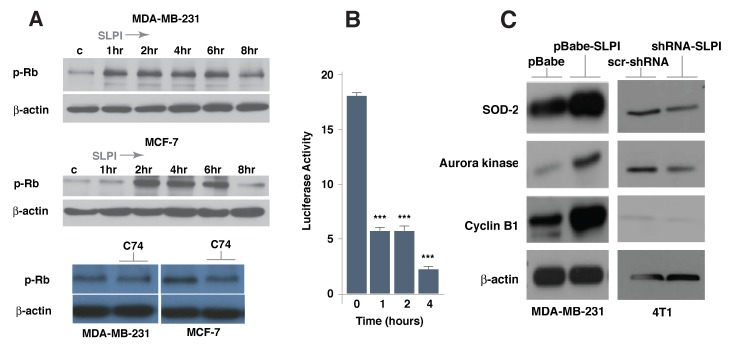
Figure 5. SLPI increases Rb phosphorylation and activates FoxM1 target genes in breast cancer cells.
A. SLPI activated Rb phosphorylation within 1-2 h. MD-MB-231 and MCF7 cells were exposed to recombinant SLPI protein (1.5 µg/mL); proteins obtained from these cells were subjected to gel electrophoresis and Western Blot analysis using antibodies directed against phospho-Rb and β-actin as a loading control. In a time dependent manner, SLPI activates Rb phosphorylation. Compound C74 repressed Rb phosphorylation. MD-MB-231 and MCF7 cells were treated with 1 µM of C74 for 16 h. B. The dynamics of SLPI-induced disruption of the physical interaction between Rb and FoxM1. Using a mammalian two-hybrid system with a pair of pBIND-Rb and pACT-FoxM1 fusion proteins with HEK293T cells, we measured the dynamics of binding of Rb to FoxM1 following recombinant SLPI protein treatment. The SLPI was added to cell media in concentration of 1.5 µg/mL. C.. Expression of FoxM1 target genes correlate with SLPI level. Western blotting was performed with lysed proteins from MDA-MB-231 cells overexpressing SLPI (pBabe-SLPI), compared to control (pBabe). SLPI was silenced in 4T1 cells using shRNA SLPI lentiviruses and compared to control cells with scr-shRNA lentiviruses. FoxM1 target genes - cyclin B1, aurora kinase B and superoxide dismutase-2 (SOD-2) - were up-regulated in cells with SLPI overexpression and down-regulated if SLPI was suppressed by shRNA.