Abstract
The complex interplay of dynamic protein plasticity and specific side-chain interactions with substrate molecules that allows enzymes to catalyze reactions has yet to be fully unraveled. Top-down ultraviolet photodissociation (UVPD) mass spectrometry is used to track snapshots of conformational fluctuations in the phosphotransferase adenylate kinase (AK) throughout its active reaction cycle by characterization of complexes containing AK and each of four different adenosine phosphate ligands. Variations in efficiencies of UVPD backbone cleavages were consistently observed for three α-helices and the adenosine binding regions for AK complexes representing different steps of the catalytic cycle, implying that these stretches of the protein sample various structural microstates as the enzyme undergoes global open-to-closed transitions. Focusing on the conformational impact of recruiting or releasing the Mg2+ cofactor highlights two loop regions for which fragmentation increases upon UVPD, signaling an increase in loop flexibility as the metal cation disrupts the loop interactions with the substrate ligands. Additionally the observation of holo ions and variations in UVPD backbone cleavage efficiency at R138 implicate this conserved active site residue in stabilizing the donor phosphoryl group during catalysis. This study showcases the utility of UVPD-MS to provide insight into conformational fluctuations of single residues for active enzymes.
INTRODUCTION
Enzymes are powerful catalysts capable of accelerating chemical reaction rates several orders of magnitude allowing biochemical processes to take place on biologically relevant timescales. Despite the enormous headway in deciphering the interplay of side-chain residues, cofactors, and overall protein plasticity that contributes to a suitable electrostatic environment amenable for promoting a given chemical reaction, a comprehensive understanding of enzymatic catalysis is still lacking.1–4 One well-studied enzyme known to undergo a large conformational change from an open inactive state to a closed active state is adenylate kinase (AK).5 Acting to maintain the energy balance in cells, this protein catalyzes the reversible phosphoryl transfer reaction starting with adenosine 5′-monophosphate (AMP) and adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP) which results in production of two adenosine 5′-diphosphate (ADP) molecules.6 Strategies involving elaborate computer simulations and ultrafast laser spectroscopy have complemented the static three-dimensional structures provided by crystallography and NMR studies to identify the specific residues of AK, in concert with a divalent Mg cofactor, which play key roles in the acceleration of phosphoryl transfer.7–22 Controversy remains over whether individual high-frequency local fluctuations in the enzyme’s structure facilitate large conformational transitions on the timescale of catalytic turnover and significantly contribute to an increase in efficiency of transferring the phosphoryl moiety.2,3,12,14,15,22–24 Given that catalytic mechanisms often involve several microscopic steps occurring over a hierarchy of time and distance, development of new tools for unraveling these complex processes would represent a compelling advance.3,22
Mass spectrometry (MS) has shown promise in recent years for the development of sensitive, higher-throughput approaches to addressing structural biology questions.25 Bottom-up strategies involving covalent chemical probes, including hydrogen/deuterium exchange (HDX), cross-linking of reactive residues, and hydroxyl radical footprinting, have cemented the pivotal role of tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) in examining the native structures of proteins.26–29 Native MS methods allow the efficient transfer of proteins and protein complexes into the gas phase in low charge states via electrospray ionization of buffered solutions that contain volatile salts, most commonly ammonium acetate.30,31 Measurements of collisional cross sections by ion mobility MS suggest the charged proteins and protein complexes maintain to a large extent the folded tertiary and quaternary structures adopted in solution.32–34 Moreover, the ability to determine binding constants and elucidate conformational changes occurring during ligand interactions and/or unfolding has been demonstrated.30,31,35–41 Time-resolved electrospray ionization (ESI) and HDX MS experiments have been previously been used to directly monitor enzymatic reactions on millisecond time scales and detect transient covalent intermediates.42–44
The development of MS/MS methods sensitive to protein structure has further advanced the utility of native MS. Electron-based activation techniques, including electron transfer dissociation (ETD)45 and electron capture dissociation (ECD),46–50 yield significant sequence coverage with abundances of the resulting fragments correlating with crystallographic B-factors.49,50 Surface-induced dissociation (SID) is another activation method that has found great utility for decoding the quaternary structures of protein-protein complexes.51 A third activation method, ultraviolet photodissociation (UVPD), offers unsurpassed levels of diagnostic backbone fragmentation for proteins via fast high-energy excitation caused by absorption of 193 nm photons.38–41,52–54 UVPD yields both holo (ligand-bound) and apo (free of ligand) product ions with ion abundances that reflect secondary or tertiary protein structure.38–41 Suppression or enhancement in UVPD cleavage efficiencies at certain positions along the protein backbone may result from variations in secondary or tertiary features occurring in other regions of the protein structure.40 Furthermore, ion mobility MS measurements of ubiquitin have demonstrated that UVPD fragmentation patterns vary for different gas-phase conformers, a particularly interesting outcome that demonstrates the sensitivity of UVPD to protein structure.55,56 Most recently UVPD fragmentation patterns were used to monitor stepwise loop movements of dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) upon binding of co-factor NADPH and inhibitor methotrexate, and to delineate conformational changes caused by single point G12X mutants of K-Ras bound to guanosine phosphate ligands.40,41 These previous studies have demonstrated the versatility of UVPD-MS for comparing ligand-bound to unbound states for a given protein, and monitoring conformational changes arising from binding different ligands or from subtle mutations in protein sequence. The aim of the present work is to evaluate the utility of UVPD for monitoring snapshots of the conformational dynamics of an active enzyme by comparison of various ligand-bound states. Probing this level of fine structural detail establishes a new benchmark for UVPD-MS.
Here we present native MS and top-down UVPD-MS of binary and ternary complexes of AK with AMP, ADP, ATP, and P1, P4-di(adenosine-5′)tetraphosphate (AP4A) inhibitor, mirroring the steps of its enzymatic cycle. Previously native MS has been used to screen metal-chelating to AKs and quantify association constants with various noncovalent inhibitors.57,58 More recently, phosphate-bound fragment ions observed upon ECD and collision-induced dissociation (CID) were used to elucidate ATP binding sites of the enzyme sequence.59 Previous comprehensive studies of the AK energy landscape along the reaction pathway at the molecular level point to the precise placement of a divalent Mg cofactor, conserved Arg residue, and conformational fluctuations in the protein as possible explanations for the efficient phosphoryl transfer and suppression of detrimental hydrolysis.2,3,12,16,19,22 Building on these results, we monitor variations in UVPD for several snapshots of AK that reflect steps along its catalytic cycle to shed light on the roles of local unfolding during a global open-to-closed transition, a divalent metal cofactor, and interactions of the ligands with a conserved residue in assembling the pre-organized active site essential for catalysis. Our work highlights the utility in developing novel approaches that may provide a deeper understanding of the general mechanism of enzyme catalysis.
EXPERIMENTAL
All experiments were performed on a Thermo Scientific Orbitrap Elite mass spectrometer (Bremen, Germany) modified as previously described52 with a Coherent Excistar 193 nm ArF excimer laser (Santa Cruz, CA) to perform photodissociation in the HCD cell. Details about the experimental methods and data analysis strategy are provided in the Supporting Information section. Figure S1 gives the sequence of AK (Gallus gallus) and the structures of the adenosine phosphate ligands, and data analysis methods are illustrated in Figures S2 – S5. A diagram of the crystal structure of AK•AP4A (PDB ID: 2C95)60 used as a model is given in Figure S6.
RESULTS & DISCUSSION
Native MS and UVPD of AK-Ligand Complexes
Native MS conditions were used to transfer complexes containing AK non-covalently bound to AMP, ADP, ATP, or AP4A into the gas phase by electrospray ionization. Low charge states (8+, 9+, 10+) characteristic of native-like proteins were observed for each protein-ligand complex (Figure S7A–F, including AK, AK•AMP, AK•ADP, AK•ATP, AK•AP4A, AK•AMP•ATP, AK•AMP•ATP-Mg, AK•ADP•ADP, and AK•ADP•ADP-Mg). A single divalent Mg cofactor only bound to the ternary complexes (Figure S7G–I). Catalytic products (AMP, ADP, ATP-Mg) were observed in the ESI mass spectra for the ternary complexes containing Mg but not when bound to the AP4A inhibitor, thus indicating that the protein adopted an enzymatically active conformation during analysis (Figure S8). For each complex examined, the most abundant charge state (9+) was isolated and subjected to 193 nm UVPD to yield the informative fragmentation patterns in Figure S9. Expansions of specific sections of the m/z range show isotopically resolvable fragment ions that are readily assigned as diagnostic sequence ions (Figure S9J). Deconvoluted spectra were created from raw UVPD spectra using Xtract to decharge the fragment ions (Figure S10). High sequence coverage (74–83%) was obtained for all nine complexes examined.
Mapping UVPD Holo Fragment Ions to Examine Ligand Binding Sites
Previously it was reported that the intrinsic stability of electrostatic interactions governing the binding of adenosine phosphate ligands allowed the survival and detection of protein fragment ions containing mono- and diphosphate groups and release of the truncated adenosine monophosphate upon CID or ECD of AK•ATP complexes in the gas phase.59 A subsequent study found that using supercharging reagents, such as m-nitrobenzyl alcohol and sulfolane, to increase the charge state of the precursor allowed production of AK fragment ions bound non-covalently to intact ATP upon ECD.61 Interestingly, UVPD has been shown to produce fragment ions retaining intact nucleotide phosphate ligands without the need for supercharging reagents for eIF4E•m7GTP, DHFR•NADPH, and K-Ras•GDP/GTP complexes.38,40,41 The retention of entire nucleotide phosphate ligands upon UVPD rather than retention of individual phosphate groups upon CID or ECD59 is attributed to the higher energy deposition upon absorption of 193 nm photons which presumably favor cleavage of backbone bonds of the protein rather than cleavage of labile phosphate bonds. In the present study, holo fragment ions containing the intact adenosine phosphate ligands were observed for each of the complexes examined. Figure S11 displays the distribution of holo fragment ions for the binary and ternary AK complexes with the specific residues containing bidirectional holo ions (e.g., bidirectional holo ions are those for which both N-terminal and C-terminal fragment ions retain the ligands and share overlapping residues) highlighted in red. These regions demarcated by the holo fragment ions are represented as red spheres on space-filled models on the crystal structure of the protein (PDB ID: 2C95)60 in Figure 1 to aid in visualization of the putative binding locations of the adenosine phosphate ligands.11,22,62–64
Figure 1.
Potential adenosine phosphate ligand binding residues derived from overlapping N- and C-terminal holo fragment ions produced by UVPD of (A) binary and (B) ternary AK•ligand complexes represented as red spheres in space-filling models of the crystal structure of the protein bound to AP4A (PDB ID: 2C95).
For two of the ternary complexes (AK•AMP•ATP and AK•ADP•ADP), the majority of holo fragment ions contained both ligands (e.g., 93 unique fragment ions contained both AMP and ATP for AK•AMP•ATP and 79 unique fragment ions contained both ADP molecules for AK•ADP•ADP) (Figure S12). Analysis of the AK•AMP complex yielded overlapping holo fragment ions from both the N- and C- terminus for residues in the AMPbd (L57, Q58) and ATPlid (D140) regions suggesting that this ligand is promiscuous in the absence of ATP (Figure 1A(1) AK•AMP). In the presence of ATP, only residues in the AMP adenosine binding region (L57, E65) yielded bidirectional AMP-bound holo fragment ions for the ternary complex (Figure 1B(1) AK•AMP•ATP). Evidence of ADP interactions were only found involving residues in the ATP adenosine binding region (S19, G20) for the binary AK•ADP complex, further supporting the high monophosphate nucleotide specificity of the AMP binding pocket (Figure 1A(2) AK•ADP).11,62–64 For the ternary complex containing two ADP molecules, N- and C-terminal holo fragment ions incorporating residues in the adenosine binding regions of both AMP (E65) and ATP (P17, S19) were identified (Figure 1B(2) AK•ADP•ADP). For the binary and ternary complexes involving ATP, both N- and C-terminal fragment ions retaining ATP spanned residues from the ATP adenosine binding (S19, G22, T23) and ATPlid (K131, R132, R138) regions (Figure 1A(3) AK•ATP, and 1B(3) AK•AMP•ATP). This finding correlates well with previous top-down MS data that identified amino acids G121–D140 in the ATPlid region as the primary binding site of ATP as well as an additional minor site at residues D141–D180.59 Prior MS data supported the role of several conserved arginines (R44, R97, R132, R138, R149) in binding ATP; however, the Gly-loop making up the ATP adenosine binding region (G18–T23) was not previously implicated59 but is identified in the current study. Even though these interactions were too labile to survive collisional activation, UVPD did not disrupt these interactions and key ATP-bound holo ions were observed from this region for both the binary and ternary complexes. In summary, mapping holo ions created upon photodissociation allows each adenosine phosphate ligand to be traced back to its respective binding pocket.11,22,62–64
Conformational Changes throughout the Catalytic Cycle
Enzymatic activity is often governed by a dynamic interplay between structure and stability, but understanding this linkage between plasticity and activity is still in its infancy. For AK, which is known to undergo a large conformational transition from an open inactive to a closed active state, it has been established that dynamic sampling of several structural microstates limits the rate of substrate molecule turnover.10,12,14–19 Unlike other protein kinases that require specific protein-protein interactions or covalent modifications to enable catalytic activity, the presence of two adenosine phosphate substrates is all that is necessary for AK to catalyze a reversible reaction; thus making it amenable to studies aimed at identifying specific residues that contribute to opening and closing and the timescale of these events. Based on these previous studies, the AMPbd and ATPlid regions are implicated as undergoing the largest conformational changes given that the rate of catalytic turnover is limited by opening of these regions after phosphoryl transfer to release product molecules.12,14,16–19,22 One of our primary aims is to assess the sensitivity of UVPD-MS to some of the more subtle structural changes AK undergoes during its catalytic cycle. In an effort to identify these we focused on AK from Gallus gallus (PDB: 2C95)60 which has abbreviated AMPbd and ATPlid regions compared to AK from E. coli (PDB: 1AKE)65 (Figure S13). These two regions still close over the active site to align the substrates for phosphoryl transfer and prevent hydrolysis, but owing to the shortened active site loops, dynamic fluctuations throughout the remainder of the enzyme during catalysis have a more significant impact.
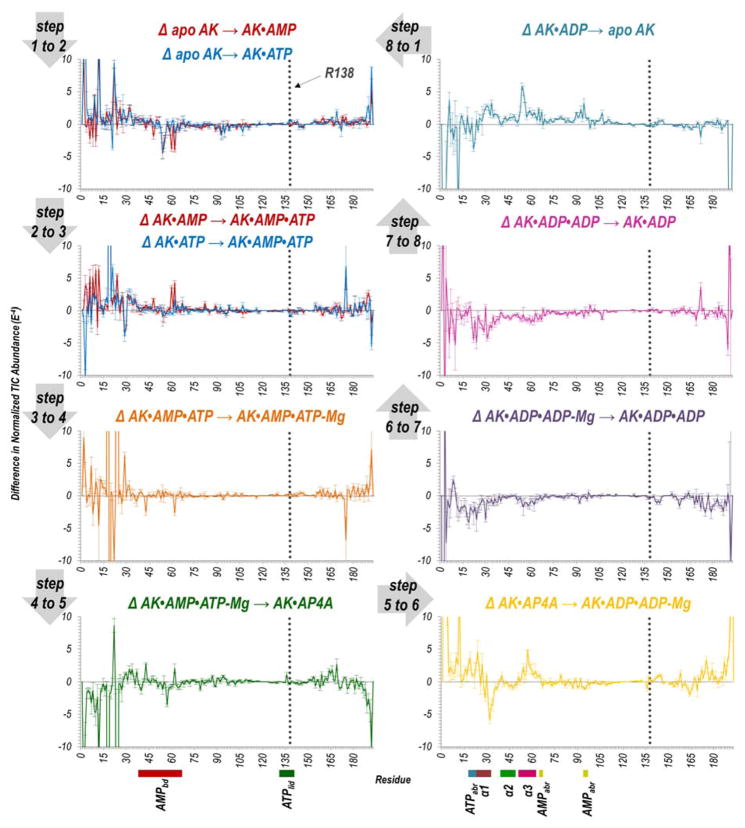
Information about relative conformational changes was inferred from backbone cleavage efficiencies across the protein determined by analysis of both holo and apo fragment ions upon UVPD. In particular, we are interested in the changes in UVPD backbone cleavage efficiencies that occur during each step of the reaction cycle. Enhancement or suppression of backbone cleavages upon UVPD has been shown to correlate with the flexibility of that region, e.g., the extent to which a given region is involved in stabilizing intramolecular interactions.39–41 Regions where UVPD fragmentation of a protein or protein complex is suppressed (relative to an analogous protein or protein complex in another state) indicates enhanced stabilization owing to conformational changes, variations in intramolecular interactions, or other factors.39–41 The efficiency of backbone cleavage upon UVPD relative to each amino acid for each AK•ligand complex is represented graphically in Figure S3. To visualize these changes in backbone cleavage efficiency for each of the eight steps of the AK catalytic cycle, difference plots were constructed by subtraction of the summed holo and apo fragment ion abundances for a given step in the cycle from the previous step (Figure 2). As shown in Figure 2, values that fall below the zero axis indicate a decrease or suppression of UVPD, whereas values that lie above the zero axis indicate an increase or enhancement of fragmentation. Considering all of the steps of the reaction cycle, most of the significant variations in backbone cleavage efficiency upon UVPD occur in the adenosine binding region of ATP and α-helices of the AMPbd. Those amino acids (representing backbone cleavage sites along the sequence of AK) for which reproducible and statistically significant variations were observed are highlighted on the structure of AK•AP4A in Figure 3 for each step of the catalytic cycle. Red-colored residues designate an increase in backbone cleavage upon UVPD compared to the previous step in the cycle, thus implying weakened or reduced intramolecular interactions. Conversely blue-colored residues denote a decrease in cleavage efficiency suggesting engagement in new intramolecular interactions that stabilize the structure. Figure 4 showcases five regions of the enzyme (α1, α2, α3 helices, AMP and ATP adenosine binding regions) found to consistently undergo significant conformational changes in each putative snapshot of the enzymatic cycle (based on the UVPD data) highlighted on the crystal structure of AK bound to AP4A.
Figure 2.
Difference plots showing the change in summed abundances of holo and apo fragment ions produced upon UVPD of each AK•ligand complex throughout the entire catalytic cycle of the enzyme. The UVPD fragmentation plot for each individual complex is shown in Figure S3. The dotted line indicates the position of R138. Relevant helices (α1, α2, α3) and regions (adenosine binding regions of AMP and ATP, AMPbd, ATPlid) are labelled underneath the x-axis using colors corresponding to Figure 4.
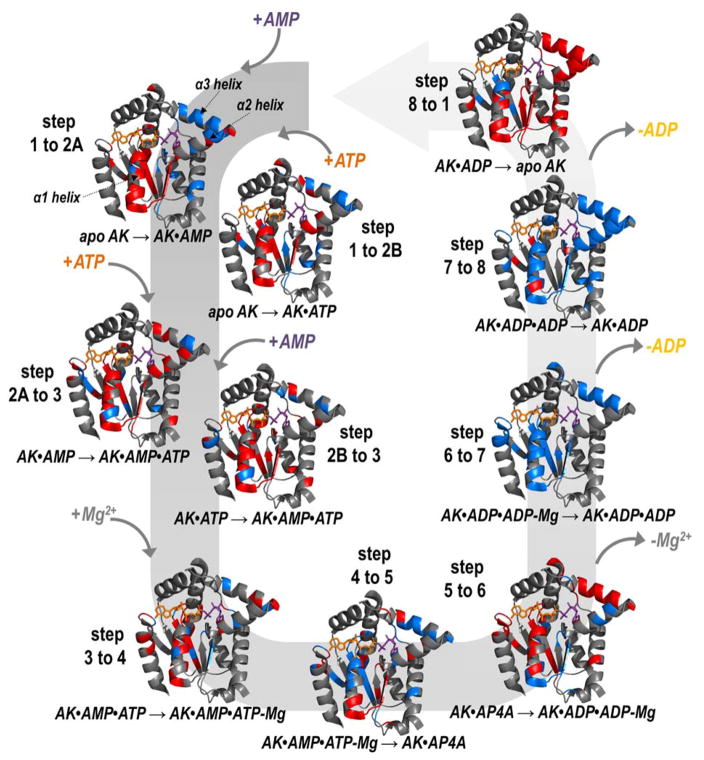
Figure 3.
Tracking the enhancement (red) and suppression (blue) of UVPD throughout the entire catalytic cycle impressed on a crystal structure of AK bound to AP4A (PDB ID: 2C95): apo AK binding to form binary complexes (step 1 to 2A,B), each transitioning to the ternary complex (step 2A,B to 3), recruiting the Mg2+ cofactor (step 3 to 4), closing into the transition state (step 4 to 5), producing two ADP molecules (step 5 to 6), losing the cofactor (step 6 to 7), and releasing ADP (step 8 to 1). The colored regions reflect statistically significant changes in UVPD backbone cleavage efficiency for the difference plots shown in Figure 2. Three key helices are labelled in step 1 to 2A.
Figure 4.
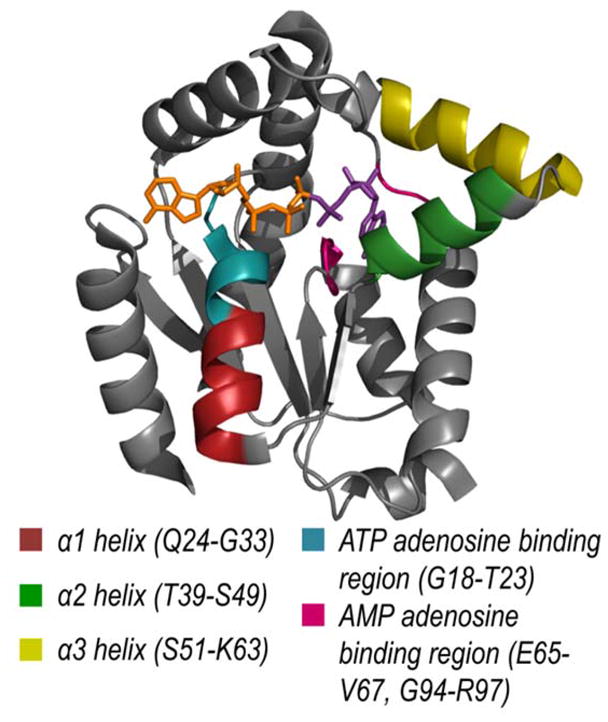
Five regions of the protein consistently undergoing significant fragmentation changes based on UVPD, indicative of conformational changes throughout the enzymatic cycle highlighted on the crystal structure of AK bound to AP4A (PDB ID: 2C95).
Following a random bi-bi mechanism during catalysis (i.e., two substrates on, two substrates off), either AMP or ATP can bind apo AK and cause suppression of backbone cleavage in the AMPbd and AMP adenosine binding region (Figure 3(step 1 to 2A)) or K21 of the ATP adenosine binding region (Figure 3(step 1 to 2B)). Enhancement in the degree of fragmentation of the α1 helix for both states suggests a global opening of the protein during binary complex formation. Addition of the second cognate ligand to each of the binary complexes to form the ternary AK•AMP•ATP complex results in similar changes in UVPD cleavage efficiencies: most notably significant enhancement of fragmentation in the α1, α2, and α3 helices (Figure 3(steps 2A, 2B to 3)). This outcome is consistent with further opening of AK to accommodate a second ligand as well as local conformational fluctuations of these three helices to align the reactive atoms of the substrate ligands during catalysis. Recruitment of the Mg2+ cofactor leads to further enhancement of fragmentation in these helical regions, a result that parallels the increased catalytic efficiency of AK as these regions dynamically sample different microstates to carry out the enzymatic function (Figure 3(step 3 to 4)). Locking the protein in the transition state with inhibitor AP4A causes significant suppression of UVPD backbone cleavage efficiency in the α1 and α3 helices. As expected this supports that the protein is trapped in a closed but catalytically inactive conformation (Figure 3(step 4 to 5)). Fragmentation throughout the α1 and α3 helices is again enhanced transitioning to the catalytically active ternary complex containing two ADP products and the Mg2+ cofactor (Figure 3(step 5 to 6)). Removal of the cofactor causes significant suppression of fragmentation throughout the entire protein, especially in the α1 and α3 helices; this corresponds to the step in which the catalytic efficiency of the protein is markedly decreased (Figure 3(step 6 to 7)). Similar suppression of UVPD is observed as one ADP product molecule is released implying local unfolding of these regions has ceased (Figure 3(step 7 to 8)). Loss of the second product ADP molecule to yield apo AK returns the protein to an open, inactive conformation, suggested by the significant enhancement in UVPD cleavage efficiency throughout the three α-helices (Figure 3(step 8 to 1)). In general, tracking the variations in UVPD fragmentation for various snapshots of the catalytic cycle specifically implicates the α-helices of the AMPbd and the adenosine binding regions of AMP and ATP as key features that undergo significant reorganization during the catalytic reaction trajectory of AK (Figure 4). This corresponds well to established results, but caution must be taken when comparing gas-phase data to results from solution.10,12,14–19,22 Previous in vacuum molecular dynamics simulations of AK conclude that although the absolute magnitude of the fluctuations is different in the gas phase (as would be expected without solvent present), the same regions of the protein (AMPbd and ATPLID) have the highest rms deviation values from the crystal structure during ligand binding and catalysis for both solution and the gas phase.66–68
Examining the Impact of the Mg2+ Cofactor
Metal ion cofactors are often required for enzyme catalysis but controversies regarding the specific role of Mg cofactors in kinase catalysis remain. Specifically, some kinases are activated by a single Mg2+ ion while for others binding of additional Mg2+ might be necessary or may result in inhibition of the enzyme.22 A recent comprehensive study of the energy landscape of AK during its reaction cycle investigated the mechanism of transition state stabilization and demonstrated a single divalent Mg2+ ion as a key player in both orienting active site groups on the ligands for efficient phosphoryl transfer and facilitating opening of the AMPbd and ATPlid after reaction catalysis.22 In addition to balancing the negative charge of the adenosine phosphate ligands in the active site, the positively charged Mg2+ maintains its position during the transition state and acts as an electrostatic pivot to anchor the donor phosphoryl group for a more favorable nucleophilic attack by the oxygen of the acceptor ligand.22,69
UVPD-MS provides complementary insight into changes of the protein conformation in response to the recruitment or release of the Mg2+ cofactor during the catalytic cycle. Examining the variations in AK fragmentation after binding and release of the metal ion reveals residues that may be engaging in new interactions (suppressed backbone cleavage) or are situated in regions that become flexible after weakening of previous interactions (enhanced backbone cleavage).39–41 Figure S14 gives an expanded view of steps 3–7 from Figure 3 demonstrating the enhancement (red) and suppression (blue) of UVPD upon addition of the Mg2+ cofactor (step 3 to 4), locking into the transition state (step 4 to 5), yielding two ADP molecules (step 5 to 6), and releasing the Mg2+ cofactor (step 6 to 7). The green ovals in Figure S14 highlight two regions that are engaged in stabilizing interactions with the phosphate groups of the adenosine substrates and exhibit significant variation in UVPD backbone cleavage efficiency as the Mg2+ cation is recruited and released. In particular, enhancement in fragmentation of the loop binding the phosphates of ATP (G15–K21) is observed upon Mg2+ binding (Figure S14(step 3 to 4) and Figure 3(step 3 to 4)). This result supports the role of Mg2+ in interrupting intramolecular interactions between the side-chains of the protein and the phosphates of the ligand to accelerate opening the AMPbd and ATPlid regions after catalysis of the phosphoryl transfer. Conversely locking the enzyme in a transition-like state with the AP4A inhibitor causes suppression of fragmentation in that same loop region (G15–K21) as well as a second loop region (K63–V67) engaged in interactions with the phosphate of AMP (Figure S14(step 4 to 5) and Figure 3(step 4 to 5)), suggesting that for this complex these stabilizing interactions have been re-established. Returning the enzyme to its catalytically active state with Mg2+ present once again yields enhanced backbone cleavage in these two loop regions (Figure S14(step 5 to 6) and Figure 3(step 5 to 6)). Removal of the Mg2+ cofactor results in suppression of fragmentation of the loop adjacent to the phosphate groups of ATP (G15–K21) as the cation is no longer present to disrupt these interactions (Figure S14(step 6 to 7) and Figure 3(step 6 to 7)). The conformational impact of addition and removal of the Mg2+ cofactor on AK revealed by UVPD-MS recapitulates the important role of the cation in stabilizing groups involved in phosphoryl transfer and accelerating opening of the enzyme after catalysis.22
Tracking Conserved Residue R138 during the Catalytic Cycle
The active site residue R138, conserved across all species of AK, has previously been implicated as a significant factor for catalysis by this enzyme. Mutation of this residue, even to a similarly positively charged Lys, drastically inhibits the rate of enzyme turnover for AK.70 This finding implies that the specific guanidinium interaction with the β-phosphate of the donor substrate is necessary, an interaction not replicated by a surrogate positively charged group.22 Additionally, x-ray crystallographic analysis of transition-state AK structures reveals that R138 shifts in concert to mirror the position of the donor phosphoryl group.22 However previous quantification of phosphoryl transfer and lid opening rates for an R138K mutant revealed that the R to K mutation only influenced the rate of transfer of the phosphoryl group, but not the rate of opening of the ATPlid region after catalysis.22
Tracking the variations in UVPD backbone cleavage efficiency specifically for R138 at various steps along the reaction trajectory supports these findings. The position of R138 is indicated by a gray dotted line in Figure 2. The most notable variations in fragmentation at this amino acid backbone position occur during steps 4 to 5, 5 to 6, and 6 to 7. As the enzyme is locked into a catalytically inactive state bound to AP4A (Figure 2(step 4 to 5)), the backbone cleavage efficiency is suppressed suggesting that the residue is strongly interacting with the phosphate of the donor substrate. Return of the enzyme to a catalytically active state (Figure 2(step 5 to 6)) results in significantly enhanced cleavage at R138 implying that the segment containing this residue regains flexibility, engaging in only transient interactions as it mirrors the movement of the donor phosphoryl group. Loss of the Mg2+ cofactor (Figure 2(step 6 to 7)) lowers the catalytic activity of the enzyme, and once again cleavage at R138 is suppressed suggesting a loss of dynamic flexibility and engagement in interactions with the donor phosphoryl group. Upon examination of the holo ions produced upon UVPD of the ternary AK•AMP•ATP complex, R138 was directly identified as interacting strongly with ATP. This result implies that the enhancement and suppression of the cleavage at this residue arises from its interaction with the phosphoryl group of the donor ligand and not some other stabilizing interaction (Figure S11B(3)). Additionally, if R138 was directly involved in lid opening, suppression of cleavage at this residue for the catalytically inactive complex (AK•AP4A) would be expected instead of the observed enhancement (Figure 3(step 4 to 5)). Nevertheless, in vacuum molecular dynamics simulations tracking the deviations of R138 from the crystal structure throughout catalysis could further confirm these findings and validate the comparison of gas-phase UVPD-MS data to crystal structure analysis.22
CONCLUSION
UVPD-MS provides multiple layers of information on the individual contributions of structural dynamics, metal cofactors, and side-chain chemistries during enzyme catalysis. Variations in UVPD backbone cleavage efficiencies were monitored to examine the dynamic plasticity of different stable states of adenylate kinase by changing the nature of the ligand to mimic the enzyme’s catalytic cycle. Changes in fragmentation efficiencies are attributed to differences in the intra- and intermolecular interactions in which the residues of AK engage as the protein binds each of the substrates, recruits a divalent cofactor (Mg2+), carries out the phosphoryl-transfer reaction, and releases the product molecules. Three α-helices of the AMPbd and the adenosine binding regions of AMP and ATP were implicated as undergoing conformational fluctuations during a global open-to-closed transition as the protein samples various structural microstates to optimize the environment for phosphoryl transfer and suppress hydrolysis. Additionally, changes in UVPD fragmentation efficiency for amino acids in the active site of the enzyme upon recruitment and removal of a divalent Mg2+ cofactor by the ternary complex highlights two loop regions that engage in interactions with the phosphate groups of the substrates. This finding supports the role of Mg2+ in accelerating opening of the AMPbd and ATPlid regions by disrupting electrostatic interactions between the side-chains and bound ligands. UVPD-MS also allowed the conformational variations of the conserved active site residue R138, known to aid in transfer of the phosphoryl group from the donor to the acceptor ligand, to be tracked. Suppression of cleavage efficiency when the enzyme is catalytically active and observation of ATP-bound holo ions at this residue echo the role of R138 in aiding the catalysis of the phosphoryl transfer. Pairing UVPD-MS with more extensive molecular dynamics simulations and integrating complementary data from other biophysical tools, such as vibrational Stark effect spectroscopy,71 will allow further validation of UVPD as a probe of protein conformation and help unravel the fundamental underpinnings of the UVPD mechanism with respect to the dominant structural or chemical factors that influence the variations in protein fragmentation caused by UVPD. In summary, this study establishes a new level of fine structural detail that can be probed with UVPD-MS. UVPD-MS appears to be sensitive to the dynamic conformational equilibria that exist as AK samples various structural microstates in the presence of substrates to align reactive atoms during catalysis.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Funding from the NIH (R01GM121714 and 1K12GM102745 (fellowship to MBC)) and the Robert A. Welch Foundation (F-1155) is acknowledged.
Footnotes
The Supporting Information is available free of charge via the internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
Supporting information contains a more detailed description of experimental methods and materials, and Figures S1–S14 including the sequence of AK and structures of the ligands, graphs showing the average mass shifts observed for binding the adenosine phosphate ligands, summed holo and apo UVPD intensities plotted per residue for all AK-ligand complexes, graphical displays of the statistical significance for the variations in backbone cleavage efficiencies, a color-coded diagram of the crystal structure of AK, and ESI and UVPD mass spectra of the AK-ligand complexes. Table S1 provides a comprehensive list of identified UVPD fragment ions for apo AK.
References
- 1.Daniel RM, Dunn RV, Finney JL, Smith JC. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2003;32:69–92. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.32.110601.142445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Henzler-Wildman KA, Thai V, Lei M, Ott M, Wolf-Watz M, Fenn T, Pozharski E, Wilson MA, Petsko GA, Karplus M, Hübner CG, Kern D. Nature. 2007;450:838–844. doi: 10.1038/nature06410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Henzler-Wildman KA, Lei M, Thai V, Kerns SJ, Karplus M, Kern D. Nature. 2007;450:913–916. doi: 10.1038/nature06407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kamerlin SCL, Warshel A. Proteins Struct Funct Bioinforma. 2010;78:1339–1375. doi: 10.1002/prot.22654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Vonrhein C, Schlauderer GJ, Schulz GE. Structure. 1995;3:483–490. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00181-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Noda L. J Biol Chem. 1958;232:237–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Abele U, Schulz Ge. Protein Sci. 1995;4:1262–1271. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560040702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sinev MA, Sineva EV, Ittah V, Haas E. Biochemistry. 1996;35:6425–6437. doi: 10.1021/bi952687j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sheng XR, Li X, Pan XM. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:22238–22242. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.32.22238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Miyashita O, Onuchic JN, Wolynes PG. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2003;100:12570–12575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2135471100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Krishnamurthy H, Lou H, Kimple A, Vieille C, Cukier RI. Proteins Struct Funct Bioinforma. 2005;58:88–100. doi: 10.1002/prot.20301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bae E, Phillips GN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:2132–2137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507527103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ådén J, Wolf-Watz M. J Am Chem Soc. 2007;129:14003–14012. doi: 10.1021/ja075055g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Arora K, Brooks CL. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2007;104:18496–18501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0706443104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hanson JA, Duderstadt K, Watkins LP, Bhattacharyya S, Brokaw J, Chu JW, Yang H. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2007;104:18055–18060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0708600104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Whitford PC, Miyashita O, Levy Y, Onuchic JN. J Mol Biol. 2007;366:1661–1671. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.11.085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Schrank TP, Bolen DW, Hilser VJ. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2009;106:16984–16989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0906510106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Daily MD, Phillips GN, Jr, Cui Q. J Mol Biol. 2010;400:618–631. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.05.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Olsson U, Wolf-Watz M. Nat Commun. 2010;1:111. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ådén J, Verma A, Schug A, Wolf-Watz M. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:16562–16570. doi: 10.1021/ja3032482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rao VVHG, Gosavi S. PLOS Comput Biol. 2014;10:e1003938. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kerns SJ, Agafonov RV, Cho YJ, Pontiggia F, Otten R, Pachov DV, Kutter S, Phung LA, Murphy PN, Thai V, Alber T, Hagan MF, Kern D. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015;22:124–131. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ferreiro DU, Hegler JA, Komives EA, Wolynes PG. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2011;108:3499–3503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1018980108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Warshel A, Bora RP. J Chem Phys. 2016;144:180901. doi: 10.1063/1.4947037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Konermann L, Vahidi S, Sowole MA. Anal Chem. 2014;86:213–232. doi: 10.1021/ac4039306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Konermann L, Tong X, Pan Y. J Mass Spectrom. 2008;43:1021–1036. doi: 10.1002/jms.1435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Fitzgerald MC, West GM. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2009;20:1193–1206. doi: 10.1016/j.jasms.2009.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cammarata M, Lin KY, Pruet J, Liu H, Brodbelt J. Anal Chem. 2014;86:2534–2542. doi: 10.1021/ac4036235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Pirrone GF, Iacob RE, Engen JR. Anal Chem. 2014;87:99–118. doi: 10.1021/ac5040242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sharon M, Robinson CV. Annu Rev Biochem. 2007;76:167–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.76.061005.090816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Heck AJR. Nat Methods. 2008;5:927–933. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hopper JTS, Oldham NJ. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2009;20:1851–1858. doi: 10.1016/j.jasms.2009.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Konermann L, Ahadi E, Rodriguez AD, Vahidi S. Anal Chem. 2012;85:2–9. doi: 10.1021/ac302789c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Schennach M, Breuker K. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2014;53:164–168. doi: 10.1002/anie.201306838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Cubrilovic D, Haap W, Barylyuk K, Ruf A, Badertscher M, Gubler M, Tetaz T, Joseph C, Benz J, Zenobi R. ACS Chem Biol. 2014;9:218–226. doi: 10.1021/cb4007002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Li H, Wongkongkathep P, Orden SLV, Loo RRO, Loo JA. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2014;25:2060–2068. doi: 10.1007/s13361-014-0928-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Li H, Wolff JJ, Van Orden SL, Loo JA. Anal Chem. 2014;86:317–320. doi: 10.1021/ac4033214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.O’Brien JP, Li W, Zhang Y, Brodbelt JS. J Am Chem Soc. 2014;136:12920–12928. doi: 10.1021/ja505217w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Cammarata MB, Brodbelt JS. Chem Sci. 2015;6:1324–1333. doi: 10.1039/c4sc03200d. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Cammarata MB, Thyer R, Rosenberg J, Ellington A, Brodbelt JS. J Am Chem Soc. 2015;137:9128–9135. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b04628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Cammarata MB, Schardon CL, Mehaffey MR, Rosenberg J, Singleton J, Fast W, Brodbelt JS. J Am Chem Soc. 2016;138:13187–13196. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b04474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Zechel DL, Konermann L, Withers SG, Douglas DJ. Biochemistry. 1998;37:7664–7669. doi: 10.1021/bi980445o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Li Z, Sau AK, Shen S, Whitehouse C, Baasov T, Anderson KS. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:9938–9939. doi: 10.1021/ja0354768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Liuni P, Jeganathan A, Wilson DJ. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2012;51:9666–9669. doi: 10.1002/anie.201204903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Lermyte F, Sobott F. PROTEOMICS. 2015;15:2813–2822. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201400516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Breuker K, Oh H, Horn DM, Cerda BA, McLafferty FW. J Am Chem Soc. 2002;124:6407–6420. doi: 10.1021/ja012267j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Breuker K, McLafferty FW. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2008;105:18145–18152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0807005105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Zhang H, Cui W, Wen J, Blankenship RE, Gross ML. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2010;21:1966–1968. doi: 10.1016/j.jasms.2010.08.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zhang H, Cui W, Gross ML, Blankenship RE. FEBS Lett. 2013;587:1012–1020. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.01.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Zhang H, Cui W, Gross ML. Int J Mass Spectrom. 2013;354–355:288–291. doi: 10.1016/j.ijms.2013.06.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Zhou M, Wysocki VH. Acc Chem Res. 2014;47:1010–1018. doi: 10.1021/ar400223t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Shaw JB, Li W, Holden DD, Zhang Y, Griep-Raming J, Fellers RT, Early BP, Thomas PM, Kelleher NL, Brodbelt JS. J Am Chem Soc. 2013;135:12646–12651. doi: 10.1021/ja4029654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Cannon JR, Cammarata MB, Robotham SA, Cotham VC, Shaw JB, Fellers RT, Early BP, Thomas PM, Kelleher NL, Brodbelt JS. Anal Chem. 2014;86:2185–2192. doi: 10.1021/ac403859a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Brodbelt JS. Anal Chem. 2016;88:30–51. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Warnke S, Baldauf C, Bowers MT, Pagel K, von Helden G. J Am Chem Soc. 2014;136:10308–10314. doi: 10.1021/ja502994b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Warnke S, Helden G, von Pagel K. PROTEOMICS. 2015;15:2804–2812. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201400480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Briand G, Perrier V, Kouach M, Takahashi M, Gilles AM, Bârzu O. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1997;339:291–297. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1997.9877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Daniel JM, McCombie G, Wendt S, Zenobi R. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2003;14:442–448. doi: 10.1016/S1044-0305(03)00132-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Yin S, Loo JA. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2010;21:899–907. doi: 10.1016/j.jasms.2010.01.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Bunkoczi G, Filippakopoulos P, Jansson A, Longman E, Delft F, Von Edwards A, Arrowsmith C, Sundstrom M, Weigelt J, Knapp S. [Google Scholar]
- 61.Yin S, Loo JA. Int J Mass Spectrom. 2011;300:118–122. doi: 10.1016/j.ijms.2010.06.032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Pai EF, Sachsenheimer W, Schirmer RH, Schulz GE. J Mol Biol. 1977;114:37–45. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90281-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Schulz GE, Müller CW, Diederichs K. J Mol Biol. 1990;213:627–630. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80250-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Tsai MD, Yan H. Biochemistry. 1991;30:6806–6818. doi: 10.1021/bi00242a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Müller CW, Schulz GE. J Mol Biol. 1992;224:159–177. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90582-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kern P, Brunne RM, Folkers G. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 1994;8:367–388. doi: 10.1007/BF00125373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Elamrani S, Berry MB, Phillips GN, McCammon JA. Proteins Struct Funct Bioinforma. 1996;25:79–88. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0134(199605)25:1<79::AID-PROT6>3.0.CO;2-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Orzechowski M, Tama F. Biophys J. 2008;95:5692–5705. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.108.139451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Baxter NJ, Blackburn GM, Marston JP, Hounslow AM, Cliff MJ, Bermel W, Williams NH, Hollfelder F, Wemmer DE, Waltho JP. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:3952–3958. doi: 10.1021/ja078000n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Yan H, Tsai M-D. In: Advances in Enzymology and Related Areas of Molecular Biology. Purich DL, editor. John Wiley & Sons, Inc; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 1999. pp. 103–134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Fried SD, Boxer SG. Acc Chem Res. 2015;48:998–1006. doi: 10.1021/ar500464j. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.