813 | 0.028 |
| Atrial septal defect/patent foramen ovale | – | 1.279 | 0.233 to 7.004 | 0.777 |
| QRS duration | ms | 1.016 | 0.980 to 1.054 | 0.393 |
| QRS fractionation | – | 1.000 | 0.063 to 15.988 | 1.000 |
| Accessory pathway | – | 0.236 | 0.043 to 1.297 | 0.097 |
| Oxygen saturation at rest | ↓1% | 1.129 | 0.891 to 1.431 | 0.314 |
| Brain natriuretic peptide (n=50) | ↑1 pmol/L | 0.981 | 0.841 to 1.144 | 0.807 |
| Cardiothoracic ratio>65 | – | 2.182 | 0.227 to 20.985 | 0.499 |
| Cardiopulmonary exercise capacity (n=50) | ||||
| Heart rate reserve | ↓1 bpm | 1.033 | 0.971 to 1.189 | 0.302 |
| Per cent predicted VO2 | ↓1% | 1.081 | 0.978 to 1.193 | 0.128 |
| VE/VCO2 slope | – | 0.953 | 0.837 to 1.083 | 0.459 |
| Right heart CMR measures | ||||
| Functional right atrial indexed volume | ↑5 mL/m2 | 1.009 | 0.983 to 1.037 | 0.493 |
| Native right atrial indexed volume | ↑5 mL/m2 | 1.008 | 0.979 to 1.038 | 0.587 |
| Atrialised RV indexed volume | ↑5 mL/m2 | 1.071 | 0.953 to 1.203 | 0.252 |
| Tricuspid regurgitant fraction | ↑1% | 0.998 | 0.949 to 1.050 | 0.953 |
| Apical septal leaflet displacement | ↑1 mm | 1.042 | 0.984 to 1.104 | 0.160 |
| Apical septal leaflet displacement/LV septal length | ↑1% | 1.040 | 0.989 to 1.093 | 0.124 |
| Functional RV end diastolic volume index | ↑5 mL/m2 | 1.021 | 0.989 to 1.093 | 0.427 |
| Functional RV stroke volume index | ↓10 mL/m2 | 1.018 | 0.845 to 1.280 | 0.904 |
| Functional RV ejection fraction | ↓5% | 2.058 | 1.168 to 3.623 | 0.012 |
| Left heart CMR measures | ||||
| LV end diastolic volume index | ↑5 mL/m2 | 0.925 | 0.744 to 1.149 | 0.481 |
| LV stroke volume index | ↓10 mL/m2 | 2.817 | 1.121 to7.092 | 0.028 |
| LV ejection fraction | ↓5% | 2.347 | 1.348 to4.082 | 0.003 |
| Cardiac index | ↓100 mL/min/m2 | 1.171 | 1.002 to1.366 | 0.047 |
| Combined right and left heart CMR measures | ||||
| Functional RV/LV end diastolic indexed volume ratio | ↑1 unit | 1.178 | 0.645 to 2.150 | 0.594 |
| Total right/left volume index | ↑1 unit | 1.059 | 0.807 to 1.390 | 0.678 |
| Severity index volume | ↑1 unit | 1.402 | 0.388 to 5.056 | 0.606 |
*Unit change in the parameter tested for hazard analysis is based on clinical relevance.
†p Values are derived from univariable Cox proportional hazard analysis.
CMR, cardiovascular magnetic resonance; LV, left ventricular; MACE, major adverse cardiovascular event; NYHA, New York Heart Association; RV, right ventricular.
Significant univariable predictors of MACE are formatted bold and italic.
Figure 2.
Freedom from death, sustained ventricular tachycardia, heart failure hospital admission or cardiac transplant stratified by lower quartile ejection fraction (left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) <51%, right ventricular ejection fraction (RVEF) <41%).
Association of CMR-derived variables with first-onset AT
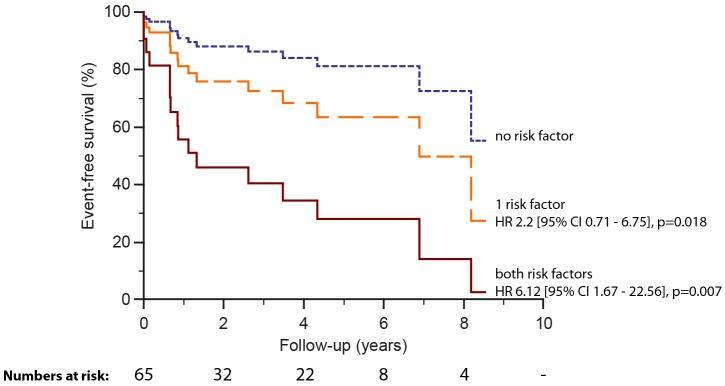
Sixty-five patients (mean age 34.5±14.8 years, 25 males) formed a subset from the original study cohort for analysis of first-onset AT (n=17). Cumulative mid-term freedom from first-onset AT at 6 months, 1 year, 5 years and 7 years was 93.7%, 83.6%, 70.3% and 60.3%, respectively. Univariable predictors are summarised in table 4. Per cent predicted peak VO2 was borderline significant (p=0.052). As the number of outcome events was relatively small we did not perform multivariable analysis. Instead, we sought to estimate the combined prognostic value of the univariable predictors. Therefore, several models were established including subsets of the univariable variables. When upper quartile RV/LV end diastolic ratio (>2.4) and upper quartile apical tricuspid septal leaflet displacement indexed to total LV septal length (>67%) were combined, the created model yielded higher rate of first-onset AT (HR 6.12, 95% CI 1.67 to 22.56, p=0.007) compared with other combined models or models using a single univariable parameter (figure 3).
Table 4.
Association of CMR with first-onset atrial arrhythmia during follow-up
| Patient factors (n=65) | Per* | HR | 95% CI | p Value† |
| Right heart CMR measures | ||||
| Functional right atrial indexed volume | ↑5 mL/m2 | 1.026 | 1.008 to1.044 | 0.005 |
| Native right atrial indexed volume | ↑5 mL/m2 | 1.026 | 1.008 to1.044 | 0.005 |
| Atrialised RV indexed volume | ↑5 mL/m2 | 1.046 | 0.967 to 1.132 | 0.262 |
| Tricuspid regurgitant fraction | ↑1% | 1.015 | 0.986 to 1.044 | 0.314 |
| Apical septal leaflet displacement | ↑1 mm | 1.035 | 0.992 to 1.081 | 0.112 |
| Apical septal leaflet displacement/LV septal length | ↑1% | 1.034 | 1.001 to 1.068 | 0.041 |
| Functional RV end diastolic volume | ↑5 mL/m2 | 1.046 | 1.004 to1.089 | 0.033 |
| Functional RV stroke volume index | ↓10 mL/m2 | 0.923 | 0.769 to 1.109 | 0.394 |
| Functional RV ejection fraction | ↓5% | 1.543 | 1.103 to2.160 | 0.011 |
| Left heart CMR measures | ||||
| LV end diastolic volume index | ↑5 mL/m2 | 0.926 | 0.813 to 1.056 | 0.253 |
| LV stroke volume index | ↓10 mL/m2 | 1.346 | 0.857 to 2.110 | 0.197 |
| LV ejection fraction | ↓5% | 1.040 | 0.951 to 1.136 | 0.395 |
| Cardiac index | ↓100 mL/min/m2 | 1.001 | 0.997 to 1.005 | 0.594 |
| Combined right and left CMR heart measures | ||||
| Functional RV/LV end diastolic indexed volume ratio | ↑1 unit | 1.546 | 1.140 to2.097 | 0.005 |
| Total right/left volume index | ↑1 unit | 1.183 | 1.063 to1.317 | 0.002 |
| Severity Index volume | ↑1 unit | 2.626 | 0.672 to 10.259 | 0.165 |
*Unit change in the parameter tested for hazard analysis is based on clinical relevance.
†p Values are derived from univariable Cox proportional hazard analysis.
CMR, cardiovascular magnetic resonance; LV, left ventricular; RV, right ventricular.
Significant univariable predictors of first-onset sustained atrial arrhythmia are formatted bold and italic.
Figure 3.
Survival curves for first-onset atrial tachycardia (n=65) stratified by univariable predictors with upper quartile functional right ventricular:left ventricular (LV) ratio (>2.4) and apical septal leaflet displacement/LV septal length (>67%) cut-offs accordingly.
Reproducibility of CMR measurements
The coefficient of variability for intraobserver reproducibility for the native RA/aRV/functional RV end diastolic volume/end systolic volume/stroke volume/EF was 2.3%/2.1%/1.4%/2.4%/1.7%/2.4%, respectively. Interobserver variabilities were 3.4%/3.2%/3.0%/4.5%/3.3%/4.0%, respectively.
Discussion
In this prospective study of adults with unrepaired EA, CMR-derived markers of biventricular function, namely RV and LV systolic dysfunction, reduced LV stroke volume and reduced cardiac index, were associated with mortality and sustained VT. Second, AT was common, preceded VT and death in all but one patient, and was associated with right but not left-sided impairment. First onset of AT showed strongest correlation with a composite of ventricular volumes and displacement of the septal tricuspid valve leaflet indexed to LV length. Indexing to LV length incorporates a measure of paradoxical interventricular septal motion and consequent impaired LV filling. Lastly, our data suggest that RV impairment precedes biventricular involvement which precedes mortality.
Association of CMR-derived biventricular EF and cardiac output with MACE
We found that standard CMR-derived parameters for ventricular dysfunction were associated with mortality and sustained VT. A 5% decrease in RVEF and LVEF, respectively, was associated with a twofold higher rate of MACE over a median of 3.4 years follow-up. In addition, biventricular impairment (lower quartile RVEF <41% and LVEF <51%, respectively) carried nearly ninefold increased rate of adverse outcome. LV stroke volume (from manual planimetry) was related to cardiac index (from flow mapping) as might be expected and like RVEF or LVEF also was associated with onset of MACE. A 10 mL/m2 decrease in LV stroke volume increased the probability of MACE nearly threefold.
RVEF and LVEF were significantly inter-related providing evidence of ventricular–ventricular interaction in unrepaired patients. This can be explained by impaired systolic RV contractility combined with tricuspid regurgitation and loss of synchrony between the native RA and aRV resulting in decreased effective RVSV and hence reduced LV preload and stroke volume. Right-sided dilatation, in the presence of an intact pericardium, causes undesirable changes to LV size and geometry, ‘stiffer’ LV and impaired LV diastolic filling. Right-sided volume overload additionally causes leftward bulging of the interventricular septum, leading to limited filling and discoordinate contraction of the LV.9 20–25
Previous studies have reported several parameters as predictors of outcomes in EA.1–5 When tested in the present study, only NYHA class >2 proved to be prognostic. We could not confirm the previous finding of peak VO2% and HRR as predictors of outcomes. However, the previous study2 included a more heterogeneous patient sample with patients that had already undergone tricuspid valve surgery and the endpoints included elective tricuspid valve surgery (16 out of 22 endpoint events); clinical decision to refer for surgery was made unblinded to peak VO2%.2 In the present study, peak VO2% was lower in patients referred for tricuspid valve surgery (n=31) during follow-up compared with the remainder, as expected.26 Most of the studied variables were more adversely affected in the group that was selected for surgery compared with the rest. This might suggest risk prediction of MACE is enhanced using the CMR-derived combined variable of lower quartile RVEF <41% and LVEF <51% and this could be tested for a potential role in facilitating earlier and more accurate surgical decision-making. However, rather than using a single variable for decision-making we suggest for clinical purposes a combination of the clinical features, NYHA class and arrhythmia propensity, with imaging markers.
Association of CMR with AT; an early marker of MACE
We showed that AT was associated with sustained VT and death during follow-up, suggesting its potential role as an early marker of adverse outcome. Furthermore, AT occurred mostly in the presence of deranged right-sided CMR indices, suggesting that right-sided dilatation and dysfunction occur first and may influence the later development of left-sided pathology. Different mechanisms have been suggested for the functional RV dilatation and dysfunction we observed in the present study including volume overload due to tricuspid regurgitation, thinner free wall of the dilated functional RV with fewer myocardial fibres and disrupted myofibril continuity. The enlarged RA, compensatory to the chronic haemodynamic stress due to right-sided volume overload and functional RV stiffness/systolic impairment, may become arrhythmogenic.27–30 We propose that the magnitude of displacement of the septal tricuspid valve leaflet indexed to total LV septal length reflects not only the severity of the atrialisation of the RV, but more specifically the degree of the paradoxical interventricular septal motion leading to adverse changes in LV geometry and impaired LV filling.9 20–25 In addition, parameters recently proposed for assessing disease severity due to their relationship to known heart failure parameters, such as the functional RV/LV end diastolic volume ratio and total right/left volume index, also correlated with outcomes in our cohort.14 15
As the number of univariable predictors was high, we sought to ascertain the discriminative value of common and easily measured CMR parameters and found the combination of two such measures resulted in a greater predictive value than when used alone. Our findings revealed a sixfold increased rate for first-onset AT when a model including functional RV/LV end diastolic volume ratio and apical tricuspid septal leaflet displacement indexed to total LV septal length was used (upper quartile RV/LV >2.4 and displacement index >67%, respectively). The functional RV/LV end diastolic volume ratio reflects the inter-related change in the ventricular volumes within an intact pericardium (transversal interaction). Combining the RV/LV end diastolic volume ratio with the indexed tricuspid septal leaflet displacement adds longitudinal interaction (atrium and ventricle) in the model. We could not confirm an association between tricuspid regurgitation and outcome, perhaps due to the high prevalence of tricuspid regurgitation (moderate/severe in 80%).
Limitations
Patients with permanent pacemaker/automated cardiac defibrillator were not included which may cause selection bias. As the CPEX and BNP were performed as a part of the clinical care, there is a limitation in testing prospective CMR data against CPEX and BNP. Nevertheless, we found no significant difference in the tested variables presented in table 1 between patients with data available from CPEX and BNP compared with patients without these data. RA and RV volumes and function are more time consuming and more challenging to measure in EA compared with structurally normal RV and consensus on the best method for quantification is lacking. We performed manual planimetry and opted to use the gold standard methods for each cardiac chamber for best interobserver and intraobserver reproducibility which we found to be satisfactory. All measures were made by a single observer measuring anonymised scans. Due to the relatively small number of outcome events, we could not perform multivariable analysis and therefore cannot determine which of the parameters being significant in univariable analyses would remain significant in multivariable analyses. The CMR-derived indices we found to be associated with outcomes in our cohort should be examined in future, larger studies with a longer period of observation to ascertain any role towards optimal timing of surgery, determine if they are modifiable by treatment such as surgery and whether their modification improves prognosis.
Conclusions
CMR-derived biventricular impairment and diminished LV stroke volume showed strong association with mortality and VT in a large, contemporary cohort of adults with unrepaired EA. AT preceded VT and death. First onset of AT was best predicted by a composite of ventricular volumes and displacement of the septal tricuspid valve leaflet indexed to LV length. These preliminary data support incorporating CMR as a prognostic tool in the periodic assessment of patients with EA.
Key messages.
What is already known on this subject?
Patients with Ebstein’s anomaly (EA) are at risk of tachyarrhythmia, congestive heart failure and sudden cardiac death. Recent studies correlated cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR)-derived measures in EA with known heart failure markers and/or exercise capacity, but its value to guide prognosis is not reported.
What might this study add?
We studied the prognostic value of CMR for significant major adverse cardiac events (MACEs) in a large, prospective, single-centre and contemporary cohort of unrepaired adult patients. CMR-derived markers of biventricular function were associated with mortality and sustained ventricular tachycardia (VT). Atrial tachyarrhythmia (AT) was common, preceded VT and death, and was associated with right-sided impairment. First onset of AT showed strongest correlation with a composite of ventricular volumes and displacement of the septal valve leaflet/LV length. Right ventricular impairment precedes biventricular involvement which precedes mortality.
How might this impact on clinical practice?
Risk prediction of MACE is enhanced using the CMR-derived biventricular impairment and this could be tested for a potential role in facilitating earlier/more accurate surgical decision-making. These data support incorporating CMR as a prognostic tool in the periodic assessment of patients with EA. However, rather than using a single variable for decision-making we suggest for clinical purposes a combination of the clinical features/New York Heart Association class/arrhythmia propensity, with imaging markers.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Mr Steven Collins and Mr Ricardo Wage for CMR IT and CMR technical support.
Footnotes
Contributors: All authors have made substantial contribution to the design, writing and critical review of the paper. RR: collecting data, planning study/design, writing paper, statistics and submitting the study. YS: collecting data, planning study/design and writing paper. GPD: statistics and critical review of the study. KN: planning and critical review of the study. WL: planning, supervising and critical review of the study. HU: review of the study. AU: supervising and review of the study. UB and BB: collecting data. SE: supervising and critical review of the study. TW: critical review of the study. DJP: critical review of the study. MAG: planning, supervising and critical review of the study. SBN: planning, supervising, writing and critical review of the study. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Funding: This project was supported by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Cardiovascular Biomedical Research Unit of Royal Brompton and Harefield National Health Service (NHS) Foundation Trust and Imperial College London. This report is independent research by the NIHR Biomedical Research Unit Funding Scheme.
Disclaimer: The views expressed in this publication are those of the author(s) and not necessarily those of the NHS, the National Institute for Health Research or the Department of Health.
Competing interests: RR was supported by the Swedish Society of Medicine, Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation and Swedish Society for Medical Research and by the Section of Clinical Physiology, Department of Molecular Medicine and Surgery, at Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden. SVB-N was supported by an Intermediate Clinical Research Fellowship from the British Heart Foundation (FS/11/38/28864).
Ethics approval: The study complies with the Declaration of Helsinki, was locally registered and approved by local ethics committee.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
References
- 1. Celermajer DS, Bull C, Till JA, et al. Ebstein’s anomaly: presentation and outcome from fetus to adult. J Am Coll Cardiol 1994;23:170–6. 10.1016/0735-1097(94)90516-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Radojevic J, Inuzuka R, Alonso-Gonzalez R, et al. Peak oxygen uptake correlates with disease severity and predicts outcome in adult patients with Ebstein’s anomaly of the tricuspid valve. Int J Cardiol 2013;163:305–8. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2011.06.047 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Oechslin EN, Harrison DA, Connelly MS, et al. Mode of death in adults with congenital heart disease. Am J Cardiol 2000;86:1111–6. 10.1016/S0002-9149(00)01169-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Brown ML, Dearani JA, Danielson GK, et al. Functional status after operation for Ebstein anomaly: the Mayo Clinic experience. J Am Coll Cardiol 2008;52:460–6. 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.03.064 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Attie F, Rosas M, Rijlaarsdam M, et al. The adult patient with Ebstein anomaly. outcome in 72 unoperated patients. Medicine 2000;79:27–36. 10.1097/00005792-200001000-00003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Park SJ, Chung S, On YK, Keun Y, et al. Fragmented QRS complex in adult patients with Ebstein anomaly and its association with arrhythmic risk and the severity of the anomaly. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2013;6:1148–55. 10.1161/CIRCEP.113.000636 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Egidy Assenza G, Valente AM, Geva T, et al. QRS duration and QRS fractionation on surface electrocardiogram are markers of right ventricular dysfunction and atrialization in patients with Ebstein anomaly. Eur Heart J 2013;34:191–200. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs362 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Walsh EP, Cecchin F. Arrhythmias in adult patients with congenital heart disease. Circulation 2007;115:534–45. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.592410 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Attenhofer Jost CH, Connolly HM, Dearani JA, et al. Ebstein’s anomaly. Circulation 2007;115:277–85. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.619338 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Kilner PJ, Geva T, Kaemmerer H, et al. Recommendations for cardiovascular magnetic resonance in adults with congenital heart disease from the respective working groups of the european Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J 2010;31:794–805. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehp586 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Yalonetsky S, Tobler D, Greutmann M, et al. Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging and the assessment of Ebstein anomaly in adults. Am J Cardiol 2011;107:767–73. 10.1016/j.amjcard.2010.10.058 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Fratz S, Chung T, Greil GF, et al. Guidelines and protocols for cardiovascular magnetic resonance in children and adults with congenital heart disease: scmr expert consensus group on congenital heart disease. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 2013;15:51 10.1186/1532-429X-15-51 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Attenhofer Jost CH, Edmister WD, Julsrud PR, et al. Prospective comparison of echocardiography versus cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in patients with Ebstein’s anomaly. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 2012;28:1147–59. 10.1007/s10554-011-9923-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Tobler D, Yalonetsky S, Crean AM, et al. Right heart characteristics and exercise parameters in adults with Ebstein anomaly: new perspectives from cardiac magnetic resonance imaging studies. Int J Cardiol 2013;165:146–50. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2011.08.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Hösch O, Sohns JM, Nguyen TT, et al. The total right/left-volume index: a new and simplified cardiac magnetic resonance measure to evaluate the severity of Ebstein anomaly of the tricuspid valve: a comparison with heart failure markers from various modalities. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 2014;7:601–9. 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.113.001467 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Fratz S, Janello C, Müller D, et al. The functional right ventricle and tricuspid regurgitation in Ebstein’s anomaly. Int J Cardiol 2013;167:258–61. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2011.12.081 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Petersen SE, Selvanayagam JB, Wiesmann F, et al. Left ventricular non-compaction: insights from cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol 2005;46:101–5. 10.1016/j.jacc.2005.03.045 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Maceira AM, Prasad SK, Khan M, et al. Reference right ventricular systolic and diastolic function normalized to age, gender and body surface area from steady-state free precession cardiovascular magnetic resonance. Eur Heart J 2006;27:2879–88. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehl336 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Carlsson M, Andersson R, Bloch KM, et al. Cardiac output and cardiac index measured with cardiovascular magnetic resonance in healthy subjects, elite Athletes and patients with congestive heart failure. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 2012;14:51 10.1186/1532-429X-14-51 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Benson LN, Child JS, Schwaiger M, et al. Left ventricular geometry and function in adults with Ebstein’s anomaly of the tricuspid valve. Circulation 1987;75:353–9. 10.1161/01.CIR.75.2.353 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Goleski PJ, Sheehan FH, Chen SS, et al. The shape and function of the left ventricle in Ebstein’s anomaly. Int J Cardiol 2014;171:404–12. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.12.037 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Brown ML, Dearani JA, Danielson GK, et al. Effect of operation for Ebstein anomaly on left ventricular function. Am J Cardiol 2008;102:1724–7. 10.1016/j.amjcard.2008.08.018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Louie EK, Lin SS, Reynertson SI, et al. Pressure and volume loading of the right ventricle have opposite effects on left ventricular ejection fraction. Circulation 1995;92:819–24. 10.1161/01.CIR.92.4.819 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Saxena A, Fong LV, Tristam M, et al. Left ventricular function in patients greater than 20 years of age with Ebstein’s anomaly of the tricuspid valve. Am J Cardiol 1991;67:217–9. 10.1016/0002-9149(91)90451-P [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Louie EK, Bieniarz T, Moore AM, et al. Reduced atrial contribution to left ventricular filling in patients with severe tricuspid regurgitation after tricuspid valvulectomy: a Doppler echocardiographic study. J Am Coll Cardiol 1990;16:1617–24. 10.1016/0735-1097(90)90311-C [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Baumgartner H, Bonhoeffer P, De Groot NM, et al. Task Force on the management of Grown-up Congenital Heart disease of the European Society of C, Association for European Paediatric C, guidelines ESCCFP. ESC guidelines for the management of grown-up Congenital heart disease (new version 2010). Eur Heart J 2010;31:2915–57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Henry WL, Morganroth J, Pearlman AS, et al. Relation between echocardiographically determined left atrial size and atrial fibrillation. Circulation 1976;53:273–9. 10.1161/01.CIR.53.2.273 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Gaynor SL, Maniar HS, Bloch JB, et al. Right atrial and ventricular adaptation to chronic right ventricular pressure overload. Circulation 2005;112:I212–8. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.104.517789 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Barbier P, Solomon SB, Schiller NB, et al. Left atrial relaxation and left ventricular systolic function determine left atrial reservoir function. Circulation 1999;100:427–36. 10.1161/01.CIR.100.4.427 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Sallach JA, Tang WH, Borowski AG, et al. Right atrial volume index in chronic systolic heart failure and prognosis. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2009;2:527–34. 10.1016/j.jcmg.2009.01.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]