Figure 3.
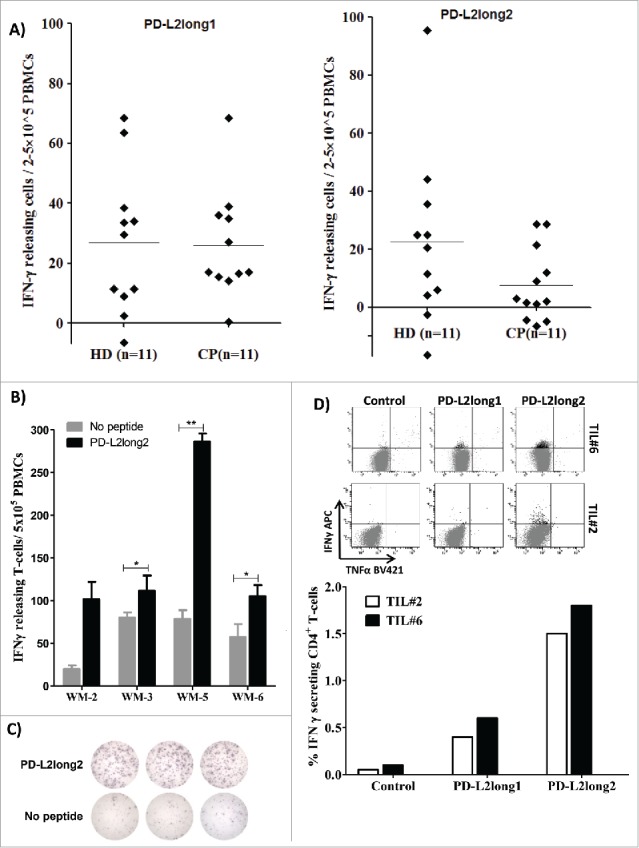
Reactivity towards long PD-L2 peptides spanning the signal peptide part of the PD-L2 sequence. (A) In vitro IFN-γ ELISPOT results. PBMCs from 11 patients with malignant melanoma and 11 healthy donors were stimulated with PD-L2long1 (PD-L29-29; SLELQLHQIAALFTVTVPKEL) or PD-L2long2 (PD-L21-25; MIFLLLMLSLELQLHQIAALFTVTV) and screened for IFNγ responses, by measuring IFNγ release in an in vitro ELISPOT assay. (B) PBMCs from four non-hodgkin lymphoma patients (WM) screened for IFN-γ responses towards PD-L2long2 (PD-L21-25) in an in vitro ELISPOT assay. All assays were made in triplicates with 3*10^6 cells per well, except one which were made in duplicates (WM-2). ** denotes as significant according to the DFR and DFR × 2; * denotes significant according to only the DFR. (C) Examples of ELISPOT well images for WM-5 patient in response to PD-L2long2. (D) Intracellular cytokine staining of tumor infiltrating T-lymphocytes (TILs) from two melanoma patients (TIL2, white bars and TIL6, black bars) shows CD4+ T cell release of IFN-Υ, upon exposure to PD-L2long1 (PD-L29-29), PD-L2long2 (PD-L21-25) and a control HIV peptide (HIV-1 pol476-484).
