Abstract
The number of births in the United States declined by 1% between 2010 and 2011, to a total of 3 953 593. The general fertility rate also declined by 1% to 63.2 births per 1000 women, the lowest rate ever reported. The total fertility rate was down by 2% in 2011 (to 1894.5 births per 1000 women). The teenage birth rate fell to another historic low in 2011, 31.3 births per 1000 women. Birth rates also declined for women aged 20 to 29 years, but the rates increased for women aged 35 to 39 and 40 to 44 years. The percentage of all births to unmarried women declined slightly to 40.7% in 2011, from 40.8% in 2010. In 2011, the cesarean delivery rate was unchanged from 2010 at 32.8%. The preterm birth rate declined for the fifth straight year in 2011 to 11.72%; the low birth weight rate declined slightly to 8.10%. The infant mortality rate was 6.05 infant deaths per 1000 live births in 2011, which was not significantly lower than the rate of 6.15 deaths in 2010. Life expectancy at birth was 78.7 years in 2011, which was unchanged from 2010. Crude death rates for children aged 1 to 19 years did not change significantly between 2010 and 2011. Unintentional injuries and homicide were the first and second leading causes of death, respectively, in this age group. These 2 causes of death jointly accounted for 47.0% of all deaths of children and adolescents in 2011.
Keywords: birth, death, teenaged fertility, infant mortality, low birth weight, mortality, multiple births, cesarean rate, vital statistics, ICD-10, revised certificates
This annual article is a long-standing feature in Pediatrics and provides a summary of the most current vital statistics data for the United States. We also include a special feature this year on data quality improvement.
METHODS
The data presented in this report were obtained from vital records: birth certificates and death certificates for residents in all US states and the District of Columbia. Birth and death data for 2010 and earlier years are final. Birth and death data for 2011 are preliminary and are based on ~100% of records for natality and >98% for mortality. More complete descriptions of vital statistics data systems are available elsewhere.1–7
Current vital statistics patterns and recent trends are presented according to age, race, and Hispanic origin as well as other birth and death characteristics. Hispanic origin and race are collected as separate items in vital records. Persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race. A number of reporting areas allow for multiple-race categories on birth and death certificates. However, until all areas revise their certificates to reflect updated reporting standards for race,8 multiple-race data are “bridged” back to single-race categories.1–4,9,10 For birth data, the mother’s marital status was reported directly in all reporting areas except for New York in 2010 and 2011. Details about the reporting of marital status in New York and editing methods and imputations as applied to other items on the birth certificate are presented in publications of the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS).11
Cause-of-death statistics in this report are based solely on the underlying cause of death compiled in accordance with the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision.12 The underlying cause of death is defined as “(a) the disease or injury which initiated the train of morbid events leading directly to death, or (b) the circumstances of the accident or violence which produced the fatal injury.”12 For certain causes of death such as unintentional injuries, homicides, suicides, drug-induced deaths, and sudden infant death syndrome, preliminary data may show lower numbers of deaths relative to final data for the same year. This undercount is a function of the truncated nature of the preliminary file, primarily because cause-of-death information may not be available or may be incomplete when preliminary data are sent to the NCHS but is available later at final data processing.
The ranking for leading causes of death is based on number of deaths.13 Infant mortality refers to the death of an infant younger than 1 year. Infant mortality rates (IMRs) were computed by dividing the total number of infant deaths in each calendar year by the total number of live births in the same year. Neonatal mortality rates (NMRs) are shown for infant deaths that occurred at less than 28 days, and postneonatal mortality rates (PNMRs) are shown for infant deaths that occurred at 28 days to <1 year of age. The denominator for both rates is the number of live births.
The latest infant mortality statistics according to race and Hispanic origin are from the 2008 period linked birth/infant death data.14 In this data set, the death certificate was linked with the corresponding birth certificate for each infant who died in the United States in 2008. The purpose of this linkage was to use additional variables available from the birth certificate, such as birth weight, to better interpret infant mortality patterns.
Birth data for 2010 and 2011 for selected items were collected by using both the 1989 (unrevised) and 2003 (revised) US Standard Certificates of Live Birth. The 2003 revision is described in detail elsewhere.15,16 For 2011, 36 states (California, Colorado, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Maryland, Michigan, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Mexico, New York, North Carolina, North Dakota, Ohio, Oklahoma, Oregon, Pennsylvania, South Carolina, South Dakota, Tennessee, Texas, Utah, Vermont, Washington, Wisconsin, and Wyoming) and the District of Columbia implemented the revised birth certificates as of January 1, 2011 (accounting for 83% of 2011 births).1
Mortality data for 2011 were collected by using both the 1989 (unrevised) and 2003 (revised) versions of the US Standard Certificate of Death. The 2003 revision is described in detail elsewhere.3,4 Thirty-six states (Arizona, Arkansas, California, Connecticut, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Maine, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, North Dakota, Ohio, Oklahoma, Oregon, Rhode Island, South Carolina, South Dakota, Texas, Utah, Vermont, Washington, and Wyoming) and the District of Columbia implemented the revised death certificates as of 2011.3 The remaining 14 states reported data in 2011 on the basis of the 1989 “unrevised” version of the death certificate. All mortality data items presented in this report are considered comparable between revisions, and revised and unrevised data are combined.
Population denominators for the calculation of birth, death, and fertility rates are estimates based on the population enumerated by the US Census Bureau as of April 1, 2010. Estimates for 2010 and 2011 and revised estimates for the intercensal period 2001–2009 were produced under a collaborative arrangement between the US Census Bureau and the NCHS. All rates for 2001–2009 (in this article) are revised on the basis of population counts from the 2000 and 2010 censuses.2 To calculate birth and death rates for these time periods, reported population data for multiple-race persons were bridged back to single-race categories.9,10 The 2010 census counts were also modified to be consistent with the 1977 Office of Management and Budget race categories.17
Data for the international comparisons of births and IMRs were obtained from the 2009–2010 United Nations Demographic Yearbook and the OECD (Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development) iLibrary Health.18,19
NATURAL INCREASE
In 2011, >1.4 million persons were added to the US population as a result of natural increase, the excess of births over deaths (Table 1).1–4 The rate of natural increase in 2011 was 4.6 persons per 1000 population.
TABLE 1.
Vital Statistics of the United States, Selected Years: 1950–2010 (Final) and 2011 (Preliminary)
| Number
|
Ratea
|
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 2010 | 2009 | 2011 | 2010 | 2009 | 2000 | 1990 | 1980 | 1950 | |
| Live births | 3 953 593 | 3 999 386 | 4 130 665 | 12.7 | 13.0 | 13.5 | 14.4 | 16.7 | 15.9 | 24.1 |
| Fertility rate | NA | NA | NA | 63.2 | 64.1 | 66.2 | 65.9 | 70.9 | 68.4 | 106.2 |
| Deaths | 2 513 171 | 2 468 435 | 2 437 163 | 8.1 | 8.0 | 7.9 | 8.5 | 8.6 | 8.8 | 9.6 |
| Age-adjusted rate | NA | NA | NA | 7.4 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 8.7 | 9.4 | 10.4 | 14.5 |
| Natural increase | 1 440 422 | 1 530 951 | 1 693 502 | 4.6 | 5.0 | 5.6 | 5.9 | 8.1 | 7.1 | 14.5 |
| Infant mortality | 23 910 | 24 586 | 26 412 | 6.05 | 6.15 | 6.39 | 6.91 | 9.22 | 12.60 | 29.21 |
| Population base (in thousands) | NA | NA | NA | 311 592 | 308 746 | 306 772 | 281 422 | 248 710 | 226 546 | 150 697 |
Population numbers are as of July 1 for 2011 and 2009 and as of April 1 in 2010, 2000, 1990, 1980, and 1950. Data sources: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/NCHS, National Vital Statistics System, and the US Census Bureau. NA, not applicable.
Rates per 1000 population except for fertility, which is per 1000 women aged 15 to 44 y of age, and infant mortality, which is per 1000 live births.
BIRTHS
In 2011, the number of births for the United States was 3 953 593, which is 1% fewer than in 2010 and 4% fewer than in 2009 (Table 1).1 The crude birth rate was 12.7 births per 1000 total population in 2011, the lowest rate ever reported for the United States. The general fertility rate (the number of births per 1000 women aged 15–44 years) also declined (by 1%) to a record low of 63.2 in 2011, from 64.1 in 2010. Birth rates declined among women aged 15 to 29 years between 2010 and 2011, reaching historic lows for ages 15 to 19 and 20 to 24 years. Rates increased for women aged 35 to 39 and 40 to 44 years.1 In 2011, the total fertility rate was 1894.5 births per 1000 women, which is a decrease of 2% compared with the rate in 2010 (1931.0) (Table 2). The total fertility rate estimates the number of births that a hypothetical group of 1000 women would have over their lifetimes on the basis of the age-specific birth rates observed in a given year.
TABLE 2.
Age-Specific Birth Rates and Total Fertility Rates by Race and Hispanic Origin of Mother: United States, 2011 (Preliminary)
| Age-Specific Birth Rate by Age of Mothera
|
Total Fertility Rateb | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15–44 yc | 15–17 y | 18–19 y | 20–24 y | 25–29 y | 30–34 y | 35–39 y | 40–44 y | ||
| Total | 63.2 | 15.4 | 54.1 | 85.3 | 107.2 | 96.5 | 47.2 | 10.3 | 1894.5 |
| Non-Hispanic white | 58.8 | 9.0 | 40.0 | 72.0 | 105.4 | 100.3 | 46.0 | 9.3 | 1778.0 |
| Non-Hispanic black | 65.5 | 24.6 | 78.9 | 112.4 | 101.8 | 74.1 | 37.9 | 9.3 | 1922.5 |
| Native Americand | 47.8 | 18.3 | 61.7 | 86.8 | 75.5 | 47.5 | 23.2 | 5.5 | 1377.0 |
| Asian or Pacific Islander | 59.9 | 4.6 | 18.2 | 41.9 | 93.6 | 114.8 | 64.1 | 15.2 | 1705.5 |
| Hispanice | 75.7 | 27.9 | 81.2 | 115.3 | 120.5 | 94.4 | 50.9 | 13.0 | 2225.0 |
Race and Hispanic origin are reported separately on birth certificates. Persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race. Race categories are consistent with the 1977 OMB standards. Forty states and the District of Columbia reported multiple-race data in 2011. Multiple-race data for these states were bridged to the single-race categories of the 1977 OMB standards for comparability with other states. Data source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/NCHS, National Vital Statistics System: natality.
Rates per 1000 women in age-specific group.
Sum of age-specific birth rates × 5 (includes rates for ages 10–14, 15–19, and 45–49 y; not shown separately).
Relates the number of births to women of all ages to women aged 15–44 y.
Includes births to Aleuts and Eskimos.
Includes all persons of Hispanic origin of any race.
Racial and Ethnic Composition
The general fertility rate decreased for 2 of the 3 largest race and Hispanic-origin groups in 2011 and declined by 2% for non-Hispanic black women and by 6% for Hispanic women. The general fertility rate for non-Hispanic white women was essentially unchanged. The rate for American Indian or Alaska Native women declined by 2% in 2011, whereas the rate for Asian or Pacific Islander women increased by 1%. Fertility rates for these 5 groups ranged in 2011 from 47.8 births per 1000 women aged 15 to 44 years for American Indian or Alaska Native women to a high of 75.7 for Hispanic women (Table 2).
Trends in Age-Specific Birth Rates
Teenaged Childbearing
The teenage (ages 15–19 years) birth rate decreased by 8% from 2010 to 2011 and reached another historic low for the United States, 31.3 births per 1000 women (Table 3).1 The teenage birth rate has decreased by 25% from 2007 and by 49% from 1991, the most recent peak. The birth rate for teenagers aged 15 to 17 years decreased by 11% from 2010 to 15.4 per 1000 in 2011, whereas the birth rate for older teenagers aged 18 to 19 years decreased by 7% to 54.1 per 1000 (Table 3).
TABLE 3.
Birth Rates for Teens According to Age, Race, and Hispanic Origin—United States, Selected Years: 1991–2010 (Final) and 2011 (Preliminary)
| Age, Race, and Hispanic Origin of Mother | Birth Ratea
|
Percentage Change
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 2010 | 2009 | 2007 | 1991 | 2010–2011 | 2007–2011 | 1991–2011 | |
| Age 15–19 y | ||||||||
| All races | 31.3 | 34.2 | 37.9 | 41.5 | 61.8 | −8 | −25 | −49 |
| Non-Hispanic whiteb | 21.8 | 23.5 | 25.7 | 27.2 | 43.4 | −7 | −20 | −50 |
| Non-Hispanic blackb | 47.4 | 51.5 | 56.7 | 62.0 | 118.2 | −8 | −24 | −60 |
| Native Americanc | 36.2 | 38.7 | 43.8 | 49.4 | 27.3 | −6 | −27 | −57 |
| Asian or Pacific Islander | 10.2 | 10.9 | 12.6 | 14.8 | 84.1 | −6 | −31 | −63 |
| Hispanicb,d | 49.4 | 55.7 | 63.6 | 75.3 | 104.6 | −11 | −34 | −53 |
| Age 15–17 y | ||||||||
| All races | 15.4 | 17.3 | 19.6 | 21.7 | 38.6 | −11 | −29 | −60 |
| Non-Hispanic whiteb | 9.0 | 10.0 | 11.0 | 11.9 | 23.6 | −10 | −24 | −62 |
| Non-Hispanic blackb | 24.6 | 27.4 | 31.0 | 34.6 | 86.1 | −10 | −29 | −71 |
| Native Americanc | 18.3 | 20.1 | 23.7 | 26.2 | 16.3 | −9 | −30 | −65 |
| Asian or Pacific Islander | 4.6 | 5.1 | 6.3 | 7.4 | 51.9 | −10 | −38 | −72 |
| Hispanicb,d | 27.9 | 32.3 | 37.3 | 44.4 | 69.2 | −14 | −37 | −60 |
| Age 18–19 y | ||||||||
| All races | 54.1 | 58.2 | 64.0 | 71.7 | 94.0 | −7 | −25 | −42 |
| Non-Hispanic whiteb | 40.0 | 42.5 | 46.2 | 50.4 | 70.6 | −6 | −21 | −43 |
| Non-Hispanic blackb | 78.9 | 85.6 | 93.5 | 105.2 | 162.2 | −8 | −25 | −51 |
| Native Americanc | 61.7 | 66.1 | 73.6 | 86.4 | 42.2 | −7 | −29 | −54 |
| Asian or Pacific Islander | 18.2 | 18.7 | 20.9 | 24.9 | 134.2 | —e | −27 | −57 |
| Hispanicb,d | 81.2 | 90.7 | 103.3 | 124.7 | 155.5 | −10 | −35 | −48 |
Race and Hispanic origin are reported separately on birth certificates. Persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race. Race categories are consistent with the 1977 OMB standards. Forty states and the District of Columbia in 2011, 38 states and the District of Columbia in 2010, 33 states and the District of Columbia in 2009, and 27 states in 2007 reported multiple-race data. Multiple-race data for these states were bridged to the single-race categories of the 1977 OMB standards for comparability with other states. Data source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/NCHS, National Vital Statistics System: natality.
Rates per 1000 women in specified group.
In 1991 excludes data for New Hampshire, which did not report Hispanic origin on the birth certificate.
Includes births to Aleuts and Eskimos.
Includes all persons of Hispanic origin of any race.
Not statistically significant.
The impact of the decline in the teenage birth rate on the number of births to teenagers over the period 1992–2011 is substantial. Overall, the teenage birth rate fell by 49% from 1991 through 2011. If the 1991 rates had continued to prevail from 1992 through 2011, an estimated 3.6 million additional births to women aged 15 to 19 years would have occurred in the United States (with >1 million of those additional births occurring between 2008 and 2011) (Fig 1).20
FIGURE 1.
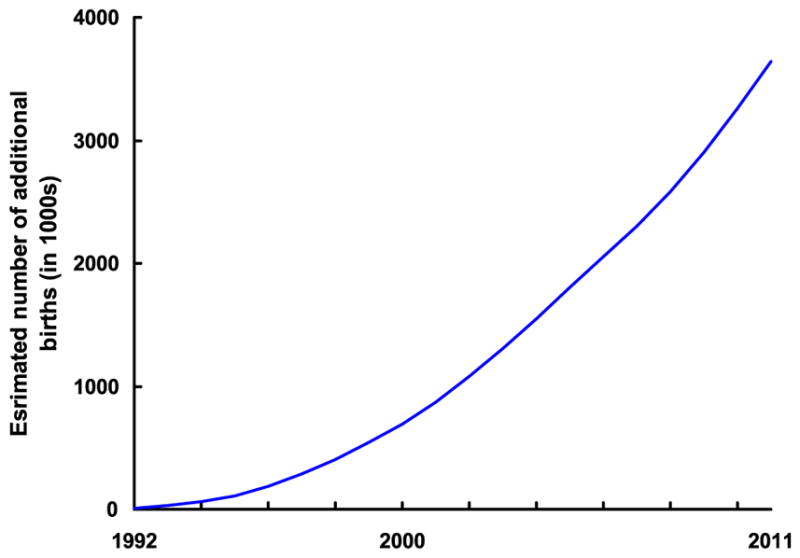
Estimated cumulative number of additional births to women aged 15–19 years from 1992 to 2011 if 1991 birth rates had continued. Note: Data for 2011 are preliminary. For information and discussion of estimation, see Hamilton and Ventura.20 Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/NCHS, National Vital Statistics System: natality.
Childbearing for Women in Their 20s and 30s
The birth rate for women aged 20 to 24 years decreased to a record low in the United States in 2011, 85.3 births per 1000 women, which is a 5% decrease from 90.0 per 1000 women in 2010.1 The rate for women aged 25 to 29 years also declined (by 1%) in 2011 to 107.2 per 1000 women (Table 2). The birth rate for women aged 30 to 34 years was unchanged from 2010 to 2011 at 96.5 births per 1000 women, whereas the birth rate for women aged 35 to 39 years increased by 3% in 2011, to 47.2 per 1000 women from 45.9 per 1000 women in 2010.1
Childbearing for Women 40 and Older
The birth rate for women aged 40 to 44 years increased by 1% in 2011, to 10.3 births per 1000 women from 10.2 per 1000 women in 2010 (Table 2). The birth rate for women aged 45 to 49 years remained unchanged in 2011 from 2010 at 0.7 (data not shown). The rates have slowly, although steadily, increased for both groups since 1990.1
Unmarried Mothers
The birth rate for unmarried women declined by 3% in 2011, to 46.1 births per 1000 unmarried women aged 15 to 44 years, marking the third consecutive decline in the rate (which has decreased by 11% since 2008).1 The total number of births to unmarried women declined by 2% in 2011, to 1 608 087. The proportion of all births to unmarried women was 40.7% in 2011, which was slightly lower than in 2010 (40.8%). The proportion of births to unmarried women declined for non-Hispanic black births, increased slightly for non-Hispanic white births, and was statistically unchanged for the remaining population groups between 2010 and 2011 (Table 4). In 2011, unmarried teenagers (women aged 15–19 years) accounted for 18% of all nonmarital births, the lowest proportion ever reported. In 1970, teenagers accounted for 50% of births to unmarried women.1
TABLE 4.
Percentage of Births with Selected Characteristics by Race and Hispanic Origin of Mother—United States, Selected Years: 1990 and 2010 (Final) and 2011 (Preliminary)
| All Races
|
Non-Hispanic White
|
Non-Hispanic Black
|
Hispanica
|
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | 2010 | 1990 | 2011 | 2010 | 1990b | 2011 | 2010 | 1990b | 2011 | 2010 | 1990b | |
| Mother | ||||||||||||
| <20 y of age | 8.4 | 9.3 | 12.8 | 6.1 | 6.7 | 9.6 | 13.7 | 15.2 | 23.2 | 12.1 | 13.1 | 16.8 |
| ≥40 y of age | 2.9 | 2.9 | 1.2 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 1.2 | 2.4 | 2.3 | 0.8 | 2.6 | 2.4 | 1.2 |
| Unmarried | 40.7 | 40.8 | 28.0 | 29.1 | 29.0 | 16.9 | 72.3 | 72.5 | 66.7 | 53.3 | 53.4 | 36.7 |
| Diabetes during pregnancy | — | 5.1 | 2.1 | — | 4.7 | 2.2 | — | 4.5 | 1.8 | — | 5.2 | 2.0 |
| Pregnancy-associated hypertension | — | 4.4 | 2.7 | — | 4.8 | 3.0 | — | 5.4 | 2.8 | — | 3.2 | 1.8 |
| Health care utilization | ||||||||||||
| Midwife-attended birthsc | — | 7.8 | 3.9 | — | 7.8 | 3.2 | — | 7.1 | 4.4 | — | 8.3 | 6.2 |
| Cesarean delivery rate | 32.8 | 32.8 | 22.7 | 32.4 | 32.6 | 23.4 | 35.5 | 35.5 | 22.1 | 32.0 | 31.8 | 21.2 |
| Weight gain of >40 lbd | — | 20.8 | 15.9 | — | 23.4 | 16.5 | — | 20.6 | 14.8 | — | 16.5 | 14.1 |
| Infant | ||||||||||||
| Birth weighte | ||||||||||||
| LBW | 8.10 | 8.15 | 7.0 | 7.09 | 7.14 | 5.6 | 13.33 | 13.53 | 13.3 | 7.02 | 6.97 | 6.1 |
| VLBW | 1.44 | 1.45 | 1.27 | 1.14 | 1.16 | 0.93 | 2.99 | 2.98 | 2.93 | 1.20 | 1.20 | 1.03 |
| Gestational agef | ||||||||||||
| Preterm birth | 11.72 | 11.99 | 10.6 | 10.49 | 10.77 | 8.5 | 16.75 | 17.12 | 18.9 | 11.66 | 11.79 | 11.0 |
| Early | 3.44 | 3.50 | 3.3 | 2.87 | 2.93 | 2.4 | 6.01 | 6.13 | 7.4 | 3.26 | 3.26 | 3.2 |
| Late | 8.28 | 8.49 | 7.3 | 7.62 | 7.84 | 6.1 | 10.74 | 10.99 | 11.5 | 8.40 | 8.53 | 7.8 |
| Multiple births | ||||||||||||
| Live births in twin deliveries (per 1000 live births) | — | 33.1 | 22.6 | — | 36.9 | 22.9 | — | 37.0 | 26.7 | — | 22.6 | 18.0 |
| Live births in higher-order multiple deliveries (per 100 000 live births) | — | 137.6 | 72.8 | — | 177.7 | 89.8 | — | 97.3 | 46.2 | — | 76.3 | 39.4 |
Race and Hispanic origin are reported separately on birth certificates. Persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race. Race categories are consistent with the 1977 OMB standards. Forty states and the District of Columbia in 2011 and 38 states and the District of Columbia in 2010 reported multiple-race data. Multiple-race data for these states were bridged to the single-race categories of the 1977 OMB standards for comparability with other states. Data source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/NCHS, National Vital Statistics System, natality. —, preliminary data not available.
Includes all persons of Hispanic origin of any race.
Excludes data for New Hampshire and Oklahoma, which did not report Hispanic origin.
Delivered by certified nurse midwives.
Mother gained >40 lb during pregnancy.
VLBW is birth weight of <1500 g (3 lb, 4 oz), and LBW is birth weight of <2500 g (5 lb, 8 oz).
Preterm indicates birth before 37 completed weeks of gestation, early preterm indicates birth before 34 completed weeks of gestation, and late preterm indicates birth between 34 and 36 completed weeks of gestation.
Cesarean Delivery
The cesarean delivery rate was unchanged in 2011 from 2010 at 32.8%, after a steady increase from 1996 to 2009 and a small decline in 2010 (Table 4). From 2010 to 2011, cesarean delivery rates declined for non-Hispanic white women and were statistically unchanged for non-Hispanic black women, but increased for Hispanic women. Since 1994, non-Hispanic black women have had the highest rates of cesarean delivery.1,2
Multiple Births
In 2010 (the latest available data), the twin birth rate declined slightly to 33.1 twins per 1000 total births, from 33.2 in 2009 (Table 4). Preliminary data on multiple births are not available. The twin birth rate increased steadily by 76% overall from 1980 to 2009. The rate increased nearly 3% annually during the 1990s but has slowed to less than one-half of 1% annually since the mid-2000s (Fig 2). The triplet/+ rate (the number of births in triplet and higher-order multiples per 100 000 total births) was 137.6 per 100 000 total births in 2010, a decrease of 10% from 2009 (153.5) (Table 4), and the lowest rate since 1995 (Fig 2). The triplet/+ rate increased by 400% during the 1980s and 1990s but has declined by 29% since the 1998 peak (193.5).
FIGURE 2.
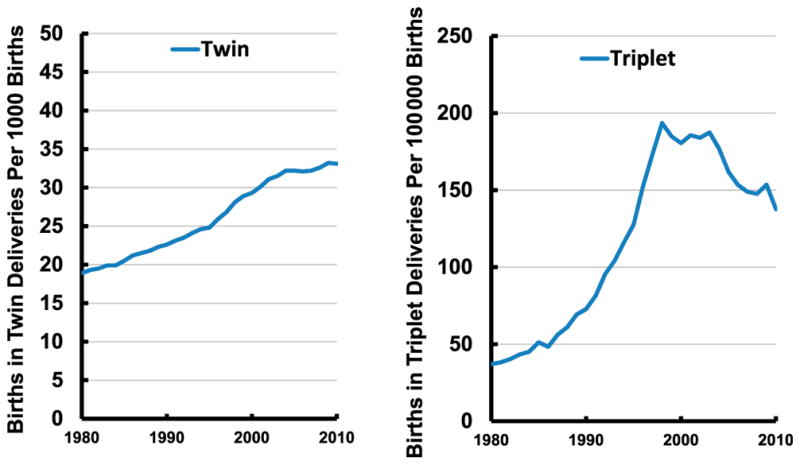
Twin and triplet birth rates: United States, 1980–2010 (final). Notes: The twin birth rate is the number of births in twin deliveries per 1000 births. The triplet birth rate is the number of births in triplet and other higher-order deliveries per 100 000 births. Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/NCHS, National Vital Statistics System: natality.
Infants in multigestation pregnancies are much more likely to be born earlier and smaller than those born in singleton pregnancies. Accordingly, they are at greater risk of early death, with twins ~5 times and triplets ~10 times as likely to die in infancy. In 2010, >5 of every 10 twins and 9 of 10 triplets were delivered preterm, compared with ~1 in 10 singletons.
Preterm Birth
In 2011, the preterm birth rate (infants delivered at <37 completed weeks of gestation per 100 births) was 11.72%, which is down for the fifth straight year.1 The rate was 11.99% in 2010. The preterm rate had been on the rise until 2006, increasing by more than one-third from 1981 to 2006 (Fig 3).1,2 Although at the lowest level in more than a decade, the 2011 rate of preterm birth is still higher than the rates during the 1980s and most of the 1990s. Declines between 2010 and 2011 were observed among infants delivered early preterm (<34 weeks) and late preterm (at 34–36 weeks). The early preterm percentage declined from 3.50% to 3.44%, whereas the late preterm percentage declined from 8.49% to 8.28% (Table 4). The total preterm rate declined significantly among births to non-Hispanic white (from 10.77% to 10.49%), non-Hispanic black (from 17.12% to 16.75%), and Hispanic (from 11.79% to 11.66%) infants.1
FIGURE 3.
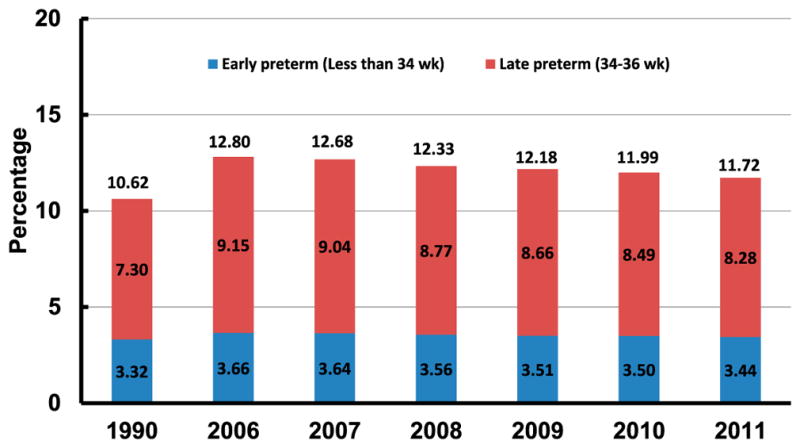
Total, early, and late preterm birth rates: United States, 1990 and 2006–2010 (final) and 2011 (preliminary). Notes: Preterm is defined as <37 completed weeks of gestation. Early preterm is defined as <34 completed weeks of gestation. Late preterm is defined as 34–36 completed weeks of gestation. Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/NCHS, National Vital Statistics System: natality
Low Birth Weight
The low birth weight (LBW; <2500 g) rate was 8.10% in 2011, a slight decline from 8.15% in 2010 (Table 4). The percentage of infants born with LBW increased by >20% from the mid-1980s through 2006, but has declined slowly, by 2%, from 2006 through 2011.1 The rate of very low birth weight (<1500 g) was essentially stable at 1.44% in 2011, whereas the rate of moderately low birth weight (1500–2499 g) declined to 6.66%. The LBW rate declined slightly between 2010 and 2011 for non-Hispanic white and non-Hispanic black births, but was not significantly changed for Hispanic births (Table 4).
Overall LBW levels have been influenced by changes in the rate of multiple births, which are much more likely to be LBW than singleton births.2 The LBW rate for singleton births only was essentially unchanged at 6.38% in 2010 from 6.36% in 20092 but is down from 6.49% in 2006. The percentage of singleton LBW increased by 10% from 1990 through 2006.
Notwithstanding the small decrease in the percentage of births at <2500 g from 2006 to 2010, the US birth weight distribution has shifted downward over the past 2 decades, reflecting increases in births <3500 g and declines in births at >3500 g.2
INFANT MORTALITY
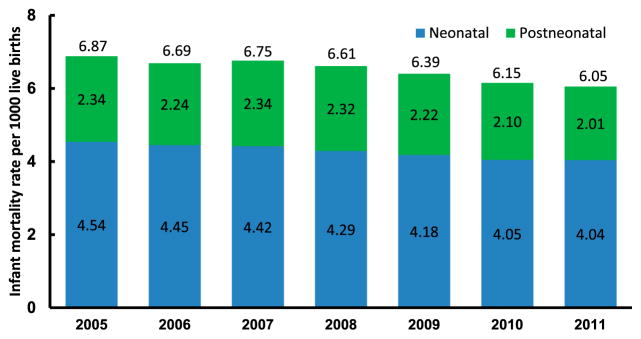
In 2011, a total of 23 910 infant deaths were reported in the United States according to preliminary data, with approximately two-thirds of infant deaths occurring during the neonatal period.3 The IMR was 6.05 infant deaths per 1000 live births, the NMR was 4.04 neonatal deaths per 1000 live births, and the PNMR was 2.01 postneonatal deaths per 1000 live births (Fig 4). The IMR has declined slowly but steadily between 2005 and 2011. Over the whole period, the IMR, NMR, and PNMR each decreased by ~13%; however, for 2011, only the PNMR (2.01) was significantly lower (by 4%) than the 2010 rate (2.10).
FIGURE 4.
Infant, neonatal, and postneonatal mortality rates: United States, 2005–2010 (final) and 2011 (preliminary). Notes: Neonatal is defined as <28 days of age, and postneonatal is defined as 28 days to <1 year of age. Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/NCHS, National Vital Statistics System: mortality (main file).
The 2008 linked birth/infant death data reveal wide and persistent variation in IMRs according to race and Hispanic origin.14 As in past years, the highest rate was for infants born to non-Hispanic black mothers,21 at 12.67 deaths per 1000 live births, which is more than double the rate of infants born to non-Hispanic white mothers (5.52). Among Hispanic population groups, rates ranged from 4.76 for Central and South American mothers to 7.29 for Puerto Rican mothers. The IMRs for most Hispanic population groups have fluctuated slightly since 2000.
Geographic Variation in Infant Outcomes
Table 5 presents 2011 preliminary data by state on percentages of preterm and LBW births and 2010 final data on IMRs and NMRs. Preliminary data on infant mortality by state are not available. For 2011, Mississippi had the highest LBW (11.8%) and preterm (16.9%) rates, whereas Alaska had the lowest LBW (6.0%) rate and Vermont the lowest preterm rate (8.8%). States in the southeastern United States had the highest IMR and NMRs. In 2010, IMRs for the states ranged from 3.75 per 1000 in Alaska to 9.67 in Mississippi. The IMR for the District of Columbia was 7.86. These geographic patterns have been observed for many years.
TABLE 5.
Percentage of Infants Born Preterm and LBW in the United States and Each State, 2011 (Preliminary), and IMR and NMR in the United States and Each State, 2010 (Final)
| State of Residence | Preterma | LBWb | IMRc | NMRd |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 11.7 | 8.1 | 6.15 | 4.05 |
| Alabama | 14.9 | 9.9 | 8.71 | 5.43 |
| Alaska | 10.4 | 6.0 | 3.75 | 1.92 |
| Arizona | 12.1 | 7.0 | 5.97 | 3.80 |
| Arkansas | 13.2 | 9.1 | 7.32 | 4.15 |
| California | 9.8 | 6.8 | 4.74 | 3.30 |
| Colorado | 10.3 | 8.7 | 5.91 | 4.33 |
| Connecticut | 10.1 | 7.7 | 5.28 | 3.98 |
| Delaware | 11.2 | 8.4 | 7.66 | 5.10 |
| District of Columbia | 13.7 | 10.5 | 7.86 | 5.46 |
| Florida | 13.0 | 8.7 | 6.54 | 4.35 |
| Georgia | 13.2 | 9.4 | 6.42 | 3.90 |
| Hawaii | 12.3 | 8.2 | 6.16 | 4.00 |
| Idaho | 10.2 | 6.1 | 4.83 | 2.72 |
| Illinois | 12.1 | 8.2 | 6.77 | 4.65 |
| Indiana | 11.6 | 8.1 | 7.62 | 4.97 |
| Iowa | 11.1 | 6.5 | 4.88 | 2.66 |
| Kansas | 11.2 | 7.2 | 6.22 | 4.28 |
| Kentucky | 13.4 | 9.1 | 6.79 | 3.32 |
| Louisiana | 15.6 | 10.9 | 7.60 | 4.25 |
| Maine | 9.6 | 6.7 | 5.40 | 3.78 |
| Maryland | 12.5 | 8.9 | 6.75 | 4.74 |
| Massachusetts | 10.5 | 7.6 | 4.43 | 3.31 |
| Michigan | 12.0 | 8.3 | 7.13 | 4.80 |
| Minnesota | 9.9 | 6.4 | 4.49 | 3.05 |
| Mississippi | 16.9 | 11.8 | 9.67 | 5.50 |
| Missouri | 11.6 | 7.9 | 6.61 | 4.14 |
| Montana | 10.8 | 7.2 | 5.89 | 3.48 |
| Nebraska | 10.6 | 6.6 | 5.25 | 3.70 |
| Nevada | 13.2 | 8.2 | 5.59 | 3.51 |
| New Hampshire | 9.5 | 7.1 | 3.96 | 2.10 |
| New Jersey | 11.7 | 8.5 | 4.81 | 3.45 |
| New Mexico | 11.8 | 8.8 | 5.64 | 3.41 |
| New York | 10.9 | 8.1 | 5.09 | 3.54 |
| North Carolina | 12.6 | 9.0 | 7.01 | 4.93 |
| North Dakota | 9.9 | 6.7 | 6.81 | 5.05 |
| Ohio | 12.0 | 8.6 | 7.71 | 5.23 |
| Oklahoma | 13.2 | 8.5 | 7.59 | 4.26 |
| Oregon | 9.1 | 6.1 | 4.94 | 3.36 |
| Pennsylvania | 11.0 | 8.2 | 7.25 | 5.14 |
| Rhode Island | 10.4 | 7.4 | 7.07 | 5.28 |
| South Carolina | 14.1 | 9.9 | 7.37 | 4.56 |
| South Dakota | 11.2 | 6.3 | 6.94 | 4.66 |
| Tennessee | 12.8 | 9.0 | 7.93 | 4.62 |
| Texas | 12.8 | 8.5 | 6.13 | 3.91 |
| Utah | 10.9 | 6.9 | 4.86 | 3.37 |
| Vermont | 8.8 | 6.7 | 4.18 | —e |
| Virginia | 11.2 | 8.0 | 6.80 | 4.61 |
| Washington | 9.8 | 6.1 | 4.50 | 3.07 |
| West Virginia | 12.7 | 9.6 | 7.28 | 3.96 |
| Wisconsin | 10.4 | 7.2 | 5.84 | 3.84 |
| Wyoming | 10.2 | 8.1 | 6.75 | 4.10 |
Data source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/NCHS, National Vital Statistics System: natality and mortality.
<37 weeks of completed gestation.
<2500 g.
Infant deaths (age <1 y) per 1000 live births.
Neonatal deaths (age <28 d) per 1000 live births.
The figure did not meet standards of reliability or precision; based on <20 deaths in the numerator.
Leading Causes of Infant Death
In 2011, 56.4% of all infant deaths (Table 6) were attributable to 5 leading causes: congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities (20.8%); disorders related to short gestation and LBW, not elsewhere classified (17.2%); sudden infant death syndrome (7.2%); newborn affected by maternal complications of pregnancy (6.6%); and accidents (unintentional injuries) (4.6%).3 These 5 leading causes of infant death are the same as in 2010.4
TABLE 6.
Deaths, Percentages of Total Deaths, and Mortality Rates for the 10 Leading Causes of Infant Death: United States, 2010 (Final) and 2011 (Preliminary)
| Causes of death and International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Codes12 | Ranka | 2011
|
2010
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | Rateb | n | % | Rateb | ||
| All causes | — | 23 907 | 100.0 | 604.7 | 24 586 | 100.0 | 614.7 |
| Congenital malformations, deformations, and chromosomal abnormalities (Q00–Q99) | 1 | 4984 | 20.8 | 126.1 | 5107 | 20.8 | 127.7 |
| Disorders related to short gestation and low birth weight, not elsewhere classified (P07) | 2 | 4116 | 17.2 | 104.1 | 4148 | 16.9 | 103.7 |
| Sudden infant death syndrome (R95) | 3 | 1711 | 7.2 | 43.3 | 2063 | 8.4 | 51.6 |
| Newborn affected by maternal complications of pregnancy (P01) | 4 | 1578 | 6.6 | 39.9 | 1561 | 6.3 | 39.0 |
| Accidents (unintentional injuries) (V01–X59) | 5 | 1089 | 4.6 | 27.5 | 1110 | 4.5 | 27.8 |
| Newborn affected by complications of placenta, cord, and membranes (P02) | 6 | 992 | 4.1 | 25.1 | 1030 | 4.2 | 25.8 |
| Bacterial sepsis of newborn (P36) | 7 | 526 | 2.2 | 13.3 | 583 | 2.4 | 14.6 |
| Respiratory distress of newborn (P22) | 8 | 514 | 2.1 | 13.0 | 514 | 2.1 | 12.9 |
| Diseases of the circulatory system (I00–I99) | 9 | 496 | 2.1 | 12.5 | 507 | 2.1 | 12.7 |
| Neonatal hemorrhage (P50–P52, P54) | 10 | 444 | 1.9 | 11.2 | 469 | 1.9 | 11.7 |
Data source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/NCHS, National Vital Statistics System: mortality, 2011 and 2010 (www.cdc.gov/nchs/deaths.htm). —, Data not applicable.
Based on 2011 data.
IMRs are per 100 000 live births.
INTERNATIONAL COMPARISONS
Births for 2010 and IMRs for 2008, 2009, and 2010 are shown in Table 7 for the United States and for 29 other countries with ≥40 000 births and an IMR less than the US rate in 2009 and 2010. Most of the data on IMRs were obtained from the OECD and the United Nations Demographic Yearbook.18,19,22 Birth data were obtained from these sources as well. Table 7 shows countries ordered from the lowest to highest IMR in 2010. Hong Kong continued to report an IMR of <2 infant deaths per 1000 live births for all 3 years. Six other countries had an IMR less than half the US rate in 2010, and only the United States reported an IMR of >6 infant deaths per 1000 live births; this number has declined since 2009 when there were 8 other countries with rates half the US rate. Possible reporting variations, greater population heterogeneity, and higher rates of LBW continue to be potential reasons for the higher IMR in the United States.23–27
TABLE 7.
Number of Live Births for 2010 and IMRs for 2008, 2009, and 2010 for 30 countries
| Country | No. of Births in 2010a | IMRb
|
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | ||
| Hong Kong | 82 095c | — | 1.7a | 1.8a |
| Japan | 1 071 304 | 2.3 | 2.4 | 2.6 |
| Finland | 60 694 | 2.3 | 2.6 | 2.6 |
| Sweden | 115 641 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| Portugal | 101 381 | 2.5 | 3.6 | 3.3 |
| Czech Republic | 117 153 | 2.7 | 2.9 | 2.8 |
| Norway | 61 442 | 2.8 | 3.1 | 2.7 |
| Republic of Korea | 470 171 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 3.5 |
| Spain | 485 252 | 3.2 | 3.2 | 3.3 |
| Denmark | 63 411 | 3.4 | 3.1 | 4.0 |
| Germany | 677 947 | 3.4 | 3.5 | 3.5 |
| Italy | 561 944 | 3.4 | 3.9 | 3.3 |
| Belgium | 129 173 | 3.5 | 3.4 | 3.7 |
| France | 802 224 | 3.6 | 3.9 | 3.8 |
| Israel | 166 255 | 3.7 | 3.8 | 3.8 |
| Greece | 114 766 | 3.8 | 3.1 | 2.7 |
| Ireland | 73 724 | 3.8 | 3.2 | 3.8 |
| Netherlands | 184 397 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 3.8 |
| Switzerland | 80 290 | 3.8 | 4.3 | 4.0 |
| Austria | 78 742 | 3.9 | 3.8 | 3.7 |
| Australia | 297 903 | 4.1 | 4.3 | 4.1 |
| United Kingdom | 807 272 | 4.2 | 4.6 | 4.7 |
| Croatia | 43 361 | 4.4 | 5.3 | 4.5 |
| Cuba | 127 746 | 4.5a | 4.8a | 4.7a |
| Canada | 379 373c | — | 4.9d | 5.1 |
| Poland | 413 300 | 5.0 | 5.6 | 5.6 |
| New Zealand | 63 897 | — | 5.2 | 5.0 |
| Hungary | 90 335 | 5.3 | 5.1 | 5.6 |
| Slovak Republic | 60 410 | 5.7 | 5.7 | 5.9 |
| United States | 3 999 386e | 6.1e | 6.4e | 6.6e |
—, Data not available.
Tables 9 and 15 in United Nations Demographic Yearbook, 2011.18
OECD iLibrary: Health, Key Table (ISSN 2075-8480).19
Data are for 2009.
Statistics Canada, CANSIM, Table 051-0004 and catalog no. 91-215-X; for infant mortality rates: Statistics Canada, CANSIM, Table 102-0504 and catalogue no. 84F0211-X.22
DEATHS
There were 2 513 171 deaths in the United States in 2011 (Table 1), 44 736 more than in 2010. Age-adjusted death rates are better indicators of the risk of mortality over time than crude death rates, because they control for changes in the age distribution of the US population. The age-adjusted death rate decreased by 1.3% from 7.5 deaths per 1000 US standard population in 2010, to 7.4 in 2011.3 This rate was a record low for the United States.3
The 2011 life tables show a difference in life expectancy at birth by sex, race, and Hispanic origin. Hispanic females have the highest life expectancy at birth (83.7 years), followed by non-Hispanic white females (81.1 years), Hispanic males (78.9 years), non-Hispanic black females (77.8 years), non-Hispanic white males (76.4 years), and non-Hispanic black males (71.6 years).3 The estimated life expectancy at birth for a given year represents the average number of years that a group of infants would be expected to live if, throughout their lifetime, they were to experience the age-specific death rates that prevailed during the year of their birth.
Deaths Among Children
A total of 20 192 children and adolescents aged 1 to 19 years died in the United States in 2011 (Table 8). The death rate for children aged 1 to 19 years was 25.6 per 100 000 population in 2011 and was not significantly different from 25.8 in 2010.
TABLE 8.
Deaths and Death Rates for the 5 Leading Causes of Childhood Death in Specified Age Groups: United States, 2010 (Final) and 2011 (Preliminary)
| Age, Causes of Death, and International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision, Codes12 | 2011
|
2010
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ranka | n | % | Rateb | n | % | Rateb | |
| Total: ages 1–19 y | |||||||
| All causes | — | 20 192 100.0 | 25.6 | 20 482 | 100.0 | 25.8 | |
| Accidents (unintentional injuries) (V01–X59, Y85–Y86) | 1 | 7196 | 35.6 | 9.1 | 7574 | 37.0 | 9.5 |
| Assault (homicide) (*U01–*U02, X85–Y09, Y87.1) | 2 | 2304 | 11.4 | 2.9 | 2478 | 12.1 | 3.1 |
| Intentional self-harm (suicide) (*U03, X60–X84, Y87.0) | 3 | 2034 | 10.1 | 2.6 | 1933 | 9.4 | 2.4 |
| Malignant neoplasms (C00-C97) | 4 | 1857 | 9.2 | 2.4 | 1863 | 9.1 | 2.3 |
| Congenital malformations, deformations, and chromosomal abnormalities (Q00–Q99) | 5 | 1045 | 5.2 | 1.3 | 1007 | 4.9 | 1.3 |
| Diseases of the heart (I00–I09, I11, I13, I20–I51) | 6 | 650 | 3.2 | 0.8 | 686 | 3.3 | 0.9 |
| Influenza and pneumonia (J09–J18) | 7 | 271 | 1.3 | 0.3 | 210 | 1.0 | 0.3 |
| Chronic lower respiratory diseases (J40–J47) | 8 | 243 | 1.2 | 0.3 | 244 | 1.2 | 0.3 |
| Cerebrovascular diseases (I60–I69) | 9 | 194 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 226 | 1.1 | 0.3 |
| Septicemia (A40–A41) | 10 | 169 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 173 | 0.8 | 0.2 |
| Age 1–4 y | — | ||||||
| All causes | 4214 100.0 | 26.1 | 4316 | 100.0 | 26.5 | ||
| Accidents (unintentional injuries) (V01–X59, Y85–Y86) | 1 | 1346 | 31.9 | 8.3 | 1394 | 32.3 | 8.6 |
| Congenital malformations, deformations, and chromosomal abnormalities (Q00–Q99) | 2 | 483 | 11.5 | 3.0 | 507 | 11.7 | 3.1 |
| Assault (homicide) (*U01–*U02, X85–Y09, Y87.1) | 3 | 370 | 8.8 | 2.3 | 385 | 8.9 | 2.4 |
| Malignant neoplasms (C00–C97) | 4 | 352 | 8.4 | 2.2 | 346 | 8.0 | 2.1 |
| Diseases of the heart (I00–I09, I11, I13, I20–I51) | 5 | 158 | 3.7 | 1.0 | 159 | 3.7 | 1.0 |
| Age 5–9 y | — | ||||||
| All causes | 2448 100.0 | 12.0 | 2330 | 100.0 | 11.5 | ||
| Accidents (unintentional injuries) (V01–X59, Y85–Y86) | 1 | 753 | 30.8 | 3.7 | 758 | 32.5 | 3.7 |
| Malignant neoplasms (C00–C97) | 2 | 442 | 18.1 | 2.2 | 439 | 18.8 | 2.2 |
| Congenital malformations, deformations, and chromosomal abnormalities (Q00–Q99) | 3 | 184 | 7.5 | 0.9 | 163 | 7.0 | 0.8 |
| Assault (homicide) (*U01–*U02, X85–Y09, Y87.1) | 4 | 122 | 5.0 | 0.6 | 111 | 4.8 | 0.5 |
| Influenza and pneumonia (J09–J18) | 5 | 61 | 2.5 | 0.3 | 37 | 1.6 | 0.2 |
| Age 10–14 y | — | ||||||
| All causes | 2947 100.0 | 14.2 | 2949 | 100.0 | 14.3 | ||
| Accidents (unintentional injuries) (V01–X59, Y85–Y86) | 1 | 861 | 29.2 | 4.2 | 885 | 30.0 | 4.3 |
| Malignant neoplasms (C00–C97) | 2 | 423 | 14.4 | 2.0 | 477 | 16.2 | 2.3 |
| Intentional self-harm (suicide) (*U03, X60–X84, Y87.0) | 3 | 276 | 9.4 | 1.3 | 267 | 9.1 | 1.3 |
| Congenital malformations, deformations, and chromosomal abnormalities (Q00–Q99) | 4 | 172 | 5.8 | 0.8 | 135 | 4.6 | 0.7 |
| Assault (homicide) (*U01–*U02, X85–Y09, Y87.1) | 5 | 147 | 5.0 | 0.7 | 150 | 5.1 | 0.7 |
| Age 15–19 y | — | ||||||
| All causes | 10 583 100.0 | 48.9 | 10 887 | 100.0 | 49.4 | ||
| Accidents (unintentional injuries) (V01–X59, Y85–Y86) | 1 | 4236 | 40.0 | 19.6 | 4537 | 41.7 | 20.6 |
| Intentional self-harm (suicide) (*U03, X60–X84, Y87.0) | 2 | 1753 | 16.6 | 8.1 | 1659 | 15.2 | 7.5 |
| Assault (homicide) (*U01–*U02, X85–Y09, Y87.1) | 3 | 1665 | 15.7 | 7.7 | 1832 | 16.8 | 8.3 |
| Malignant neoplasms (C00–C97) | 4 | 640 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 601 | 5.5 | 2.7 |
| Diseases of the heart (I00–I09, I11, I13, I20–I51) | 5 | 307 | 2.9 | 1.4 | 342 | 3.1 | 1.6 |
Data source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/NCHS, National Vital Statistics System: mortality, 2011 and 2010 (www.cdc.gov/nchs/deaths.htm) and unpublished tabulations. —, Data not available; *, United States specific ICD code.
Based on 2011 data.
Rate per 100 000 population in specified group.
For all children aged 1 to 19 years, the leading cause of death was accidents (unintentional injuries), which accounted for 35.6% of all deaths in 2011 and 37.0% of all deaths in 2010. The second leading cause of death was homicide, accounting for 11.4% of all deaths in 2011 and 12.1% of all deaths in 2010. Between 2010 and 2011, the death rate decreased significantly for unintentional injuries, homicide, heart disease, and cerebrovascular diseases. But the death rate increased significantly for suicide. Rates did not change significantly for the other leading causes of death among children.
Improvement of Data Quality
National implementation of the 2003 revision of the US Certificate of Live Birth has been long delayed, but all US jurisdictions are expected to implement the latest revision by January 1, 2014. A key goal of this revision was to improve data quality, particularly the quality of the health and medical information.16 A number of strategies, such as a detailed guide for facilities for capturing medical and health data, were developed with this goal in mind.28 Although only limited information on the completeness and accuracy of the 2003 revision-based health data is available, initial studies suggest that some concerns with data quality remain.29
The NCHS, the National Association for Public Health Statistics and Information Systems (NAPHSIS), and individual state/jurisdictional vital statistics partners are using multiple strategies to assess and improve birth data quality. For example, the NCHS and NAPHSIS are collaborating to develop interactive e-learning training for hospital staff (both birth information specialists and clinical staff) and to promote the universal use of the detailed training materials already available. The NCHS and NAPHSIS are also working together to develop national standards for the automatic transfer of medical/health birth certificate data directly from the hospital electronic records to state electronic birth registration systems30 by using HL7- and IHE-based standards; a pilot project is underway in Utah.
A new NCHS/NAPHSIS joint committee has been charged with identifying key birth data quality concerns and developing effective approaches to resolving them across the nation. Initial objectives of the committee include the following: (1) identifying model processes for state-to-hospital feedback on data quality issues, (2) developing approaches to promote hospital understanding of the importance and uses of birth data and techniques to improve hospital buy-in, and (3) identifying sources of problems with the prenatal care data and developing approaches to improving quality.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists also has recently launched the “reVITALize” campaign, which should have an important impact on the future quality of birth certificate obstetric data. The campaign goals include national standardization of obstetric clinical data definitions for electronic health records and birth certificates.31 The Centers for Disease Control and Preventions’s NCHS and NAPHSIS are participating in this effort and expect to incorporate these definitions for the birth certificate once finalized.
Finally, the NCHS has recently entered into new 5-year contracts with the 57 registration areas. A central goal of the new contracts is to substantially improve data timeliness and quality via increased standardization, performance requirements, and targeted support for jurisdictions where needed. As these expanded improvement efforts begin to take effect, the overall quality of birth data should improve and become more consistent across items and jurisdictions.
CONCLUSIONS
Vital statistics are a valuable tool for monitoring the health of the US population. The value of vital statistics will improve through efforts to advance data quality, particularly the quality of the health and medical information. Multiple strategies to assess and improve birth data quality are currently being implemented. As these efforts take effect, the quality of the data are expected to improve.
Acknowledgments
We thank Michelle J.K. Osterman, Stephanie J. Ventura, T.J. Mathews, Marian F. MacDorman, Jiaquan Xu, and Sherry L. Murphy for contributions to the manuscript and Yashodhara Patel for content review.
ABBREVIATIONS
- IMR
infant mortality rate
- LBW
low birth weight
- NAPHSIS
National Association for Public Health Statistics and Information Systems
- NCHS
National Center for Health Statistics
- NMR
neonatal mortality rate
- OMB
Office of Management and Budget
- PNMR
postneonatal mortality rate
Footnotes
FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE: The authors have indicated they have no financial relationships relevant to this article to disclose.
FUNDING: No external funding.
References
- 1.Hamilton BE, Martin JA, Ventura SJ. Births: preliminary data for 2011. [Accessed November 15, 2012];Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2012 61(5):1–20. Available at: www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr61/nvsr61_05.pdf. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Martin JA, Hamilton BE, Ventura SJ, et al. Births: final data for 2010. [Accessed November 15, 2012];Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2012 61(1):1–72. Available at: www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr61/nvsr61_01.pdf. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hoyert DL, Xu JQ. Deaths: preliminary data for 2011. [Accessed November 15, 2012];Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2012 61(6):1–52. Available at: www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr61/nvsr61_06.pdf. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Murphy SL, Kochanek KD. Deaths: final data for 2010. [Accessed November 15, 2012];Natl Vital Stat Rep. Available at: www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/dvs/deaths_2010_release.pdf.
- 5.National Center for Health Statistics. Natality public use file and CD-ROM. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; [Accessed November 2, 2012]. Available at: www.cdc.gov/nchs/data_access/VitalStatsOnline.htm. [Google Scholar]
- 6.National Center for Health Statistics. Mortality public use file and CD-ROM. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; [Accessed September 14, 2012]. Available at: www.cdc.gov/nchs/data_access/VitalStatsOnline.htm. [Google Scholar]
- 7.National Center for Health Statistics. Data release policy. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; 2000. [Accessed November 2, 2012]. Available at: www.cdc.gov/nchs/nvss/dvs_data_release.htm. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Office of Management and Budget. Revisions to the standards for the classification of federal data on race and ethnicity. [Accessed November 2, 2012];Federal Register 62FR58781-58790. 1997 Oct 30; Available at: www.whitehouse.gov/omb/fedreg_1997standards.
- 9.Ingram DD, Parker JD, Schenker N, et al. United States Census 2000 population with bridged race categories. Vital Health Stat 2. 2003;(135):1–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Schenker N, Parker JD. From single-race reporting to multiple-race reporting: using imputation methods to bridge the transition. [Accessed November 2, 2012];Stat Med. 2003 22(9):1571–1587. doi: 10.1002/sim.1512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.National Center for Health Statistics. User guide to the 2010 Natality Public Use File. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; [Accessed November 2, 2012]. Available at: www.cdc.gov/nchs/about/major/dvs/Vitalstatsonline.htm. [Google Scholar]
- 12.World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2009. 10th revision. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Heron M. Deaths: leading causes for 2009. [Accessed January 16, 2013];Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2012 61(7):1–96. Available at: www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr61/nvsr61_07. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mathews TJ, MacDorman MF. Infant mortality statistics from the 2008 period linked birth/infant death data set. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2012;60(5):1–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.National Center for Health Statistics. [Accessed November 2, 2012];U.S. standard certificate of live birth. 2003 revision. Available at: www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/dvs/birth11-03final-ACC.pdf.
- 16.National Center for Health Statistics. [Accessed November 2, 2012];Report of the panel to evaluate the U.S. standard certificates and reports. Available at: www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/dvs/panelreport_acc.pdf.
- 17.Office of Management and Budget. Race and ethnic standards for federal statistics and administrative reporting. [Accessed November 2, 2012];Statistical Policy Directive 15. 1977 Available at: http://wonder.cdc.gov/wonder/help/populations/bridged-race/directive15.html. [PubMed]
- 18.United Nations. United Nations Demographic Yearbook, 2011. New York, NY: United Nations; 2012. Tables 9 and 15. [Google Scholar]
- 19.OECD iLibrary. [Accessed November 2, 2012];Health: key tables from OECD. Available at: www.oecd-ilibrary.org/social-issues-migration-health/infant-mortality_20758480-table9.
- 20.Hamilton BE, Ventura SJ. NCHS data brief, no. 89. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; 2012. [Accessed November 2, 2012]. Birth rates for U.S. teenagers reach historic lows for all age and ethnic groups. Available at: www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/databriefs/db89.pdf. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.MacDorman MF, Mathews TJ. NCHS data brief, no. 74. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; 2011. [Accessed October 19, 2011]. Understanding racial and ethnic disparities in US infant mortality rates. Available at: www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/databriefs/db74.htm. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Statistics Canada. CANSIM, table 051-0004 and catalogue no. 91-215-X; for infant mortality rates: CANSIM, table 102-0504 and catalogue no. 84F0211X. Ottawa, Canada: Statistics Canada; [Accessed November 2, 2012]. Available at: http://www5.statcan.gc.ca/cansim/a33?RT=TABLE&sortby=id&themeID=3867&spMode=tables&lang=eng. [Google Scholar]
- 23.MacDorman MF, Martin JA, Mathews TJ, Hoyert DL, Ventura SJ. Explaining the 2001–2002 infant mortality increase in the United States: data from the linked birth/infant death data set. Int J Health Serv. 2005;35(3):415–442. doi: 10.2190/TJ2N-DADV-1EP5-5C7F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sepkowitz S. International rankings of infant mortality and the United States’ vital statistics, natality data collecting system: failure and success. Int J Epidemiol. 1995;24(3):583–588. doi: 10.1093/ije/24.3.583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kramer MS, Platt RW, Yang H, Haglund B, Cnattingius S, Bergsjo P. Registration artifacts in international comparisons of infant mortality. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2002;16(1):16–22. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3016.2002.00390.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.MacDorman MF, Mathews TJ. NCHS Data Brief, no. 23. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; 2009. [Accessed November 2, 2012]. Behind international rankings of infant mortality: how the United States compares with Europe. Available at: www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/databriefs/db23.htm. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.MacDorman MF, Mathews TJ. Behind international rankings of infant mortality: how the United States compares with Europe. Int J Health Serv. 2010;40(4):577–588. doi: 10.2190/HS.40.4.a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.National Center for Health Statistics. Guide to completing the facility worksheets for the certificate of live birth and report of fetal death. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics; 2006. 2003 revision. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sutton S. Assessing the quality of data from the 2003 birth certificate revision in two states. Paper presented at: National Center for Health Statistics Conference; Washington, DC. August 6–8, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hoyert DH, Khan H, Martin JA, Williamson M. Developing vital records standards for electronic health records systems. Paper presented at: National Center for Health Statistics Conference; Washington, DC. August 6–8, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 31.American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. [Accessed January 16, 2013];Revitalize conference and campaign. Available at: www.acog.org/About_ACOG/ACOG_Departments/Patient_Safety_and_Quality_Improvement/reVITALize_Conference_and_Campaign.