Abstract
Sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium-ATPase2a (SERCA2a), a critical regulator of calcium homeostasis is known to be decreased in heart failure. Patients with myocarditis or dilated cardiomyopathy develop autoantibodies to SERCA2a suggesting that they may have pathogenetic significance. In this report, we describe epitope mapping analysis of SERCA2a in A/J mice that leads us to make five observations: (i) SERCA2a contains multiple T cell epitopes that induce varying degrees of myocarditis. One epitope, SERCA2a 971-990 induces wide spread atrial inflammation without affecting non-cardiac tissues; the cardiac abnormalities could be non-invasively captured by echocardiography, electrocardiography and magnetic resonance microscopy imaging. (ii) SERCA2a 971-990-induced disease was associated with the induction of CD4 T cell responses and the epitope preferentially binds MHC class II/IAk rather than IEk. By creating IAk/ and IEk/SERCA2a 971-990 dextramers, the T cell responses were determined by flow cytometry to be Ag-specific. (iii) SERCA2a 971-990-sensitized T cells produce both Th1 and Th17 cytokines. (iv) Animals immunized with SERCA2a 971-990 showed Ag-specific Abs with enhanced production of IgG2a and IgG2b isotypes, suggesting that SERCA2a 971-990 can potentially act as a common epitope for both T cells and B cells. (v) Finally, SERCA2a 971-990-senstized T cells were able to transfer disease to naïve recipients. Together, these data indicate that SERCA2a is a critical autoantigen in the mediation of atrial inflammation in mice and that our model may be helpful to study the inflammatory events that underlie the development of conditions such as atrial fibrillation in humans.
Introduction
The intracellular membranous network, sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) found in the muscle cells is important in the regulation of calcium (Ca2+) homeostasis; it involves the participation of sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) as a major Ca2+ transporter (1–4). Three major and 13 sub-isoforms of SERCA have been reported in humans. SERCA1 gene encodes SERCA1a, 1b and 1c (5–7); SERCA2 gene encodes for SERCA2a, 2b, 2c, and 2d (only at mRNA level); whereas SERCA3 exists in six isoforms (SERCA3a to SERCA3f) (1, 3, 4, 8–11). All isoforms exist, except SERCA2c, SERCA2d and SERC3d to SERCA3f in mice and rats (1, 12). Amongst these, SERCA2a is expressed specifically in cardiomyocytes with greater expression in atria than in ventricles (13–15), slow-twitch skeletal muscle cells (16), and in vascular smooth muscle cells (17). While SERCA2b is expressed ubiquitously (18), SERCA2c has been recently reported to be expressed in the left ventricles (LV) in humans (19). In contrast, SERCA1 isoforms are expressed in the fast twitch skeletal muscle. SERCA3 proteins can be expressed in various tissues including hematopoietic cell lineages (4, 20–22). Thus, the functions of each isoform are likely tissue-dependent.
SERCA2a plays an indispensable role in the contractility of the heart. During contraction, action potential propagating along cardiomyocyte membranes and their invaginations, T-tubules, results in the influx of Ca2+ by opening the L-type Ca2+ channels, which then triggers the release of more Ca2+ through ryanodine receptors from the SR (23). The majority of this cytosolic Ca2+ must be sequestered by SR membrane-bound SERCA2a, which facilitates Ca2+-uptake by the SR, resulting in the relaxation of cardiomyocyte, and a minor pathway being Ca2+ extrusion via the plasma membrane Na+/Ca2+-exchanger (24, 25). Any alterations in the SERCA2a function can disturb contractibility of heart leading to heart failure (HF) (25–29).
The importance of SERCA2a in the pathogenesis of HF is well documented. Altered expression of SERCA2a has been reported in major heart diseases including ischemic heart disease, cardiomyopathies and congestive HF (29–33), in which downregulated expression of SERCA2a can result in both systolic and diastolic heart dysfunctions (34). Conversely, overexpression of SERCA2a can improve the contractile function of failing hearts and also diminish cardiac fibrosis in congestive HF by altering TGF-β signaling (35, 36). Genetically altered mouse models also support these observations. For example, SERCA2a deletion is embryonically lethal; homozygous mice do not survive (37, 38); heterozygous mice with one functional allele can survive but they suffer from severe cardiac insufficiency/hypertrophy and death (39). Likewise, mice with conditional deletion of SERCA2a in cardiomyocytes can develop end-stage HF several weeks after deletion (40, 41). Conversely, transgenic mice overexpressing SERCA2a in the cardiomyocytes show improved heart functions and increased Ca2+ storing abilities with no physiologic, (e.g. heart/body weight ratios), or histological (hypertrophy of cardiomyocytes) abnormalities (42, 43). Because patients with myocarditis or dilated cardiomyopathy show autoantibodies to SERCA2a (44, 45), SERCA2a-reactive Abs may have pathogenetic significance. In support of this proposition, mice immunized with SERCA2a can develop autoimmune myocarditis potentially mediated by SERCA2a-reactive Abs (46, 47). The antigenic determinants of SERCA2a were unknown including the T cell epitopes if any, however. Here, we describe the identification of multiple immunodominant epitopes of SERCA2a in A/J mice and show that one of these epitopes, SERCA2a 971-990, induces mainly, atrial inflammation by potentially acting as a common epitope to both T cells and B cells.
Materials and Methods
Mice
A/J mice (6- to 8-wk-old, male, H-2a) were obtained from the Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME) and the animals were maintained according to the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee guidelines, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, Lincoln, NE. Euthanasia was performed using carbon dioxide in conformity with the panel on Euthanasia, the American Veterinary Medical Association.
Peptide synthesis
Peptide library for SERCA2a was created by designing 80 overlapping acetylated peptides (20-mers with an overlap of 10 aas) containing acetyl group at the N-terminal end since the acetylated peptides have been shown to be better presented by the APCs (48–50). All these peptides, bovine RNase 43-56 (VNTFVHESLADVQA), biotinylated hen egg lysozyme (HEL) 46-61 (YNTDGSTDYGILQINSR) (Neopeptide, Cambridge, MA) and moth cytochrome C (MCC) 82-103 (FAGLKKANERADLIAYLKQATK) (GenScript, Piscataway, NJ) were synthesized by 9-fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl chemistry. The purity of peptides was ascertained by high-performance liquid chromatography to be more than 90%, and their identity was confirmed by mass spectroscopy. Ultra-pure water was used to dissolve the peptides and multiple aliquots of peptides were stored at −20°C until further use. But, some of these peptides required addition of dimethyl sulfoxide as indicated with a foot note in the Table S1.
Immunization procedures
Peptide/CFA emulsions that contain Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37RA extract (5 mg/ml, Difco Laboratories, Detroit, MI) were prepared and administered subcutaneously into mice on days 0 and 7 in the inguinal and sternum regions (51–53). In pooled settings, pools were made to include 3 to 5 peptides of 50 μg each, and for immunization with individual peptides, 50 to 100 μg of each was used. All animals received pertussis toxin (PT) (List Biological Laboratories, Campbell, CA; 100 ng/mouse i.p.,) on days 0 and 2 after the first immunization. For proliferation assay involving CD4 T cells, one dose of SERCA2a 971-990 emulsion was administered. Mice that received no peptides and those that received CFA and PT alone served as controls.
Histology
Whole heart, and samples of liver, lung, kidney, skeletal muscle and brain were collected at termination on day 21; they were fixed in 10% phosphate-buffered formalin and processed to obtain 5 μm serial sections with ~150 μm apart from each other. All sections were stained with H&E and examined by board-certified pathologists blinded to treatment and the total numbers of inflammatory cell foci were determined as we have described previously (49, 50). The degree of inflammation in hearts was scored as normal (0), mild (1–5 foci), moderate (6–25 foci), and severe (26 or more foci) as previously described (54). Fibrosis was assessed using Masson’s trichrome staining (55).
Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
Hearts were examined for the presence of T cells and non-T cells. For detection of T cells, paraffin sections were stained with rabbit anti-mouse CD3 (clone, SP7, 1:100, Abcam, Cambridge, MA), rat anti-mouse CD4 (clone, GK1.5, 1:100, Leinco Technologies, Fenton, MO) and rat anti-mouse CD8 (clone, 53-6.7, 1:100, Leinco), and their corresponding isotype controls. For non-T cells, i.e. neutrophils, macrophages, and B cells, rat anti-mouse Ly6G (clone, 1A8, 1:250, Leinco), rabbit anti-mouse CD11b (clone, EPR1344, 1:3500, Abcam) and rat anti-mouse CD19 (clone, 6OMP31, 1:1000, ThermoFisher, San Diego, CA) and their corresponding isotype controls were used. For SERCA2a expression, sections were stained with rabbit anti-mouse SERCA2a (clone, EPR9392, 1:250, Abcam) or its isotype control as primary Abs. Briefly, after deparaffinization, rehydration, and blockade of endogenous peroxidase activity with 3% hydrogen peroxide, Ag retrieval was performed by treating the sections with 10 mM sodium citrate buffer (pH 6.0) in a water bath at 98°C for 15 to 40 min or using a pressure cooker. After blocking with 5% non-fat dry milk for 30 minutes, sections were incubated with primary Abs at 4°C overnight, followed by incubation with goat anti-rabbit IgG or donkey anti-rat IgG conjugated with HRP (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA; and Abcam) as secondary Abs for 2 hours at room temperature (RT). After adding diaminobenzoic acid as a substrate for color development, sections were counterstained with hematoxylin. For quantitative evaluation of T cells (CD3+, CD4+ and CD8+) and non-T cells (Ly6G+ CD11b+ and CD19+) in the atria, three to five random areas (1.5 to 3.0 mm2) from representative sections were selected from severely affected animals, and nuclear staining was confirmed using nuclear V9 software (Aperio Technologies, Vista, CA). Number of cells positive for each marker were counted and normalized to a 1 mm2 area using Aperio ImageScope Analysis Software (Leica Biosystems, MN) as we have described previously (49).
Immunofluorescence staining
After perfusion, hearts from naïve mice were embedded in optimal cutting temperature compound and cryosections (7–10 μm) were made and stored at −80°C until further use. Sections were rehydrated with 1x PBS for 5 mins and fixed with 4% (w/v) paraformaldehyde pH 7.4 for 40 minutes at RT followed by blocking. Staining was performed to include rabbit anti-mouse SERCA2a or its isotype control as primary Abs, overnight at 4°C. Sections were washed and incubated with goat anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 647 (1:100, Abcam) for two hours in dark at RT. Finally, sections were stained with wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) Alexa Fluor 488 conjugate (ThermoFisher) for 30 minutes as a cell membrane marker (56). After washing, sections were mounted using fluoromount mounting medium and analyzed using Olympus FV500-IX81 laser scanning confocal microscope (LSCM; Olympus America Corporation, Central Valley, PA). Confocal images were acquired using the sequential dual laser-line excitation/emission mode (488nm for WGA membrane marker, and 633nm for SERCA2a (12, 57).
Electrocardiography (ECG)
ECG was performed on the anesthetized animals immunized with or without SERCA2a 971-990 (on day 23) with 3-lead ECG system (PowerLab 8/30, AD Instruments Inc., Colorado Springs, CO) and heart rates and ECG signals were monitored and recorded on LabChart 8 software (AD Instruments Inc.). The ECG waveforms recorded from individual animals were analyzed separately using ECG analysis module of LabChart 8 software, to derive average wave intervals and peak amplitudes for the groups (49).
Echocardiography and Image Analysis
Transthoracic echocardiography was performed in anesthetized animals immunized with or without SERCA2a 971-990 on day 23, and a research sonographer, blinded to the study groups, performed the measurements and analyzed the data as we reported previously (49, 50). Closed-chest imaging was performed in the short-axis view at the mid-LV level, verified by the presence of prominent papillary muscles, using a commercially available echocardiography system (Vivid 7, General Electric, Wauwatosa, WI) with an M12-L linear array transducer. Image depth was 1.5 cm, with the acquisition of 293.6 frames/second, second harmonic imaging and electrocardiographic gating. From the raw 2D image of the mid-LV, anatomical M-mode through the anteroseptal and inferolateral segments was used to measure the width of the intraventricular septum at diastole and the internal diameter of the LV at diastole and systole. End-diastolic volume (EDV) and end-systolic volume (ESV) were calculated using the Tiechholz formula: LV Volume = [7/ (2.4 + left ventricular internal diameter (LVID)] * LVID3. A cardiac cycle was defined from the peak of one R wave to the peak of the following R wave. Three consecutive heart beats were measured and the average was used for analysis.
Magnetic resonance microscopy (MRM) imaging
MRM imaging was used to determine cardiac abnormalities in mice immunized with SERCA2a 971-990 during days, 38 to 39 as we have described previously (50, 58). Anesthetized animals were placed in the animal holder equipped with respirometry and pulse oximetry to gate the respiratory and cardiac signals, and body temperature was monitored using a rectal thermometer. MRM imaging was performed using a wide-bore (89 mm) 9.4 T vertical-bore magnet (Varian, Inc., Walnut Creek, CA) equipped with triple axis gradients of 100 G/cm and a 4-cm radio-frequency imaging coil. Short axis slices (images) of hearts captured in eight-time frames using an echo-based cine pulse sequence were analyzed using Segment software (Segment v1.8 R1430, Medviso, Sweden) to assess LV wall thickness, EDV, ESV, stroke volume (SV) and ejection fraction (EF).
T cell proliferation assay
Lymph nodes (maxillary, mandibular, axillary, inguinal and popliteal) and spleens were collected at termination on day 21 post-immunization and single cell suspensions were obtained by treating the cells with RBC-lysing buffer (1x ammonium chloride potassium buffer, Lonza, Walkersville, MD). After washing, the pellets were dissolved in growth medium consisting of RPMI medium, FBS (10%), sodium pyruvate (1 mM), L-glutamine (4 mM), 1x each of non-essential amino acids and vitamin mixture, and penicillin-streptomycin (100 U/ml) (Lonza). To determine proliferative responses to SERCA2a peptides in naïve mice, splenocytes were used. In some experiments, CD4 T cells were enriched from lymph node cells (LNCs) and splenocytes to a purity of ~95 % by negative selection based on magnetic separation using IMAG (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA) (53). Cells were stimulated in triplicates with the indicated peptides (0–100 μg/ml) at a density of 5×106 cells/ml for two days, and cells in medium alone or those stimulated with RNase 43-56 served as controls. To stimulate CD4 T cells, syngeneic irradiated splenocytes loaded with peptides were used as APCs at a ratio of 1:1 (0–50 μg/ml). After pulsing with tritiated (3[H])-thymidine (1 μCi/well; MP Biomedicals, Santa Ana, CA) for 16 hours, proliferative responses were measured as cpm using a Wallac liquid scintillation counter (Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA). For easy depiction, where indicated, T cell responses are shown as fold changes derived by dividing the cpm values of cultures stimulated with peptides by the cpm values of unstimulated cultures (medium controls).
Detection of major MHC class II alleles
Flow cytometrically, expression of IAk and IEk molecules was tested in splenocytes obtained from naïve A/J mice using rat anti-mouse IAk (clone, 14V.18, ThermoFisher), anti-mouse IEk (clone, 14-4-4S, ThermoFisher), anti-mouse CD11b (clone, M1/70, eBioscience, San Diego, CA), anti-mouse CD11c (clone, N418, eBioscience) and anti-mouse CD19 (clone, 1D3, Leinco) Abs and their isotype controls and 7-aminoactinomycin D (7-AAD, Invitrogen, Waltham, MA). The percent IAk+ and IEk+ populations were determined in the live populations using FlowJo software.
MHC class II-binding assay
To determine the affinities of peptides binding to IAk allele, soluble IAk monomers were expressed using the constructs that we had reported previously (59–61). However, for IEk allele, we needed to design new IEk constructs and express soluble IEk monomers.
Creation of IEk constructs and expression of soluble IEk monomers
Extracellular portions of IEk-α and IEk-β chains that respectively contain the leucine zipper domains of Fos and Jun transcriptional factors were synthesized (Genscript). The IEk-β construct was also designed to include the nucleotide sequence of the CLIP 88-102 (gtgagccagatgcggatggctactcccttgctgatgcgtccaatg) linked with thrombin cleavage site (LVPRGS) such that upon expression, the CLIP-linked IEk protein could be obtained, and the peptides of interest could then be exchanged with CLIP. The constructs were ligated to pAcDB3 vector and sequenced. Soluble IEk molecules were then expressed in the baculovirus using sf9 cells as we have previously described (57, 59, 60). The IEk proteins were purified on anti-IEk column (clone, M5/114, BioXcell, West Lebanon, NH), and concentrated using Amicon Ultra centrifugal filters (Millipore). Empty IEk molecules were then obtained by treating the proteins with thrombin (20 units/mg) (Novagen, Madison, WI) to release the CLIP peptide.
Reaction mixtures were then prepared to include thrombin-cleaved IAk or IEk monomers (0.35 μg), competitor peptides (SERCA2a 971-990, 0.00001 μM to 100 μM, and constant amounts of the biotinylated reference peptides HEL 46-61 (for IAk) or MCC 82-103 (for IEk) (1 μM), (62–64) in a buffer containing 50 mM sodium phosphate pH 7.0, 100 mM sodium chloride, 1 mM EDTA, and 1x protease inhibitor (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO). The mixtures were incubated at RT overnight. In addition, anti-IAk (clone, 10-2.16, BioXcell), and anti-IEk Abs (10 μg/ml) were coated separately onto 96-well white fluorescence plates in 0.2 M sodium phosphate buffer, pH 6.8, and incubated overnight at 4°C. Plates were washed five times with wash buffer (1x; Perkin Elmer), and then blocked with 2% bovine casein (Sigma-Aldrich) for 2 hours at RT. After washing, the above peptide reaction mixtures were added in duplicates and the plates were incubated on a rocker at RT for 1 hour followed by washing as above. Finally, after adding 100 μl of europium-labeled streptavidin ([SA]; (0.1 μg/ml) and dissociation-enhanced lanthanide fluoroimmunoassay (DELFIA) enhancement solution (Perkin Elmer) sequentially, fluorescence intensity was measured at excitation/emission wavelengths of 340/615 nm using a Victor Multilabel Plate Reader (Perkin Elmer). The IC50 values were calculated based on the concentrations of competitor peptides that prevented 50% binding of the reference peptides (HEL 46-61 or MCC 82-103) as described previously (49, 50, 54).
Creation of MHC class II/IAk or IEk dextramers to determine Ag-specificity of T cells
To enumerate the frequencies of Ag-specific CD4 T cells, we created both IAk and IEk dextramers. To create IAk dextramers for SERCA2a 971-990, the nucleotide sequence (cctttgccgctcattttccagatcacaccgctgaatctgacccagtggctgatggtgctg) was inserted into the existing IAk-β construct that we had described previously (59, 60), whereas IAk/RNase 43-56 (control) dextramers were readily available in our laboratory (59, 65). For creation of IEk dextramers, we inserted the nucleotide sequence of SERCA2a 971-990 as above, and MCC 82-103 (control) (tttgccggtttaaagaaggcaaacgaacgtgcagatctcatcgcctatctaaaacaagctactaag) (62–64). In addition, we inserted the BirR-A site (LGGIFEAMKMELRD) for biotinylation in the 3′end of Fos sequence in the IEk-α construct (60). All three constructs, i.e. IAk/SERCA2a 971-990, IEk/SERCA2a 971-990 and IEk/MCC 82-103 were expressed in the sf9 cells using baculovirus expression system. After affinity-column purifications using anti-IAk and anti-IEk Abs, soluble IAk/SERCA2a 971-990, IEk/SERCA2a 971-990 and IEk/MCC 82-103 monomers were biotinylated and dextramers were derived using SA/fluorophore-conjugated dextran molecules as we have described previously (60, 61).
For dextramer staining, LNCs obtained from immunized animals were stimulated with SERCA2a 971-990 for two days and IL-2 medium was then added. Viable cells were harvested by Ficoll density-gradient centrifugation on day 4, and cells were rested in the IL-2 medium. Cells harvested on days, 7 to 9 post-stimulation were stained with IAk- (SERCA2a 971-990 and RNase 43-56) or IEk-dextramers (SERCA2a 971-990 and MCC 82-103) followed by anti-CD4 and 7-AAD. After washing, cells were acquired by flow cytometry and the percent dextramer+ cells were analyzed using FlowJo software (59–61).
Cytokine secretion
LNCs obtained from animals immunized with SERCA2a 971-990 were restimulated with or without specific peptide or RNase 43-56 (50 μg/ml), and culture supernatants were collected on day 3. Samples were analyzed for cytokines using beads conjugated with capture and detection Abs and standard curves were obtained by serially diluting the lyophilized mouse cytokine standard mix, consisting of IL-2, IFN-γ, IL-6, IL-10, IL-17A and TNF-α as recommended by the manufacturer (BD Biosciences). First, capture bead/cytokine Ab conjugates were mixed and added to a tube containing diluted standards or test samples, followed by addition of detection Abs, and the mixtures were incubated at RT for 2 hours. After washing, and acquisition by flow cytometry, data were analyzed by FCAP Array Software (BD Biosciences) (49, 50).
Detection of SERCA2a 971-990-reactive Abs
Serum samples were collected from mice immunized with or without SERCA2a 971-990 on day 21 post-immunization for measurement of SERCA2a-reactive Abs by ELISA. In brief, 96-well polystyrene microtiter plates were coated with or without SERCA2a 971-990 or irrelevant control (RNase 43-56) (10 μg/ml) in 1x coating buffer (eBioscience) and the plates were incubated at 4°C overnight. After washing with 1x PBS/0.05% Tween-20 and blocking with 1x PBS/2% BSA/5% normal goat serum for 1.5 hours at RT, serum samples (1:100) were added in duplicates, and the plates were incubated at 37°C for 1 hour. After washing, HRP-labeled donkey anti-mouse IgG (Santa Cruz, Dallas, TX) or HRP-labeled goat anti-mouse IgM, IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b and IgG3 (Southern Biotech, Birmingham, AL) were used as secondary Abs. Plates were incubated at RT for 2 hours, and 1x tetramethylbenzidine solution was then added as a substrate (eBioscience). Reactions were stopped using 1M phosphoric acid and the plates were read at 450 nm using an automated ELISA reader (BioTek instruments, Winooski, VT), and OD values were measured (50, 66).
Induction of experimental autoimmune myocarditis by adoptive transfer of Ag-sensitized T cells
Mice were immunized with or without SERCA2a 971-990 in CFA twice with an interval of a week and at termination on day 14, lymphocytes were prepared from spleens and lymph nodes. Cells were stimulated with Con-A (2.5×106 cells/ml; 2.5 μg/ml; Sigma-Aldrich) for two days. Viable cells were harvested and injected through retro-orbital sinus (50 to 60×106 cells/animal) into naïve mice primed with LPS (25 μg/mouse ip., on the day -4 and day 0). PT was administered ip., (100 ng/mouse) on days, 0 and 2 post-transfer. The LPS/PT-primed naïve mice and those that received Con-A-stimulated naïve splenocytes served as controls, and on day 14, animals were euthanized to collect tissues for histology.
Statistics
We used the non-parametric Wilcoxon rank sum test to test differences between groups for inflammatory foci, and infiltrates, LNC and splenocyte responses, echocardiography/MRM, MHC class II expression/binding affinities, and dextramer staining, cytokines and Ab responses. Student’s t-test was used for CD4 T cell responses. In determining T cell responses for some peptides with varied background levels, cpm values were scaled within the replicates and doses, using a constant multiplier determined by the average cpm values (49). p ≤ 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Identification of an immunodominant epitope from SERCA2a that induces atrial inflammation in A/J mice
SERCA2a is a 998 aas long protein expressed specifically in the cardiac muscle (1, 4, 46). To identify the immunodominant epitopes we sought to create an epitope library by generating 80 peptides of 20-mers with 10 aas as overlaps between each (Table S1). First, we screened for the ability of SERCA2a peptides to induce inflammation in the heart muscle by creating 18 pools with 3 to 5 peptides, in each (Table S2). Three wks after immunization, hearts were collected for assessment of inflammation by H&E staining. This analyses led us to identify 10 pools that showed varying degrees of myocarditis with a disease incidence ranging from 20% to 80% (pools I, XII, XV and XVII: 20%; pools III, VI and XI: 40% and pools VII, IX and XVIII: 80%) (Table S2). The numbers of inflammatory foci in the affected animals ranged from 1 to 68. Regardless of the presence or absence of disease, however, we determined T cell responses using LNCs from immunized animals in a recall assay to all the immunogenized peptides by using RNase 43-56 as an irrelevant control. The data presented in Table S2 show that the T cell responses were noted for one or more peptides in each of the pools that induced the disease with responses to be up to 4-folds. Conversely, the T cell responses for most peptides in pools that did not induce myocarditis (pools II, IV, V, VIII, X, XIII, XIV and XVI) were either lacking or the responses were less than two-fold (Table S2), suggesting that myocarditogenicity of SERCA2a peptides may be related to their ability to induce T cell responses.
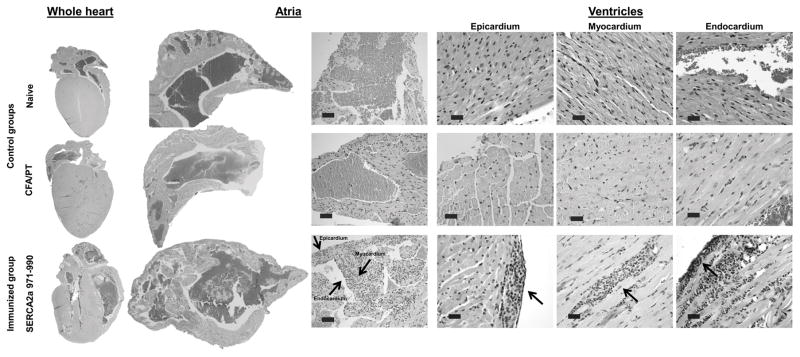
Next, we chose a panel of 13 peptides representing the pools that were associated with myocarditis as described above (pools I, III, VI, VII, IX, XI, XV, XVII and XVIII; Table S2) for further characterization. Expectedly, heart sections from naïve and CFA/PT control groups were negative for inflammatory infiltrates (Table 1). In contrast, animals immunized with six of the 13 peptides showed infiltrates leading us to identify SERCA2a 971-990 as the most potent myocarditogenic epitope followed by SERCA2a 161–180 and SERCA2a 951-970. Their respective disease incidences were 100%, 40%, and 20% and the number of inflammatory foci was 29.50 ± 8.00, 2.50 ± 0.64 and 40.00 ± 39.00 (Table 1). In fact, the inflammatory foci in two additional animals from the SERCA2a 971-990-immunized group were so extensive that their numbers could not be counted. The infiltrates predominantly contained mononuclear cells and granulocytes. More importantly, comparison of inflammation between different parts of heart tissue revealed that the inflammatory foci were evident in the atria of all animals immunized with SERCA2a 971-990 (100%, 11/11). In contrast, ventricles were affected in only ~60% (7/12) of animals and 70% (5/7) of these animals had only mild disease and the remaining two had moderate to severe disease (Table 1 and Fig. 1, left panel: whole heart). By assessing the disease severity, sections from both right and left atrial had severe inflammation in 55% of animals (>26 foci); the remaining animals showed moderate (27%, 3/11: 6 to 25 foci) or mild disease (18%, 2/11: 1 to 5 foci) (Table 1). However, when inflammation was noted, all three layers of heart muscle namely, endocardium, myocardium, and epicardium were consistently affected in the atria as compared to ventricles in the SERCA2a 971-990-immunized animals (Fig. 1, middle panel: atria; and right panel: ventricles). Likewise, mild to moderate fibrosis was noted in the atria of severely affected animals (data not shown). Furthermore, since the epitope, SERCA2a 971-990 is common to both (SERCA2a and SERCA2b) isoforms, and SERCA2b isoform is expressed preferentially in non-cardiac tissues, we examined skeletal muscle, liver, lung, kidney, and brain samples from animals immunized with SERCA2a 971-990. None of these organs showed inflammatory foci but, perivascular and peribronchiolar aggregates suggestive of interstitial pneumonia were detected in isolated sections from the lungs of SERCA2a 971-990-immunized group relative to controls (data not shown). We thus identified SERCA2a 971-990 as an epitope that preferentially induces atrial inflammation, and this epitope was chosen for further characterization.
Table 1.
Histological evaluation of myocarditis induced by SERCA2a peptides
| Group | Total incidence (%) | Severity of lesions†
|
Total inflammatory foci (Mean ± SEM) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atria | Ventricle | |||||||||
|
| ||||||||||
| Number of animals affected (%) | ||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||
| Normal | Mild | Moderate | Severe | Normal | Mild | Moderate | Severe | |||
| Naive | 0/5 (0) | 5 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 5 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 |
| CFA/PT | 0/5 (0) | 5 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 5 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 |
| SERCA2a 31-50 | 1/5 (20) | 5 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 4 | 0 (0) | 1 (20) | 0 (0) | 8.00 ± 0.00 |
| SERCA2a 161-180 | 4/10(40) | 6 | 4 (30) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 7 | 3 (30) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2.50 ± 0.64* |
| SERCA2a 171-190 | 1/5(20) | 4 | 1 (20) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 4 | 1 (20) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2.00 ± 0.00 |
| SERCA2a 311-330 | 0/5 (0) | 5 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 5 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 |
| SERCA2a 331-350 | 0/5 (0) | 5 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 5 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 |
| SERCA2a 401-420 | 1/5 (20) | 4 | 1 (20) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 5 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 5.00 ± 0.00 |
| SERCA2a 471-490 | 0/5 (0) | 5 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 5 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 |
| SERCA2a 481-500 | 0/5 (0) | 5 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 5 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 |
| SERCA2a 591-610 | 0/5 (0) | 5 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 5 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 |
| SERCA2a 601-620 | 0/5 (0) | 5 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 5 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 |
| SERCA2a 821-840 | 0/5 (0) | 5 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 5 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 |
| SERCA2a 951-970 | 2/10 (20) | 8 | 1 (10) | 0 (0) | 1 (10) | 9 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (10) | 40.00 ± 39.00 |
| SERCA2a 971-990 | 12/12 (100) | 0 | 2 (18) | 3 (27) | 6 (55)¥ | 5 | 5(41) | 1 (8) | 1 (8) | 29.50 ± 8.00***δ |
severity assessed based on the number of inflammatory foci: normal, 0; mild, 1–5; moderate, 5–25; severe, 26 and above
p< 0.001,
p< 0.05 vs. naïve and CFA/PT group
foci in two animals could not be counted as the lesions were extensive; and
atria from one mouse were not available
Figure 1. SERCA2a 971-990 induces mainly atrial inflammation.
Groups of mice were immunized with or without SERCA2a 971-990 in CFA, and after 3 wks, hearts were collected for histology. Serial sections of 5 μm thickness were made, and the sections were stained with H&E to detect inflammatory foci. The left panel shows inflammatory foci in the whole heart sections from SERCA2a 971-990-immunized mice, but not in control groups (naïve and CFA/PT). Similarly, the middle panel depicts sections from SERCA2a 971-990-immunized animals, in which, widespread diffuse inflammatory foci -comprised of mononuclear cells and granulocytes were detected in the atria involving all three layers namely, epicardium, myocardium and endocardium (arrows); such changes were lacking in the control groups. The right panel shows a few small foci in the ventricles in all three layers from the SERCA2a 971-990 group (arrows), whereas sections from control groups were normal. Representative sections from SERCA2a 971-990 (n=12 mice), and naïve and CFA/PT groups are shown (n=5 mice each).
Immunohistochemical analysis of hearts from SERCA2a 971-990-immunized mice reveals the presence of immune cells and differential expression of SERCA2a between atria and ventricles
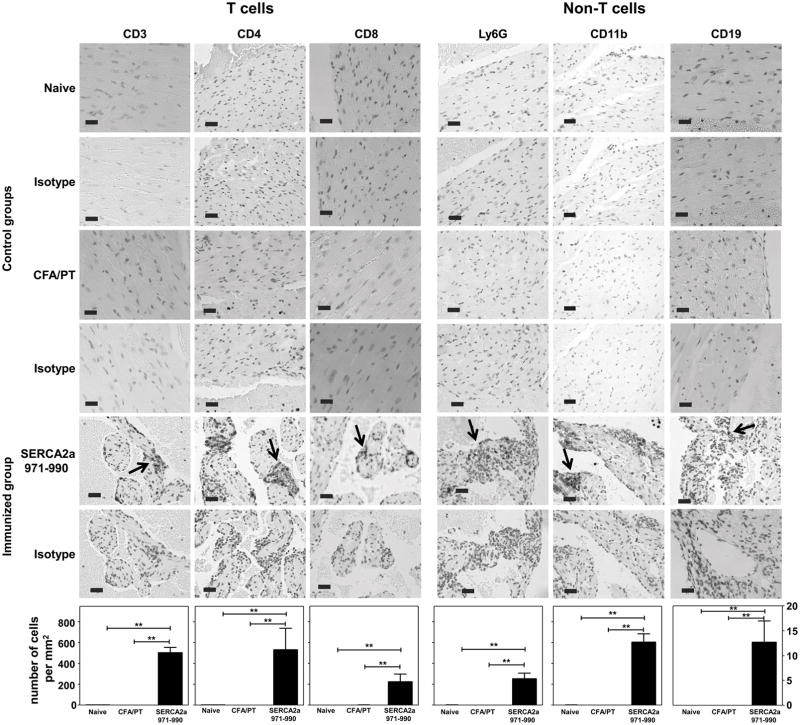
Using IHC, we sought to characterize the heart infiltrates by quantitatively analyzing T cells (CD3+, CD4+ and CD8+) and non-T cells (neutrophils: Ly6G+, macrophages: CD11b+ and B cells: CD19+). We focused on atria since inflammation because consistently detected in the atria than ventricles. As shown in figure 2, cells positive for CD3, CD4 and CD8 were present in all the sections from SERCA2a 971-990-immunized animals (Fig. 2, left panel) with CD4+ T cells (533.82 ± 206.77) present with higher frequency than CD8+ T cells (226.34 ± 94.46) (Fig. 2, lower panel). Similarly, among the non-T cell populations, macrophages were detected more frequently (608.11 ± 138.81) than neutrophils (255.19 ± 66.16) and B cells (12.75 ± 4.23). None of the sections from naïve or CFA/PT groups revealed the presence of any of the cell types tested (Fig. 2), suggesting that the inflammatory cells infiltrated in response to SERCA2a 971-990-immunizations.
Figure 2. Inflammatory infiltrates in hearts from animals immunized with SERCA2a 971-990 reveals the presence of T cells and non-T cells.
Heart sections derived from mice immunized with or without SERCA2a 971-990 were evaluated for the presence of T cells (CD3, CD4 and CD8) and non-T cells (Ly6G, CD11b and CD19) by immunohistochemistry. Ag retrieval was performed on the deparaffinized sections as described in the methods section. Numbers of immunopositive cells were then determined using the nuclear V9 software. Each bar represents mean ± SEM values (n= 4 to 6 mice per group). **p ≤ 0.01.
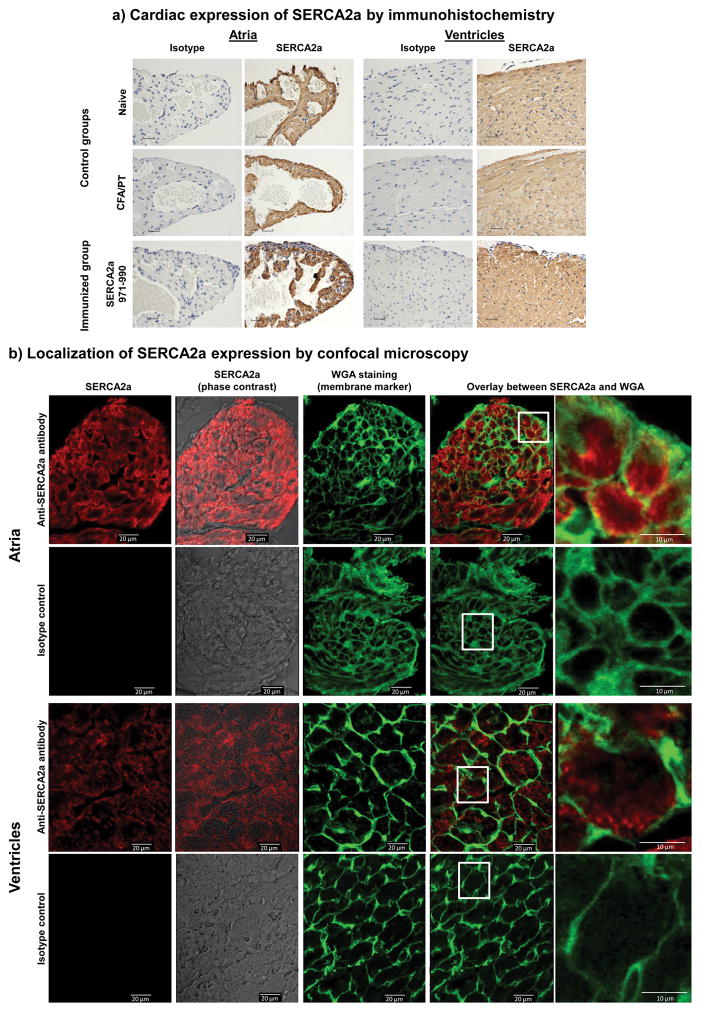
We then analyzed expression of SERCA2a to determine variations, if any, between atria and ventricles of hearts in A/J mice. We noted that SERCA2a was detected in all groups, and the staining with an anti-SERCA2a Ab was ascertained to be specific by using isotype control (Fig. 3a). Evidently, SERCA2a-expression appeared to be more concentrated in the atria than ventricles regardless of whether the animals were immunized with or without SERCA2a 971-990 (Fig. 3a, left and right panels) suggesting a possible relationship between the occurrence of inflammation and compartmentalization of expression of SERCA2a in the heart.
Figure 3. Evaluation of cardiac expression of SERCA2a by immunohistochemistry and confocal microscopy.
a) Cardiac expression of SERCA2a by immunohistochemistry. Deparaffinized heart sections from animals immunized with or without SERCA2a 971-990 were immunostained with anti-SERCA2a Ab or isotype control following antigen retrieval as described in Methods. Both atria and ventricles were diffusely immunostained with the Ab in all groups. (n=5 to 10 mice per group). b) Localization of SERCA2a expression by confocal microscopy. Cryosections prepared from naïve hearts were stained with or without rabbit anti-mouse SERCA2a or isotype control as primary Abs followed by staining with anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 647-conjugated secondary Ab, and wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) Alexa Fluor 488 conjugate which was used as a membrane marker. Fluorescence emissions were analyzed by LSCM. Atrial and ventricle sections are shown to depict sections representing staining with anti-SERCA2a alone (column 1), anti-SERCA2a overlay with phase contrast image (column 2); WGA alone (column 3); and overlay images of anti-SERCA2a and WGA (column 4) with the indicated insets magnified in column 5. Representative sections from four animals are shown.
Immunofluorescence analysis reveals expression of SERCA2a within cardiomyocytes, but close to the membrane
Using confocal microscopy, we investigated the localization of SERCA2a using Alexa Fluor 647 conjugate, and WGA as a cell membrane marker, which emit red, and green fluorescence, respectively (12, 67). The analysis revealed that SERCA2a was detected Ag-specifically within the cells in both atria and ventricles as staining with the isotype control were absent (Fig. 3b). Furthermore, by overlaying the images obtained with Alexa Fluor 647 representing the SERCA2a signal, and WGA, it was apparent that SERCA2a expression occurred within cardiomyocytes (Fig. 3b, column 4). However, detection of yellow-fluorescence representing the combination of both red and green fluorescence in the cell boundaries (Fig. 3b, column 5) suggests that SERCA2a expression may be seen close to the cell membrane, raising the question as to the significance of such an expression in cardiomyocytes.
Cardiac abnormalities can be detected non-invasively in SERCA2a 971-990-induced carditic animals
To determine whether heart abnormalities can be detected non-invasively in vivo analyzed in live animals, we used echocardiography and MRM techniques, as we have described previously (49, 50, 58) and have included ECG analysis. At 23 days post-immunization with SERCA2a 971-990, echocardiography showed a trend towards decreasing EF and fractional shortening, markers of LV systolic function as compared to healthy mice (Table 2). There were also other more subtle indicators of LV remodeling, such as increasing LVID in systole and increasing EDV (Table 2). ECG analysis also revealed a significant difference in markers of repolarization (QT interval and JT intervals, Tpeak-Tend interval and a trend with T wave amplitude indicating an underlying abnormality in the myocardial tissue (Table 2). Specifically, the Tpeak-Tend interval is a marker of ventricular arrhythmogenesis and electrical instability (68). These findings suggest that subclinical LV remodeling is occurring at 23 days post-immunization. These remodeling features become more apparent by day 38 and with improved resolution of rodent MRM. At this time, there is a further increase in ESV and a further decline in EF and SV with increased LV wall thickness (Fig. S1). Taken together, the data suggest that structural and functional abnormalities of hearts in animals immunized with SERCA2a 971-990 can be detected by ECG and echocardiography or MRM techniques.
Table 2.
Assessment of cardiac abnormalities in mice immunized with or without SERCA2a 971-990 by echo- or electrocardiography
| Parameters | Naïve mice | SERCA2a 971-990-immunized mice |
|---|---|---|
| Echocardiography | ||
| IVSd cm | 0.08 ± 0.000 | 0.08 ± 0.010 |
| LVIDd cm | 0.33 ± 0.010 | 0.34 ± 0.020 |
| LVPWd cm | 0.065 ± 0.005 | 0.064 ± 0.004 |
| LVIDs cm | 0.2 ± 0.018 | 0.224 ± 0.023 |
| EDV (T) ml | 0.095 ± 0.009 | 0.106 ± 0.015 |
| ESV (T) ml | 0.025 ± 0.006 | 0.032 ± 0.009 |
| EF (T) % | 76.61 ± 3.855 | 71.80 ± 4.248 |
| % FS | 40.377 ± 3.553 | 36.014 ± 3.786 |
| SV ml | 0.070 ± 0.004 | 0.074 ± 0.007 |
| LVD Mass ASE (g) | 0.660 ± 0.005 | 0.664 ± 0.006 |
| HR | 490.333 ± 11.203 | 540 ± 13.259 |
| Avg Beats | 3.000 ± 0.000 | 3.000 ± 0.000 |
| Electrocardiography | ||
| RR interval (s) | 0.120 ± 0.001 | 0.113 ± 0.001** |
| Heart rate (BPM) | 500.108 ± 5.845 | 532.258 ± 6.871** |
| PR interval (s) | 0.033 ± 0.001 | 0.034 ± 0.001 |
| P duration (s) | 0.015 ± 0.001 | 0.015 ± 0.001 |
| QRS interval (s) | 0.008 ± 0.000 | 0.008 ± 0.000 |
| QT interval (s) | 0.018 ± 0.001 | 0.015 ± 0.001* |
| QTc (s) | 0.052 ± 0.003 | 0.043 ± 0.002* |
| JT interval (s) | 0.010 ± 0.001 | 0.007 ± 0.000** |
| Tpeak Tend interval (s) | 0.007 ± 0.001 | 0.004 ± 0.000** |
| P amplitude (μV) | 121.657 ± 17.058 | 109.677 ± 4.406 |
| Q amplitude (μV) | −25.858 ± 5.745 | −24.959 ± 4.156 |
| R amplitude (μV) | 713.211 ± 83.796 | 581.836 ± 25.933 |
| S amplitude (μV) | −36.910 ± 12.329 | −98.980 ± 27.776* |
| ST height (μV) | 45.015 ± 12.170 | 28.783 ± 13.680 |
| T amplitude (μV) | 136.547 ± 34.257 | 179.258 ± 22.088 |
Data represents mean ± SEM;
p ≤ 0.05; and
p< 0.01
SERCA2a 971-990-induced T cell responses were restricted to CD4 T cells
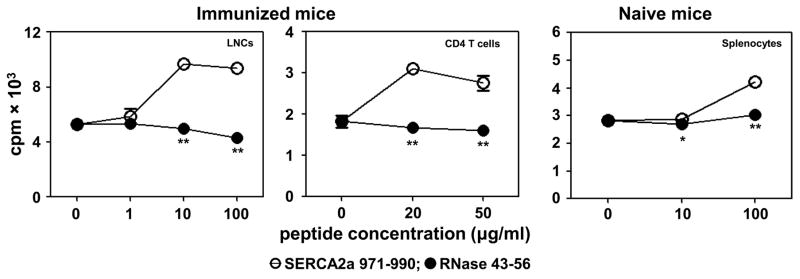
In a recall assay, we used LNCs obtained from immunized mice and stimulated the cells with SERCA2a 971-990 or control (RNase 43-56). Figure 4, left panel shows that the LNCs responded to SERCA2a 971-990 dose-dependently with a significant increase in the proliferative responses relative to medium or control (RNase 43-56). We then enriched CD4 T cells from immunized animals by magnetic separation. After ascertaining their purity (~95%), cells were stimulated with syngeneic irradiated splenocytes as APC, pulsed with SERCA2a 971-990 or RNase 43-56. As shown in Figure 4, middle panel, CD4 T cells responded to SERCA2a 971-990, but not to control (RNase 43-56), suggesting that the MHC class II-restricted CD4 T cells respond to SERCA2a 971-990. Furthermore, by evaluating proliferative responses in naïve mice, we noted that the naïve repertoire of A/J mice contained SERCA2a-reactive T cells as cells from naïve animals responded to SERCA2a 971-990 antigen-specifically (Fig. 4, right panel). The data suggest that the endogenous repertoire of T cells in A/J mice contain a proportion of SERCA2a-reactive T cells that may expand in response to SERCA2a 971-990 in immunized animals.
Figure 4. SERCA2a 971-990 induces CD4 T cell response.
Groups of mice were immunized with or without SERCA2a 971-990. At termination on day 21, LNCs and splenocytes were prepared, and CD4 T cells were enriched from immunized animals by magnetic separation. Cells were stimulated with SERCA2a 971-990 or RNase 43-56 (control) for two days and after pulsing with 3[H]-thymidine for 16 hours, proliferative responses were measured as cpm. Data from three individual experiments each involving 3 mice are shown for LNCs and splenocytes, and for CD4 T cells, data obtained from one of the two experiments involving 8 mice are shown. Comparisons were made between SERCA2a 971-990 and medium control and RNase 43-56. **p< 0.01.
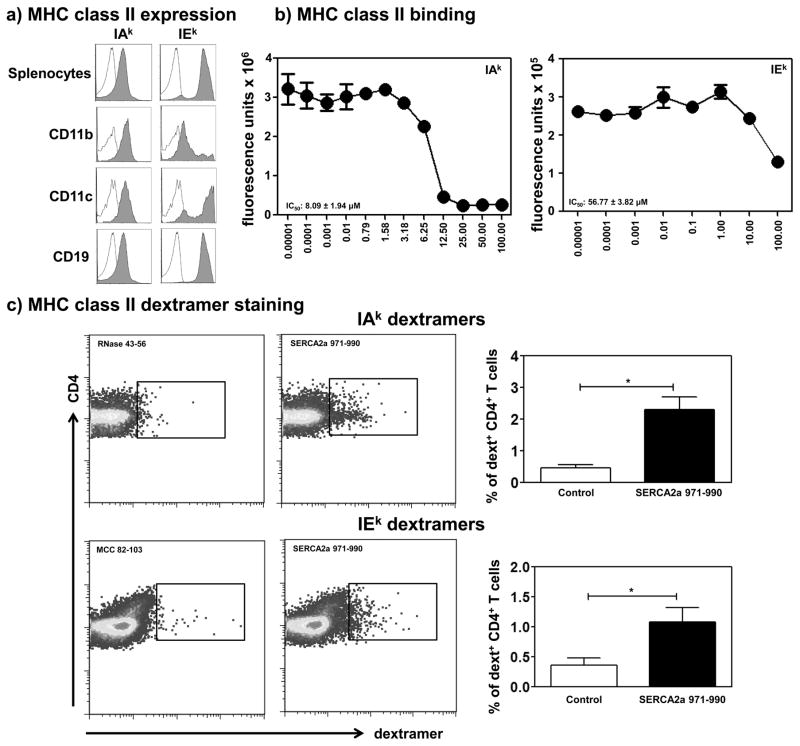
SERCA2a 971-990 is a better binder of MHC class II/IAk allele than IEk allele
CD4 T cell responses require presentation of peptides by MHC class II molecules, and we needed to confirm their expression in A/J mice. Flow cytometric analysis revealed that splenocytes from naïve mice express both IAk and IEk, and their patterns were similar between all three professional APCs (CD11b+ macrophages, CD11c+ dendritic cells and CD19+ B cells) (Fig. 5a). Next, we examined the ability of SERCA2a 971-990 to bind IAk and IEk molecules in an MHC binding assay. This effort required the creation of empty IEk molecules, and we had previously described the generation of IAk molecules (59–61). We created IEk-α and IEk-β constructs and after verifying protein expression in the baculovirus expression system and Ab affinity-column purification, the CLIP 88-102-tethered IEk monomers were treated with thrombin to generate empty IEk molecules. The IAk and IEk molecules thus derived were used in a fluorescence-based DELFIA assay to determine the IC50 values for SERCA2a 971-990 using HEL 46-61 and MCC 82-103 as reference peptides respectively for IAk and IEk alleles (49, 50, 54, 64). These analyses revealed that SERCA2a 971-990 was found to bind IAk molecule with an IC50, 8.09 ± 1.94 μM (Fig. 5b). Under similar conditions, the IC50 value obtained with IEk molecule was 56.77 ± 3.82 μM, leading us to conclude that SERCA2a 971-990 is a better binder of IAk than IEk molecule.
Figure 5. SERCA2a 971-990 is a good IAk binder and induces antigen-specific T cell responses.
a) MHC class II expression. Splenocytes from naïve mice were stained with CD11b, CD11c, CD19, IAk and IEk Abs or isotype controls and 7-AAD. Cells were acquired by flow cytometry to determine the cells positive for each marker. Empty plots, isotype controls; and filled plots, specific Abs. b) MHC class II binding. Reaction mixtures containing the constant amounts of reference peptides (HEL 46-61 for IAk and MCC 82-103 for IEk) and CLIP-cleaved, empty soluble IAk or IEk molecules with varying amounts of test peptide (SERCA2a 971-990) were incubated for 14 to 16 hours at RT. The mixtures were transferred to plates that were previously coated with anti-IAk or anti-IEk Abs, and after washing, europium-labeled SA and DELFIA enhancer were added sequentially to measure the fluorescence intensities. The IC50 mean ± SEM values are shown from four individual experiments. C) MHC class II dextramer staining. LNCs obtained from immunized animals were stimulated with SERCA2a 971-990 and the cells were rested in the IL-2 medium. Cells were harvested on days, 7 or 9 post-stimulation, and stained with IAk/SERCA2a 971-990 and RNase 43-56 (control) (top panel), and IEk/SERCA2a 971-990 and MCC 82-103 (control) dextramers (bottom panel), anti-CD4 and 7-AAD. After washing, cells were acquired by flow cytometry, and the dextramer+ CD4+ cells were enumerated using FlowJo software. Left panels represent the representative flow cytometric plots; right panels represent mean ± SEM values obtained from 4 individual experiments, each involving 2 to 3 mice. *p ≤ 0.05.
T cell responses induced by SERCA2a 971-990 are Ag-specific
We recently established dextramer technology that permitted us to enumerate the frequencies of Ag-specific T cells in a variety of experimental systems (57, 61, 69, 70). We created MHC class II dextramers for IAk molecule tethered with SERCA2a 971-990 by assembling the peptide sequence into the existing IAk construct as we described previously (59–61). To generate IEk monomers tethered with SERCA2a 971-990 or MCC 82-103, we replaced the sequence of CLIP 88-102 with the sequences of SERCA2a 971-990 and MCC 82-103 in the newly created IEk-β constructs as described above. Biotinylation site was introduced into the IEk-α construct. All IAk and IEk constructs were then expressed using the baculovirus expression system and the IAk/SERCA2a 971-990 and IEk/SERCA2a 971-990 or MCC 82-103 monomers were purified by Ab-affinity columns. After biotinylation, dextramers were derived by conjugating, IAk and IEk monomers with SA/fluorophore-conjugated dextran molecules (59–61).
For dextramer staining, we used two sets of dextramers namely, IAk/SERCA2a 971-990 (specific) and RNase 43-56 (control) (57, 59, 61) and IEk/SERCA2a 971-990 (specific) and MCC 82-103 (control) (64). LNCs harvested from immunized animals were stimulated with SERCA2a 971-990 and later rested in the IL-2 medium were analyzed for their ability to bind dextramers by flow cytometry. Fig. 5c shows binding of Ag-sensitized CD4 T cells to both IAk/ and IEk/SERCA2a 971-990 dextramers. The staining was specific since the staining intensities obtained with the corresponding control dextramers (RNase 43-56 or MCC 82-103) were negligible (Fig. 5c, left panel). The respective mean ± SEM values in percentages were as follows: IAk dextramers: SERCA2a 971-990, 2.30 ± 0.41 vs. RNase 43-56, 0.47 ± 0.10 (p= 0.02) and IEk dextramers: SERCA2a 971-990, 1.09 ± 0.23 vs. MCC 82-103, 0.37 ± 0.11 (p= 0.05) (Fig. 5c, right panel). The data suggest that the T cell responses induced with SERCA2a 971-990 were Ag-specific and might have contributed to the cardiac inflammation found in the immunized animals.
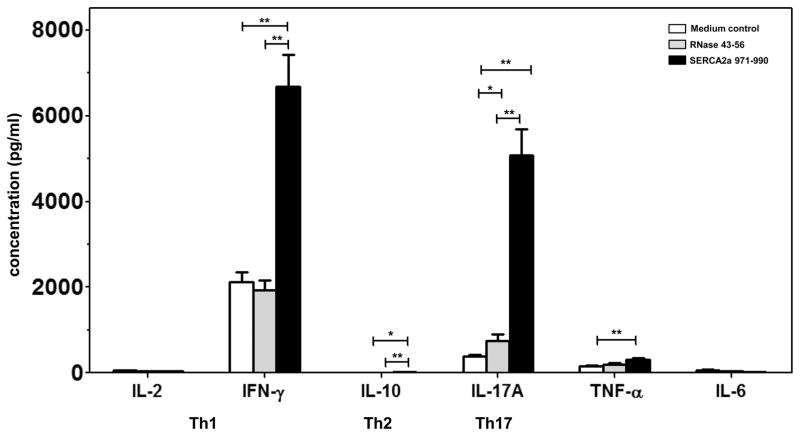
Evaluation of the pathogenic potential of SERCA2a 971-990-sensitized T cells reveals detection of Th1 and Th17 cytokines
Using a panel of cytokine Abs for Th1 (IL-2 and IFN-γ), Th2 (IL-10), Th17 (IL-17A), TNF-α and IL-6, we determined the cytokine production by bead array analysis (49, 50). LNCs obtained from immunized animals were stimulated with or without SERCA2a 971-990 (specific) and irrelevant control (RNase 43-56) and the culture supernatants harvested on day 3 were used for cytokine analysis. The analyses revealed the presence of all cytokines tested, but their amounts varied in the order of Th1 and Th17 cytokines followed by TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-10 (Fig. 6). When the cytokine responses were compared between SERCA2a 971-990-stimulated cultures and controls, it was clear that production of IFN-γ, IL-17, TNF-α but not IL-6 was significantly elevated in the immunized group (Fig. 6). These inflammatory cytokines are expected to be increased in the settings of autoimmunity. It is to be noted, however, that the production of IL-10 being an anti-inflammatory cytokine, was also increased in SERCA2a 971-990 cultures, but its amount was negligible vis-a-vis inflammatory cytokines, in particular, IFN-γ (17.07 ± 3.18 vs 6682.85 ± 749.44; 394-fold) and IL-17 (17.07 ± 3.18 vs 5080.41 ± 601.74; 298-fold). These observations suggest a possible relationship between the ability of SERCA2a peptides to produce proinflammatory cytokines and the occurrence of myocarditis in the immunized animals.
Figure 6. SERCA2a 971-990 induces mainly Th1 and Th17 responses.
LNCs obtained from immunized animals were stimulated with or without SERCA2a 971-990 or RNase 43-56 and the culture supernatants were harvested on day 3 post-stimulation. Cytokine production was analyzed for a panel of Th1 (IL-2 and IFN-γ), Th2 (IL-10) and Th17 (IL-17A), and TNF-α and IL-6 cytokines by cytokine bead array analysis as described in the methods section. Data represent mean ± SEM values combined from six individual experiments, each involving 2 to 3 mice. *p<0.05, **p< 0.01.
To address the above theme, we first evaluated T cell responses using a panel of 12 other SERCA2a peptides. In a proliferation assay, LNCs obtained from immunized animals responded to the immunized peptides in an Ag-specific manner, as expected, and the responses to control (RNase 43-56) were negligible (Fig. S2, panel a and panel b). However, by relating the T cell responses to the disease-inducing abilities of each peptide, we identified two patterns of peptides, i.e. peptides that induce T cell responses but with mild myocarditis (SERCA2a 31-50, SERCA2a 161-180, SERCA2a 171-190, SERCA2a 401-420 and SERCA2a 951-970), and peptides that induce T cell responses but not disease (SERCA2a 311-330, SERCA2a 331-350, SERCA2a 471-490, SERCA2a 481-500, SERCA2a 591-610, SERCA2a 601-620 and SERCA2a 821-840) (Fig. S2, panel a and b, and Table 1). To determine whether mild disease induced with some of the SERCA2a peptides may be related to their differential cytokine production, we tested the supernatants representing two peptides namely, SERCA2a 31-50 and SERCA2a 161-180. Although their cytokine patterns were largely similar to the potent peptide that we had described above (SERCA2a 971-990; Fig. 6), the amounts of cytokines produced varied. Importantly, SERCA2a 31-50 produced mainly IFN-γ (Fig. S2c, left panel), whereas SERCA2a 171-190 was found to be a poor producer of IFN-γ and IL-17 (Fig. S2c, right panel). These data indicate that production of proinflammatory cytokines, in particular, IFN-γ and IL-17 together may contribute to SERCA2a 971-990-induced myocarditis, but other factors may also play a role.
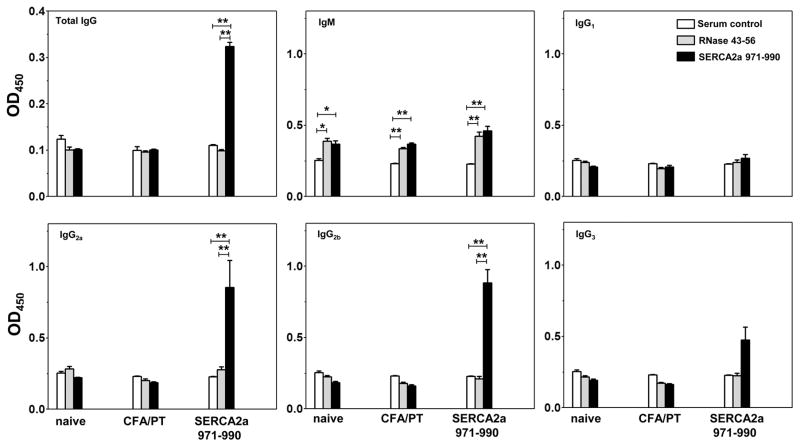
SERCA2a 971-990 may be a B cell epitope
We asked whether animals immunized with SERCA2a peptides produce Ag-specific, autoantibodies, and if so, what their isotypes are, given the dominance of Th1 than Th2 responses. We addressed this question by analyzing the sera samples obtained from SERCA2a 971-990-immunized animals for total IgG, and various isotypes by using SERCA2a 971-990 (specific) and RNase 43-56 (irrelevant control) as plate-bound Ags by ELISA (Fig. 7). In addition, we used two other control groups namely, sera from naïve mice and CFA/PT groups. These comparisons led us to make three observations: (i) Sera from the immunized animals reacted specifically to SERCA2a 971-990, but not RNase 43-56, and the amount of total IgG was significantly elevated in animals immunized with SERCA2a 971-990 as compared with naïve or CFA/PT groups. (ii) While reactivity to IgM isotype was not specific to SERCA2a 971-990 as sera from naïve and CFA/PT groups yielded similar reactivity suggesting a background response, the amounts of IgG1 and IgG3 were not significantly different in SERCA2a 971-990-immunized animals; and (iii) Production of two other isotypes namely, IgG2a and IgG2b was significantly elevated in the SERCA2a 971-990 group Ag-specifically, and such a reactivity was absent for RNase 43-56 (Fig. 7). Because the total IgG and two IgG isotypes (IgG2a and IgG2b) were significantly elevated in SERCA2a 971-990-immunized animals, (which also showed Ag-specific IFN-γ and IL-17A responses in significant amounts [Fig. 6]), SERCA2a 971-990 can potentially act as a common epitope for both B cells and T cells; moreover, IFN-γ and IL-17A might influence isotope switching (71).
Figure 7. SERCA2a 971-990-induced Abs are antigen-specific.
Serum was collected from mice on day 21 post-immunization, and the 1:100 diluted samples were added to low-binding plates that were previously coated with or without SERCA2a 971-990 or RNase 43-56 (control), and then blocked with BSA. After adding HRP-conjugated, rat anti-mouse IgG or goat-anti-mouse detection Abs for different isotypes, plates were read at 450 nm to derive the OD values. (Sera were used from 5 to 7 animals per group). *p< 0.05, **p< 0.01.
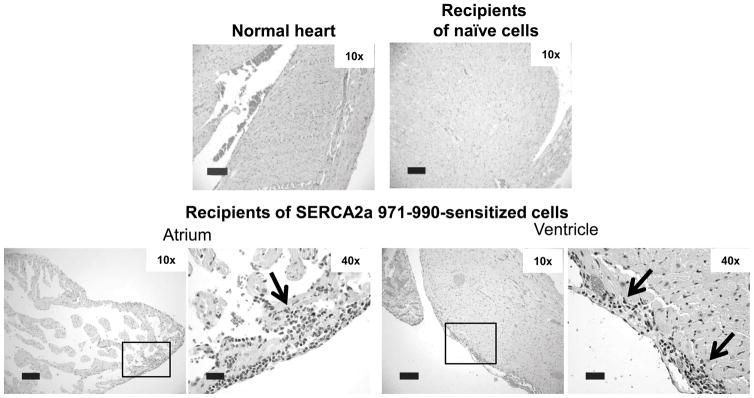
SERCA2a 971-990-reactive T cells are pathogenic
To determine that the SERCA2a 971-990-sensitized T cells are pathogenic, we used an adoptive transfer protocol. Lymphocytes obtained from immunized animals were stimulated with a polyclonal activator, Con-A, and the viable cells were injected into naïve mice primed with LPS and PT as we have previously described (49, 50). Heart sections prepared at termination on day 14 post-transfer showed lesions tended to be more in the atria than ventricles in animals that received the SERCA2a 971-990-sensitized T cells (Fig. 8). In contrast, heart sections from naïve mice or those that received naïve splenocytes and LNCs stimulated with Con-A were negative for inflammation. These findings are consistent with our previous observations that the animals receiving cells sensitized with an irrelevant control, RNase 43-56 also do not show lesions in the hearts (49). The data further reinforce the proposition that SERCA2a 971-990 induces cardiac inflammation through the generation of autoreactive T cells.
Figure 8. SERCA2a 971-990-reactive T cells can transfer disease to naïve recipients.
Lymphocytes obtained from mice immunized with or without SERCA2a 971-990 were stimulated with Con-A for two days and the viable cells were administered by retro-orbital route into LPS-primed naïve mice. Animals were euthanized on day 14 post-transfer, and hearts were examined for inflammatory changes by H&E staining. Sections from normal heart and recipients of naïve cells show no cardiac inflammation. Recipients of cells from mice immunized with SERCA2a 971-9 show atrial inflammation and epicardial inflammation adjacent to a ventricle. Section from normal heart and recipients of naïve cells (n=2 to 3 mice); and cells from SERCA2a 971-990-iimunized mice were shown (n=4 mice).
Discussion
In this report, we have described the characterization of an immunodominant epitope of SERCA2a that induces mainly atrial inflammation in A/J mice by generating Ag-specific T cell and Ab responses. SERCA2a, 110 kDa protein, is a membrane enzyme accounts for ~40% of the protein in the SR (1, 2, 4), and because of the critical role in the Ca2+ homeostasis for sustained cardiac contractility, SERCA2a is being used as a therapeutic target in HF patients (72). SERCA2a is conserved in both animal and plant kingdoms and has been implicated in cellular proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis and signal transduction events (73–75). That SERCA2a may act as an autoantigen has been proposed because patients with myocarditis and dilated cardiomyopathy can carry SERCA2a-reactive autoantibodies (29, 44, 47, 76). Experimentally, autoimmune myocarditis in SERCA2a-immunized mice was ascribed to autoantibodies that are believed to enter through T-tubules or their pores to bind SERCA2a (46, 47), but the antigenic determinants were unknown. Furthermore, because T cell help is critical for B cells to produce Abs, and autoimmune myocarditis is typically mediated by T cells (77–80), we sought to characterize the immunodominant epitopes of SERCA2a and determine their ability to induce cardiac autoimmunity.
For initial screening, a total of 80 overlapping peptides made in 18 pools were used to immunize A/J mice, and after identifying the positive pools that resulted in myocarditis, selected peptides were used for individual testing. These analyses led us to identify 13 peptides that induced disease of varying severity, and we selected SERCA2a 971-990 as the potent disease-inducer for further characterization. Remarkably, the disease induced with SERCA2a 971-990 was distinct in that inflammation and fibrosis were confined to atria in the majority of animals and ventricles were less frequently affected. When they were affected, however, inflammation was noted in all three layers of the heart, (epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium) leading to the conclusion that SERCA2a 971-990 can act as an autoantigen in the induction of atrial inflammation. Atrial fibrillation (AF) is one of the common arrhythmias seen in clinical practice (81). There is growing evidence that atrial inflammation may act as an important trigger of AF (82). This is important because cardiac fibrosis being considered as one hallmark of AF can progressively arise from various causes (83). In fact, overt or low-grade subclinical inflammation, including expression of various inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, can culminate into apoptosis of cardiomyocytes, recruitment of fibroblasts and extracellular matrix deposition and also progression from paroxysmal to chronic AF or recurrence of AF (83, 84). Therefore, anti-inflammatory treatment options are being considered in the management of AF patients (82, 85). We thus propose that SERCA2a 971-990 induced atrial myocarditis model may be useful to study the AF that occurs in humans, but the relevant immunodominant epitopes of SERCA2a may be influenced by HLA haplotypes.
While the structural and functional abnormalities of hearts in SERCA2a 971-990-immunized animals could be captured noninvasively by echocardiography and MRM imaging, IHC analysis revealed the presence of CD4 T cells to be more than CD8 T cells, and non-T cells in the decreasing order of macrophages, neutrophils and B cells. Of these, detection of increased numbers of CD4 T cells than CD8 T cells, and macrophages signify the hallmarks of delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) reaction, as expected in a T cell mediated disease (86–88); neutrophils might have emigrated as a part of the ongoing inflammatory process. As reported previously in other mouse strains (89), A/J mice also carry a proportion of T cells that are double positive for both CD4 and CD8 coreceptors, and the presence of CD8 T cells in heart infiltrates may represent this subset of T cells. Detection of B cells, may suggest a role for them alone or together with T cells in the mediation of atrial inflammation.
Mechanistically, we first determined that SERCA2a 971-990 induces T cell responses by using LNCs from immunized animals. To prove their Ag-specificity, we decided to create MHC class II dextramers for SERCA2a 971-990. This effort required us to create dextramers for two different MHC class II alleles (IAk and IEk) as A/J mice express both. Initially, we confirmed that SERCA2a 971-990 binds both alleles with the affinity being better for IAk than IEk, but both IAk- or IEk-tethered, SERCA2a 971-990 dextramers bind CD4 T cells with specificity suggesting that SERCA2a 971-990 displayed by both alleles can trigger T cell responses. In addition, by using splenocytes from naïve mice, we noted that their peripheral repertories contain a proportion of SERCA2a 971-990-reactive T cells. Reports indicate that SERCA2a is expressed at a low level in the fetal thymus in both humans and mice (1) and detection of SERCA2a-reactive T cells may mean that the developing thymocytes might have escaped negative selection as reported for other autoantigens like cardiac myosin and proteolipid protein (90, 91). Translationally, if such a scenario exists in humans, then the genetically susceptible individuals can potentially carry SERCA2a-reactive T cells making them vulnerable to the development of atrial myocarditis in infection or non-specific inflammatory conditions that can trigger autoreactive T cells through bystander activation (92).
We next investigated the pathogenic potential of T cell responses induced by SERCA2a 971-990 by evaluating cytokine production and the analysis revealed the dominance of both IFN-γ-producing Th1 and IL-17A-producing Th17 responses followed by TNF-α. Although IL-10 production was also noted in SERCA2a 971-990-sensitized cultures, the amount was negligible in relation to IFN-γ and IL-17A implying that the effects of inflammatory cytokines are expected to prevail in the local milieu as we have recently noted with two mitochondrial Ags, adenine nucleotide translocator1 (50) and branched chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase kinase (49). Generally, it is held that the pathogenic self-reactive T cell responses are steered towards Th1 and Th17 cytokine phenotypes (93–95). However, unlike the autoimmune myocarditis model induced by cardiac myosin heavy chain-alpha 334-352, in which some degree of contradiction exists as to whether Th1 cytokines act as pro- or anti-inflammatory (96), detection of comparable amounts of both Th1 and Th17 cytokines in SERCA2a 971-990-senstized cultures may point to a possibility that both subsets of cytokines may contribute to the disease pathogenesis. In support of this proposition, T cells sensitized with SERCA2a 971-990 could transfer the disease to naïve mice. However, it should be noted that a theme is now emerged that while Th1 cytokine, IFN-γ mediates initiation of myocarditis, IL-17A is essential for progression of myocarditis leading to dilated cardiomyopathy (55, 94, 97). In our model, we have not investigated whether one subset of Th cytokines is dispensable over the other (Th1 vs Th17) in the induction of atrial myocarditis as mice deficient for IFN-γ or IL-17 on A/J background are not available. We believe that both cytokines are essential for disease-induction by SERCA2a 971-990 based on the observation that two other epitopes that induce only mild disease generate mainly IFN-γ (SERCA2a 31-50) or underproduction of both IFN-γ and IL-17A (SERCA2a 161-180) in relation to SERCA2a 971-990.
We also investigated whether SERCA2a 971-990 can induce Abs since B cells were detected in the heart sections from SERCA2a 971-990-immunized animals, but not in the control groups. Analysis of Ab responses revealed that the sera obtained from SERCA2a 971-990-immunized group showed significantly higher amounts of total IgG, and IgG2a and IgG2b isotypes. Since SERCA2a 971-990-sensitized T cells produce a significant amount of IFN-γ that can induce isotype switching of IgG2a (98), and to a lesser extent that IL-17A can also influences IgG2b-switching (71), the SERCA2a 971-990-specific T cells might have facilitated isotype switching in SERCA2a 971-990-specific B cells. Whether SERCA2a 971-990-reactive Abs induce the disease like SERCA2a 971-990-reactive T cells is currently unknown. This effort involves the generation of large quantities of Ag-specific polyclonal sera or monoclonal Abs to be able to test in an adoptive transfer setting.
In summary, we have described that SERCA2a 971-990 is a major immunodominant epitope that induces preferentially atrial inflammation in A/J mice. SERCA2a expression has been reported to be more in atria than ventricles (15), and we confirm that A/J mice also follow a similar pattern (Fig. 3a). While, this finding provides support for the preferential occurrence of inflammation in atria, how SERCA2a-reactive T cells can possibly see the Ag expressed by the SR is currently unknown. Reports suggest that SR lies close to the T-tubules which are the invaginations of the plasma membrane (12), and it may be possible that SERCA2a 971-990 located in the C-terminal cytoplasmic loop may gain an access to the cell membrane by unknown mechanism. It may be possible that the local resident APCs may display peptide fragments of SERCA2a, and such a possibility has been shown for cardiac myosin in A/J mice (99, 100). Likewise, acquisition of self-Ags by the APCs may be possible through phagocytosis of dead cells or autophagy (101). Similarly, it is possible that misfolded intracellular proteins as might occur due to mutations in mitochondrial proteins like pyruvate dehydrogenase, superoxide dismutase and branched chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase kinase (102–105) or self-Ags undergoing post-translational modifications acting as neoantigens, can be seen by the immune system as foreign, leading to the induction of autoimmune responses (106). Whether these speculative theories are relevant to SERCA2a remain to be investigated in the future. We had expected that SERCA2a 971-990-immunized mice might show inflammatory changes in non-cardiac tissues because SERCA2b that expresses ubiquitously also carry this epitope in both humans and mice, but it was not the case. Such a finding may also lend support for a proposition that the immunodominant epitopes of SERCA2a might be presented by the local APCs within the hearts, but not in other organs. Furthermore, in addition to SERCA2a 971-990, epitope mapping also revealed the existence of at least 12 other epitopes capable of inducing T cell responses and they were grouped into those that induce only mild or no disease. While the existence of such a large number of immunodominant epitopes within a single protein is relatively unusual, the finding that A/J mice express two MHC alleles may facilitate the presentation of multiple epitopes. The availability of such a model system may also create opportunities to investigate the phenomenon of intramolecular epitope spreading in inflammatory cardiomyopathies induced by cardiotropic pathogens like Coxsackie virus B and Trypanosoma cruzi.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Source of support: This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health [HL114669].
BK, CM, AG and JR: Conceived and designed the experiments; BK, CM, RB, MZA, VKS and JLS: performed the in vivo and in vitro experiments; BK, SSN, RAR, PKM, YZ, RAS and DS: performed histology, and immunofluorescence and confocal microscopy; JJR: analyzed the data; and BK, JLS, and JR: wrote the paper. We thank the sonographer, Leanne Harmman for the echocardiogram images.
New abbreviations
- AF
Atrial fibrillation
- 7-AAD
7-aminoactinomycin D
- Ca2+
calcium
- DELFIA
dissociation-enhanced lanthanide fluoroimmunoassay
- DTH
delayed-type hypersensitivity
- ECG
electrocardiography
- EDV
end-diastolic volume
- EF
ejection fraction
- ESV
end-systolic volume
- HEL
hen egg lysozyme
- HF
heart failure
- 3[H]-thymidine
tritiated-thymidine
- IHC
immunohistochemistry
- LNCs
lymph node cells
- LSCM
laser scanning confocal microscope
- LV
left ventricular
- LVID
left ventricular internal diameter
- MCC
moth cytochrome C
- MRM
magnetic resonance microscopy
- PT
pertussis toxin
- RT
room temperature
- SA
streptavidin
- SERCA
sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase
- SR
sarcoplasmic reticulum
- SV
stroke volume
- WGA
wheat germ agglutinin
Footnotes
6. Conflict of interest
The authors declare no financial or commercial conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Periasamy M, Kalyanasundaram A. SERCA pump isoforms: their role in calcium transport and disease. Muscle & nerve. 2007;35:430–442. doi: 10.1002/mus.20745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Martonosi AN, Pikula S. The structure of the Ca2+-ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Acta Biochimica Polonica. 2003;50:337–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Misquitta C, Mack D, Grover A. Sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca 2+(SERCA)-pumps: link to heart beats and calcium waves. Cell calcium. 1999;25:277–290. doi: 10.1054/ceca.1999.0032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wuytack F, Raeymaekers L, Missiaen L. Molecular physiology of the SERCA and SPCA pumps. Cell calcium. 2002;32:279–305. doi: 10.1016/s0143416002001847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Brandl CJ, Green NM, Korczak B, MacLennan DH. Two Ca2+ ATPase genes: homologies and mechanistic implications of deduced amino acid sequences. Cell. 1986;44:597–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90269-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Brandl C, Martin D, MacLennan D. Adult forms of the Ca2+ ATPase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Expression in developing skeletal muscle. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1987;262:3768–3774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Guglielmi V, Vattemi G, Gualandi F, Voermans NC, Marini M, Scotton C, Pegoraro E, Oosterhof A, Kósa M, Zádor E. SERCA1 protein expression in muscle of patients with Brody disease and Brody syndrome and in cultured human muscle fibers. Molecular genetics and metabolism. 2013;110:162–169. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2013.07.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gunteski-Hamblin AM, Greeb J, Shull G. A novel Ca2+ pump expressed in brain, kidney, and stomach is encoded by an alternative transcript of the slow-twitch muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase gene. Identification of cDNAs encoding Ca2+ and other cation-transporting ATPases using an oligonucleotide probe derived from the ATP-binding site. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1988;263:15032–15040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lytton J, Westlin M, Burk SE, Shull GE, MacLennan DH. Functional comparisons between isoforms of the sarcoplasmic or endoplasmic reticulum family of calcium pumps. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1992;267:14483–14489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lipskaia L, Limon I, Bobe R, Hajjar R. Calcium cycling in synthetic and contractile phasic or tonic vascular smooth muscle cells. INTECH Open Access Publisher; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Van den Bosch L, Eggermont J, De Smedt H, Mertens L, Wuytack F, Casteels R. Regulation of splicing is responsible for the expression of the muscle-specific 2a isoform of the sarco/endoplasmic-reticulum Ca2+-ATPase. Biochemical Journal. 1994;302:559–566. doi: 10.1042/bj3020559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lipskaia L, Keuylian Z, Blirando K, Mougenot N, Jacquet A, Rouxel C, Sghairi H, Elaib Z, Blaise R, Adnot S. Expression of sarco (endo) plasmic reticulum calcium ATPase (SERCA) system in normal mouse cardiovascular tissues, heart failure and atherosclerosis. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Research. 2014;1843:2705–2718. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.08.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zarain-Herzberg A, MacLennan D, Periasamy M. Characterization of rabbit cardiac sarco (endo) plasmic reticulum Ca2 (+)-ATPase gene. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1990;265:4670–4677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.MacLennon D, Brandl C, Korczak B, Green N. Amino-acid sequence of a Ca2-Mg2-dependent ATPase from rabbit muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum, deduced from its complementary DNA sequence. Nature. 1985;316:696–700. doi: 10.1038/316696a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lüss I, Boknik P, Jones LR, Kirchhefer U, Knapp J, Linck B, Lüss H, Meissner A, Müller FU, Schmitz W. Expression of cardiac calcium regulatory proteins in atrium v ventricle in different species. Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology. 1999;31:1299–1314. doi: 10.1006/jmcc.1999.0962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Zhang KM, Hu P, Wang SW, Wright LD, Wechsler AS, Spratt JA, Briggs F. Fast-and slow-twitch isoforms (SERCA1 and SERCA2a) of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase are expressed simultaneously in chronically stimulated muscle fibers. Pflügers Archiv European Journal of Physiology. 1997;433:766–772. doi: 10.1007/s004240050343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wu KD, Bungard D, Lytton J. Regulation of SERCA Ca 2+ pump expression by cytoplasmic [Ca 2+] in vascular smooth muscle cells. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology. 2001;280:C843–C851. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.2001.280.4.C843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Arai M, Otsu K, MAcLENNAN DH, Periasamy M. Regulation of sarcoplasmic reticulum gene expression during cardiac and skeletal muscle development. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology. 1992;262:C614–C620. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.3.C614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Dally S, Bredoux R, Corvazier E, Andersen JP, Clausen JD, Dode L, Fanchaouy M, Gelebart P, Monceau V, Del Monte F. Ca2+-ATPases in non-failing and failing heart: evidence for a novel cardiac sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase 2 isoform (SERCA2c) Biochemical Journal. 2006;395:249–258. doi: 10.1042/BJ20051427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Anger M, Samuel JL, Marotte F, Wuytack F, Rappaport L, Lompré AM. The sarco (endo) plasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase mRNA isoform, SERCA 3, is expressed in endothelial and epithelial cells in various organs. FEBS letters. 1993;334:45–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81677-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Martin V, Bredoux R, Corvazier E, van Gorp R, Kovàcs T, Gélébart P, Enouf J. Three Novel Sarco/endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) 3 Isoforms EXPRESSION, REGULATION, AND FUNCTION OF THE MEMBERS OF THE SERCA3 FAMILY. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2002;277:24442–24452. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M202011200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chaâbane C, Corvazier E, Bredoux R, Dally S, Raïes A, Villemain A, Dupuy E, Enouf J, Bobe R. Sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca 2+ ATPase type 3 isoforms (SERCA3b and SERCA3f): distinct roles in cell adhesion and ER stress. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 2006;345:1377–1385. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.05.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Periasamy M, Bhupathy P, Babu GJ. Regulation of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase pump expression and its relevance to cardiac muscle physiology and pathology. Cardiovascular research. 2008;77:265–273. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvm056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Scheitlin CG. Experimental and Computational Study of Calcium Homeostasis in Sheared Endothelial Cells: Role of Mitochondria. The Ohio State University; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Periasamy M, Huke S. SERCA pump level is a critical determinant of Ca 2+ homeostasis and cardiac contractility. Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology. 2001;33:1053–1063. doi: 10.1006/jmcc.2001.1366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Feridooni HA, Dibb KM, Howlett SE. How cardiomyocyte excitation, calcium release and contraction become altered with age. Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology. 2015;83:62–72. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Braunwald E. The war against heart failure: the Lancet lecture. The Lancet. 2015;385:812–824. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61889-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bers DM. Altered cardiac myocyte Ca regulation in heart failure. Physiology. 2006;21:380–387. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00019.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bers DM, Eisner DA, Valdivia HH. Am Heart Assoc. 2003. Sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ and heart failure. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Arai M, Alpert NR, MacLennan DH, Barton P, Periasamy M. Alterations in sarcoplasmic reticulum gene expression in human heart failure. A possible mechanism for alterations in systolic and diastolic properties of the failing myocardium. Circulation Research. 1993;72:463–469. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.2.463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Flesch M, Schwinger R, Schnabel P, Schiffer F, Gelder Iv, Bavendiek U, Südkamp M, Kuhn-Regnier F, Böhm M. Sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca 2+ ATPase and phospholamban mRNA and protein levels in end-stage heart failure due to ischemic or dilated cardiomyopathy. Journal of molecular medicine. 1996;74:321–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00207509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wu P, Zhai Y, Li D. The function and significance of SERA2a in congestive heart failure: an analysis of gene therapy trials. Histology and histopathology. 2017:11878. doi: 10.14670/HH-11-878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Talukder M, Zweier JL, Periasamy M. Targeting calcium transport in ischaemic heart disease. Cardiovascular research. 2009;84:345–352. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvp264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Schmidt U, Hajjar RJ, Helm PA, Kim CS, Doye AA, Gwathmey JK. Contribution of abnormal sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase activity to systolic and diastolic dysfunction in human heart failure. Journal of molecular and cellular cardiology. 1998;30:1929–1937. doi: 10.1006/jmcc.1998.0748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Shi J, Dai W, Hale SL, Brown DA, Wang M, Han X, Kloner RA. Bendavia restores mitochondrial energy metabolism gene expression and suppresses cardiac fibrosis in the border zone of the infarcted heart. Life sciences. 2015;141:170–178. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2015.09.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Liu Y, Huang H, Xia W, Tang Y, Li H, Huang C. NADPH oxidase inhibition ameliorates cardiac dysfunction in rabbits with heart failure. Molecular and cellular biochemistry. 2010;343:143–153. doi: 10.1007/s11010-010-0508-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ji Y, Lalli MJ, Babu GJ, Xu Y, Kirkpatrick DL, Liu LH, Chiamvimonvat N, Walsh RA, Shull GE, Periasamy M. Disruption of a single copy of the SERCA2 gene results in altered Ca2+ homeostasis and cardiomyocyte function. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2000;275:38073–38080. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M004804200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Periasamy M, Reed TD, Liu LH, Ji Y, Loukianov E, Paul RJ, Nieman ML, Riddle T, Duffy JJ, Doetschman T. Impaired cardiac performance in heterozygous mice with a null mutation in the sarco (endo) plasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase isoform 2 (SERCA2) gene. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1999;274:2556–2562. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.4.2556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Schultz JEJ, Glascock BJ, Witt SA, Nieman ML, Nattamai KJ, Liu LH, Lorenz JN, Shull GE, Kimball TR, Periasamy M. Accelerated onset of heart failure in mice during pressure overload with chronically decreased SERCA2 calcium pump activity. American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 2004;286:H1146–H1153. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00720.2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Li L, Louch WE, Niederer SA, Aronsen JM, Christensen G, Sejersted OM, Smith NP. Sodium accumulation in SERCA knockout-induced heart failure. Biophysical journal. 2012;102:2039–2048. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.03.045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Li L, Louch W, Niederer S, Andersson K, Christensen G, Sejersted O, Smith N. Calcium dynamics in the ventricular myocytes of SERCA2 knockout mice: a modeling study. Biophysical journal. 2011;100:322–331. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.11.048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Baker DL, Hashimoto K, Grupp IL, Ji Y, Reed T, Loukianov E, Grupp G, Bhagwhat A, Hoit B, Walsh R. Targeted overexpression of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase increases cardiac contractility in transgenic mouse hearts. Circulation research. 1998;83:1205–1214. doi: 10.1161/01.res.83.12.1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.He H, Giordano FJ, Hilal-Dandan R, Choi DJ, Rockman HA, McDonough PM, Bluhm WF, Meyer M, Sayen MR, Swanson E. Overexpression of the rat sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ ATPase gene in the heart of transgenic mice accelerates calcium transients and cardiac relaxation. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 1997;100:380. doi: 10.1172/JCI119544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kühl U, Melzner B, Schäfer B, Schultheiss HP, Strauer B. The Ca-channel as cardiac autoantigen. European heart journal. 1991;12:99–104. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/12.suppl_d.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Morad M, Näbauer M, Schultheiss H-P. New Concepts in Viral Heart Disease. Springer; 1988. Antibodies and autoantibodies against ADP/ATP carrier enhance calcium current in isolated ventricular myocytes; pp. 236–242. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sharaf A, Narula J, Nicol PD, Southern J, Khaw B. Cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase, an autoimmune antigen in experimental cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 1994;89:1217–1228. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.89.3.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Khaw B, Narula J, Sharaf A, Nicol P, Southern J, Carles M. SR-Ca2+ ATPase as an autoimmunogen in experimental myocarditis. European heart journal. 1995;16:92–96. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/16.suppl_o.92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Pummerer CL, Luze K, Grässl G, Bachmaier K, Offner F, Burrell SK, Lenz DM, Zamborelli TJ, Penninger JM, Neu N. Identification of cardiac myosin peptides capable of inducing autoimmune myocarditis in BALB/c mice. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 1996;97:2057. doi: 10.1172/JCI118642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Krishnan B, Massilamany C, Basavalingappa RH, Gangaplara A, Kang G, Li Q, Uzal FA, Strande JL, Delhon GA, Riethoven JJ. Branched chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase kinase 111–130, a T cell epitope that induces both autoimmune myocarditis and hepatitis in A/J mice. Immunity, Inflammation and Disease. 2017 doi: 10.1002/iid3.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Basavalingappa RH, Massilamany C, Krishnan B, Gangaplara A, Kang G, Khalilzad-Sharghi V, Han Z, Othman S, Li Q, Riethoven JJ. Identification of an Epitope from adenine nucleotide translocator 1 that induces inflammation in heart in A/J mice. The American journal of pathology. 2016;186:3160–3175. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.08.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Fontes JA, Barin JG, Talor MV, Stickel N, Schaub J, Rose NR, Čiháková D. Complete Freund’s adjuvant induces experimental autoimmune myocarditis by enhancing IL-6 production during initiation of the immune response. Immunity, inflammation and disease. 2017;5:163–176. doi: 10.1002/iid3.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Cihakova D, Barin JG, Afanasyeva M, Kimura M, Fairweather D, Berg M, Talor MV, Baldeviano GC, Frisancho S, Gabrielson K. Interleukin-13 protects against experimental autoimmune myocarditis by regulating macrophage differentiation. The American journal of pathology. 2008;172:1195–1208. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.070207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Massilamany C, Gangaplara A, Basavalingappa RH, Rajasekaran RA, Khalilzad-Sharghi V, Han Z, Othman S, Steffen D, Reddy J. Localization of CD8 T cell epitope within cardiac myosin heavy chain-α 334–352 that induces autoimmune myocarditis in A/J mice. International journal of cardiology. 2016;202:311–321. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.09.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Massilamany C, Gangaplara A, Steffen D, Reddy J. Identification of novel mimicry epitopes for cardiac myosin heavy chain-α that induce autoimmune myocarditis in A/J mice. Cellular immunology. 2011;271:438–449. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2011.08.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Wu L, Ong S, Talor MV, Barin JG, Baldeviano GC, Kass DA, Bedja D, Zhang H, Sheikh A, Margolick JB. Cardiac fibroblasts mediate IL-17A–driven inflammatory dilated cardiomyopathy. Journal of Experimental Medicine. 2014;211:1449–1464. doi: 10.1084/jem.20132126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Nandi SS, Duryee MJ, Shahshahan HR, Thiele GM, Anderson DR, Mishra PK. Induction of autophagy markers is associated with attenuation of miR-133a in diabetic heart failure patients undergoing mechanical unloading. American journal of translational research. 2015;7:683. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Massilamany C, Gangaplara A, Jia T, Elowsky C, Kang G, Riethoven JJ, Li Q, Zhou Y, Reddy J. Direct staining with major histocompatibility complex class II dextramers permits detection of antigen-specific, autoreactive CD4 T cells in situ. PloS one. 2014;9:e87519. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Massilamany C, Khalilzad-Sharghi V, Gangaplara A, Steffen D, Othman SF, Reddy J. Noninvasive assessment of cardiac abnormalities in experimental autoimmune myocarditis by magnetic resonance microscopy imaging in the mouse. Journal of visualized experiments: JoVE. 2014 doi: 10.3791/51654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Massilamany C, Gangaplara A, Chapman N, Rose N, Reddy J. Detection of cardiac myosin heavy chain-α-specific CD4 cells by using MHC class II/IA k tetramers in A/J mice. Journal of immunological methods. 2011;372:107–118. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2011.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Reddy J, Bettelli E, Nicholson L, Waldner H, Jang MH, Wucherpfennig KW, Kuchroo VK. Detection of autoreactive myelin proteolipid protein 139–151-specific T cells by using MHC II (IAs) tetramers. The journal of immunology. 2003;170:870–877. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.2.870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Massilamany C, Upadhyaya B, Gangaplara A, Kuszynski C, Reddy J. Detection of autoreactive CD4 T cells using major histocompatibility complex class II dextramers. BMC immunology. 2011;12:40. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-12-40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Fremont DH, Dai S, Chiang H, Crawford F, Marrack P, Kappler J. Structural basis of cytochrome c presentation by IEk. Journal of Experimental Medicine. 2002;195:1043–1052. doi: 10.1084/jem.20011971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Kasson PM, Rabinowitz JD, Schmitt L, Davis MM, McConnell HM. Kinetics of Peptide Binding to the Class II MHC Protein I− Ek. Biochemistry. 2000;39:1048–1058. doi: 10.1021/bi9921337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Wu LC, Tuot DS, Lyons DS, Garcia KC, Davis MM. Two-step binding mechanism for T-cell receptor recognition of peptide–MHC. Nature. 2002;418:552–556. doi: 10.1038/nature00920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Massilamany C, Steffen D, Reddy J. An epitope from Acanthamoeba castellanii that cross-react with proteolipid protein 139–151-reactive T cells induces autoimmune encephalomyelitis in SJL mice. Journal of neuroImmunology. 2010;219:17–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2009.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Storck S, Delbos F, Stadler N, Thirion-Delalande C, Bernex F, Verthuy C, Ferrier P, Weill J-C, Reynaud C-A. Normal immune system development in mice lacking the Deltex-1 RING finger domain. Molecular and cellular biology. 2005;25:1437–1445. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.4.1437-1445.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Massilamany C, Gangaplara A, Jia T, Elowsky C, Li Q, Zhou Y, Reddy J. In situ detection of autoreactive CD4 T cells in brain and heart using major histocompatibility complex class II dextramers. Journal of visualized experiments JoVE. 2014 doi: 10.3791/51679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Sonin DL, Wakatsuki T, Routhu KV, Harmann LM, Petersen M, Meyer J, Strande JL. Protease-activated receptor 1 inhibition by SCH79797 attenuates left ventricular remodeling and profibrotic activities of cardiac fibroblasts. Journal of cardiovascular pharmacology and therapeutics. 2013;18:460–475. doi: 10.1177/1074248413485434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Krishnan B, Massilamany C, Basavalingappa RH, Rajasekaran RA, Kuszynski C, Switzer B, Peterson DA, Reddy J. Versatility of using major histocompatibility complex class II dextramers for derivation and characterization of antigen-specific, autoreactive T cell hybridomas. Journal of immunological methods. 2015;426:86–94. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2015.08.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Massilamany C, Krishnan B, Reddy J. Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II Dextramers: New Tools for the Detection of antigen-Specific, CD4 T Cells in Basic and Clinical Research. Scandinavian journal of immunology. 2015;82:399–408. doi: 10.1111/sji.12344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Mitsdoerffer M, Lee Y, Jäger A, Kim HJ, Korn T, Kolls JK, Cantor H, Bettelli E, Kuchroo VK. Proinflammatory T helper type 17 cells are effective B-cell helpers. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2010;107:14292–14297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1009234107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Kawase Y, Hajjar RJ. The cardiac sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase: a potent target for cardiovascular diseases. Nature Clinical Practice Cardiovascular Medicine. 2008;5:554–565. doi: 10.1038/ncpcardio1301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Berridge MJ, Lipp P, Bootman MD. The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology. 2000;1:11–21. doi: 10.1038/35036035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Waldron RT, Short AD, Meadows JJ, Ghosh TK, Gill DL. Endoplasmic reticulum calcium pump expression and control of cell growth. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1994;269:11927–11933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Abeele FV, Skryma R, Shuba Y, Van Coppenolle F, Slomianny C, Roudbaraki M, Mauroy B, Wuytack F, Prevarskaya N. Bcl-2-dependent modulation of Ca 2+ homeostasis and store-operated channels in prostate cancer cells. Cancer cell. 2002;1:169–179. doi: 10.1016/s1535-6108(02)00034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Corradi D, Callegari S, Maestri R, Benussi S, Alfieri O. Structural remodeling in atrial fibrillation. Nature Clinical Practice Cardiovascular Medicine. 2008;5:782–796. doi: 10.1038/ncpcardio1370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Marrack P, Kappler J, Kotzin BL. Autoimmune disease: why and where it occurs. Nature medicine. 2001;7:899. doi: 10.1038/90935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Muller AM, Fischer A, Katus HA, Kaya Z. Mouse models of autoimmune diseases-autoimmune myocarditis. Current pharmaceutical design. 2015;21:2498–2512. doi: 10.2174/1381612821666150316123711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Reddy J, Massilamany C, Buskiewicz I, Huber SA. Autoimmunity in viral myocarditis. Current opinion in rheumatology. 2013;25:502–508. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e3283620036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Yeh ET. Autoimmunity and the pathogenesis of myocarditis. Circulation. 1994;89:1318–1319. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.89.3.1318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Chugh SS, Havmoeller R, Narayanan K, Singh D, Rienstra M, Benjamin EJ, Gillum FR, Kim Y-H, McAnulty JH, Zheng Z-J. Worldwide epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: a Global Burden of Disease 2010 Study. Circulation. 2013 doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.005119. CIRCULATIONAHA. 113.005119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Guo Y, Lip GY, Apostolakis S. Inflammation in atrial fibrillation. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2012;60:2263–2270. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2012.04.063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Dzeshka MS, Lip GY, Snezhitskiy V, Shantsila E. Cardiac Fibrosis in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015;66:943–959. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2015.06.1313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Hu YF, Chen YJ, Lin YJ, Chen SA. Inflammation and the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2015;12:230–243. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2015.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Harada M, Van Wagoner DR, Nattel S. Role of inflammation in atrial fibrillation pathophysiology and management. Circulation Journal. 2015;79:495–502. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-15-0138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Biedermann T, Kneilling M, Mailhammer R, Maier K, Sander CA, Kollias G, Kunkel SL, Hültner L, Röcken M. Mast cells control neutrophil recruitment during T cell–mediated delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions through tumor necrosis factor and macrophage inflammatory protein 2. Journal of Experimental Medicine. 2000;192:1441–1452. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.10.1441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Schwartz A, Askenase PW, Gershon RK. Regulation of delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions by cyclophosphamide-sensitive T cells. The Journal of Immunology. 1978;121:1573–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Miller SD, Vanderlugt CL, Begolka WS, Pao W, Yauch RL, Neville KL, Katz-Levy Y, Carrizosa A, Kim BS. Persistent infection with Theiler’s virus leads to CNS autoimmunity via epitope spreading. Nature medicine. 1997;3:1133–1136. doi: 10.1038/nm1097-1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Freeman LM, Lam A, Petcu E, Smith R, Salajegheh A, Diamond P, Zannettino A, Evdokiou A, Luff J, Wong PF. Myeloma-induced alloreactive T cells arising in myeloma-infiltrated bones include double-positive CD8+ CD4+ T cells: evidence from myeloma-bearing mouse model. The Journal of Immunology. 2011;187:3987–3996. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1101202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Anderson AC, Nicholson LB, Legge KL, Turchin V, Zaghouani H, Kuchroo VK. High Frequency of Autoreactive Myelin Proteolipid Protein–Specific T Cells in the Periphery of Naive Mice. Journal of Experimental Medicine. 2000;191:761–770. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.5.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Lv H, Lipes MA. Role of impaired central tolerance to α-myosin in inflammatory heart disease. Trends in cardiovascular medicine. 2012;22:113–117. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2012.07.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.McCoy L, Tsunoda I, Fujinami RS. Multiple sclerosis and virus induced immune responses: autoimmunity can be primed by molecular mimicry and augmented by bystander activation. Autoimmunity. 2006;39:9–19. doi: 10.1080/08916930500484799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Cihakova D, Rose NR. Pathogenesis of myocarditis and dilated cardiomyopathy. Advances in immunology. 2008;99:95–114. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(08)00604-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Nindl V, Maier R, Ratering D, De Giuli R, Züst R, Thiel V, Scandella E, Di Padova F, Kopf M, Rudin M. Cooperation of Th1 and Th17 cells determines transition from autoimmune myocarditis to dilated cardiomyopathy. European journal of immunology. 2012;42:2311–2321. doi: 10.1002/eji.201142209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Myers JM, Cooper LT, Kem DC, Stavrakis S, Kosanke SD, Shevach EM, Fairweather D, Stoner JA, Cox CJ, Cunningham MW. Cardiac myosin-Th17 responses promote heart failure in human myocarditis. JCI insight. 2016:1. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.85851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Cunningham MW. Cardiac myosin and the TH1/TH2 paradigm in autoimmune myocarditis. The American journal of pathology. 2001;159:5. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)61665-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Baldeviano GC, Barin JG, Talor MV, Srinivasan S, Bedja D, Zheng D, Gabrielson K, Iwakura Y, Rose NR, Cihakova D. Interleukin-17A is dispensable for myocarditis but essential for the progression to dilated cardiomyopathy. Circ Res. 2010;106:1646–1655. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.213157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Hasbold J, Hong JSY, Kehry MR, Hodgkin PD. Integrating signals from IFN-γ and IL-4 by B cells: positive and negative effects on CD40 ligand-induced proliferation, survival, and division-linked isotype switching to IgG1, IgE, and IgG2a. The Journal of Immunology. 1999;163:4175–4181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Smith SC, Allen PM. Expression of myosin-class II major histocompatibility complexes in the normal myocardium occurs before induction of autoimmune myocarditis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 1992;89:9131–9135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Smith SC, Allen PM. Neutralization of endogenous tumor necrosis factor ameliorates the severity of myosin-induced myocarditis. Circulation research. 1992;70:856–863. doi: 10.1161/01.res.70.4.856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Ansari A, Wang Y, Danner D, Gravanis M, Mayne A, Neckelmann N, Sell K, Herskowitz A. Abnormal expression of histocompatibility and mitochondrial antigens by cardiac tissue from patients with myocarditis and dilated cardiomyopathy. The American journal of pathology. 1991;139:337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Baker MJ, Palmer CS, Stojanovski D. Mitochondrial protein quality control in health and disease. British journal of pharmacology. 2014;171:1870–1889. doi: 10.1111/bph.12430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Mattiazzi M, D’Aurelio M, Gajewski CD, Martushova K, Kiaei M, Beal MF, Manfredi G. Mutated human SOD1 causes dysfunction of oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria of transgenic mice. Journal of biological chemistry. 2002;277:29626–29633. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M203065200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Dahl HH, Brown G, Brown R, Hansen LL, Kerr D, Wexler I, Patel M, De Meirleir L, Lissens W, Chun K. Mutations and polymorphisms in the pyruvate dehydrogenase E1α gene. Human mutation. 1992;1:97–102. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380010203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Novarino G, El-Fishawy P, Kayserili H, Meguid NA, Scott EM, Schroth J, Silhavy JL, Kara M, Khalil RO, Ben-Omran T. Mutations in BCKD-kinase lead to a potentially treatable form of autism with epilepsy. Science. 2012;338:394–397. doi: 10.1126/science.1224631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Ireland JM, Unanue ER. Processing of proteins in autophagy vesicles of antigen-presenting cells generates citrullinated peptides recognized by the immune system. Autophagy. 2012;8:429–430. doi: 10.4161/auto.19261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.