Abstract
In this study, the differences in reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and abscisic acid (ABA) accumulation in senescing leaves were investigated by early-senescence-leaf (esl) mutant and its wild type, to clarify the relationship among ABA levels, ROS generation, and NADPH oxidase (Nox) in senescing leaves of rice (Oryza sativa). The temporal expression levels of OsNox isoforms in senescing leaves and their expression patterns in response to ABA treatment were determined through quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR). Results showed that the flag leaf of the esl mutant generated more O2- concentrations and accumulated higher ABA levels than the wild-type cultivar did in the grain-filling stage. Exogenous ABA treatment induced O2- generation; however, it was depressed by diphenyleneiodonium chloride (DPI) pretreatment in the detached leaf segments. This finding suggested the involvement of NADPH oxidase in ABA-induced O2- generation. The esl mutant exhibited significantly higher expression of OsNox2, OsNox5, OsNox6, and OsNox7 in the initial of grain-filling stage, followed by sharply decrease. The transcriptional levels of OsNox1, OsNox3, and OsFR07 in the flag leaf of the esl mutant were significantly lower than those in the wild-type cultivar. The expression levels of OsNox2, OsNox5, OsNox6, and OsNox7 were significantly enhanced by exogenous ABA treatments. The enhanced expression levels of OsNox2 and OsNox6 were dependent on the duration of ABA treatment. The inducible expression levels of OsNox5 and OsNox7 were dependent on ABA concentrations. By contrast, exogenous ABA treatment severely repressed the transcripts of OsNox1, OsNox3, and OsFR07 in the detached leaf segments. Therefore, OsNox2, OsNox5, OsNox6, and OsNox7 were probably involved in the ABA-induced O2- generation in the initial stage of leaf senescence. Subsequently, other oxidases activated in deteriorating cells were associated with ROS generation and accumulation in the senescing leaves of the esl mutant. Conversely, OsNox1, OsNox3, and OsFR07 were not associated with ABA-induced O2- generation during leaf senescence.
Introduction
Leaf senescence is the final stage of leaf development and is controlled by various internal and external factors [1, 2]. This process is a genetically programmed metabolism of self-destruction as a form of programmed cell death. In this process, reactive oxygen species (ROS) act as important signaling molecules and toxic substances, which participate in the genetic regulation of leaf senescence and accelerate the completion of organ senescence [3–5].
ROS, such as superoxide radical (O2-) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), have been considered essential signaling molecules and key regulators of plant biological processes, including stomatal movement, pathogen defense, hormone signal transduction, programmed cell death, and plant growth and development [6–8]. Plasma membrane nicotine adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase is closely associated with the production and accumulation of ROS, which transfers electrons from cytoplasmic NADPH to O2 to form O2-; O2- undergoes dismutation to produce H2O2 [9]. In the roots of wheat (Triticum durum D.) seedlings, NADPH oxidase participates in the nickel-induced production of ROS to respond to oxidative stress caused by nickel treatment [10]. NADPH oxidase-dependent H2O2 production is also an intermediate step in the NaCl-induced elevation of calcium (Ca) in wheat roots [11]. In Arabidopsis, AtrbohD and AtrbohF encoding NADPH oxidases contribute to ROS production to regulate Na+/K+ homeostasis and improve the salt tolerance of Arabidopsis seedlings [12, 13]. In cultured tobacco (Nicotiana benthamiana) cells, the accumulation of ROS induced by NbrbohA and NbrbohB is involved in resistance against pathogenic infections [14]. NtrbohD is necessary in ABA-induced H2O2 accumulation to improve resistance against various stresses [15]. In maize (Zea mays), ZmrbohA, ZmrbohB, ZmrbohC and ZmrbohD are responsible for the biphasic response of ROS generation in ABA signaling transduction [16]. Therefore, NADPH oxidase is the main source of ROS in plant tissues and suspension culture cells; this enzyme plays important roles in regulating biological processes and responding to diverse environmental stimuli and aging factors [13, 17, 18]. In rice, nine genes encoding NADPH oxidase have been identified within the genome, and individual OsNox isoforms exhibit unique stress-response characteristics and distinct functions in response to various environmental stresses [19, 20]. OsNox2 (OsrbohA) and OsNox6 (OsrbohE) participate in the regulations of ROS-dependent signaling pathways in plant immune response [21]. Therefore, NADPH oxidase-induced ROS production is involved in multiple signaling pathways to respond to various stresses and aging factors; individual isoforms of NADPH oxidase exhibit distinct regulation patterns to manipulate ROS generation [20, 22]. However, the accurate molecular functions of OsNox isoforms manipulating ROS generation during the leaf senescence of rice remain ambiguous and thus should be investigated.
The function of NADPH oxidase in ROS generation in response to various stresses in plant tissues is mediated by abscisic acid (ABA). ABA plays important regulatory roles in plant responses and adaptation to various stressors, including drought, salinity, low temperature, and other biotic and abiotic factors [23, 24]. NADPH oxidase is involved in ABA-induced ROS production; as a result, antioxidant defense systems against oxidative damage are also stimulated to respond to various stress conditions [17, 25, 26]. NADPH oxidase-induced ROS generation involves rate-limiting second messengers in ABA signaling [27]. ABA-induced ROS production via NADPH oxidase is involved in the closure of stomata and the activation of plasma membrane Ca2+ channels in leaf guard cells; thus, responses to environmental stresses are stimulated [15, 28]. During leaf senescence, ROS accumulate and antioxidant enzymes change in senescing leaves; NADPH oxidase activities and ABA levels are also enhanced in senescing leaves [29, 30]. H2O2 and ABA are key regulatory factors that mediate the progression of leaf senescence; exogenous H2O2 or ABA application can induce or accelerate leaf senescence [5, 29–31]. However, studies have yet to fully elucidate the regulatory mechanism of NADPH oxidase involved in ROS generation and ABA signaling during leaf senescence. The molecular patterns of NOX isoforms implicated in ROS generation in response to ABA should be further investigated in the senescing leaves of rice.
In this study, genotypic differences in ROS generation and ABA accumulation were investigated in the leaves of two rice cultivars, namely, early-senescence-leaf (esl) mutant and its corresponding wild type. The enhancing effects of exogenous ABA-induced O2- production from NADPH oxidase were analyzed in detached leaf segments. The temporal expression levels of OsNox isoforms during leaf senescence and their expression patterns in response to ABA treatment were determined through quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) to clarify the possible relationship among OsNox isoform transcription, O2- generation, and ABA levels in senescing leaves.
Materials and methods
Plant materials and experimental treatments
Two rice cultivars, namely, an indica rice cultviar (Fu142) and its mutant with an esl phenotype, were used in this study. The esl mutant was derived from Fu142 cultivar (Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica) by gamma-irradiated mature seeds, and the stable esl inherited mutant was obtained by successive self-pollination. The identification of plant phenotype was performed from the M2 to M8 generations. M9 seeds were used in this experiment. The esl mutant was similar to the wild-type cultivar in plant morphology, plant height, and growth period until the late tillering stage. No visible differences were observed between the esl mutant and the wild-type cultivar in seedling and early tillering stages. However, the flag leaf of the esl mutant displayed exacerbated lesions and accelerated senescence symptoms in the grain-filling stage. The rusty lesions initially appeared on the tip of the leaf blade and then progressively spread downward to cover the whole leaf surface. Finally, the whole flag leaf of the esl mutant was nearly withered at approximately the 20th day of the grain-filling stage; as a result, agronomic traits and grain yield deteriorate [5].
Rice seeds were sown in a seedling nursery on April 25 and transplanted on May 20. Field experiments were performed at the experimental farmland of Zijingang campus (30°18´N, 120°04´N), Zhejiang University in Hangzhou, China. The field plots were arranged by following a random design with three replications for each cultivar. Each replication was planted in 10 × 12 rows, and plant spacing was 18 cm × 18 cm, with one rice seedling for each hill. The field trail was managed in accordance with local cultivation practices. Soil type was periodically waterlogged paddy soil, with 1.69 g/kg total N, 24.5 mg/kg available P, and 103.7 mg/kg exchangeable K. The rice plants were sampled in the grain-filling stage. A total of 50–70 rice plants with uniform anthesis time were randomly selected and tagged in each plot, and the flag leaves of the tagged plants were sampled during a 7-day interval, with three independent biological replicates at 9:00 a.m. The fresh samples were immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen and kept at −80°C for further experimental analyses.
Two supplement experiments were conducted using the detached leaf segments to investigate the effect of exogenous ABA on OsNox isoforms with respect to O2- generation. The fully extended leaves on the topmost position of rice plants were carefully detached in the booting stage. The leaves from rice plants at that time remained green and did not exhibit visual stress symptoms. In Expt. I (incubating concentration treatment), the detached leaf segments of rice plant were exposed to four ABA concentration treatments: 10, 50, 100, and 500 μM [5]. For each treatment, 25 mL of ABA solution was added to Petri dishes, with 4 dishes for each incubating concentration. After 6 h of incubation at 28°C in darkness, the leaf segments were sampled for subsequent analysis. In Expt. II (incubating duration treatment), the topmost fully extended leaves of rice plants were detached in the booting stage, and the detached leaf segments were floated on the solutions containing 25 mL of 100 μM ABA in Petri dishes placed at 28°C in darkness [5]. The leaf segments were subsequently sampled at 0, 0.5, 1, 3, 6, and 12 h after incubation. Before these immersions were performed, the leaf segments were placed in distilled water for 2 h to eliminate wound stress. The samples exposed to distilled water were as control, and three replications were prepared for Expt. I and II.
Determination of leaf O2- production
The production of O2- in sample was measured through Wang’s method with a slight modification [32]. Fresh leaf sample (0.50 g) was homogenized with 5 mL of 65 mM potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.8) in ice, and then the homogenate was centrifuged at 10000 g for 15 min at 4°C, and 2 mL of supernatant was mixed with 0.4 mL of 10 mM hydroxylamine hydrochloride and incubated for 20 min at 25°C to produce NO2-, and then 2 mL of 17 mM sulphanilic acid and α-naphthylamine were added separately, followed by incubating for 20 min at 25°C. Subsequently, 6 mL of trichloromethane was added into the mixture and shook well, and centrifuged at 10 000 g for 3 min. The upper pink aqueous phase was measured at 530 nm by a spectrophotometer. The production rate of O2- was calculated according to the standard NaNO2 concentration gradient using the same procedures.
Tissue localization of O2-
The localization of O2- was implemented as Romero-Puertas’s protocol with a slight modification [33]. Superoxide in leaf reacts with nitroblue tetrazolium chloride (NBT) and produces the blue formazan precipitates. Leaf segments were gently immersed in a 0.1% solution of NBT in 50 mM potassium phosphate buffer (pH 6.4), containing 10 mM Na-azide and 0.01% tween-20, and then were illuminated until appearance of dark spots, characteristic of blue formazan precipitates. After that, the leaf segments were bleached by immersing in boiling ethanol for 20 min until spots were clearly visible.
ABA analysis
Endogenous ABA analysis was carried out using the UPLC-ESI-qMS/MS method [34]. Fresh leaf samples were crushed to a fine powder, and then soaked in 1 mL of extraction solvent (methanol: formic acid: water = 15: 1: 4) at −30°C for 24 h. After centrifugation at 10000 g for 15 min, the supernatant was transferred to a 96-well collection plate, and the pellet was re-extracted with 0.2 mL of extraction solvent, before combining with the first supernatant. The supernatant was evaporated and then reconstituted with formic acid, and subjected to UPLC-ESI-qMS/MS analysis [34].
RNA isolation and cDNA preparation
Total RNA was extracted from the leaf samples with Trizol reagent according to the manufacturer’s protocol (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The RNA quality was checked with a spectrophotometer (NanoDropTM 1000, Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA), and then 1 μg of RNA was treated with 1 unit of DNaseI (Promega) at 37°C for 15 min to remove the possible contamination of genomic DNAs. The ReverTra Ace qPCR reverse transcriptase Kit (TOYOBO, OSAKA, JAPAN) was used for cDNA synthesis with an oligo (dT) primer. The reaction was conducted at 37°C for 15 min and then stopped by heating at 95°C for 5 min. The concentration of cDNA was about 20 ng μL-1.
Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR
Aliquots of cDNA mixtures were used as the templates for quantitative real-time PCR analysis by SYBR Green Real-time PCR Master Mix reagent Kit (TOYOBO, OSAKA, JAPAN). Reactions were performed on a Bio-Rad CFX96 (Bio-Rad, USA) according to the manufacture’s protocols. 1 μL cDNA was added to 10 μL SYBR buffer, and 1.6 μL 10 mM primer pairs in a final 20 μL reaction volume. The gene-specific primer pairs were designed by Primer Premier 5.0 (Premier, Canada) as listed in Table 1. The qRT-PCR conditions were 94°C for 30 s, followed by 40 cycles of 94°C for 5 s, 58°C for 10 s, and 72°C for 15 s. To verify the specificity of each primer set and optimize PCR conditions of the annealing temperature and PCR efficiency, the fluorescence signal specificity of PCR amplification was detected for each primer pairs and their melting curve (from 58°C to 94°C) was examined prior to the experimental measurements. Actin was used as the internal control gene. The samples were normalized using Actin expression, and the relative expression levels were analysed using the 2-ΔΔCT method [35]. The average value and standard error were calculated from three independent biological replicates.
Table 1. Sequence of primers for ACTIN and OsNox isoform genes used for real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction.
| Gene | Accession No. | Primer pairs | Products (bp) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forward primer (5’ → 3’) | Reverse primer (5’ → 3’) | |||
| ACTIN | X16280 | 5’-CAGCACATTCCAGCAGATGT-3’ | 5’-TAGGCCGGTTGAAAACTTTG-3’ | 198 |
| OsNox1 | NM_001049555 | 5’-GCGATGCTCGTTCTGCTCTC-3’ | 5’-GGTCGTGCGAAATGGGTCTT-3’ | 106 |
| OsNox2 | NM_001050700 | 5’-CAAGCCAAGCACTGAGCCA-3’ | 5’-GAACAGTCCAGCCATTATCCC-3’ | 149 |
| OsNox3 | NM_001051260 | 5’-GGCATCCCTTCTCCATCAC-3’ | 5’-CTCGCAAGCCTTCCCAAAC-3’ | 113 |
| OsNox4 | NM_001062318 | 5’-CGCTACTCCGTGGTATGGTGA-3’ | 5’-GTCTTGTTGAAACGCCTCTGC-3’ | 127 |
| OsNox5 | NM_001062650 | 5’-TTGGGATAATGGCTGGGTTG-3’ | 5’-TGGTGTTGCGGCATACTGG-3’ | 159 |
| OsNox6 | NM_001068491 | 5’-CTCCTCATCGTCGTCTACCTCC-3’ | 5’-AAAGCATCAATGGCACAGCA-3’ | 112 |
| OsNox7 | NM_001069802 | 5’-CCGAACAAACGGAGACTGGA-3’ | 5’-CGCCTAGCTCGCTGAATGAA-3’ | 101 |
| OsFR01 | NM_001060176 | 5’-CACCACCTCTACGCCCTCTT-3’ | 5’-GAACACGCCAGGCAGGAT-3’ | 84 |
| OsFR07 | NM_001059431 | 5’-TGCGGAACCGTGGAACTA-3’ | 5’-CTCCCTCACCTGAACGAAGA-3’ | 84 |
Statistical analysis
All determinations were performed in at least three independent experiments. Statistical differences were analyzed by analysis of variance (ANOVA) using the SPSS statistical software package (Chicago, USA). Differences were considered significant at a probability level of P ≤ 0.05 or 0.01. Standard deviation (SD) was calculated and shown in the figures.
Results
ABA enhanced the production of O2- during leaf senescence
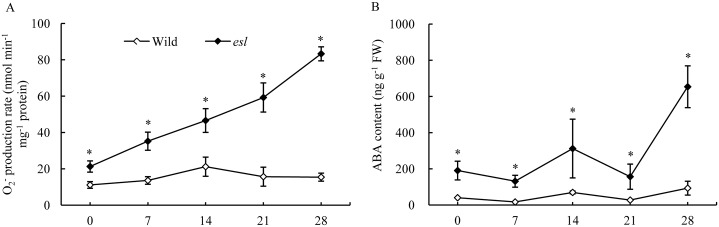
As reported in our previous study, the flag leaf of the esl mutant rice exhibited early senescence symptoms and significantly higher H2O2 level than the wild-type cultivar did in the grain-filling stage, and increasing H2O2 was closely associated with the regulation of leaf senescence in esl mutant rice after anthesis [5]. In this study, the flag leaf of the esl mutant showed significantly higher and progressively enhancive O2- production rate than its wild-type cultivar did in the grain-filling stage (p ≤ 0.05) (Fig 1A, S1 Table). The endogenous ABA level in senescing flag leaf of esl mutant was significantly higher than that in wild-type cultivar (p ≤ 0.05) (Fig 1B, S1 Table), suggesting that the production of O2- in the senescing flag leaf of the esl mutant was probably associated with ABA level in the grain-filling stage.
Fig 1. O2- production rate and ABA contents in the flag leaves of two rice cultivars in the grain-filling stage.
Vertical bars represent standard errors (n = 3).
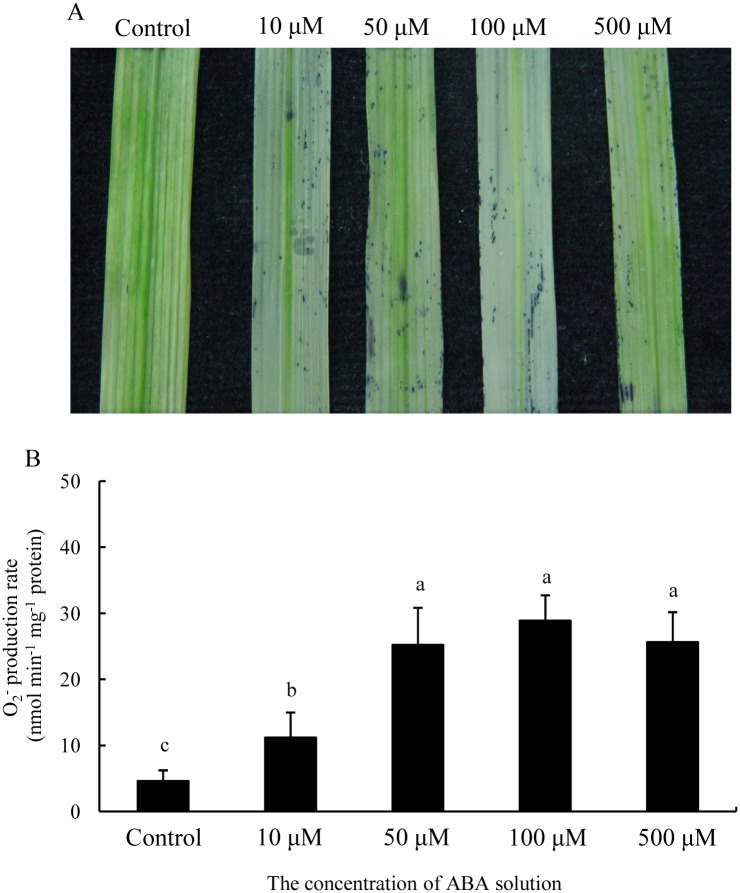
The detached leaf segments were incubated in exogenous ABA solutions with different concentrations to demonstrate the effect of ABA on O2- generation in the senescing leaf. The tissue localization of O2- showed that exogenous ABA treatments obviously enhanced the formation of blue formazan deposit in the detached leaf segments (Fig 2A), and the production rate of O2- in detached leaf segments was significantly enhanced by various concentrations of ABA solutions (p ≤ 0.05) (Fig 2B, S2 Table).
Fig 2. O2- production in detached leaf segments incubated by various concentrations of exogenous ABA solutions.
Significant differences (p ≤ 0.05) between ABA doses are indicated by different letters.
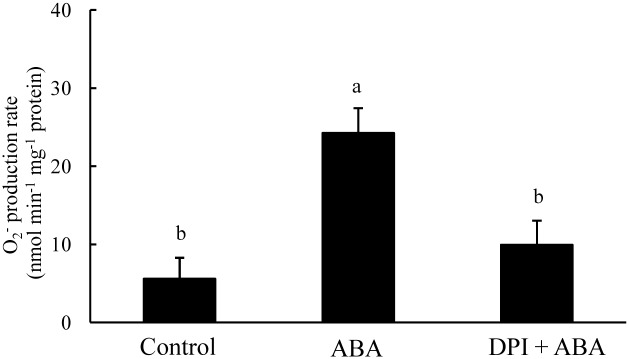
Diphenyleneiodonium chloride (DPI), an inhibitor of NADPH oxidase, was used to investigate the involvement of NADPH oxidase in ABA-induced O2- production. The detached leaf segments were firstly incubated in DPI solution for 6 h and then immersed in exogenous ABA solution. In Fig 3, O2- generation caused by exogenous ABA in the detached leaf segments was repressed by DPI pretreatment (p ≤ 0.05, S3 Table); thus, ABA-induced O2- production was primarily associated with NADPH oxidase.
Fig 3. Involvement of NADPH oxidase in ABA-induced O2- production in detached leaf segments.
The DPI concentration is 25μM, and ABA concentration is 100μM; Significant differences (p ≤ 0.05) between different treatments are indicated by different letters.
Genotypic-dependent differences in the transcriptional profile of various OsNox isoform genes during leaf senescence
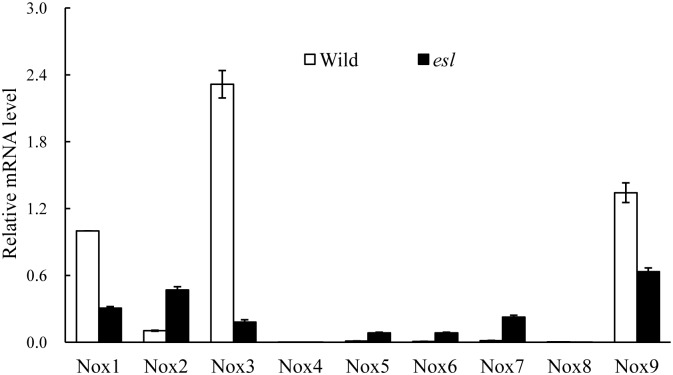
The esl mutant displayed significantly higher transcripts for OsNox2, OsNox5, OsNox6, and OsNox7 isoforms in the flag leaf than the wild-type cultivar did. The esl mutant exhibited strikingly lower expression abundance for OsNox1, OsNox3, and OsFR07 isoforms in the heading stage than the wild-type cultivar did (Fig 4, S4 Table). The transcripts of OsNox4 and OsFR01 were not detected in the leaves of the two rice cultivars (Fig 4).
Fig 4. Comparison of the expression of OsNox isoforms in the flag leaves of two rice cultivars in the booting stage.
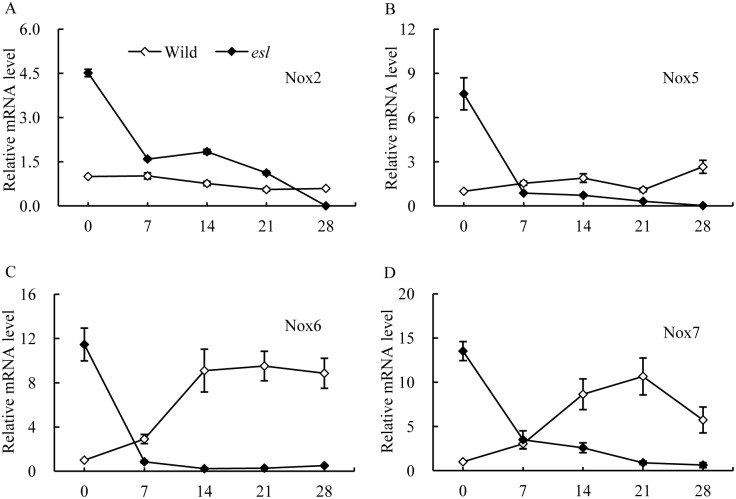
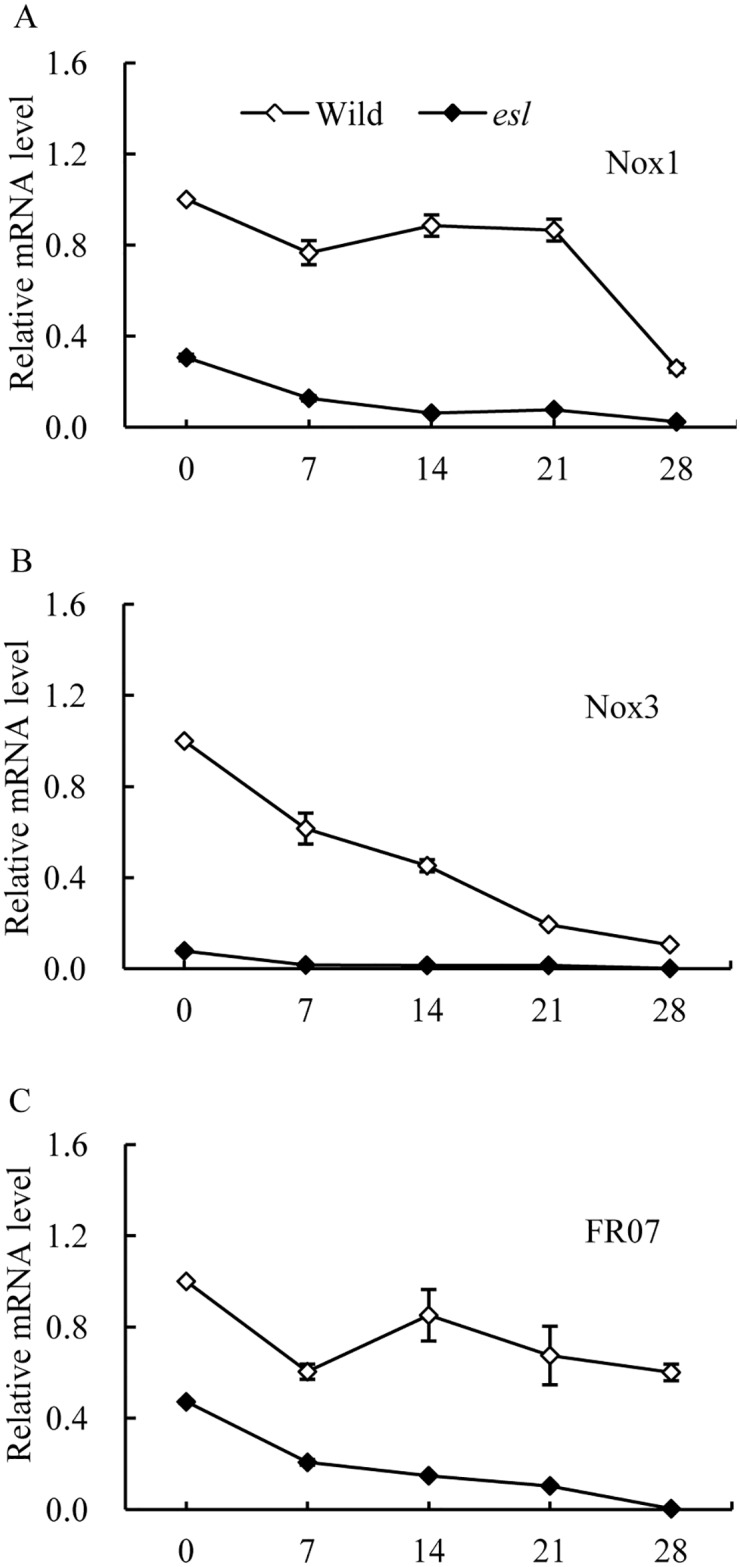
In Fig 5, the temporal transcriptional patterns of OsNox2, OsNox5, OsNox6, and OsNox7 in the flag leaf of the esl mutant were strikingly higher than those in the wild-type cultivar in the initial stage of grain filling, and then sharply decreased. By contrast, the wild-type cultivar exhibited relatively consistent expression patterns of OsNox2 and OsNox5 in the grain-filling stage, and increasing expression levels of OsNox6 and OsNox7 in the mid-late stage of grain filling (S5 Table). However, the temporal expression patterns of OsNox1, OsNox3 and OsFR07 isoforms in the flag leaf of esl mutant were significantly lower than those in wild type during the whole grain-filling stage (Fig 6, S5 Table). These results suggested that the transcripts of OsNox2, OsNox5, OsNox6, and OsNox7 isoforms were probably associated with the O2- generation in the senescing flag leaf of the esl mutant in the initial stage of grain filling.
Fig 5. Temporal expression patterns of OsNox2, OsNox5, OsNox6, and OsNox7 in the flag leaves of two rice cultivars in the grain-filling stage.
Fig 6. Temporal expression patterns of OsNox1, OsNox3, and OsFR07 in the flag leaves of two rice cultivars in the grain-filling stage.
Association of ABA-induced O2- generation with the transcripts of various OsNox isoforms in the detached leaf segments
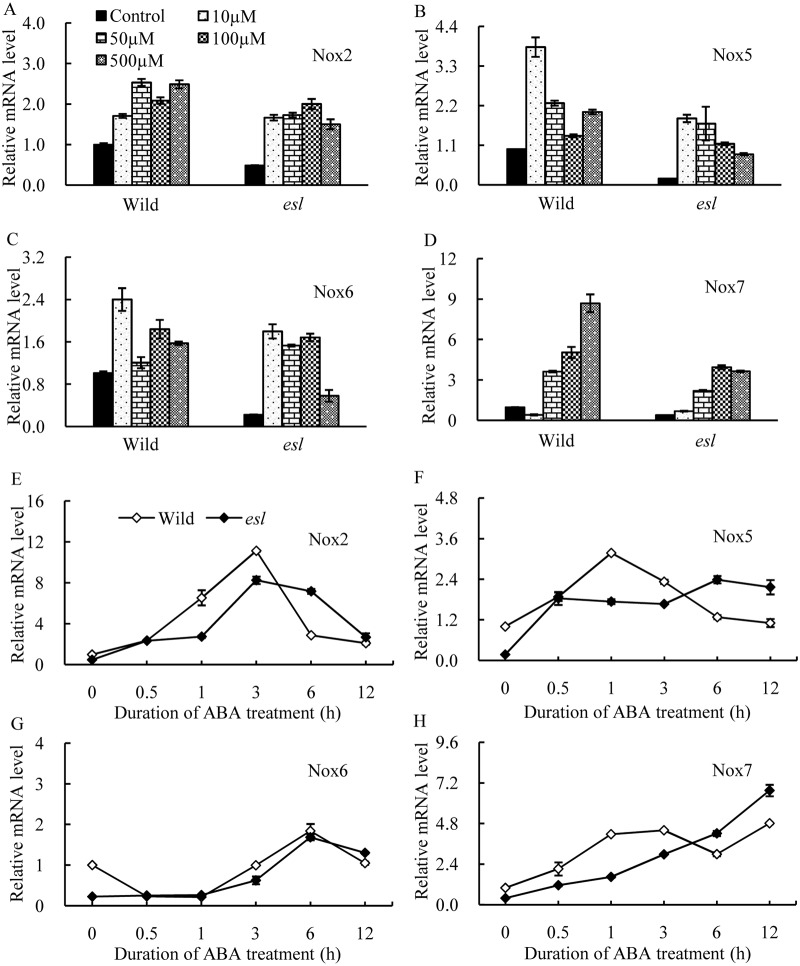
The transcriptional expression levels of OsNox isoforms in response to exogenous ABA were investigated in the detached rice leaf segments to clarify the regulatory relationship between ABA and OsNox transcripts involved in O2- generation. In Fig 7, exogenous ABA treatments severely repressed the transcripts of OsNox1, OsNox3, and OsFR07 regardless of ABA concentrations (S6 Table), suggesting that these three OsNox isoforms were negatively correlated with ABA hormone and were not involved in the ABA-induced O2- generation. By contrast, the transcripts of OsNox2, OsNox5, OsNox6, and OsNox7 were significantly enhanced by exogenous ABA treatments (Fig 8A–8D, S6 Table). The enhanced expression levels of OsNox2 and OsNox6 caused by ABA treatment were variable with the duration of ABA treatment, regardless of rice genotypes or ABA concentration (Fig 8A and 8C). The transcript of OsNox2 reached its peak level at 3 h after 100 μM ABA treatment. OsNox6 reached the highest expression at 6 h after ABA treatment (Fig 8E and 8G). The effects of exogenous ABA on the transcripts of OsNox5 and OsNox7 in the two rice cultivars were dependent on ABA concentrations. For instance, OsNox5 displayed the highest expression at 10 μM ABA; by contrast, the expression of the corresponding transcript was reduced in two rice cultivars as the ABA concentration was increased (Fig 8B). The temporal expression pattern of OsNox5 held relatively consistent after 0.5 h incubated in 100 μM ABA solution (Fig 8F). OsNox7 showed a promoting transcript pattern with the increase in ABA concentration (Fig 8D). The temporal expression levels of OsNox7 in the two rice cultivars were gradually enhanced with the duration of ABA treatment and exhibited a dependence on the duration of ABA treatment (Fig 8H). These results indicated that the response expression of OsNox5 and OsNox7 to exogenous ABA treatment varied widely depending on ABA levels. OsNox5 responded to low ABA level; conversely, OsNox7 was mainly involved in the response to high ABA level. Such diversity possibly played a complementary role in detecting the changes in ABA and in inducing O2- production at various ABA levels during leaf senescence.
Fig 7. Transcriptional analyses of OsNox1, OsNox3, and OsFR07 in the detached leaf segments of two rice cultivars incubated at 10, 50, 100, and 500 μM ABA solutions for 6 h.
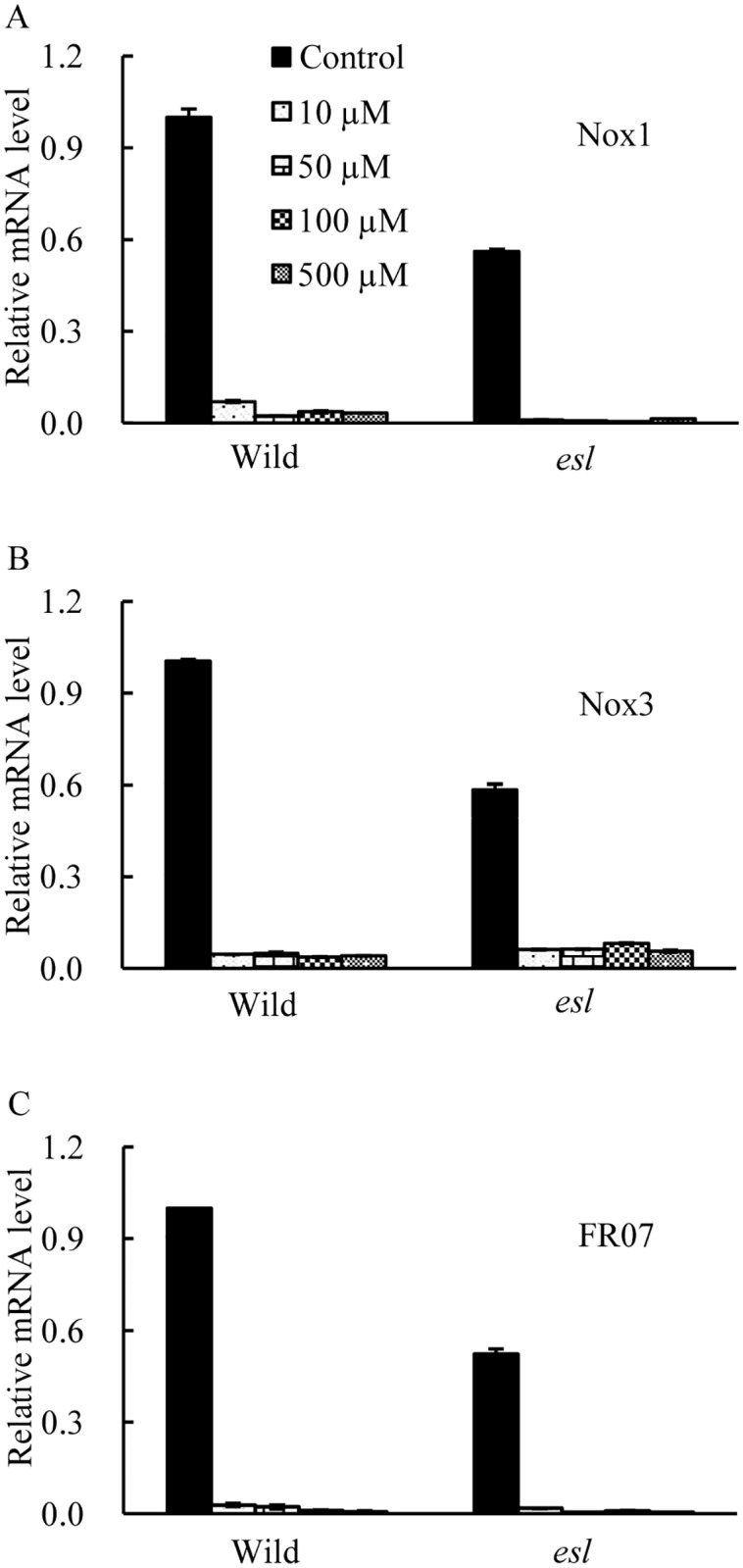
Fig 8. Transcriptional analyses of OsNox2, OsNox5, OsNox6, and OsNox7 in the detached leaf segments of two rice cultivars treated with exogenous ABA solutions.
A, B, C, and D respectively indicate the comparison of the expression levels of OsNox2, OsNox5, OsNox6, and OsNox7 treated with various concentrations of exogenous ABA solutions for 6 h; E, F, G, and H respectively illustrate the temporal expression patterns of OsNox2, OsNox5, OsNox6, and OsNox7 treated with 100 μM exogenous ABA solution.
Discussion
ROS as ubiquitous messengers of stress responses likely play a signaling role in various adaptive processes [36]. ROS production by NADPH oxidase is involved in the ABA signaling pathway to activate appropriate responses and acclimate under various stress conditions [4, 10, 17]. Under water stress condition, ROS originated from NADPH oxidase participates in ABA signal transduction; as a result, antioxidant enzyme activity is enhanced [37]. ROS, such as H2O2 derived from NADPH oxidase, has been considered a key factor mediating programmed cell death and tissue aging in plants [36, 38]. In most species, the distinctive feature of plant senescence is the increase in the levels of ROS and ABA hormone, accompanied by changes in enzyme activities related to ROS production and scavenging [5, 39]. H2O2 is involved in the ABA-induced leaf senescence in rice [29]. Our previous study demonstrated that H2O2 is required for leaf senescence, and ABA-induced H2O2 generation is closely associated with the regulatory metabolism of leaf senescence [5]. In the present study, the flag leaf of the esl mutant promoted the O2- production and increased the ABA levels during leaf senescence (Fig 1, S1 Table). The exogenous ABA treatment induced the O2- production in the detached leaf segments (Fig 2, S2 Table). The DPI pretreatment severely repressed the ABA-induced O2- production in the detached leaf segments (Fig 3, S3 Table). Therefore, the present results implied that the ABA-induced O2- production was probably involved in the regulation of leaf senescence process. NADPH oxidase was required for the O2- production during ABA signal transduction. Thus, NADPH oxidase is closely associated with the ROS-dependent regulation of ABA-induced leaf senescence.
Plant NADPH oxidase has been known as a respiratory burst oxidase homolog (rboh) and is homologous to the catalytic subunit (gp91phox) of a phagocytic NADPH oxidase [40]. In Arabidopsis, at least 10 rboh isoforms are found, AtrbohB plays an essential regulatory role in the embryogenesis of germinating seeds, and AtrbohC is likely involved in root hair development [40–42]. AtrbohD and AtrbohF exhibit the multifarious functions in pathogen recognition and stomatal regulation [12, 27]; these findings indicate that distinct rboh isoforms in Arabidopsis show functional diversity in plant development and stress responses. In rice, nine OsNox isoforms possibly perform diverse functions in stress response and tissue development [21]. The NOX activation is mediated by cytosolic Ca2+ spike during stress response [22]. Exogenous Ca2+ treatment increases the NADPH oxidase activity in leaves [37]. In our study, the flag leaf of the esl mutant showed significantly lower transcript levels for OsNox1, OsNox3, and OsFR07 than the flag leaf of the wild-type cultivar did (Figs 4 and 6, S4 Table); this result was probably attributed to low Ca2+ levels in the senescing leaf of the esl mutant (data not shown). Furthermore, the deprivation of apoplastic Ca2+ by EGTA chelation significantly depressed the transcripts of OsNox1, OsNox3, and OsFR07 in the detached leaf segment. In contrast, the expression of OsNox1 and OsNox3 is strongly stimulated by Ca2+ or drought treatments; the expression of OsFR07 is upregulated by salt stress [20]. In Arabidopsis rhd2 mutant, that lacks a functional AtrbohC gene and exhibits a defective root hair growth, AtrbohC controls the development of root hair by producing ROS that regulated plant cell expansion through the activation of Ca2+ channels [18]. Besides, AtrbohC (At5g51060) of Arabidopsis thaliana possesses the close relationship or similar functions with OsNox1 of Oryza sativa [20]. Therefore, OsNox1, OsNox3, and OsFR07 were likely associated with Ca2+ signal in rice, and the low Ca2+ content in senescing leaf limited the transcripts of OsNox1, OsNox3, and OsFR07 in the esl mutant. Exogenous ABA treatment repressed the transcripts of OsNox1, OsNox3, and OsFR07 in the detached leaf segments (Fig 7, S6 Table). Therefore, these isoforms were probably not the major participators which involved in ABA signaling during leaf senescence.
The ROS production induced by the expression of OsNox2 is involved in Ca2+ signaling and in response to plant immune stress [21]. The ROS generation stimulated by OsNox2 is closely associated with the regulation of plant development and drought response [20]. The expression of OsNox5 is upregulated in the leaves of rice under drought or high temperature conditions [20]. A study on OsrbohA and OsrbohE knockdown rice plants revealed that OsrbohA(OsNox2) and OsrbohE (OsNox6) are involved in the ROS production in suspension culture cells of rice; after these cells are inoculated with pathogens at different intervals, OsNox2 contributes to ROS production in the early phase, whereas OsNox6 is responsible for ROS production in the late phase; thus, signaling pathways are regulated at different phases during immune responses [21]. In our study, the flag leaf of the esl mutant yielded higher expression levels of OsNox2, OsNox5, OsNox6, and OsNox7 than the flag leaf of the wild-type cultivar did in the initial stage of leaf senescence; the expression levels then decreased sharply until day 7 post-anthesis (Figs 4 and 5). Studies on dnd1 mutant plants with mutation in the gene encoding the plasma membrane-localized Ca2+-conducting CNGC2 channel, have revealed that the appearances of early senescence-associated phenotypes are accompanied by decreased Ca2+ levels in dnd1 leaves; the application of a Ca2+ channel blocker hastens the senescence of detached wild-type leaves [43]. Therefore, our results indicated that OsNox2, OsNox5, OsNox6, and OsNox7 in the esl mutant were probably responsible for ROS production in the initial stage of leaf senescence; afterward, the remarkable decrease in the transcripts of OsNox2, OsNox5, OsNox6, and OsNox7 in the esl mutant was likely regulated by decreasing Ca2+ levels in senescing leaves.
Recently, a novel rice C2H2-type zinc finger protein, ZFP36, has been discovered, which was involved in ABA-induced antioxidant defense by regulating the expression of OsrbohE (OsNox6) and OsrbohB (OsNox7), suggesting OsNox6 and OsNox7 were essential for ABA signaling [44]. Besides, ABA treatment stimulated NOX activity to produce ROS in plant guard cells in response to ABA [17, 45], whereas the transcripts of Nox isoform genes were affected by exogenous or endogenous ABA level [15, 27]. In this study, the expression levels of OsNox2, OsNox5, OsNox6, and OsNox7 were significantly enhanced by exogenous ABA treatment (Fig 8A–8D). Among them, the expressions of OsNox5 and OsNox7 were dependent on ABA concentrations (Fig 8B and 8D). Thus, OsNox5 and OsNox7 were associated with distinct ABA concentrations in plant tissues. OsNox5 responded to low ABA levels, and OsNox7 was probably involved in the response to high ABA levels, thereby possibly playing a complementary role in detecting changes in ABA and in inducing O2- production at distinct ABA levels during leaf senescence. The enhanced expression levels of OsNox2, OsNox5, OsNox6, and OsNox7 isoforms by ABA treatment exhibited different temporal patterns, and the transcript peaks of OsNox2, OsNox5, OsNox6, and OsNox7 were at 3, 1, 6, and 12 h after incubating through a 100 μM ABA solution, respectively (Fig 8E–8H). In maize, a similar phenomenon has been observed in the expression levels of various Zmrboh isoforms, which exhibit distinct biphasic responding expression to ABA treatment; as a consequence, ROS continuously accumulate in the tissues of maize [16]. The diversity of the temporal transcriptions of OsNox2, OsNox5, OsNox6, and OsNox7 in leaf tissues probably plays a complementary role in detecting ABA accumulation and inducing O2- production.
However, a contradiction was detected between the decreasing transcript levels of OsNox2, OsNox5, OsNox6, and OsNox7 isoforms from day 7 post-anthesis and the continuous accumulation of O2- in senescing leaves in the leaf senescence stage. One possible explanation for this disparity is the presence of NADPH oxidases and other sources that generate ROS in senescing leaf cells. Numerous enzymes, including cell wall peroxidase, polyamine oxidase, oxalate oxidases, glycolate oxidases, and xanthine oxidases, and reactions, such as fatty acid oxidation, induce ROS generation [46, 47]. The same phenomena have been observed in rice leaves exposed to drought stress and maize leaves treated with exogenous ABA solution [9, 47]. Another interesting disparity was discovered on the transcripts of OsNox6 and OsNox7 in the leaves of the wild-type cultivar; the transcripts gradually increased on day 7 post-anthesis (Fig 6C and 6D). By contrast, the O2- production rate of the corresponding blade remained relatively constant in the wild-type rice (Fig 1). These phenomena may result from the relatively high SOD activity in the wild-type leaves (data not shown) to eliminate O2- accumulation by dismutation timely. Thus, the transcripts of OsNox2, OsNox5, OsNox6, and OsNox7 in the esl mutant are probably involved in ROS generation in the initial stage of leaf senescence. Once leaf senescence started, the transcripts of the four OsNox isoforms were repressed because of Ca2+ deficiency in the senescing leaves of the esl mutant. Other oxidases in deteriorating cells subsequently induced ROS generation and accumulation.
Supporting information
(XLSX)
(XLSX)
(XLSX)
(XLSX)
(XLSX)
(XLSX)
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Zhenzhen Cao (China National Rice Research Institute, China) for excellent technical assistance and Dr. Kai Fan (Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, China) for valuable suggestions.
Abbreviations
- ABA
abscisic acid
- DPI
diphenyleneiodonium chloride
- esl
early-senescence-leaf
- H2O2
hydrogen peroxide
- NADPH
nicotine adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- NBT
nitroblue tetrazolium chloride
- NOX
NADPH oxidase
- O2-
superoxide radical
- qRT-PCR
quantitative real-time reverse transcription PCR
- ROS
reactive oxygen species
Data Availability
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.
Funding Statement
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31271655), the Project Funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2015M580560), and the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (No. 2016J01100). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Lim PO, Kim HJ, Nam HG. Leaf senescence. Annual Review of Plant Biology. 2007; 58:115–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.57.032905.105316 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zhou C, Gan S. Senescence In: Pua E, Davey M, eds. Plant developmental biology: biotechnological perspectives. Berlin: Springer; 2009; 151–169. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lin JN, Kao CN. Effects of oxidative stress caused by hydrogen peroxide on senescence of rice leaves. Bot Bull Acad Sin. 1998; 39:161–165. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Apel K, Hirt H. Reactive oxygen species: metabolism, oxidative stress, and signal transduction. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2004; 55:373–399. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.55.031903.141701 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Li Z, Wang F, Lei B, Cao Z, Pan G, Cheng F. Genotypic-dependent alteration in transcriptional expression of various CAT isoenzyme genes in esl mutant rice and its relation to H2O2-induced leaf senescence. Plant Growth Regul. 2014; 73:237–248. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lamb C, Dixon RA. The oxidative burst in plant disease resistance. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 1997; 48:251–275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zhang X, Zhang L, Dong F, Gao J, Galbraith DW, Song CP. Hydrogen peroxide is involved in abscisic acid-induced stomatal closure in Vicia faba. Plant Physiol. 2001; 126:1438–1448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Laloi C, Apel K, Danon A. Reactive oxygen signalling: the latest news. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2004; 7:323–328. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2004.03.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Duan ZQ, Bai L, Zhao ZG, Zhang GP, Cheng FM, Jiang LX, et al. Drought-stimulated activity of plasma membrane nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase and its catalytic properties in rice. J Integr Plant Biol. 2009; 51:1104–1115. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2009.00879.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hao F, Wang X, Chen J. Involvement of plasma-membrane NADPH oxidase in nickel-induced oxidative stress in roots of wheat seedlings. Plant Sci. 2006; 170:151–158. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yang Y, Xu S, An L, Chen N. NADPH oxidase-dependent hydrogen peroxide production, induced by salinity stress, may be involved in the regulation of total calcium in roots of wheat. J Plant Physiol. 2007; 164:1429–1435. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2006.08.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Torres MA, Dangl JL, Jones JDG. Arabidopsis gp91phox homologues AtrbohD and AtrbohF are required for accumulation of reactive oxygen intermediates in the plant defense response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002; 99:517–522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.012452499 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ma L, Zhang H, Sun L, Jiao Y, Zhang G, Miao C, et al. NADPH oxidase AtrbohD and AtrbohF function in ROS-dependent regulation of Na+/K+ homeostasis in Arabidopsis under salt stress. J Exp Bot. 2012; 63:305–317. doi: 10.1093/jxb/err280 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Yoshioka H, Numata N, Nakajima K, Katou S, Kawakita K, Rowland O, et al. Nicotiana benthamiana gp91phox homologs NbrbohA and NbrbohB participate in H2O2 accumulation and resistance to Phytophthora infestans. Plant Cell. 2003; 15:706–718. doi: 10.1105/tpc.008680 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hao F, Zhang J, Yu Z, Chen J. Involvement of NADPH oxidase NrtbohD in the rapid production of H2O2 induced by ABA in cultured tobacco cell line BY-2. Prog Nat Sci. 2008; 18:267–271. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lin F, Ding H, Wang J, Zhang H, Zhang A, Zhang Y, et al. Positive feedback regulation of maize NADPH oxidase by mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in abscisic acid signalling. J Exp Bot. 2009; 60:3221–3238. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erp157 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Jiang M, Zhang J. Involvement of plasma-membrane NADPH oxidase in abscisic acid- and water stress-induced antioxidant defense in leaves of maize seedlings. Planta. 2002; 215:1022–1030. doi: 10.1007/s00425-002-0829-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Foreman J, Demidchik V, Bothwell JH, Mylona P, Miedema H, Torres MA, et al. Reactive oxygen species produced by NADPH oxidase regulate plant cell growth. Nature. 2003; 422:442–446. doi: 10.1038/nature01485 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wong HL, Pinontoan R, Hayashi K, Tabata R, Yaeno T, Hasegawa K, et al. Regulation of rice NADPH oxidase by binding of Rac GTPase to its N-terminal extension. Plant Cell. 2007; 19:4022–4034. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.055624 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wang GF, Li WQ, Li WY, Wu GL, Zhou CY, Chen KM. Characterization of rice NADPH oxidase genes and their expression under various environmental conditions. Int J Mol Sci. 2013; 14:9440–9458. doi: 10.3390/ijms14059440 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yoshie Y, Goto K, Takai R, Iwano M, Takayama S, Isogai A, et al. Function of the rice gp91phox homologs OsrbohA and OsrbohE genes in ROS-dependent plant immune responses. Plant Biotechnol. 2005; 22:127–135. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sagi M, Fluhr R. Production of reactive oxygen species by plant NADPH oxidases. Plant Physiol. 2006; 141:336–340. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.078089 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Finkelstein RR, Gampala SS, Rock CD. Abscisic acid signaling in seeds and seedlings. Plant Cell. 2002; 14:S15–45. doi: 10.1105/tpc.010441 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Xiong L, Schumaker KS, Zhu JK. Cell signaling during cold, drought, and salt stresses. Plant Cell. 2002; 14:S165–183. doi: 10.1105/tpc.000596 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jiang M, Zhang J. Effect of abscisic acid on active oxygen species, antioxidative defence system and oxidative damage in leaves of maize seedlings. Plant Cell Physiol. 2001; 42:1389–1395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jiang MY, Zhang JH. Abscisic acid and antioxidant defense in plant cells. Acta Bot Sin. 2004; 46:1–9. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kwak JM, Mori IC, Pei ZM, Leonhardt N, Torres MA, Dangl JL, et al. NADPH oxidase AtrbohD and AtrbohF genes function in ROS-dependent ABA signaling in Arabidopsis. EMBO J. 2003; 22:2623–2633. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg277 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Pei ZM, Murata Y, Benning G, Thomine S, Klüsener B, Allen GJ, et al. Calcium channels activated by hydrogen peroxide mediate abscisic acid signaling in guard cells. Nature. 2000; 406:731–734. doi: 10.1038/35021067 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hung KT, Kao CH. Hydrogen peroxide is necessary for abscisic acid induced senescence of rice leaves. J Plant Physiol. 2004; 161:1347–1357. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2004.05.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Li Z, Su D, Lei B, Wang F, Geng W, Pan G, et al. Transcriptional profile of genes involved in ascorbate glutathione cycle in senescing leaves for an early senescence leaf (esl) rice mutant. J Plant Physiol. 2015; 176:1–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2014.09.020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Neill S, Desikan R, Clarke A, Hurst RD, Hancock JT. Hydrogen peroxide and nitric oxide as signalling molecules in plants. J Exp Bot. 2002; 53:1237–1247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wang A, Luo G. Quantitative relation between the reaction of hydroxylamine and superoxide anion radicals in plants. Plant Physiol Commun. 1990; 6:55–57. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Romero-Puertas MC, Rodriguez-serrano M, Corpas FJ, Gomez M, Delrio LA, Sandalio LM. Cadmium-induced subcellular accumulation of O2- and H2O2 in pea leaves. Plant Cell Environ. 2004; 27:1122–1134. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kojima M, Kamada-Nobusada T, Komatsu H, Takei K, Kuroha T, Mizutani M, et al. Highly sensitive and high-throughput analysis of plant hormones using MS-probe modification and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: an application for hormone profiling in Oryza sativa. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009; 50:1201–1214. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcp057 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Schmittgen TD, Livak KJ. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat Protoc. 2008; 3:1101–1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bhattacharjee S. Reactive oxygen species and oxidative burst: roles in stress, senescence and signal transduction in plants. Curr Sci. 2005; 89:1113–1121. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Jiang M, Zhang J. Cross-talk between calcium and reactive oxygen species originated from NADPH oxidase in abscisic acid-induced antioxidant defence in leaves of maize seedlings. Plant Cell Environ. 2003; 26:929–939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Rogers HJ. Is there an important role for reactive oxygen species and redox regulation during floral senescence? Plant Cell Environ. 2012; 35:217–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2011.02373.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Price AM, Aros Orellana DF, Stevens R, Acock R, Buchanan-Wollaston V, Stead AD, et al. A comparison of leaf and petal senescence in wallflowers (Erysimum linifolium) reveals common and distinct patterns of gene expression and physiology. Plant Physiol. 2008; 147:1898–1912. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.120402 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Marino D, Dunand C, Puppo A, Pauly N. A burst of plant NADPH oxidases. Trends Plant Sci. 2012; 17:9–15. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2011.10.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Müller K, Carstens AC, Linkies A, Torres MA, Leubner-Metzger G. The NADPH-oxidase AtrbohB plays a role in Aradidopsis seed after-ripening. New Phytol. 2009; 184:885–897. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.03005.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Liu SG, Zhu DZ, Chen GH, Gao XQ, Zhang XS. Disrupted actin dynamics trigger an increment in the reactive oxygen species levels in the Arabidopsis root under salt stress. Plant Cell Rep. 2012; 31:1219–1226. doi: 10.1007/s00299-012-1242-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ma W, Smigel A, Walker RK, Moeder W, Yoshioka K, Berkowitz GA. Leaf senescence signaling: the Ca2+-conducting Arabidopsis cyclic nucleotide gated channel2 acts through nitric oxide to repress senescence programming. Plant Physiol. 2010; 154:733–743. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.161356 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Zhang H, Liu Y, Wen F, Yao D, Wang L, Guo J, et al. A novel rice C2H2-type zinc finger protein, ZFP36, is a key player involved in abscisic acid-induced antioxidant defence and oxidative stress tolerance in rice. J Exp Bot. 2014; 65:5795–5809. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru313 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Zhang Y, Zhu H, Zhang Q, Li M, Yan M, Wang R, et al. Phospholipase dalpha1 and phosphatidic acid regulated NADPH oxidase activity and production of reactive oxygen species in ABA-mediated stomatal closure in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2009; 21:2357–2377. doi: 10.1105/tpc.108.062992 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Grant JJ, Loake GJ. Role of reactive oxygen intermediates and cognate redox signaling in disease resistance. Plant Physiol. 2000; 124:21–29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Xue B, Zhang A, Jiang M. Involvement of polyamine oxidase in abscisic acid-induced cytosolic antioxidant defense in leaves of maize. J Integr Plant Biol. 2009; 51:225–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2008.00766.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
(XLSX)
(XLSX)
(XLSX)
(XLSX)
(XLSX)
(XLSX)
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting Information files.